PSYCH
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Behavioral Phenotypes
Observable traits and characteristics resulting from the interaction of genetics and environment, influencing behavior.
Cognitive Profile
Individual's unique pattern of cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
Genetic Disorder
An illness caused by abnormalities in an individual's DNA.
Williams Syndrome
A genetic condition characterized by developmental delays and intellectual disabilities. Caused by a microdeletion. Their strengths are in vocabulary and short term memory but not in visual spatial functioning or perceptual planning
Hyperacusis
Increased sensitivity to certain frequencies and volumes of sound.
Global vs Local Processing
Different ways individuals perceive and interpret information globally (overall picture) or locally (details).
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)
A genetic disorder causing insatiable hunger and obesity. Caused by a deletion on paternally derived chromosome 15. 25-30% of cases present with maternal uniparental disomy (UPD)
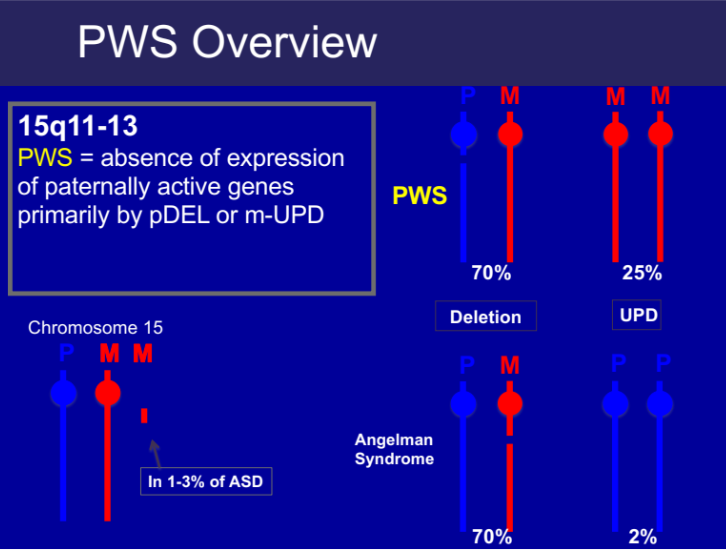
Genomic Imprinting
Differential expression of genetic material depending on its parental origin.
Sensory Processing Disorder
A neurodevelopmental disorder that affects the brain's ability to process sensory stimuli correctly, leading to significant problems in sensory organization that impact various areas of daily life.
Sensory Integration
A systematic process where sensory receptors capture external and internal stimuli, transform them into information sent to the brain, and determine motor and behavioral responses.
4 phases of sensory integration
Registration
Modulation
Discrimination
Response
Sensory Processing Disorder
Defined by changes in one or more of the phases of sensory integration being altered. It is unclear whether it is a stand-alone disorder or a collection of symptoms.
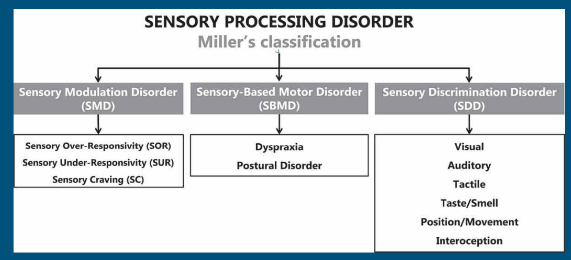
Sensory Modulation Disorder (SMD)
A classification under Miller's Model characterized by difficulty regulating responses to sensory stimulation, including subtypes like Sensory Over Response (SOR), Sensory Under Responsivity (SUR), and Sensory Craving (SC).
Sensory Based Motor Disorder (SBMD)
A classification under Miller's Model characterized by difficulty with balance, motor coordination, performance of skilled; non-habitural and habitual motor tasks. Includes the subtypes: dyspraxia and postural disorder
Dyspraxia
Coordination and movement hindered
Postural disorder
Body stabilization issues and motor function
Sensory discrimination disorder (SDD)
Difficulty interpreting specific characteristics of sensory stimulation and affects any sensory system
Poor Sensory Perception
A classification under Schaaf's Model involving difficulty in identifying, discriminating, and interpreting sensory information in more than one sensory system.
Schaaf’s Model
Developed from patterns of SPD that compares atypical people to normal kids. It’s classification is based on the Ayres Sensory Integration Test and the Sensory Integration and Praxis Test
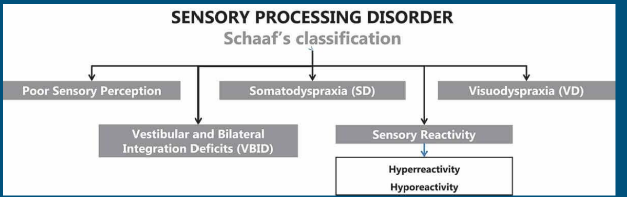
5 common patterns (Schaaf’s model)
Poor sensory perception, somatodyspraxia, vestibular and bilateral integration deficits, visuodyspraia, sensory reactivity
Somatodyspraxia
A classification under Schaaf's Model involving poor sensory perception, especially tactile, along with signs of poor motor planning in new motor tasks.
Vestibular and Bilateral Integration Deficits
A classification under Schaaf's Model involving poor vestibular processing along with difficulties in related motor functions like muscle tone, balance, and coordination.
Visuodyspraxia
A classification under Schaaf's Model involving poor visual perception and visual motor coordination.
Sensory Reactivity
A classification under Schaaf's Model involving excessive reactions that interfere with daily activities, including hyperreactivity and hyporeactivity.
