Anatomy and Physiology - Chapter 8 Joints and Movement
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
articulation of joint
place where two bones come together
freely moveable to no apparent movement
structure correlated with movement
how joints are named
according to bones or parts united at the joint
according to only one of the articulating bones
by latin equivalent of common name
structural classes of joints
based on major tissue type that binds bones
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
functional classes of joints
based on degree of motion
synarthrosis- immovable
amphiarthrosis- slightly movable
diarthrosis - freely movable
synarthrosis
usually fibrous joints
immoveable
amphiarthrosis
usually cartilaginous
slightly moveable
diarthrosis
usually synovial
freely moveable
characteristics of fibrous joints
united by dense fibrous connective tissue
between bones in close contact
have no joint cavity
move little or none (synarthrotic)
Types of fibrous joints
sutures
synedesmoses
gomphoses
sutures
seams between bones of the skull
not ossified in adults
synostosis
ossifed suture
epiphyseal plate
synedesmoses
bones farther apart than suture and joined by ligaments
some movement
radioulnar syndesmosis
gomphoses
specialized joints
pegs that fit into sockets
inflammations (gingivitis and periodontal disease)
tooth in socket (inflammation causes tissue destruction)
cartilaginous joints
unite two bones by means of cartilage
usually amphiarthrotic
sychondrosis
symphysis
synchondrosis
joined by hyaline
little or no movement (synarthrotic)
epiphyseal plate
joint between the first rib and sternum
symphysis
pubic symphysis
intervertebral discs
