Muscular System
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
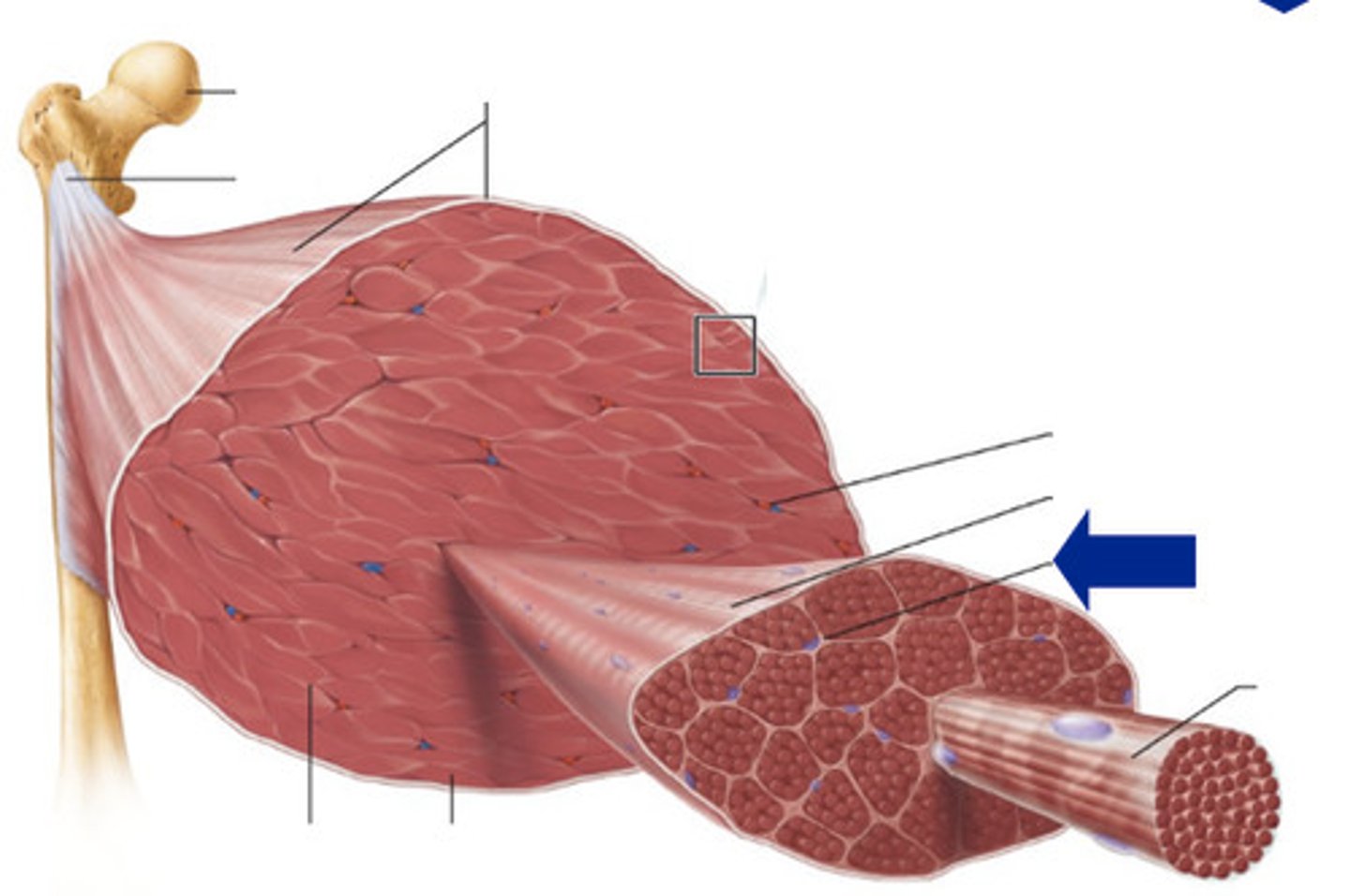
Fascia
sheet of dense connective tissue that separates individual muscles and helps hold them in position
Epimysium
sheath of connective tissue that surrounds a skeletal muscle (beneath the fascia)
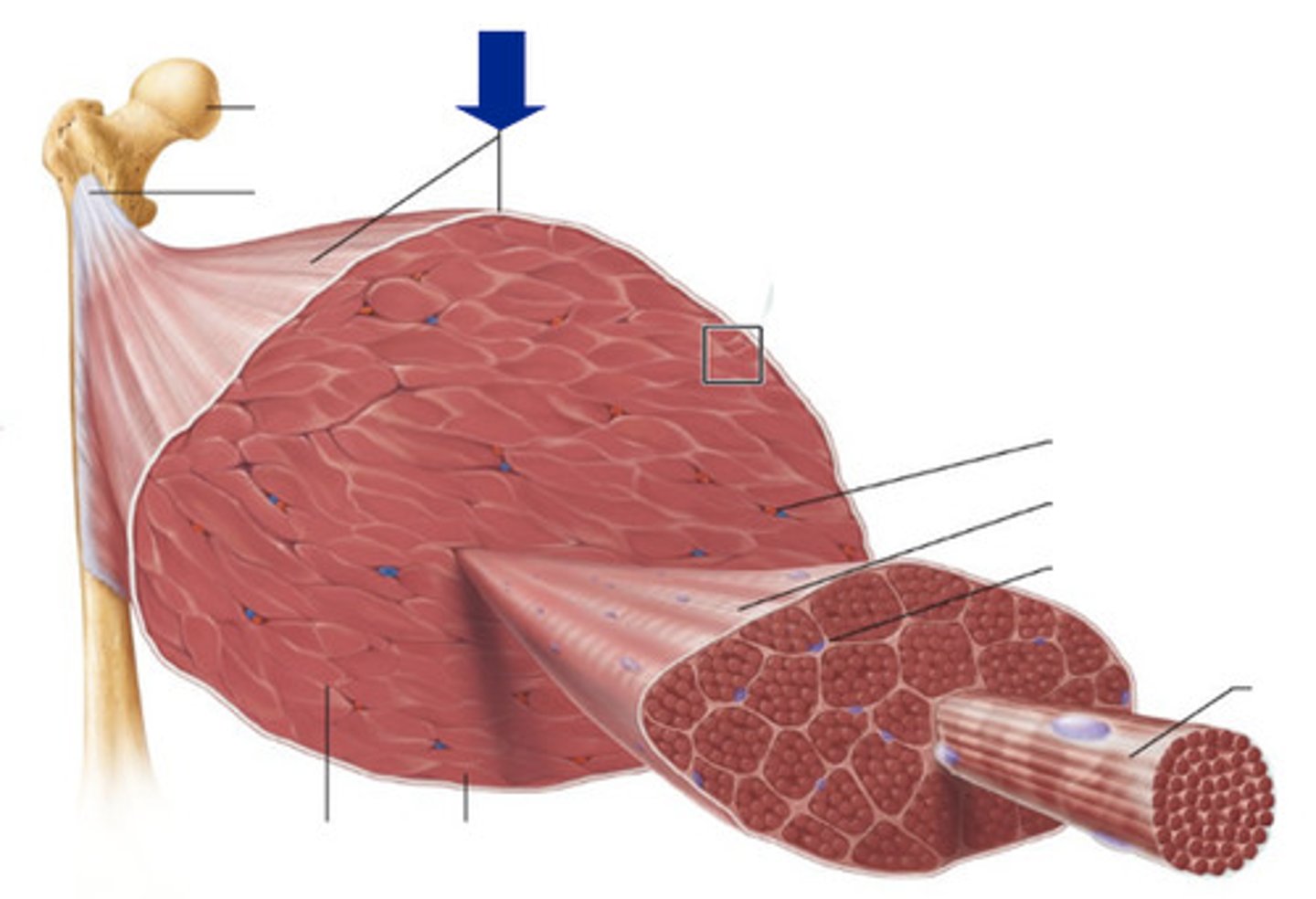
Perimysium
sheath of connective tissue that encloses a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers (fascicle)
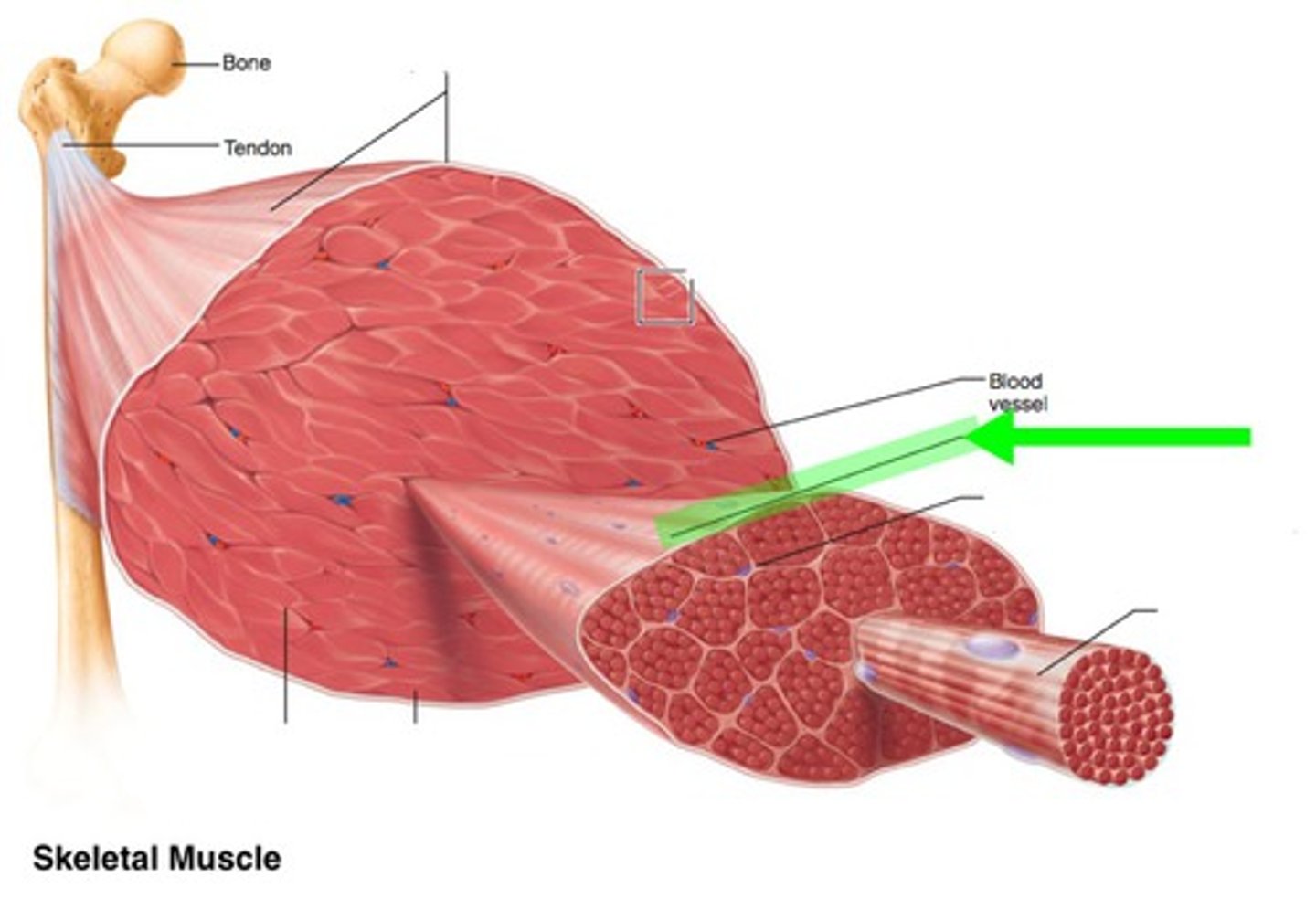
Endomysium
sheath of connective tissue surrounding each skeletal muscle fiber
Tendon
cordlike connective tissue that connects muscle to bone
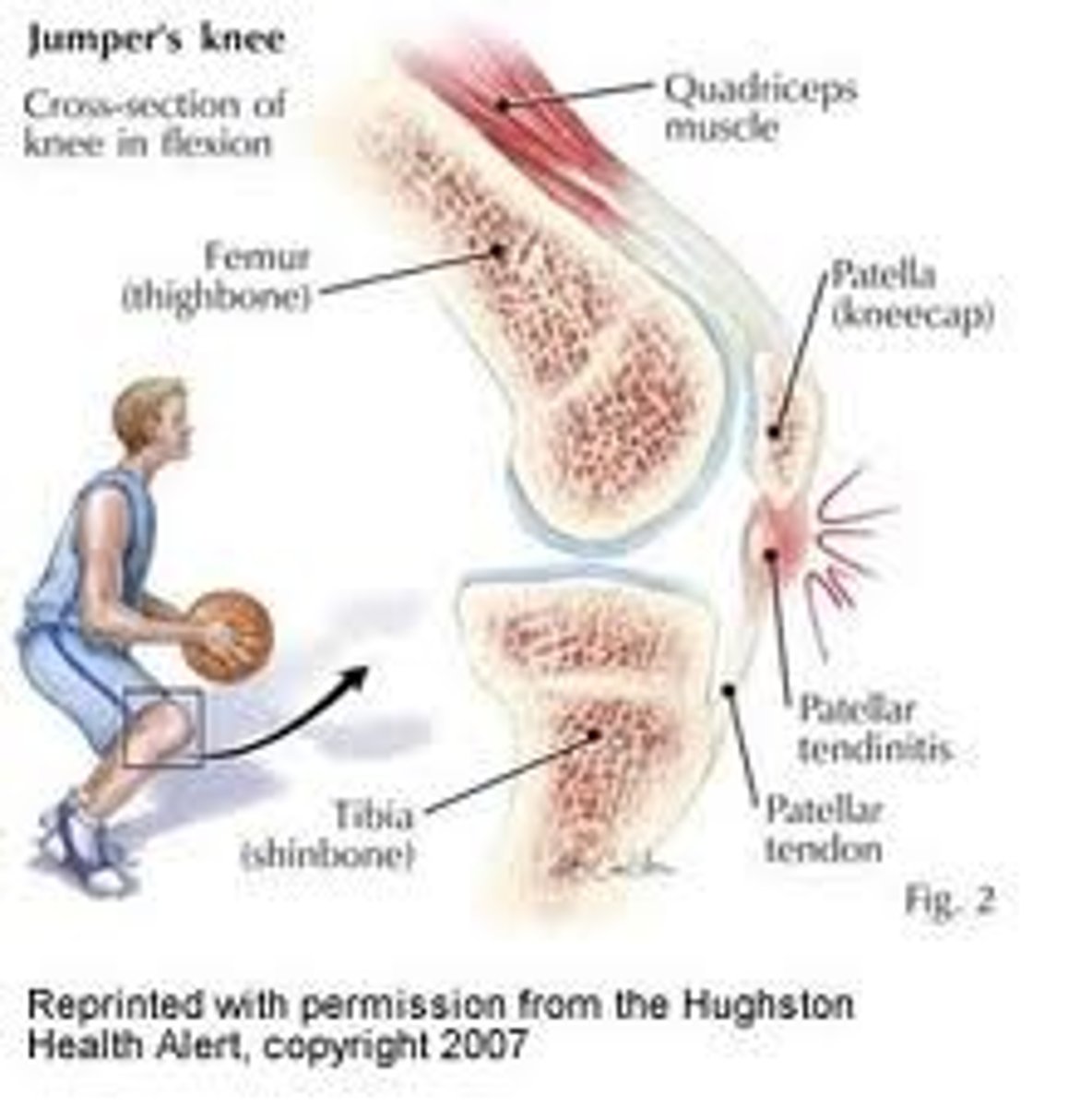
Tendinitis
inflammation of a tendon
Sprain
an injury to the ligament

Strain
