Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
yes
All nervous structures outside of the CNS
no
All sensory and motor nerves including
Spinal nerves
Cranial nerves
Sensory ganglia
Sensory receptors
Motor nerves begins
Begin in ventral grey horn
Motor nerves
Innervate both voluntary skeletal muscles and involuntary
Somatic vs. visceral
Innervate muscles at neuromuscular junction
Sensory nerves
Receptors receive information from the world around us
Mechanoreceptors
Touch/pressure
Mechanoreceptors types
Meissner’s Corpuscle
Pacinian Corpuscle
Pacinian Corpuscle
Light pressure
AKA tactile Corpuscle
Meissner’s Corpuscle
Deep pressure
AKA Lamellar Corpuscle
Nociceptors
Pain
Thermoreceptors
temperature
Proprioceptors
Awareness of Position, movement, balance
Proprioception definition
Sense of position in space
Proprioception
Receptors in muscles, tendons, ligaments, skin, etc.
Detect changes in length, tension, and position
Proprioception examples
Neuromuscular spindles (stretch)
Golgi tendon organs (tension/muscle force)
Vestibular system of inner ear (balance, whole body position)
Chemoreceptors
Respond to chemicals
Olfactory nerve
Smell
Taste buds
Flavor
Carotid body & sinus
Blood CO2 and pressure
Photoreceptors
Rods and cones in retina detect Light
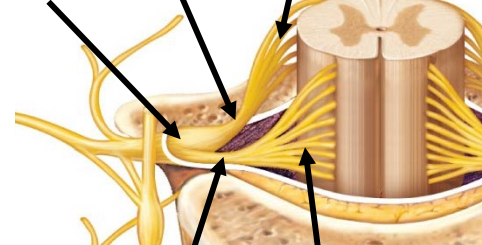
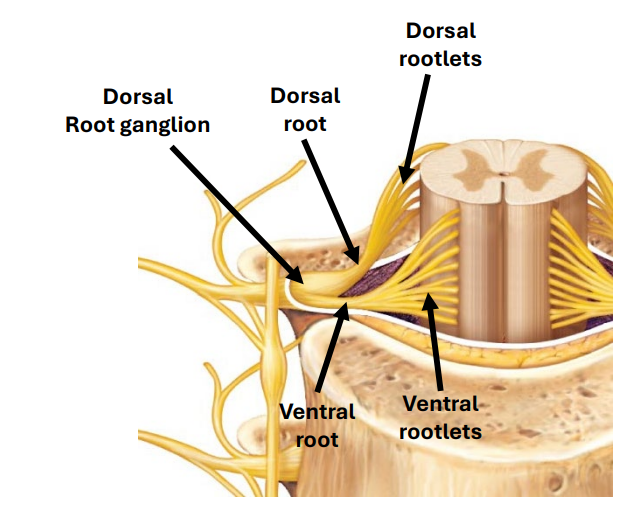
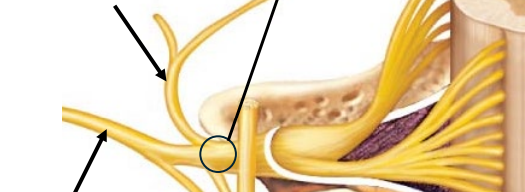
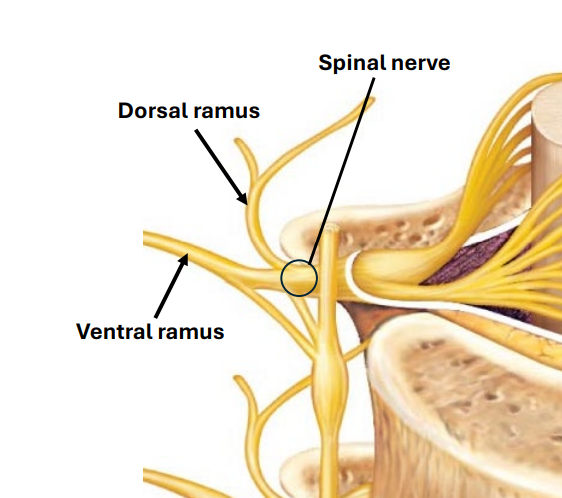
Dermatomes
“Map” of sensory innervation of skin
Dermatomes strips
Represented by specific spinal cord level
Pair of sensory nerves (left and right)
T4
Nipple
T10
Umbilicus (AKA navel, belly button)
Total sensation loss requires
Total sensation loss requires damage to THREE adjacent spinal nerve levels
Shingles
rash along entire dermatome
viruses
reside in dorsal root ganglion and travel along nerve axons
Referred Pain
Pain in organs results in perceived pain elsewhere
Referred Pain involves
Visceral sensory (from organs)
Somatic sensory (skin)
visceral signals enter
spinal cord at same level as somatic, through same DRG
Because shared region in spinal cord, brain perceives additional pain in non -organ regions
Nervous plexuses
Intertwined network of nerves
Give off many branches that innervate bones, muscles, skin, etc.
