Inorganic chemistry
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
210 Terms
What is needed for a collision to be successful
Correct orientation and particles must have activation energy
Activation energy definition
The minimum energy required for a reaction to take place
How does rate of reaction change during a reaction
Starts at its quickest, and the rate gradually slows down
What factors can alter rate of reaction
Concentration/pressure
Temperate
Catalyst
Surface area
How does conc/pressure effect ror
Particles are closer together so particle collisions are more frequent collisions so more effective collisions
How to measure ror experimentally (2 ways)
Measuring the decrease in mass using a balance during a reaction or measuring the volume of gas produced
Catalyst definition
When a substance isn’t used up in a reaction and decreases the activation energy
Homogeneous catalyst
Catalyst thats in the same physical state as the reactants
Heterogeneous catalyst
Catalyst thats a different physical state as the reactants (usually solids with gaseous reactants)
How do catalysts work
Reactants are adsorbed onto the surface of the catalyst, where the reaction happens, then the products are desorbed
Benefits of using a catalyst
Lower cost than increasing temp/pressure
Reduces energy needed without being used up
Less CO2 produced as less energy needed
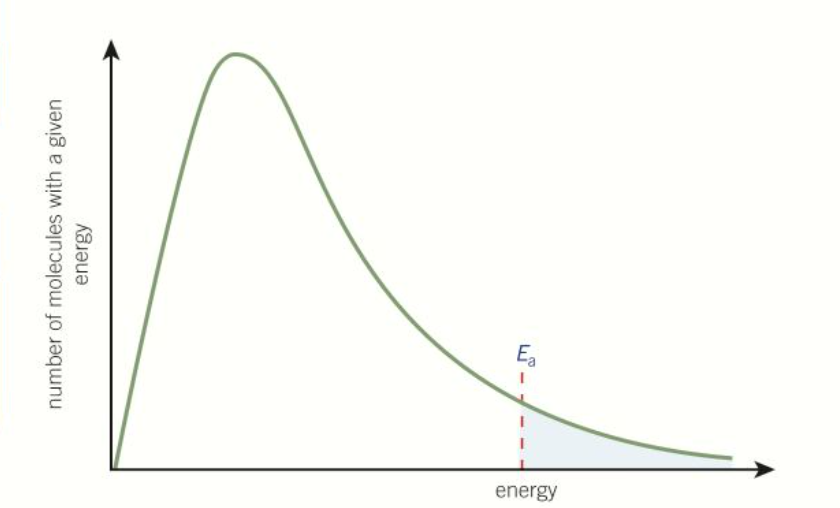
What does the boltzmann distribution look like
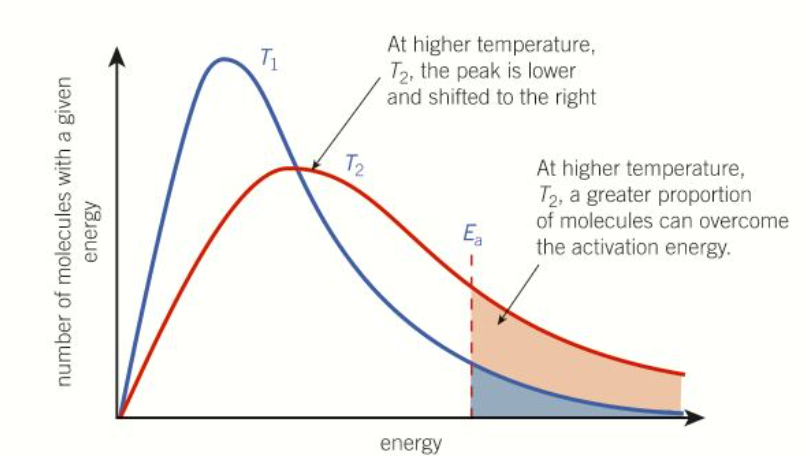
How does boltzmann distribution change with temperature
T2 = higher temp
What does the area under the boltzmann distribution represent
The number of molecules
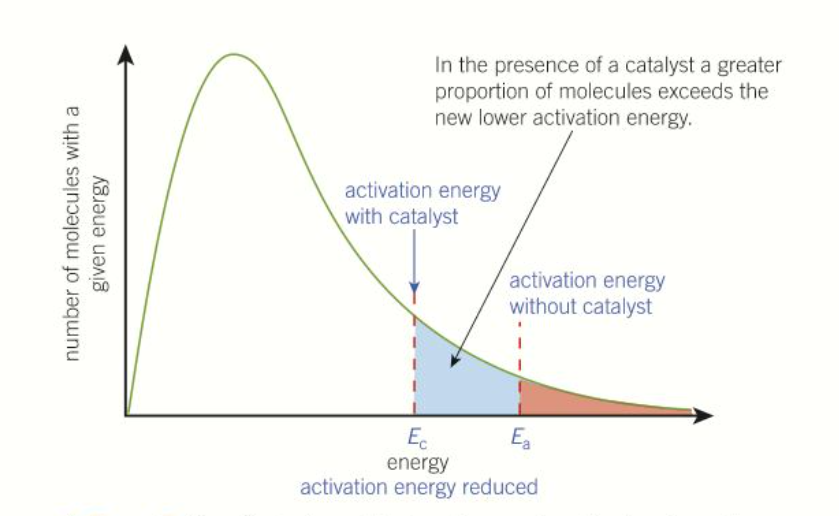
How does a catalyst affect the boltzmann distribution
What makes a system in dynamic equilibrium
When the products are being made at the same rate as reactants are being made in a closed system and the concentrations do not change
What is le Chatelier’s principle
The equilibrium will move to minimise an external change
How does changing concentration affect equilibrium
An increase to one of the sides will shift the equilibrium to the opposite side, and a decrease to one of the sides will shift the equilibrium to that side
How does changing temperature affect equilibrium
Decreasing temperature will shift the equilibrium in the exothermic direction, increasing temperature will shift the equilibrium in the endothermic direction
How does changing pressure affect equilibrium
If pressure is increased, the equilibrium will shift to the direction with less gaseous moles and if pressure is decreased, the equilibrium will shift to the direction with more gaseous moles
Equation for Kc
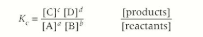
What does the value of Kc tell us about the equilibrium
Greater than 1: Shifted to the right (products)
1: in the middle
Less than 1: shifted to the left (reactants)
Benefits of a homogeneous catalyst
Increases reaction rate more than hetero because its mixed in with the reactants
Benefits of a heterogeneous catalyst
Easier to remove the catalyst from the reaction mixture
How does surface area affect the rate of reaction
Increasing the surface area will increase the number of molecules that can collide which will increase the frequency of collisions, hence frequency of successful collisions
