Edexcel IGCSE Physics - (Unit 8) Astrophysics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Units for Astrophysics (Topic 8)
kilogram, meter, meter/second, meter/second², newton, second, newton/kilogram (skip as necessary)
The universe is...
a large collection of billions of galaxies
A galaxy is...
a large collection of billions of stars
Our solar system is in...
the Milky Way Galaxy
An object's gravitational field strength (g) is determined by its...
size and mass
Massive objects have...
high gravitational fields.
Planets with large radii have...
weaker gravitational fields at their surfaces (since it's far away from the center.)
Weight (N) calc
Mass (kg) * Gravitational Field Strength (N/kg)
Gravitational force
An attractive force that acts between any two objects and pulls them together.
Orbits
Periodic motions usually caused by gravitational forces around celestial bodies.
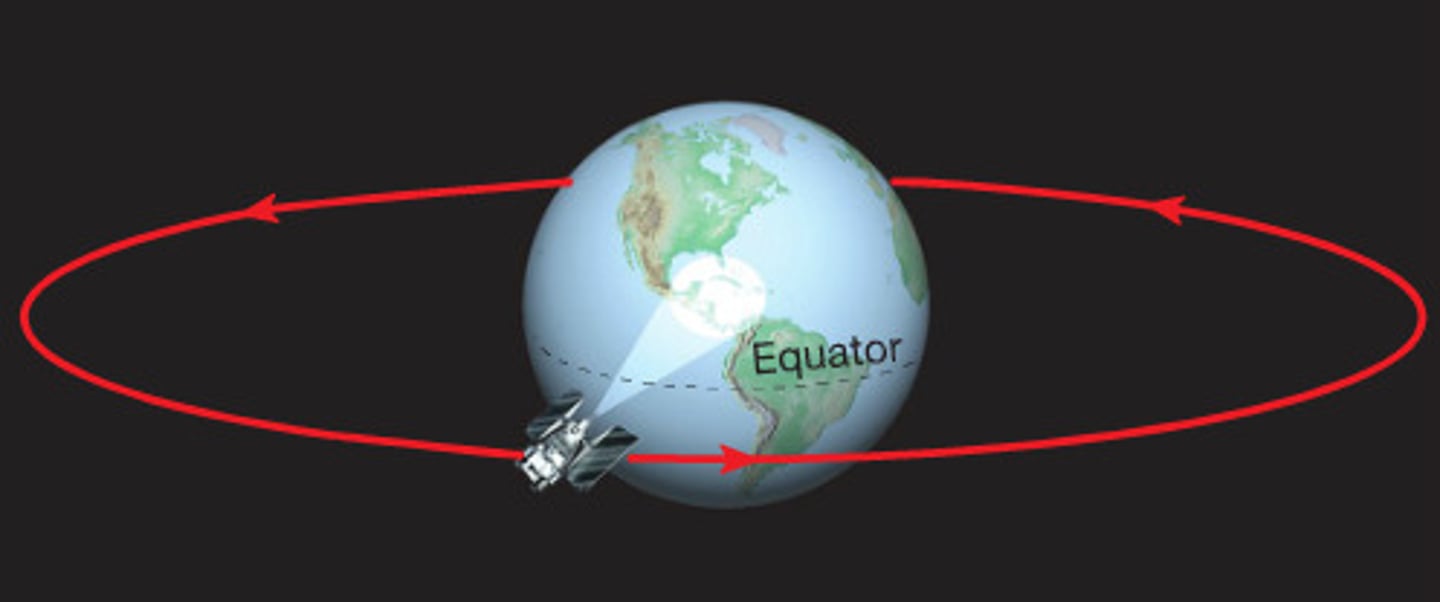
Geostationary Orbits
A circular orbit around the equator line fixed to the Earth's rotation speed (used by satellites to fixate over one location).