an injury to a muscle or tendon

Skeletal muscle fiber
single cell that contracts (exerts a pulling force) in response to stimulation and relaxes when stimulation ends; also known as myofiber
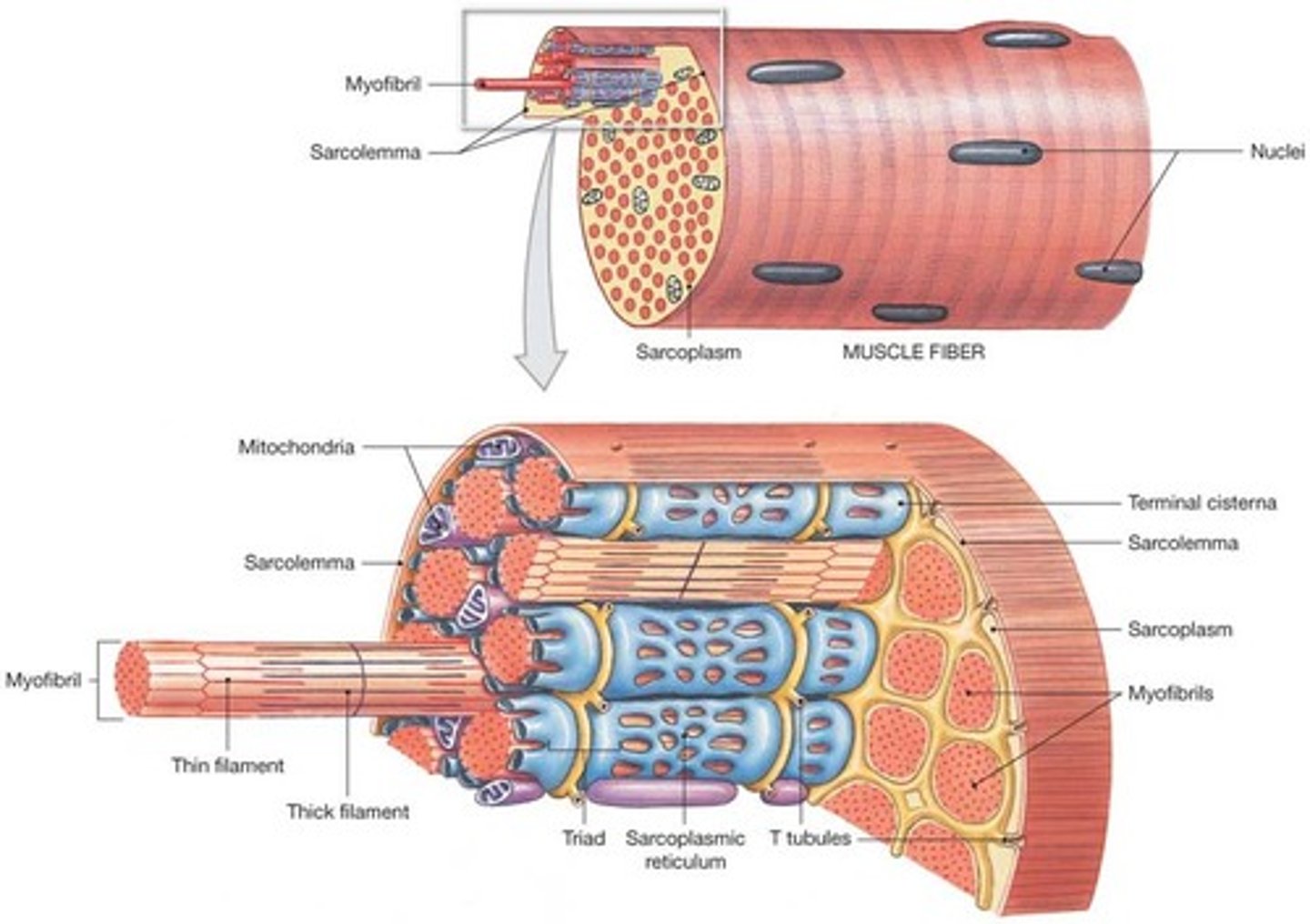
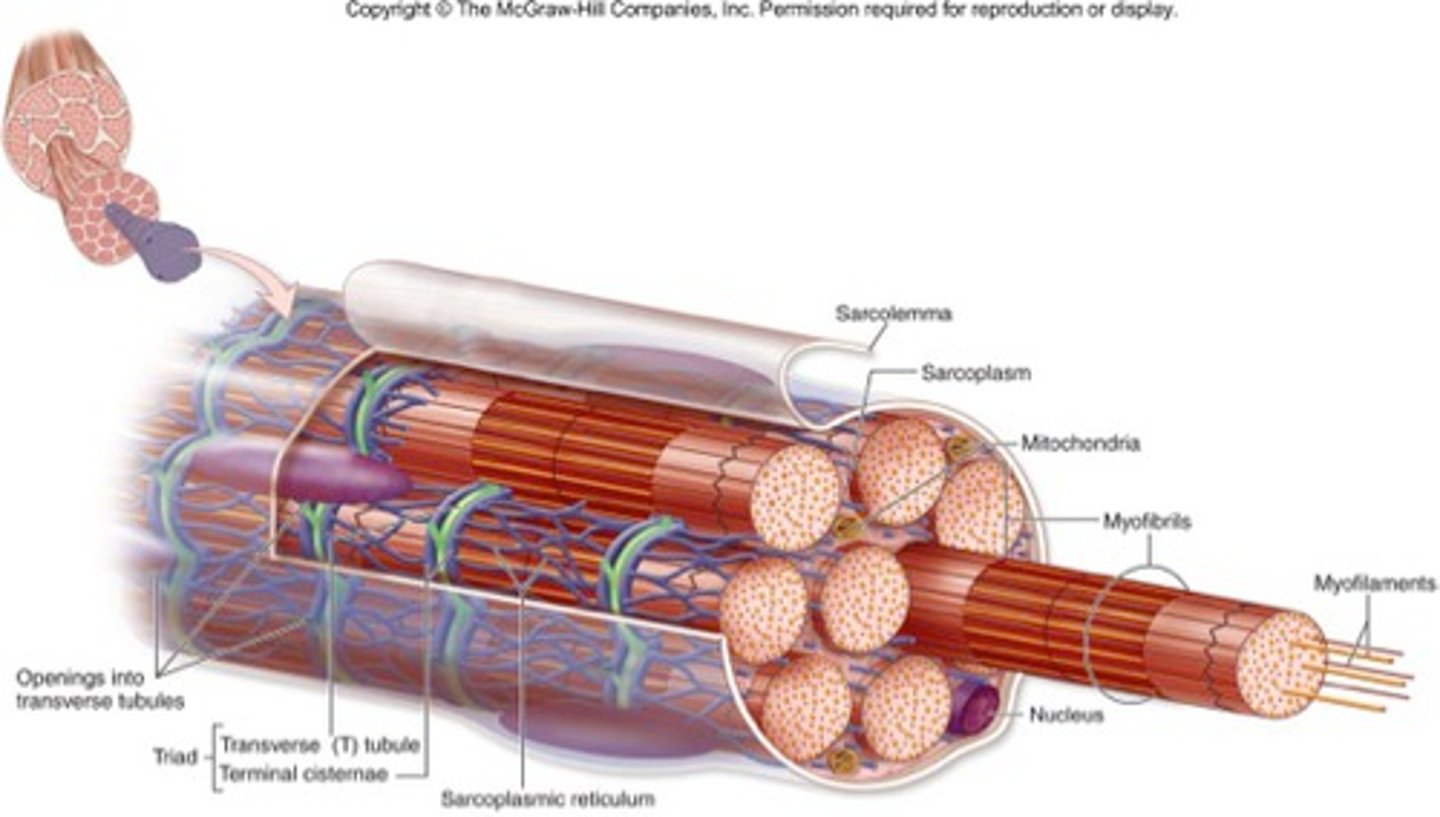
Sarcolemma
the cell membrane in a muscle cell
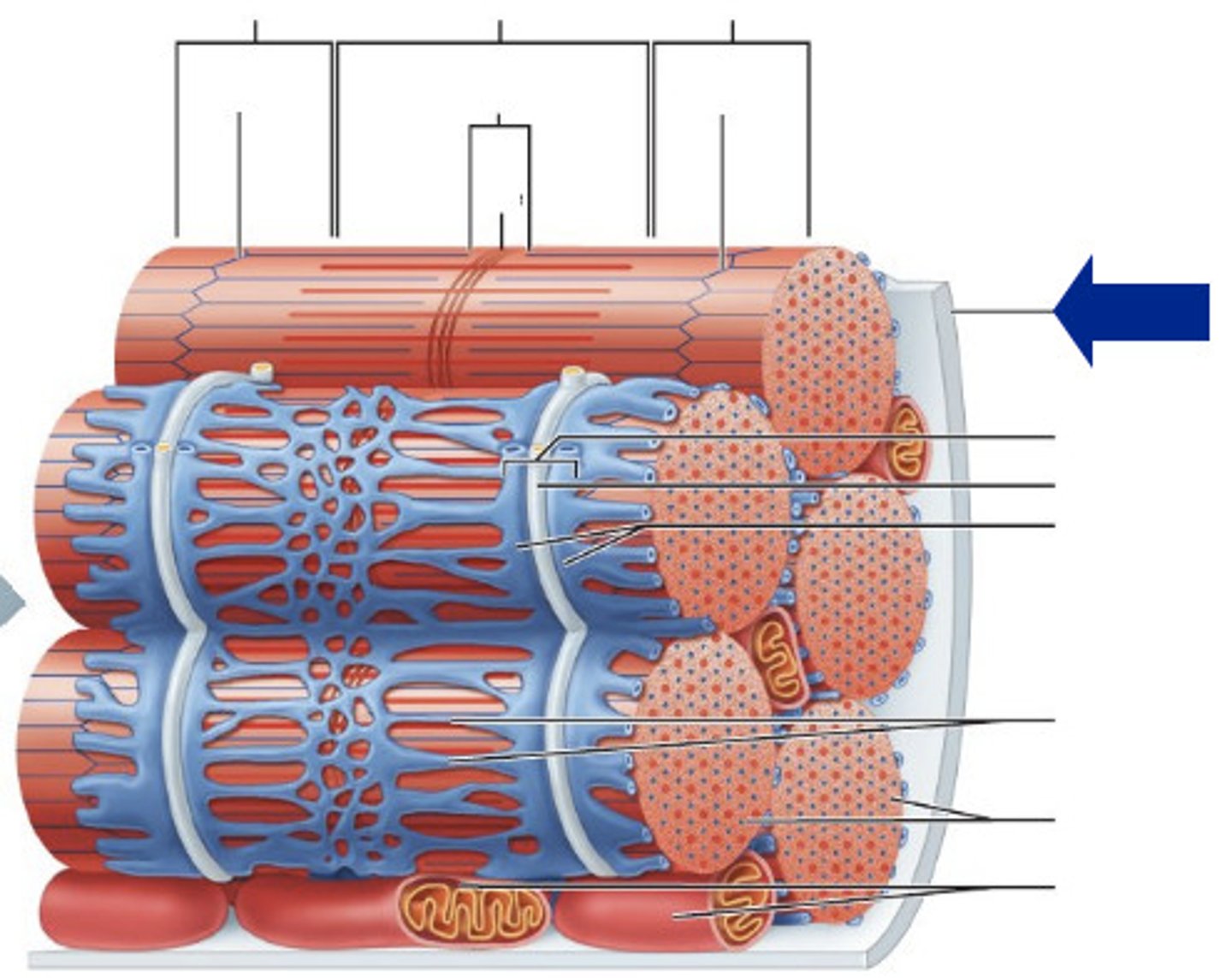
Sarcoplasm
the cytoplasm in a muscle cell
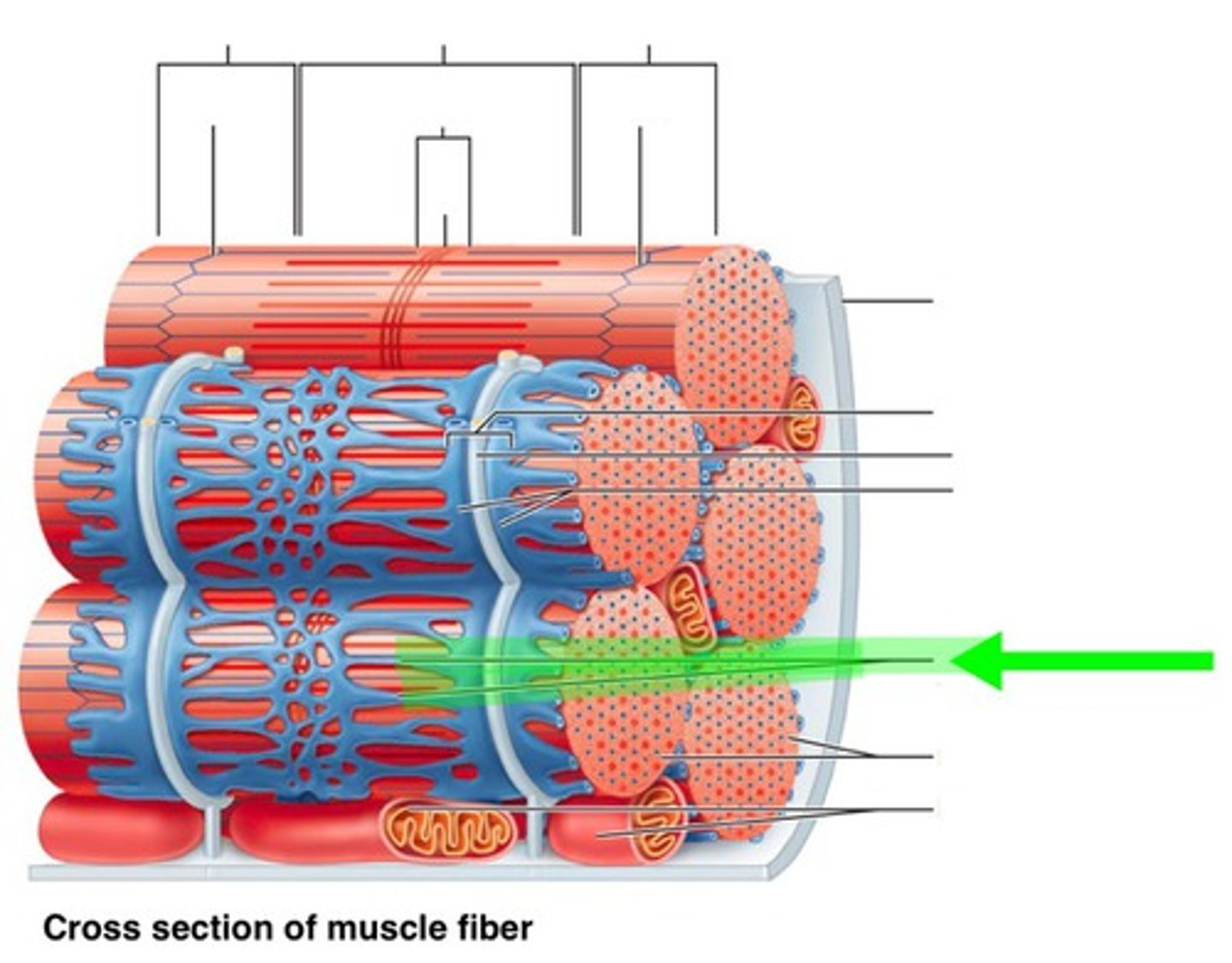
Myofibril
contractile fiber in striated muscle cells that play a fundamental role in contractions
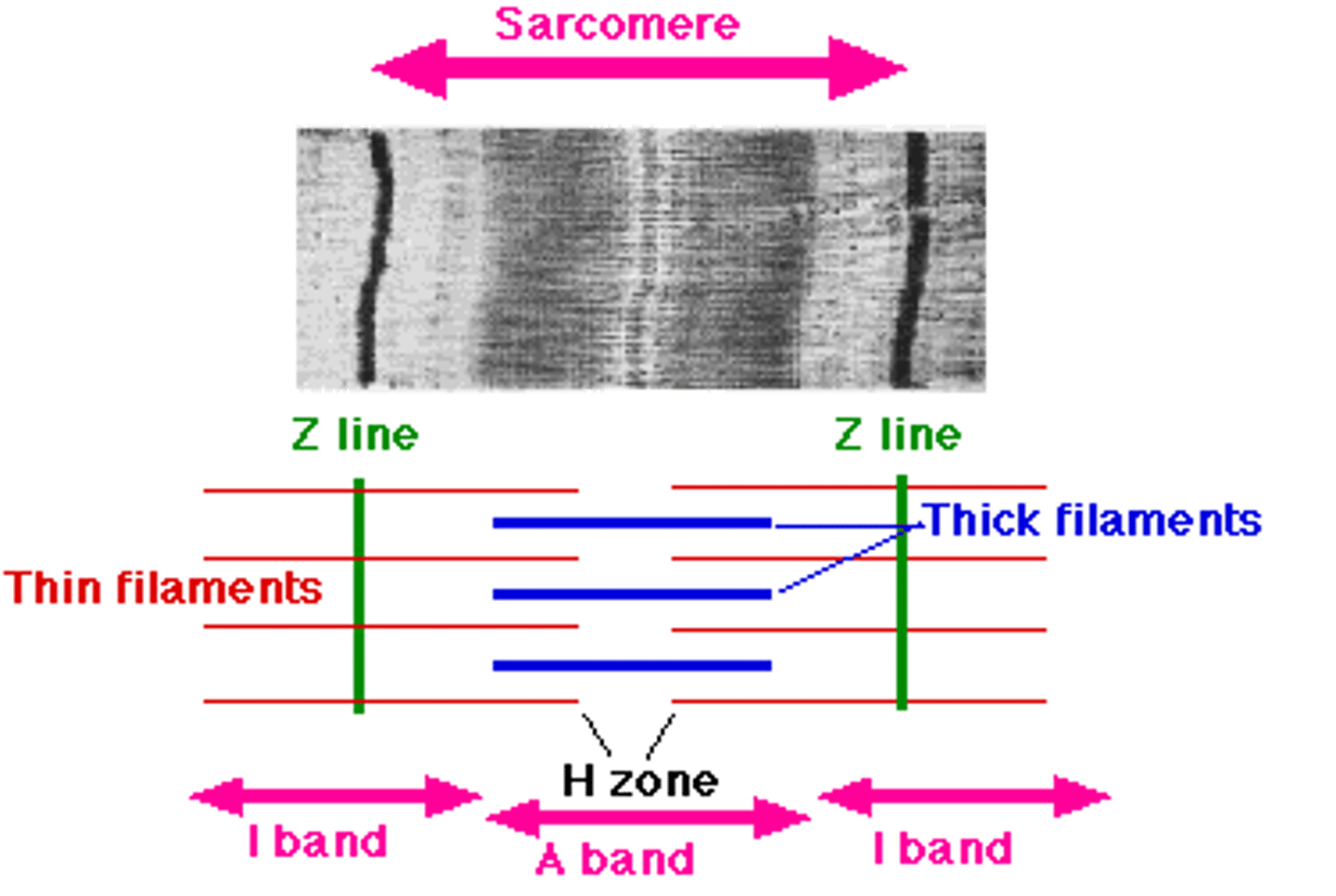
Sarcomere
structural unit of a myofibril and the functional unit of muscle contraction
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
membranous network of channels and tubules within a muscle fiber; stores calcium ions