Electronegativity definition
The ability for atoms to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bonds
What is the Pauling scale
The measure of electronegativity
What does electronegativity difference dictate
Bond type
How do simple molecular substances interact in polar solvents
Does not dissolves in water
How to represent a hydrogen bond on a diagram
Dashed line between H nucleus and lone pair
What can increase london forces?
The number of electrons in the molecule
If all of the atoms are in a longer and thin structure
Order of intermolecular forces in strength
London forces < permanent dipole dipole < hydrogen bonding
Are non polar substances soluble in polar solvents
No
Is a non polar substance soluble in a non polar solvent
Yes (e.g. hexane)
Why is the solubility of polar molecules are hard to predict?
Depends on the strength of the dipole
How do london forces come about?
Random movement of electrons produces a changing dipole which will induce a dipole on the neighbouring molecules. London forces are the attraction due to these instantaneous dipole.
How do permanent dipole dipole forces arise?
In a polar molecule, the permanent dipoles attract each other so the molecules form an arrangement with positive and negative charges adjacent
What are the anomalous properties of water due to hydrogen bonds
Higher B.P./M.P, high viscosity and surface tension, liquid water is more dense than ice
Why is water less dense than ice
The hydrogen bonds form a open lattice structure which is less dense than liquid structure
What elements form hydrogen bonds
H/N/O/F
Hydrogen bond definition
A strong dipole dipole interaction between a positive hydrogen nucleus and a lone pair of electrons
Symbol for dipoles

What is a polar molecule
A non symmetrical molecule with polar bonds so there is an overall dipole
Factors that affect electronegativity
Nuclear charge, atomic radius and shielding
How many hydrogen bonds does a water molecules form
2 hydrogen bonds
Why are non polar substances insoluble in polar solvents
The intermolecular forces are weaker in the substance so there will not be enough interaction between solvent and solute to dissolve
Why is a non polar substance soluble in a non polar solvent
Because the intermolecular forces interact and weaken in the simple molecular lattice, causing the solvent to move apart and allow the substance to dissolve
How does nuclear charge affect electronegativity
The more protons the stronger the attraction between the nucleus and the bonding pair
How does atomic radius affect electronegativity
Closer to the nucleus means stronger attraction between the nucleus and bonding pair
How does shielding affect electronegativity
Less shells of electrons between the nexulus and shared pair causes stronger attraction
Defintion of a bronsted lowry base
proton acceptor
Definition of a bronsted lowry acid
proton donor
How can H2O act like an acid and a base
It can accept a proton to form a hydronium ion, and donate a proton to become a hydroxide ion
What type of acid is ethanoic acid (2 words)
weak monobasic
What type of acid is sulfuric acid
Strong dibasic acid
What does “p” mean in chemistry generally
-log of the quantity
Calculating pH for strong acids
The acids fully dissociate, meaning [acid] = n[H+] where n is the number of hydrogens that the acid can donate
pH = ?
