Exam 3 - Muscles
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
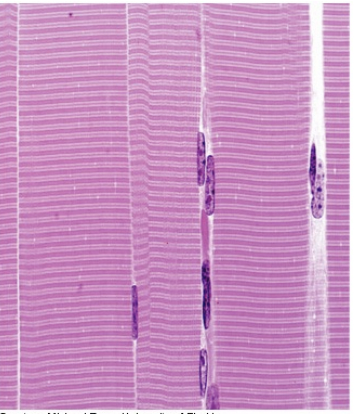
what type of muscle is this?
skeletal muscle
Characteristics of skeletal muscle/where it is found
has striations and is very structured
voluntary
found in tendons to attach bones
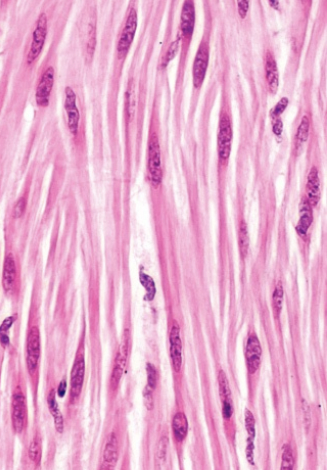
What type of muscle is this?
smooth muscle
Characteristics of smooth muscle/where it is found
involuntary muscle that lacks striations
-cells are a fusiform shape
found in walls of hollow organs
bladder, stomach, intestine, blood vessels, ariways
arranged in stacking sheets that are arranged in 90 degree angle from each other to encourage contraction
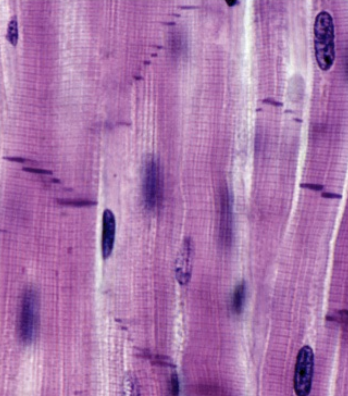
What type of muscle is this?
cardiac muscle
Characteristics of cardiac muscle/where it is found
striated with intercalated disc (where two cells come together from end to end)
located in the heart
has ion channels to spread charge
Functions of muscle tissue
movement
stabilization of body position
storage and movement of substances
heat generation
Properties of muscle tissue
electrical excitability
response to stimuli to produce contraction
contractility
muscles shorten forcibly when stimulated
extensibility
able to stretch between contractions
elasticity
able to return to resting length
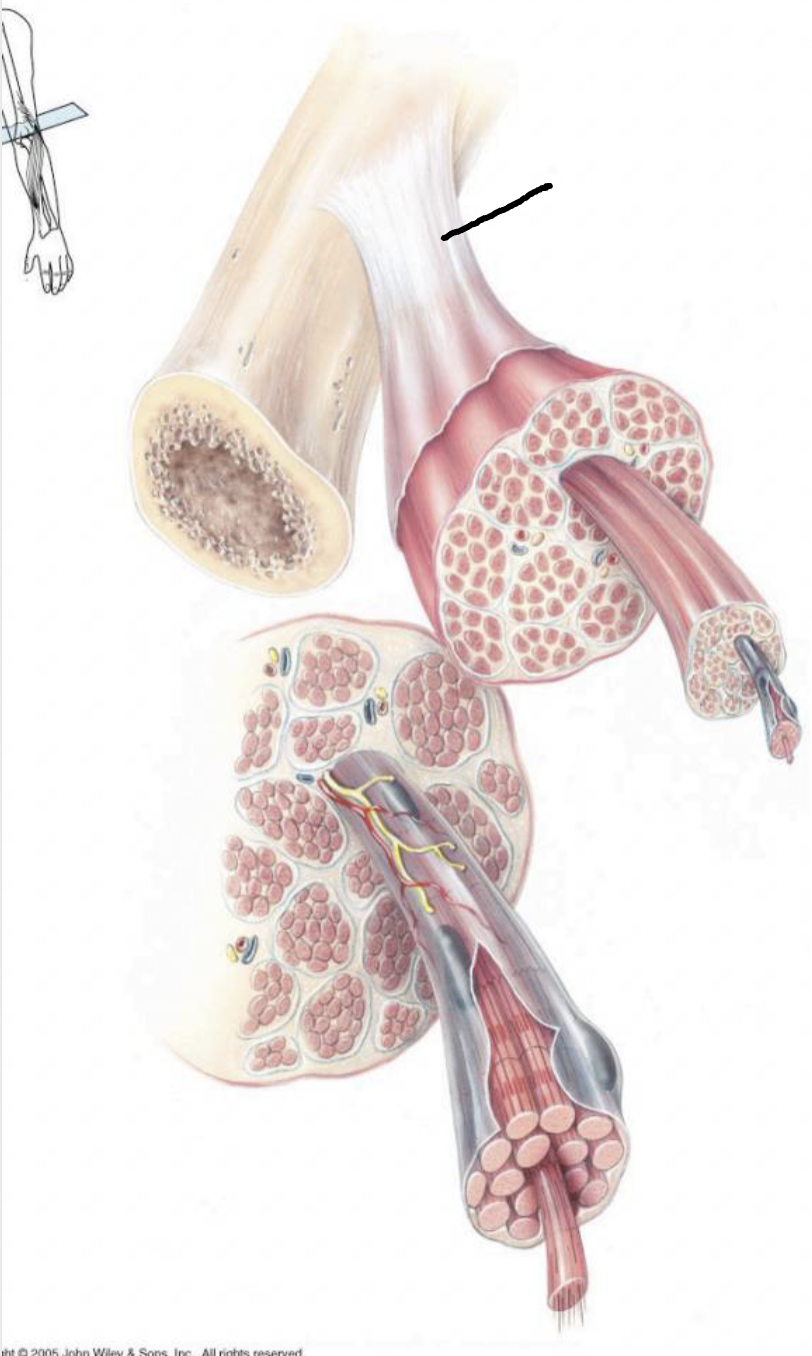
what muscle feature is this?!
