Atomic Theory & Chemical Composition
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
First Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous atoms, forming 1 mole of gaseous cations
FINE = First Ionization energy INcreases East (→)
First Ionization Energy Equation
Gas Goes Positive, Electron Goes Solo
Molar Concentration (Molarity)
Moles over Liters Makes Molarity
The amount of solute (in moles) dissolved in 1 liter of solution.
Dimensional Analysis
Basic Steps:
Write down the quantity with units
Multiply by conversion factors (fractions equal to 1) to cancel units
Simplify until you get the desired units
Stoichiometric Mole Ratios in Reactions
"Coefficients Connect Moles"
Use the balanced equation coefficients as conversion factors between species
Partial Pressure & Stoichiometry
"Pressure Follows Proportion"
Use stoichiometric ratios to find unknown partial pressures
Electron Sub shells (Smart People Don’t Forget)
s, p, d, f → easy way to remember subshell order
"Electron subshells are the rooms electrons roam—each with a shape, a limit, and a quantum story."
Aufbau Principle
Rule that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first before moving to higher ones
Electrons fill orbitals in a specific order:
1s → 2s → 2p → 3s → 3p → 4s → 3d → 4p → 5s → …
Hund’s Rule
“Empty Seats First!”
Think of electrons on a bus—they don't like sitting together unless they have to!
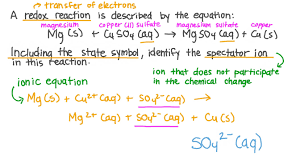
What are spectator ions in a chemical reaction?
🔍 Spectator ions are ions that do not participate in the chemical change during a reaction. They appear unchanged on both sides of the ionic equation.
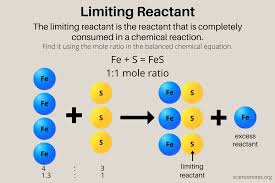
What is the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction?
The limiting reactant is the substance that gets used up first, limiting the amount of product that can be formed.
🧠 Think of it like the ingredient you run out of when baking cookies—you can’t make more no matter how much flour or sugar you have left.
What is a thermodynamic system?
🧊 A thermodynamic system is the part of the universe we choose to study—specifically the matter and energy exchanges happening within defined boundaries.
It’s separated from the surroundings by a real or imaginary boundary, and interactions across the boundary—like heat or work—are key to thermodynamic analysis.
What are the surroundings in a thermodynamic context?
🌐 Surroundings refer to everything outside the thermodynamic system—the rest of the universe that can interact with the system via energy or matter exchange.
What are the three common types of thermodynamic systems?
Thermodynamic systems are classified based on how they exchange energy and matter with their surroundings:
“Open door, closed window, isolated cave.”
Open door → everything flows in and out
Closed window → only light (energy) passes
Isolated cave → nothing gets in, nothing gets out
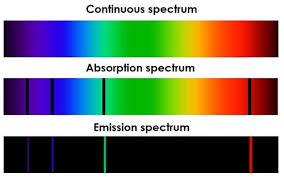
What is a line spectrum in chemistry and physics?
A line spectrum is a set of discrete, colored lines that represent specific wavelengths of light emitted or absorbed by atoms or molecules.
It’s a fingerprint of an element—each has a unique pattern based on its electron transitions between energy levels.
Who are the alkaline earth metals?
Alkaline earth metals are Group 2 elements in the periodic table
How does reactivity change down the group of alkali metals?
Alkali metal become more reactive as you move down the group.
Why?
Larger atomic radius → outer electron farther from nucleus
Weaker attraction to nucleus → easier to lose the lone valence electron
Lower ionization energy → less energy needed to react
How do alkaline earth metals form +2 cations?
“Group 2 gives two.” Simple and direct: Group 2 metals lose 2 electrons → +2 cation
Alkaline earth metals (Group 2: Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra) have two valence electrons in the outermost shell.
How do alkaline earth metals react with water?
Reactivity increases down Group 2
These reactions form:
Metal hydroxides (e.g., Ca(OH)₂)
Hydrogen gas (H₂) is released
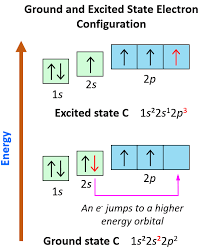
What happens when an electron absorbs energy to move between orbitals?
