chapter 1 environmental science
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
environment
consists of all the living and nonliving things around us
Environmental science
the study of how the natural world works, how the environment affects us, and how we affect it
Natural resources
the substances and energy sources that we take from the environment and rely upon to survive
Renewable natural resources
are replenished over short periods
inexhaustible
inexhaustible
Sunlight, wind, and wave energy are perpetually renewed
exhaustible
Timber, water, animal populations, and fertile soil take months to years to replenish
Nonrenewable natural resources
are formed much more slowly than we use them and are no longer available once depleted
ecosystem services
such as air and water purification, cycling of nutrients, climate regulation, pollination, and waste recycling
Agricultural revolution
grow crops and domesticate animals
Industrial revolution (mid-1700s)
shifted life toward an urban society powered by
Ecological footprint
the cumulative area of land and water needed to provide resources and waste disposal for a typical person
overshoot
surpassing Earth’s capacity to sustainably support our population
Humans are using renewable resources 68% faster than they are being replenished
natural capital
its store of resources and ecosystem services, is like a bank account
Currently, we are drawing down Earth’s natural capital, a practice that is unsustainable
interdisciplinary
multiple disciplines together
natural studies
focus on how the natural world works
social sciences
address human interactions and institutions
ES is…
interdisciplinary
Environmental studies
emphasize the social sciences
Environmentalism
a social movement dedicated to protecting the natural world from undesirable changes brought on by human actions
ES vs Environmentalism
Environmental science involves the scientific study of the environment and our interactions with it
Environmentalism is a social movement dedicated to protecting the natural world from undesirable changes brought on by human actions
Science
a systematic process for learning about the world and testing our understanding about it
Descriptive science
involves researching organisms, materials, and systems that are new or not well-known.
Hypothesis-driven science
uses experiments to test hypotheses as part of the scientific method
scientific method
a formalized technique for testing ideas
hypothesis
A question arises from the observation, which the scientist then attempts to explain
scientific method
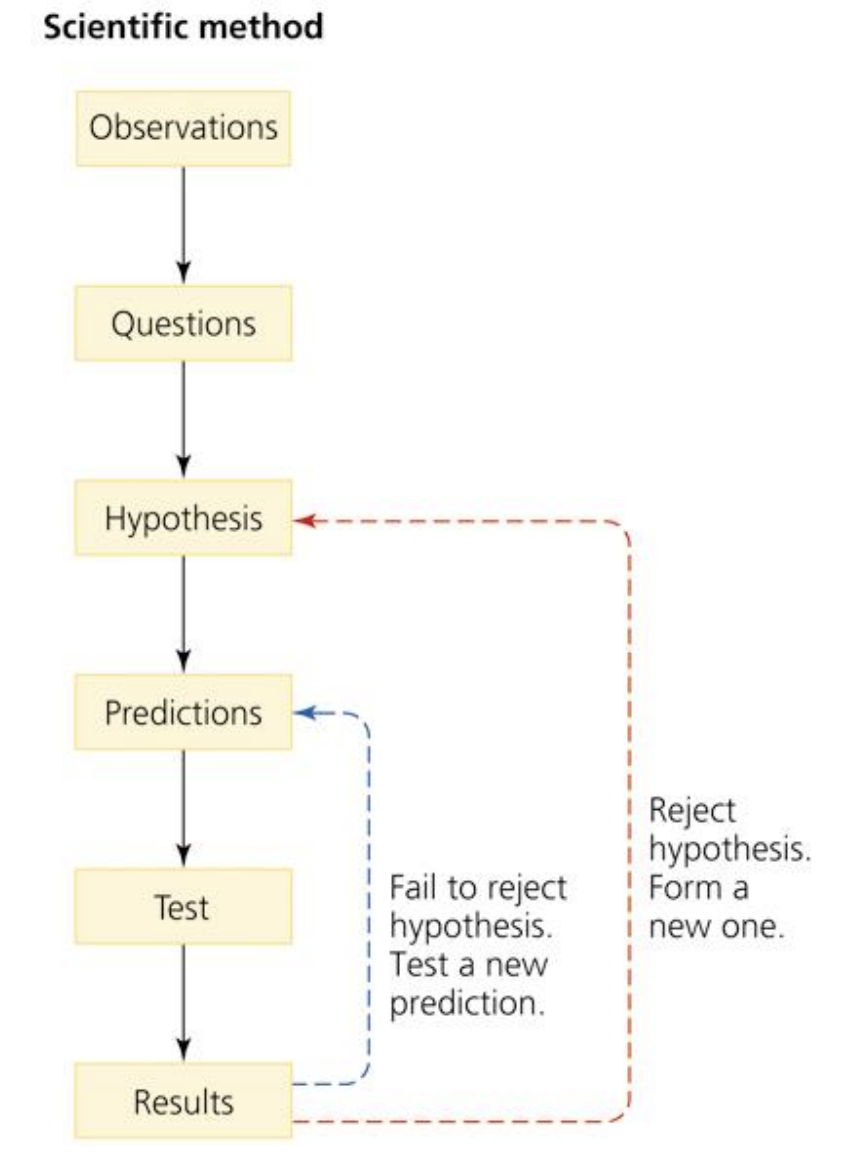
predictions
can be directly and unequivocally tested by an
independent variable
the condition that changes and is to be tested
dependent variable
the resulting condition that depends on the independent variable
controlled experiment
only the independent variable is changed
The treatment part of the experiment receives the change.
The control does not receive the change and serves as a point of comparison.
Quantitative data