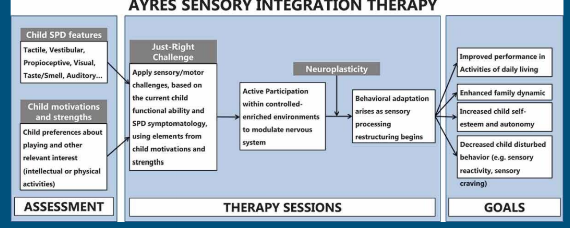
Ayres Sensory Integration Therapy
A therapy that focuses on reducing sensory difficulty in daily life, increases children self esteem, improve family dynamics and quality of life. It is made up of “fair” challenges to the child. It relies on neural plasticity, enriched environments, and active participation
Motion Sensing Game Based Therapy
The goal is to improve bodily-kinesthetic coordination and social participation. Utilizes the Wii. Lots of short term positive outcomes related to fine and gross motor skills, balance, social participation, etc

Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD)
A condition where the brain has trouble receiving and responding to information that comes in through the senses, leading to difficulties in processing and responding to sensory stimuli.
Cognitive Capacity
The ability of an individual to process and retain information, make decisions, and solve problems.
Symptoms of SPD
Hyperactivity, hypoactivity, poor self esteem, impariments in behavior, irritability, etc

Point Mutation
A type of mutation involving the substitution of a single base pair, which can result in different amino acids being incorporated into a protein.
Missense Mutation
A type of point mutation where a single amino acid is replaced by another in the protein chain, potentially affecting protein function.
Nonsense Mutation
A type of point mutation where a premature stop codon is introduced, leading to truncated and often nonfunctional proteins.
X-Linked Disorders
Genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes located on the X chromosome, with some primarily affecting males due to their hemizygous nature.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Single base substitution which alters the production of phenylalanine hydroxylase. It is characterized by intellectual disability, microcephaly, abnormal gait, and seizures
Tay-Sachs disease
An autosomal recessive disorder causes by a mutation in the gene. It causes a deficiency in enzyme hexosaminidase (Hex-A). It is characterized by neurological deterioration, deafness, blindness, seizures, and fatality by 5
Neurofibromatosis
An autosomal dominant disorder causes by a nonsense mutation. It is characterized by lumps (fibromas), cafe-au-lait spots, ADHD, hypermobility
Rett syndrome
An x linked dominant disorder that is fatal for male embryos. It is characterized by post-natal microcephaly, hand-wringing, progressive deterioration and loss of skills.
Teratogens
Substances capable of disrupting embryonic or fetal development and causing malformations.
Critical periods of development
Specific times during development when organs are vulnerable to toxins, viruses, and genetic abnormalities, potentially leading to birth defects.
Rubella (German measles)
A viral infection that can cause birth defects if contracted during pregnancy, leading to conditions like deafness, cataracts, heart defects, microcephaly, and intellectual disability.
TORCH Infections
Toxoplasmosis, Other (HIV, Syphilis, and others), Rubella (German Measles), Cytomegalovirus, and Genital Herpes
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
A condition caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy, leading to cognitive deficits, low birth weight, slowed growth, and physical and behavioral abnormalities.
Congenital Syphilis
Syphilis that is passed from a mother to her baby during pregnancy, potentially causing severe health issues.
Genital Herpes
An infection caused by the herpes simplex virus, with type 2 being the usual cause of genital herpes.
Neonatal Herpes Simplex
Herpes simplex virus infection in newborn babies, often transmitted during delivery (85%) and can lead to severe health complications.
Congenital Zika Syndrome
A condition in babies caused by Zika virus infection during pregnancy, leading to birth defects like microcephaly, decreased brain tissue, damage to eye, limited range of joint motion, and too much muscle tone
Low Birth Weight (LBW)
Babies born weighing less than 2500 grams or 5.5 lbs.
Premature Birth
Birth that occurs before 37 weeks of gestation, increasing the risk of health issues for the baby.
Early preterm delivery
Delivery that occurs before 32 weeks.
Neonatal Mortality
Death of a newborn within the first 28 days of life, with preterm birth being a significant factor.
Causes of Premature Birth
Factors such as maternal infections, substance abuse, and maternal age that can contribute to babies being born prematurely.
Gestational Weeks
Number of weeks a baby has been in the womb.
Multifetal Pregnancy
Pregnancy with more than one fetus.
Executive Function Deficits
Cognitive impairments affecting attention, learning, and behavior.
Small for gestational age
Refers to babies born below the 10th percentile in weight for their gestational age. Refers to neonates.
Name some general risk factors on prenatal development
Nutrition, stress, mother’s age, teratogens
Rubella vaccine (MMR) indications
Infants >12 months, susceptible adolescents and adults, women of childbearing age (especially outside of the US)
Treatment for congenital syphilis
Penicillin
HSV 1 vs HSV 2
HSV 1 - Most commonly infects mouth and lips, causing sores
HSV 2 - Genital herpes, but can also infect mouth
Very low birth weight (VLBW)
Babies born below 1500 grams or 3.3 lbs
Extremely low birth weight (ELBW)
Babies born below 1000 grams or 2.25 lbs
Micropreemie
Babies born below 800 grams or 1.8 lbs
Intrauterine growth restricted (IUGR)
Refers to babies born below the 10th percentile in weight for their gestational age. Refers to fetuses.
Name some predictors of having a preterm birth
Multifetal pregnancy, history of preterm labor, sex organ abnormailites, mid trimester bleeding
Postconceptional age (PCA)
Dates the onest of humann development from the presumed date of ovulation
Gestational age (GA)
Measured from the first day of the last menstural period, which is 2 weeks earlier than the PCA