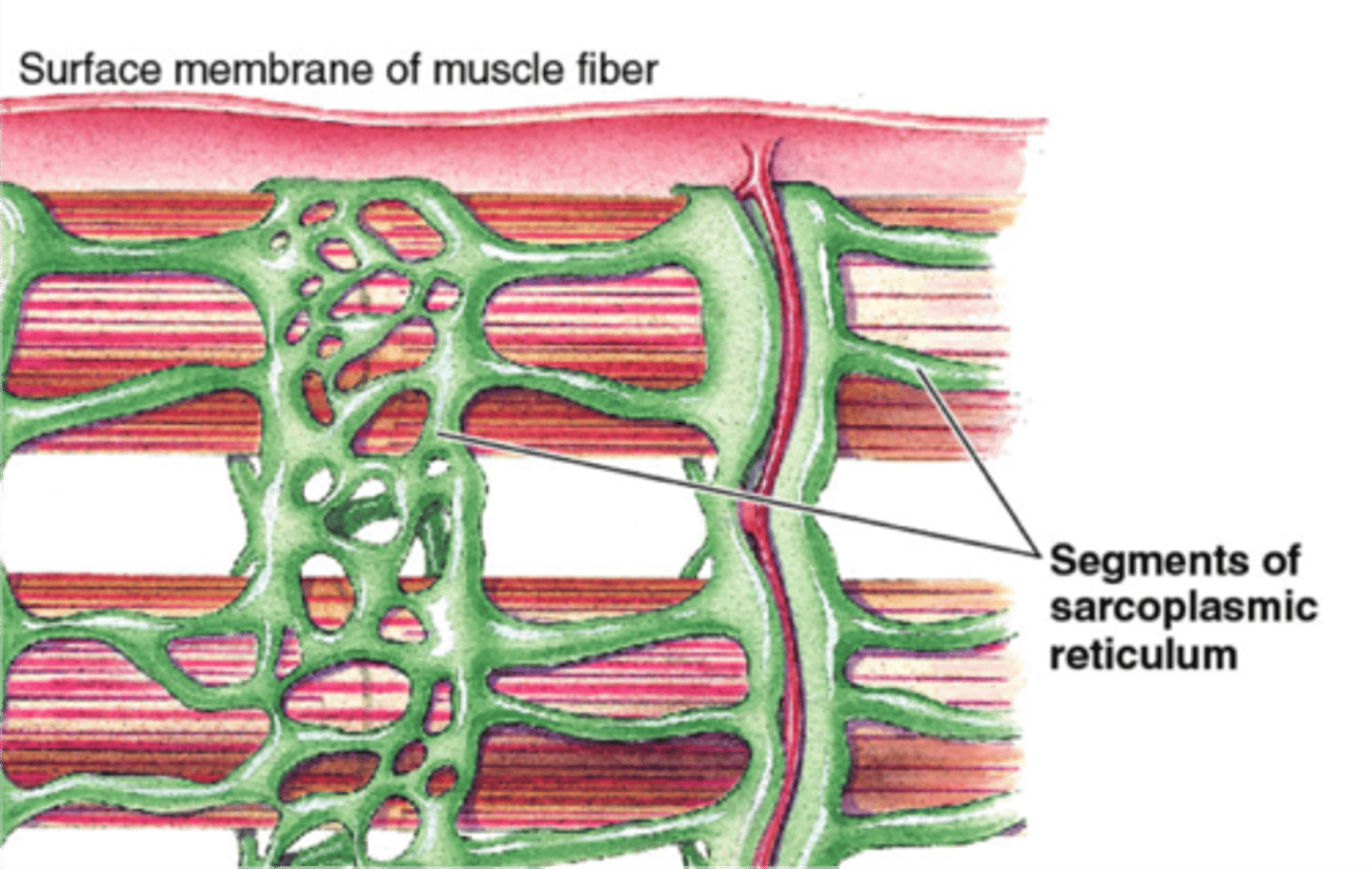
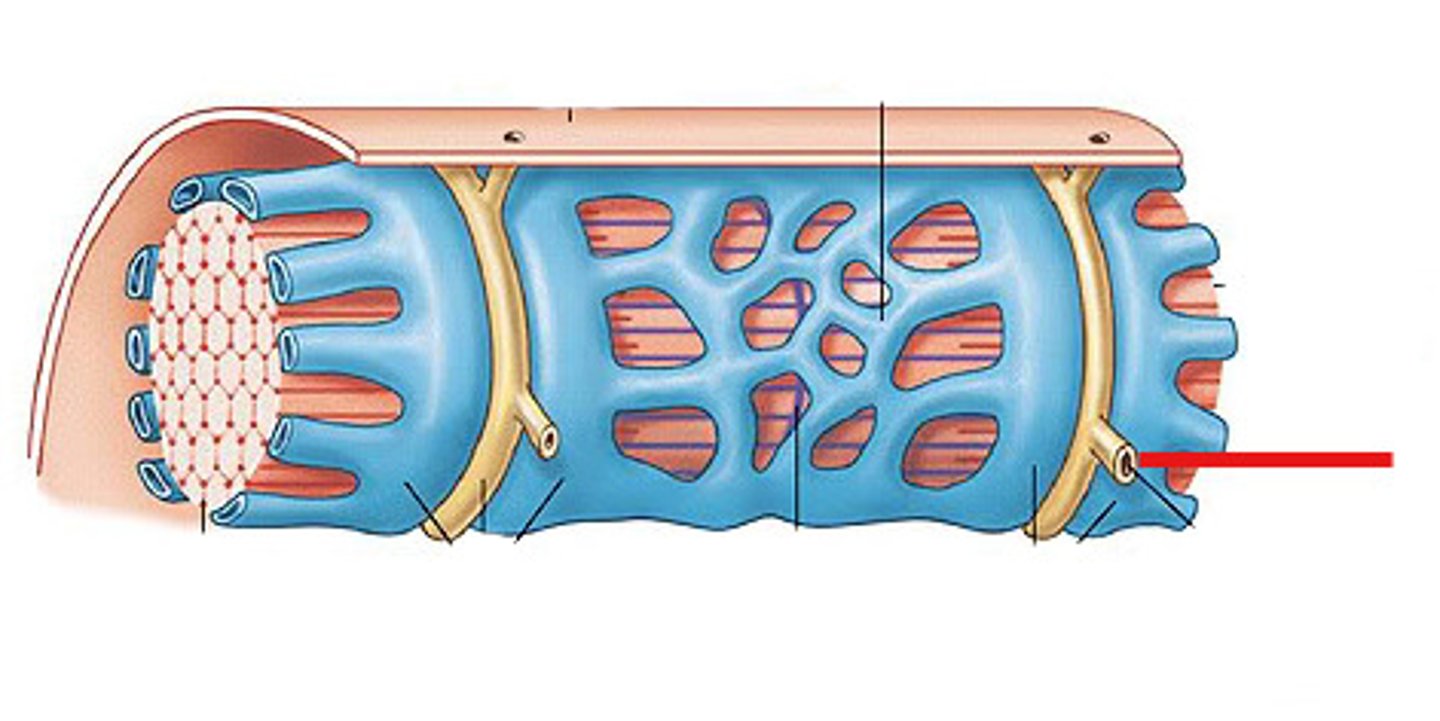
Transverse tubules
membranous channels that extend deep inward into the cell from the sarcolemma
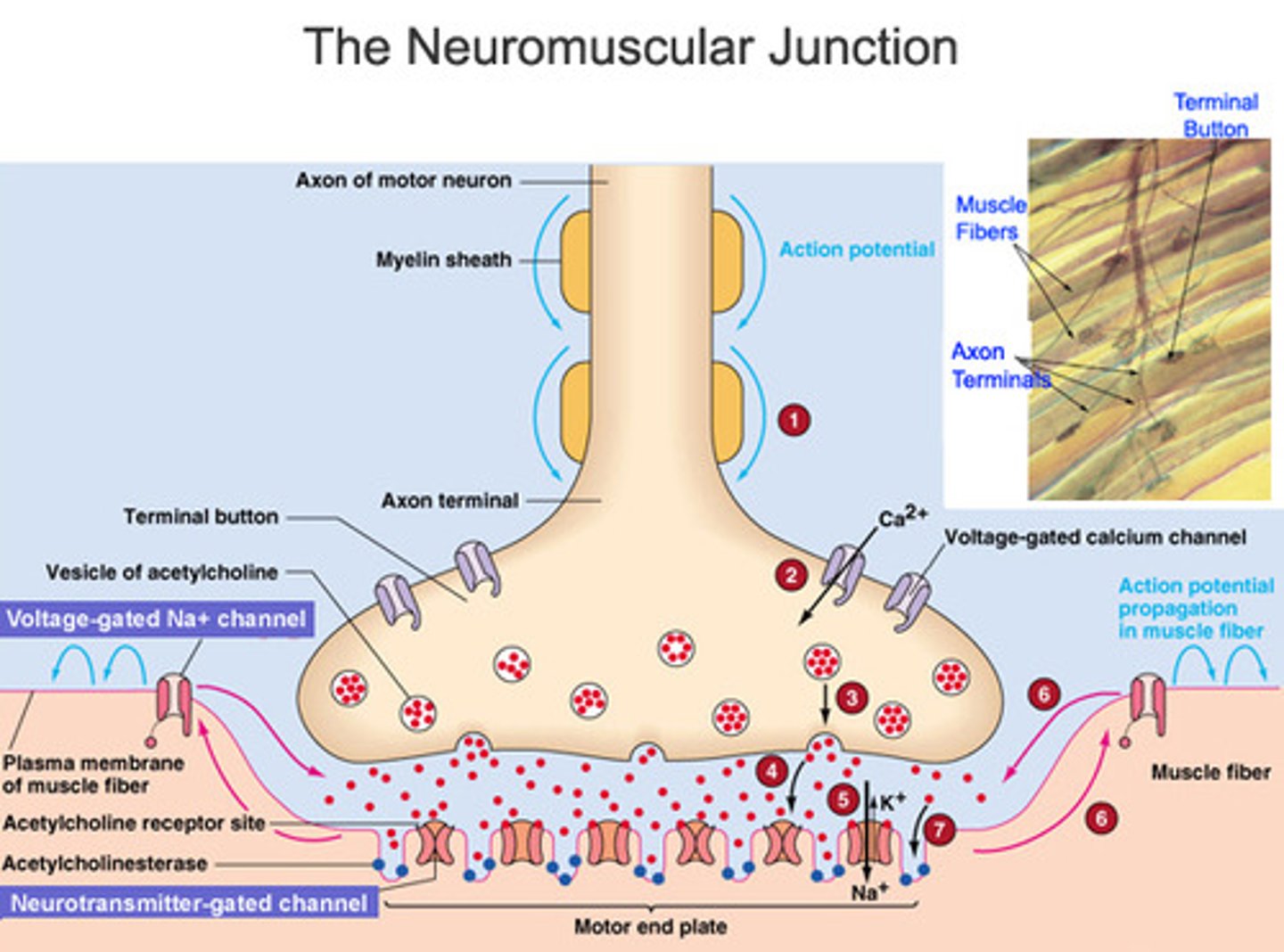
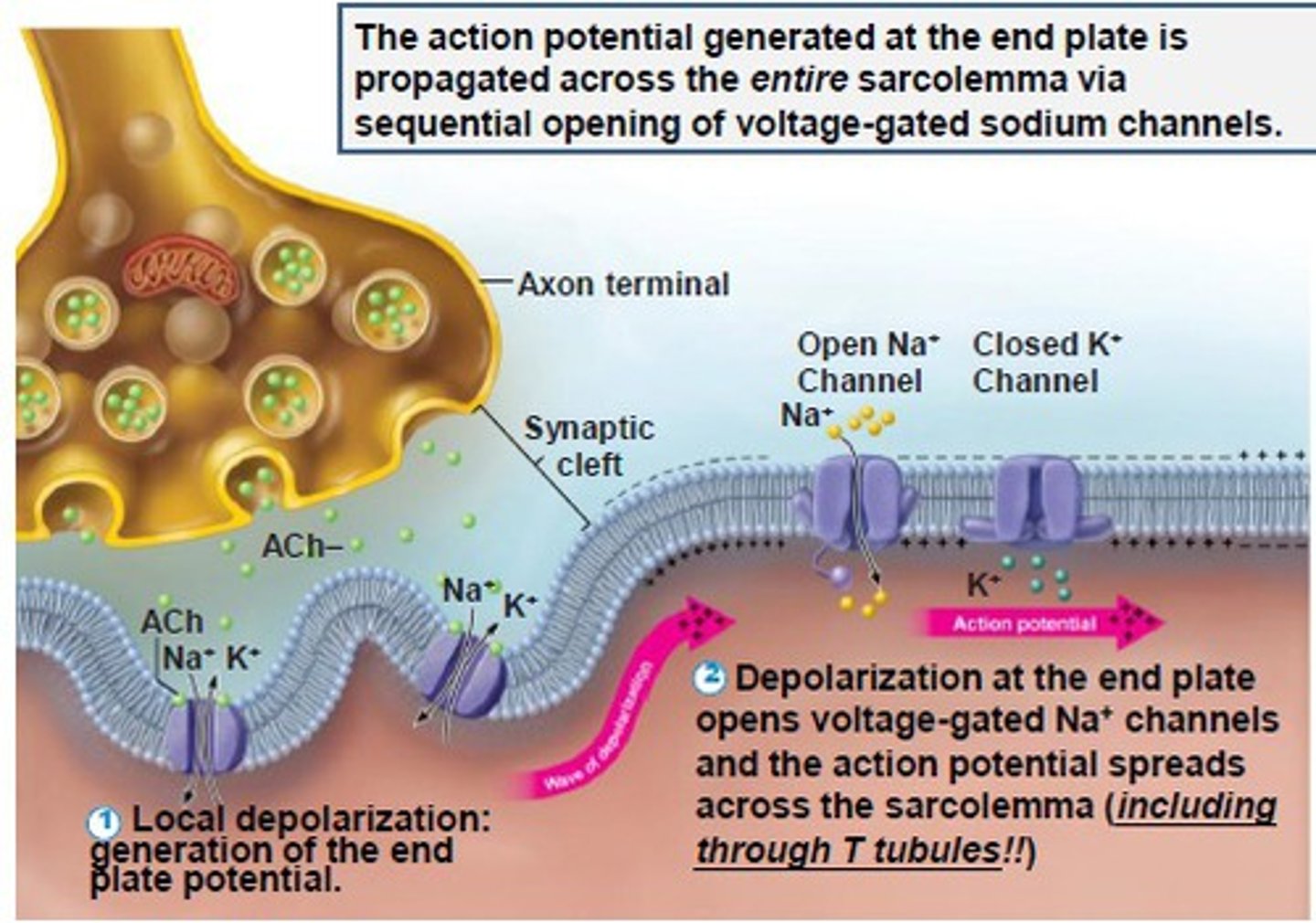
Neuromuscular Junction
synapse between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber
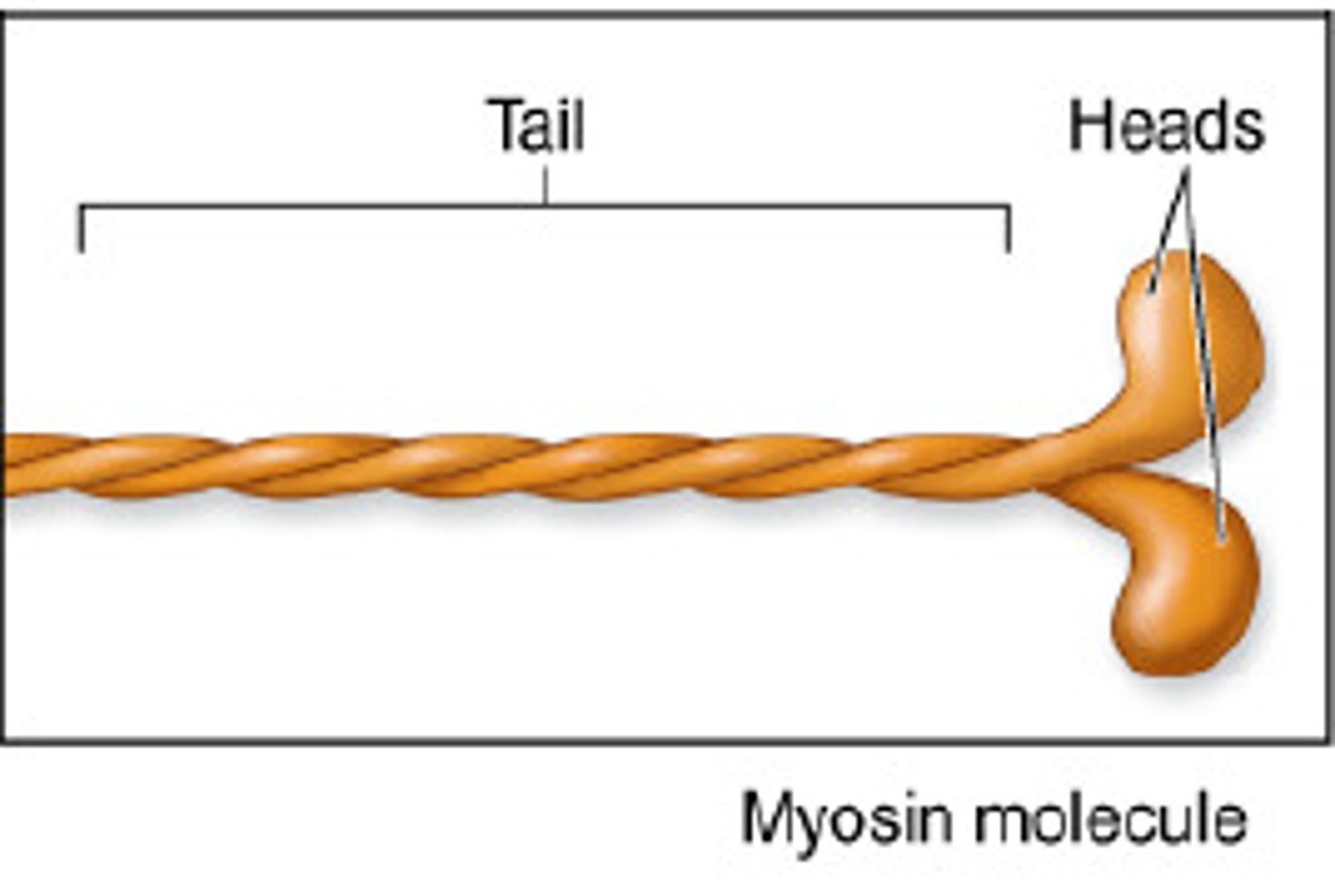
Myosin
two twisted protein strands with globular heads; part of the thick filament
Actin
globular proteins with a binding site for myosin heads to attach; part of the thin filament
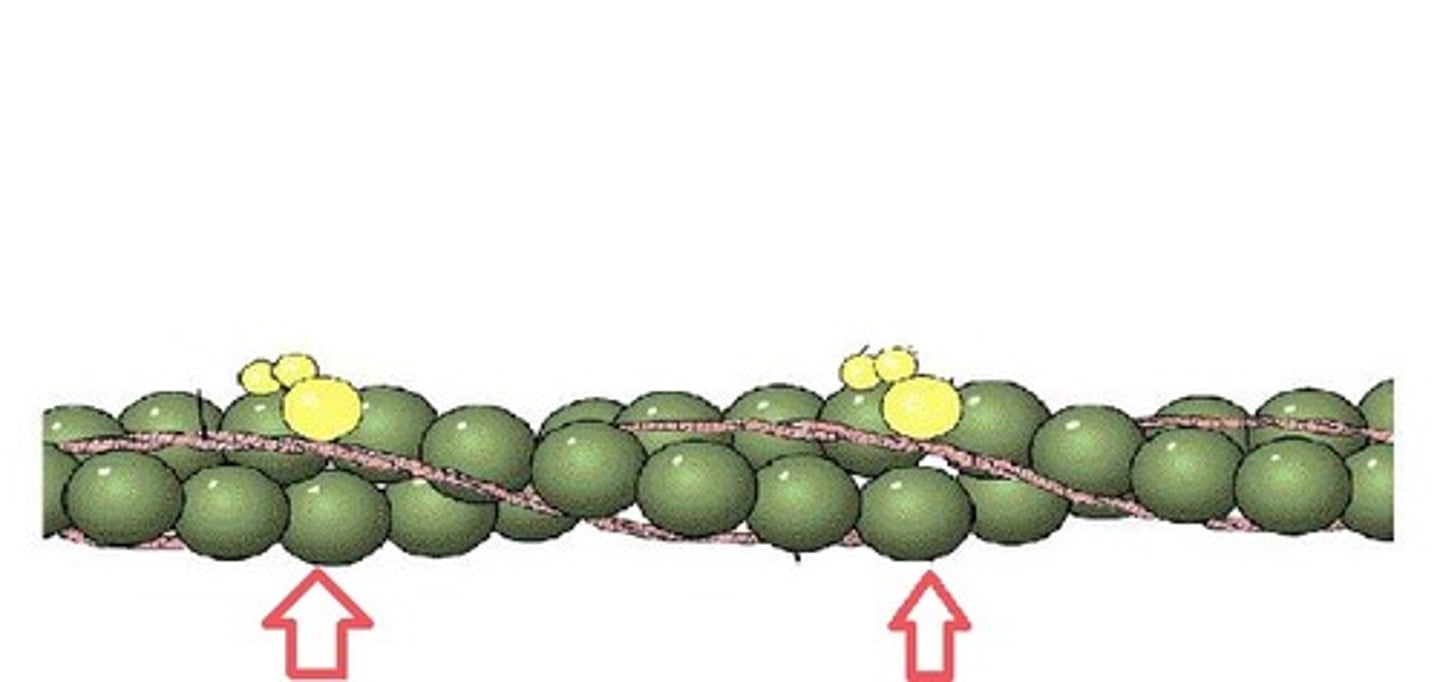
Troponin
complex of three proteins associated with tropomyosin
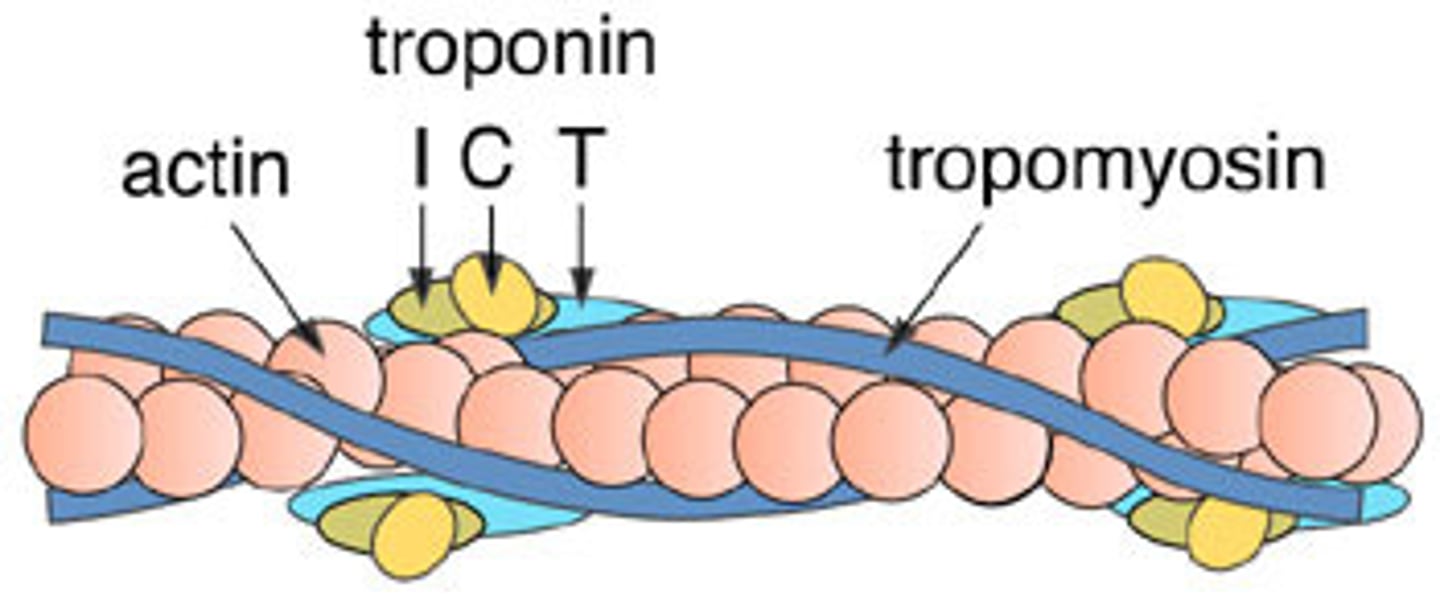
Tropomyosin
regulatory protein that blocks the myosin binding site on actin