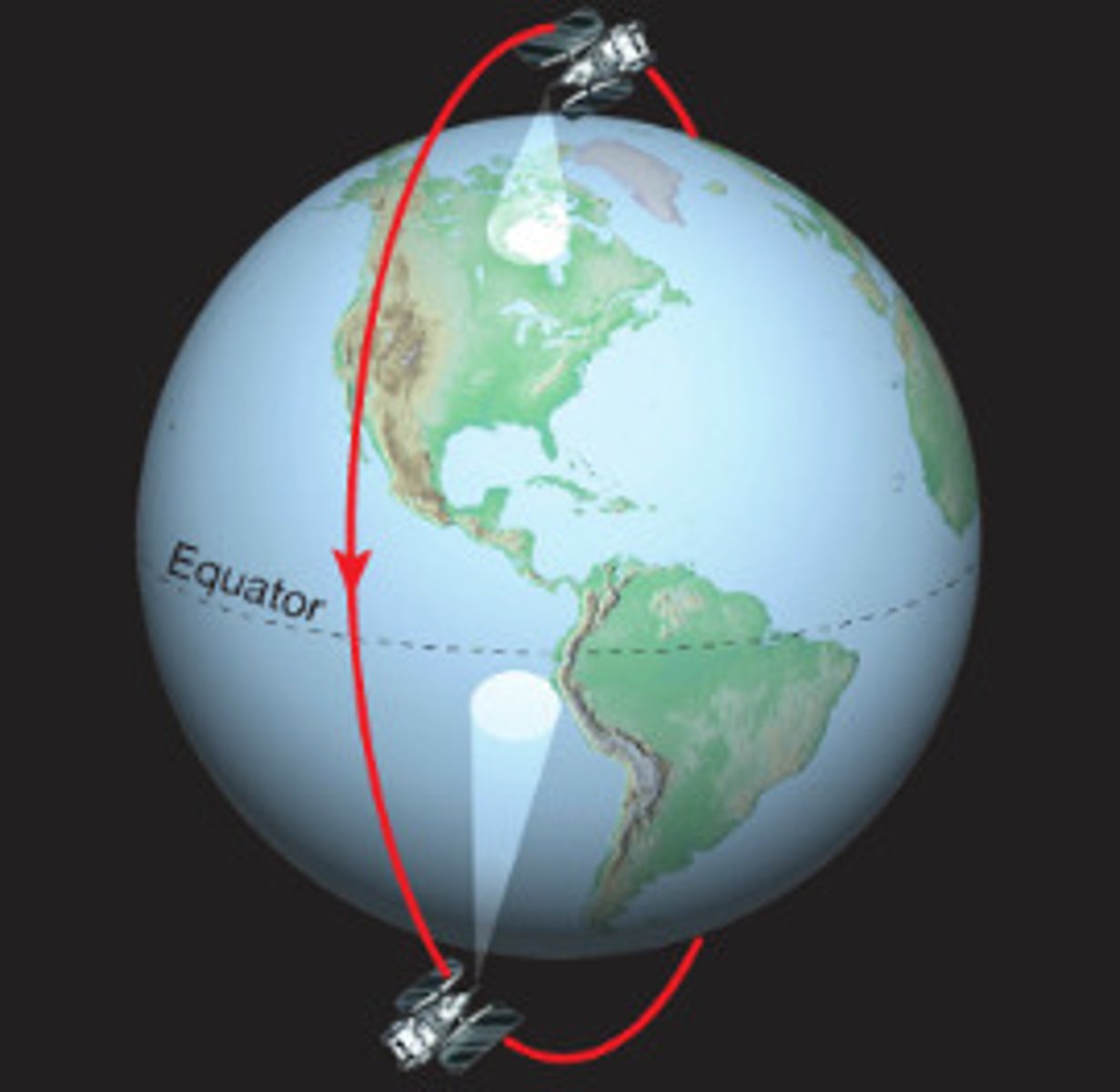
Polar Orbits
A path going over the north and south poles (used by satellites to always move over new locations).
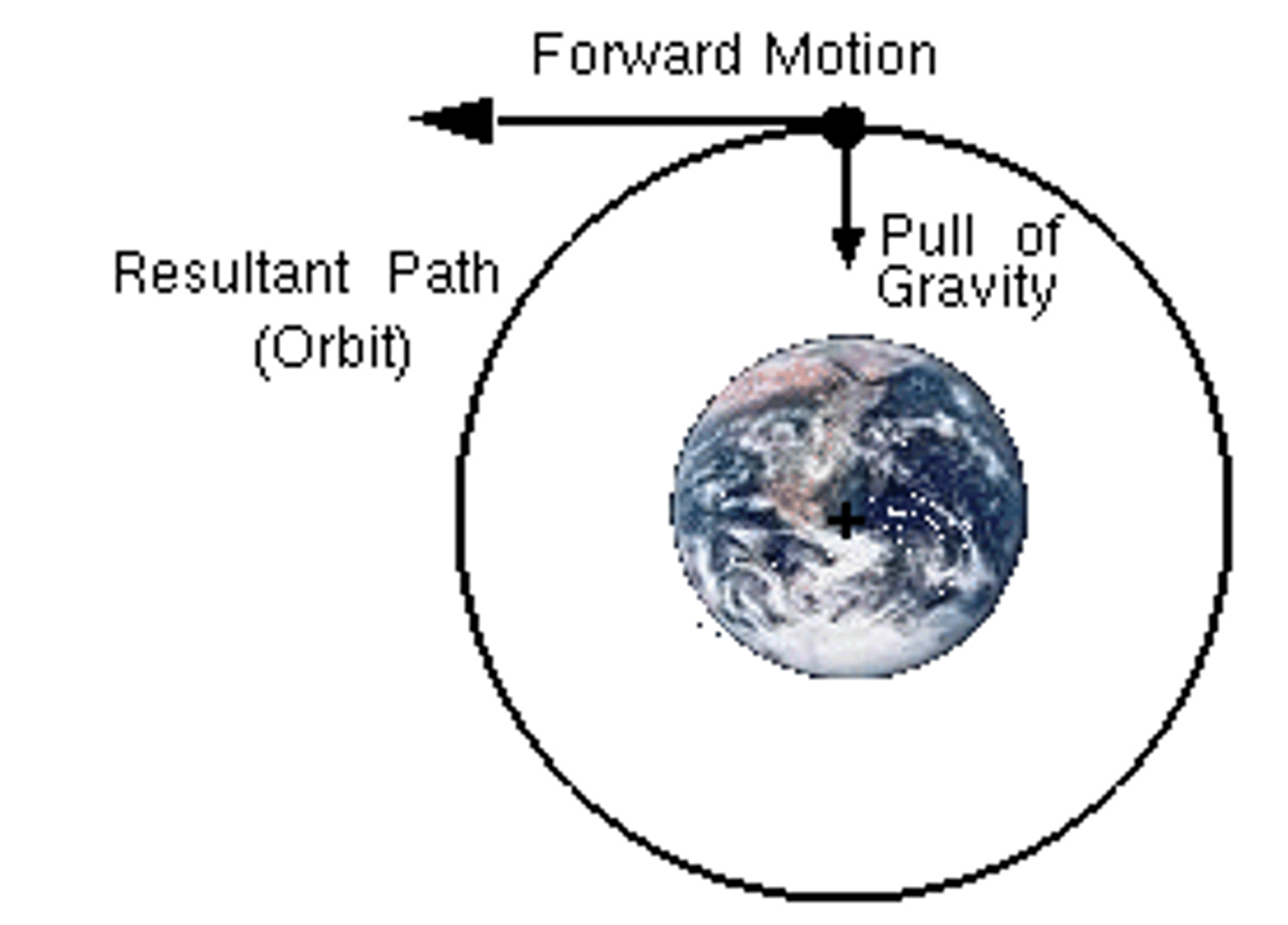
Why objects stay in the solar system
They are held in by the gravitational pull of the sun but are kept in orbit by their velocity and energy.
