Introduction to Sensory Pathways and Reflexes
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Tract
collection of axons with a common origin
Fasciculus
same as tract
Funiculus
two or more fasciculi
Nucleus
collection of cell bodies within the CNS
Ganglion
collection of cell bodies within the PNS
Contralateral
opposite side
Ipsilateral
same side
Fasciculus cuneatus
lateral in the cord
Fasciculus gracilis
medial in the cord
Conscious pathways starts
from a receptor
Conscious pathways end
in the cerebral cortex
Ascending pathways
afferent (general somatic afferent)
Descending pathways
efferent (somatic motor)
Neurons in GSA pathways (conscious)
3 (or 4 for pain/temp and light (gross) touch
First cell body for GSA pathways
dorsal root ganglion
Second cell body for GSA pathways
posterior horn of gray OR brainstem (closed medulla)
Third cell body for conscious pathways
dorsal thalamus - ventral posterior lateral nucleus (VPL))
Third cell body for reflex pathways
ventral posterior medial (VPM)
Last axon synapse location for conscious sensory pathways
Area 3, 1, 2 in the post-central gyrus of the cerebral cortex
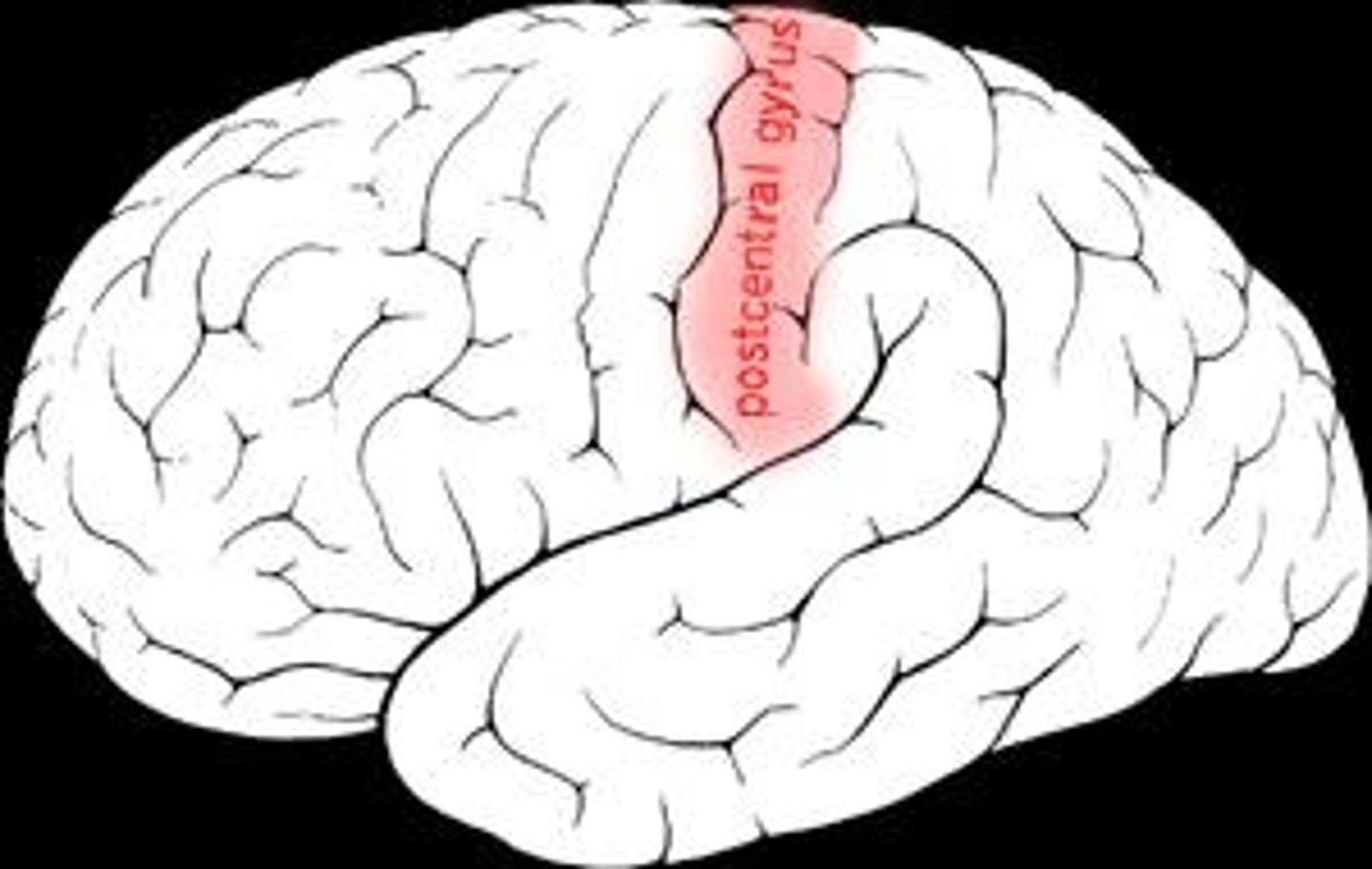
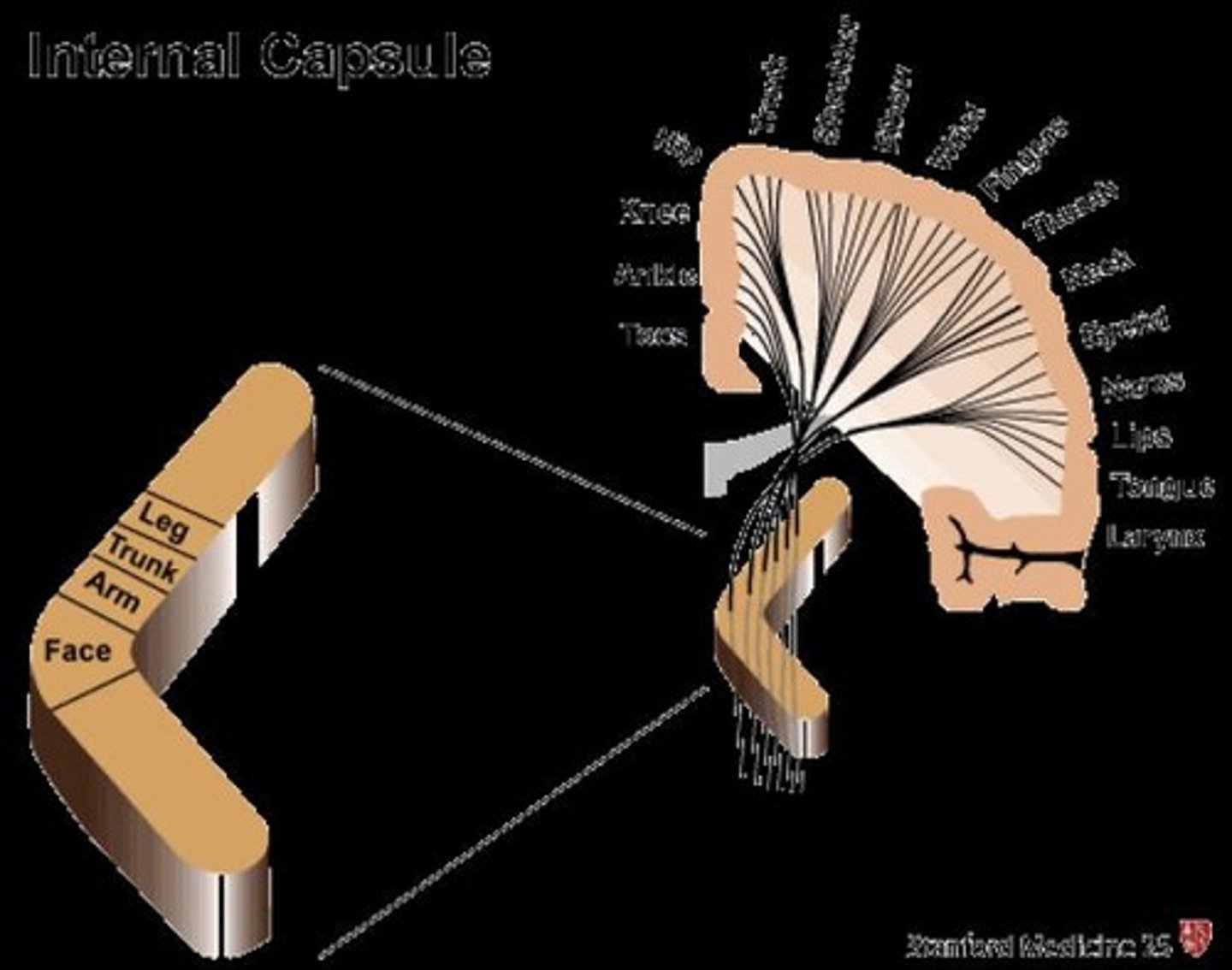
Internal capsule
White matter structure - tract
Types of tactile stimuli
Two-point tactile touch, Light (gross) touch, Pressure, Vibration
Two-point tactile touch
The ability to discriminate 1 and 2 points
Proprioception
Sense of where the body is in space
Where does the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the lower extremity start?