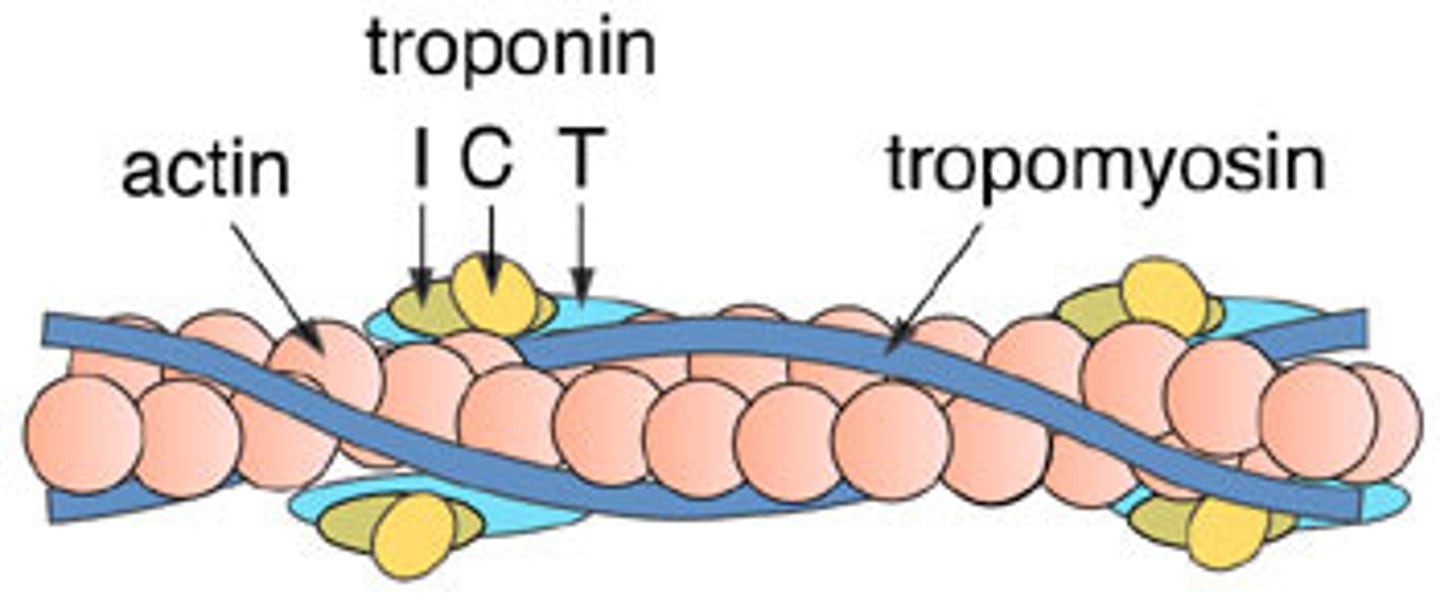
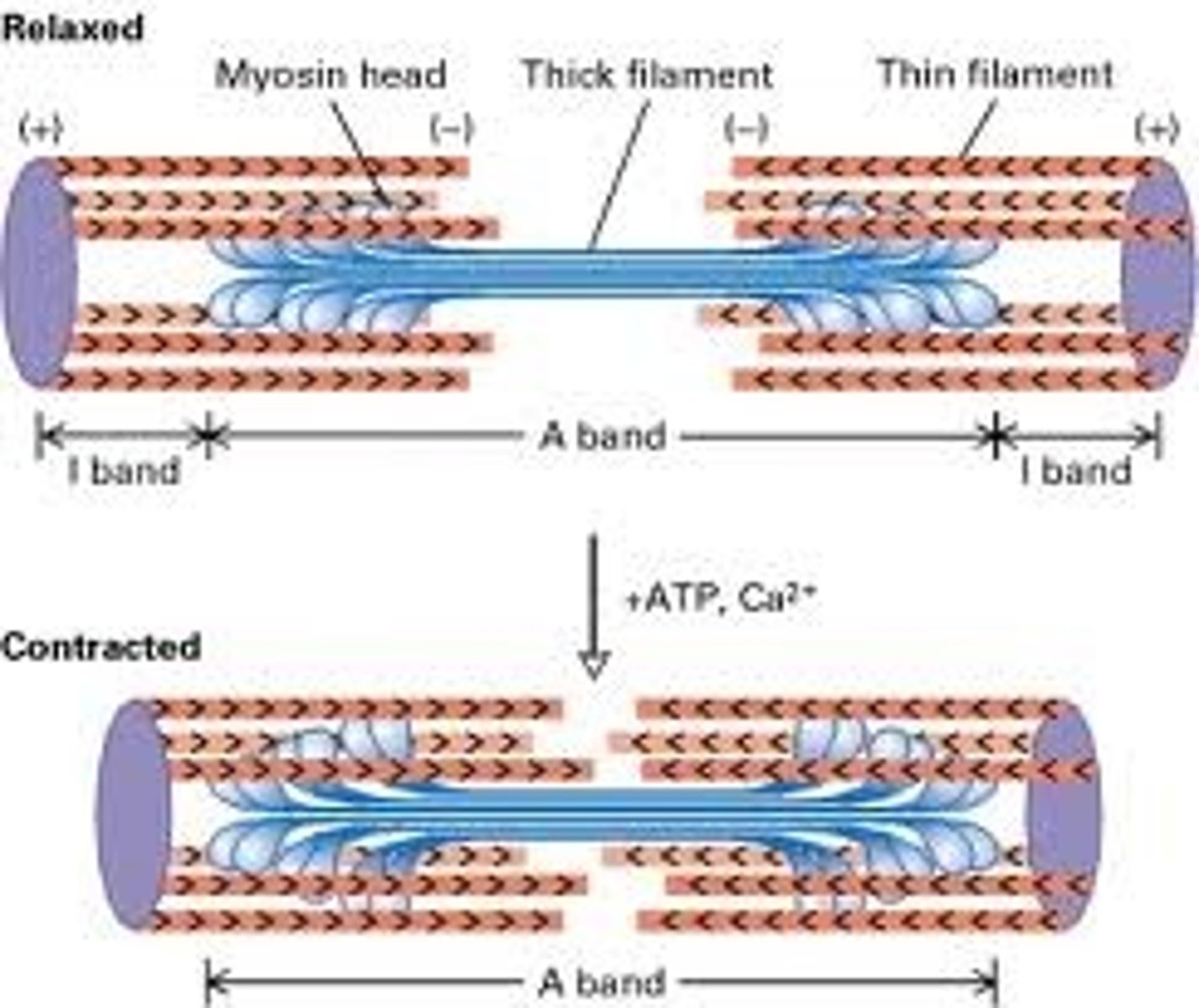
Sliding Filament Model
the model for muscle contraction in which muscle proteins slide past each other to generate force
Rigor Mortis
the condition in which skeletal muscles partially contract and become rigid after death

Muscular Dystrophy
X-linked disorder caused by the mutation of the protein dystrophin; no anchoring of actin to the sarcolemma
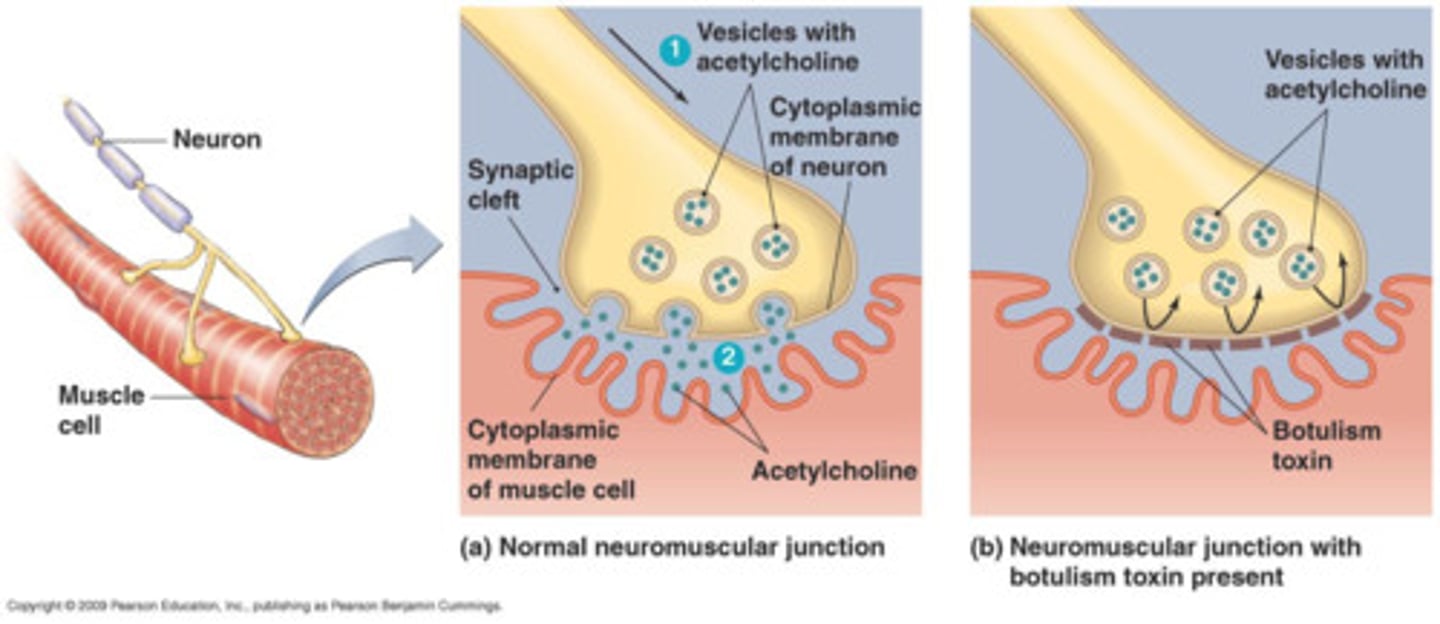
Botulinum Toxin
neurotoxin produced by the bacteria clostridium bacterium; prevents fusion of acetylcholine to the cell membrane and leads to paralysis of muscles
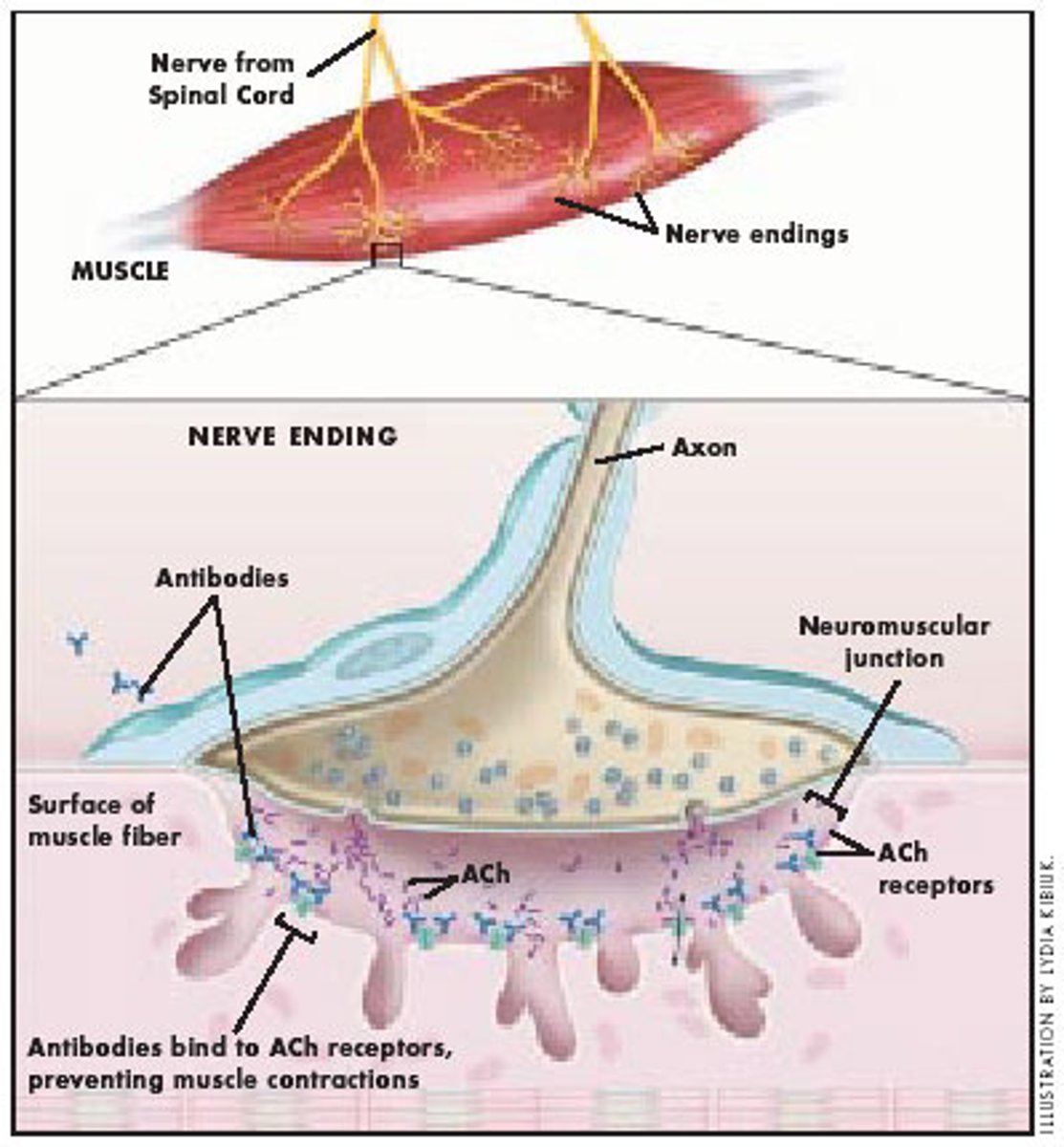
Myasthenia Gravis
autoimmune disease caused by antibodies attaching ACh receptors on the sarcolemma; results in less muscle contraction