Due to gravitational force, moons...
orbit their planets
Due to gravitational force, planets...
orbit the sun
Due to gravitational force, artificial satellites...
orbit the earth
Due to gravitational force, comets...
orbit the sun
Orbits of Comets
Highly elliptical, speeding up when near the sun due to larger gravitational force and melting of frozen ice crystals.
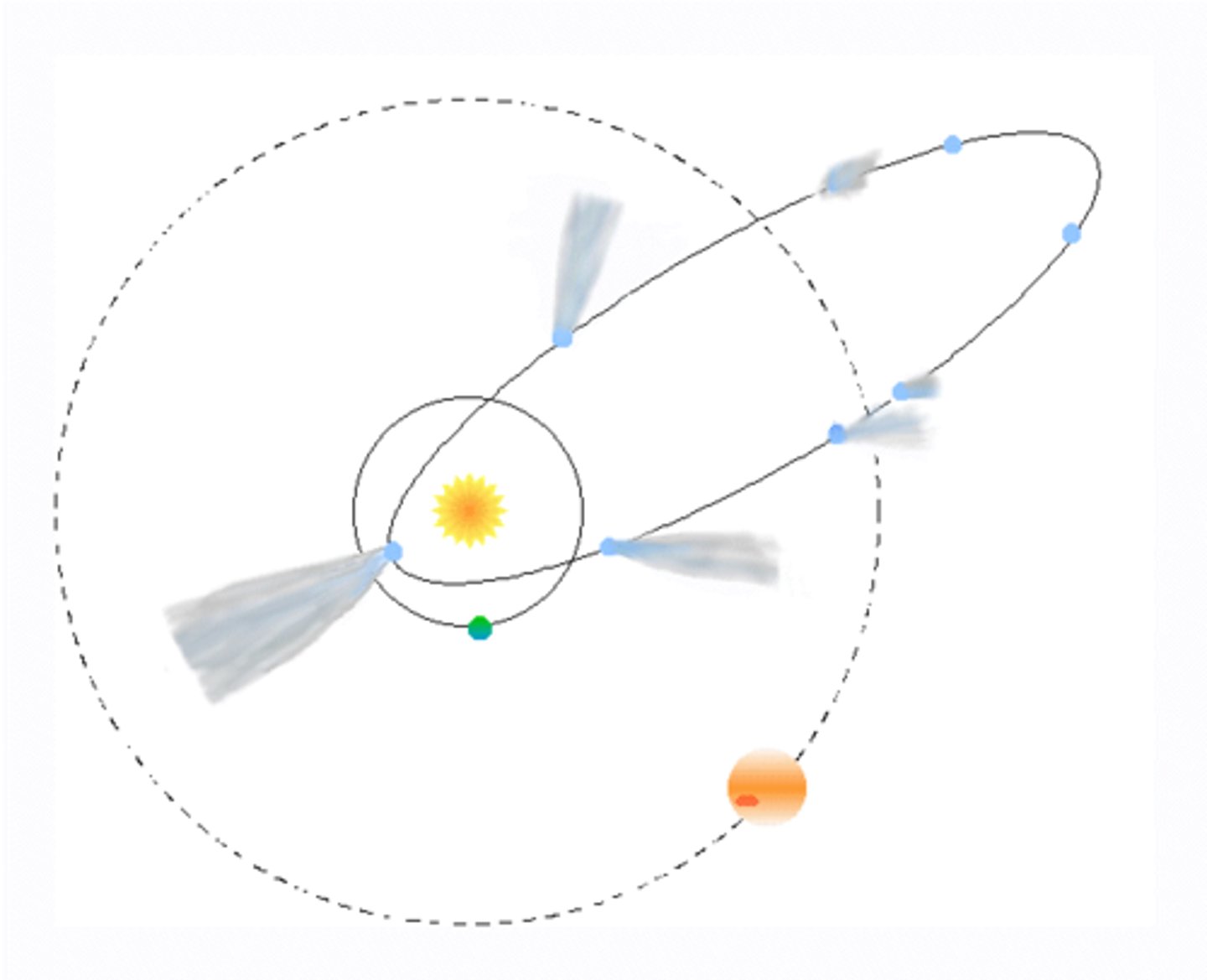
Orbits of moons and planets
Slightly elliptical with a near constant orbital speed.
