Clin Med Rhinitis, Sinusitis, Pharyngitis, etc.
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
What is rhinitis?
inflammation of the nasal mucosa
What is rhinitis characterized by?
-Sneezing
-Rhinorrhea
-Obstruction of the nasal passages
-Conjunctival, nasal, and pharyngeal itching
-Lacrimation
What are types of rhinitis?
-Allergic
-Vasomotor
-Rhinitis medicamentosa
What is allergic rhinitis?
symptoms occurring in a relationship to allergen exposure
can be either seasonal or chronic
What is vasomotor rhinitis?
rhinitis symptoms w/o allergic etiology or tissue eosinophilia
What is rhinitis medicamentosa?
rhinitis from prolonged use of nose drops
ex. Afrin
What can cause seasonal rhinitis?
-trees (spring)
-summer (summer)
-pollens (fall)
What are common causes of chronic allergic rhinitis?
-mold
-pets
-dust mites
-environment
What is atopic syndrome?
a syndrome characterized by a tendency to be "hyperallergic" or "supersensitive"
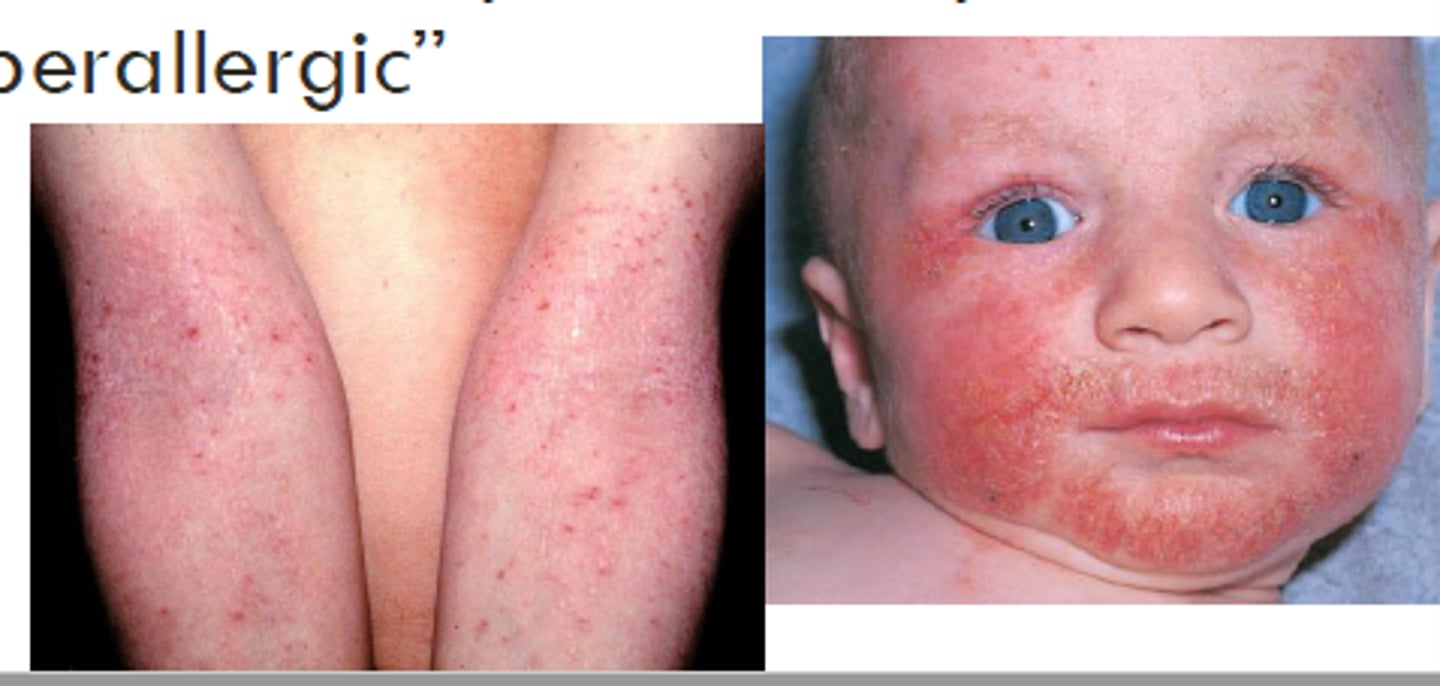
What is the classic triad of atopy?
-Asthma
-Allergic Rhinitis
-Atopic dermatitis
Allergic rxn is often associated with...?