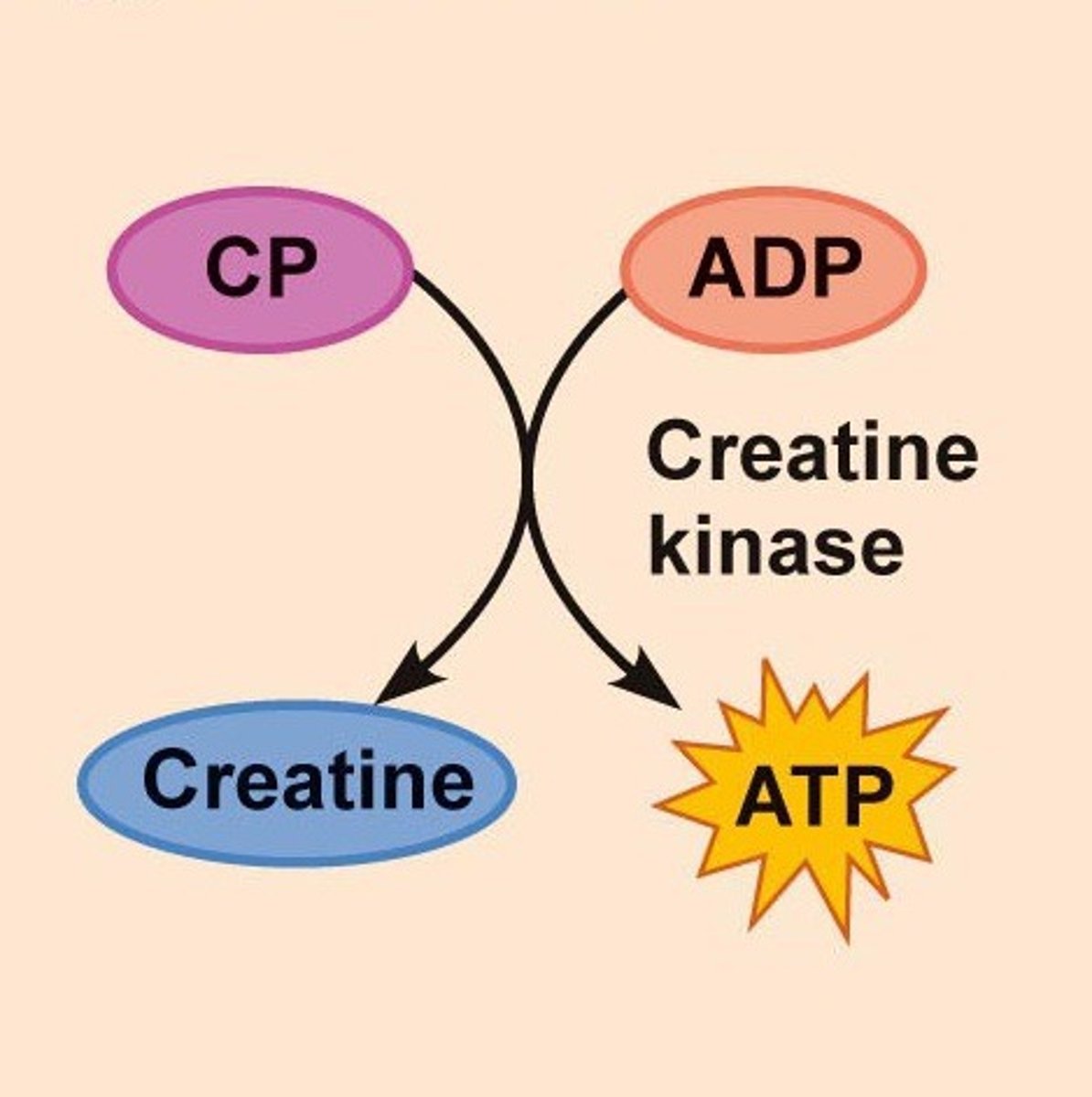
Creatine Phosphate
molecule in muscle that stores extra energy in phosphate bonds
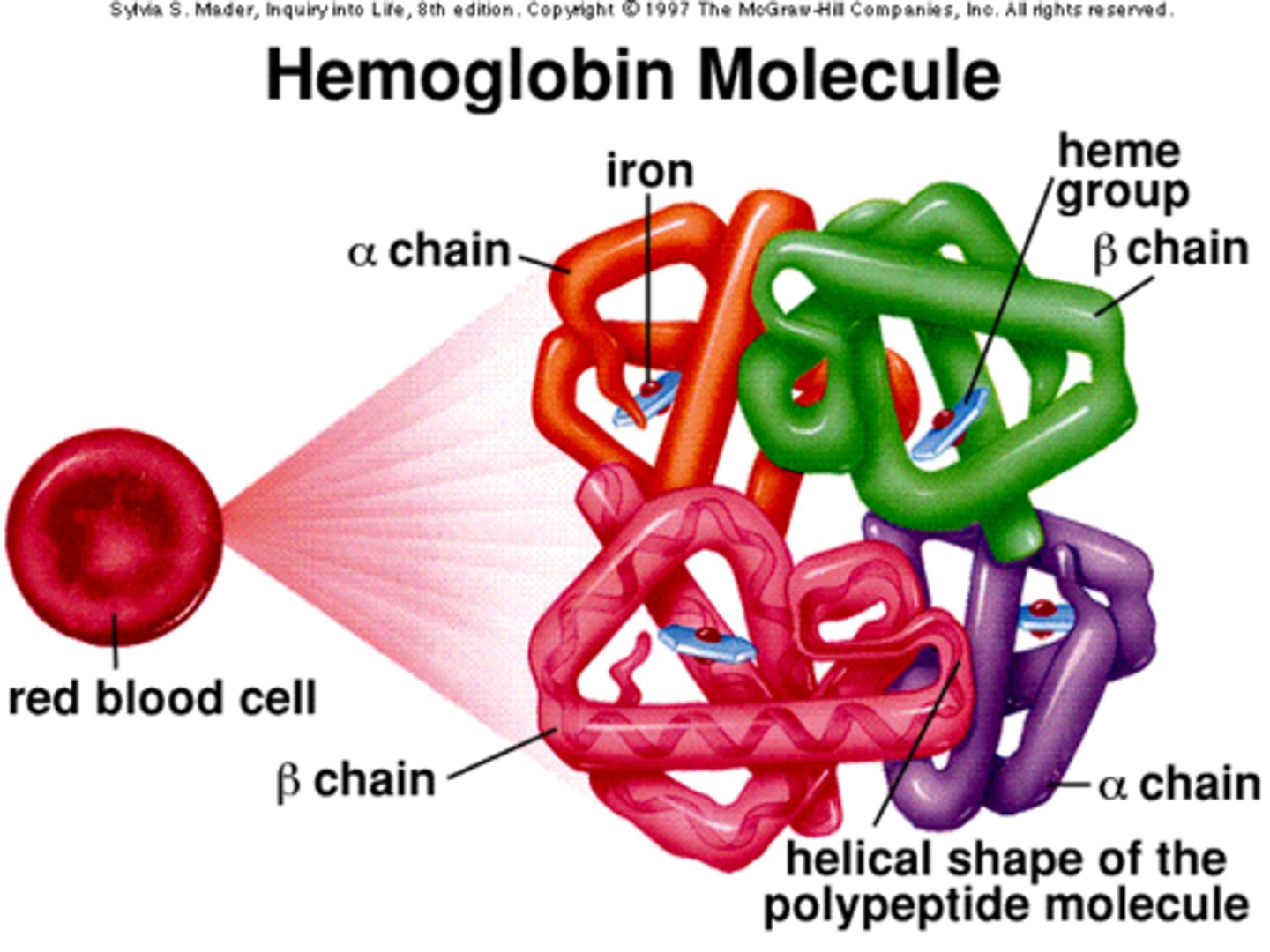
Hemoglobin
oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells
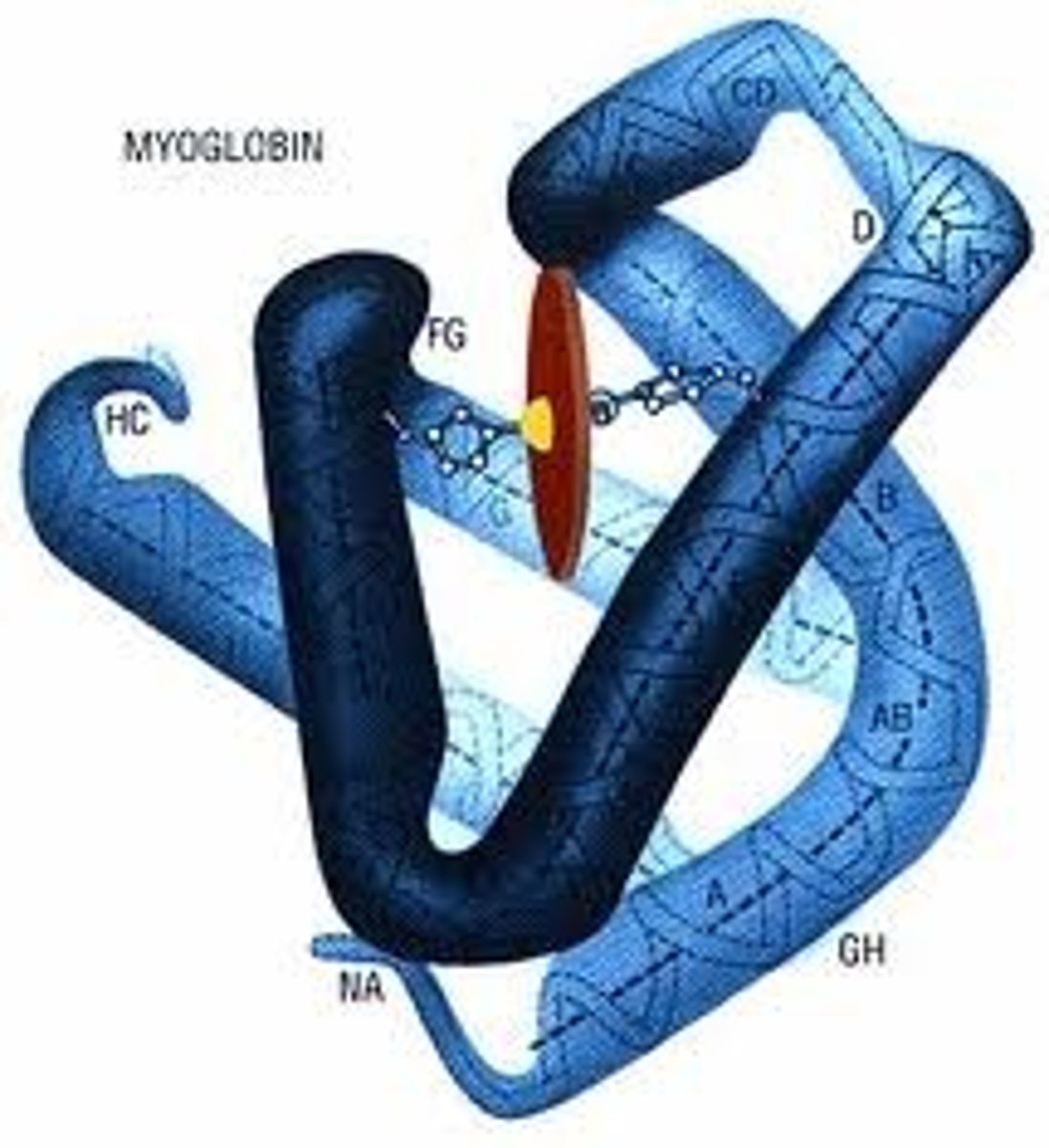
Myoglobin
oxygen-storing protein in muscle tissue
Oxygen Debt
the amount of oxygen that liver cells require, after anaerobic exercise, to convert the accumulated lactic acid into glucose, plus the amount muscle cells require to restore ATP and creatine phosphate to their original concentrations and return blood and tissue oxygen levels to normal

Fatigue
a condition where a muscle, after being exercised strenuously for an extended period, experiences a decreased ability to contract