The amount of energy absorbed equals the energy difference between the two orbitals
When an electron absorbs energy, it jumps from a lower energy orbital to a higher one—entering an excited state.
Where can you find the mass number and atomic number of an isotope?
“A superscript above the symbol shows the atom’s heft.” The higher that number, the heavier the isotope! Or like Carbon-14 for mass number.
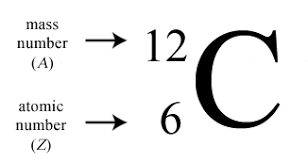
How do you calculate the number of neutrons in an isotope?
Mass minus atomic = neutron magic.” Just subtract the atomic number from the mass number to reveal the neutron count!
How does net charge tell you if an isotope gained or lost electrons?
Neutral atom: electrons = protons → net charge = 0
Cation (positive charge): fewer electrons than protons → electrons lost
Anion (negative charge): more electrons than protons → electrons gained
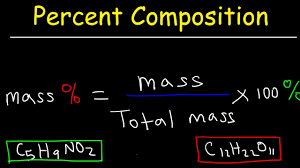
What is mass percent and how do you calculate it?
Mass percent (also called percent by mass) expresses the ratio of the mass of a component to the total mass of the mixture or compound, multiplied by 100
What happens during β⁻ decay?
In β⁻ decay, a neutron is converted into a proton, and an electron (β⁻ particle) is emitted from the nucleus.
🧪 Nuclear reaction:
n → p⁺ + e⁻ + ν̄ₑ (anti-neutrino also released)
🧬 Example:
Carbon-14 → Nitrogen-14 + β⁻
What are gamma rays and why are they significant?
Gamma rays (γ-rays) are a form of ionizing electromagnetic radiation with very high energy and short wavelength.
🧬 They are typically emitted during nuclear decay, often following alpha or beta decay, when the nucleus releases excess energy.
What happens during alpha decay?
In alpha decay, an unstable nucleus emits an alpha particle, which is made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons — identical to a helium-4 nucleus.
🧪 Effect on the nucleus:
Atomic number ↓ by 2
Mass number ↓ by 4
Why do elements gain or lose electrons during chemical reactions?
Elements tend to gain or lose electrons to achieve a full valence shell, mimicking the stable electron configuration of the nearest noble gas.
Why is nitrogen gas (N₂) often used as an inert atmosphere in chemical reactions?
N₂ is an inert gas due to its strong triple bond (N≡N), which makes it very unreactive under standard conditions.
What is the Lewis structure of nitrogen gas (N₂)?
The Lewis structure of N₂ shows a triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms, with each nitrogen having one lone pair.
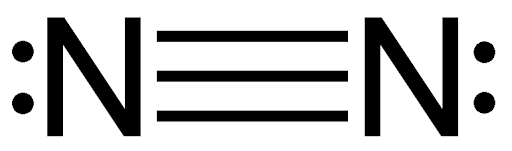
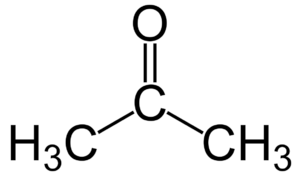
What is the structure of acetone?
Acetone (C₃H₆O) is the simplest ketone
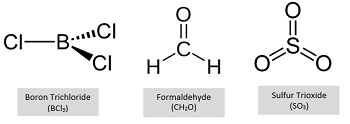
What is trigonal planar molecular geometry and when does it occur?
Trigonal planar geometry occurs when a central atom forms three bonds and has no lone pairs, arranging atoms 120° apart in a flat, triangular shape.
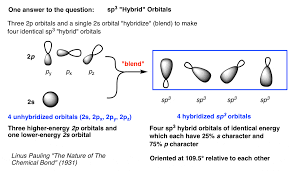
How is orbital hybridization determined?
You can determine hybridization by counting the regions of electron density (bonds + lone pairs) around an atom
What is a dication in chemistry? (Double the loss, double the charge)
Lose two electrons → gain a +2 charge