-Atopic dermatitis
-Food
-Urticaria
-Asthma
T/F: If you're asthmatic, you are more likely to have rhinitis.
True!
What is the allergic cascade for rhinitis?
exposure --> early phase response --> inflammation --> late phase response
What is the exposure phase of the allergic cascade?
an allergen (like pollen or dust) enters the nose, sensitizing the mast cells
What is the early-phase/humeral reaction of allergic rhinitis?
occurs within 10-15 minutes of allergen exposure
sensitized mast cells release mediators like histamine, which cause itchy nose, runny nose, and sneezing.
What is the inflammation phase of the allergic cascade?
cytokines bring WBCs to the affect area, causing irritation and inflammation that lead to congestion and postnasal drip
What is the late phase response of the allergic cascade?
the inflammation leads to the release of even more histamine and mediating chemicals, which worsen symptoms.
What are symptoms of rhinitis?
-episodic rhinorrhea
-sneezing
-obstruction of nasal passages
-lacrimation
-pruritis
What are signs of rhinitis?
-nasal mucosa pale & boggy
-conjunctiva congested and edematous
-nasal mucosa swelling
-nasal polyps
What are Ddx of allergic rhinitis?
-Vasomotor rhiniits
-Structural abnormalities of the nasopharynx
-Irritant exposure
-URI
-Pregnancy with edema of the nasal mucosa
-Rhinitis medicamentosa
-Drug induced (beta blockers, ace inhibitors, cocaine)
What are some allergic rhinitis diagnostics?
-Nasal secretions
-Serum IgE
-Intracutaneous testing
-Intradermal testing
-ELISA blood testing
What would the nasal secretions of a pt with allergic rhinitis show?
smear will show lots of eosinophils
What would the serum IgE of a pt with allergic rhinitis show?
frequently elevated but not specific for just IgE
What kind of intracutaneous testing could you do to diagnose a pt with allergic rhinitis?
puncture or prick skin testing
When would you use intradermal testing to diagnose a pt with allergic rhinitis?
if intracutaneous test is negative as intradermal is more sensitive
ELISA blood testing detects total __________.
IgE
Why is skin testing a preferable diagnostic for allergic rhinitis?
it's a rapid, sensitive, cost-effective modality to detect IgE-mediated diseases
Skin testing needs to be performed by an allergy expert given the risk of __________________.
anaphylaxis
What are examples of H1 antihistamines that can be used for tx of allergic rhinitis?
Pills & sprays
-Cetirizine (Zyrtec) 5-10 mg daily
-Desloratadine (Clarinex) 5 mg daily
-Fexofenadine (Allegra) 60 mg BID or 180 mg daily
-Loratadine (Claritin) 10 mg daily
-Levocetirizine (Xyzal) 2.5-5 mg/day
-Azelastine (Astelin) nasal spray, puff each nostril BID
-Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) 25-50 mg q 4-6 hours, children 1-2 mg/kg
What is the maximum dose of Benadryl you can give to a kid each day?
50 mg/day

What are examples of intranasal steroids that can be used for tx of allergic rhinitis?
-Budesonide (Rhinocort)
-Mometasone (Nasonex)
-Fluticasone (Flonase)
-Triamcinolone (Nasacort AQ)

Can you get rhinitis medicamentosa from intranasal steroids?
NO!
Cromolyn sodium (NasalCrom) nasal spray is a _________ cell stabilizer. It is more useful for episodic exposure to _________ hair.
mast; cat
T/F: Singular causes a better response than intranasal steroid.
False - intranasal steroid causes a better response than Singulair.
Can you combine Montelukar (Singulair) with other therapies?
Yes!
What can Montelukast (Singulair) treat?
allergic rhinitis associated with asthma
people with triad use this
What is pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)?
nasal decongestant that relieves congestion and can cause side effects, so it should not be used continuously.

Decongestants are relatively contraindicated in pts with...?
-HTN
-Pts receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy
-Pts with closed angle glaucoma, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease, hyperthyroidism, or bladder neck obstruction.
T/:F: Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) can be combined with Zyrtec, Allergra, and Claritin.
True!
T/F: Oxymetazoline HC10 (Afrin) is for chronic use.
False - chronic use can cause rhinitis medicamentosa.
In terms of allergic rhinitis tx, start with _____ _____________. If this causes minimal relief of symptoms, you can add a ________________ ________________.
