History of Psychology Exam 9-11
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Who was Clever Hans?
A horse that people thought could answer math problems.
Who promoted behaviorism?
John B. Watson
behaviorism focused on what
focused on only what could be seen, heard, or touched
Watsons psychology
•Watson's Psychology
-only observable behavioral acts
-described objectively
-Rejected all mentalistic concepts
•image, mind, consciousness-meaningless
-Consciousness had no value for behavioral psychology
What was the most important antecedent to Watson's psychology
animal psychology
Tropism definition
Loeb's theory of animal behavior based on an involuntary forced movement
Who introduced the rat maze as a standard method for the study of learning
Willard Small
Who began using the word behavior
Charles Henry Turner
Why was animal psychology a difficult profession?
not well respected in academia
always concerned with funding
poor career prospects
Who ignites and bring more objectivity the animal psychology field?
Ivan Pavlov
Objectivity definition
tendency to base judgements and interpretation on external data rather than subjective factors like feelings, beliefs, and experiences
Oskar Pfungst investigated Hens to see if he was clever and what did he find?
- he was not receiving intentional signals from owner
- horse used subtle cues from the keeper
Who believed that psychology must study overt behavior
Edward Thorndike
Whose approach to learning was connectionism
Edward Thorndike
Connectionism definition
Thorndikes approach to learning was based on connections between stimuli and responses
- argued that behavior must be reduced to its simplest elements
Who had the 1st dissertation to use animal subjects
Edward Thorndike
Who built puzzle boxes?
Edward Thorndike
The puzzle box results
- responses were random at 1st
on subsequent trials, random behaviors were less frequent until learning was complete
Thorndike's Law of Effect
acts that produce satisfaction in a given situation become associated with that situation; when the situation recurs, the act is likely to recur
Thorndike's Law of Exercise
the more an act or response is used in a given situation, the more strongly the act becomes associated with that situation
Thorndike trial and error learning
learning based on repetition of response tendencies that lead to success
Pavlov became interested in animal psychology after reading who's book?
Darwin
What 3 things were Pavlov interested in?
Functions of the nerves of the heart
Digestive glands
Conditioned reflexes
What are conditioned reflexes- Pavlov?
reflexes that are conditional or dependent on the formation of an association or connection between stimulus and response
Pavlov attempted to use the
experimental method to eliminate sources of error
Why did Pavlov design the Tower of Silence?
- way to control any outside influences
- air tight steel doors
- windows covered in extra thick glass
E.B. Twitmyer discovery involved
His 1904 doctoral research found that subjects having a knee-jerk test began to react to things other than the hammer (conditioned reflex)
Alois Kreidl found that
goldfish learned to anticipate being fed by the vibrations in the water
Who was a Russian physiologist, neurologist, and psychiatrist
Vladimir M. Bekhterev
What was Vladimir M. Bekheterev do?
•reflexive movements (withdrawing one's finger from electric shock) could be elicited by a conditioned stimulus (A buzzer at the time of shock)
Who was an enemy of Pavlov, had a suspicious death, and his son was executed?
Vladimir M. Bekheterev
Who founded behaviorism, but did not originate it?
John B. Watson
How did Watson become interested in psychology?
he was attracted to psychology by Angell and Loeb
What psychologist favored animal subjects?
Watson
Watson ran a lab at what university
John Hopkins
What 2 things did Watson believe have no value in psychology?
Psychic or mental concepts have no value for a science of psychology
Watson wanted behaviorism to be a
of practical value and applied to the real world
Watsons demise
- marriage was detoriating and he fell in love with a student
-Forced to resign
-No university wanted to hire him
What was Watson's 2nd career?
advertising
What companies did Watson work for
Did some work for Johnson's baby powder
He invented the coffee break to push Maxwell house coffee
Did an ad for ponds face cream
Queen Marie of Romania endorsed it
How did Watson promote behaviorism
lectures, radio talks, advertisements
Watson was very critical of child rearing practices
- thought that parents should not hug or kiss children
What were Watson's views on women?
Outspoken women- sexually dissatisfied
Once sexually satisfied- docile, quiet, and satisfied
Women lose sexual appeal by the age of 40
Totally over the hill by age 40
Watson was asking that psychology now be defined as
· the science of behavior (not consciousness)
· a purely objective, experimental natural science
· with no use of mentalistic ideas or terms
· use only behavioral concepts such as stimulus and response
·the study of BOTH animal and human behavior
Watson's Goal
Predict and Control Behavior
Criticism to Watson's behaviorism
Use of animal
Rejection of introspection
Behaviorism became popular between the 1920's and 1930's.
