Biological compounds 1.1
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Name 4 key organic ions in living organisms
Magnesium ions
Iron ions
Calcium ions
Phosphate ions
What is the role of phosphate in living organisms?
Used to produce nucleotides
What is the role of magnesium in plants
It is used to produce chlorophyll
What is the role of calcium in living animals
It is used to strengthen tissues such as bones
What’s is the role of iron in animals
Iron is found in haemoglobin and is involved in the transport of oxygen
Why is waters high specific heat capacity important for organisms
Waters needs a large amount of heat to raise the temperature, enabling endothermic to resist fluctuations in core temperature and to maintain optimum enzyme activity
Why does water have high surface tension?
Due to ordered arrangement and cohesion at the surface of water
Why is waters high latent heat of vaporisation important for organisms
When water evaporates it has a cooling effect. This is important in homeostasis organisms can loose heat through sweating or panting
Why is the high surface tension of water important for organisms
-Enables the transport of water and nutrients through plant stems and small blood vessels in the body
-Allows small insects to walk on water
What is a monosaccharide?
Simple sugar
Give examples of monosaccharides
Alpha glucose
Beta glucose
fructose
Galactose
What is a disaccharide?
Molecule formed by the condensation of two monosaccharides forming a glycosidic bond
What are examples of disaccharides
Sucrose
maltose
lactose
What is the name of the bond formed when two monosaccharide react?
Glycosidic bonds
What is the reaction for lactose?
Glucose + galactose → lactose + water
What is the reaction for maltose?
Glucose + glucose → maltose + water
What is the reaction for sucrose
Glucose+ fructose → sucrose + water
What is a polysaccharide?
A polymer of monosaccharides formed by many condensation reactions
Give some examples of polysaccharides
Starch
cellulose
Glycogen
How is starch formed?
By two polymers of alpha glucose - amylose + amylopectin
What is the function of cellulose
Provides structural strength to cell wall
Describe the structure of amylose.
Alpha glucose- glycosidic bond + coiled+ unbranched
Describe the structure of amylopectin
Alpha 1,4 and alpha 1,6 glycosidic bond + branched
How is glycogen produced?
By many condensation reactions between alpha glucose
How does the structure of glycogen relate to its function?
It is highly branched
Easily hydrolysed to alpha glucose which can be transported to where ever the energy is needed
What is the function of starch and glycogen?
Insoluble store of glucose
Differentiate between monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids
Monounsaturated fatty acids contain only one double carbon bond
Polyunsaturated fatty acids have more than one double carbon bond
Why is water polar?
Because the oxygen end of the molecule has a negative charge and the hydrogen atoms have a positive charge.
The uneven distribution of charge is called a dipole
what is a metabolite?
A molecule formed or used in metabolic reactions
Describe hydrogen bonding between water molecules
When two molecule are in close contact the opposing charges forming a hydrogen bond.
The attraction between water molecules is called cohesion
Explain how a triglyceride is formed