4 Major plexuses
Cervical
Brachial
Lumbar
Sacral
ALL plexuses
Both motor & sensory
Derive from ventral rami
The Cervical Plexus C1-C4
Arises from cervical enlargement
Muscles and skin of neck
The Cervical Plexus
PHRENIC NERVE
C3, C4, C5
Diaphragm
The Brachial Plexus C5-T1
Motor
Sensory
The Brachial Plexus C5-T1 Motor
Muscles of shoulder & upper limb
The Brachial Plexus C5-T1Sensory
Skin of shoulder & upper limb
The Brachial Plexus: The Axillary Nerve
motor
Deltoid muscle
The Brachial Plexus: The Axillary Nerve
Sensory
Skin of shoulder
The Brachial Plexus: The Axillary Nerve
Damage to nerve
Limited arm abduction and loss of shoulder sensation
The Brachial Plexus Musculocutaneous Nerve
Motor
Muscles of anterior arm
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
The Brachial Plexus Musculocutaneous Nerve Sensory
Lateral skin of forearm
The Brachial Plexus Musculocutaneous Nerve
Damage to nerve
Greatly reduced Arm flexion, forearm supination
Numbness/pain in lateral forearm
The Brachial Plexus Radial Nerve
Motor
Extensors of arm, forearm, wrist, & digits
Ex. Triceps, extensor carpi muscles, extensor digitorum
The Brachial Plexus Radial Nerve
Sensory
Portions of posterior & lateral arm & forearm
The Brachial Plexus Radial Nerve
Damage to nerve
Arm, wrist, digit extension
Numbness/pain in posterior arm/forearm
Wrist drop
Radial nerve damage →Inability to extend wrist
If wrist involuntarily drops into flexion → radial nerve damage
The Brachial Plexus The Ulnar Nerve
motor
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Part of flexor digitorum profundus
Hypothenar muscles
Lumbricals III & IV (medial 2)
The Brachial Plexus The Ulnar Nerve
seonsory
Numbness/pain
Medial skin of hand
Ulnar nerve damage Funny bone
Compression or damage to ulnar nerve at elbow
Pain/numbness at site of damage and medial hand
Ulnar nerve damage Claw hand
Severe/chronic damage to nerve
Lumbricals affected
Extensor digitorum extends metacarpophalangeal joint
The Brachial Plexus Median Nerve
motor
Flexors of wrist
Thenar muscles
Lumbricals I & II
The Brachial Plexus Median Nerve
Sensory
Numbness/pain
Skin of palm & digits
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Inflammation of tissue in carpal tunnel
All digit flexors pass through with median nerve
Damage/impingement of median nerve
Painful swelling, limited mobility, numbness of skin
Median Nerve Damage at wrist
Ape Hand
Loss of thumb opposition
Lumbosacral plexus Femoral Nerve
Motor
Quadriceps
Lumbosacral plexus Femoral Nerve
Sensory
Skin of anterior thigh and leg
Lumbosacral plexus Femoral Nerve
Damage to nerve
Inability to extend knee
Numbness/pain in skin of anterior lower limb
Lumbosacral plexus Obturator nerve
motor
Adductor muscles
Lumbosacral plexus Obturator nerve
Damage to nerve
Inability to adduct thigh
Lumbosacral plexus Sciatic nerve
Motor
Hamstrings
Lumbosacral plexus Sciatic nerve
Sensory
Posterior thigh
Lumbosacral plexus Sciatic nerve
Damage to nerve
Weakened thigh extension Inability to flex leg
Gluteal injection
Not many nerves to damage & avoids sciatic nerve
Sciatica
Posterior lower limb pain/numbness
Possible weakness of posterior lower limb muscles
Lumbosacral Plexus Tibial Nerve
Motor
All posterior leg muscles
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Tibialis Posterior
Flexor hallucis longus
Lumbosacral Plexus Tibial Nerve
Damage to nerve
Reduced ability to plantarflex, flex digits, invert
Lumbosacral Trunk Common Fibular Nerve
2 branches
Deep fibular nerve
superficial fibular nerve
Deep fibular nerve
motor
muscles of anterior leg
Deep fibular nerve
nerve damage
Reduced or absent dorsiflexion, digit flexion, inversion
Superficial Fibular Nerve
Motor
muscles of lateral leg
Superficial Fibular Nerve
Nerve Damage
Eversion
Foot drop
Damage to deep fibular nerve: In ability to dorsiflex
Patient lifts foot off floor
If foot falls into plantar flexion deep fibular nerve damage
The Lumbosacral Plexus The Pudendal Nerve
Motor & sensory to the Pelvic floor/ diaphragm Damage to the Pudendal Nerve can cause
The Lumbosacral Plexus The Pudendal Nerve
Incontinence
Cannot contain urine/feces
The Lumbosacral Plexus The Pudendal Nerve
Prolapse
Vagina and/or anal canal inverts outside of body
Pudendal Nerve Block
Can be used in obstetrics for pain relief during childbirth