Cramp
a painful condition in which a muscle undergoes a sustained involuntary contraction
Fast Twitch Fibers
fibers that fatigue easily, produce new filaments of actin & myosin and enlarge muscle fibers also known as white fibers

Slow Twitch Fibers
fibers that are fatigue resistant; develop more mitochondria & capillary networks; also known as red fibers

Muscular Hypertrophy
the enlargement of muscles that are forcefully exercised

Muscular Atrophy
the decrease in size and strength of an unused muscle
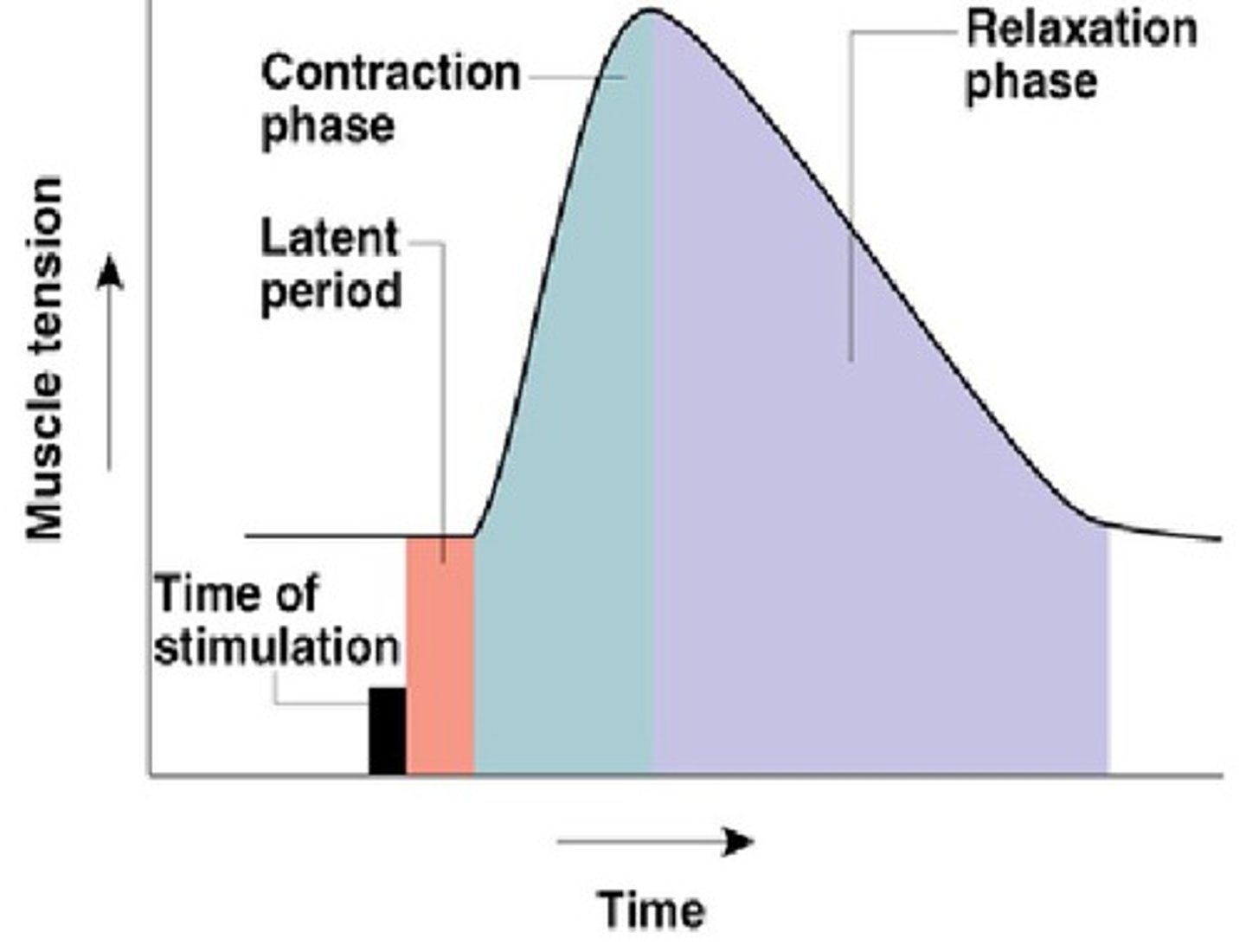
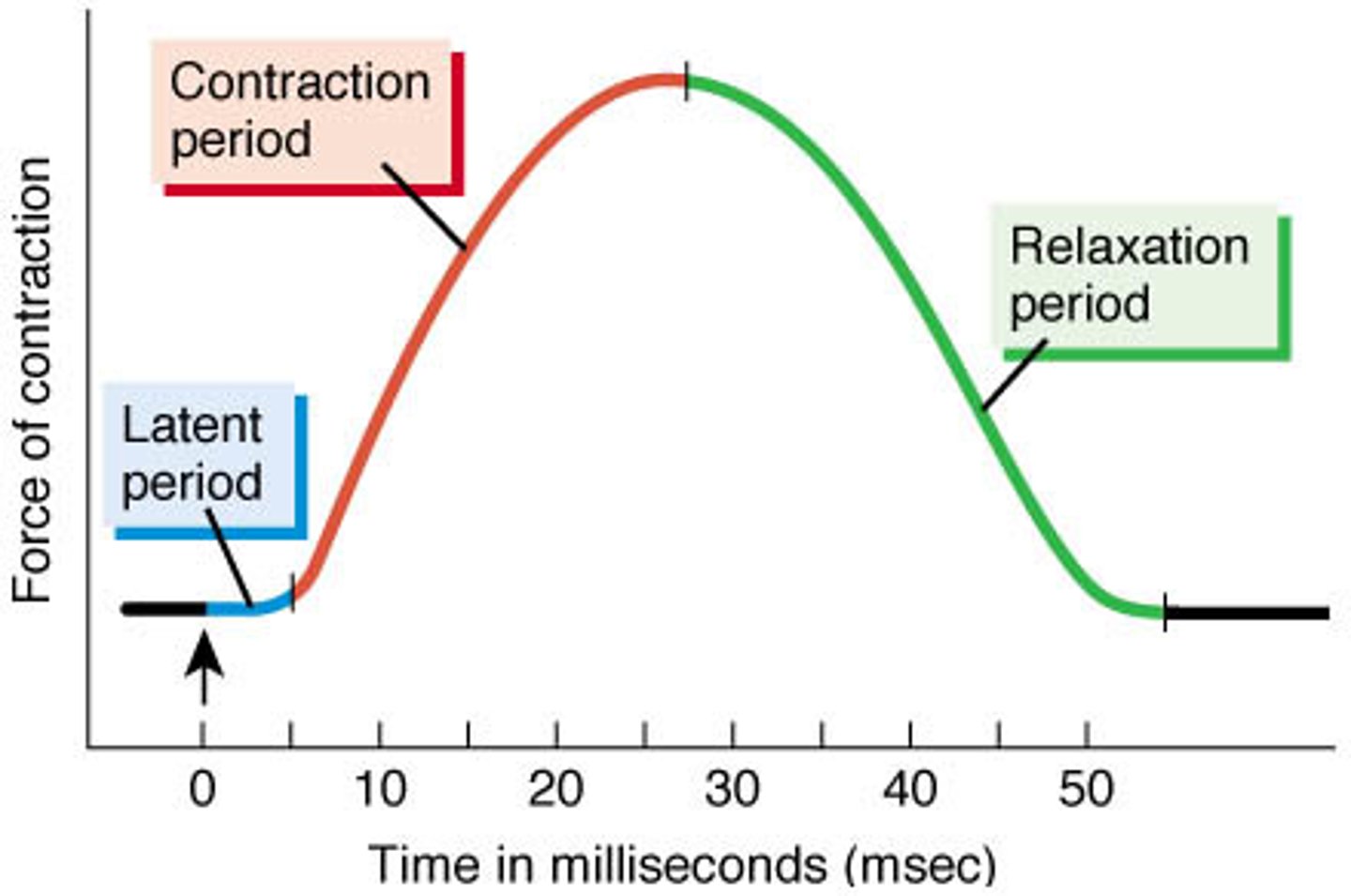
Twitch
single contraction of a muscle fiber followed by relaxation
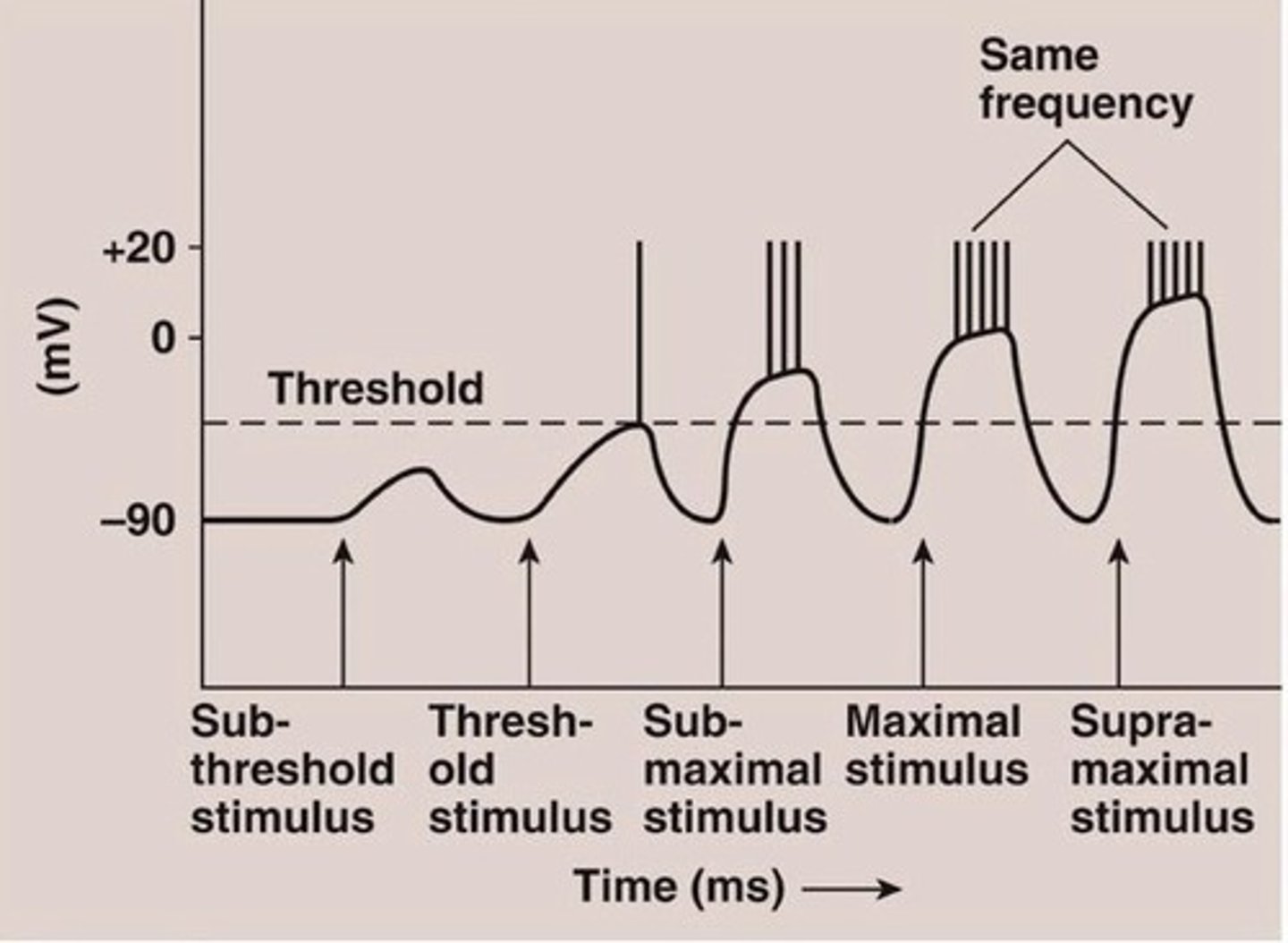
Threshold Stimulus
