Cloning & Biotech
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Name some immobilised enzymes in industry
• Glucose isomerase
• Penicillin acylase
• Lactase
• Aminoacylase
• Glucoamylase
Suggest why using immobilised enzymes rather than free enzymes may be cheaper in industrial processes.
- Bioreactors can be run continuously for long periods, so less emptying and cleaning is needed
- The product will not be contaminated with enzyme, therefore the extraction of the enzyme from the product will not be needed
- The immobilised enzyme can be reused
- The process can run over a wider temperature range
What is glucose isomerase used for?
The conversion of glucose to fructose
What is penicillin acylase used for?
The formation of semisynthetic penicillins (to which some penicillin resistant organisms are not resistant)
What is lactase used for?
The hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose
What is Aminoacylase used for?
The production of pure samples of L-amino acids
What is glucoamylase used for?
The conversion of dextrins to glucose.
Glucose Isomerase
- Produces fructose from glucose
- Fructose is sweeter than sucrose & glucose, therefore used as a sweetener in food industries
- Glucose is produced from cheap, starch rich plant material, and glucose isomerase is then used to turn cheap glucose into marketable fructose

Penicillin acylase
- It makes semi synthetic penicillins from naturally produced penicillins
- Many bacteria are resistant to naturally occurring penicillins, but are still vulnerable to semi synthetic penicillins
- Therefore this immobilised enzyme is important in treating infections caused by bacteria resistant to naturally occurring penicillins

Lactase
- Immobilised lactase hydrolyses lactose to glucose and galactose, giving lactose free milk
- Many people are lactose intolerant

Aminoacylase
- Produces pure samples of L-amino acids
- L-amino acids are used in the production of pharmaceuticals, organic chemicals, cosmetics, and food

Glucoamylase
- Amylase enzymes break starch down into short chain polymers called dextrins
- The final breakdown of dextrins to glucose is catalysed by immobilised glucoamylase
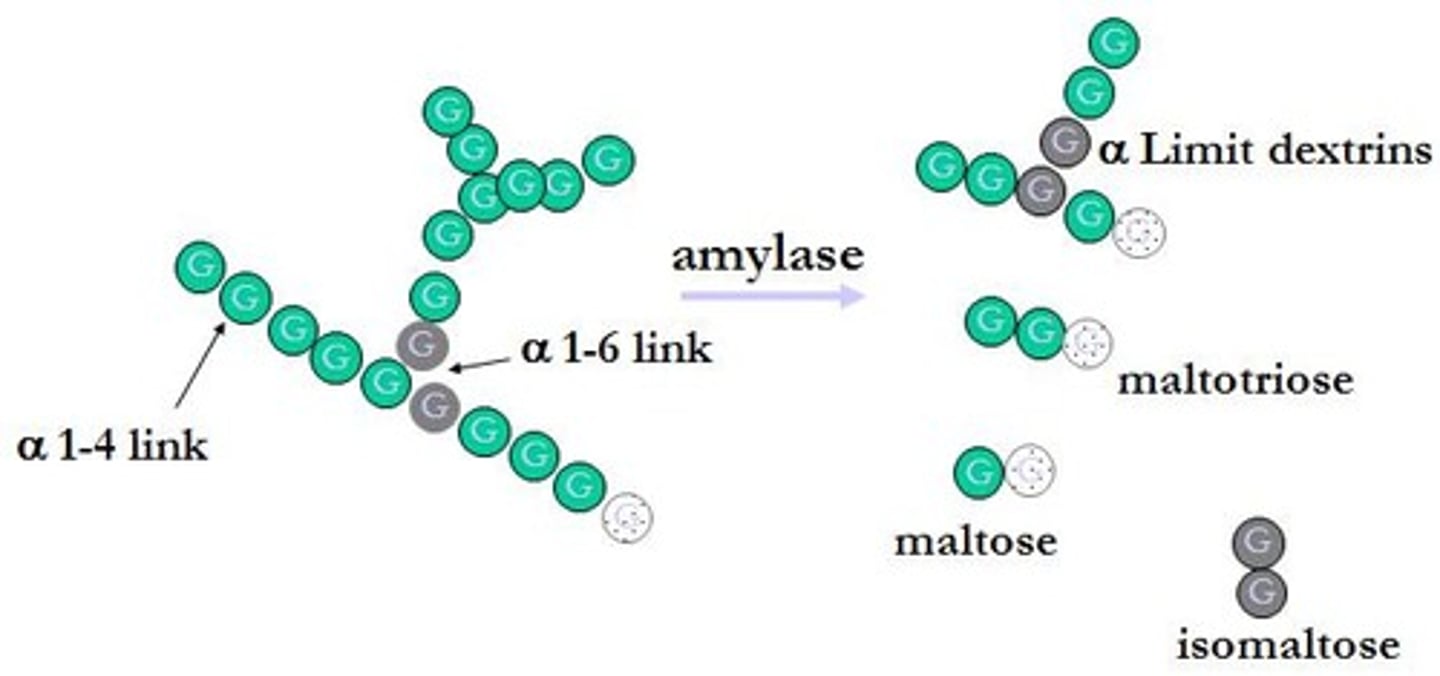
What are immobilised enzymes?
The enzymes are attached to an insoluble material to prevent mixing with the product
4 Methods of Immobilisation
Encapsulation
Entrapment
Cross-linked
Carrier-bound
Encapsulation
Enzyme is trapped in a semi-permeable membrane

Entrapment
Enzyme is trapped in silica gel matrix
Cross-linked
Covalent or ionic bonds between the amino acids of the enzymes, sometimes using glutaldehyde
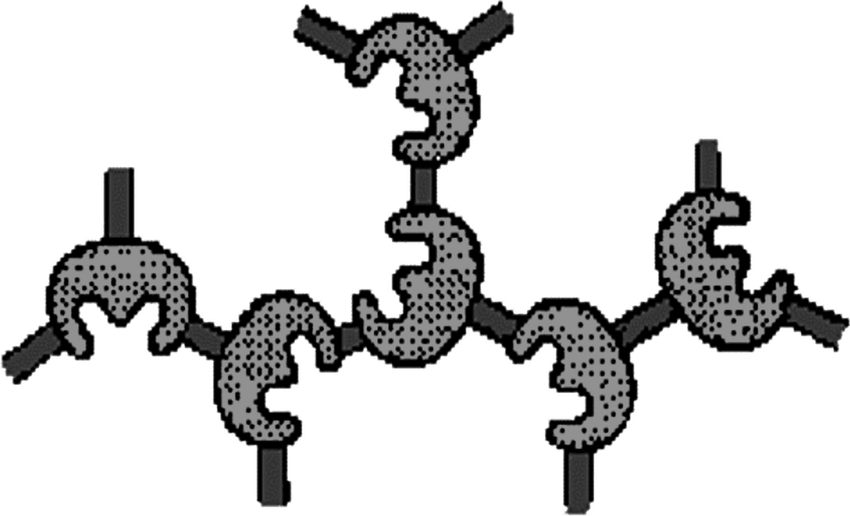
Carrier-bound
The enzyme is attached to a carrier, such as activated carbon or clay

What are the advantages of immobilised enzymes?
Enzyme can be removed to be used again
There is less downstream processing / leads to a purer product
More stable than free enzymes.
What does less downstream processing mean?
After the reaction is complete, there is less work needed to purify the final product.
There will be less downstream processing because in a typical reaction with free enzymes, the enzymes would have to be removed, but if the enzymes are immobilised, then they wouldn’t be mixed in the solution.
The enzyme doesn’t need to be extracted from it
Why is being more stable than free enzymes good?
They are less likely to be denatured by pH changes or high temperatures
What are the disadvantages of immobilised enzymes?
The process of immobilising an enzyme can reduce its activity as it cannot mix freely with its substrate
Higher initial cost of equipment (bioreactor) to set up the reaction
Higher cost of using immobilised enzymes vs free enzymes
More complex procedure and therefore higher possibility of technical issues
Why do we use a fermenter / bioreactor?
To culture microorganisms on an industry scale
What are fermenters/bioreactors?
Sealed, sterile, aseptic units.
Why are they sealed, sterile, aseptic units?
It means that the product is not contaminated and the microorganisms are not in competition with other microorganisms
Limiting factors in growing bacterial colonies:
- Temperature
- Nutrients available
- Oxygen levels
- Change in pH
- Build up of waste
Temperature
Need to maintain the optimum temperature for enzyme controlled reactions such as aerobic respiration
Nutrients Available
Provided through the nutrient medium (usually a liquid broth). The nutrient level will become insufficient to support further growth and reproduction unless more nutrients are added.
Oxygen levels
Needed for aerobic respiration
Change in pH
This will fall as CO₂ is produced.
This impacts enzymes involved in metabolic processes, such as respiration, and therefore a pH buffer is used
Build up of Waste
As bacterial numbers rise, anaerobic respiration may occur, which can lead to the build up of ethanol/lactic acid which can kill the microorganisms
Fermenters
Microorganisms are cultured in fermenters. These cultures can be grown on an industrial scale in a bioreactor.