H1 Antihistamines; intranasal steroid spray
What are immunotherapy/hyposensitization tx options for allergic rhinitis?
repeated SQ injections of gradually increasing concentrations of allergen
over 3-5 year period
Immunotherapy/hyposensitization for allergic rhinitis is best used in what kind of pt's?
pts with severe, persistent symptoms that are refractory to environmental control and drug therapy
What are causes of vasomotor rhinitis?
-Chemical odors
-Temperature & humidity variations
-Position changes
What is the tx for rhinitis medicamentosa?
Stop using the nasal spray that caused it!

What are the paranasal sinuses?
-Frontal
-Ethmoid
-Sphenoid
-Maxillary
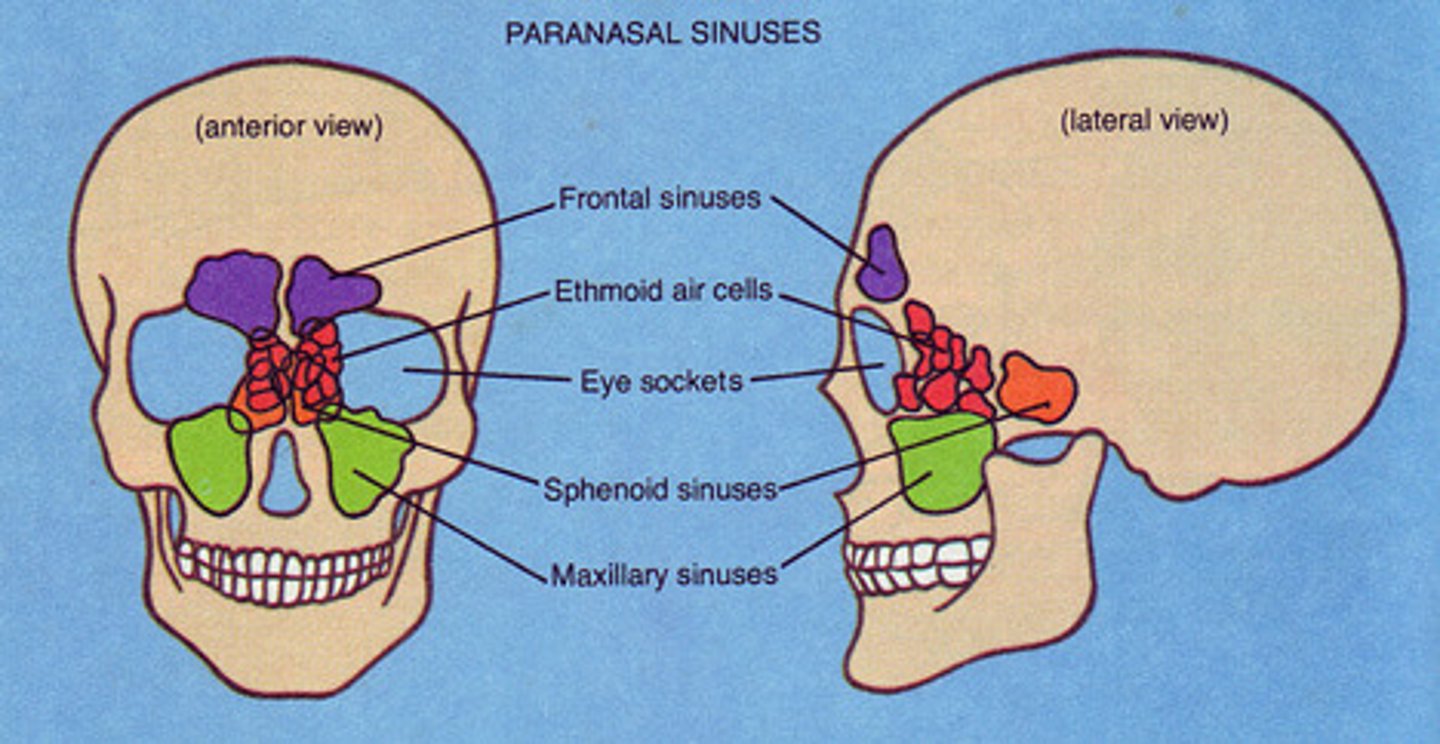
What is the order of sinuses most commonly involved in sinusitis?
1. Maxillary (most common)
2. Ethmoid
3. Frontal
4. Sphenoid
How is sinusitis usually classified?
