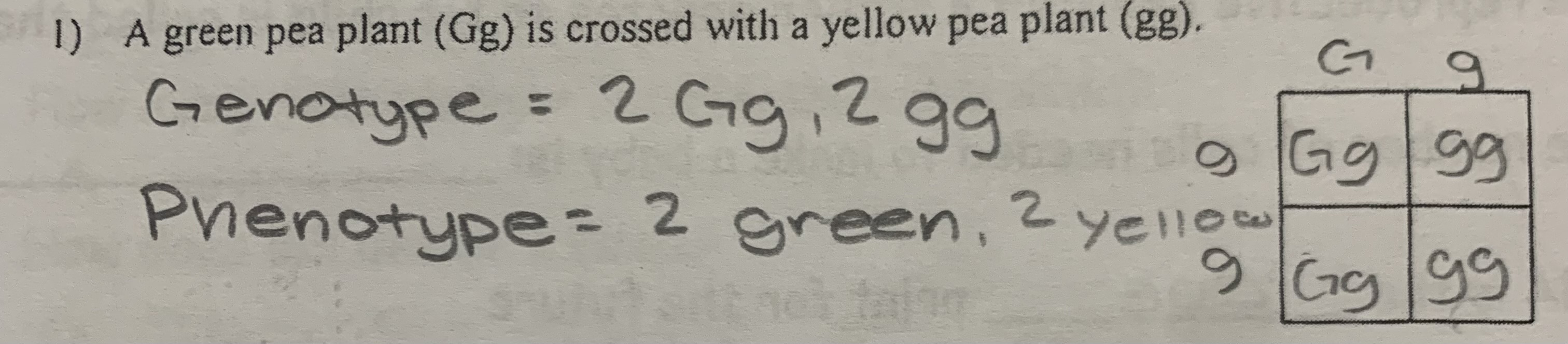science exam
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
TRUE OR FALSE
matter
anything that takes up space
has volume and mass
TRUE OR FALSE
pure substance
a substance where every sample is the same in every way
TRUE OR FALSE
asexual/sexual reproduction
asexual (mitosis)
requires a single parent
produces offspring identical to its parent
sexual (meiosis)
two individuals contribute genetic material
produce offspring with a combination of genetic information from their parents
TRUE OR FALSE
do all cells have a nucleus
false prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus
TRUE OR FALSE
homogenous and heterogenous mixtures
heterogenous
a mixture where the substances aren’t evenly mixed
ex. salad
homogenous
a mixture where the molecules of each substance are equally mixed
you can’t see the different parts of the mixture
ex. sugar dissolved in water
TRUE OR FALSE
static electricity
when electricity gathers in one place
TRUE OR FALSE
trait inheritance and alleles (dominant & recessive)
dominant alleles
the allele that is always expressed
homozygous dominant (RR)
recessive alleles
the allele that gets masked
only expressed when both alleles are recessive
homozygous recessive (rr)
heterozygous (Rr)
genotype= 2 GG, 2 Gg
phenotype (physical)= 4 green pea plants
TRUE OR FALSE
symbols for metric conversions
M (mega)
k (kilo)
h (hecto)
da (deka)
g (grams), L (litres), m (meters) BASE UNITS
d (deci)
c (centi)
m (milli)
TRUE OR FALSE
solvent and solute
solute
the substance that gets dissolved
solvent
the substance that dissolves the solute
TRUE OR FALSE
5 different types of asexual reproduction
binary fission
duplicates its genetic material by elongating
budding
uses mitosis to produce a bud of cells
when large enough will break off and live on its own
vegatation propagation
when a plant produces runners, or horizontal stems that grow into a new plant
regeneration
when animals regrow lost parts
sporulation
when a parent plant create hundreds of spores which germinate and produce offspring
TRUE OR FALSE
differences between genes, traits and alleles
gene
a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein, influencing a particular TRAIT.
traits
observable characteristics that are passed down through generations
alleles
different variations of a GENE
each individual inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent
TRUE OR FALSE
covalent and ionic bonds
covalent bonds
formed by sharing electrons between atoms
BOTH ATOMS CONJOIN
Non-metals Covalently bond with non-metals
ionic bonds
2 atoms that aren’t neutral joining together (the amount of electrons and protons are not equal)
BOTH ATOMS WITH DIFFERENT CHARGES.
charges
positive= more protons
negative= more electrons
neutral= equal amount of protons and electrons
TRUE OR FALSE
types of animals that use external fertilization
External Fertilization
the sperm and eggs are released into an external environment.