tendon
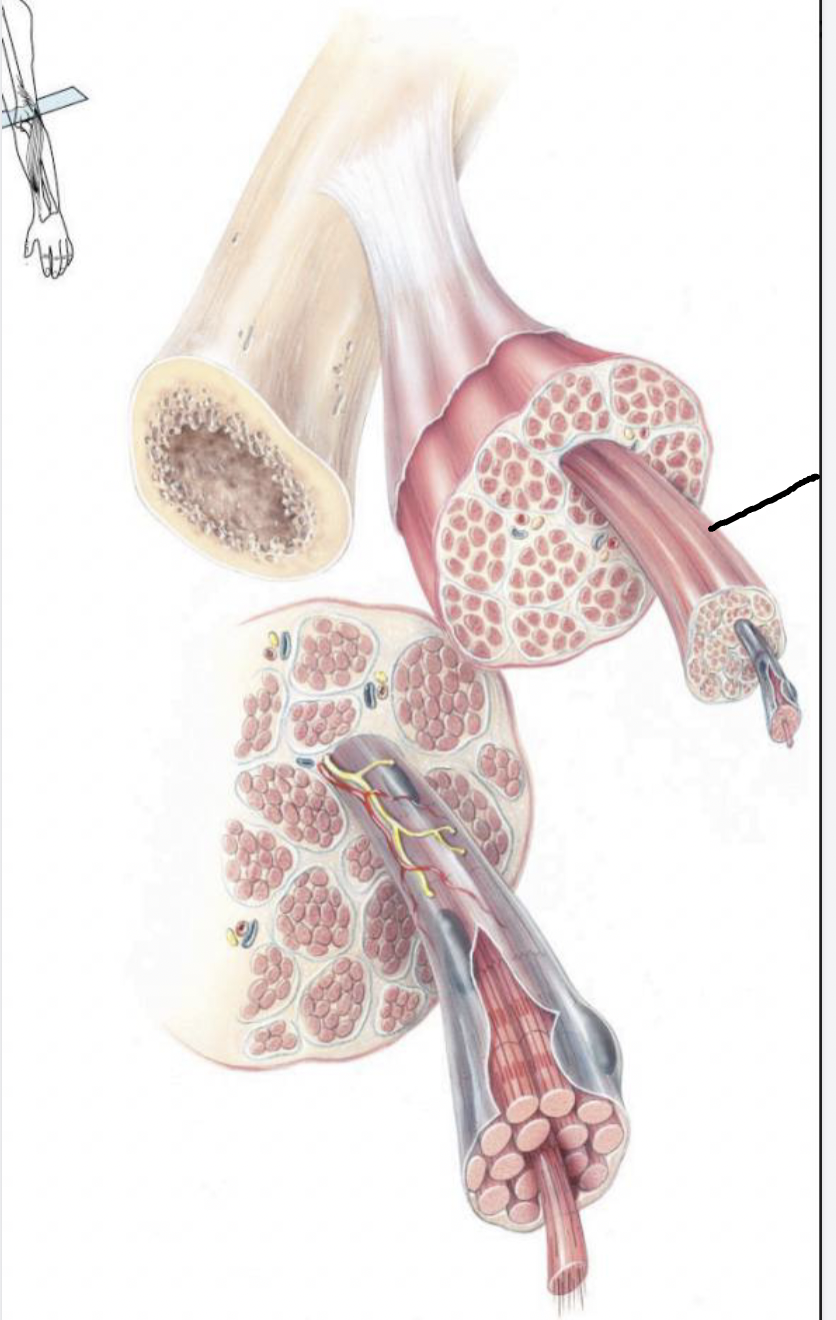
what muscle feature is this?!
fascicle
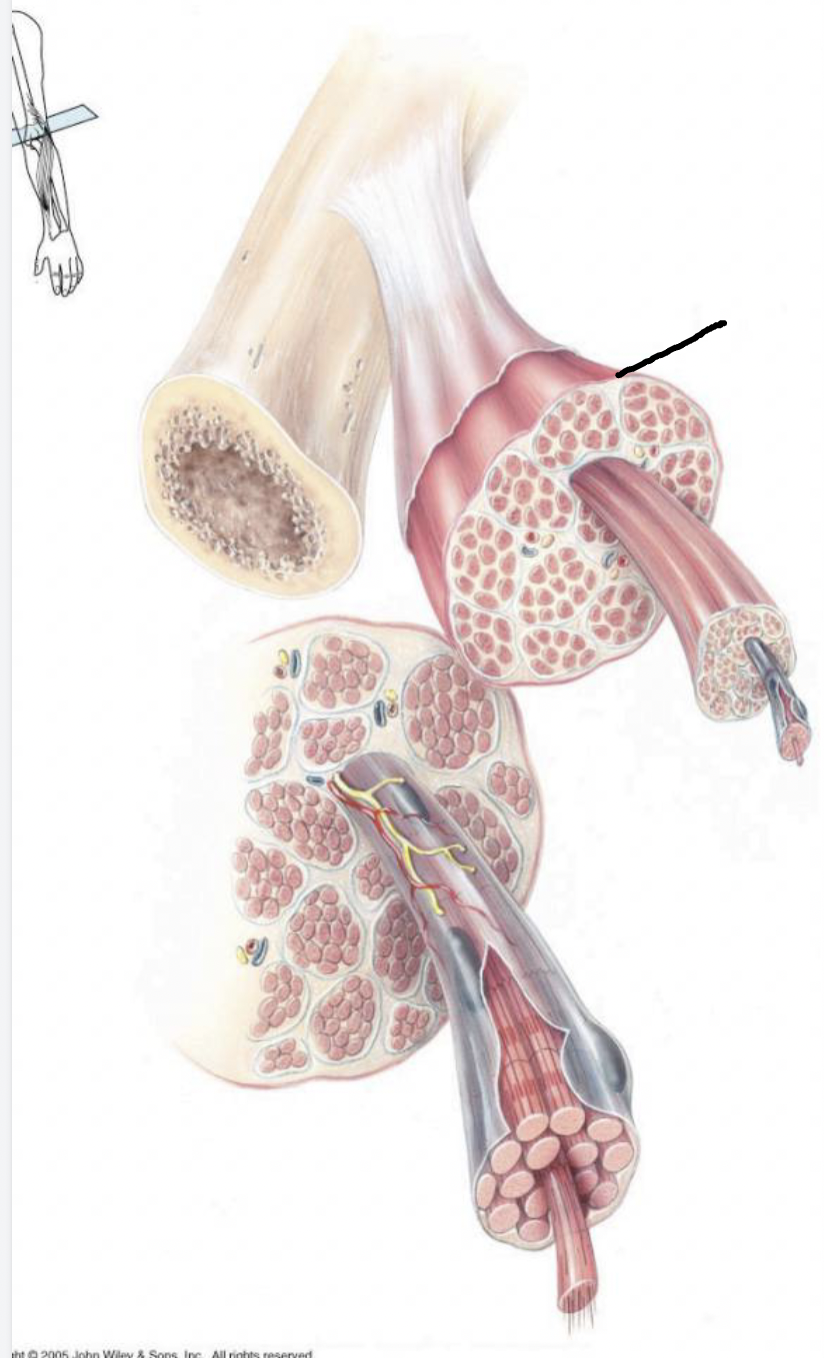
what muscle feature is this?!