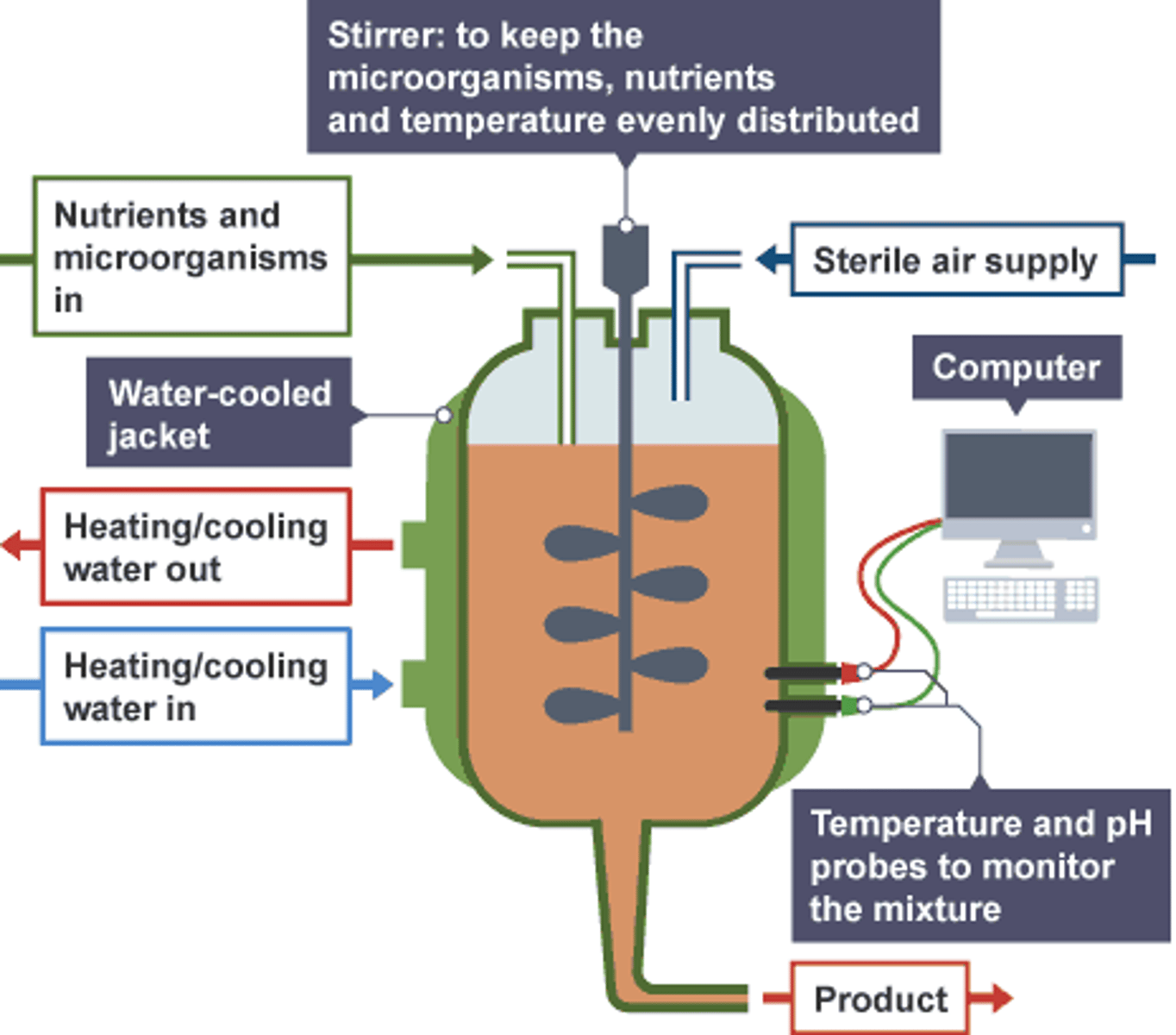
Aseptic Fermenter Parts:
- Motor
- Paddle
- pH control reservoir
- Gas exhaust outlet
- Filtered air inlet
- Cool water inlet
- Nutrient inlet
Motor
Turns the paddle to mix contents
Paddle
Mixes the contents and creates smaller air bubbles
pH control reservoir
pH buffers are added to prevent the condition from becoming too alkaline, reducing yield
Gas exhaust outlet
Prevents pressure building up
Filtered air inlet
Oxygen for respiraiton
Cool water inlet
Penicillium produces heat during growth, temperature can be monitored and cooling water runs through the water jacket
Nutrient inlet
The medium containing nutrients for the growth of penicillium is added here
Why is asepsis important?
- Avoids any unwanted microbes that would compete for nutrients
- Decrease the yield of product
- Contamination of the product
- Change the conditions in the fermenter
What is batch fermentation?
Microorganisms starter population is mixed with a specific quantity of nutrient solution, then allowed to grow for a fixed period of time
The products are then removed and the tank emptied

What is batch fermentation also known as?
A closed culture
When is batch fermentation stopped?
The process is stopped before the death/decline phase and the products harvested (secondary metabolites production higher in stationary phase)
What is continuous fermentation?
Microorganisms are inoculated into a sterile medium, and is added continually to the culture once it has reached its exponential point of growth
What happens to the waste products, desired products, and microorganisms in continuous fermentation?
