Unit 5 GEO
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
agriculture
the process by which humans alter the landscape in order to raise crops and livestock for consumption and trade
the evolution of agriculture
first (neolithic) agricultural revolution → second agricultural revolution (1700s) → green revolution (1960s)
fertile crescent
present-day middle east from the Mediterranean to the Persian gulf
excellent farmland
crops: barley, wheat, lentils, olives, oats, rye
animals: sheep, goats, cattle, pigs
silk road
trading routes used around the 1st century CE centred on the ____ _____. The routes remain largely valid for the period 500 BCE to 500 CE.
first (neolithic) Agricultural revolution
the origin of farming, marked by the first domestication of plants and animals
began in the fertile crescent 10,000 - 12,000 years ago
traits
Domestication → Raising plants and animals for human use.
Simplistic tools and manual labor
Subsistence Farming → When farmers consume the crops that they grow and raise.
Transition away from hunter-gatherer lifestyle
Second Agricultural Revolution
Beginning in the 1700’s, the advances of the Industrial Revolution were used to increase food supplies and support population growth.
The Industrial Revolution → A set of changes in technology that dramatically increased manufacturing productivity, reshaping how people worked, behaved, and where they lived.
The Enclosure Acts → A series of laws enacted by the British Government that enabled landowners to purchase and enclose land for their own use that had previously been common land used by peasant farmers.
Similar movements occurred throughout Europe
green revolution
Beginning in the 1960’s, it was the third agricultural revolution which involved the development of better and more efficient farming equipment and practices that led to increased production around the world.
Massive population growth in 20th century, mostly in developing regions of the world, necessitated increased production
Use of biotechnology
Development of higher-yielding, disease-resistant, faster-growing varieties of plants
Increased use of fertilizer and pesticides to reduce agricultural losses
Development of more large-scale irrigation projects
Double cropping (growing more than one crop in a year)
Seed Hybridization → The process of breeding together two plants that have desirable characteristics.
GMOs → Genetically Modified Organisms, produced when humans use engineering techniques to change the DNA of a seed.
Von Thunen’s Model of Agricultural Land Use
An economic model that suggested a pattern for the types of products farmers would produce at different positions relative to the market where they sold their goods.
Created 1826 by German farm owner and economist Johann von Thunen
Believed decisions regarding what to produce were based largely on transportation costs and that these costs were proportional to distance from the market
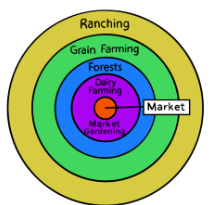
Von Thunen’s Key Assumptions
A city is an isolated region within which all agricultural products are sold at a central market
Markets are situated in the middle of plains that are flat and featureless and within which all land has similar characteristics
Farmers are rational economic producers (want to make as much money as possible)
intensive farming
Agriculture that involves greater inputs of capital and paid labor relative to the space being used
Ex. market gardening, plantation, mixed crop/livestock
extensive farming
Agriculture that uses fewer inputs of capital and paid labor relative to the amount of space being used.
Ex. shifting cultivation, nomadic herding, ranching
horticulture
a type of agriculture that includes market gardening and dairy farming.
_________ produces perishable items and farmers need to get them to the market quickly
distance decay
A geographical theory that states that the interaction between two places decreases as the distance between them increases.
Bid Rent Theory
A geographical economic theory that explains that price and demand for real estate decreases as the distance from the city center (market) increases. There is less land close to the center/market, so it is more expensive there.
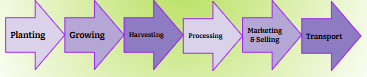
commodity chain
a process used by corporations to gather resources, transform them into goods, and then transport them to customers
economy of scale
The cost advantage experienced by a company when it increases its level of output.
With better access to resources, markets, and better technology due to globalization, companies can increase their efficiency (output).
More efficient production leads to more profit for the company and lower prices for the consumer
fair trade
Trade between companies in developed countries and producers in developing countries that tries to ensure farmers are paid a fair wage.
Slightly increases price for consumers
Unfair trade practices contribute to poverty and oppression
food desert
A community where there is no access to fresh, healthy, affordable food options because there is a lack of grocery stores or farmer’s markets.
Caused by business owners not opening food stores in low income areas due to lack of profit opportunities
Abundance of fast food or convenience stores instead
Can occur in rural and urban areas
Low income & low access communities
urban agriculture
The practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around towns or cities.
Includes micro farming (container gardening, roof gardens, vertical farming, hydroponics, traditional home gardening)
double cropping
Planting and harvesting on the same parcel of land twice per year.
Can reduce soil quality if not done carefully
Can prevent need for additional land for agriculture
intercropping
When farmers grow two or more crops simultaneously on the same field.
Can help replenish soil and reduce runoff
Leads to higher yields
Could require more fertilizer use and irrigation
terrace farming
When humans build a series of steps into the side of a hill, creating flat surfaces for the purpose of agriculture.
Used primarily in East Asia, Northern Africa, South America
value-added specialty crops
Crops that have some other product added to them to make them unique and able to sell at a higher price.
Ex. turning berries into jam, turning wheat into flour, turning corn into ethanol, etc.
Can help small farmers compete with larger farms/corporations
agribusiness
The integration of various steps of production in the food-processing industry.
Includes large-scale commercial agriculture and also the steps of processing and production, transportation, marketing, retail, and research and development
Highly commercial, highly mechanized, uses chemicals and biotechnology to raise crops and animals