Pregnancy & Embryonic Development
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Prenatal development
encompasses time period of these events:
fertilization of an egg cell; implantation of zygote in the uterus; multiple cell divisions to initiate growth and directionality of embryo; development of embryo into the fetus; maturation of organ systems in the fetal body; to the point of birth
Gestation
desribes this period of prenatal development
Gestation, in humans, takes place over course of
40 weeks, about 9 months
Prenatal development is divided into:
3 trimesters (each one is 3 months in duration)
In the first trimester:
major germ layers are created and internal “scaffolding” of embryo is created
the germ layers give rise to all major tissues of the body (cardiovascular structures, skin, nervous tissue, etc)
In the second trimester:
there is continued development of major organs and organ systems. The embryo starts to look like a human body
In third trimester:
there is significant growth of body and its systems. these organs start to become functional
The _____ trimester is the period during which the viability of the embryo is most vulnerable.
first; only 40% of conceptions survive during this period.
________ is a key step that occurs during the first trimester
Gastrulation
Gastrulation involves a series of steps to create major germ layers
These germ layers ultimately create the major tissues and organs of the body. Directionality of the embryonic body is also established here.
During gastrulation, 3 germ layers created are:
ectoderm; mesoderm; endoderm
_____ develops during the first trimester
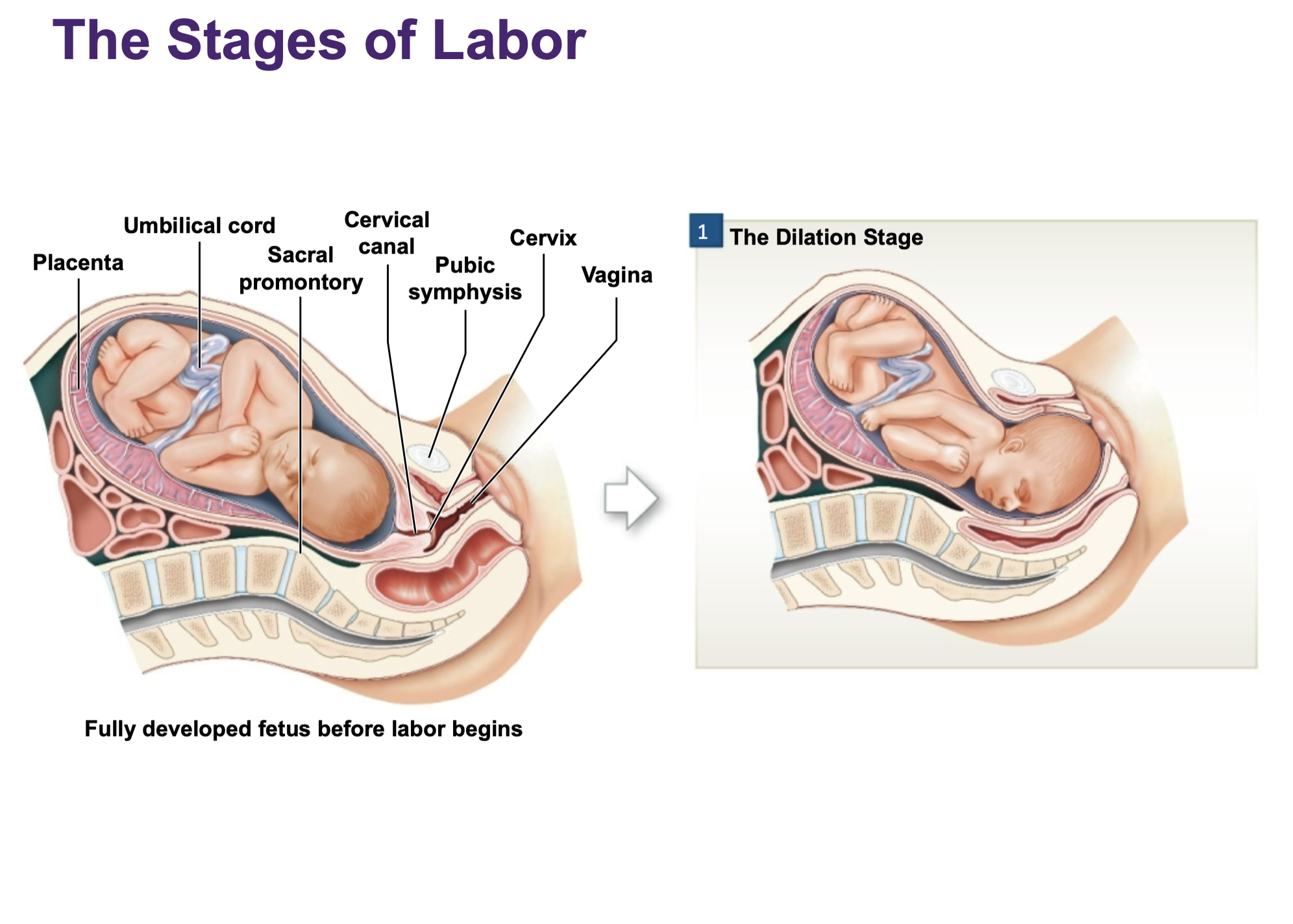
Placenta
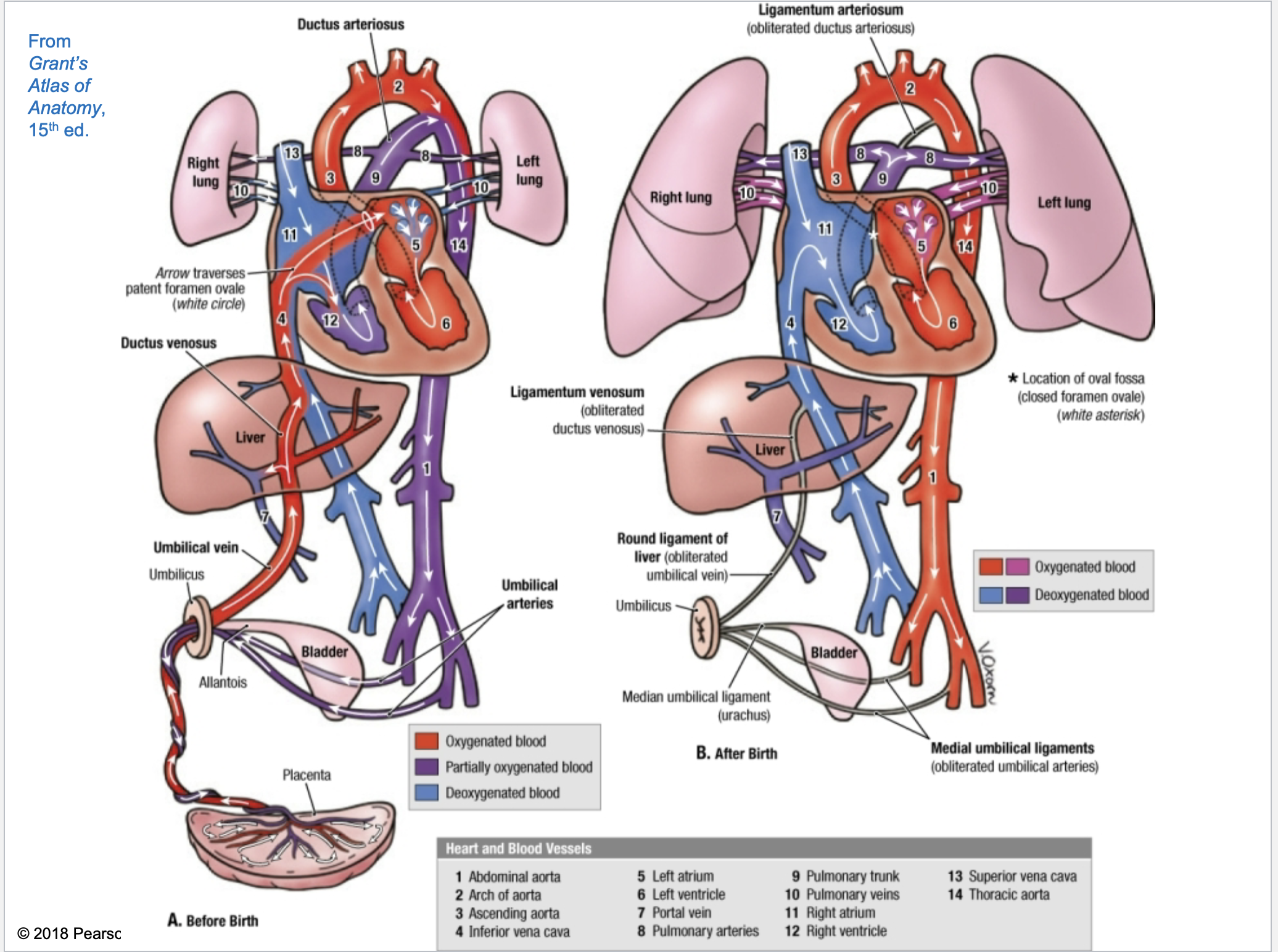
Umbilical cord physically connects
embryonic/fetal body with the placenta
Placenta is physically adjacent to the
uterine wall in the mothers body
Umbilical cord contains multiple blood vessels
Inside umbilical cord, there are ____ umbilical vein and ____ umbilical arteries
1 vein; 1 arteries
The umbilical ____ carries O2 and nutrient rich blood away from mother/placenta and carries that blood into the fetal body
vein
the umbilical ____ carry the waste blood and O2 poor blood out of the fetal body and bring this blood back to the placenta so that it can be replenished w O2 and nutrients
arteries
Umbilical blood vessels enter and exit the fetal body at the
umbilicus (belly button)
In the fetal body, there are also bypasses (shortcuts) that exist in the fetal heart and the liver. In the fetal heart, the blood largely bypasses the fetal lungs.
Remember that the fetus is in a liquid environment. There is no mechanical breathing taking place in the fetal lungs. Gas and nutrient exchange is taking place at the interface between the uterine wall and the placenta. It is not necessary in the fetal body to send a significant amount of blood towards the lungs. That is why these bypasses exist. After birth, however, these bypasses should seal off. This then forces blood to enter into the newborn’s lungs.
Amnion
holds in the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus
for a woman in labor, when her water breaks, it indicates that the amnion has torn allowing the fluid to escape.
Note: the mucus plug that forms at the base of the uterus to serve to prevent entry of bacteria into uterus
organogenesis
process of organ formation during 1st trimester
Organ maturation
takes place during 2nd and 3rd trimester
By birth, most organs have formed but are still maturing
the lungs tend to be the last organs to mature
uterus will increase in length; by time the pregnancy is full term, the uterus and its contents will weigh ~ 22 pounds (avg)
Mothers digestive organs remain active, but they have been displaced upwards because of expansion of uterus
urinary bladder in mother’s body will be pushed down upon by the expanded uterus. that is, the bladder is pushed in the ____ direction. this is why prego women feel urge to urinate so much.
