[OCR] GCSE Biology: B3
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
What is the central nervous system made up of?
Neurons- which go to all parts of the body.
What is the name given to a change in the environment?
The body has lots of sensory receptors which can detect a change in environment (a stimulus).
What is an example of a receptor that detects light and change in temperature?
Receptors in your eyes detect light and receptors in your skin detect touch and temperature change.
What happens after a stimulus is detected by receptors?
The information is sent as nervous (electrical) impulses along sensory neurons to the central nervous system.
What is the central nervous system composed of?
The brain and spinal cord.
What does the CNS do with the response?
It co-ordinates the response (decides what to do about the stimulus and tells something to do it).
Where does the CNS send the information to?
It sends the information to an effector (muscle or gland) along a motor neurone. The effector then responds accordingly (e.g muscle contracts).
What are electrical impulses passed along?
The axon of a neurone.
What is the name of the branched endings of a neuron and what are their purposes?
Dendrites which connect with lots of other neurones.
Why are some axons surrounded by fatty (myelin) sheath?
Because it acts as an electrical insulator, speeding up the electrical impulse.
Why are neurons long?
They are long which speeds up the impulse (connecting with another neuron slows the impulse down, so one long neuron is much quicker than lots of short ones joined together).
What is the connection between two neurons called?
A synapse.
What do electrical impulses release?
They trigger the release of transmitter chemicals, which diffuse across the gap. These chemicals bind to receptor molecules in the membrane of the next neurone which sets off a new electrical impulse.
What is a reflex arc?
Automatic responses (done without thinking) which prevent you from injuring yourself- they are faster than normal responses.
What is NOT involved in the reflex arc?
The conscious brain. The sensory neurone connects to a relay neurone in the spinal cord or in the unconscious part of the brain.
What is an example of the reflex arc in action?
1)Bee stings finger.
2)Stimulation of the pain receptor.
3)Message travels along the sensory neurone.
4)Message is passes along a relay neurone.
5)Message travels along a motor neurone.
6)Message reaches muscle- it contracts- arm moves away from bee.