They are continually removed, keeping the culture volume in the reactor the same
Advantages of Batch Culture
- Easy to set up and maintain
- If contamination occurs, only one batch is lost
- Very useful for process involving the production of secondary metabolite
Disadvantages of Batch Culture
- Growth rate is slower because nutrient level declines with time
- Less efficient, fermenter is not in operation all of the time
Advantages of Continuous Culture
- Growth rate is higher as nutrients are continuously added to the tank
- More efficient, fermenter operates continuously
- Very useful for the processes involving the production of primary metabolites
Disadvantages of Continuous Culture
Set up is more difficult, maintenance of required growing conditions can be difficult to achieve
If contamination occurs, huge volumes of products may be lost
Pour plate
Used to identify the number of colony forming units in a solution - may involve a serial dilution
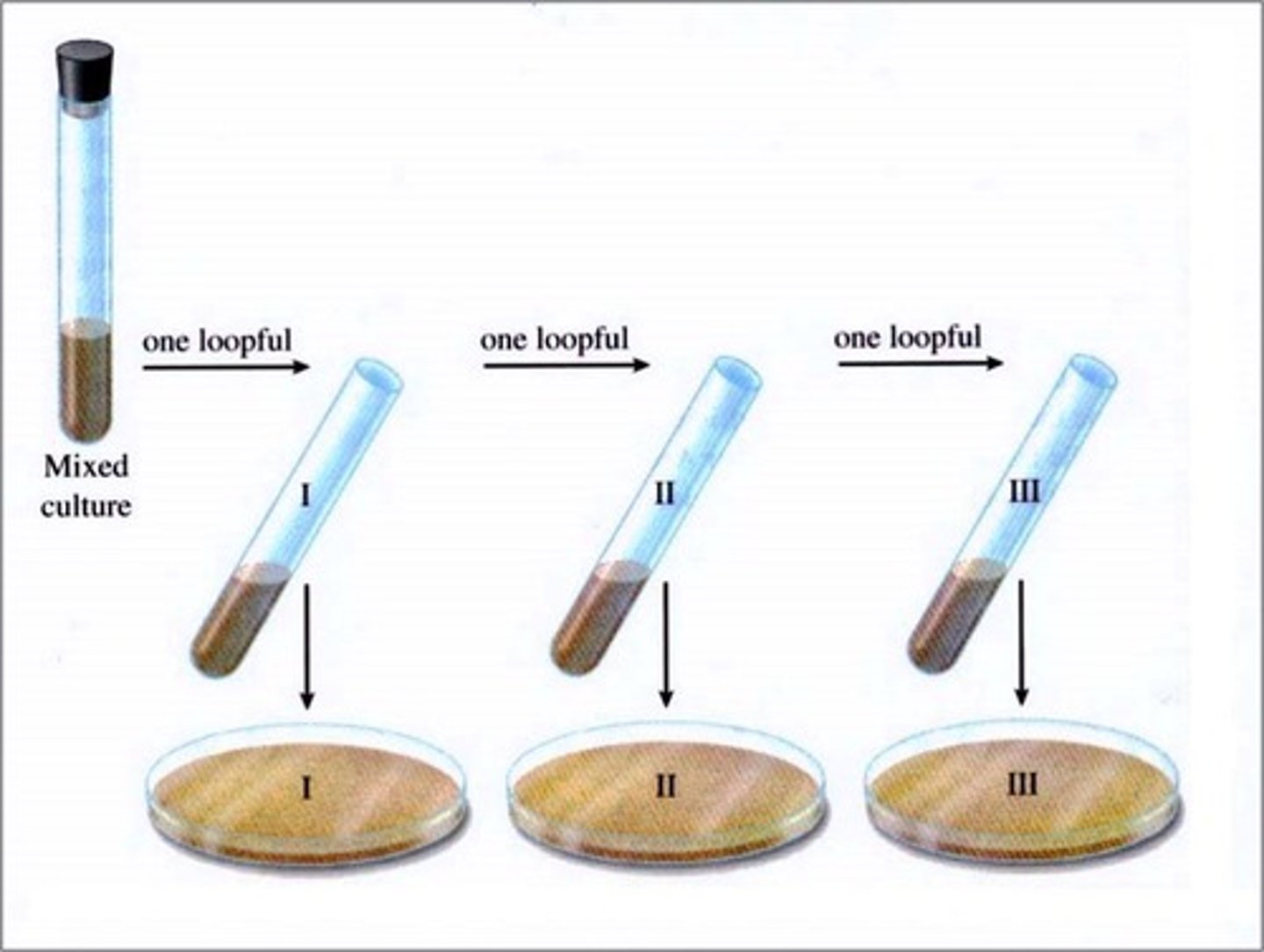
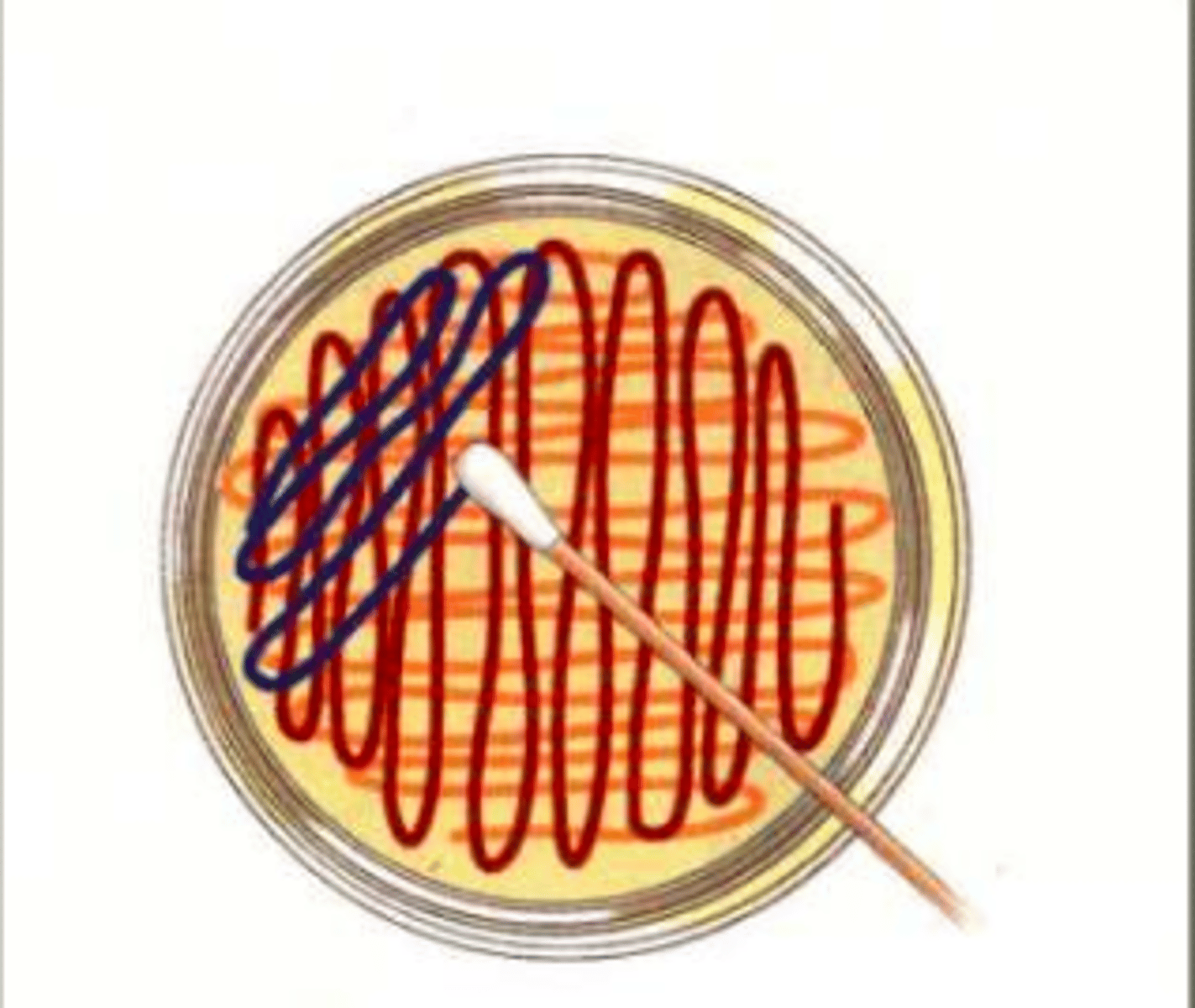
Lawn plate
Use a spreader to spread out the bacterial colonies
These can be used to identify colonies that have been genetically engineered
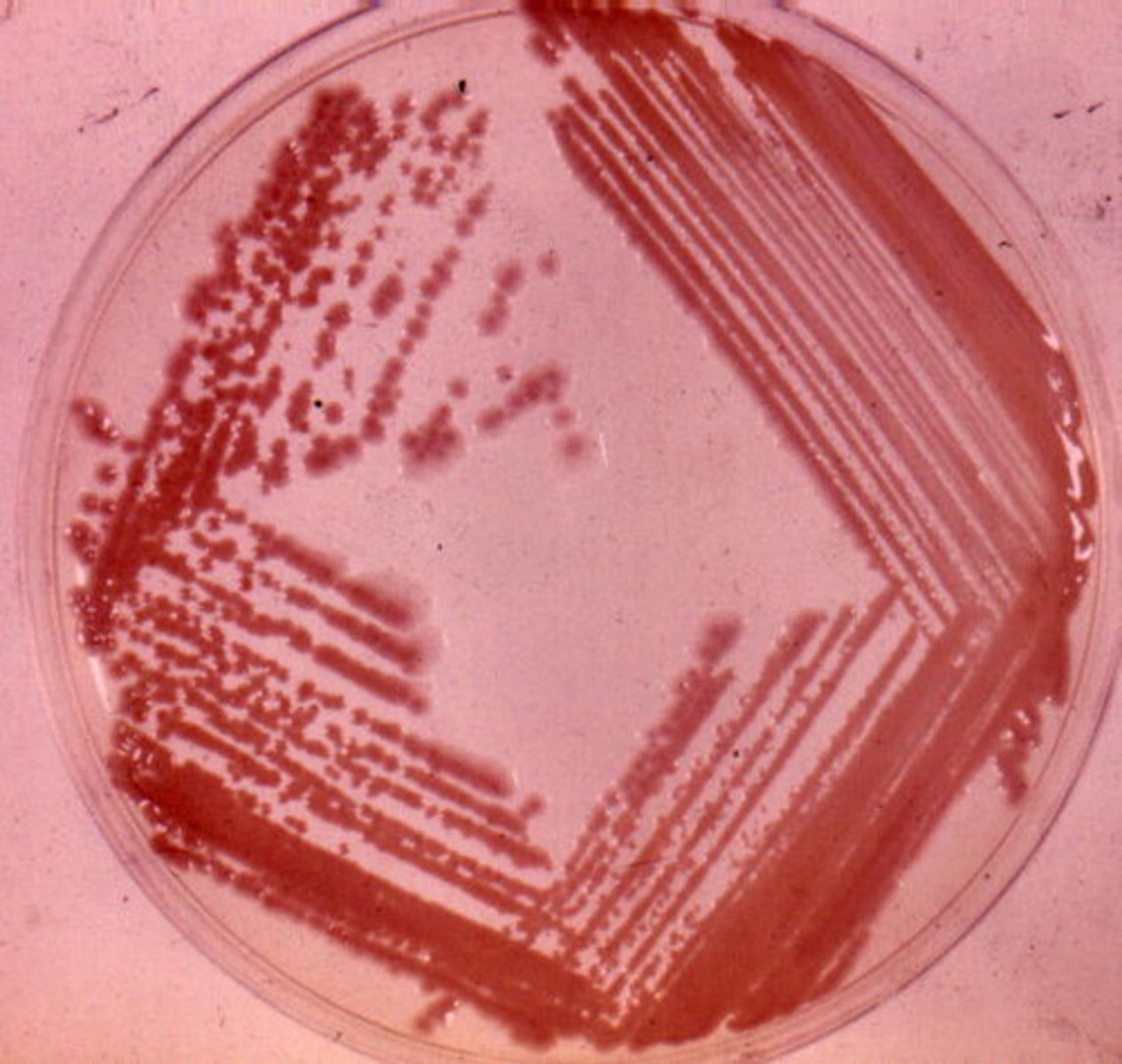
Streak plate
Used to separate colonies of bacteria
Why do we use aseptic conditions?
To avoid any unwanted microbes that would:
compete for nutrients
change the conditions in a fermenter
decrease the yield of product
contaminate the batch
Plates should not be incubated at 35 degrees
Could lead to the growth of human pathogens
Flaming the neck of tube
Causes air to expand and push bacteria away, so less likely to settle in the tube.