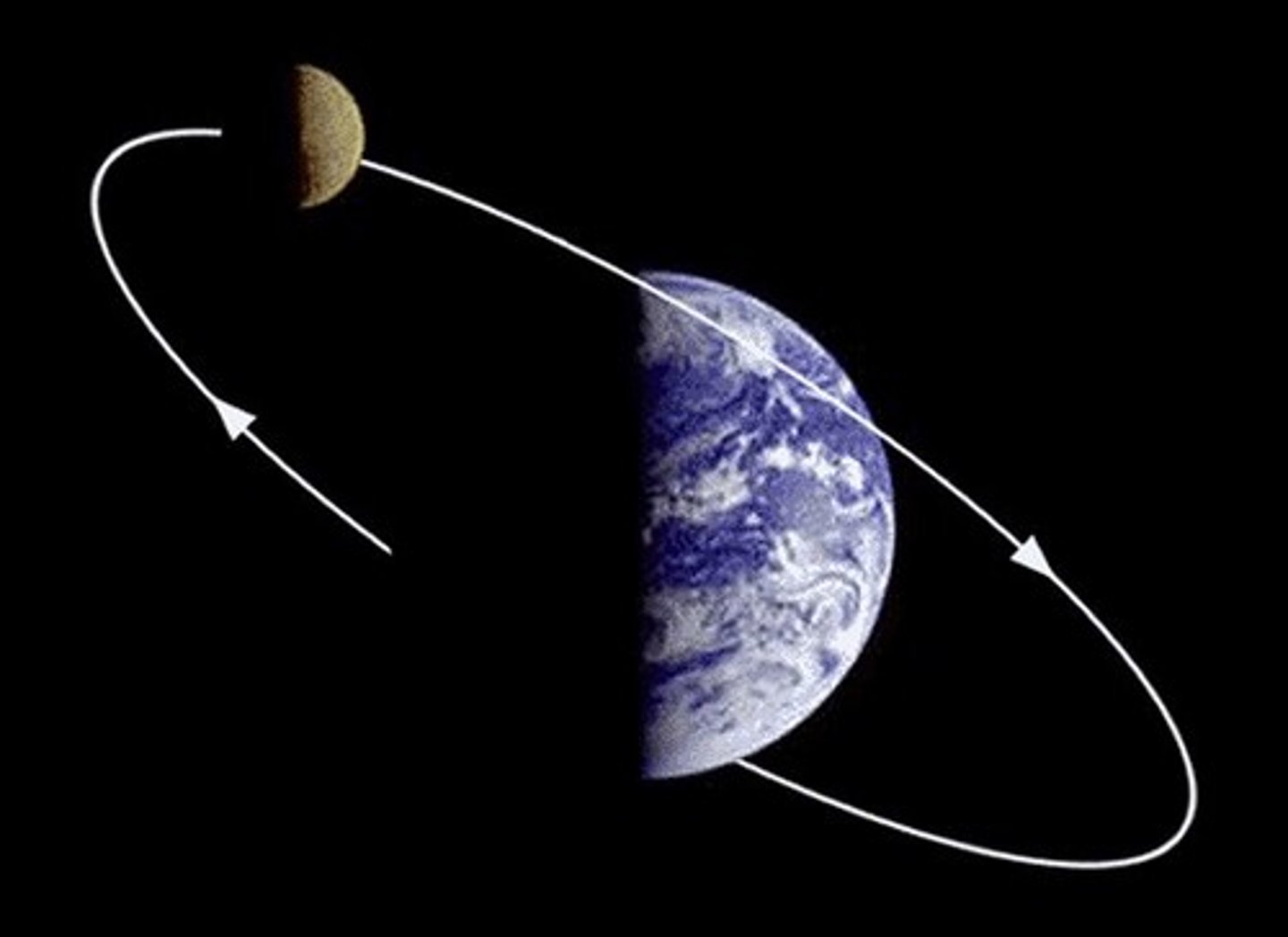
Orbital Speed (km/s) Calc
[ 2π * Orbital Radius (km) ] / Time Pd. (s)
![<p>[ 2π * <strong>Orbital Radius</strong> (km) ] / <strong>Time Pd.</strong> (s)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3abaf8f1-ed09-4f6a-97ad-72bb2febdf16.png)
Classification of Stars
They all emit visible light at different frequencies; the frequency determines the star's color and temperature.
The spectrum of colored stars
(Cool to Hot) Red (3,000°C,) orange, yellow, white, blue (30,000°C)

Nebula
A cloud of gas and dust particles which are drawn together by gravitational forces. This increases temperature and pressure, causing fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei, releasing heat and light energy.
Main Sequence Star
A normal star where the forces of its nuclear fusion's radiative outward pressure and the gravitational inwards pressure balance, making it stable. (The sun is at this stage.)
Red Giant
A large, reddish star which has ran out of hydrogen for nuclear fusion and has therefore collapsed inwards. Due to increased temperature, fusion of helium nuclei begins, and the red (cooled due to high S.A.) star expands greatly.
White Dwarf
A very dense star of high mass that has collapsed inwards due to no helium for fusion. White light is emitted as the compression makes temperature increase. The star cools and changes color to black.
Stellar evolution of stars with a similar mass to the sun
They expand massively, becoming a red giant, and then a white dwarf and a black dwarf.