Labelled eye diagram:
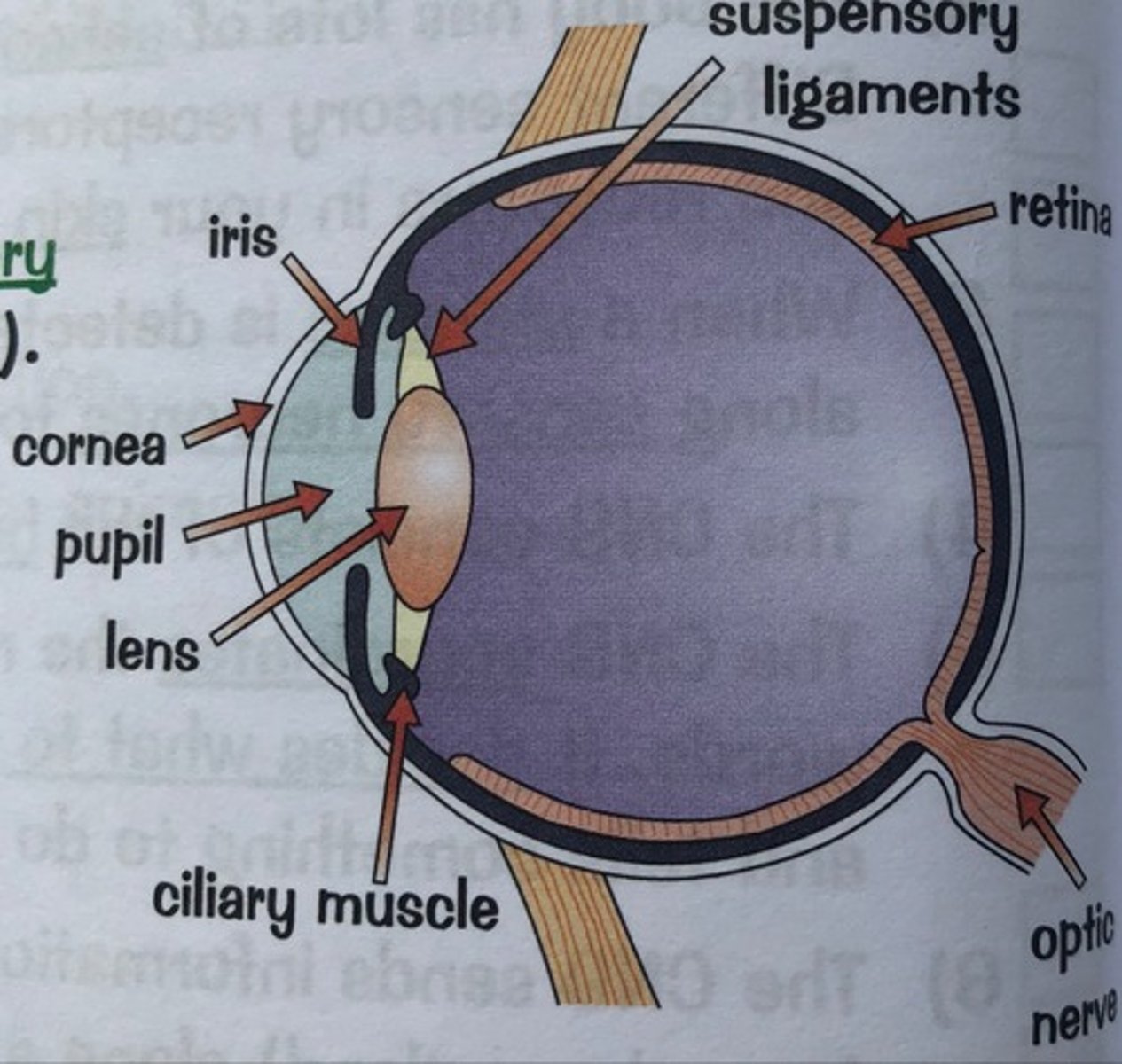
What is the function of the cornea?
The cornea refracts light into the eye.
What is the function of the iris?
The iris controls how much light enters the pupil.
What is the function of the lens?
The lens refracts light, focusing it onto the retina.
What is the function of the ciliary body?
The ciliary body contains ciliary muscles, which are attached to the suspensory ligaments- they work together to alter the shape of the lens.
What is the function of the retina?
The retina is the light sensitive part an it is covered in receptors called rods and cones, which detect light.
What are rods most sensitive to?
Rods are more sensitive in dim light but cannot sense colour.
What are cones most sensitive to?
Cones are sensitive to different colours but are not so good in dim light.
What is the function of the optic nerve?
The optic nerve carries impulses from the receptors to the brain.
How does the eye alter to look at distant objects?
The military muscle relaxes, which allows the suspensory ligaments to pull tight. This pulls the lens into a less rounded shape so light is refracted less.
How does the eye alter ti look at close objects?
The military muscle contracts, which slackens the suspensory ligaments. The lens becomes a more rounded shape, so light is refracted more.
What does it mean if someone is long sighted?
They are unable to focus on near objects.
What causes some people to be long sighted?
When the lens is the wrong shape and does not bend the light enough or the eyeball is too short. The images of near objects are brought into focus behind the retina.
How can you correct long sightedness?
You can use glasses or contact lenses with convex lens to correct it.
What does it mean if someone is short sighted?
They are unable to focus on distant objects.
What causes some people to be short sighted?
When the lens is the wrong shape and bends the light too much or the eyeball is too long. The images of distant objects are brought into focus in front of the retina.
How can you correct short sightedness?
You can use glasses or contact lens with concave lenses to correct it or corneal laser surgery.
What does it mean if someone is red-green colour blind?
It is caused when red or green cones in the retina are not working properly.
How can red-green colour blindness be reduced?
It cannot be cured but tinted lenses can be used to help people see colours normally.