epimysium
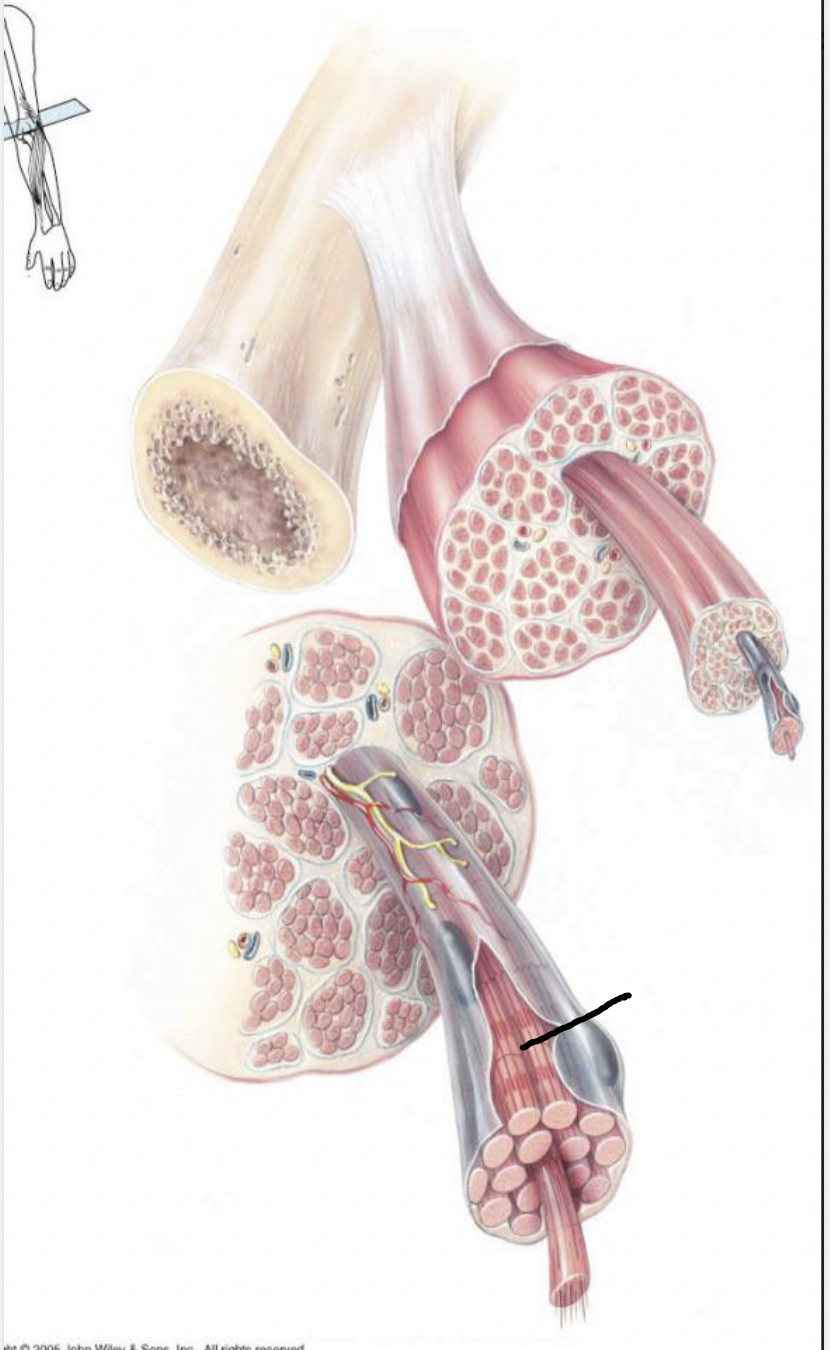
what muscle feature is this?!
muscle fiber/cell
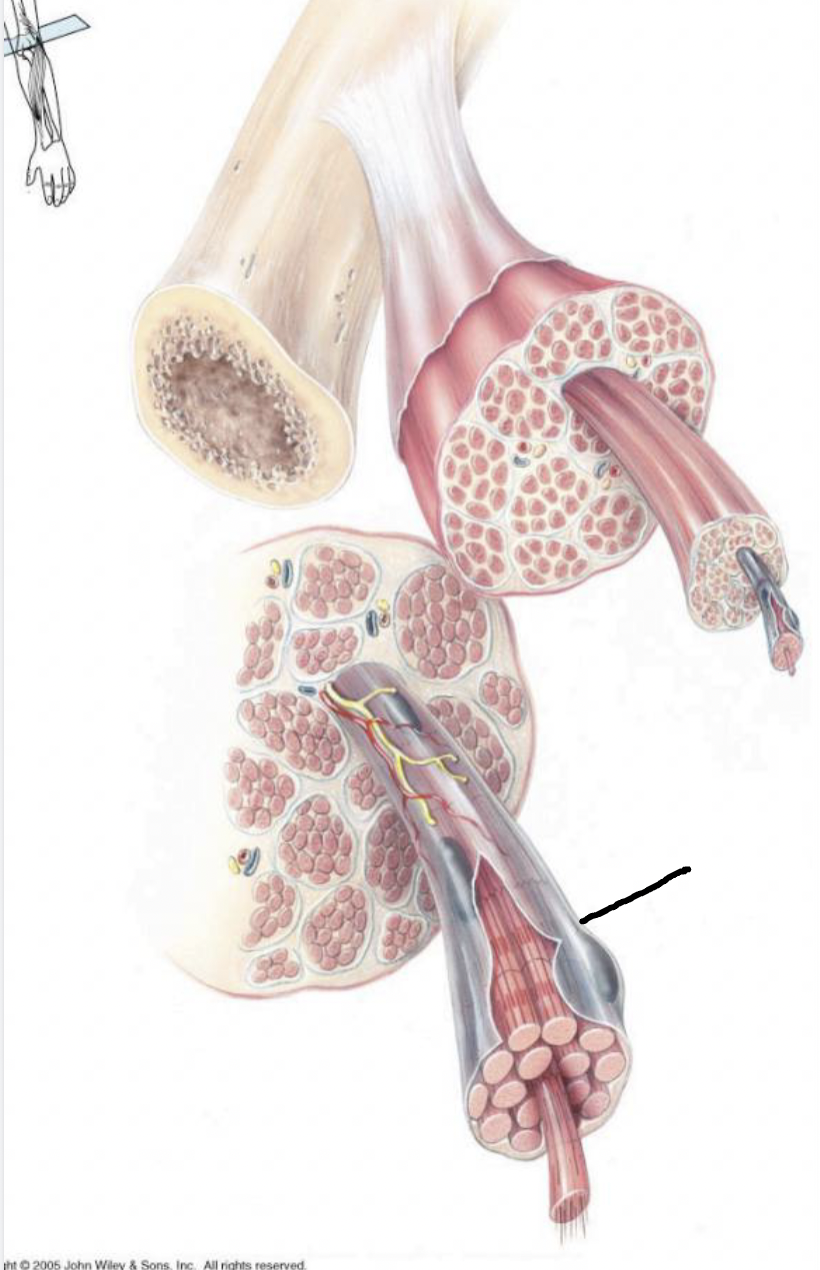
what muscle feature is this?!