(ex.: bodies of water)
Fishes like Salmon and Trout
Amphibians like frogs and toads

SHORT ANSWER
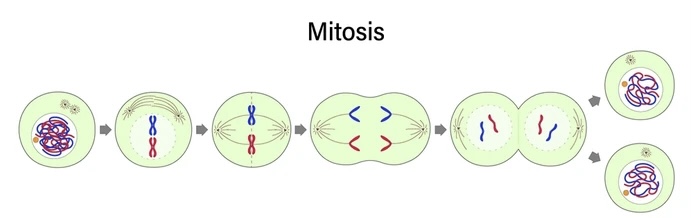
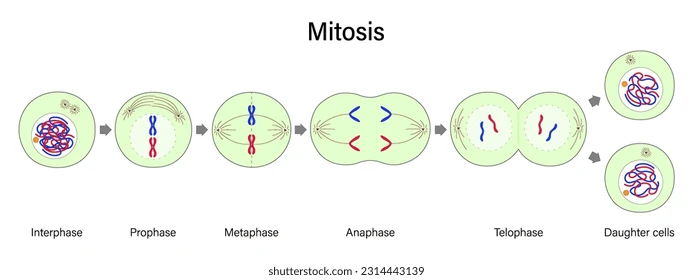
all the stages of PMAT
interphase
cell grows
replicates DNA
prepares for cell divison
prophase
chromosomes become visible
membrane disappears
metaphase
chromosomes are pulled by spindle fibres
anaphase
there are twice as many chromosomes in the cell