One molecule of glycerol forms ester bonds with three fatty acids via condensation reactions
What are properties of triglycerides
Energy store -
Protection- fats often stored around delicate organs
Thermal insulator- when stored under skin acts as thermal insulator which reduces heat loss
What is a phospholipid?
A typed of lipid formed by condensation of one molecule of glycerol, two molecules of fatty acid and a phosphate group
Describe the positive result of an emulsion test
White cloudy emulsion forms
Define a protein
Proteins are polymers made of the monomer animo acids
How are polypeptides formed
Many amino acid monomers joined together in condensation reactions forming peptide bonds
Describe the general structure of an amino acid
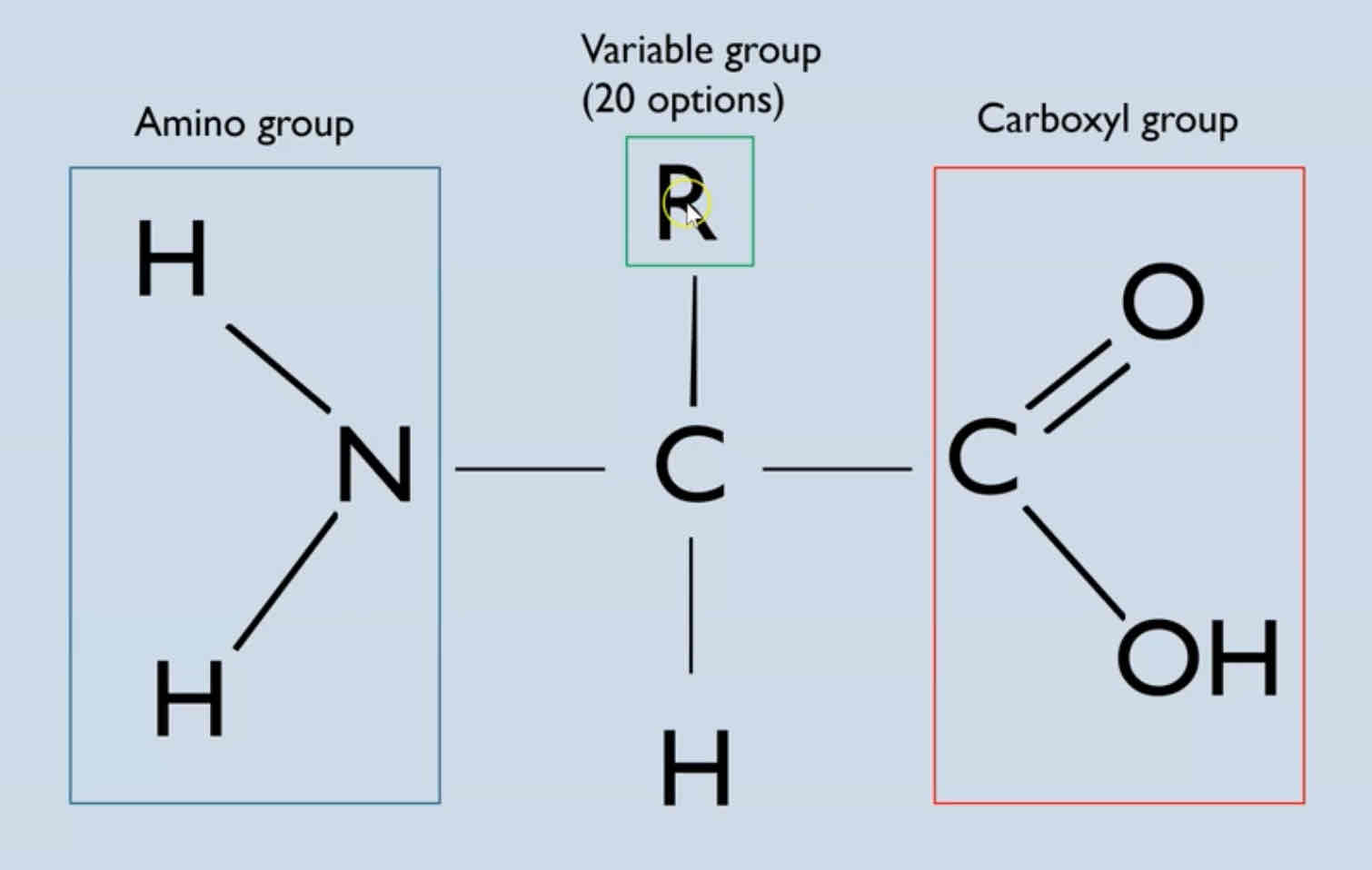
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The individual sequence of amino acid in a polypeptide chain
Describe the secondary structure of a protein
The sequence of amino acids cause parts of a protein molecule to bend into alpha helix or fold into beta pleated sheets
Describe the tertiary structure of protein
The further folding of the secondary structure to form a unique 3D shape. Held in place by ionic Hydrogen and disulphide bonds
Describe the quaternary structure of a protein
Interactions of more than one polypeptide chain
May involve the addition of prosthetic groups
Describe how the structure of fibrous proteins relates to their function
-Long polypeptide chains folded parallel
-Little tertiary structure aside from cross links for strength
-This makes them insoluble and good for structural roles
Describe how the structure of globular proteins relates to their function
Spherical compact highly folded with complex tertiary/ quaternary structures
Hydrophilic R group table outwards
hydrophobic R group faced inwards
Name the food test used to identify to identify proteins
Biuret test
What is the difference between reducing and non reducing sugar?
A reducing sugar has a free aldehyde or ketone functional group so can act as a reducing agent
A non reducing sugar doesn’t have a free aldehyde or ketone functional group so it cannot act as a reducing agent
Describe the positive result for reducing sugars
Colour change from green to yellow to brown to orange to brick red
Describe the positive result for non reducing sugars
Colour change from green to yellow to orange brown to brick red
Describe the result of a positive buiret test
pale blue to purple
Describe the iodine potassium iodine test for starch
Add iodine KL solution
Colour change from orange to blue black in the presence of starch
What is meant by a low density lipoprotein?
-A combination of triglycerides from saturated fats and protein
-Blocks receptor sites reducing cholesterol absorption
-“bad” lipoproteins
How do LDLs contribute to the risk of cardiovascular disease?
High blood cholesterol level caused by LDLs leads formation of atherosclerosis plaques
How is cellulose formed?
By many condensation reactions joining beta glucose by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
Relate the structure of phospholipids to their functions
Glycerol backbone attached to two hydrophobic fatty acid tails and one hydrophilic polar phosphate head
Forms phospholipid bilayer in water-component of cell membrane
Tails are outward- waterproofing
Describe the structure of cellulose
Long straight chains lie parallel together by many hydrogen bonds. This is a fibril