junction between manubrium and the body of the sternum
synovial joints
allow considerable movement (diarthrotic)
most joints that unite bone of appendicular skeleton
complex
bursae
complexity of synovial joints
articular hyaline cartilage
joint cavity and capsule
synovial membrane and fliud
bursae of synovial joints
pockets of synovial fluid
bursitis
types of synovial joints
plane or gliding
saddle
hinge
pivot
ball-and-socket
ellipoid (condyloid)
plane or gliding joints
monoaxial (movement in 1 plane)
articular processes between vertebrae, intercarpal and intertarsal joints
pivot joints
monoaxial
articulation between dens of axis (C2) and atlas (C1) of the spine
proximal radioulnar joint
saddle joints
biaxial
carpmetacarpal joint of the thumb
hinge joints
similar in structure and function to a door hinge
monoaxial
elbow and knee
ellipsoid (condyloid joint)
modified ball and socket
biaxial
atlantooccipital joint (where C1 meets the skull)
metacarpophalangeal joints of the hand (knuckles)
ball-and-socket joints
multiaxial - movement in all planes
shoulder and hip
movement in joints
when discussing types of movement, refer to the anatomical position, either starting in the anatomic position and moving away from that position or moving a part back towards the anatomic position
gliding
two surface glide over one another
intercarpal and intertarsal
angular movement
flexion and extension (hyperextension and plantar and dorsiflexion)
abbduction and adduction
circular movement
rotation
pronation and suppination
circumduction
flexion
occur in sagittal plane
angle gets smaller
usually bending
extension
occur in sagittal plane
angle gets bigger
usually straightening
dorsiflexion
like walking on heels
plantar flexion