Labelled brain diagram:
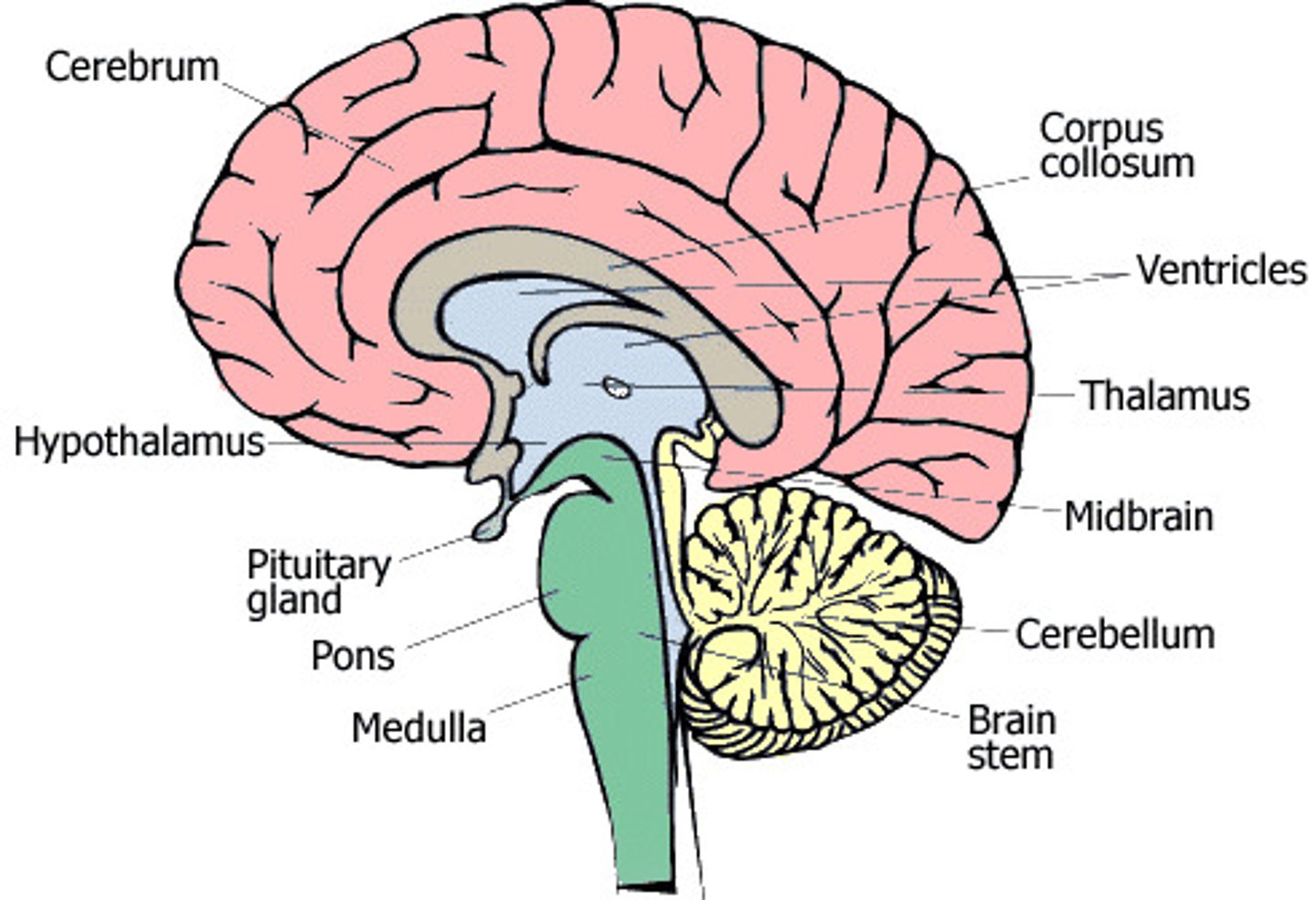
What is the function of the cerebrum?
It is responsible for things like consciousness, intelligence, memory and language.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
It is involved in maintaining body temperature at normal level (37 degrees). it also produces hormones that control the pituitary gland.
What is the function of the pituitary?
A gland that produces many important hormones, some of those involved in the menstrual cycle.
What is the function of the medulla?
It controls unconscious activities like breathing and heart rate.
What is the function of the cerebellum?
It is responsible for muscle coordination.
How do scientist study the brain?
>Case studies to learn about the brain- carry out detailed studies of people who have abnormal brain function.
>If part of the brain has been damaged, the effect this has on the patient can tell you a lot about what the damaged part if the brain does.
>fMRI scanners- shows parts of the brain that are activated.
>Examining the brains of people who have died.
How is investigation brain function tricky?
>If you are severely brain damaged, it may be unethical to study them as they cannot give informed consent.
>People have to donate their brain for research when they die.
>fMRI scanners- it is not known for sure whether the same pattern of activity would occur in a normal situation- problems interpreting the results.
In what ways is it hard to treat brain problems?
>Hard to prepare damage to the CNS as neurone do not readily prepare themselves.
>If a problem occurs in a part of the nervous system that is not easy to access, it can be hard to treat.
>Treatment for problems int he nervous system may lead to permanent damage.
What is the endocrine system made up of?
Endocrine glands.
Where are hormones released?
Hormones are released directly into the blood. The blood then carries them to other parts of the body. They travel all over the body but they only affect particular cells in particular places.
What is the name given to the cells that are affected by hormones?
Target cells- they have the right receptors to respond to that hormone.
What is the name given to an organ that contains target cells?
A target organ.
What is adrenaline?
Adrenaline is a hormone related by the adrenal glands (located just above the kidneys).
What is the purpose of adrenaline?
Adrenaline prepares the body for a 'fight or flight' situation- run or stay? It does this by activating processes that increases the supply of oxygen and glucose to cells.
How does adrenaline effect the heart?