At the receptor in the lower extremity
Where is the first cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV (lower extremity)
In the dorsal root ganglion in the lumbar sacral region.
Through which tract does the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the lower extremity move after the first cell body?
Fasciculus gracilis.
Where is the second cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the lower extremity?
In the nucleus gracilis in the closed medulla.
Where does the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the lower extremity cross over?
In the low medulla at the sensory decussation.
What tract does the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the lower extremity move through after crossing over?
Medial lemniscus.
Where is the third cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the lower extremity?
In the VPL of the dorsal thalamus.
Where does the last axon of the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the lower extremity move to?
From VPL to area 3, 1, 2.
Lesion below sensory decussation results in
Ipsilateral deficit
Lesion above sensory decussation results in
Contralateral deficit
Lesion in fasciculus gracilis results in
Ipsilateral deficit of conscious 2-point tactile, pressure, vibration and proprioception of the lower extremity
Where does the conscious pathway for 2PTPPV for the upper extremity start?
It starts at the receptor in the upper extremity.
Where is the first cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for two-point tactile, pressure, vibration, and proprioception for the upper extremity?
In the dorsal root ganglion in the cervical region (C5-T1).
What tract does the first axon for the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the upper extremity first move through?
Fasciculus cuneatus.
Where is the second cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the upper extremity?
In the nucleus cuneatus in the closed medulla.
Where does the conscious sensory pathways for 2PTPPV for the upper extremity cross over?
In the low medulla at the sensory decussation.
What tract does the pathway for conscious 2PTPPV for the upper extremity move through after crossing over?
The medial lemniscus.
Where is the third cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the upper extremity?
In the VPL of the dorsal thalamus.
Where does the last axon of the conscious sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the upper extremity move to?
From the VPL to area 3, 1, 2.
What tracts are in the posterior funiculus of white
Fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus.
What is the starting point of the conscious sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
Receptor in the lower extremity or upper extremity
Where is the first cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
Dorsal root ganglion
What is the tract of the first axon in the conscious sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
Short axon in Lissauer's tract
Where is the second cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
Posterior horn of gray
Where does the pathway cross over in the conscious sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
Ventral white commissure
In which tract of the spinal cord does the conscious sensory pathway for pain and temperature travel after crossing over?
Lateral spinothalamic tract in the lateral funiculus
Where is the third cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
VPL of the dorsal thalamus
What is the final destination of the last axon in the conscious sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
Area 3, 1, 2
Where does the conscious sensory pathway for light touch start?
At the receptor in the lower extremity or upper extremity.
Where is the first cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for light touch?
In the dorsal root ganglion.
What is the name of the tract of the short axon in the conscious sensory pathway for light touch?
Lissauer's tract.
Where is the second cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for light touch?
Posterior horn of gray.
Where does the conscious sensory pathway for light touch cross over?
Ventral white commissure.
In which funiculus does the conscious sensory pathway for light touch travel?
In the ventral/anterior funiculus as the ventral spinothalamic tract.
Where is the third cell body located in the conscious sensory pathway for light touch?
In the VPL of the dorsal thalamus.
Where does the last axon of the conscious sensory pathway for light touch move to?
From the VPL to area 3, 1, 2.
What is the sensory decussation responsible for?