ballerina on toes
abduction
moving of a body part away from the central axis of the body
adduction
moving of a body part toward the central axis of the body
rotation
occur about an axis
move head to right and left
pronation
forearms and feet
palms down
flat feet
suppination
forearms and feet
palms up
arched feet
circumduction
form a cone in space with a body part
elevation
shoulders and jaw
close mouth
depression
shoulders and jaw
open mouth
protraction
shoulders and jaw
shoulders forward
retraction
shoulders and jaw
shoulders back
excursion
cow chewing cud
opposition
bring thumb and pinky together
reposition
thump and pinky apart
inversion
ankle
turn sole of foot medially
eversion
ankle
turn sole of foot laterally
range of motion influenced by
shape of articular surfaces forming joint
amount and shape of cartilage covering surfaces
strength and location of ligaments and tendons
location of muscles associated with joint
amount of fluid in and around the joint
amount of use/disuse of joint
amount of pain in and around the joint
osteoarthritis
wear and tear
rheumatoid arthritis
caused by transient infection or autoimmune disease
lyme disease
tick vector
gout
metabolic disorders of unknown casue (idiopathic)
types of fibrous joints
-syndesmoses
-sutures
-gomphoses
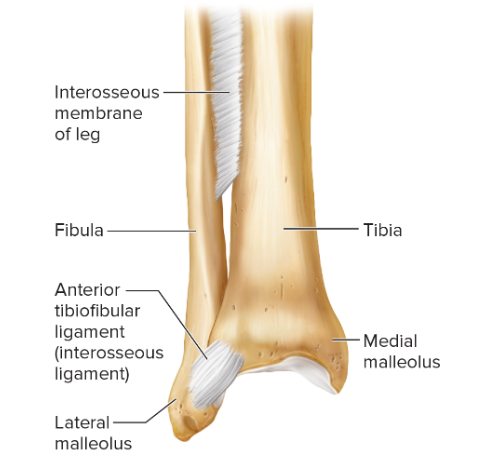
syndesmoses
-bones are bound by a sheet
-somewhat flexible
-amphiarthrotic joint
suture
-found betwen flat bones of the skull
-bones grow together and unite by a thin layer of dense connective tissue (sutural ligament)
-sutures replace fontanels
-immovable, synarthrotic
gomphoses
-union of coneshaped bony process in a bony socket
-immovable, synarthrotic
cartilaginous joints