endomysium
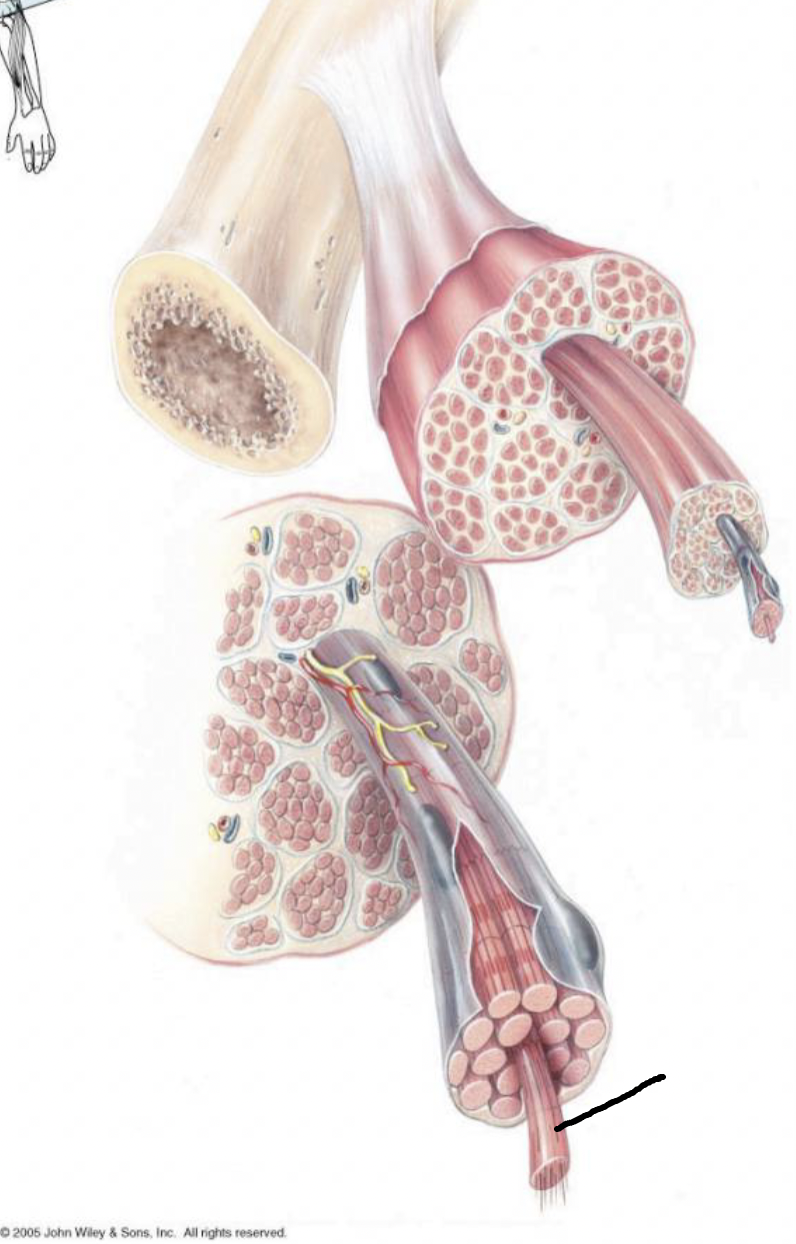
what muscle feature is this?!
myofibril
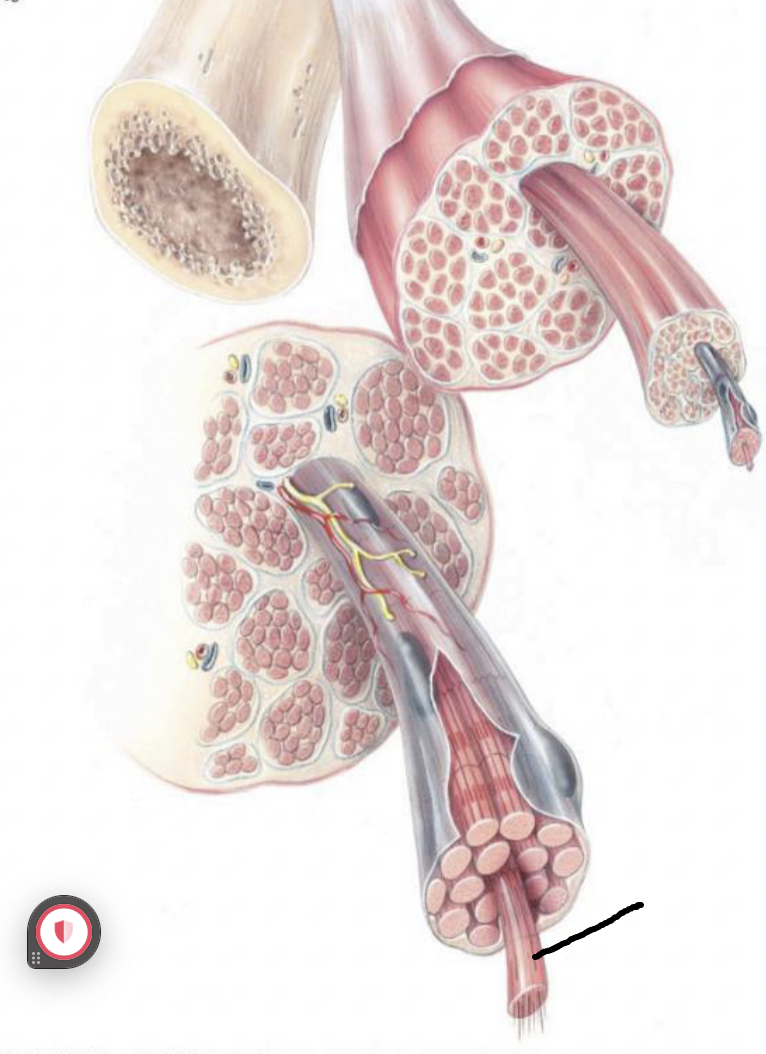
what muscle feature is this?! (covering)
perimysium
Epimysium
fibrous connective tissue covering the entire muscle unit
continuous with tendon
Perimysium
fibrous connective tissue covering the fascicle
Endomysium
fibrous connective tissue covering the muscle fiber (each cell)
Tendon
fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
continuous with periosteum to convey force of contraction to bone
Aponeurosis
thin sheet of connective tissue connecting muscles to bone
-similar to tendons
Fascicle
bundle of fibers surrounded by perimysium
Myofibrils
the contractile elements separated into sarcomeres
bundles of protein within a cell
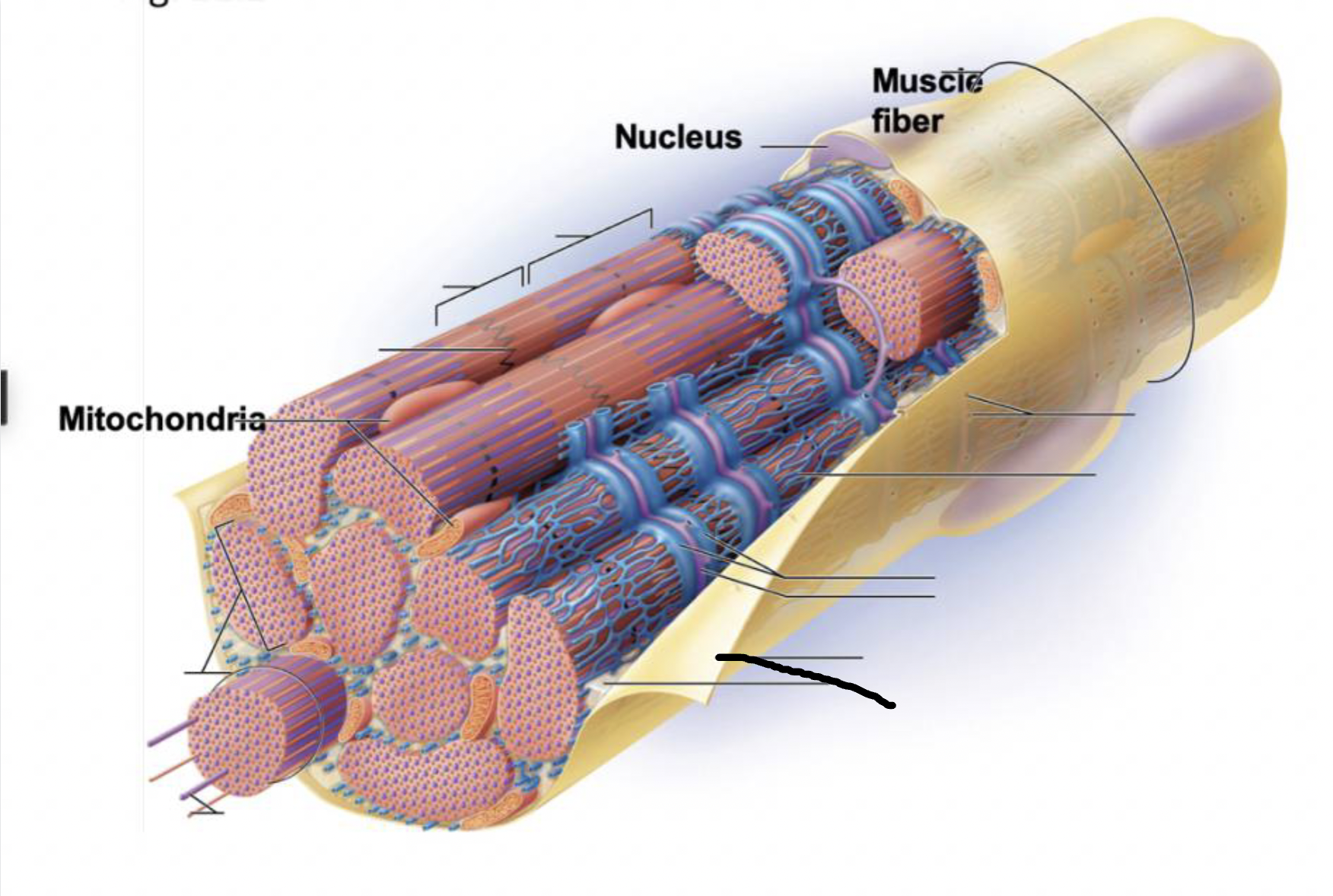
what muscle feature is this?!