telophase
nuclear membrane reappears
spindles disappear
SHORT ANSWER
diagram of PMAT
SHORT ANSWER
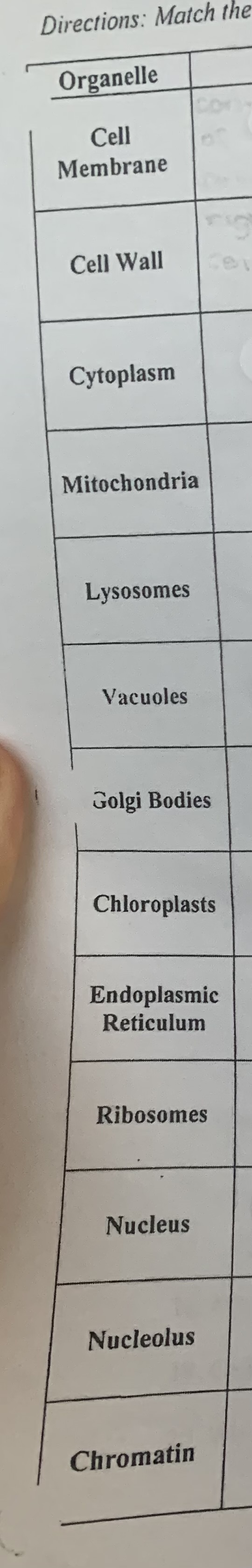
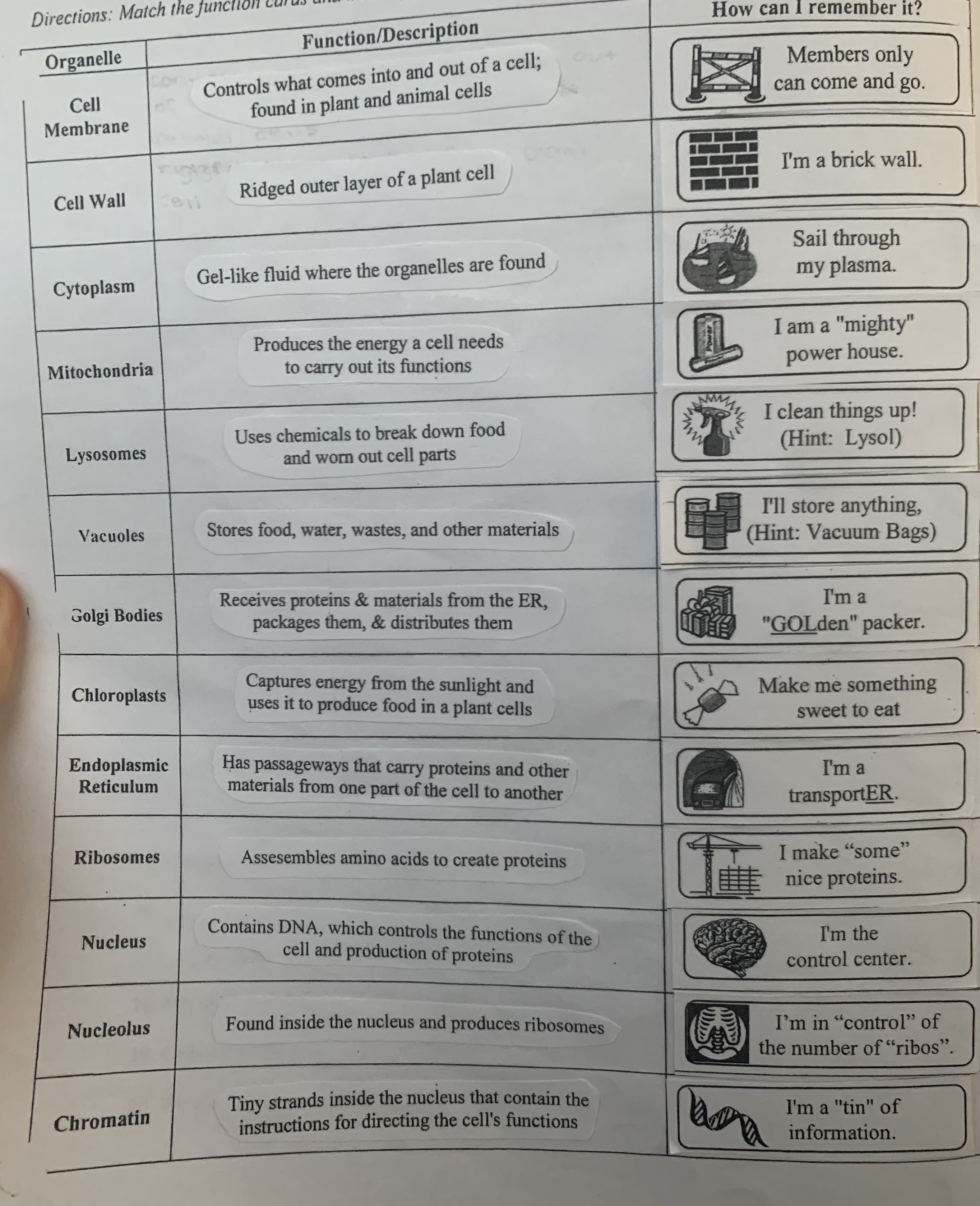
know your cell organelles and their functions
SHORT ANSWER
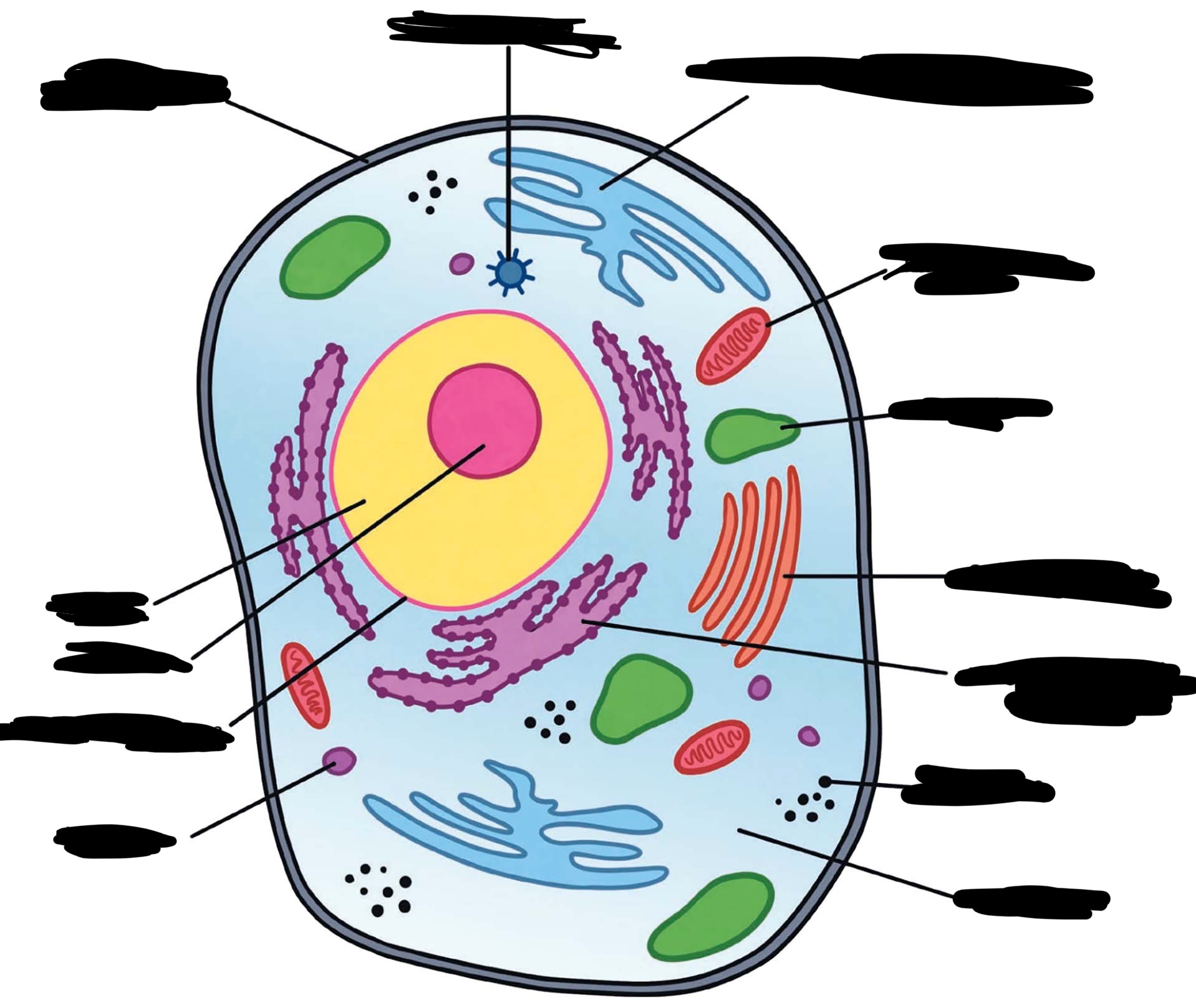
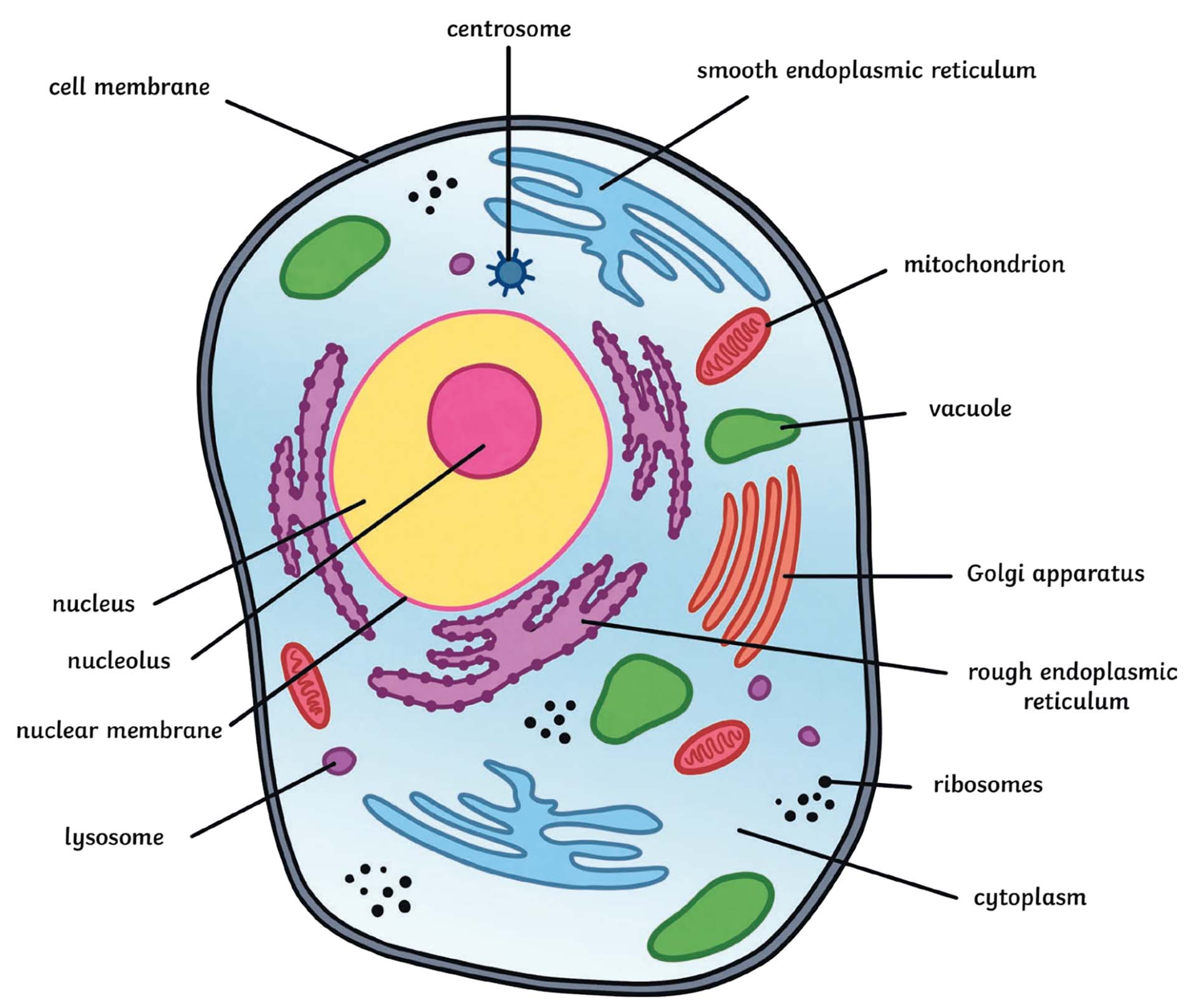
animal cell diagram
SHOW YOUR WORK
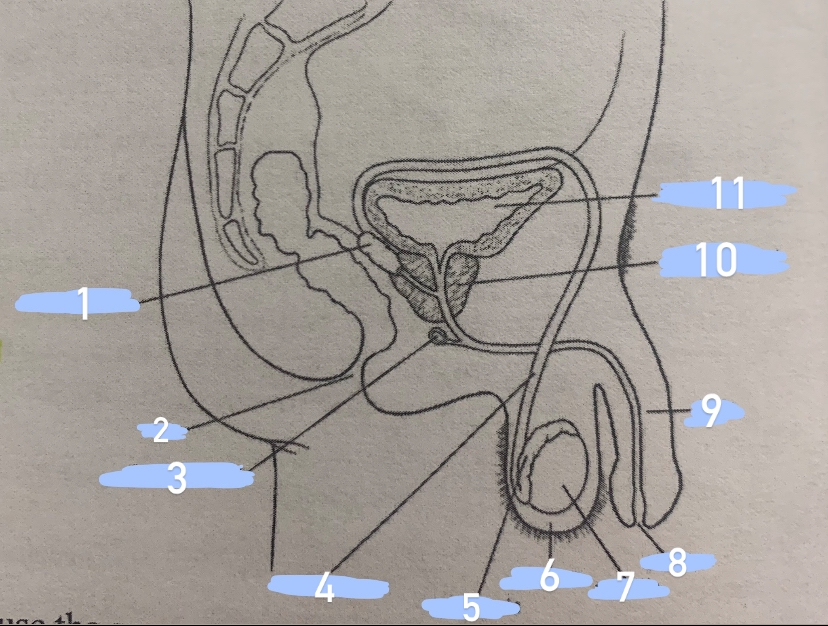
male reproductive structure