expressed in numbers
manipulative experiments
The researcher actively chooses and manipulates the independent variable.
– These are not always possible, such as in the case of global climate change
Natural experiments
compare how different variables are expressed in naturally occurring, but different, contexts.
– The independent variable varies naturally, and scientists search for correlation, or statistical association, between variables.
Line graphs
show trends in a variable over time.
Bar graphs
compare single measurements between groups, such as average algae surface coverage
Scatter plots
reveal any correlations between two variables
pie charts
show percentage breakdowns of a measurement, such as algae species
theory
a widely accepted, well-tested explanation of one or more cause-and-effect relationships that have been extensively validated by a great amount of testing
paradigm
or dominant view, is replaced by another
Ethics
a branch of philosophy that studies how people decide what is good and bad, right and wrong
Ethical standards
criteria that help make this distinction.
– Categorical imperative advises us to treat others as we would prefer to be treated ourselves.
– Principal of utility holds that something is right when it produces the greatest practical benefit for the most people.
Relativists
believe that ethics vary with social context
environmental ethics
The application of ethical standards to the relationships between humans and nonhuman entities
Anthropocentrism
a human-centered view that evaluates costs and benefits of actions solely on their impact on people
Biocentrism
ascribes inherent value to both human and nonhuman life
Ecocentrism
judges actions based on their effects on ecological systems, which contain both living and nonliving elements and relationships between them
John Muir
promoted a preservation ethic, believing that the environment should be protected in a pristine, unaltered state. (Sierra Club)
– He worked with Teddy Roosevelt to increase protected areas, such as in the Sierra Nevada mountains
Gifford Pinchot
promoted the conservation ethic, that people should put natural resources to use, but have a responsibility to use them wisely
Environmental justice
nvolves the fair and equitable treatment of all people with respect to environmental policy and practice, regardless of their income, race, or ethnicity
Fossil fuels have allowed us to:
power the machinery of the industrial revolution
increase crop yields
run vehicles and transportation networks
and distribute consumer goods.
solutions to environmental problems that have arisen because of our consumption
– Renewable energy sources are replacing fossil fuels.
– Soil conservation, high-efficiency irrigation, and organic agriculture are making food production more sustainable.
– Our technology is becoming more energy efficient.
– Laws and technologies have reduced air and water pollution.
– Identifying endangered habitats and species (protection).
– Better waste management to conserve resources.