-connected by hyaline or fibrocartilage
-synchondroses
-symphyses
synchondroses
—bands of hyaline cartilage
-typically temp structures that disappear during growth
-once growth/ossification is complete, the joint becomes a synotosis, which is synarthrotic, immovable
symphysis
-articular surfaces are covered by a thin layer of hyaline cartilage
-connected by a pad of fibrocartilage
-limited movement when forces compress or deform the fibrocartilage pad (ex., pregnancy, intervertebral discs)
-amphiarthrotic
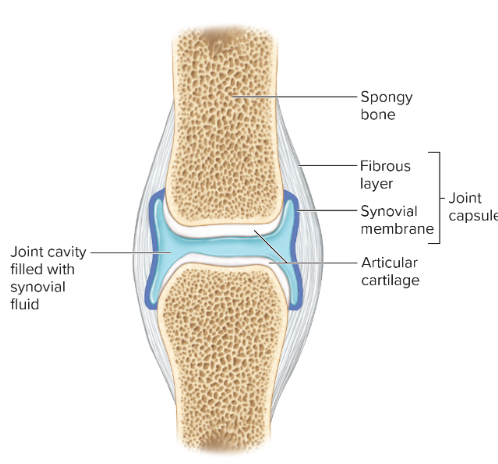
synovial joints
-most joints of the skeletal system are classified as this
-diarthrotic
-articular cartilage, joint capsule, synovial membrane which secretes synovial fluid
articular cartilage
-thin layer of hyaline cartilage
-resists wear
-minimizes friction
-covers the end of bones in a synovial joint
ligaments
-bundles of strong collagen fibres
-stabilizes joint & binds articular ends of bones
-help prevent excessive movement at the joint
-inelastic, tightens when the joint is stressed
joint capsule
-holds together the bones of synovial joints, prevents bone ends from being pulled apart
-2 layers
- outer fibrous layer consists of dense connective tissue that attach to the periosteum
-inner layer consists of loose connective tissue called the synovial membrane
-covers all surfaces of the joint besides the parts covered by articular cartilage
synovial membrane
-covers the synovial cavity into which it secretes synovial fluid
-can have vili which increase surface area
-can store adipose tissue & form movable fatty pads in the joint
-reabsorbs fluid, which helps when joint cavity is injured or infected
-thin, only a few cells thick
synovial fluid