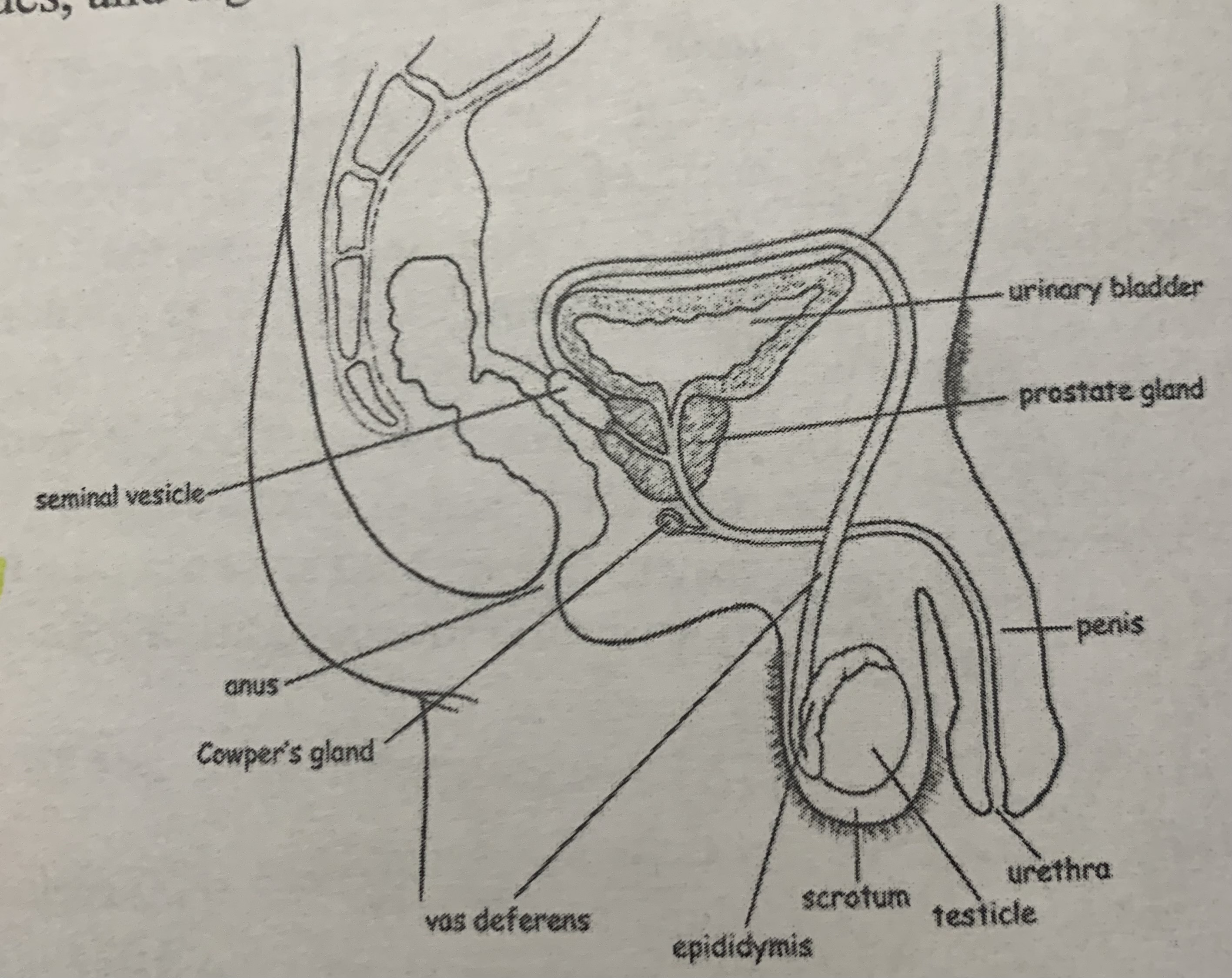
SHOW YOUR WORK
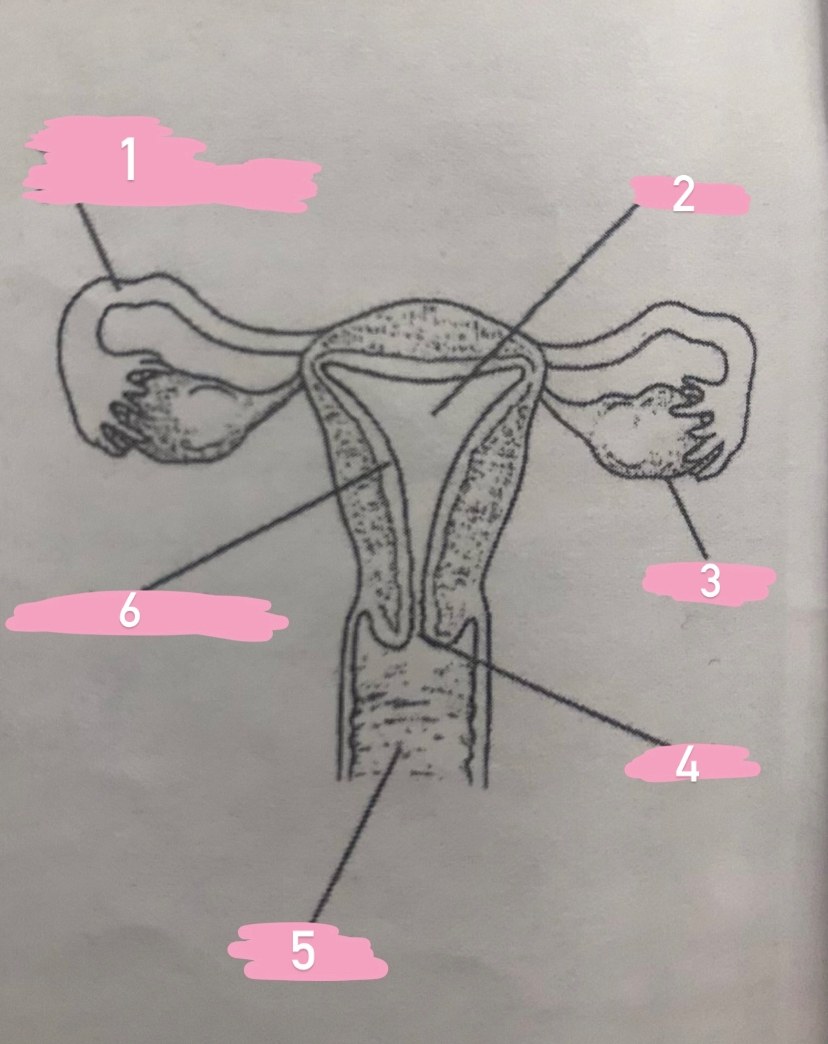
female reproductive structure
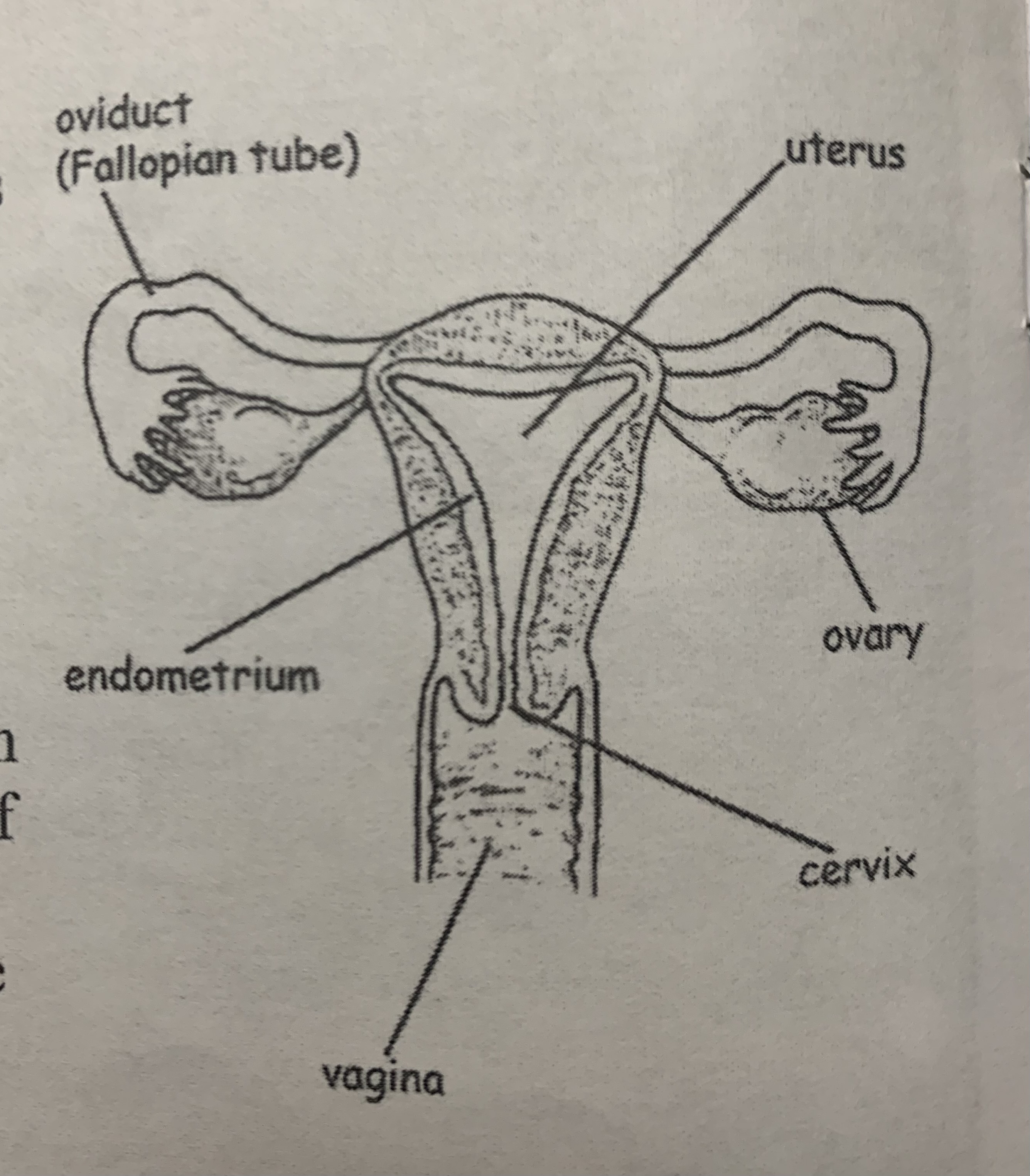
MULTIPLE CHOICE
pregnancy
When an offspring is developing in a womb
when sperm enter the ovum and fertilizes an egg
Drinking or smoking can cause an unnatural birth
FASD= Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Disorder
MULTIPLE CHOICE