Conscious two-point tactile, pressure, vibratory, and proprioception of upper and lower extremities.
What does the ventral white commissure transmit?
Conscious pain, temperature, and conscious light (gross, superficial) touch.
What does the anterolateral system/spinothalamic pathway involve?
Pain and temperature pathway and light gross touch.
What does the medial lemniscal pathway or dorsal column pathway involve?
Two-point tactile, vibratory, pressure, and proprioception.
Reflex pathways endpoint
End anywhere other than the thalamus (midbrain or medulla).
Where does the reflex sensory pathway for pain and temperature start?
At the receptor in the lower extremity or upper extremity.
Where is the first cell body located in the reflex sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
Dorsal root ganglion.
Where is the second cell body located in the reflex sensory pathway for pain and temperature?
Posterior horn of gray.
Where does the reflex sensory pathway for pain and temperature cross over?
Ventral white commissure.
In which tract does the reflex sensory pathway for pain and temperature travel?
Spinotectal tract.
Where does the reflex sensory pathway for pain and temperature end?
In the tectum of the dorsal part of the midbrain.
Where does the reflex sensory pathway for 2PTPPV for the lower extremity start?
At the receptor in the lower extremity or upper extremity.
Where is the first cell body located in the reflex sensory pathway for the lower extremity?
In the dorsal root ganglion in the lumbar sacral portion of the cord.
Where is the second cell body located in the reflex sensory pathway for the lower extremity?
In Clarke's nucleus in the cord.
Does the reflex sensory pathway for the lower extremity cross over?
No, it does not cross.
In which tract does the reflex sensory pathway for the lower extremity travel?
In the dorsal cerebellar tract.