Stellar evolution of stars with greater mass than the sun
They expand to become a red supergiant (massive) and explode into a supernova. Most become neutron stars, but insanely massive stars become black holes.
Apparent Magnitude (*)
The apparent brightness of a star as seen from a point in space (far, bright stars can look identical to close, dim stars)
Absolute Magnitude (*)
The actual brightness of a star at a standard distance of 32.6 light years from Earth.
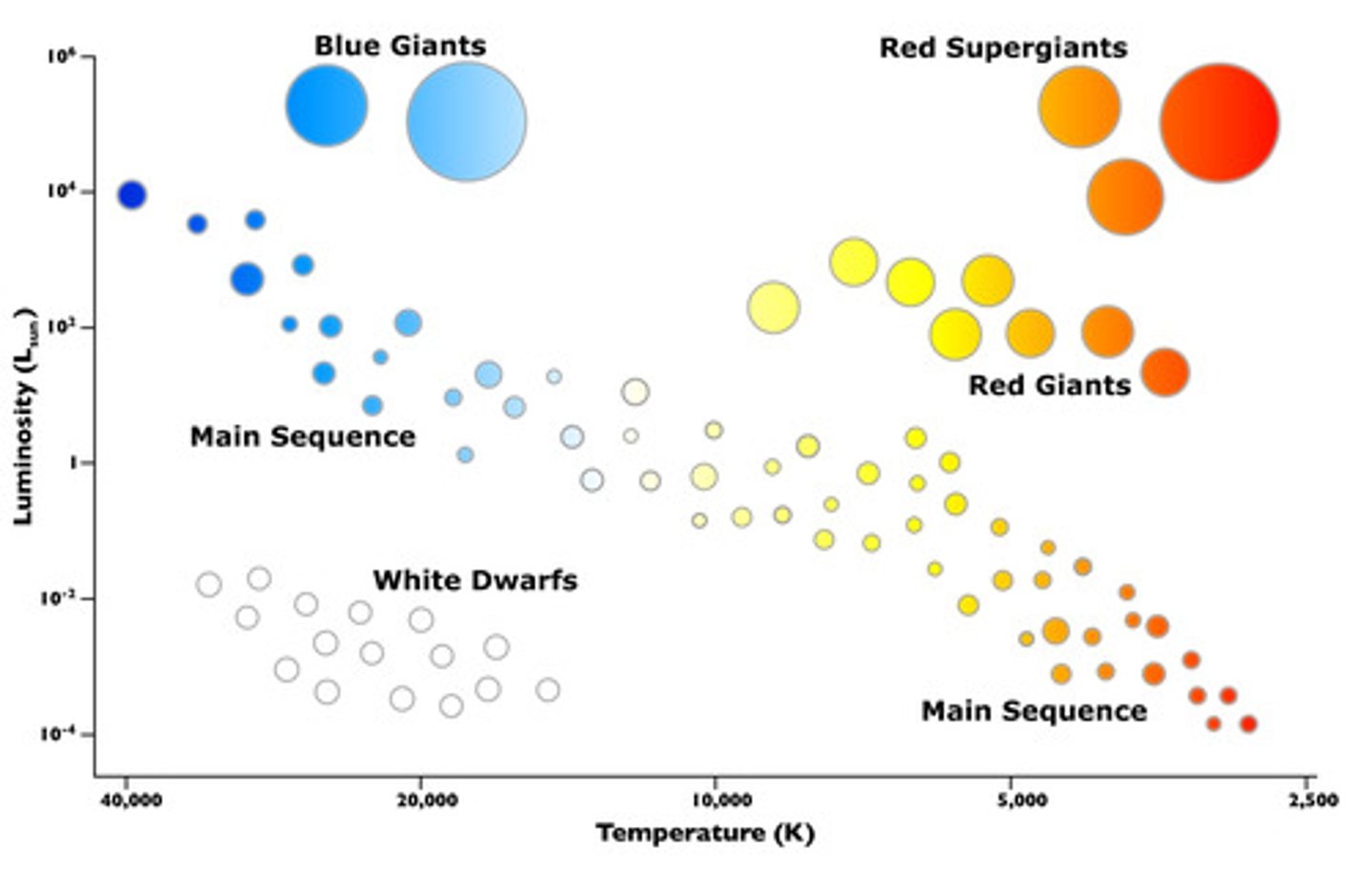
Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram (*)
A graph relating the surface temperatures and absolute brightness of stars, where the surface temperature gets cooler going along the x-axis.