sarcolemma
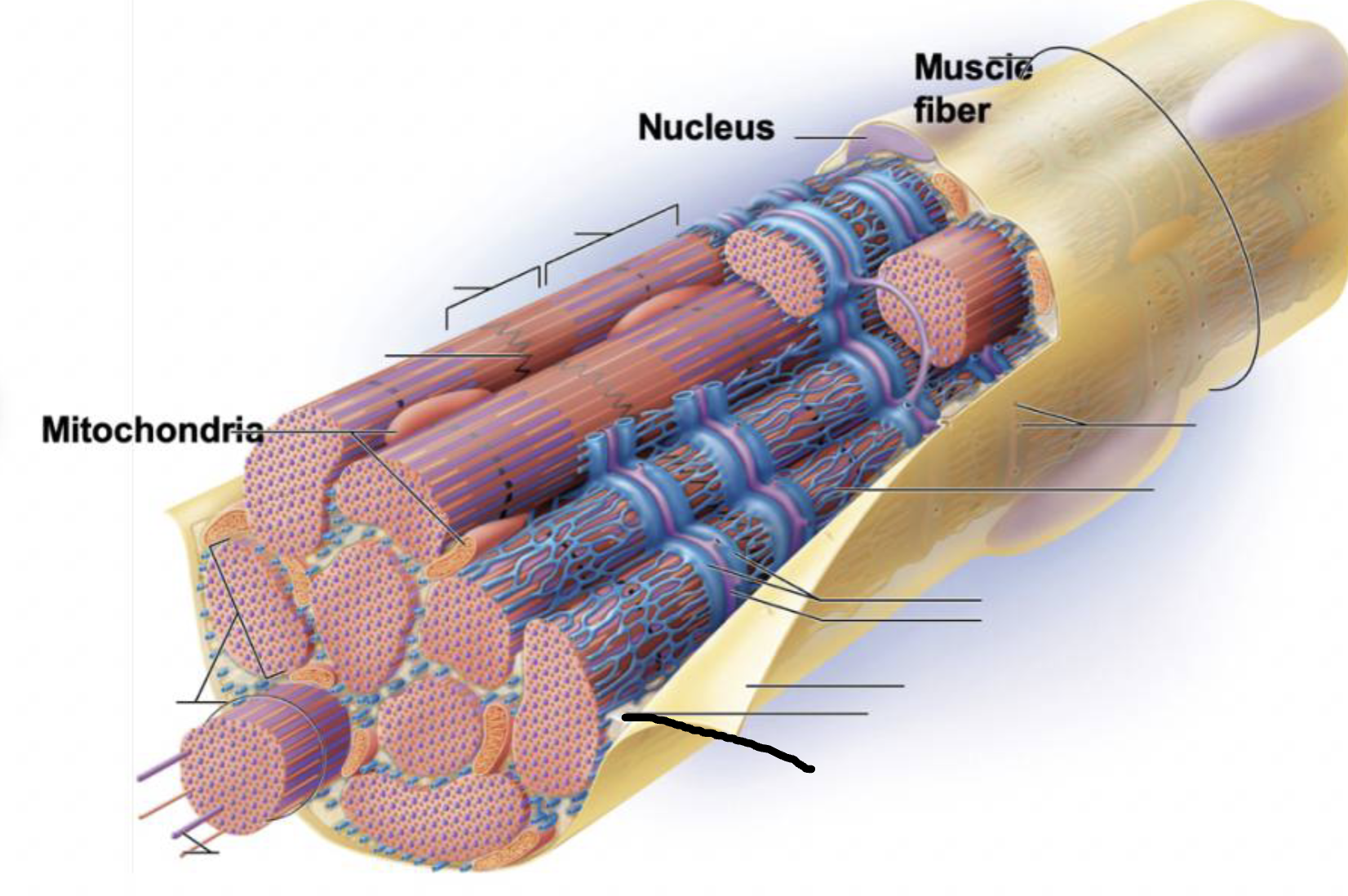
what muscle feature is this?!