How does the reflex sensory pathway exit the cerebellum?
Via the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
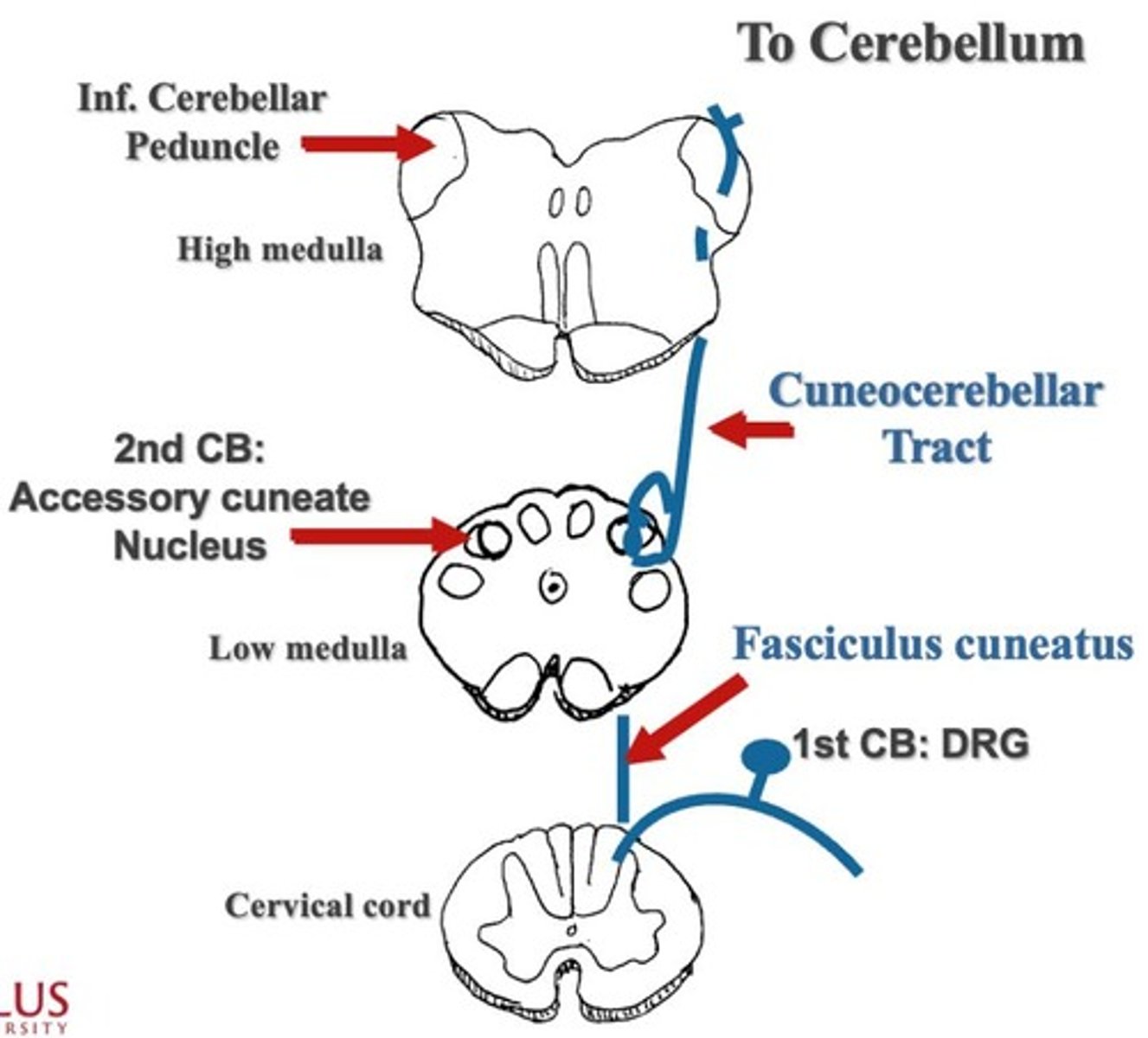
Reflex sensory pathway for upper extremity
Starts at the receptor in the lower extremity or upper extremity, first cell body is in the dorsal root ganglion in the cervical cord, travels fasciculus cuneatus, second cell body is Accessory cuneate nucleus in the medulla, no crossing, travels in the Cuneocerebellar tract, exits the cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle towards the cerebellar.
Cerebellum modulation
Modulates voluntary motor activity.
Source of proprioceptive information
Comes from muscle spindles in the muscles regarding information about change in length, and from Pacinian and free nerve endings in joints to determine if they are flexed and extended.
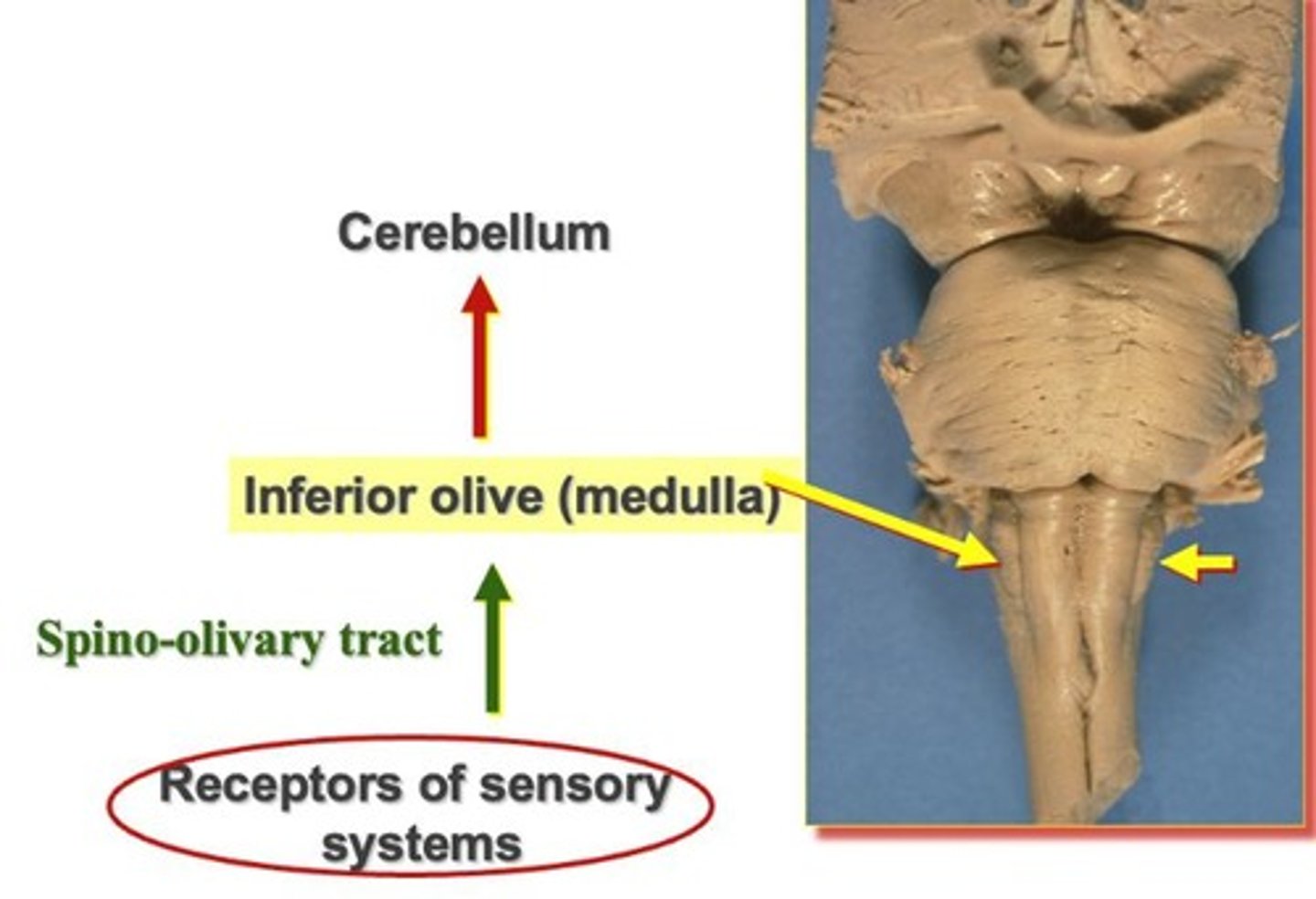
Reflex sensory pathway for spino-olivary tract
Starts at receptors of sensory systems that give information about muscles, travels in the spino-olivary tract, travels to inferior olive of medulla (lateral), information travels to cerebellum to modulate motor activity by the sensory input.
Reflex sensory pathway for spino-reticular tract
Starts at all general receptors, travels via the spinoreticular tract, information travels to the reticular activating system involved in pain transmission and emotional response to pain.
Pain transmission
Transmitted by myelinated axons (A delta) to somatosensory cortex and unmyelinated axons (C fibers) to the reticular formation to the thalamus and to the limbic brain, which do not go to the cortex.
Reticular formation
Found in the core of the brainstem, has two components: sensory (reticular activating system) and motor, transmits information to the thalamus and cortex responsible for the awakened state.
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