chromosome/sexual reproduction
chromosomes are made up of genes
Humans have 46 Chromosomes (Sperm 23, Egg 23)
Gametes: Sex cells (Sperm, and Egg)
body cell (paired)
sex cell (not paired)
MULTIPLE CHOICE
physical and chemical changes
physical change
no new substances are formed
ex. ice melting
chemical change
always causes atleast one new substance, with new properties, to be formed
ex. burning paper
MULTIPLE CHOICE
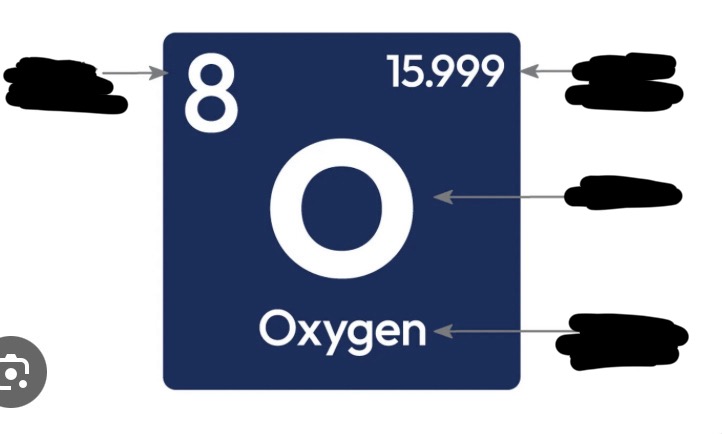
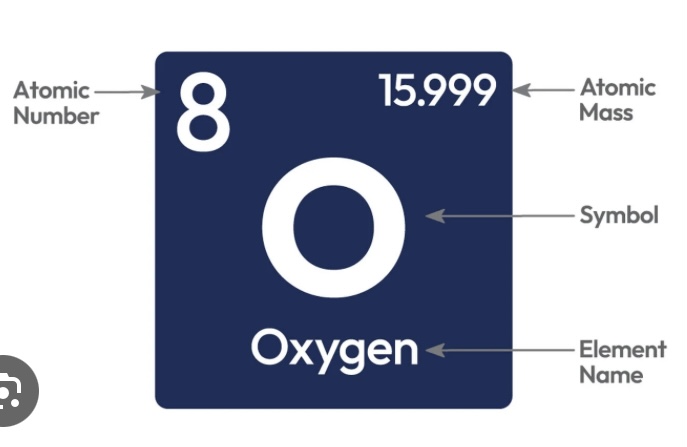
periodic table of elements and it’s arrangement
Arranges elements by increasing atomic number (the number of protons in an atom's nucleus)
protons & electrons = atomic number
neutrons = atomic mass (rounded) - atomic number
Horizontal rows= Periods
Vertical columns= Groups
left side= metals
right side= non-metals
MULTIPLE CHOICE
electricity and charges and their attractions
