Chapter 8: The Phillips curve
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
If we drop the P=P^e assumption, what is the relationship between price level, expected price level, and the unemployment rate?
An increase in expected price level leads to, a one for one, increase in actual price level. So if wage setters expect a higher price level, they set a higher nominal wage, which leads in turn to an increase in the price level. The increase in price level from last period to this period is higher inflation.
Given P^e, a decrease in the unemployment rate leads to a higher nominal wage, which leads to a higher price level.
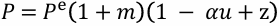
What is the relation between inflation, expected inflation and unemployment rate?
An increase in expected inflation leads to an increase in actual inflation. Given pi^e, an increase in m or z leads to an increase in pi.
Given pi^e, a decrease in u leads to an increase in pi.
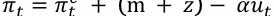
How does the increase in price level lead to an increase in inflation?
Given last period’s price level, a higher expected price level this period implies a higher expected rate of increase in the price level from last period to this period - that is, higher expected inflation. Thus, the fact that an increase in the expected price level leads to an increase in the actual price level can be restated as: an increase in expected inflation leads to an increase in inflation.
What is the inflation equation which depicts the relationship in the Phillips curve? When inflation expectations are anchored.
Negative relation between unemployment and inflation. inflation varies pi dash=pi^e. Considering Inflation this year is not a good predictor of inflation next year.
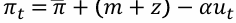
What is anchored inflation?
When people’s long term expectations of inflation remain relatively stable
What is the Phillips curve relation when expectations are de-anchored and inflation does not settle around pi dash.
This means that inflation this year is a good predictor of inflation next year. Suppose expected inflation this year depends on a constant value 𝜋 dash with weight 1−θ, and partly on inflation last year with weight θ:
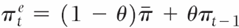
How does expected inflation vary with theta?
When θ equals zero, we get the original Phillips curve, a relation between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate
When θ is positive, the inflation rate depends not only on the unemployment rate, but also on last year’s inflation rate
When θ equals 1, the the unemployment rate affects not only inflation, but rather the change in inflation rate. High unemployment leads to decreasing inflation, low unemployment leads to increasing inflation.
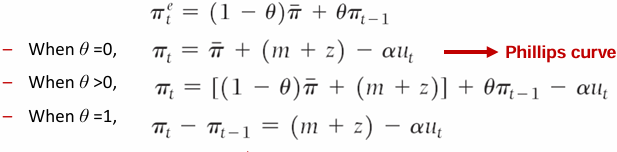
So what does the relationship between unemployment and inflation depend on?
On how people form expectations of inflation (based in turn on behaviour of inflation)
What are some critiques of the Phillips curve?
Critics said that a trade-off between unemployment and inflation could only exist if wage-setters systematically underpredicted inflation - unlikely for them to make the same mistake forever
If the govt attempted to sustain lower unemployment by accepting higher inflation, the trade-off would ultimately disappear. The unemployment rate could not be sustained below a certain level that they called the un.
Equation for natural rate of unemployment
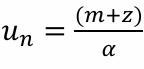
What is the relation between the inflation rate, the expected inflation rate, and the deviation of the unemployment rate from the natural rate of unemployment
If unemployment is at the natural rate, then inflation will be equal to expected inflation. If unemployment is bellow the natural rate, inflation will be higher than expected. If unemployment is above the natural rate, inflation will be lower than expected.
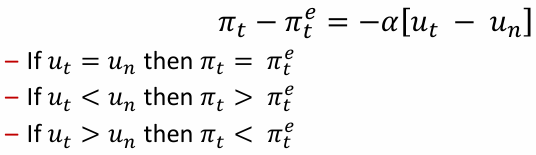
What is wage indexation
A provision that automatically increases wages in line with inflation