-log[H+]
General form for Ka (acid dissociation constant) and units
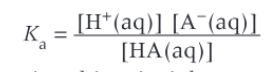
What is pKa relationship to Ka
pKa = -logKa
How do Ka and pKa vary depending on the strength of the acid
As acid strength increases, Ka increases and pKa decreases
Expression for Ka of a weak acid (without approximations)
E
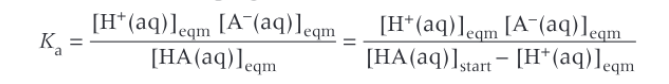
Expression for Ka for a weak acid with approximations

Approximations for calculation pH of a weak acid
That the concentration of hydrogen ions are equal to the concentration of anions (there are some H+ from the water)
We assume the concentration of the acid at equilibrium is equal to the concentration of the acid at the start, as not a lot dissociates
Kw expression and value at 298K
10^-14
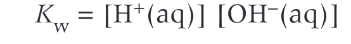
How to calculate pH of a strong base
Kw/[OH-] = [H+] and n[OH-]→[base]
What is a buffer system
Reduces the effect of acids and bases on the system
What components make up a buffer solution
HA and A-
Ways to prepare buffer solutions
Using a salt and acid or partial neutralisation (excess of weak acid with a strong base)
What happens when H+ is added to a buffer solution
H+ ions react with conjugate base, the equilibrium shifts toward the acid which reduces the H+ ions
What happens when OH- is added to a buffer solution
OH- + H+ → H20, so equilibrium shifts toward the H+ + A- as HA dissociates
When [HA] = [A-]
pH = pKa
What is the healthy pH of blood, and the bounds in which pH is safe
7.4, 7.35-7.45
What is the buffer system in the blood
Carbonic acid
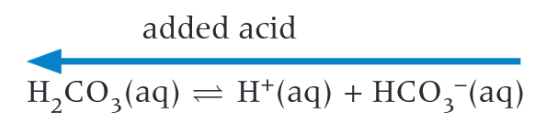
How to use a pH meter
You must calibrate the pH meter by dipping in a solution of known concentration of acid/alkali and a neutral solution, depending if we are using an excess of acid/alkali
What is the equivalence point of a titration
The centre of the vertical section of a pH curve, which is wherethe volume of one solution exactly reacts with the volume of the other solution
The colour of an end point to a titration
A colour inbetween the colour of the the conjugate base and weak acid
An indicator is a weak acid, which way is the equilibrium shifted toward when in excess of acid
To the left
At the end point, pKa =
pH
Over what range to indicators change colourq
2 pH
To choose a suitable indicator, what must the pH where it changes colour relate to in the titration