Also kills bacteria on the neck of the tube
The lid should be held above the dish when adding solutions
Avoids contamination with bacteria from the air
When incubating the plate, they should be kept upside down
Prevents condensation droplets from forming on the lid and dripping onto the agar surface, which can contaminate the culture and interfere with colony growth
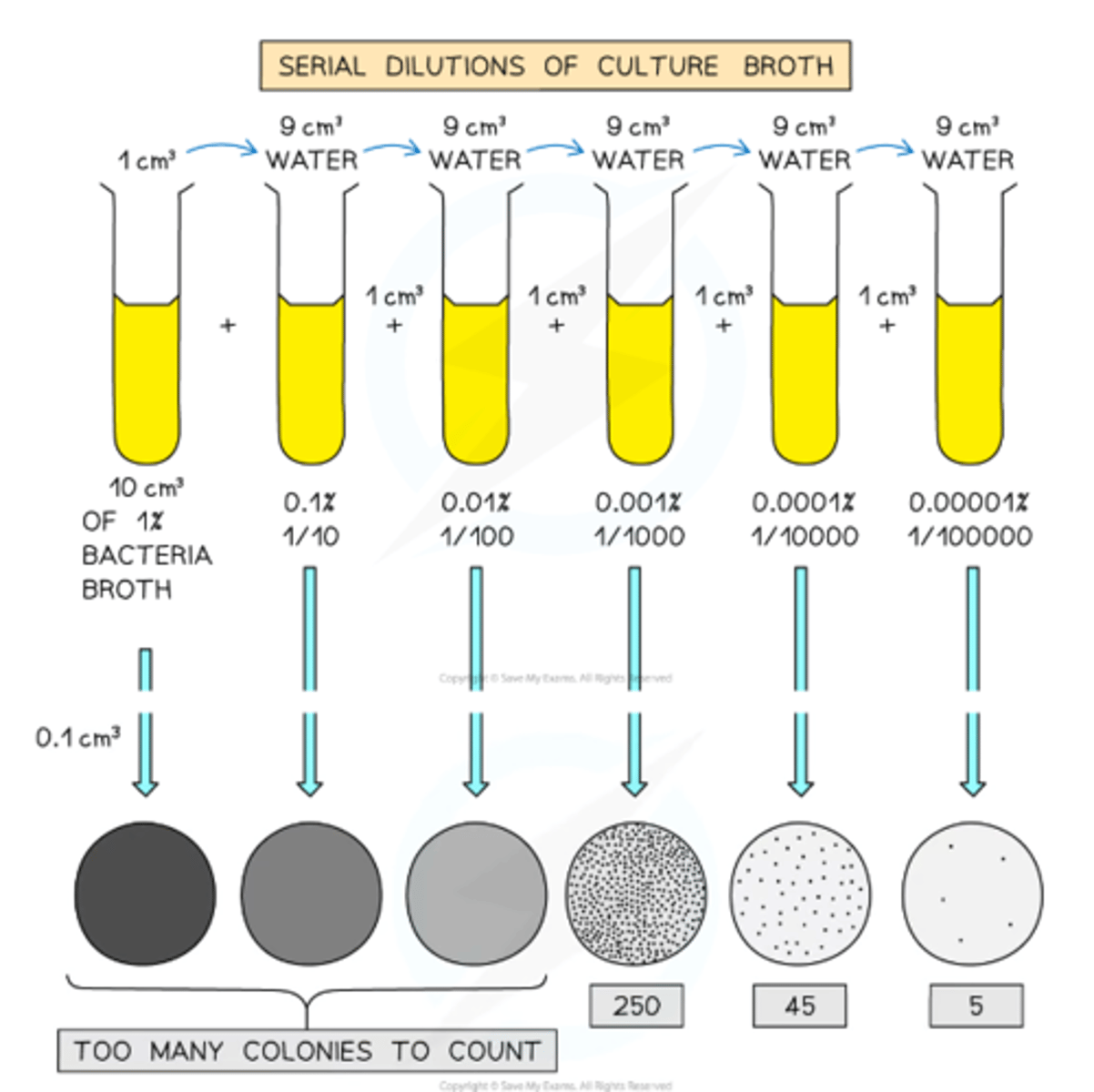
What is the problem with the cultured bacteria?
With cultured bacteria, there may be too numerous to count as there are so many colonies, or the colonies overlap, forming a lawn.
What is the solution to this?
Use a serial dilution method to dilute the bacteria in the broth before plating them onto the agar
Apparatus
Sterile agar plates -The agar can be made sterile by boiling
Diluted bacterial broth with a concentration of 1 x 108 CFU mm-3
Pipettes
Spreaders
Bunsen burner
Gloves
Goggles
Incubator
Fridge
Factors Affecting the Growth of Microorganisms Process
Spread a sample of the diluted bacterial broth onto the surface of each of the sterile agar plate
Tape the lid shut
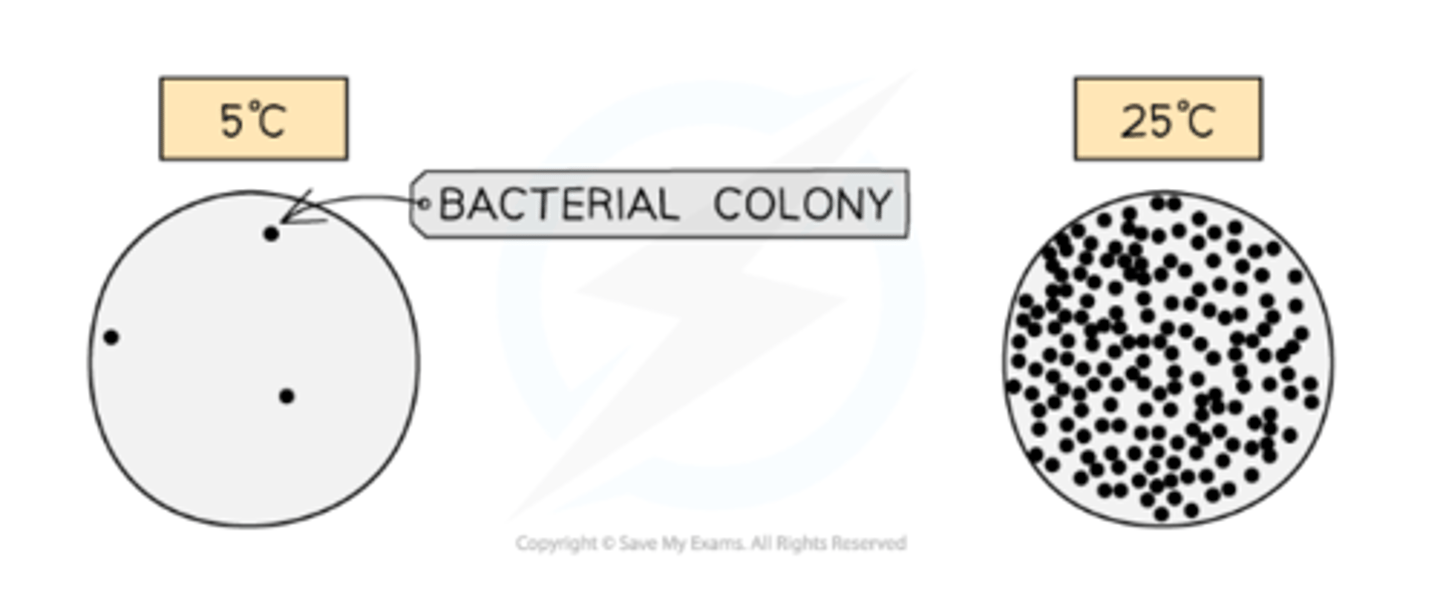
Keep three of the agar plates in the fridge overnight 5°C
Keep three of the agar plates in the incubator overnight at 25°C
Remove the agar plates the next morning and count the number of colonies, keeping the lid on as you count
Calculate the average number of colonies that have formed and compare the results at each temperature
Results
Overnight, the bacterial colonies will grow large enough that they can be easily counted
The bacteria that were cultured at 25°C are expected to have developed at a much faster rate with many more colonies visible
The bacteria cultured at 5°C are expected to have formed fewer colonies which are much smaller in size, or even no colonies at all
What explains the difference in speed bacteria was developed in the different temperatures?
This difference is due to the fact that 25°C provides a temperature close to the optimum for enzyme activity in the bacteria. As a result, the rate of growth is much faster than those cultured at 5°C as enzymes' cellular reactions will be very slow
Variations on this investigation
- We can investigate the effect of pH and nutrient availability using a very similar method to the one detailed above
- pH can be altered using different buffer solutions with different pH levels to the broth
- Nutrient availability can be altered by using different agar plates with different nutrient contents
How else can you measure growth instead of counting the colonies?