inferior
technical term for labor is
parturition
labor involves a series of strong, rhythmic contractions of the uterine wall. the goal of labor is the expulsion of fetus
labor occurs in 3 stages:
In order:
dilation stage
expulsion stage
placental stage
Dilation stage
The cervix dilates, the fetus is pushed by muscular contractions into the cervical canal, and the amnion ruptures – water breaking
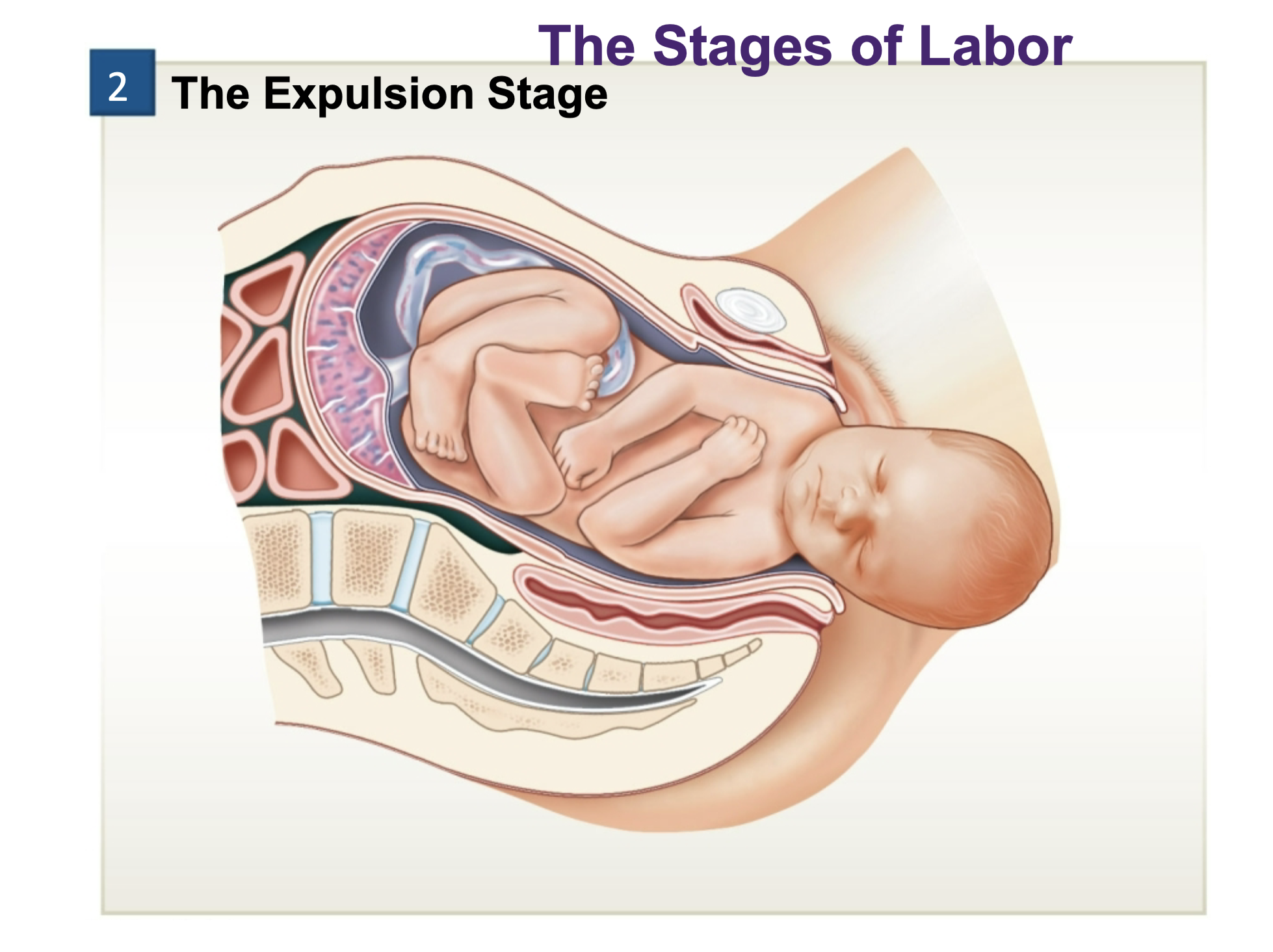
Expulsion stage
The movement of the fetus through the cervical canal and vagina
Delivery can be helped by episiotomy or cesarian section
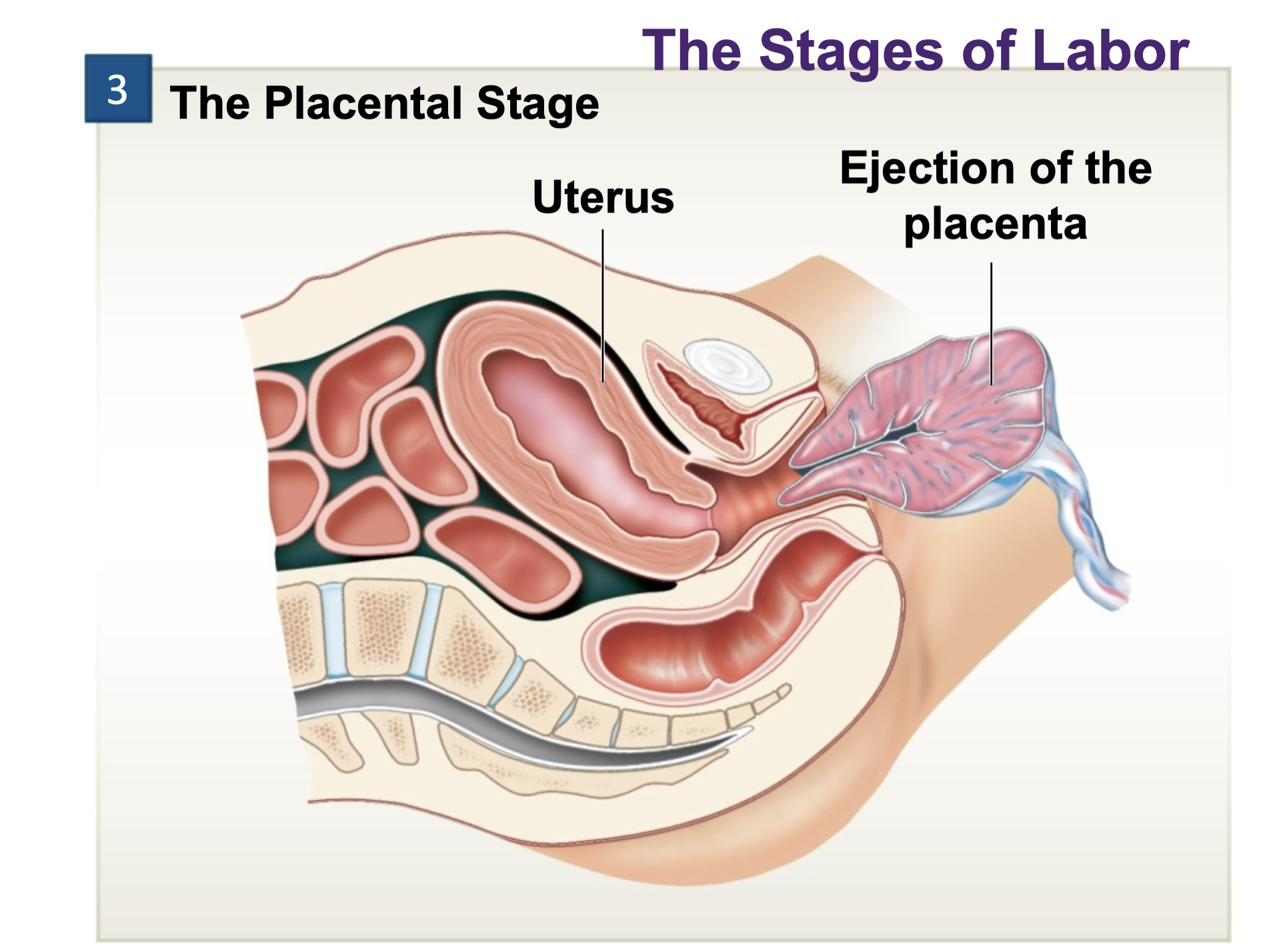
Placental stage
Ejection of the placenta (afterbirth)
Amnion tears during
dilation stage (water breaking)
Fetus emerges during
expulsion stage
Placenta emerges during
placental stage (after birth)
Premature labor refers to
labor that begins prior to full development being reached.
Fetusus born prior to 36/37 weeks are considered to be premature. In this case, these babies will survive provided they receive adequate medical care. Fetuses born before 24 weeks will usually not survive because organ systems have not developed enough to sustain life outside the womb.
The first month after birth is referred to as
neonatal period
During neonatal period, following should occur in the newborn’s body
lungs will fill w air
breathing commences
heart bypasses (shortcuts) should slowly begin to seal shut
HR should drop to ~80-130 bmp
digestive organs start working
kidneys become active and start filtering the blood
metabolism increases to sustain adequate warmth for the newborn