Should encompass the range where the vertical section of a titration is
Graph of strong acid - strong base titration
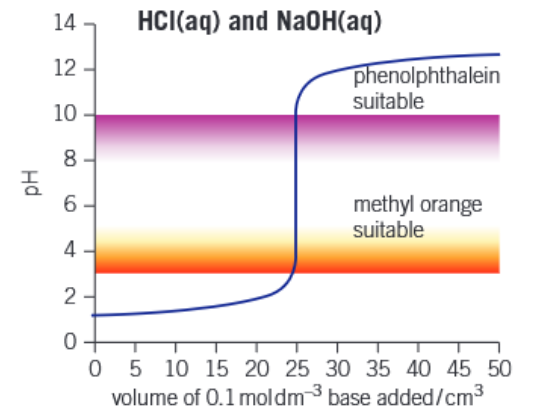
Graph of weak acid - strong base titration
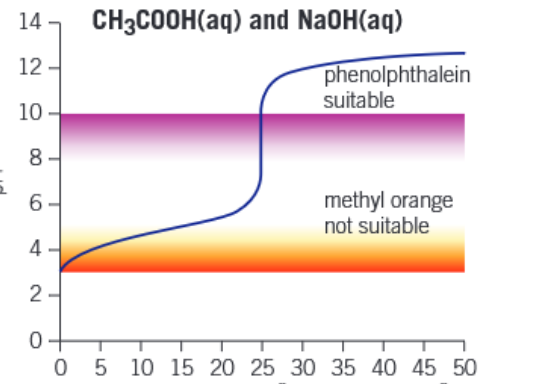
Graph of strong acid - weak base titration
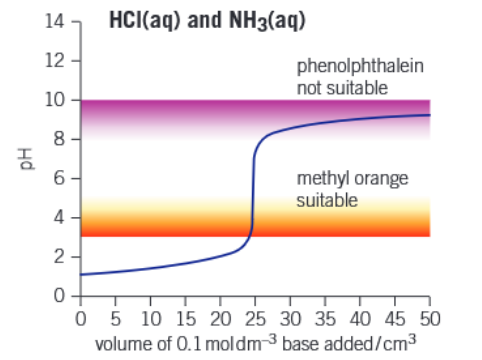
Graph of weak acid - weak base titration
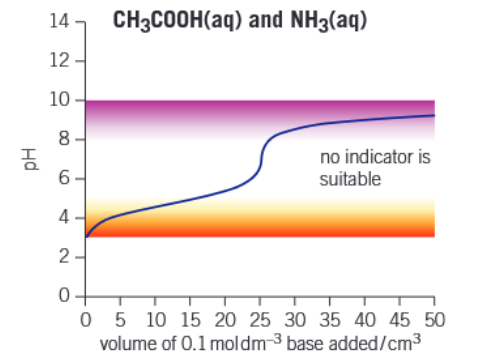
Lattice enthalpy definition
The enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of 1 mol of an ionic lattice from its gaseous ions under standard conditions
Is lattice enthalpy exo or endo and why
Lattice enthalpy is exothermic because strong electrostatic forces are formed between the oppositely charged ions to achieve a more stable state
Standard enthalpy change of formation definition
The enthalpy change that accompanies the formation of 1 mol of a substance from its constituent elements in their standard states under standard conditions
What is standard enthalpy of atomisation
The enthalpy change when changing an element into a monoatomic gas
Is enthalpy change of atomisation endo or exo
Endothermic because energy is required to break bonds to form a gas
First ionisation energy definition
The minimum energy required to remove 1 electron from each atom is 1 mol of gaseous atoms to form 1 mol of gaseous 1+ ions
Is ionisation endo or exo
Endothermic because energy is required to overcome the electrostatic forces between the positive nucleus and the negative electron
What is an electron affinity
When an electron is added to an atom/ion
Is the first electron affinity exo or endo
First electron affinity is exothermic as the negative electron is attracted to a positive nucleus
Is second electron affinity endo or exo
Endothermic because energy is required to force an electron toward a negatively charged ion
Standard enthalpy change of solution definition
The enthalpy change accompanying 1 mole of a solute being completely dissolved in a solute Iunder standard conditions
Is enthalpy change of solution endo or exo
Can be either depending on the relative magnitudes of the enthalpy change of hydration and lattice enthalpy
How to draw a dissolved ion
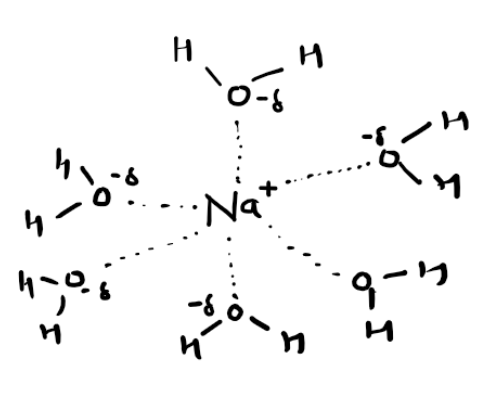
How to find enthalpy change of solution experimentally
Put a thermometer in a polystyrene cup with water and add the ionic solid, use the mass of the solution and c of water in q=mcT to find enthalpy