-Duration of illness
-Etiology
-Pathogen type
What is acute rhinosinusitis?
inflammatory condition involving the nasal sinuses
sinusitis < 4 weeks of duration
What is chronic rhinosinusitis>
sinusitis > 12 weeks of duration
What is the cause of acute rhinosinusitis?
-Viral
-Bacterial
-Anaerobes
What are examples of viruses that cause acute rhinosinusitis?
-Rhinovirus
-Influenza virus
-Parainfluenza virus
What are examples of bacteria that cause acute rhinosinusitis?
-Strep. pneumococcus (most common)
-H. influenza
-M. catarrhalis
-Staph
-Strep group A
What are the noninfectious causes of acute rhinosinusitis?
-Allergic
-Barotrauma
-Chemical irritants
-Nasotracheal and nasogastric tubes
-Tumors
-Granulomatosis disease
-CF
Infxn in the ____________ sinus is more common in adults, whereas infxn in the ____________ sinus is more common in children.
maxillary; ethmoid
T/F: Infx in the frontal and sphenoid sinuses are rare and serious complications are more likely.
True!
What are clinical manifestations of acute rhinosinusitis?
-Fever
-Nasal congestion
-Purulent rhinorrhea
-Cough (PND)
-H/A
-Tooth pain/halitosis
What are signs of acute rhinosinusitis?
-Pain on palpation
-PND
-Nasal d/c
-Inflammatory changes
Dx of acute rhinosinusitis is usually ____________ bc it's difficult to determine if it's bacterial vs. viral.
clinical
Longer duration of symptoms usually means what kind of infection? How would you treat?
bacterial; abx frequently prescribed (85-95% of cases)
T/F: Radiographs are usually necessary to dx acute rhinosinusitis.
False!
What are used to evaluate persistent, recurrent, or chronic sinusitis?
CT sinus
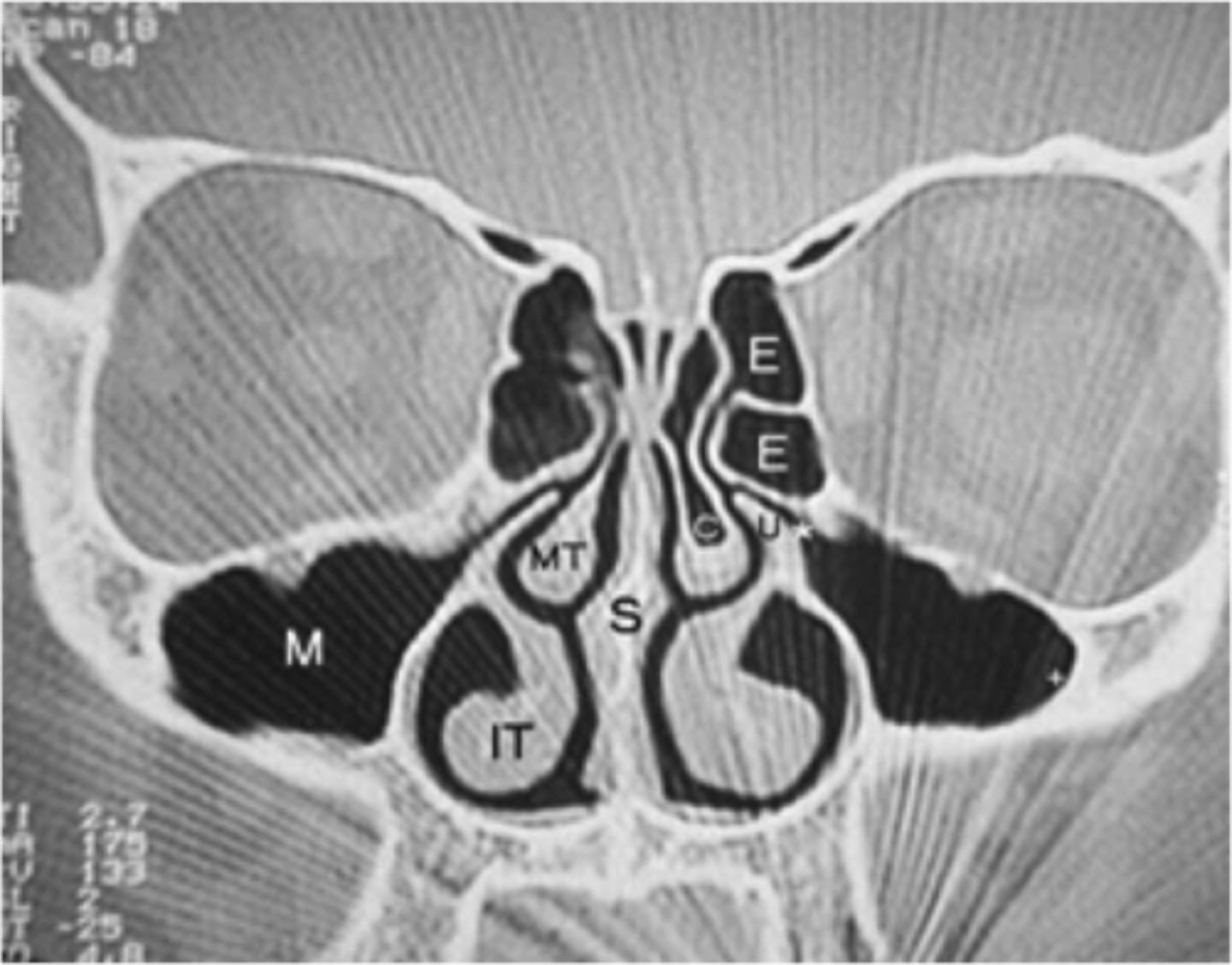
What abxs can be prescribed for pts with acute rhinosinusitic sx for 10-14 days?