Used for sending information from general sensation receptors to the reticular formation.
RAS and consciousness
Reticular formation transmits information from the reticular activating system to the cortex and thalamus; compression can result in unconsciousness.
Principles of Sensory Systems
Includes parallel pathways (more than one pathway), relay nuclei (change message, sharpen it or inhibit a message), topographical representation (hand takes up more information and neighborhoods are preserved), and most sensory pathways cross (except reflex pathways for two-point tactile touch).
Topographical organization in sensory cortex
Relates to the anterior and posterior vascular system and stroke.
Dorsal root ganglion
First cell body location for sensory pathways in both lower and upper extremities.
Clarke's nucleus
Second cell body location in the reflex sensory pathway for the lower extremity.
Accessory cuneate nucleus
Second cell body location in the reflex sensory pathway for the upper extremity.
Cuneocerebellar tract
Pathway traveled by sensory information from the upper extremity to the cerebellum.
Dorsal cerebellar tract
Pathway traveled by sensory information from the lower extremity to the cerebellum.
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
Exit point for sensory information traveling from the cerebellum.
Spinothalamic tract
Part of the anterolateral system affected by diseases impacting white matter of the spine.
Ventral white commissure
Pathway for pain and temperature and light gross touch.
Emotional response to pain
Involves the reticular activating system in pain transmission.
Myelinated axons (A delta)
Transmit sharp pain to the somatosensory cortex.
Unmyelinated axons (C fibers)
Transmit dull pain to the reticular formation and limbic brain.
Lower extremities
Represented medially in the sensory homunculus.
Upper extremities
Represented laterally in the sensory homunculus.