-contains stem cells, which may help in ligament regeneration
-consistency similar to uncooked egg white
-moistens the smooth cartilaginous surfaces of the joint
-supplies articular cartilages with nutrients obtained from blood vessels of synovial membrane
menisci
-synovial joint divided into two compartments
-articluar discs of fibrocartilage
-attaches to the fibrous layer of the joint capsule
-cushions the articulating surfaces of the knee joint and help distribute body weight
bursae
-fluid filled sacs
-inner lining of synovial membrane
-contain synovial fluid
-found between the skin and underlying bony prominerces (olecranon, knee)
-cushion and aid movement of tendons and ligaments
-names of bursae indicate locations
shapes of synovial joints
-ball and socket
-condylar
-plane
-hinge
-pivot
-saddle
ball and socket joints
-bone with egg shaped head that articulates with a cup shaped cavity of another bone
-allows for a wider range of motion than any other type of bone
-multiaxial movement
-hip and shoulder
condylar joints
-also called an ellipsoidal joint
-ovoid bone end fits into the elliptical cavity of another bone
-joints between the metacarpals & phalanges
-biaxial movement (back and forth & side to side)
plane joints
-articulating surfaces are nearly flat or slightly curved
-nonaxial movement (back-and-forth + twisting)
-joints in wrist, ankle, articular process of vertebrae, sacroiliac, sternocoastal regions
hinge joints
-convex surface of one bone fits into the concave surface of another bone
-uniaxial
-elbow, joints between phalanges, knee
-bending and straightening motion
pivot joints
-also called trochoid joint
-cylindrical surface of one bone rorates in a ring formed of bone and ligament