Use turbidity as a measure
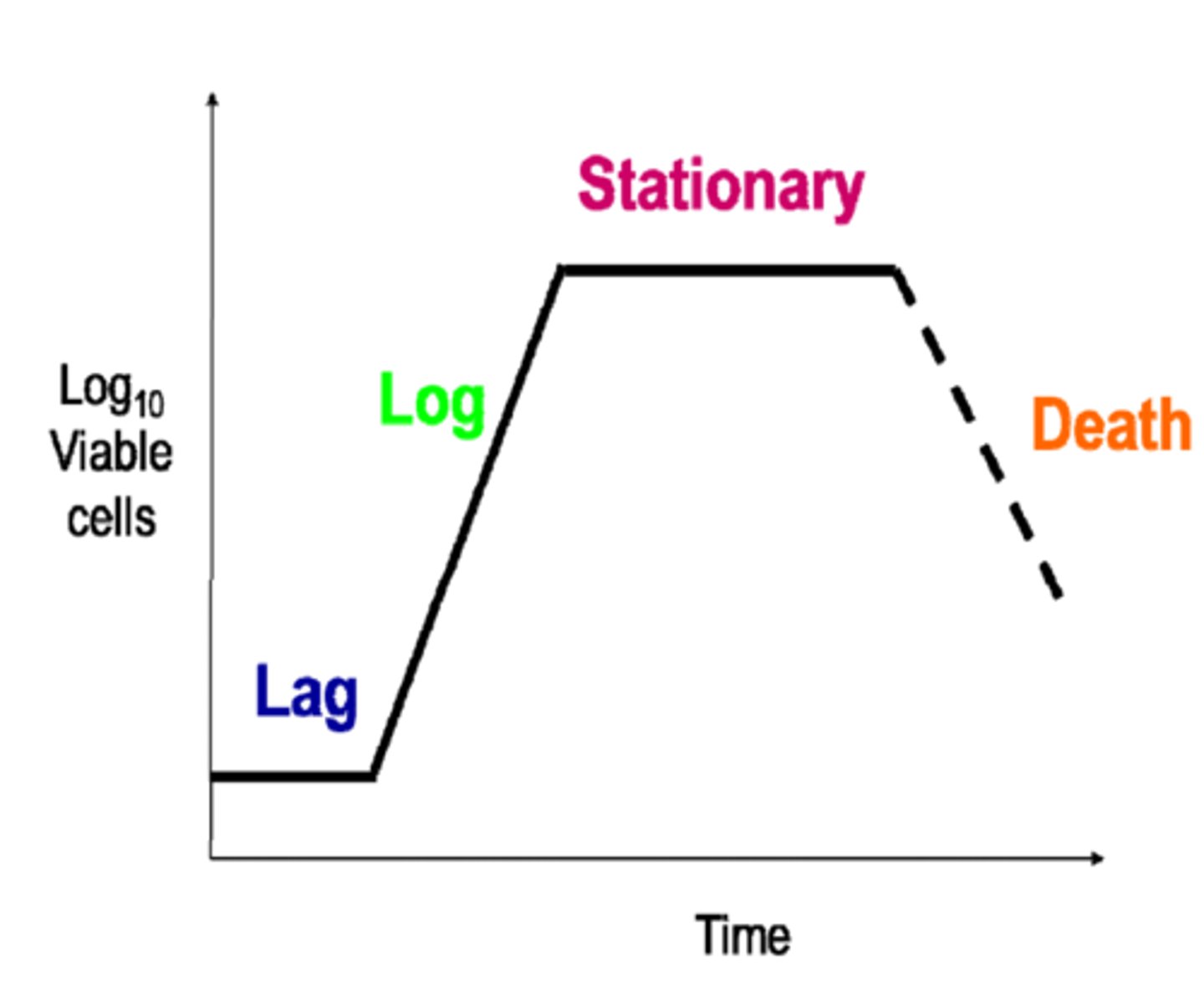
Standard Population Growth Curve
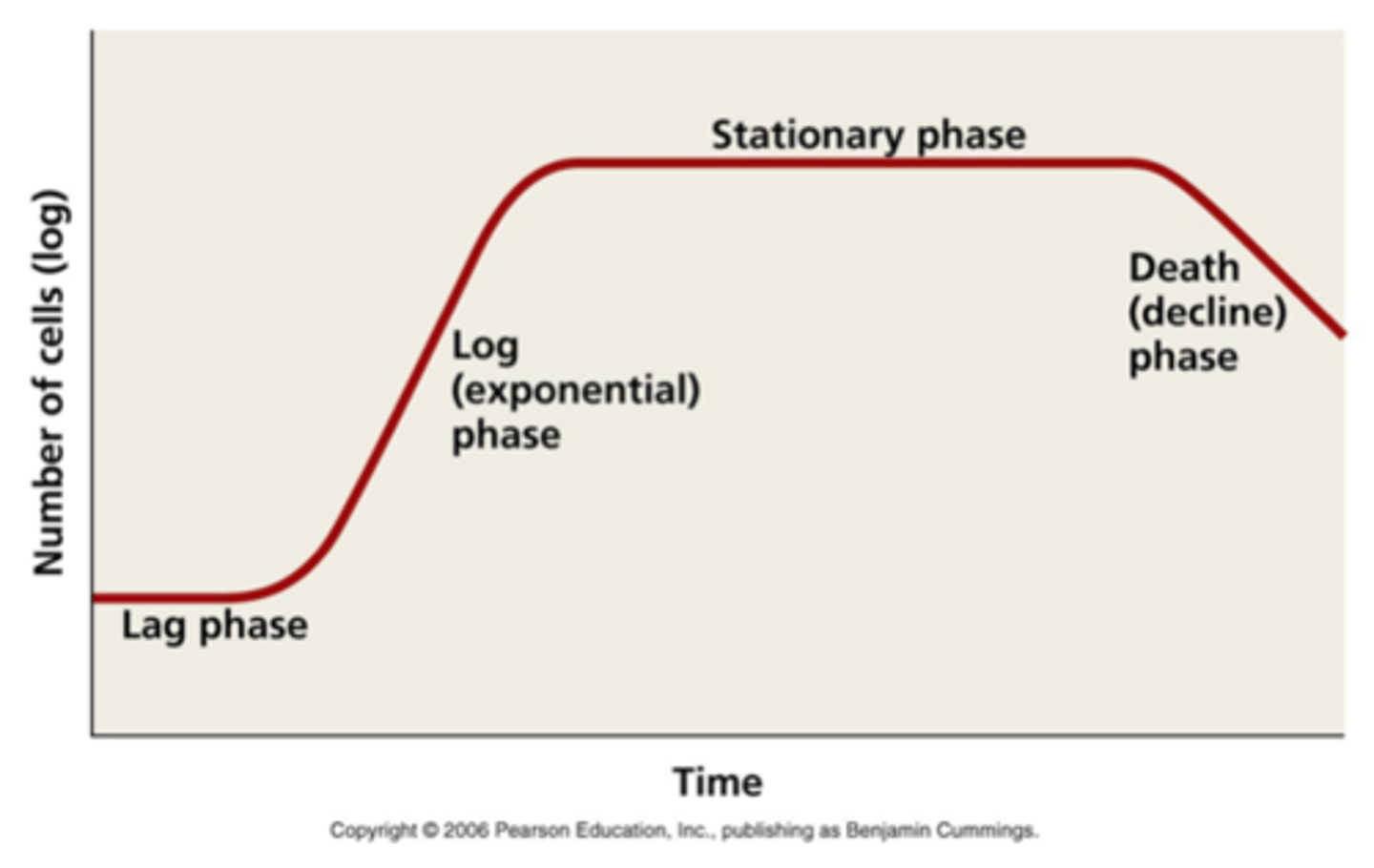
Lag phase
The population size increases slowly as the microorganism population adjusts to its new environment and gradually starts to reproduce
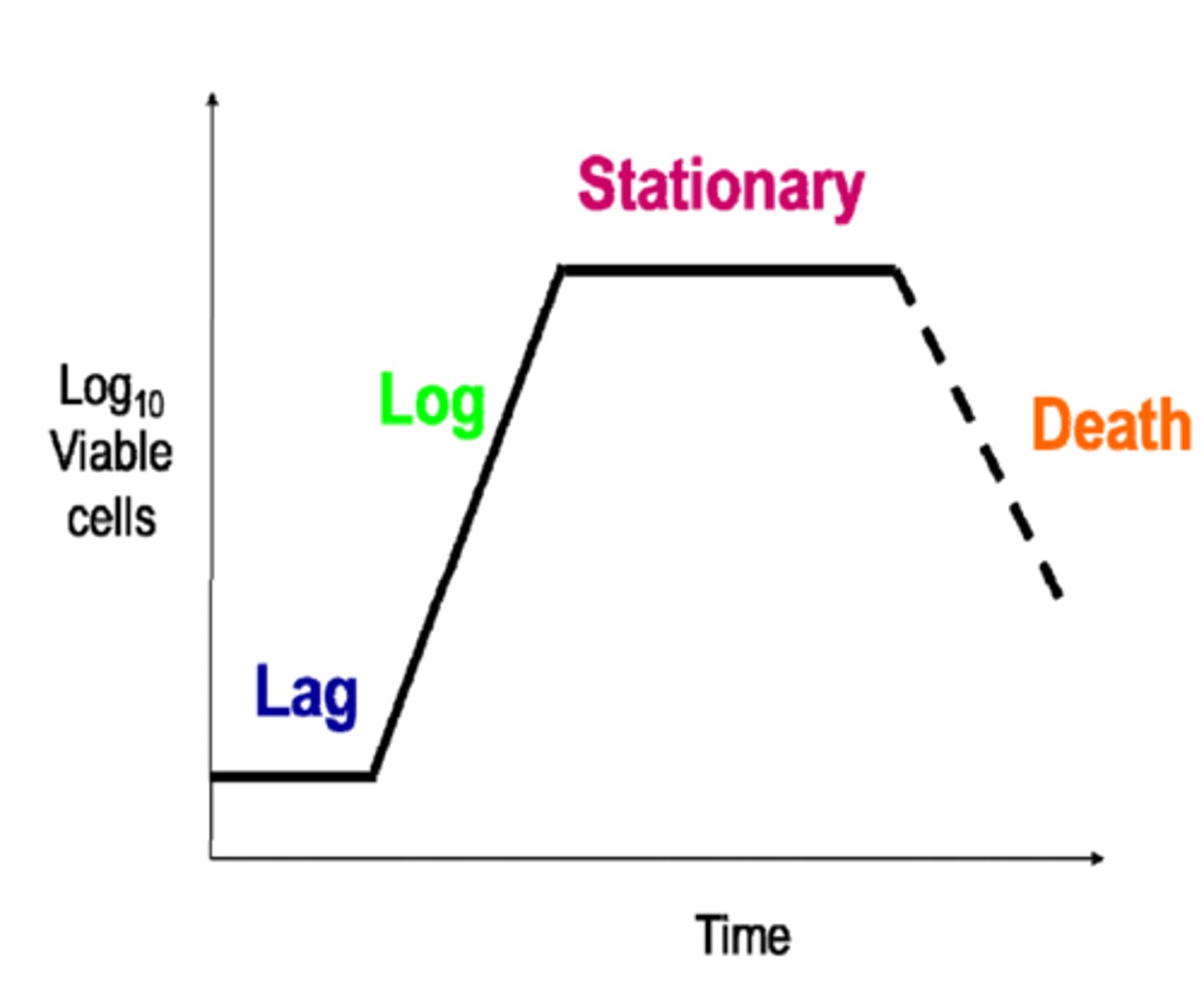
Log phase
With high availability of nutrients and plenty of space, the population moves into exponential growth (the population doubles with each division)