sarcoplasma
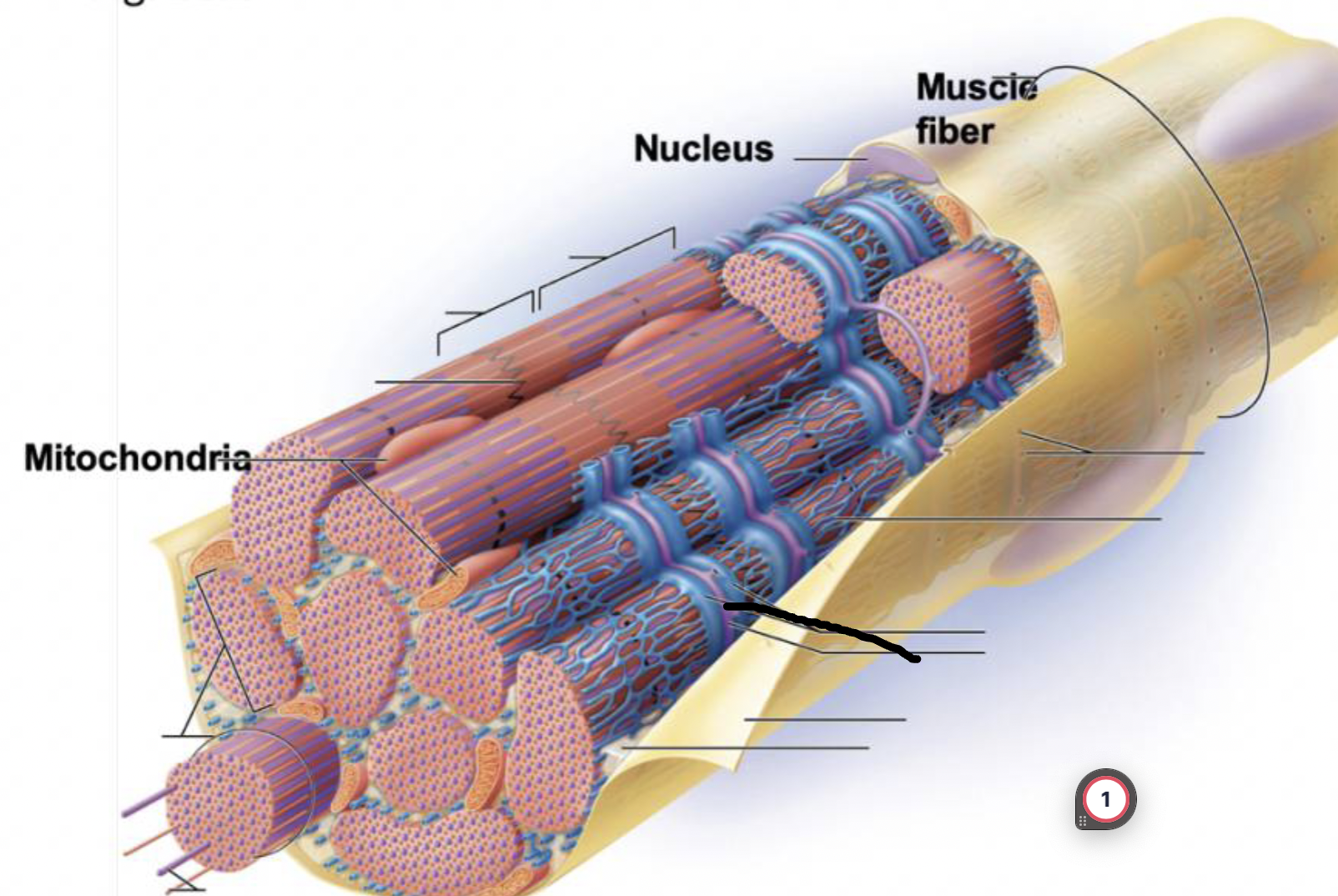
what muscle feature is this?!
transverse tubule
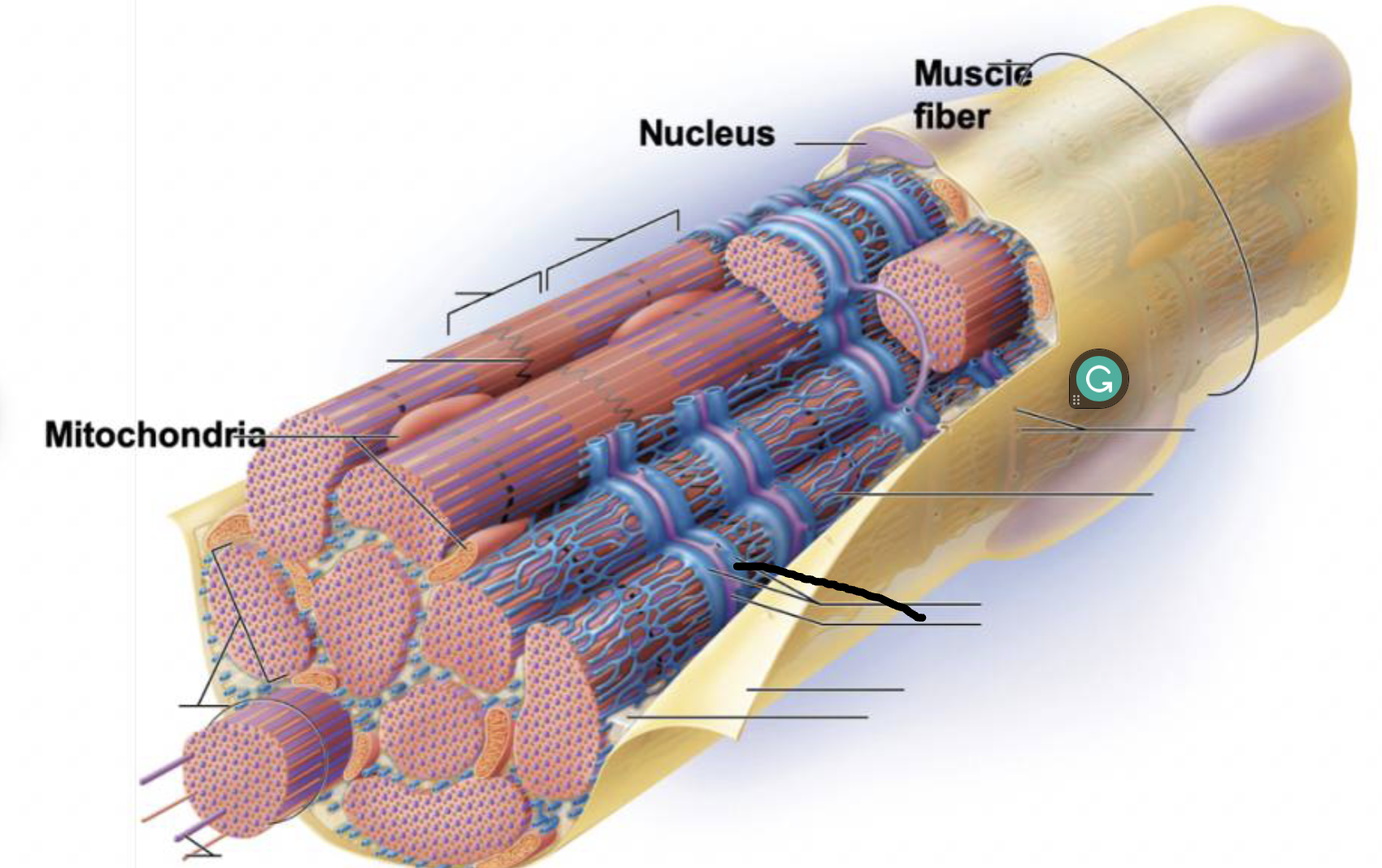
what muscle feature is this?!