-uniaxial
-radius & ulna, neck
saddle joints
-forms between bones with concave & convex regions
-joint between carpal, metacarpal betwen thumb
insertion
movable end of a muscle
origin
fixed end of a muscle
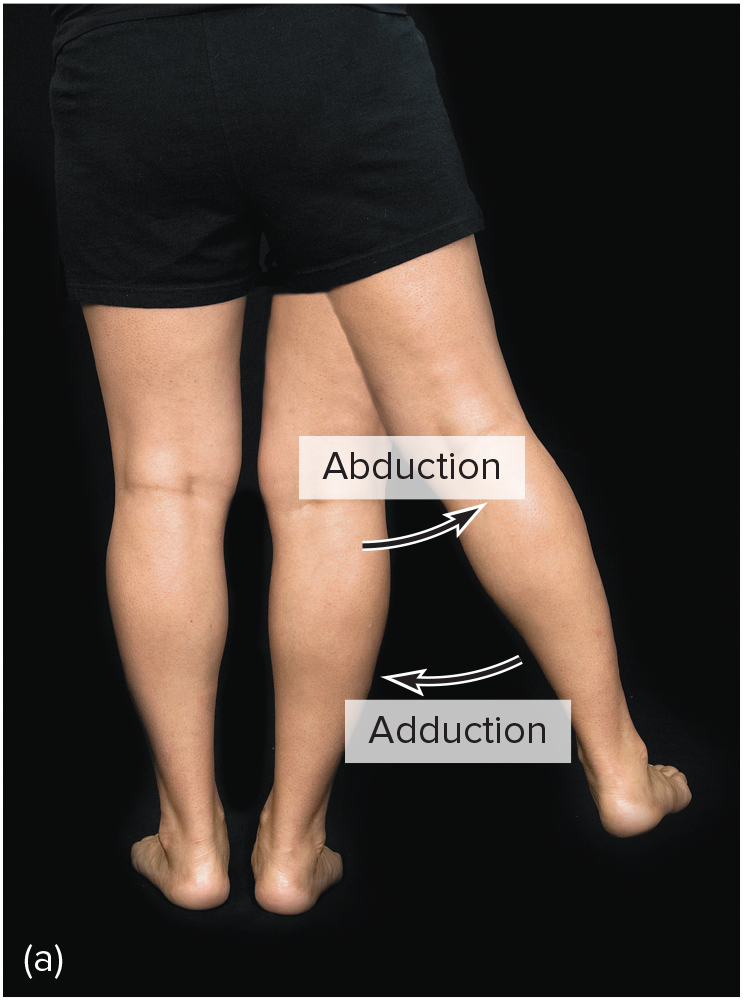
abduction
moving away from the midline
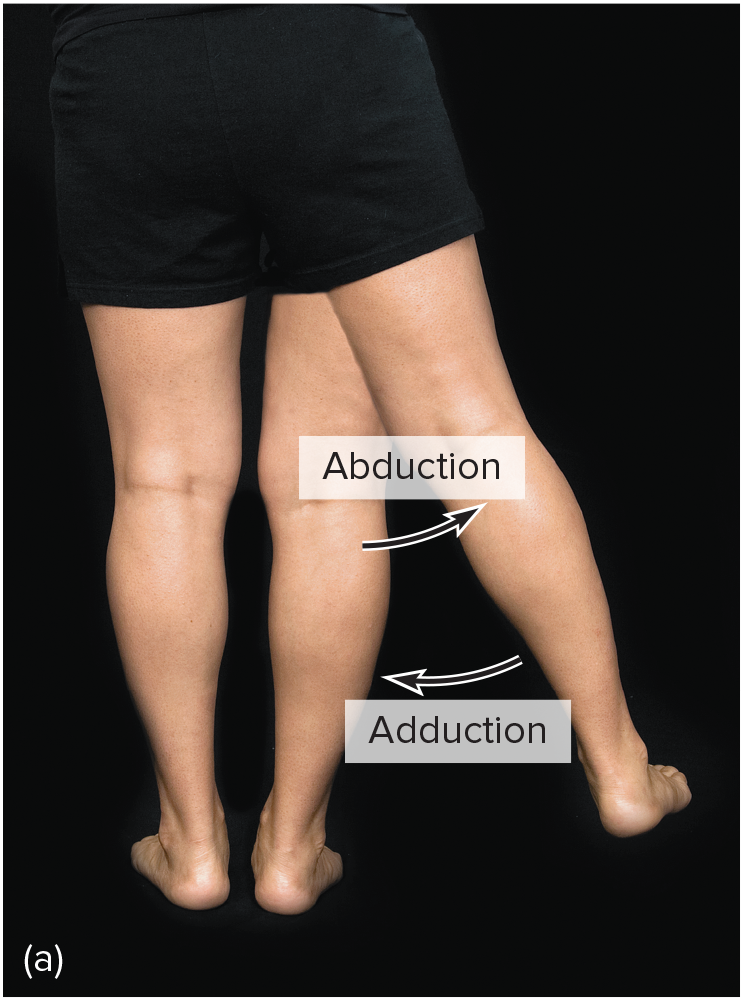
adduction
moving toward the midline
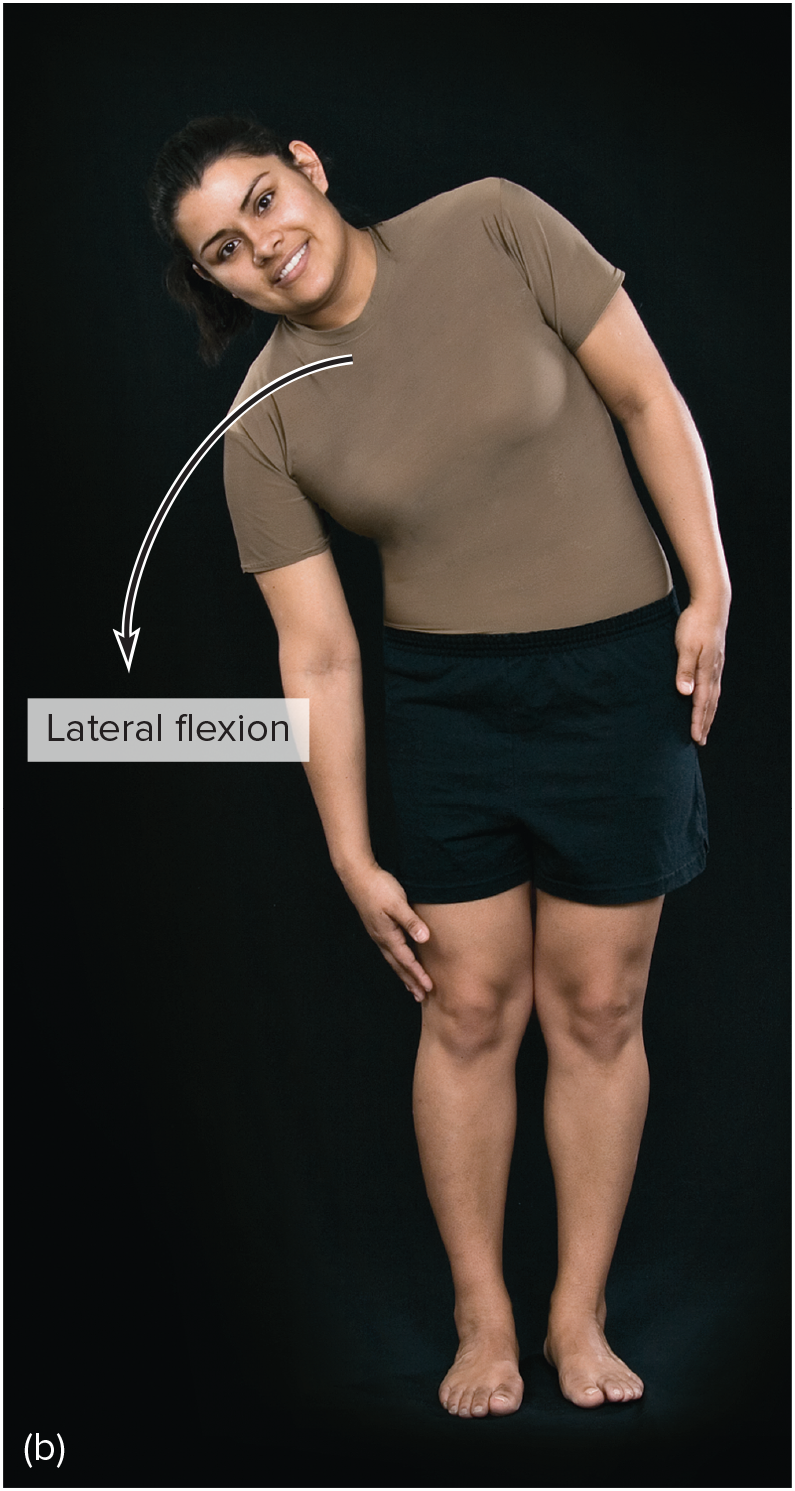
flexion
bending parts at a joint so that the angle between them decreases and the parts come closer together
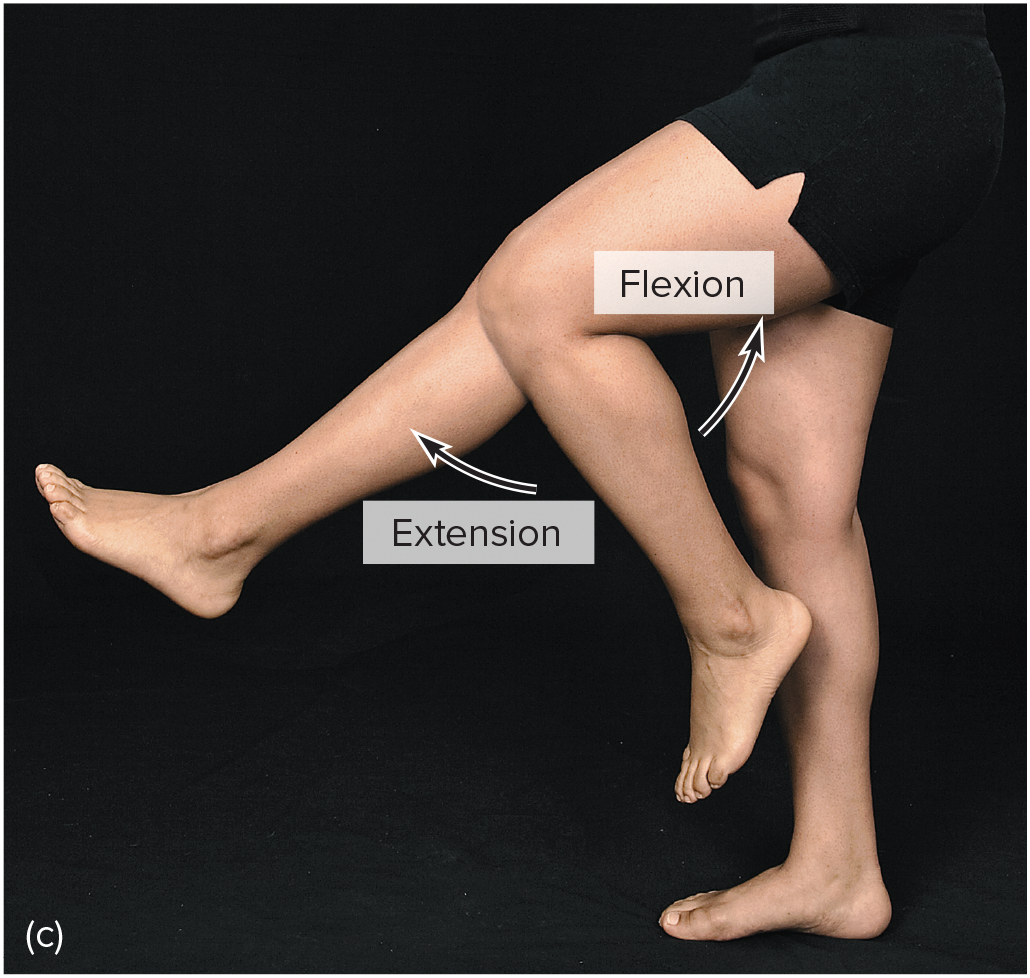
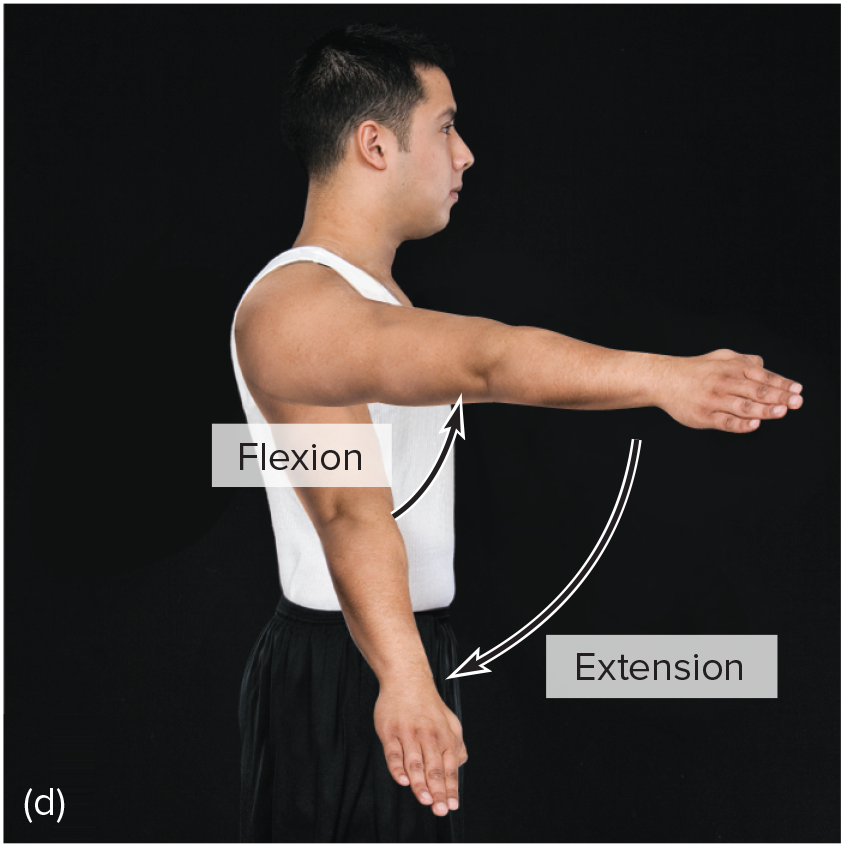
extension
moving parts at a joint so that the angle between them increases and the parts move farther apart
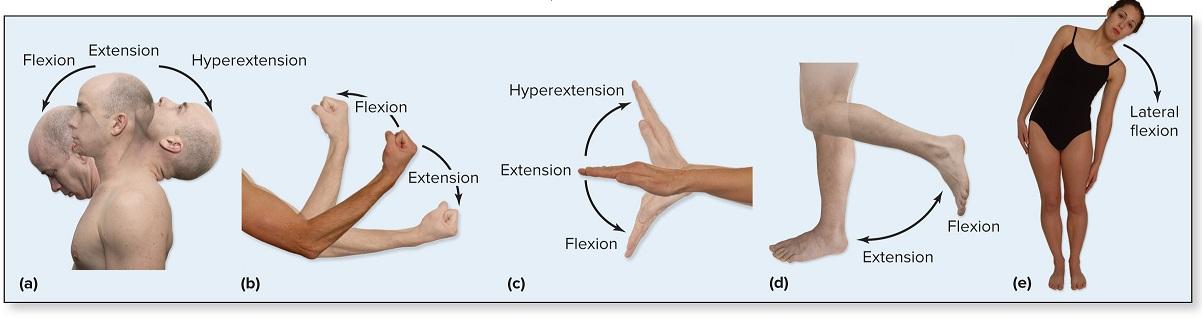
hyperextension
extension of parts at a joint beyond anatomical position (bending the head back beyond the upright position) abnormal extension beyond normal range of motion resulting in injury
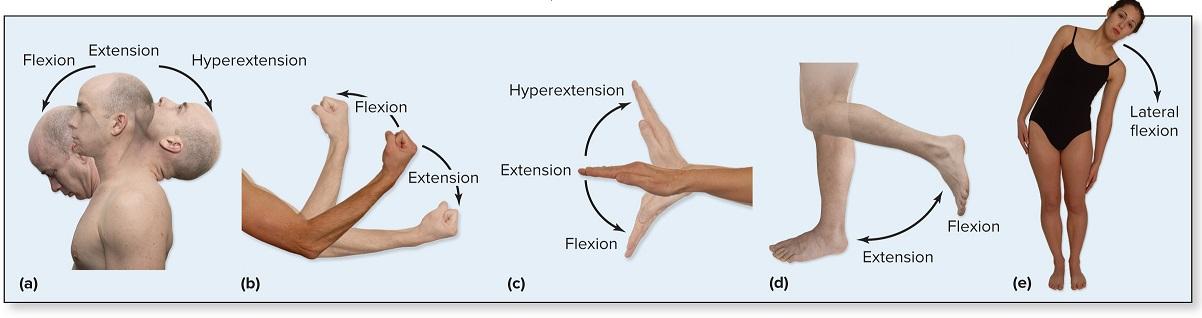
dorsiflexion
movement at the ankle that moves the anterior portion of the foot closer to the shin (rocking on heels)
plantar flexion
Movement at the ankle that moves the anterior portion of the foot farther from the shin (walking on one's toes).
rotation
Moving a part around an axis (twisting the head from side to side). Medial (internal) rotation is the turning of a limb on its longitudinal axis so its anterior surface moves toward the midline, whereas lateral (external) rotation is the turning of a limb on its longitudinal axis in the opposite direction.
circumduction
Moving a part so that its end follows a circular path (moving the finger in a circular motion without moving the hand).
supination