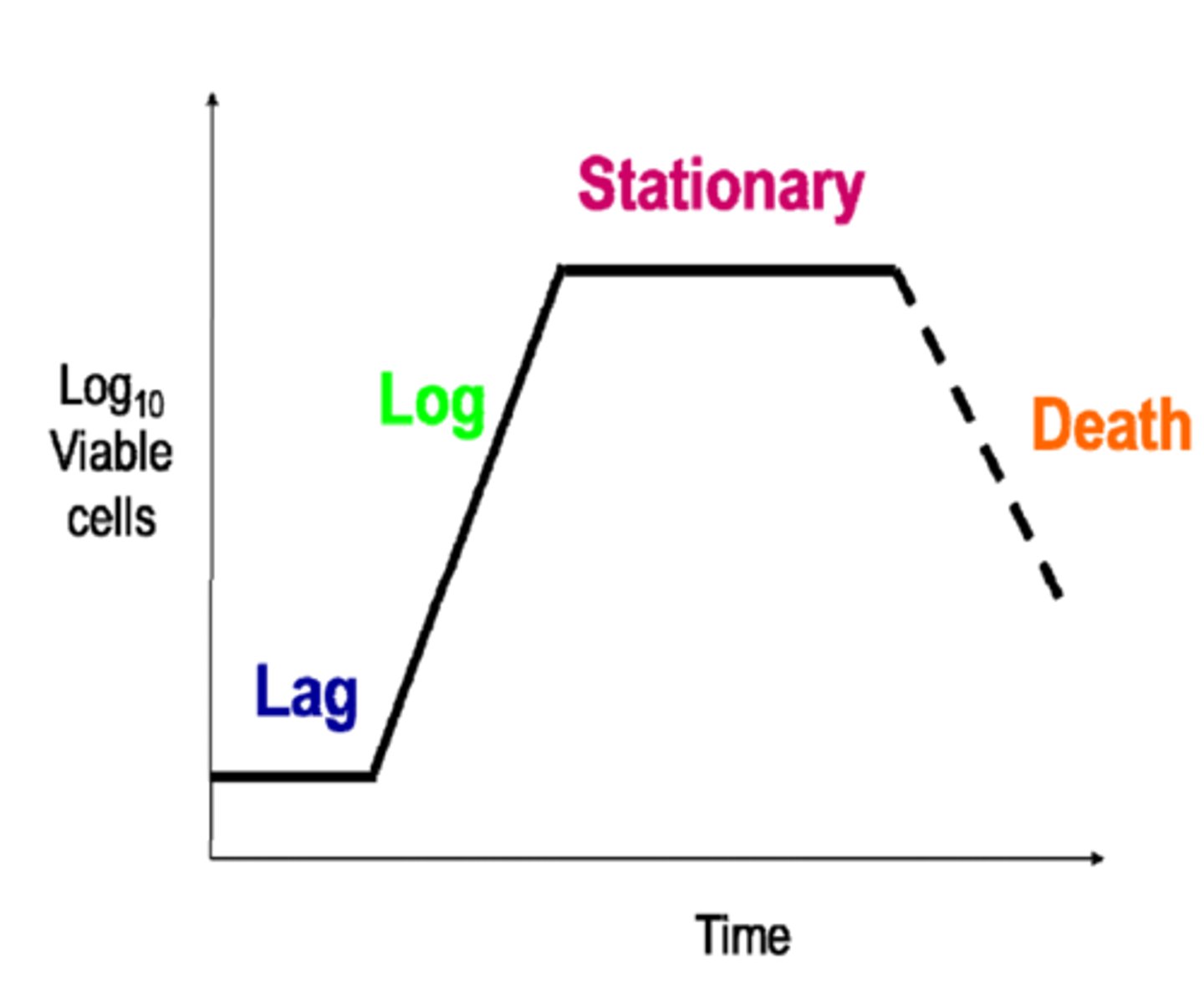
Stationary phase
Occurs when the population reaches its maximum as it is limited by resources e.g. nutrients, toxic substances.
The number of microorganisms dying = the number being reproduced by binary fission
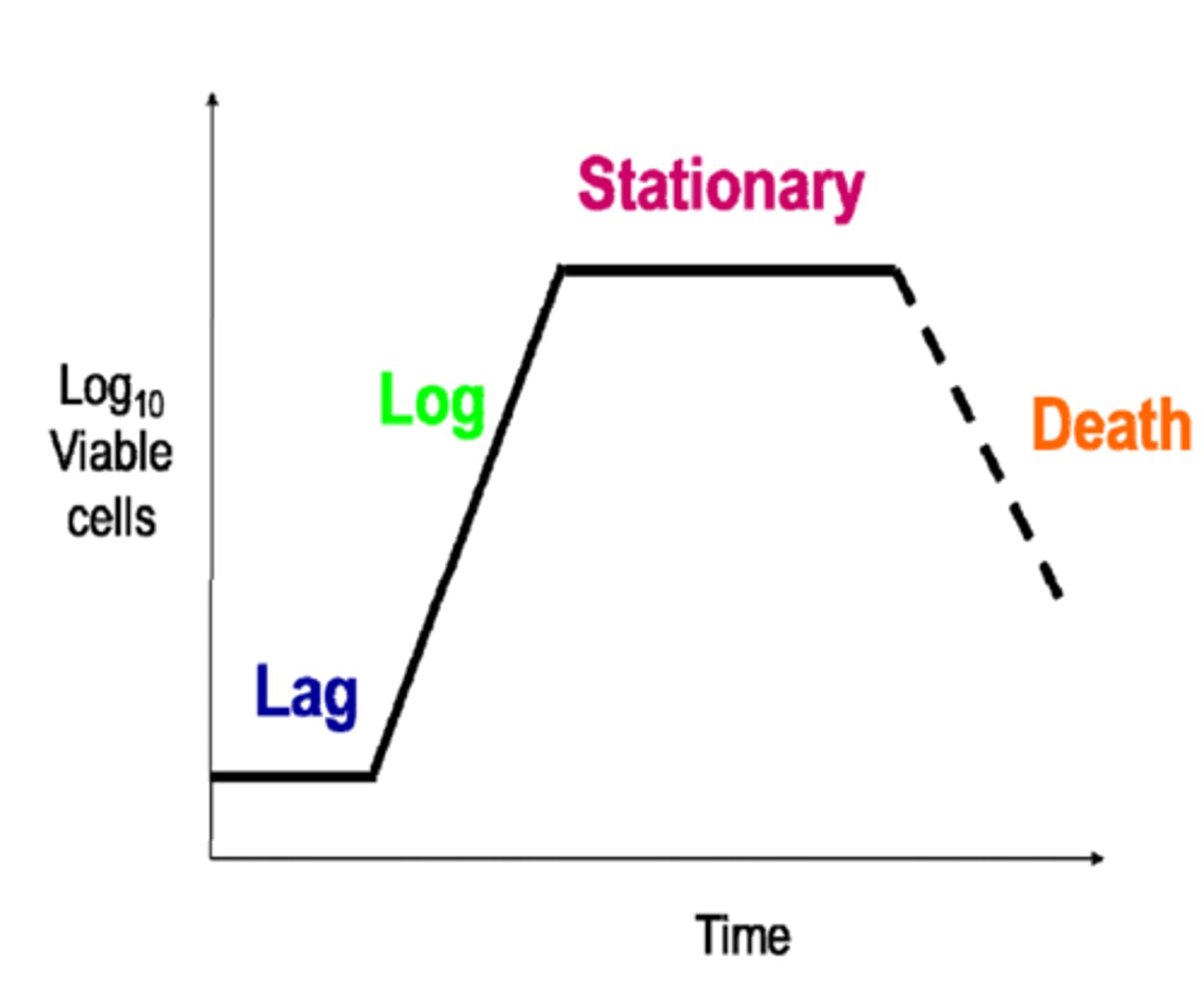
Decline phase
Occurs due to lack of nutrients and death due to toxic substance build up. Death rate exceeds reproduction rate
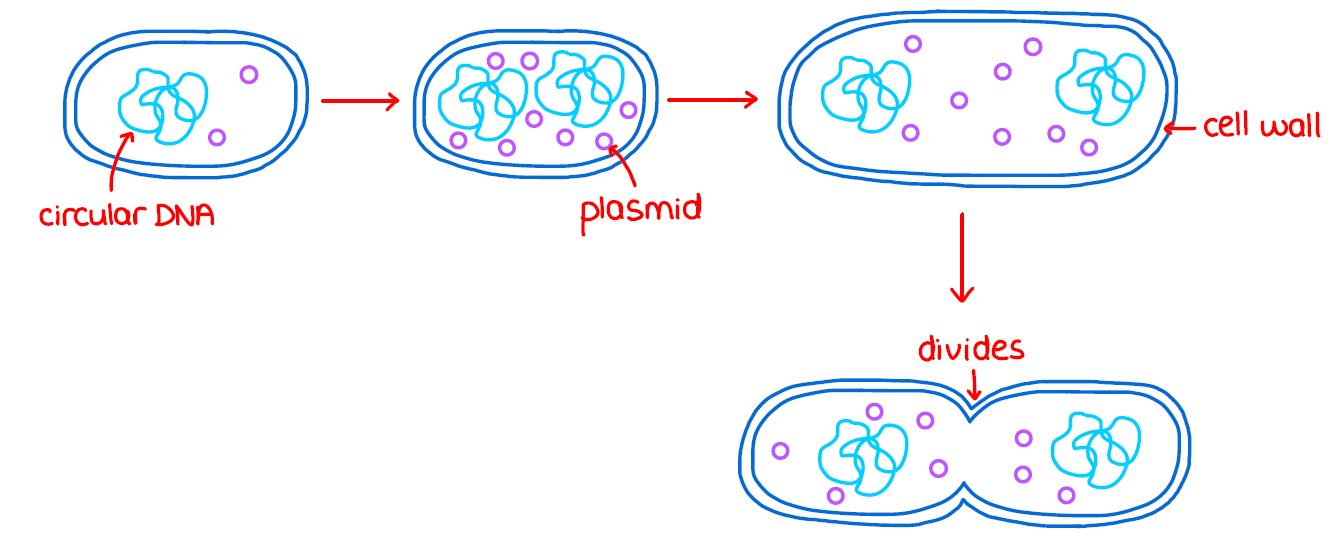
What is the binary fission process?
