Topic 6 - alkenes, alcohols and analytical techniques
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Why do alkenes show E/Z isomerism?
They have limited/ restricted rotation around the C=C double bond that have different groups on each carbon.
What is E/Z isomerism?
It is a form of stereoisomerism (same molecular formula but different spacial arrangement of atoms in space).
What is trans/cis isomerism?
Trans = E isomerism
Cis = Z isomerism
What are the type of covalent bonds?
Sigma bond - single bond
Pi bond - second bond in a double bond
What is a sigma bond and how does it form?
It is a single bond and can be formed from three ways.
The overlap of two s orbitals (spherical shapes) eg H2
An s orbital and a p orbital (spherical shape and dumbbell shape)
Two sides of p orbitals (horizontal overlap of two dumbbell shapes)

What is a pi bond and how is it formed?
It is the second bond in a double bond and it caused by the overlap of two vertical p orbitals.
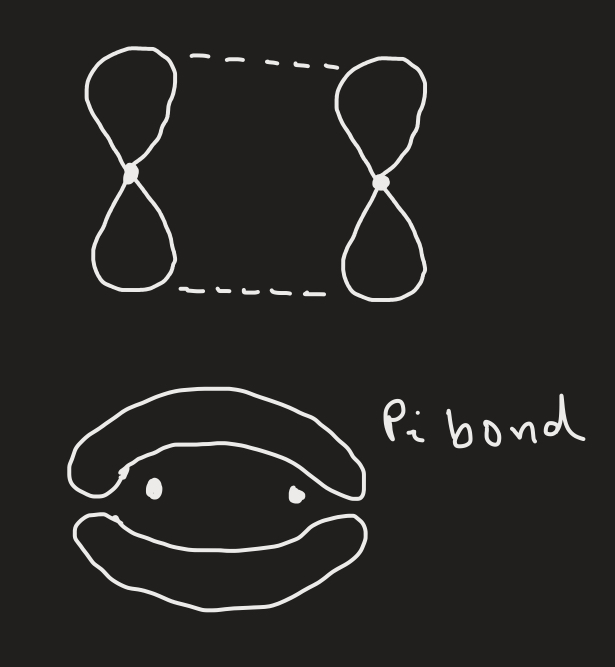
Which bond is stronger - sigma bond or pi bond?
Sigma bond is stronger
Are alkene more reactive than alkanes and why?
Alkenes are more reactive as pi bonds can break easier and they are unsaturated so they can undergo addition reactions.
What can C=C bonds be attacked by and why?
They can be attacked by electrophiles as the double bonds form an electron rich area. This reaction can be called electrophillic addition.
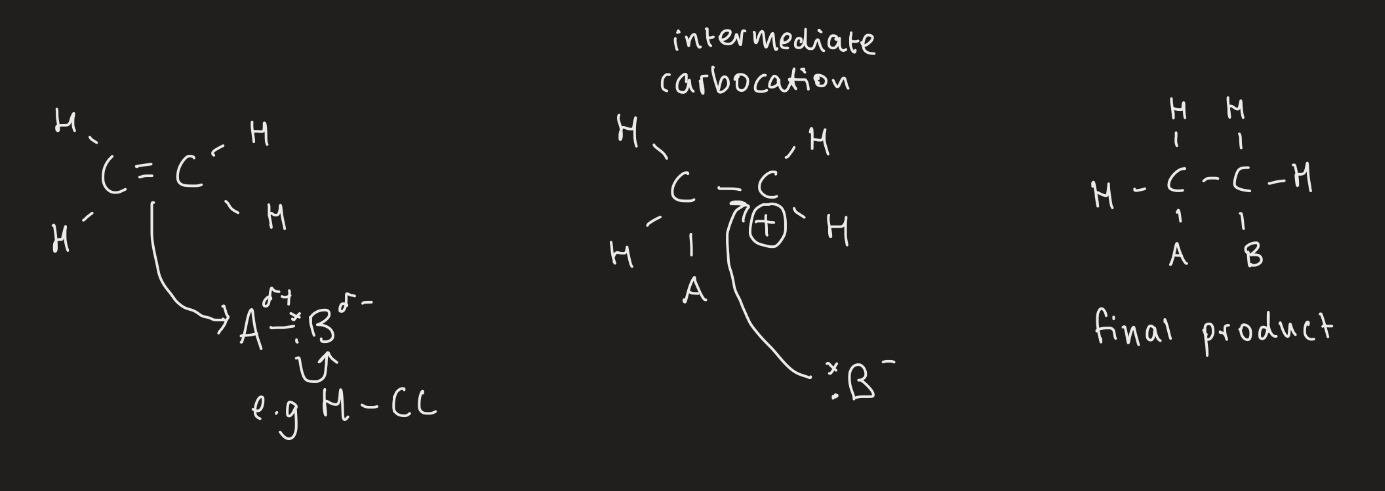
What is the general mechanism for elcetrophillic addition?