-Amoxicillin 500 mg PO TID (most common)
-Augmentin 875 mg PO BID
-Doxycycline 100 mg PO BID
-Clindamycin 300 PO TID
Other than abx, what other treatments can be used for acute rhinosinusitis?
-Decongestants
-Humidified air
-Supportive treatment (fluids, rest, ibuprofen)
What are complications of sinusitis?
-Chronic sinusitis
-Potts puffy tumor
-Orbital celluliits
-Abscess
-Meningitis
What is Potts puffy tumor?
a surgical emergency and a rare complication of frontal sinusitis
characterized by osteomyelitis of the frontal bone with an associated subperiosteal abscess
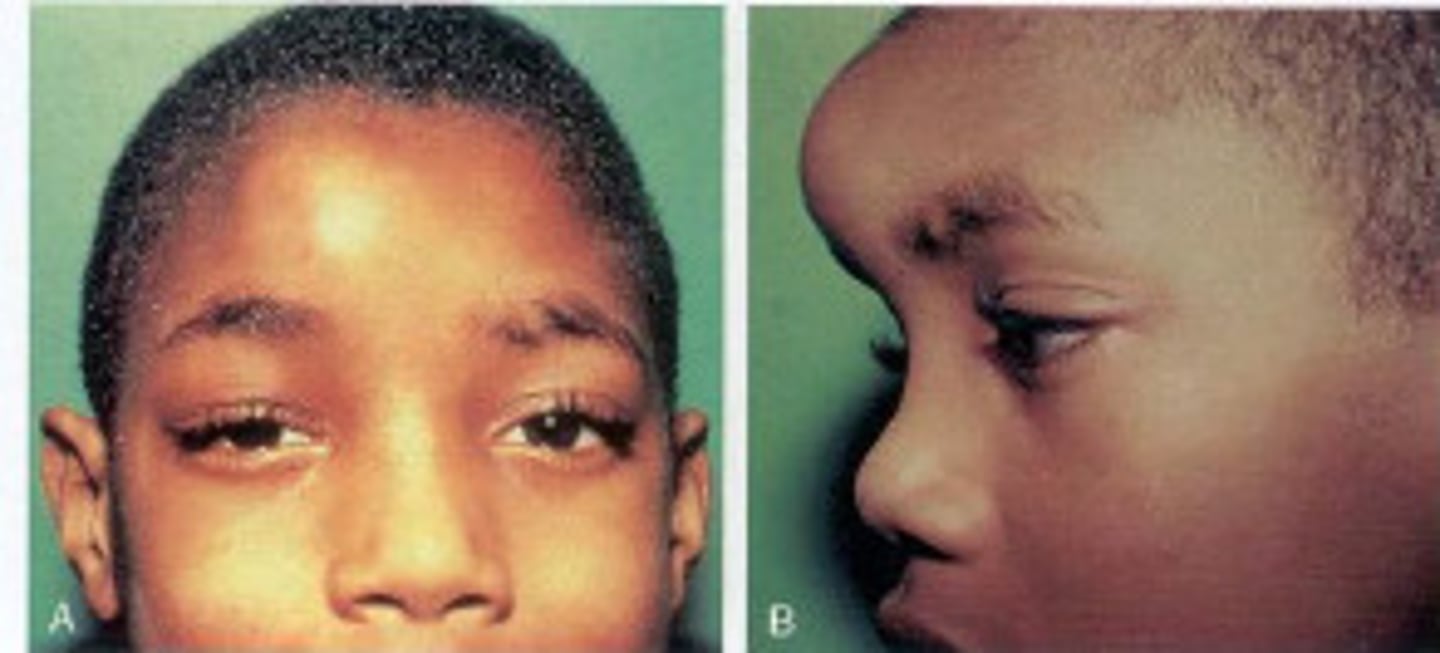
How long do sx last in chronic sinusitis? What is the etiology?