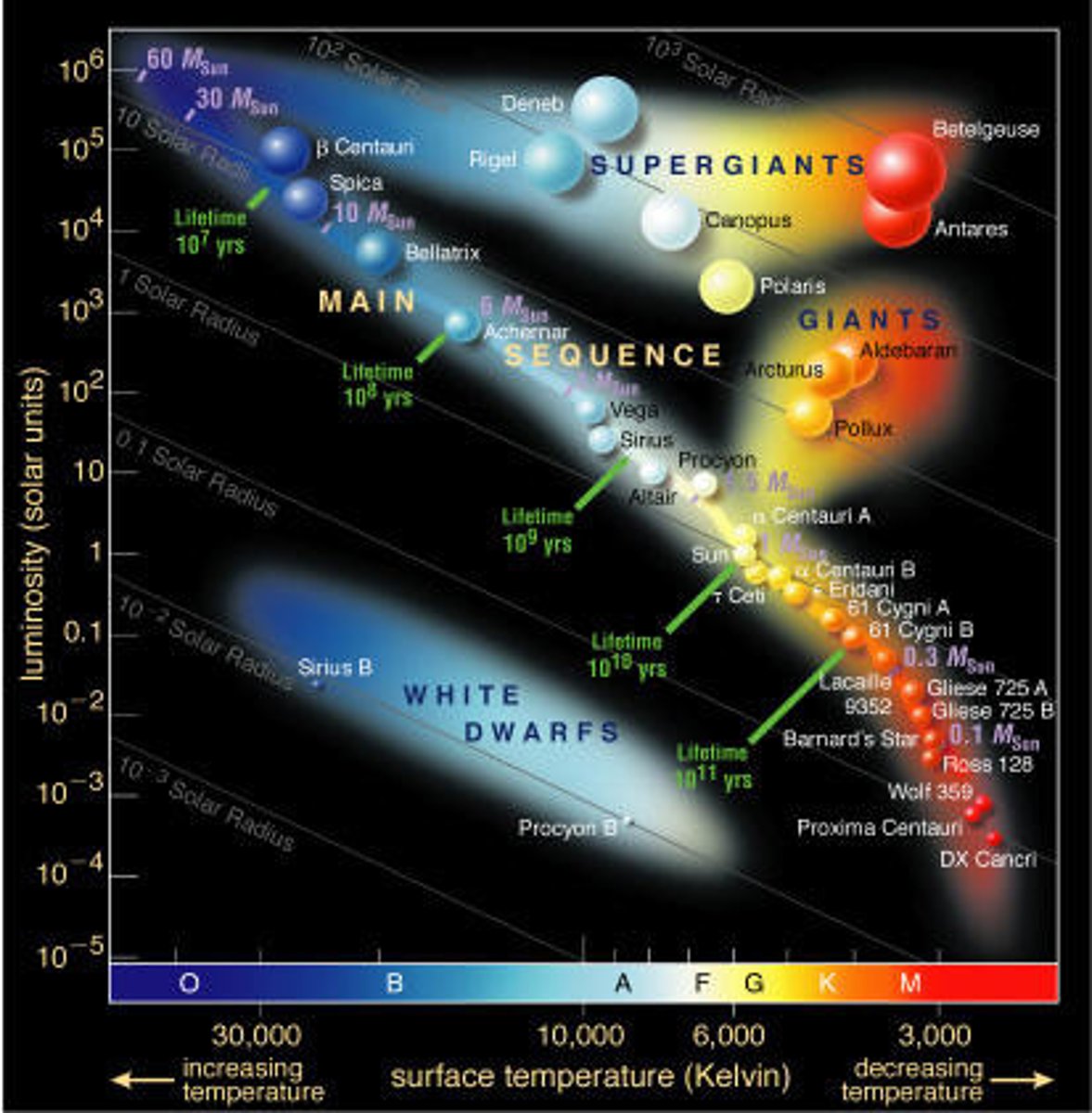
Placement of stars (HR diagram) (*)
Supergiants (mid-top to top right,) Giants (below supergiants,) Main Sequence (top left to bottom right diagonal strip) and White Dwarfs (central bottom left area.)
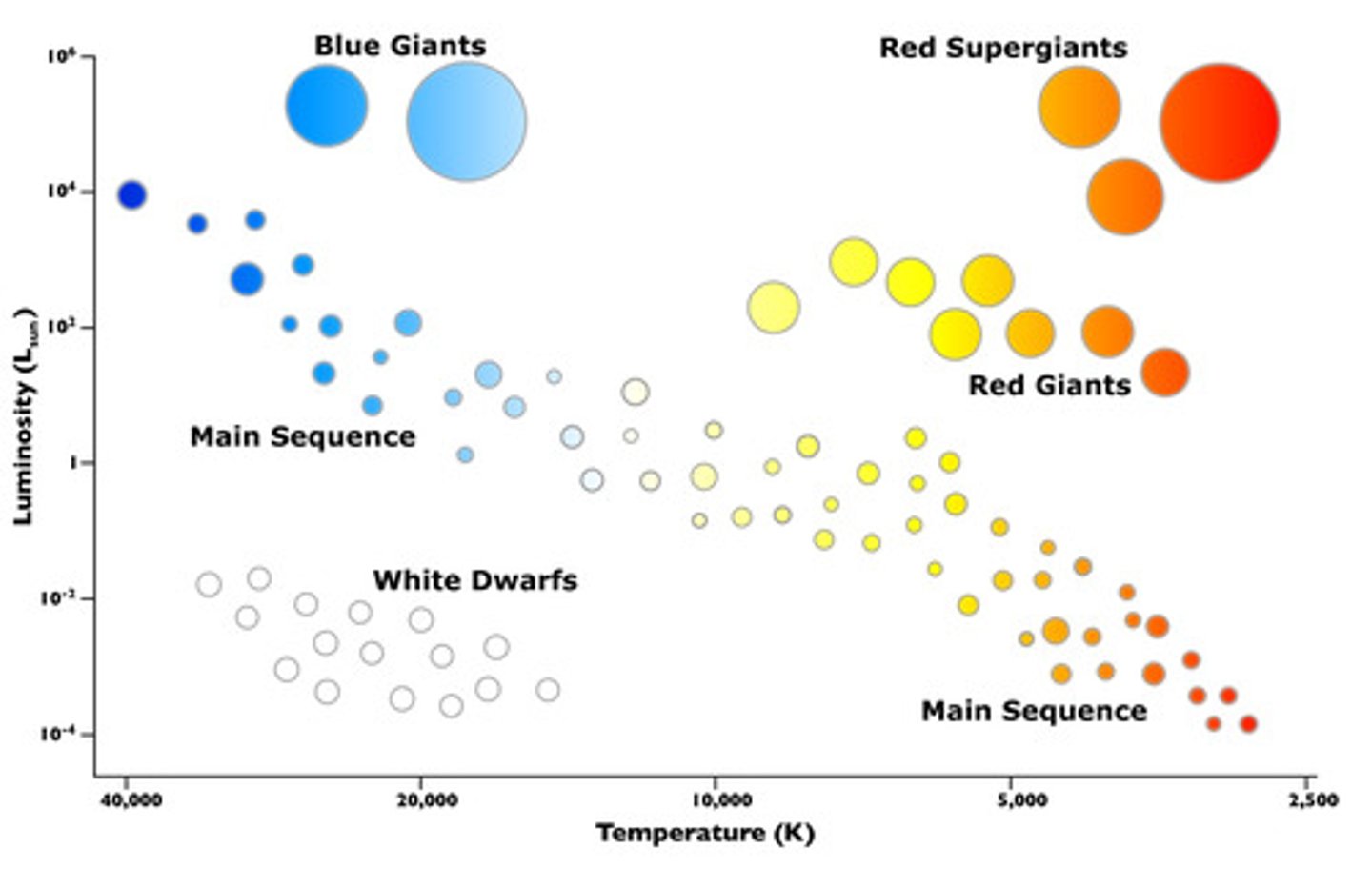
Axes (HR diagram) (*)
X-axis: decreasing temperature (30000 to 3000°K); Y-axis: increasing luminosity (10⁻⁵ to 1 to 10⁵)
Big Bang Theory (BBT) (*)
A theory that the universe formed by energy and matter from a hot and dense place which exploded 14 billion years ago (and is still expanding/cooling today).

Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) (*)
It can be detected everywhere in the universe; these waves (of thermal radiation) have redshifted from gamma waves into microwaves over time, showing that objects in the universe have distributed uniformly (more or less).
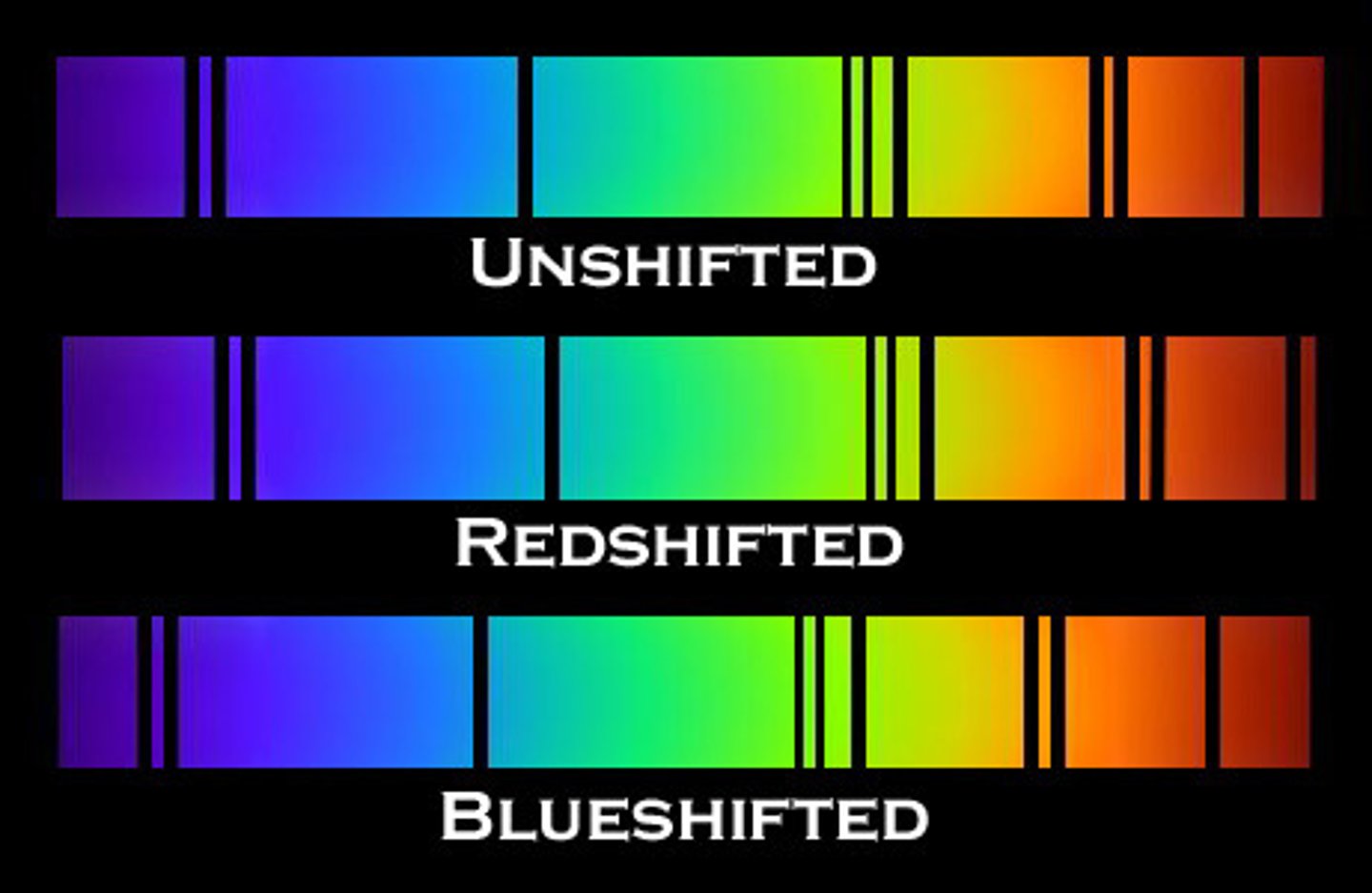
Red shift (*)
The increase in the wavelengths of light due to an object moving away from an observer, shifting toward the red end of the spectrum.