Rotation of the forearm so the palm is upward or facing anteriorly (in anatomical position). Supine refers to the body lying face up
pronation
Rotation of the forearm so the palm is downward or facing posteriorly (in anatomical position). Prone refers to the body lying face down.
eversion
Turning the foot so the plantar surface faces laterally.
inversion
Turning the foot so the plantar surface faces medially
protraction
Moving a part forward (thrusting the head forward).
retraction
Moving a part backward (pulling the head backward).
elevation
Raising a part (shrugging the shoulders).
depression
Lowering a part (drooping the shoulders).
glenohumoral (shoulder) joint
-ball-and-socket joint
-rounded head of humerus and shallow glenoid cavity of ulna
-protected by the coracoid and acromion processes of the scapula
-held together by dense connective tissue of ligaments & muscle
-capable of large range of movement
-flexion, extension, adduction,rotation, abduction, circumduction, extension
joint capsule of shoulder
-attached along the surface of the glenoid cavity
-very loose
-muscles, ligaments and tendons surround and reinforce it
rotator cuff
-formed by the tendons of several muscles
-supports + reinforces shoulder joint
-sports related movements can injure the cuff
-if injury occurs and rest + meds dont work surgery might be needed
coracohumeral ligament
-broad band of connective tissue
-connects coracoid process to the greater tubercle
-strengthens superior portion of joint capsule
glenohumeral ligament
-3 bands of fibers that appear as thickenings in ventral wall of joint capsule
-xtend from the edge of the glenoid cavity to the lesser tubercle and the anatomical neck of the humerus.