symptoms lasting >3 months
bacterial or fungal etiology
In chronic sinusitis, clinical manifestations are not as _______________. A _______________ can be ordered for evaluation. The pt should be referred to _______________ for further evaluation. Treatment could include abx for ____-____ days, decongestants, nasal steroids, or surgery if infxn is recurrent or failure of medical management.
dramatic; CT scan; ENT; 14-28
What is pharyngitis?
inflammation of the pharynx
What causes viral pharyngitis?
-Rhinovirus
-Coronavirus
-Parainfluenza
-EBV
-Coxsackievirus
-HSV
What is the most common bacterial cause of pharyngitis?
Group A B hemolytic streptococcal pyogenes
Group A B hemolytic streptococcal pyogenes is primarily a disease of children ages...? It is uncommon among children...?
5-15 yo
<3 yo
What are clinical manifestations of viral pharyngitis?
more likely to be slower in onset and last longer over time
What are clinical manifestations of bacterial pharyngitis?
tends to have an abrupt onset. pain is described as sharp, often associated with fever, chills, malaise, hot potato voice (raspy) if tonsils are enlarged, and H/A
What is true about viral pharyngitis?
-fever is rare
-no cervical lymphadenopathy
-no pharyngeal exudates
-may have cough, URI symptoms
What are signs of strep pharyngitis?
-pain
-erythema (injection/beefy red, strawberry tongue with strep, petechiae of soft palate)
-tonsillar hypertrophy
-exudate
-halitosis
-cervical lymphadenopathy
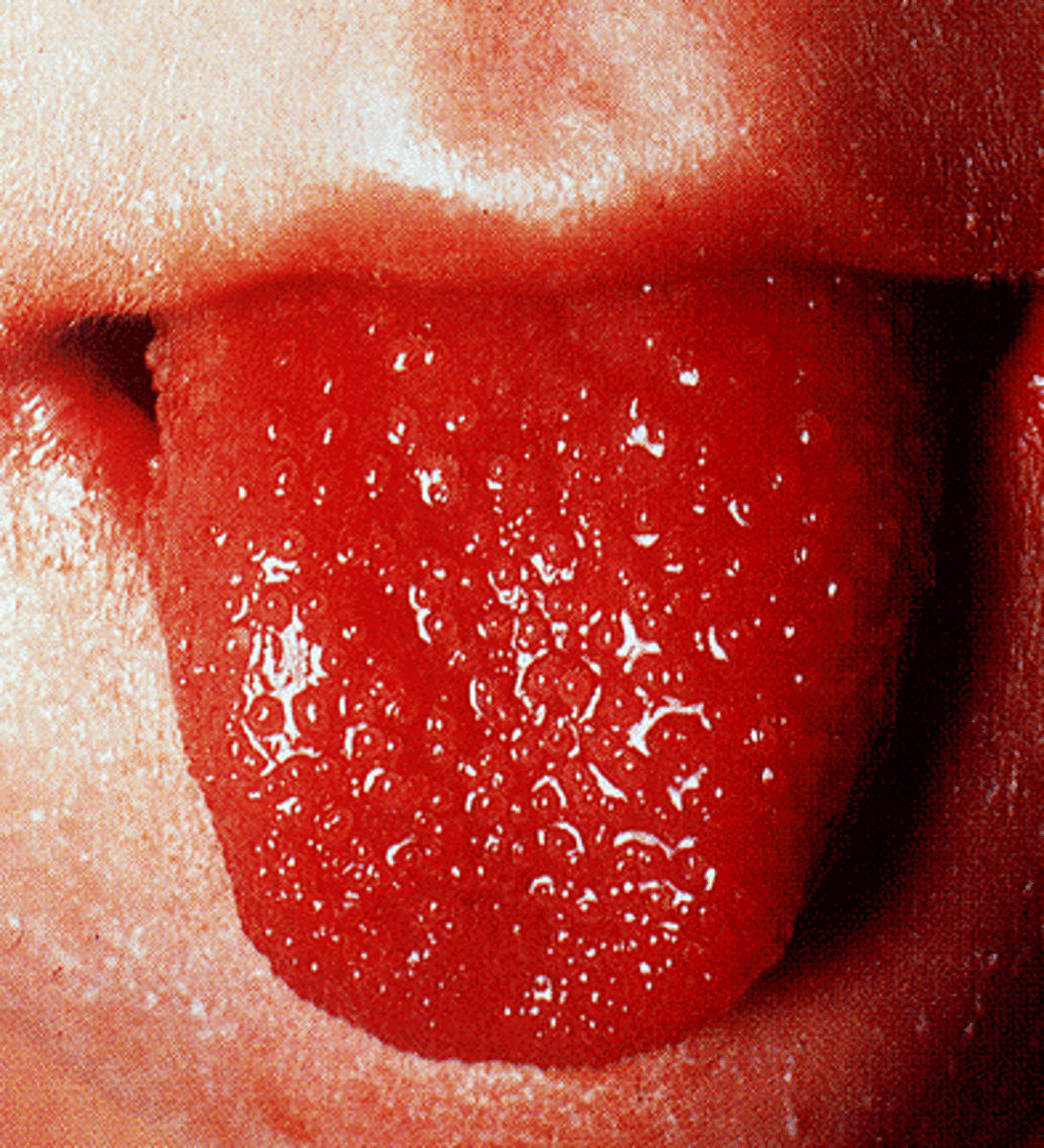
What are lab dx used for pharyngitis?
-rapid strep screen for Group A strep
-throat culture (C&S)
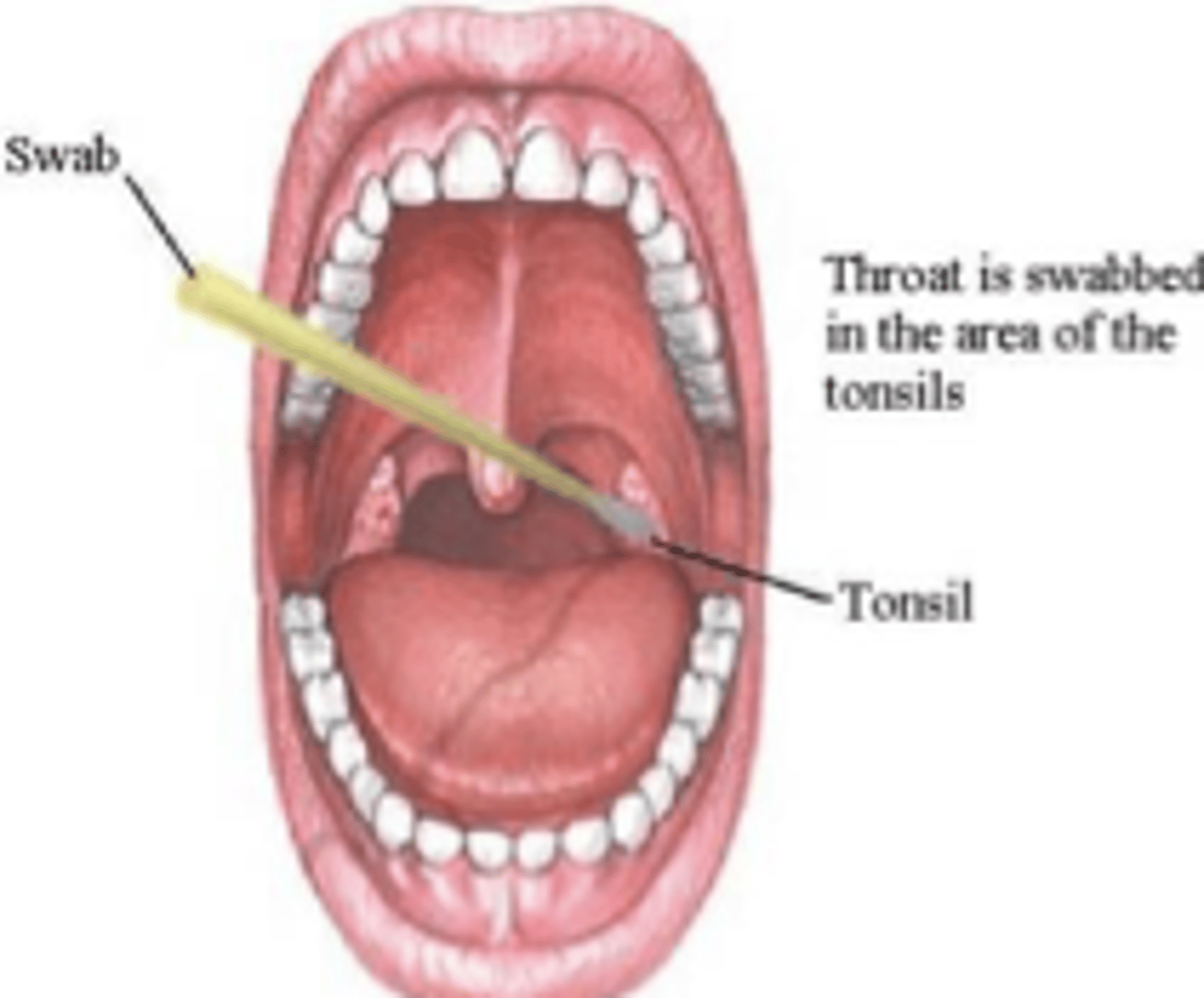
Where should you swab for a throat culture?