Red shift (of galaxies) (*)
In more distant galaxies, it is greater as they are moving faster. This suggests that galaxies are becoming less densely packed, and the universe is expanding.
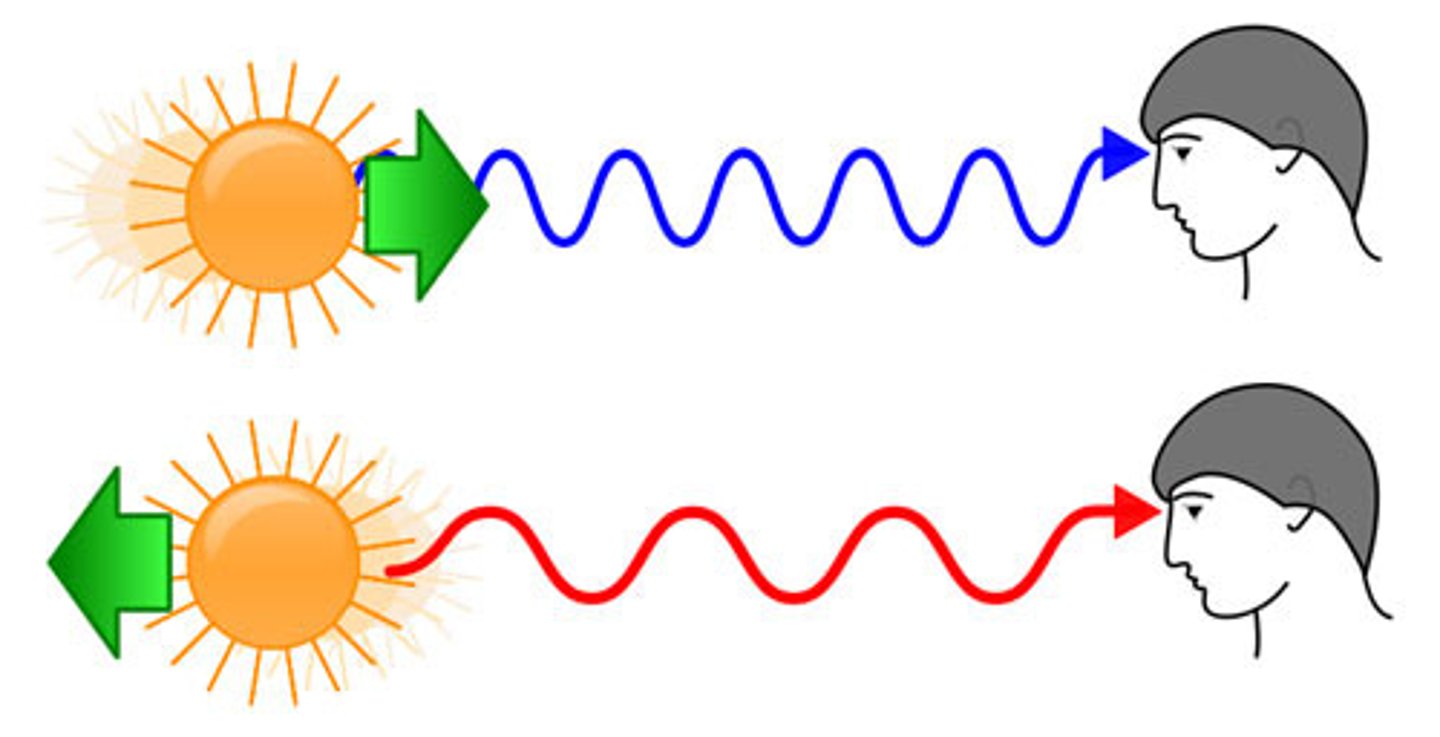
Doppler shift (*)
Wave sources moving relative to an observer appear to have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies in front of them.
Doppler shift calc (*)
[Alt Text: The relationship between change in wavelength, wavelength, velocity of a galaxy, and the speed of light.]
![<p><em><span style="text-decoration:underline">[Alt Text: The relationship between change in wavelength, wavelength, velocity of a galaxy, and the speed of light.]</span></em></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7ea7b4db-b74c-4a8a-b82f-e4835ae3a4e8.png)
Doppler shift calc tips (*)
READ THE QUESTION: The speed of light is always constant, galaxies are always moving away, a reference wavelength should be provided, and you're most likely to work out a galaxy's wavelength or velocity.