•By the 1920s:
-Universities were offering courses in behaviorism
-Term was becoming acceptable in the professional journals
•By 1930, so popular -No university could avoid teaching it
Watson's method of behaviorism
Stimulus response
-Observation
- testing methods
-The verbal report method
-The conditioned reflex method
Watson believed that the ______ is more important than the _____
experimenter, subject
Watson's primary subject matter is
elements of behavior
Watson's underlying belief
all areas of behavior would be considered in objective stimulus response terms
Watson's 3 specific areas of focus in behaviorism
emotions
instincts
thoughts
What did Watson believe about instincts
At first, he accepted the role of instincts
Next, he eliminated the concept of instinct
Finally, said that instincts are socially conditioned responses
Watson became an extreme environmentalist so he denied the existence of what?
capacities, temperaments, or talents
What did Watson think about behaviors?
They could be traced to early childhood training
Watson believed that emotions were
not a conscious process
Watson's explanation of emotions
the objective stimulus situation, the overt bodily response, and the internal physiological changes
What are the 3 primary learned reactions in infants
fear, rage, and love
Little Albert conditioned to fear what 3 things?
white rat, white rabbits, Santa Claus masks
Conditioning of little Albert leads Watsons to what?
reject the notion of the unconscious because it could not be objectively observed
Who hears of Watsons Little Albert's study during one of Watson's talks and what was her interest?
Mary Cover Jones
her interest: can conditioning be used to remove a fear
Mary did a study with 3-year-old Peter who feared rabbits and what did she do?
eliminated the fear response through conditioning
slowly introducing a rabbit when Peter was eating
What does Watson think about the thought process
Thinking is talking silently
thinking is subvocal talking that relies on the same muscular habits as overt speech
Psychology captured and captivated the public's attention
General public was convinced psychology
health, happiness, and prosperity
Karl Lashley was a supporter of behaviorism and came up with 2 principles
Law of mass action- efficiency of learning depends on the amount of tissue in the brain that is available
Principle of equipotentiality- the brain has the capacity to transfer memory to the portion of the brain the is damaged
William McDougall
- believed that consciousness was necessary
introspection was necessary in determining meaning of responses
What contributions did Watsons have to psychology?
furthered applied psychology to education, social work, and mental health agencies
Who invented the IQ zoo?
Keller and Marian Breland
What techniques did Keller and Marian Breland use at the IQ zoo?
Used basic conditioning techniques from Skinner
The animals from the IQ zoos went to what places?
Roles in movies, commercials, and television shows
Three stages of behvaiorism
Watson's behaviorism
Neo behaviorism- included the work of Tolman, Hull, and Skinner
Core of study of psychology is learning
Neo-Neo Behaviorism or sociobehaviorism- included Bandura and Rotter
operationism
The position that the meaning of a scientific concept depends upon the procedures or operations used to determine or prove them
operationism insists what? Also, they believe that there is no place for what?
Insistence on discarding pseudo- problems
No place for consciousness
Edward Tolman purposive behaviorism definition
Tolman's system combined the objective study of behavior with the consideration of purposiveness or goal orientation in behavior
intervening variable
unobserved and inferred factors within the organism that are the actual determinants of behavior
Tolman's learning theory definition
repeated performance of a task strengthens the learned relationship between environmental cues and the organism's expectation (cognitive approach)
The learned relationships for Tolman's learning theory
sign gestalts or cognitive map
Forerunner to contemporary Cognitive Psychology
Tolman

Clark Hull believed we should view humans as ______
-Describes human nature in mechanistic terms
-Regarded human behavior as automatic
-behaviorists should view subjects as machines
Hull proposed 4 methods in scientific research
•Simple observation, systematic controlled observation, and the experimental testing of hypotheses
-Fourth method:
•Hypothetico-deductive method: involved
•WHAT WE KNOW AS THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD!!!
Who invented hypothetico- deductive method
Hull
- what we know as the scientific method
2 kinds of drives- Hull
•Primary-
-associated with innate biological needs
-vital for survival
•Examples: food, water, air, temperature regulation, urination, sleep, sexual activity, pain relief
•Learned or Secondary (develop from primary drives)
-relate to situations or environmental stimuli that serve to reduce primary needs
•Example: burn your hand on the stove, tissue damage produces the primary drive (pain relief) ; other environmental stimuli become associated with the reduction of the primary drive (ex. sight of red burner) lead to withdrawing your hand
Who invented the need reduction theory?