swab the tonsillar pillars and posterior pharyngeal wall
What are centor criteria?
a set of criteria which may be used to identify the likelihood of a bacterial infxn in adult pts complaining of a sore throat
pts are judged on 4 criteria, with 1 point added for each positive criteria
What are the 4 centor criteria?
1. hx of fever
2. tonsillar exudates
3. tender anterior cervical adenopathy
4. absence of cough
What do -1, 0, or 1 point(s) indicate according to centor criteria?
no abx or throat culture necessary (risk of strep. infxn <10%)
What do 2 or 3 points indicate according to centor criteria?
should receive a throat culture and treat with an abx if culture is + --> 2-3 days later
(risk of strep. infxn 32% if 3 criteria, 15% if 2)
What do 4 or 5 points indicate according to centor criteria?
consider rapid strep test and or culture (risk of strep. infxn 56%)
The likelihood of has GAS ____________ with the number of CENTOR criteria. However, the CENTOR criteria are most useful in identifying pts for whom neither ____________ tests nor ____________ therapy are necessary.
increases; microbiologic; antimicrobial
Why are abx for strep given?
to reduce the symptoms, prevent complications (Rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis)
What is an example of a steroid tx option for strep pharyngitis?
one time dose of IM Decadron 10 mg
PO PCN (Pen VK) is the drug of choice for strep pharyngitis, however _______________ is used more frequently.
Amoxicillin
What tx is used in pts who can not tolerate PO meds and are least likely to comply with regime for strep pharyngitis?
IM Benzathine PCN or Procaine PCN G
What tx is used in PCN allergic pts for strep pharyngitis?
macrolide family (Zithromax, Biaxin)
*Need to be cautious with the potential of resistant*
T/F: Cephalosporins (Ceftin, Omnicef) are also excellent meds to use for strep pharyngitis but are often more expensive.
True!
What are supportive tx options for pharyngitis?
-antipyretics
-analgesics
-fluids
-rest
-salt water gargles
-magic mouth wash
-avoid spreading germs
-surgical management for recurrent tonsillar infxns
When is surgical management for recurrent tonsillar infxns considered?
if there are 6 or more episodes in 1 year
What is magic mouthwash?
formulas with a combination of:
-abx
-antihistamine
-antifungal
-steroid
-local anesthetic/pain reliever
-antacid
How often magic mouthwash formulations used?
q 4-6 hrs
What are complications of streptococcal infxns?
-Acute Rheumatic Fever
-Peritonsillar or retro pharyngeal abscess
-Scarless Fever
-Post strep. Glomerulonephritis
-Chronic Strep carriers
-Impetigo
-Cellulitis
-Sinusitis
-OM
-Mastoiditis
What test is used to confirm post strep. glomerulonephritis?
Anti-DNAase B titer
What is acute rheumatic fever (ARF)?
a multi system disease resulting from an autoimmune rxn to infxn with group A streptococcus pyogenes
Almost all of the problems caused by ARF resolve spontaneously except...?
cardiac valvular disease (rheumatic heart disease)
How long after onset of strep infxn does AFR occur? What age does it affect?
2-3 weeks
children ages 5-14 years
ARF and RHD are diseases of ______________.
poverty