minimum strength of stimulation required to cause a contraction
Latent Period
time between a stimulus and the beginning of a response in a muscle fiber
Summation
the combination of individual twitches where the muscle is unable to relax
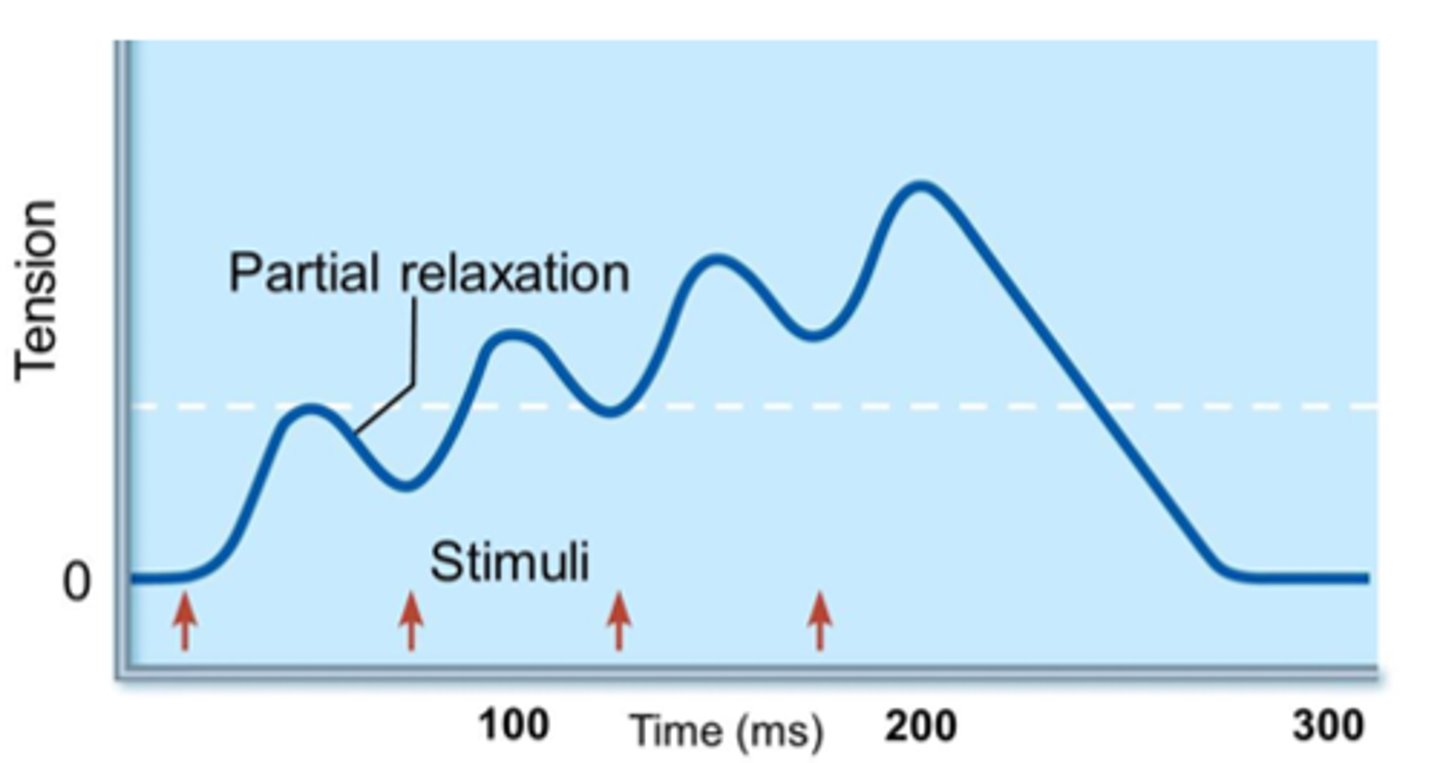
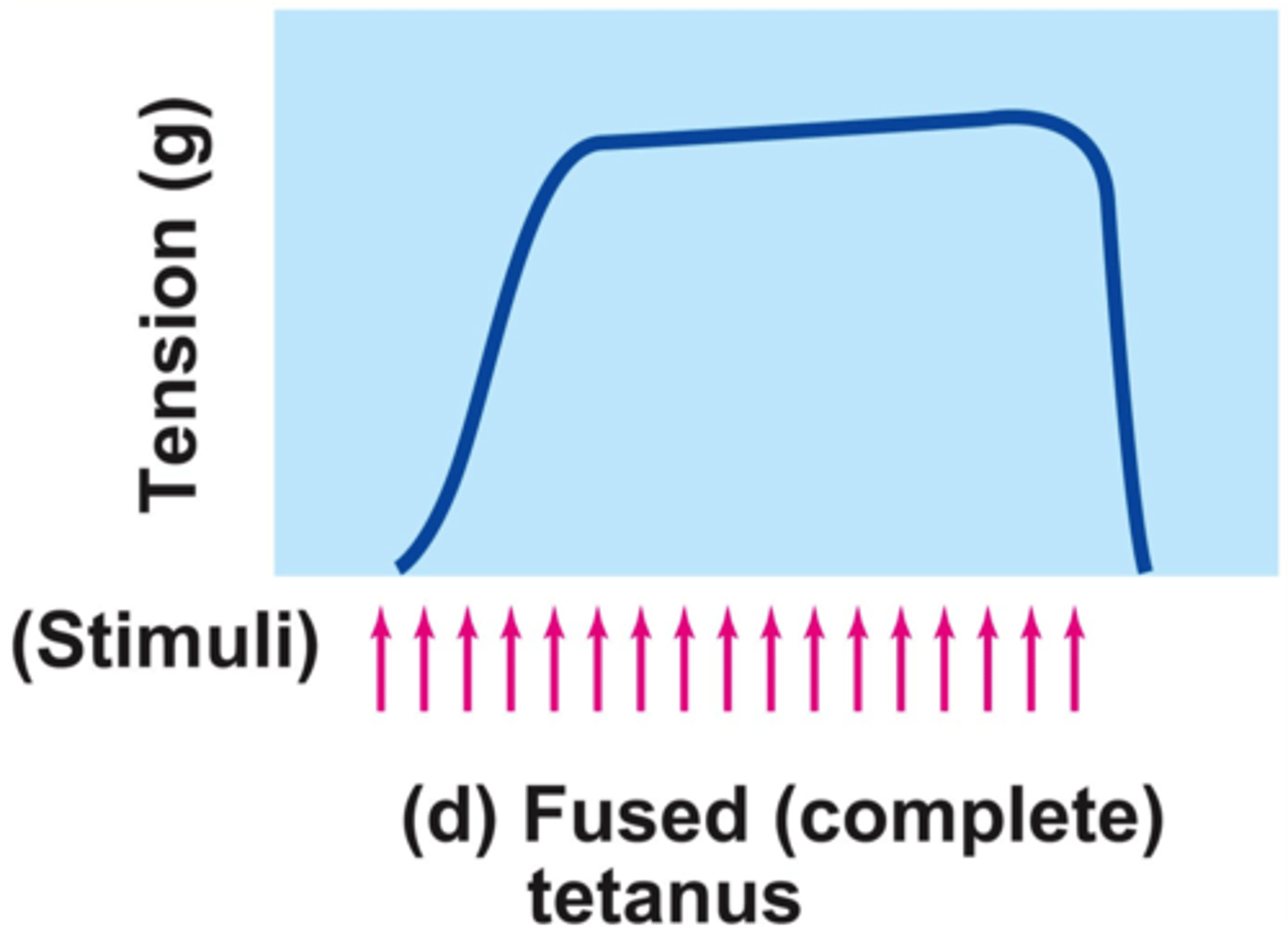
Tetanus
a sustained contraction caused by high frequency stimulation that lacks any relaxation
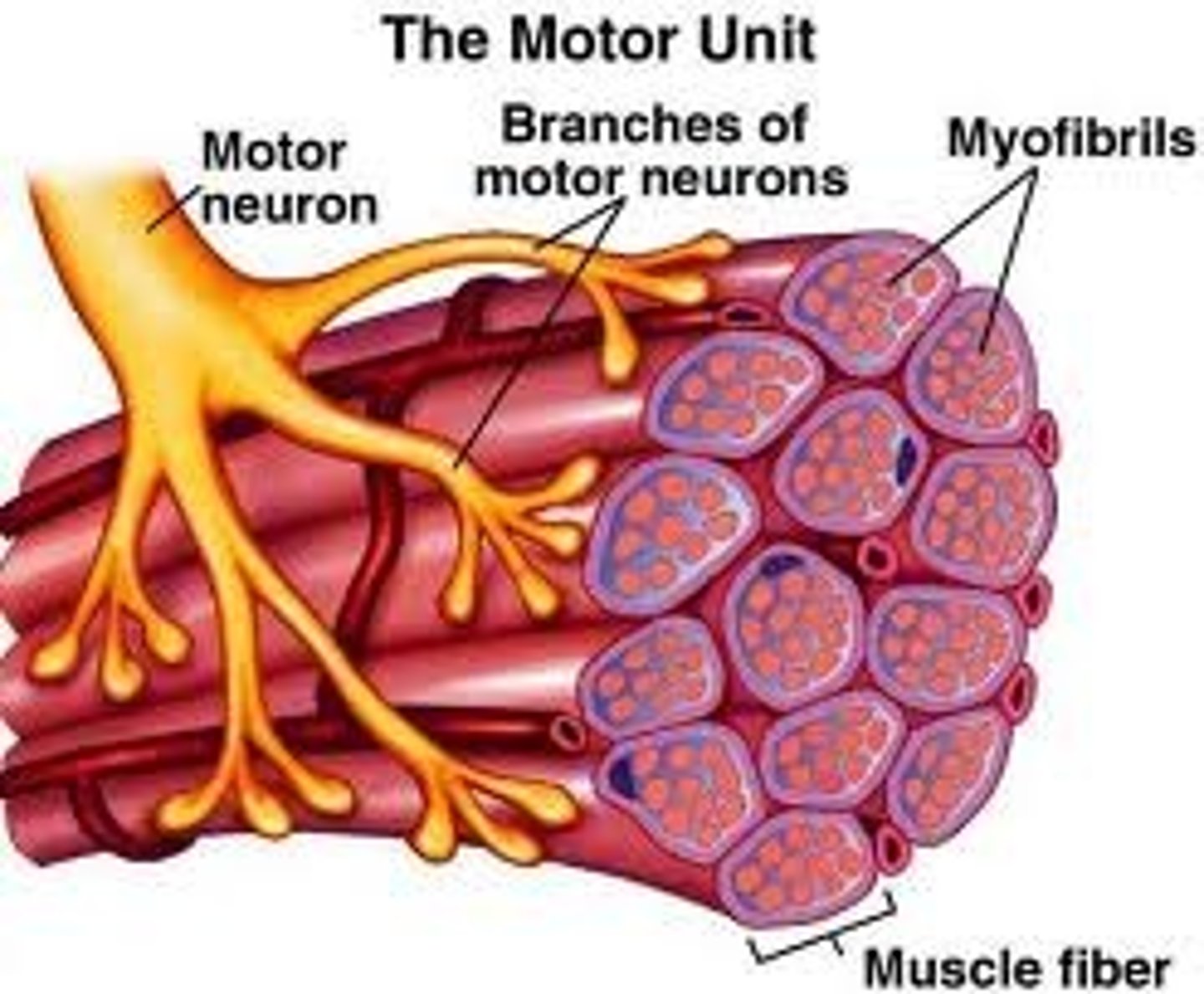
Motor Unit
a motor neuron and the muscle fibers that it controls
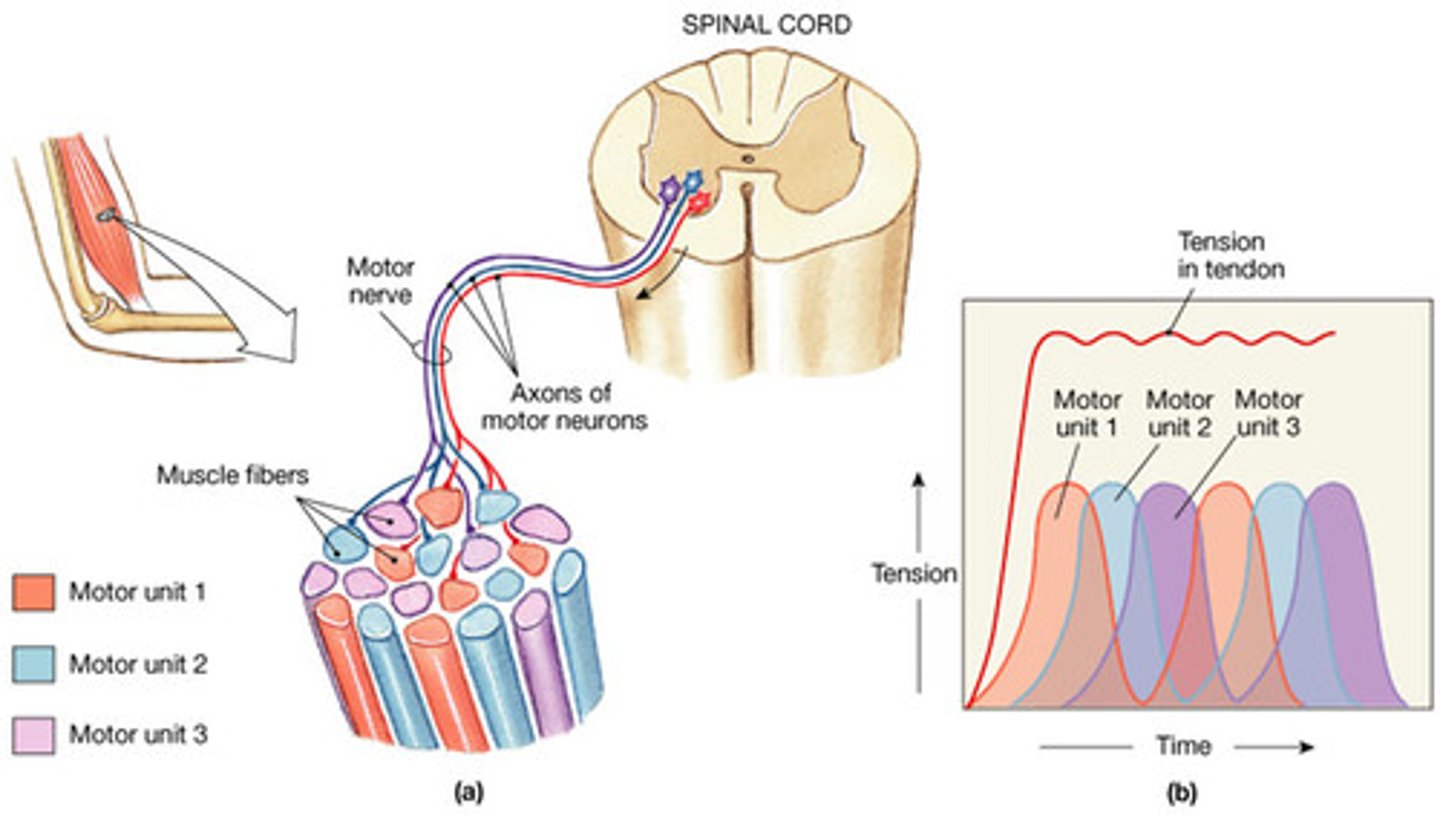
Recruitment
increase in the number of motor units taking place in a muscle contraction
Muscle Tone
ongoing low-level contraction of some fibers in otherwise resting skeletal muscle
Isotonic Contraction
a contraction that creates force and moves a load by shortening the muscle