1) The single circular DNA molecule undergoes DNA replication. Any plasmids present also undergo DNA replication
2) The parent cell divides into 2 genetically identical daughter cells
3) The 2 daughter cells each contain a single copy of the circular DNA molecule and a variable number of plasmids
Formula to calculate the rate of cell division by binary fission:
N = N₀ x 2ⁿ
N = the final number of bacteria
N₀ = the initial number of bacteria
ⁿ = the number of divisions
Why are logarithmic scales useful when investigating microorganisms?
Allows for a wide range of values to be displayed on a single graph
Log Scale Pros
The log scale is easily identifiable as there are not equal intervals between the numbers on the y-axis
The wide range of cell numbers fit easily onto the same scale
What are primary metabolites?
Primary metabolites are molecules needed for the cells normal function, like amino acids, proteins, enzymes
What are secondary metabolites?
Products produced by the microorganisms that are not part of its normal growth (like antibiotics)
Do all microorganisms produce secondary metabolites?
Nah
Primary & Secondary metabolite graph
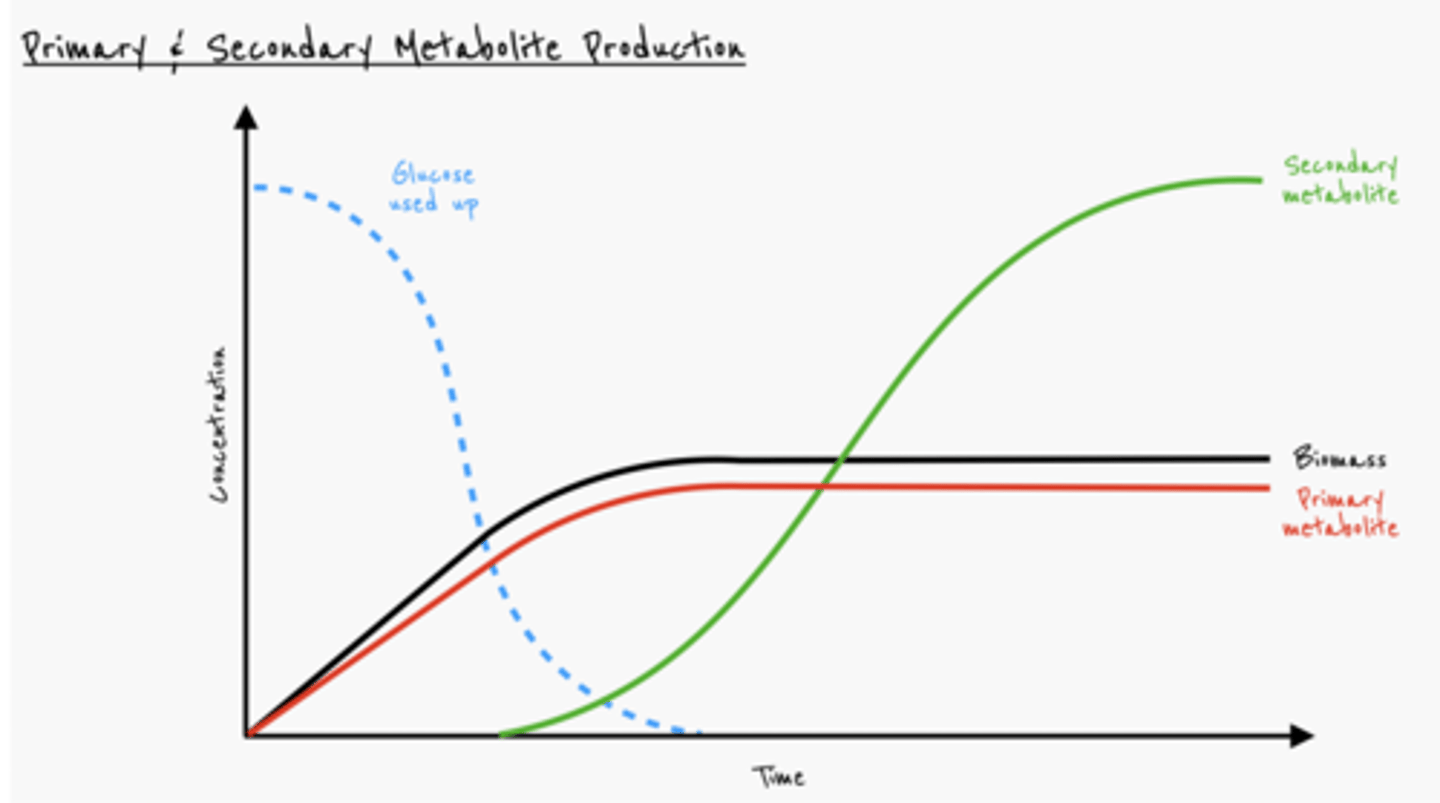
Advantages
Animals are less efficient than microorganisms at converting energy into biomass
Microorganisms reproduce more quickly than plants and animals, so selective breeding is quicker
Microorganisms can be grown on substrates that are waste products of other industries, such as whey
Advantages of Microorganisms making Food
Animals are less efficient than microorganisms at converting energy into biomass
Microorganisms reproduce more quickly than plants and animals, so selective breeding is quicker
Microorganisms can be grown on substrates that are waste products of other industries, such as whey
Quick and easy growth of large numbers
Microorganisms can be grown anywhere at any time, and can be grown on waste products
Single cell protein is healthier as it has lower fat content
They can be made to taste like anything
Microorganisms can be genetically modified and there are no welfare issues to consider when growing them
Disadvantages of Microorganisms making Food
Growth conditions also ideal for contaminating microorganisms, so aseptic conditions are needed
If conditions aren't optimal, then microorganisms may produce toxins
Separation of microorganisms/proteins from nutrient medium and possible contaminants is necessary
Single-cell protein does not have the same flavour and texture as real meat
Some people don't like the idea of eating microorganisms grown on waste
Some people have concerns about eating genetically modified food
If single-cell protein is consumed in large quantities, then health problems caused by high uric acid may occur
What is biotechnology?
The large-scale commercial use of living organisms for human consumption and produces food, drugs, and other products

Name the Major Applications of Biotechnology
- Healthcare & medical processes
- Agriculture
- Industry
- Food science
Why are microorganisms used to carry out biotechnological processes?
- Wide range of waste materials can be used as cheap growth mediums
- Can be genetically engineered
- Can use low temperature & pressures (cheaper)
- Products can be separated easily from the microorganisms
What are some more reasons why microorganisms are used to carry out biotechnological processes?
- Rapid life cycles
- Fast reproduction
- Growth conditions that are easily created all year round
- Nutrient requirements are cheap
- They grow and synthesise proteins rapidly
Suggest the advantage to an organism of naturally producing an antibiotic as a by-product of its metabolism
Resistance / can grow on unwanted nutrients
Explain why microorganisms are particularly useful in treating water
They break down the organic waste into less harmful substances
What is vegetative propagation?
Natural cloning/asexual reproduction in plants
What are the vegetative organs of plants?
- Root and shoot tips
- Axillary buds
- Vascular cambium
Where are axillary buds?