Hull
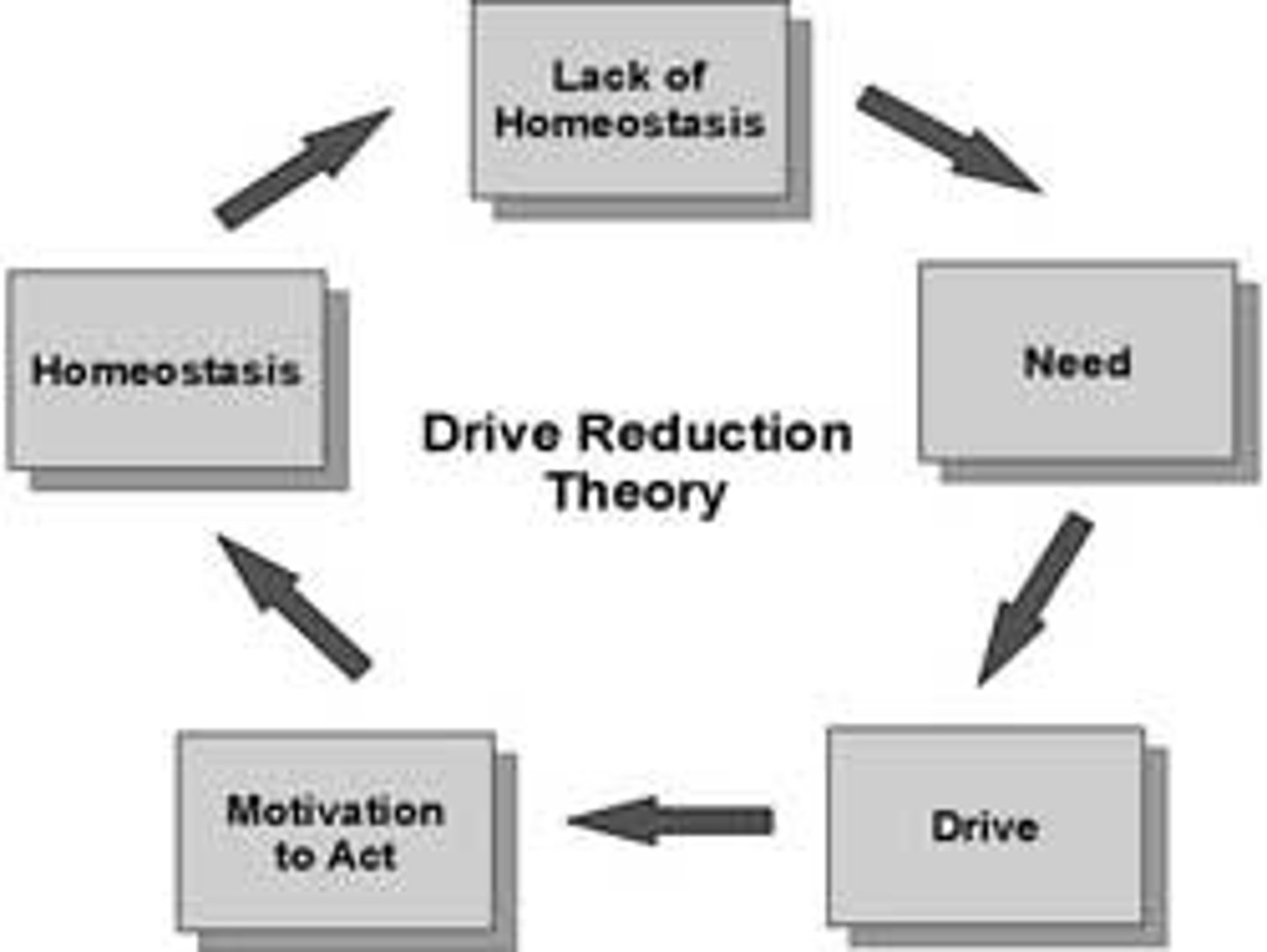
Hull believes that learning cannot occur without __________
Learning cannot occur without reinforcement -reinforcement is necessary to reduce drives!