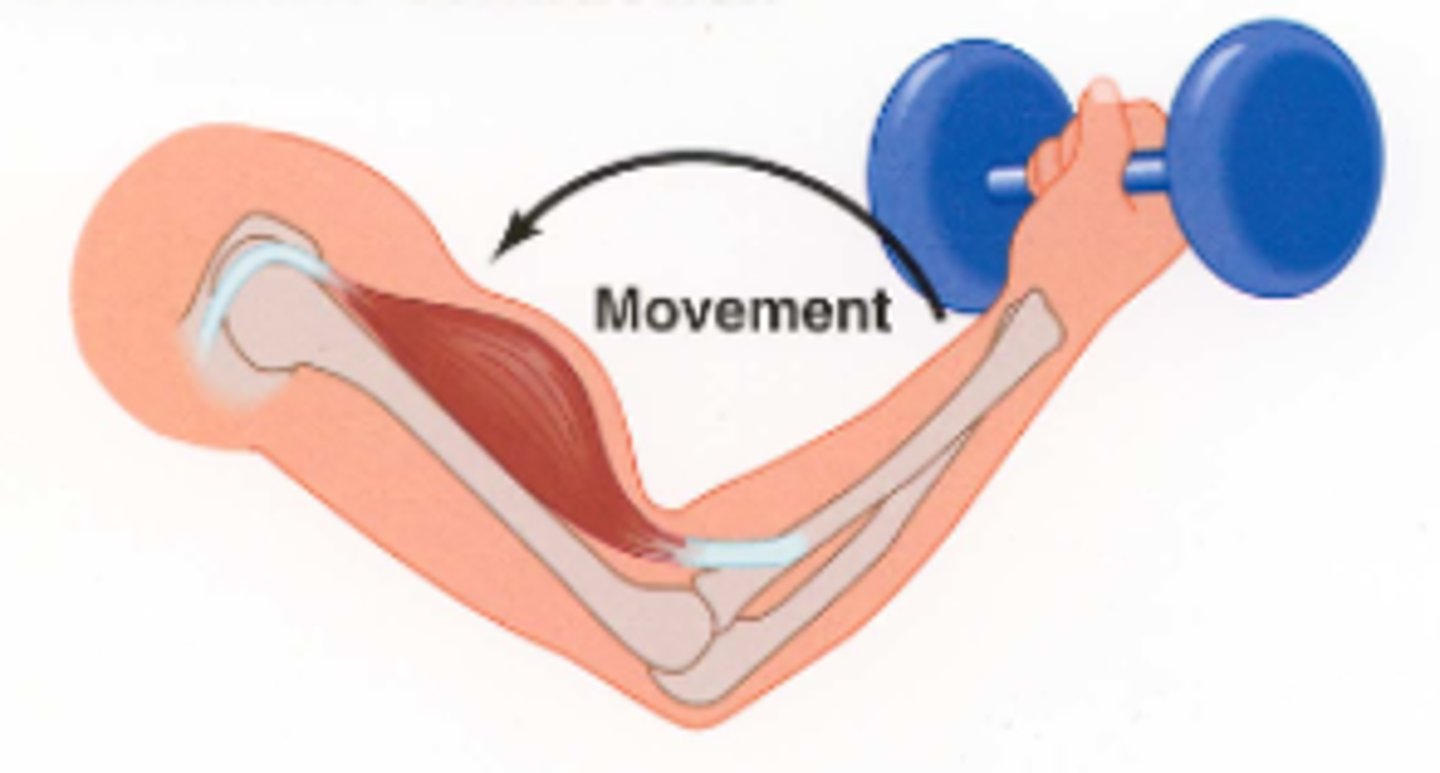
Isometric Contraction
a contraction that creates force without shortening

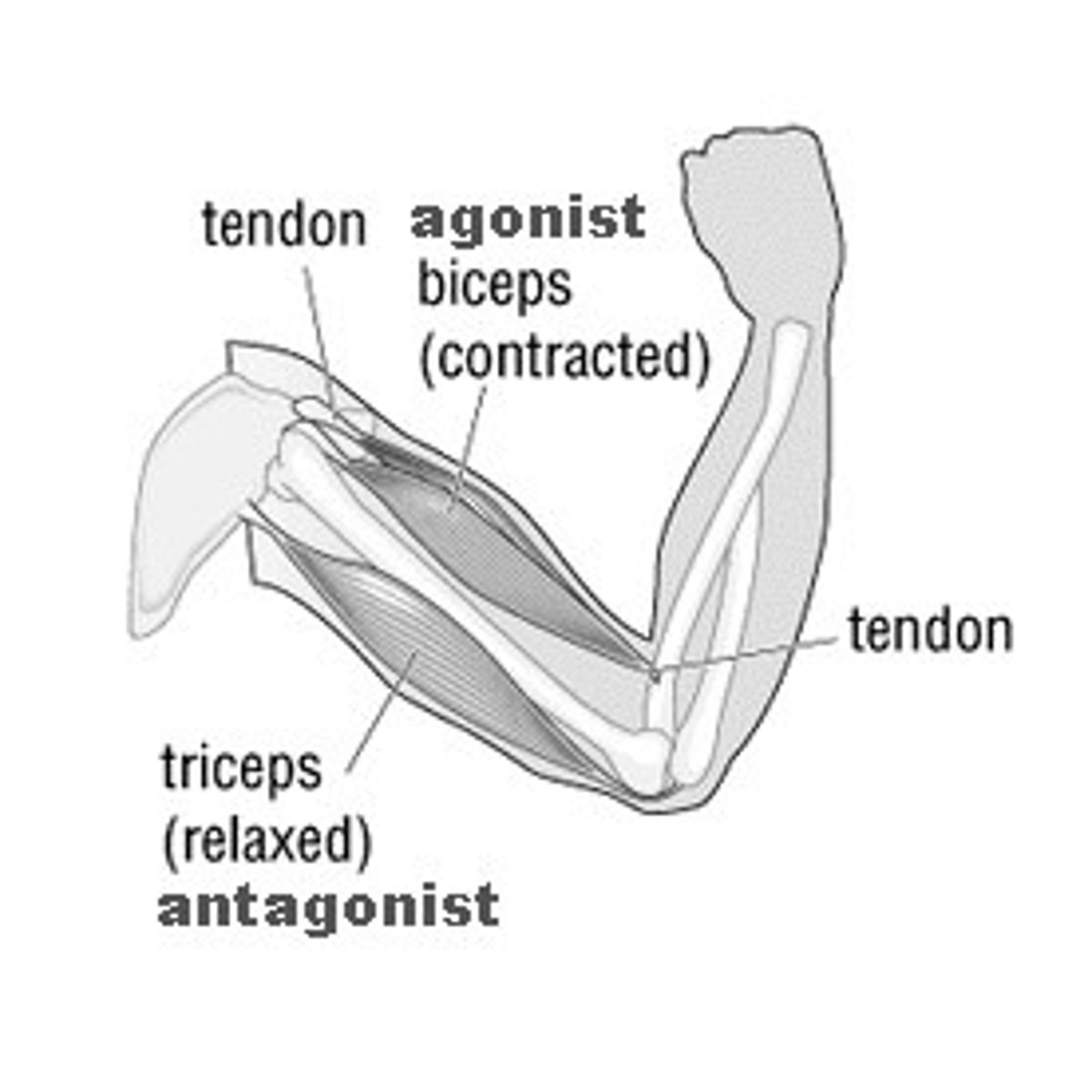
Origin
end of a muscle that attaches to a relatively immovable part
Insertion
end of a muscle attached to a moveable part
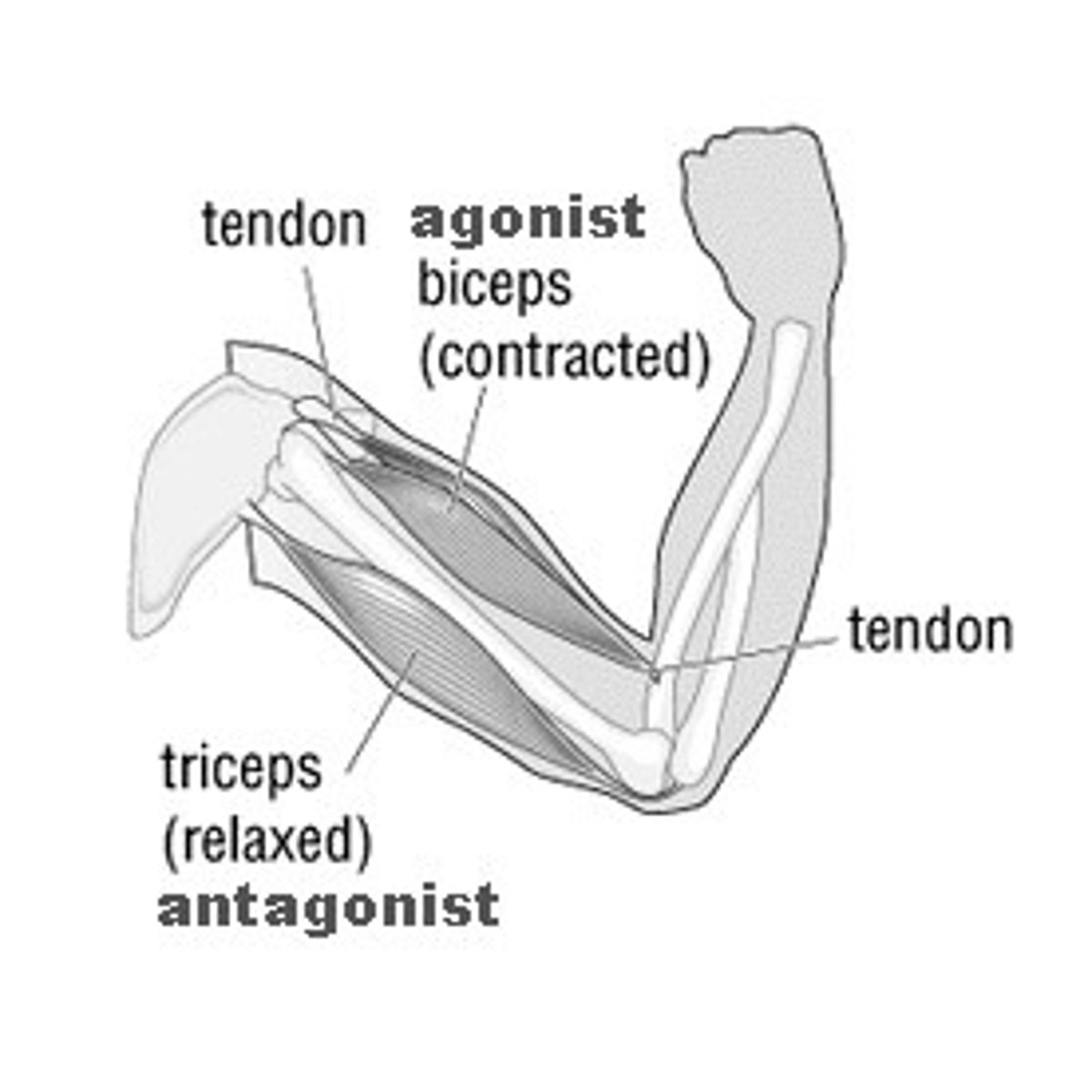
Prime Mover
muscle that provides most of the particular body movement; also called an agonist
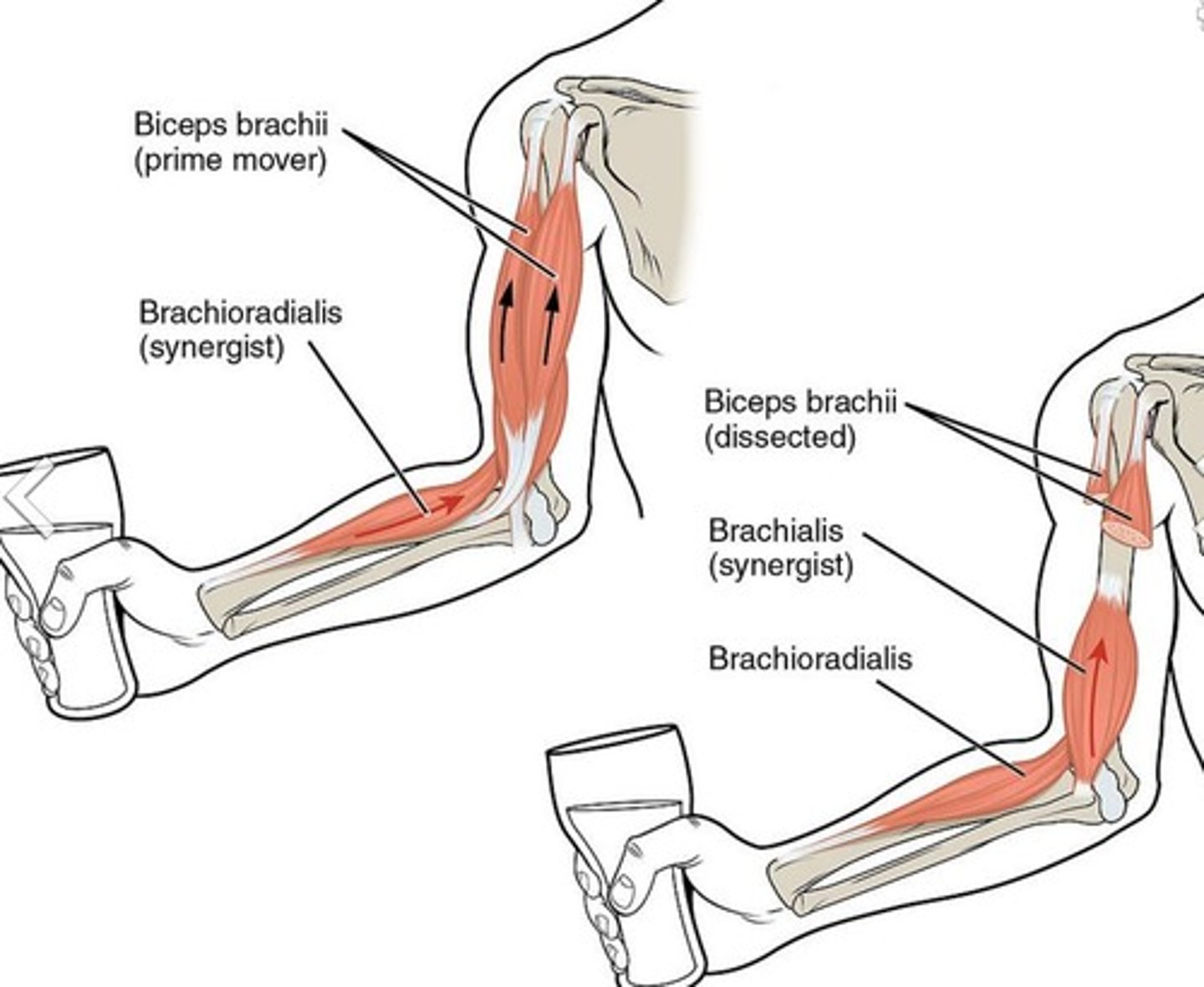
Synergist
muscle that assists the action of an agonist
Antagonist
muscle that opposes a particular movement
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle fibers
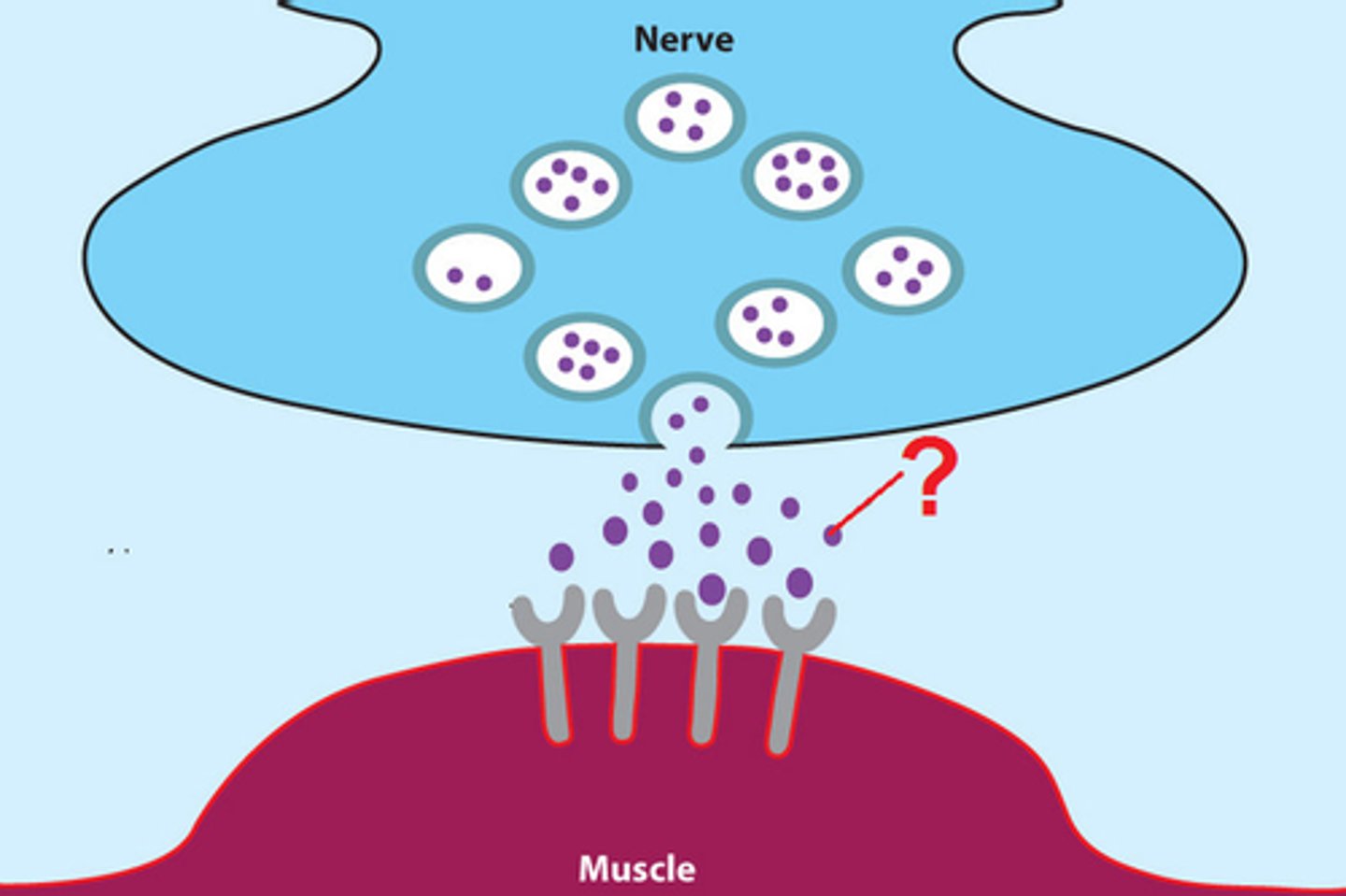
Motor End Plate
specialized muscle fiber membrane that contains receptors for neurotransmitters