Where leaves and the stem meet
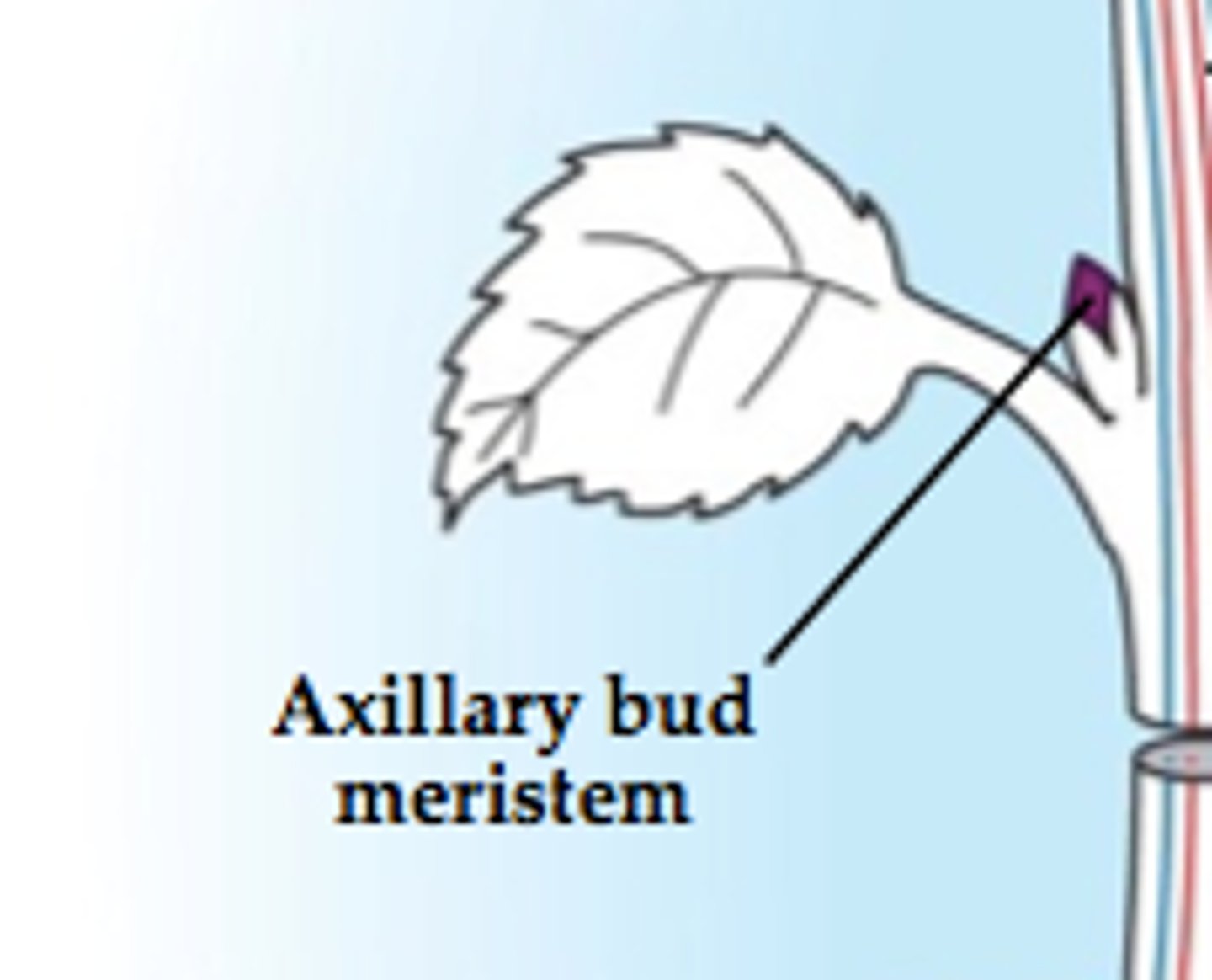
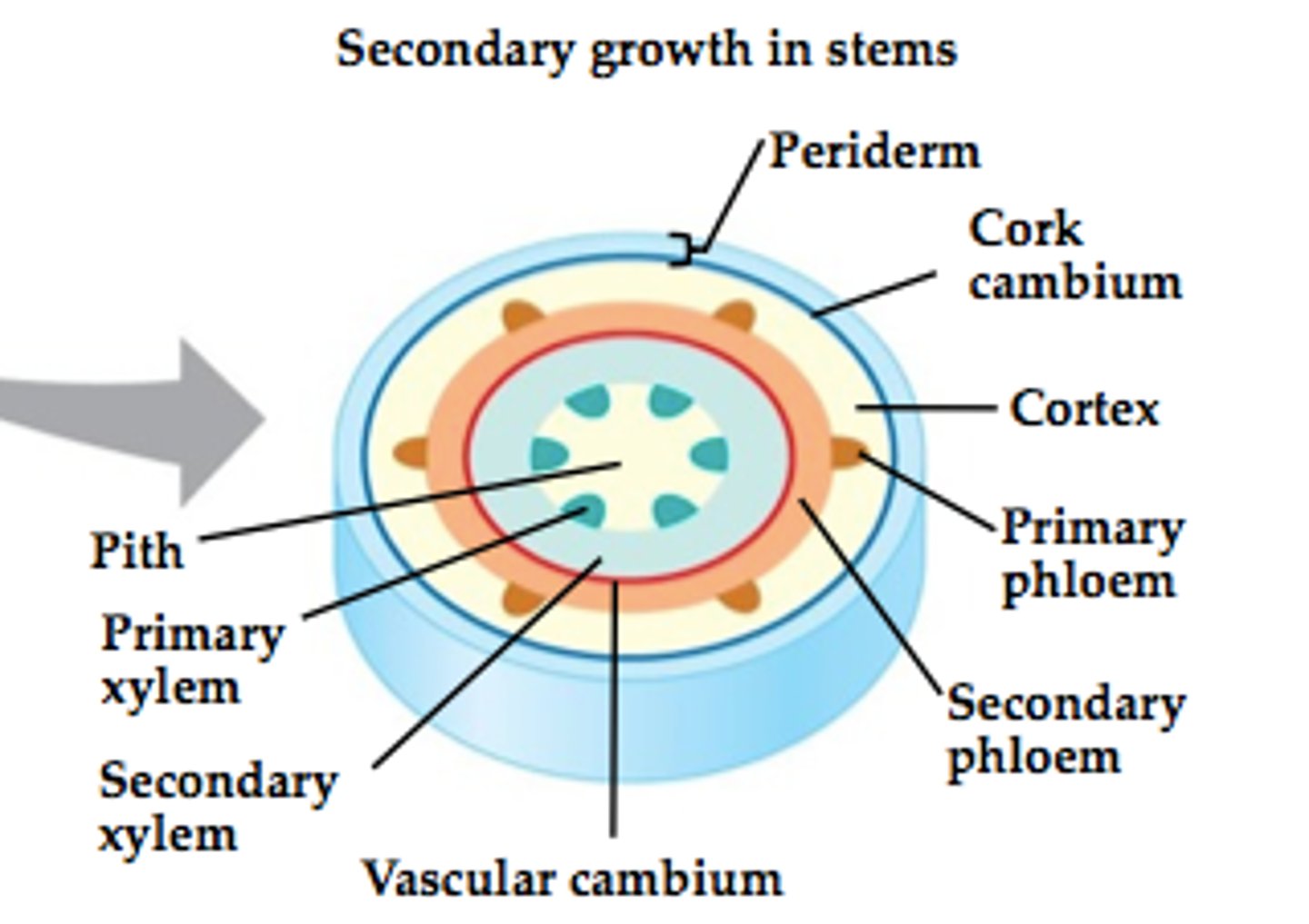
Where is vascular cambium?
Between xylem and phloem
Vegetative Reproduction Process
Over time, a plantlet forms at the vegetative organs and remains attached to its parent plant
These plantlets are clones of their parents as no other DNA has been introduced
At maturity, the plantlet becomes detached from its parent and can live independently, when it is capable of photosynthesising by itself
The new plants all have the same phenotype, so are uniform
What are runners/stolons?
Modified stems that grow horizontally above ground. The buds on these stems produce roots and shoots
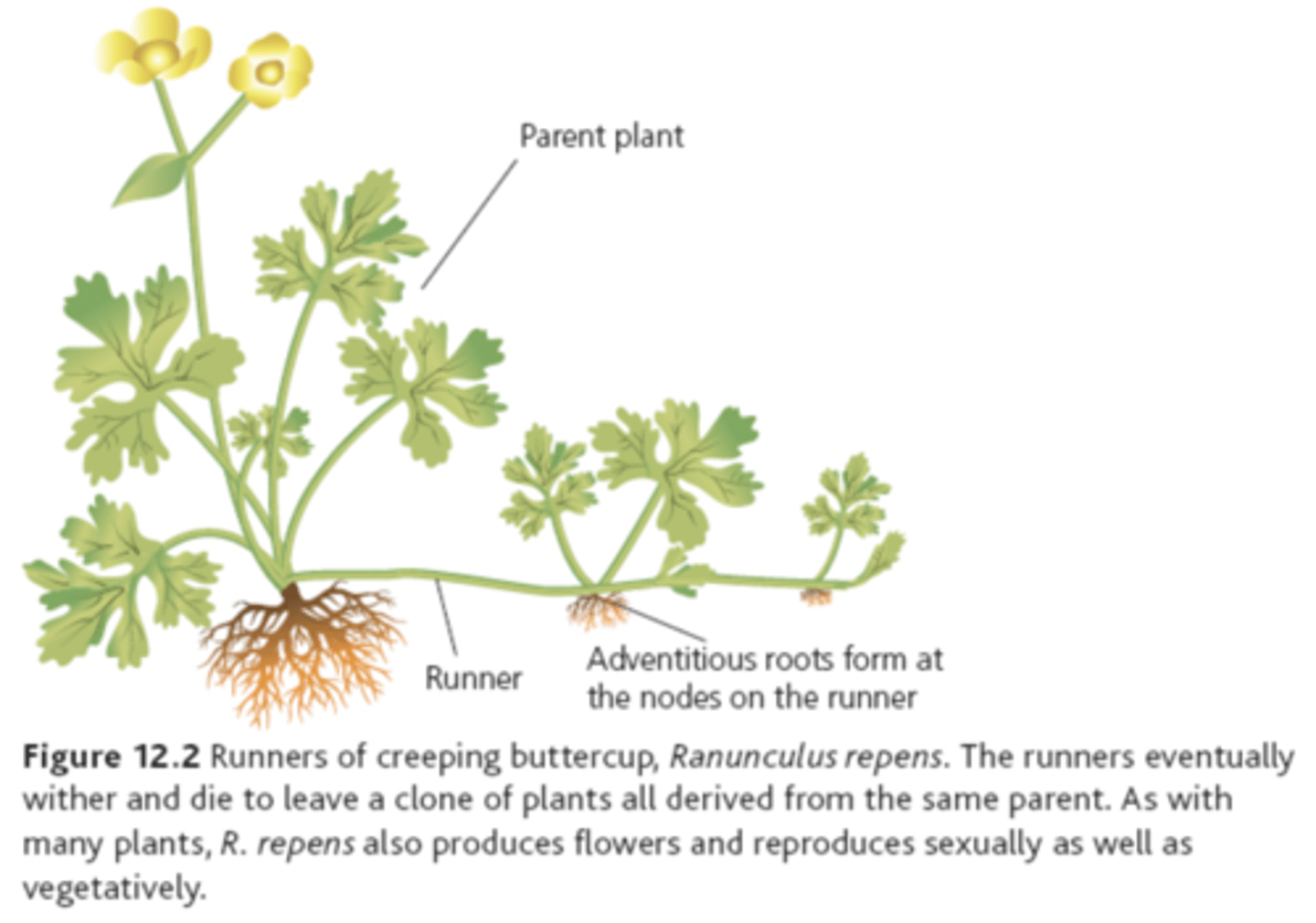
What are roots that form under the nodes of runner called?
Adventitious Roots
Will the plantlet be okay when the runner dies?
The plantlet is self sustaining so yh
What is propagation?
The reproduction of organisms (like plants) through methods like cuttings
Why don't methods of propagation require seeds?
It is asexual reproduction
A well as runners/stolons, how else can plants can propagate asexually?
Using tubers, bulbs, suckers