Adrenaline binds to specific receptors in the heart- this causes the heart muscle to contract more frequently with more force so heart rate and blood pressure increase. Increased blood flow ti the muscles means the cells receive more oxygen and glucose for increased respiration.
How does adrenaline effect the liver?
Adrenaline binds to receptors in the liver. This causes the liver to break down its glycogen stores to release glucose. This increases blood glucose level, so theres more glucose in the blood to be transported to the cells.
What happens when the brain detects a stressful situation?
It sends nervous impulses to the adrenal glands, which respond by screwing adrenaline which gets the body ready for action.
How does the body control hormone levels (and other substances) in the blood?
Through negative feedback systems. When the body detects that the level if a substance has gone above or below the normal level, it triggers a response to bring the level back to normal again.
What is thyroxine and why is it important?
Thyroxine is a hormone released by the thyroid gland in the neck. It regulates metabolic rate.
What is metabolic rate?
The speed at which chemical reactions in the body occur. It is important for loads of processes in the body, such as growth and protein synthesis.
When and where is thyroxine released?
Thyroxine is released in response to thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) which is released from the pituitary gland.
How does a negative feedback system control the amount of thyroxine in the blood?
It keeps the thyroxine at the right level. When the level of thyroxine in the blood is higher than normal, the secretion of TSH from the pituitary gland is inhibited. This reduces the amount of thyroxine released from the thyroid gland so the level in the blood falls back towards normal.
What is testosterone and what is its function?
It is the main male sex hormone which is produced in the testes. It stimulates sperm production and is important for the development of the male reproductive system.
What is oestrogen and what is its function?
It is the main female sex hormone which is produced in the ovaries. It is involved in the menstrual cycle and promotes female sexual characteristics (e.g breast development).
What is progesterone and what is its function?
It is produced in the ovaries and it helps to support pregnancy. It is involved in the menstrual cycle.
What is FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinising hormone)and what are their functions?
These hormones are released from the pituitary gland in the brain. They help to control the menstrual cycle.
What is the menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle is the monthly sequence of events in which the female body releases an egg and prepares the uterus (womb) in case it receives a fertilised egg.
What is stage one of the menstrual cycle?
Day one is when the menstruation starts. The uterus lining breaks down and is released.
What is stage two of the menstrual cycle?
The lining of the uterus builds up again, from day 4 to day 14, into a which spongy later full of blood vessels ready to receive a fertilised egg.
What is stage three of the menstrual cycle?
An egg develops and is released from an ovary at around day 14. This is called ovulation.
What is stage four of the menstrual cycle?
The lining is then maintained for about 14 days until day 28. If no fertilised egg has implanted into the uterus wall by day 28, the spongy lining starts to break down again and the whole cycle starts over.
What are FSH's functions in the menstrual cycle?
>It causes an egg to mature in one of the ovaries.
>To stimulate the ovaries to produce oestrogen.
What are the functions of oestrogen in the menstrual cycle?
>Causes the lining of the uterus to thicken and grow.
>Stimulates the production of LH.
>Inhibits the production of FSH so that only one egg is released one each cycle.
What are the functions of LH in the menstrual cycle?
>Stimulates the release of an egg at day 14 (ovulation).
>Indirectly stimulates progesterone production.
What are the functions of progesterone in the menstrual cycle?
>Maintains the lining of the uterus. When the level of progesterone falls and there is a low oestrogen level, the lining breaks down.
>Inhibits the production of FSH and LH.
>A low progesterone level allows FSH to increase.. and then the whole cycle starts again.
How are hormones uses to promote natural pregnancy?
Some women have low levels of FSH which causes their eggs to mature, resulting in no ovulation and infertility. The hormones FSH and LH can be injected by these women to stimulate ovulation.
What is IVF?
In vitro fertilisation is the process of collecting eggs from the woman's ovaries and fertilising them in a lab using the man's sperm. These are then grown into embryos.
What is given to the women before egg collection in IVF?
FSH and LH are given before egg collection to stimulate egg production.
What happens once the embryos are grown in IVF?
When they are tiny balls of cells, one or two of them are transferred to the woman's uterus to improve the chance of pregnancy.
How does the injection help to prevent pregnancy and how effective is it?
>It is effective for up to 3 months.
>Stimulates the production of thick cervical mucus by using progesterone- preventing the sperm from reaching the egg.
>Overall, it is 99% effective.
How does the implant help to prevent pregnancy and how effective is it?
>It is effective for 3 years.
>It is inserted beneath the skin of the arm. Stimulates the production of thick cervical mucus by using progesterone- preventing the sperm from reaching the egg.