terminal cisternae
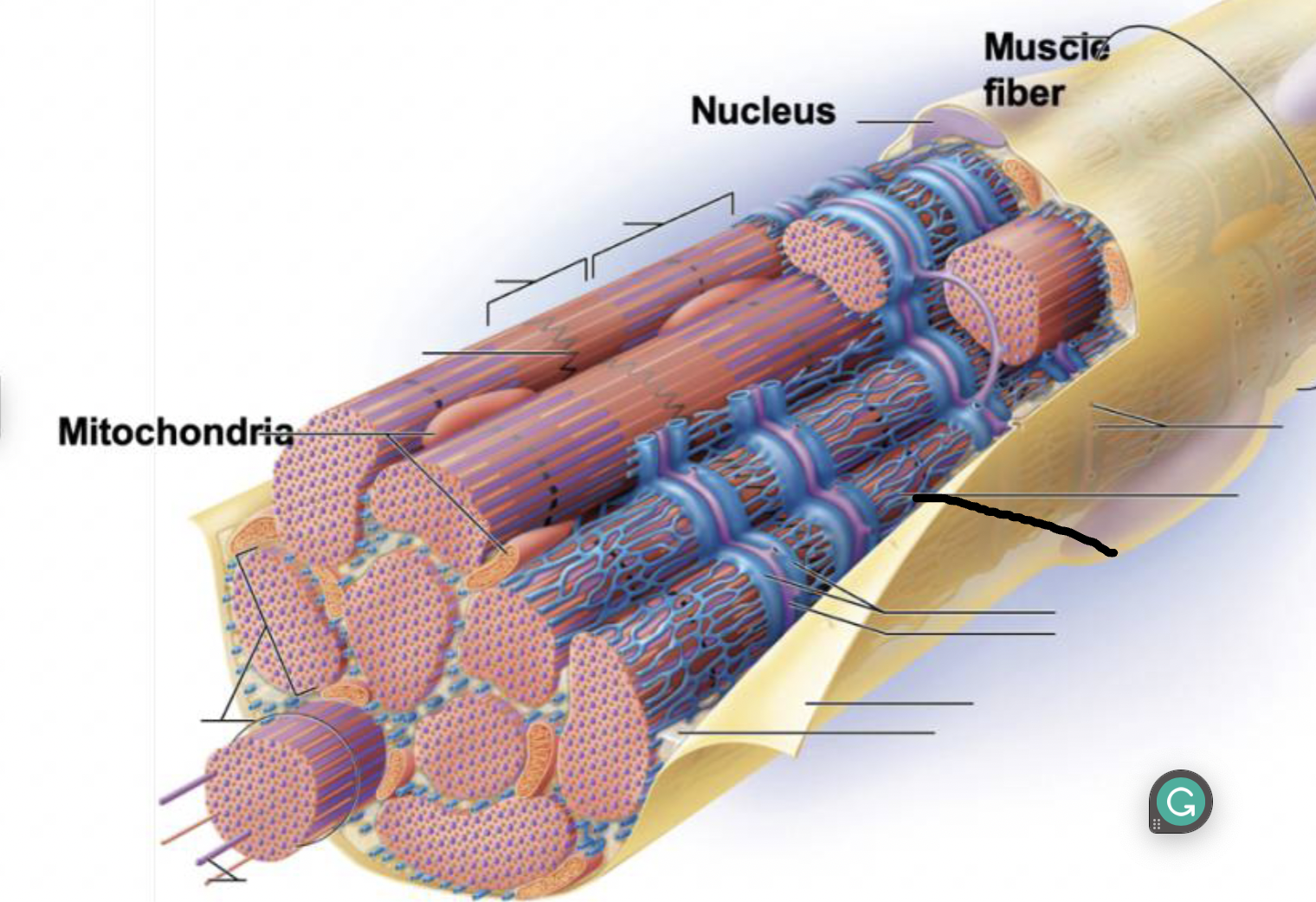
what muscle feature is this?!
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
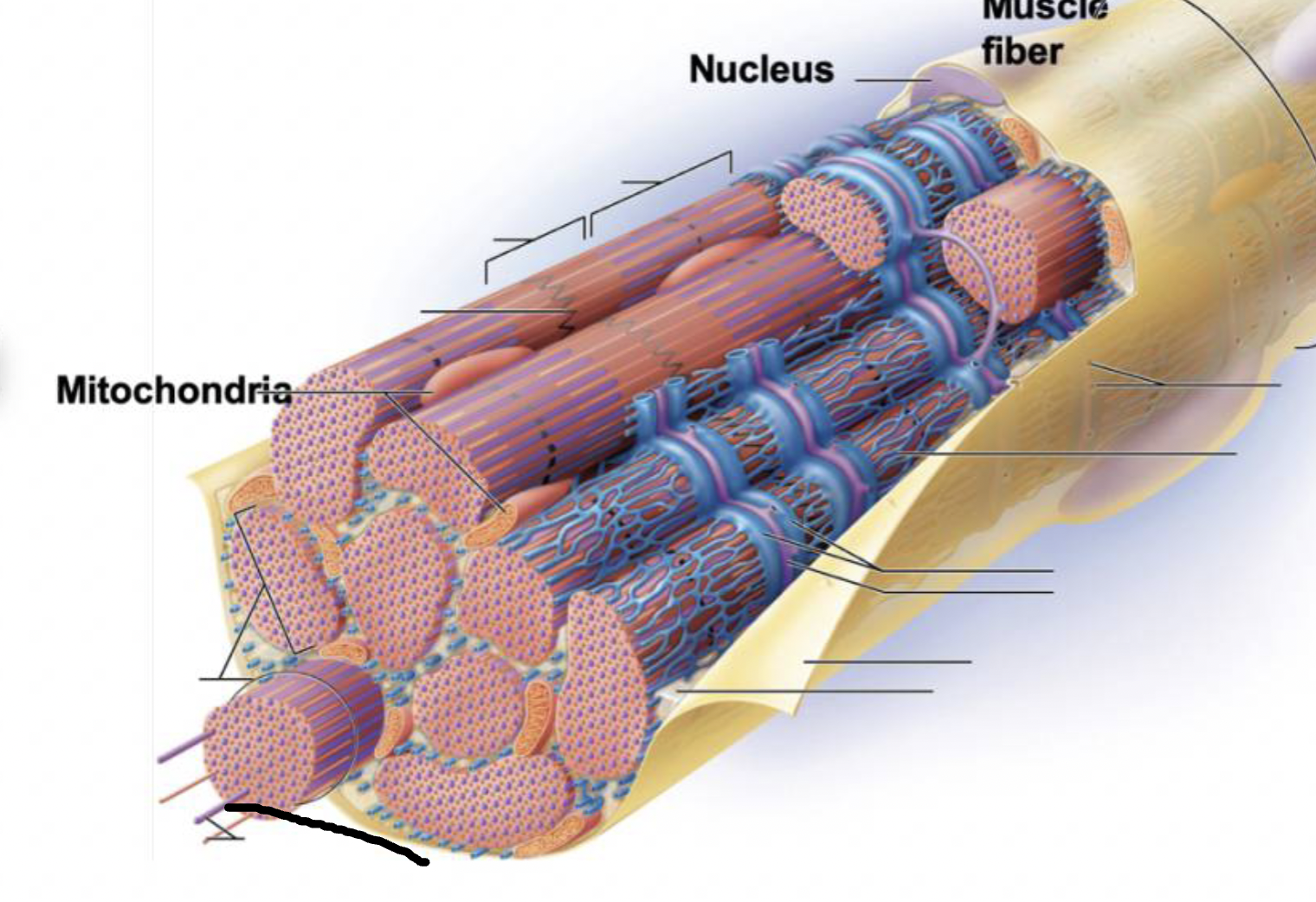
what muscle feature is this?!