A pair of electrons are transferred from C=C bond to electrophile (the delta positive region)
The bond in the electrophile is broken
A positive ion called a carbocation is produced and a negative ion is produced from the original electrophile
The negative ion bonds with the carbocation
How does electrophilic addition of a halogen work if there is no dipole?
There is an induced dipole due to the repulsion of the electrons from the negative region on the alkene.
How many possible products are there for an asymmetrical alkene?
There are 2 possible products depending on where to H atom attaches across the double bond and therefore what carbocation is produced.
What is the order of stability of carbocations?
Weakest - primary, secondary, tertiary - strongest
The most stable carbocation is the major product.
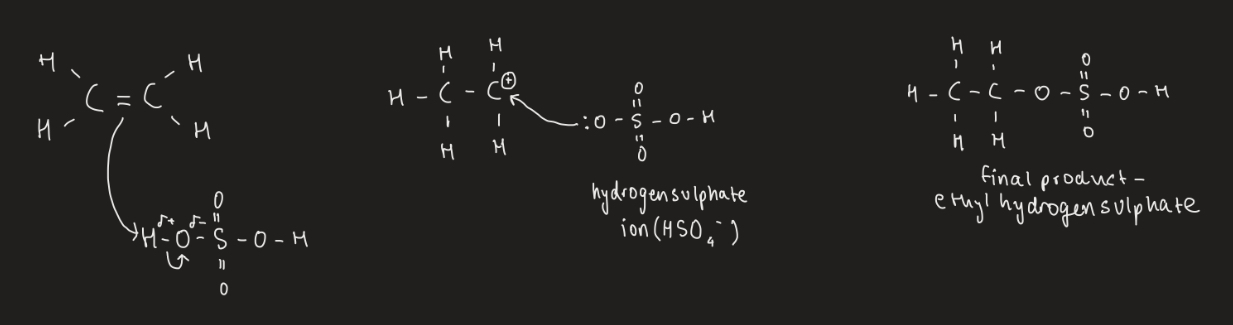
What is produced trough the electrophilic addiction of an alkene and sulphuric acid?
Alkyl hydrogen sulphate eg ethyl hydrogen sulphate
Show the electrophilic addition of ethene and sulphuric acid.
What is a polymer?
Long chained molecule made of repeating units of one monomer.
What is a monomer?
Small molecule that join together to make a polymer.
What are the two types of polymerisation?
Addition polymerisation
Condensation polymerisation
How many products are there for addition polymerisation?
1 product from one type of monomer.
How many products are there for condensation polymerisation?
2 products - polymer and a small molecule of H2O or HCl
What are the uses of polymers?
Plastic bags, raincoats, tyres, pipes, nonstick pans.
What are the monomers for both types of polymerisation?
Addition - alkenes
Condensation - 2 functional groups
What bond is formed for both polymerisations?
Addition - sigma bond
Condensation - ester bond or amide bond
What are the by products for both polymerisations?
Addition - no by products
Condensation - H2O or HCl
What are examples of both polymerisations?
Addition - ethene —→ polyethene
Condensation - dicarboxylic acid + diol —→ polyester
What are the backbones for both types of polymerisations?
Addition - C-C bonds
Condensation - hetroatoms (O,N)
What are plasticisers and what do they do?
They can be added tp polymers tp modify its properties to make it more flexible. This happens by weakening its intermolecular forces so the polymer chains can slide over each other.
What are some examples of plasticised plastics?
PVC
Electric insulation
Floor tiles
What type of intermolecular forces are in alcohols?
Van der Waals and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding between adjacent alcohol.
Why is the boiling point of alcohols a lot higher than alkanes/ alkenes?
Alcohols have hydrogen bonding and alkenes/ alkanes only have van der Waals. Hydrogen bonding is stronger than van der Waals meaning alcohols have a higher boiling point. Requires more energy to overcome.
Are alcohols soluble in water?
They are solvable as they are polar like water and can hydrogen bond with water.
However, the longer the chain is, the less soluble it is.
Why do we produce ethanol on an industrial scale?
Ethanol can be used for recreation use and in sterilisation to kill bacteria.
Why are alcohols useful intermediates in the chemical industry?
As they are easily made and easily converted into other compounds eg haloalkanes, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and esters.
What are the two ways to produce ethanol?
Fermentation of carbohydrates
Reaction of ethene with steam
What is the equation for the fermentation of carbohydrates?
C6H12O6 —> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
What are the conditions for the fermentation of carbohydrates?
Temperature = 30 degrees Celsius
Pressure = 1atm
Catalyst = enzymes in yeast (zymase)
Other = anaerobic
What are the raw materials needed for fermentation of carbohydrates and are they renewable or nonrenewable?
Glucose and starch
Renewable
What type of process is used for the fermentation of carbohydrates?
Batch (made in small quantities)
What is the reaction rate for the fermentation of carbohydrates?
It is a slow process
What is the purity of ethanol in the fermentation of carbohydrates?
Low purity (15% purity) - must distil the alcohol
What is the equation for the fermentation of carbohydrates?