Overall, it is 99% effective.
How does the Intrauterine System (IUS) help to prevent pregnancy and how effective is it?
>It is effective for 3-5 years.
>A T-shaped piece of plastic that is inserted into the uterus. It thins the lining of the uterus to reduce the chance of fertilised egg implanting- uses progesterone
How does the mini-pill prevent pregnancy and how effective is it?
>Has to be taken everyday.
>Overall, it is 99% effective.
>Prevents ovulation by inhibiting the production of FSH and LH. However, this is not true for all types of mini-pill.
How does the combined pill prevent pregnancy and how effective is it?
>Taken is a 21 day pill, 7 days no pill cycle.
>Progesterone and oestrogen involved- Prevents ovulation by inhibiting the production of FSH.
>Overall, it is 99% effective.
How does the patch prevent pregnancy and how effective is it?
>Worn on the skin in a 4 week cycle- replaced once a week for 3 weeks then no patch worn for a week.
>Progesterone and oestrogen involved- Prevents ovulation by inhibiting the production of FSH.
>Overall, it is 99% effective.
What is a barrier method (in regards to contraception)?
They try to stop the egg and sperm meeting.
How does a condom prevent pregnancy and how effective is it?
>98% effective.
>Worn over the penis during intercourse to prevent sperm entering the vagina.
How does a female condom prevent pregnancy and how effective is it?
>95% effective.
>Worn inside the vagina during intercourse.
What is a diaphragm and how effective is it?
>92-96% effective.
>Fits over the cervix to stop sperm from meeting the egg. It has to be fitted by a GP/Nurse the first time its used and has to be used with a spermicide.
What is a intrauterine device (IUD) and how effective is it?
>99% effective, can be kept in for up to 10 years.
>T-shaped devices that contain copper. They are inserted into the uterus and prevent sperm from surviving. They also alter the lining of the womb so that fertilised eggs cannot implant.
What are 'natural' methods and how effective are they?
>Least effective methods as they rely on timing.
>Not having sex when the woman is most fertile or withdrawal (the man pulling out the penis before ejaculation.
What is sterilisation and how effective is it?
>99% effective.
>A surgical procedure to cut or tie tubes in the reproductive system. In women, the procedure means eggs are prevented from travelling from the ovaries to the uterus. In men, it prevents sperm from being ejaculated.
What factors must you consider with both hormonal and non-hormonal methods of contraception?
>Side effects (e.g hormonal causes acne, headaches).
>Possibility of 'doing it wrong' (e.g withdrawal- need the right time and the patch- may not replace it at the right time).
>Medical input (e.g prescription pills or one trip visit to the doctors).
>Length of action- long lasting methods (e.g IUDs).
>Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)- passed on from person to person- condoms are the only method that prevents these.
What are auxins and what is their function?
Auxins are plant hormones which control growth at the tips of shoots and roots. They move through the plant in solution.
How is auxin produced?
Auxin is produced in the tips and diffuses backwards to stimulate the cell elongation process which occurs in the cells just behind the tips.
What do auxins promote?
Auxins promote growth in the shoot, but actually inhibits the growth in the root. It is also involved in the growth responses of plants to light (phototropism) and gravity (gravitropism).
What happens when a shoot tip is exposed to light?
The shoots are positively phototropic and they accumulate more auxin on the side that is in the shade than the side that is in the light. This makes the cells bro faster on the shaded side,so the shoot bends towards the light.
What happens when shoot grows sideways?
The shoots are negatively gravitropic and the gravity produces an unequal distribution of auxin in the tip, with more auxin on the lower side. This causes the lower side to grow faster, bending the shoot upwards.
What happens when a root grows sideways?
The roots are positively gravitropic as auxin is on its lower side; but in a root the extra auxin inhibits growth. This means the cells on top elongate faster, and the root bends downwards.
What happens when a root is exposed to light?
The roots are negatively phototropic and more auxin cumulates on the more shaded side. the auxin inhibits cell elongation on the shaded side, so the root bends downwards back into the ground.
Plant growth responses experiment:

What is seed germination?
Seed germination is when a seed starts to grow into a plant.
What is the purpose of the hormone gibberellin?
Gibberellin stimulates seed germination, stem growth and flowering. It stimulates the stems of the plants to grow by stem elongation- this helps plants grow tall. Auxin and gibberellin can work together to have a really big effect on plant growth.
What is the purpose of the hormone ethene?
Ethene is produced by raging leaves. It stimulates cells that connect the leaf to the rest of the plant to expand- this breaks the cell walls and causes the leaf to fall off the plant. It also stimulates the enzymes that cause fruit to ripen.