Primary reinforcement- Hull
The reduction of a primary drive is fundamental to his learning theory
Secondary reinforcement- Hull
-those things associated with things that reduce the primary drive
•also serve to reduce the need (ex. Seeing a vending machine which has been associated with reducing thirst)
S-R associations are strengthened by the number of reinforcements that have occurred - Habit Strength
The world's most influential psychologist for decades
B. F. Skinner
This behaviorist was not concerned with the organism
Skinner
Skinner the empty organism approach definition
not concerned with speculating about what might be occurring inside the organism--
Skinner proposed that humans are controlled and operated on by forces in the ______
environment
Skinner believed that behavior could be
predicted and controlled
Skinner believed that a learning situation involved behavior emitted by an ________
organism
Skinner called it operant conditioning because the organism operates on the
environment
Skinner Box
rat had to press a bar to get food
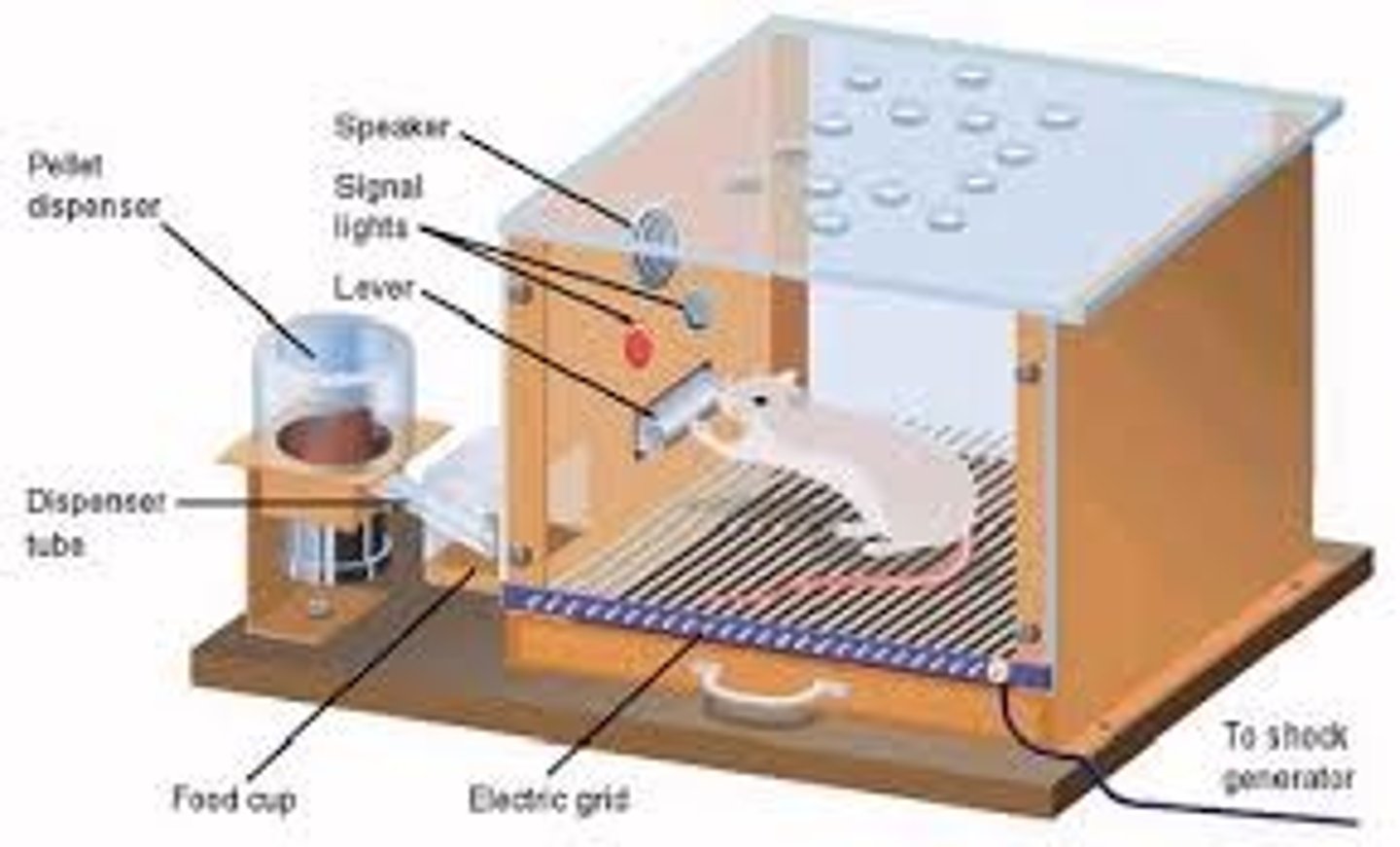
Skinner's law of acquisition
When we get reinforced the behavior increases
fixed ratio Skinner
•Reinforcer is presented after a predetermined number of responses
-For a fixed ratio schedule of 3, the rat has to press the bar three times to get a pellet.
fixed interval Skinner
•Organism is reinforced after a specific time interval -use of timing device
-Ex. once every 20 seconds
Skinner variable ratio
•The number is changed each time the animals receives reinforcement
•Delivery schedule is unpredictable
- For example: 3 presses to get a pellet, then 10, then 1, then 7 and so on.
variable interval Skinner
•Reinforcement is delivered after a random (unpredictable) amount of time
•Example: first 20 seconds, then 5, then 35, then 10 and so on.
Successive approximation skinner
an explanation for the acquisition of complex behavior that has a low probability of occurring in normal events