Like charges repel each other
(+) and (+) or (−) and (−) push away
Unlike charges attract each other
(+) and (−) pull together
neutral attraction= equal amount of postive and negative charges
MULTIPLE CHOICE
compounds and ionic bonds
compound
a substance formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded
ionic bonds
an electrostatic attraction between two atoms where one atom tranfers an electron to the other atom
CHEMISTRY
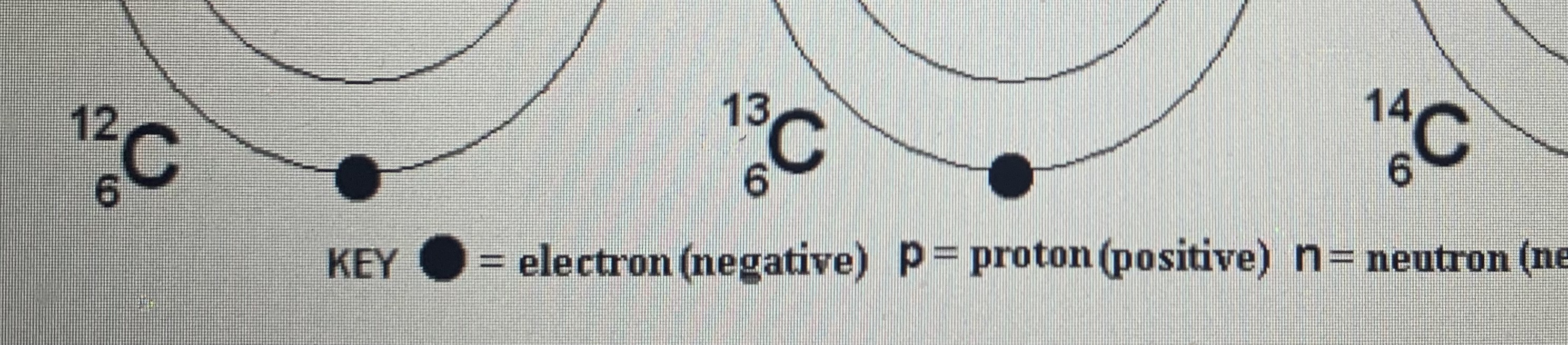
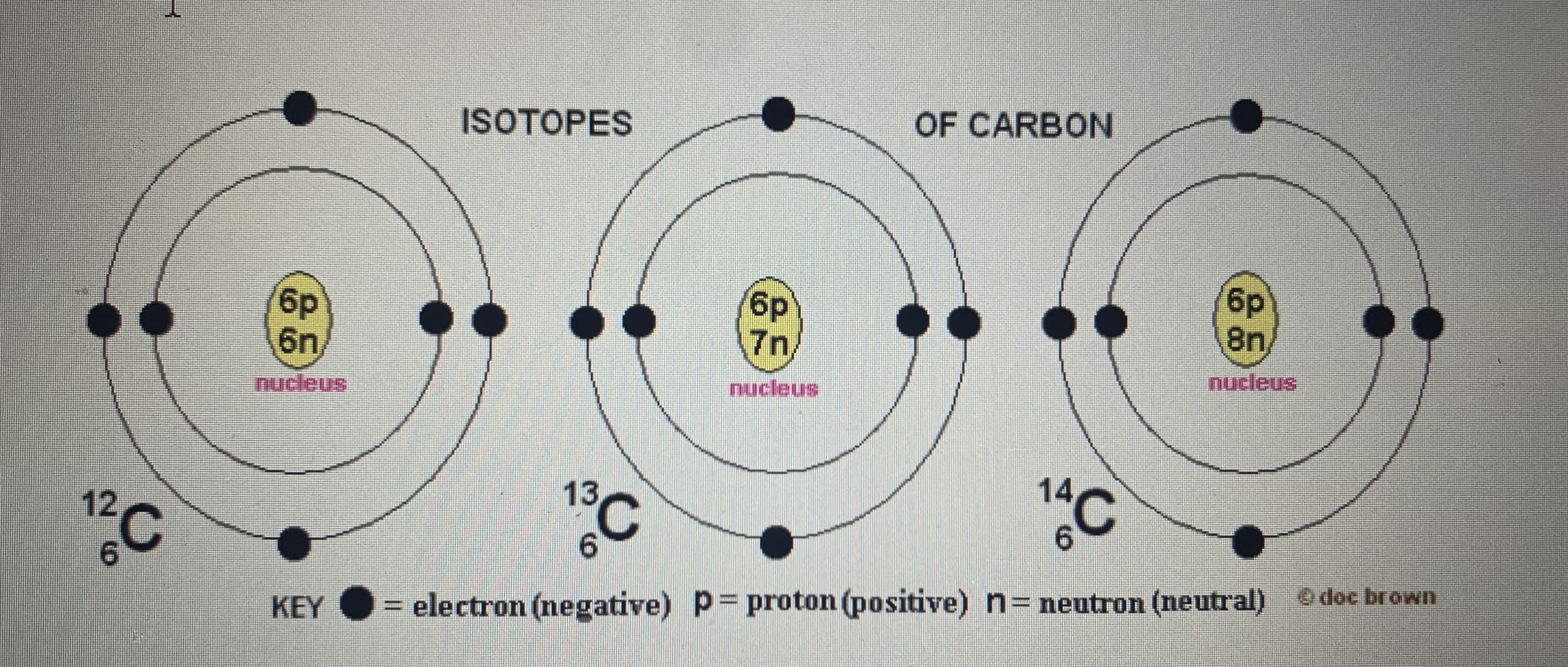
bohr diagrams of an isotope of a given atom
Isotopes: Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
The more Neutrons just means it’s heavier
2-8-8 rule
GENETICS
punnet squares
ex. a green pea plant (GG) is being crossed with a yellow pea plant (gg)
genotype: 2 Gg, 2 gg
phenotype: 2 green plants, 2 yellow plants