myofilaments
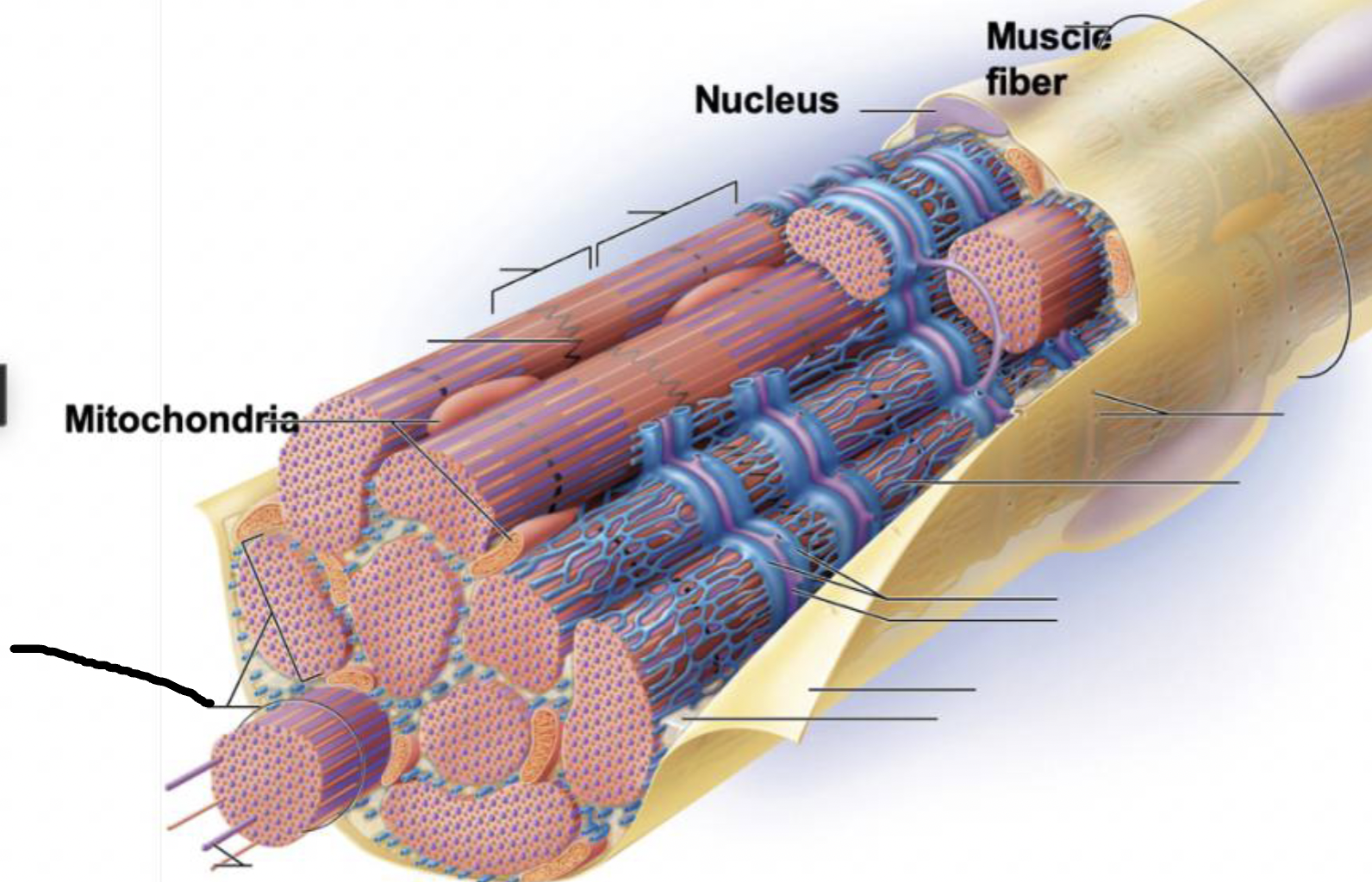
what muscle feature is this?!
myofibril
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane deep to the endomysium, covering entire muscle cell
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of muscle fiber
not a lot of it, encases myofibrils
contains glycogen and myoglobin
T-tubules
infolding of sarcolemma penetrating through the cell
associate with 2 terminal cisternae of SR to form a triad
convey electrical signals deep into muscle cell
Myofibrils
long protein cords that contract- composed of myofilaments
thick, thin, and elastic
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
smooth ER surrounding myofibril
stores calcium and end in terminal cisternae
Sarcomere
1 unit of myofibril from one Z-disc to the next
contractile unit
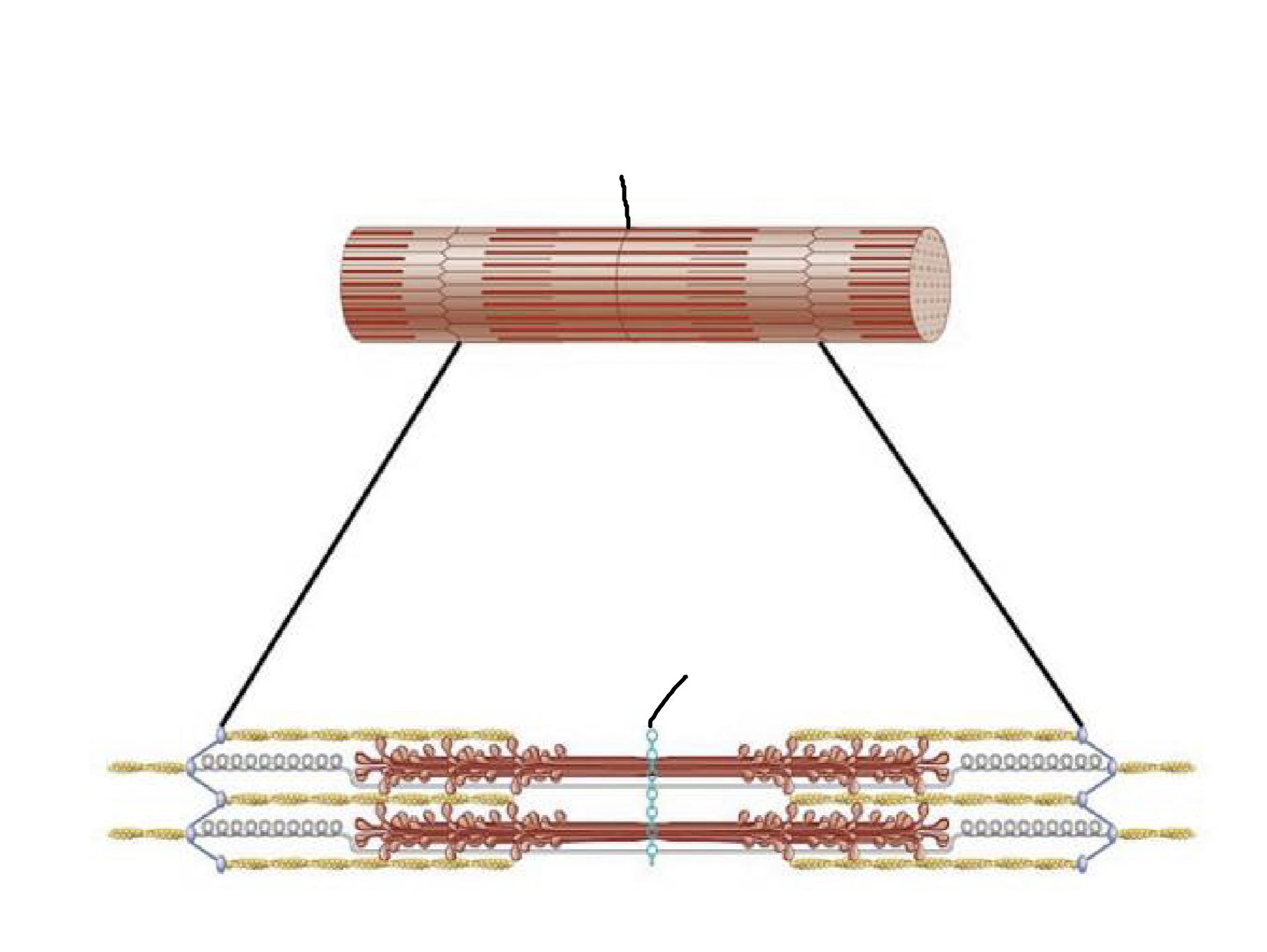
what muscle feature is this?!
M-line
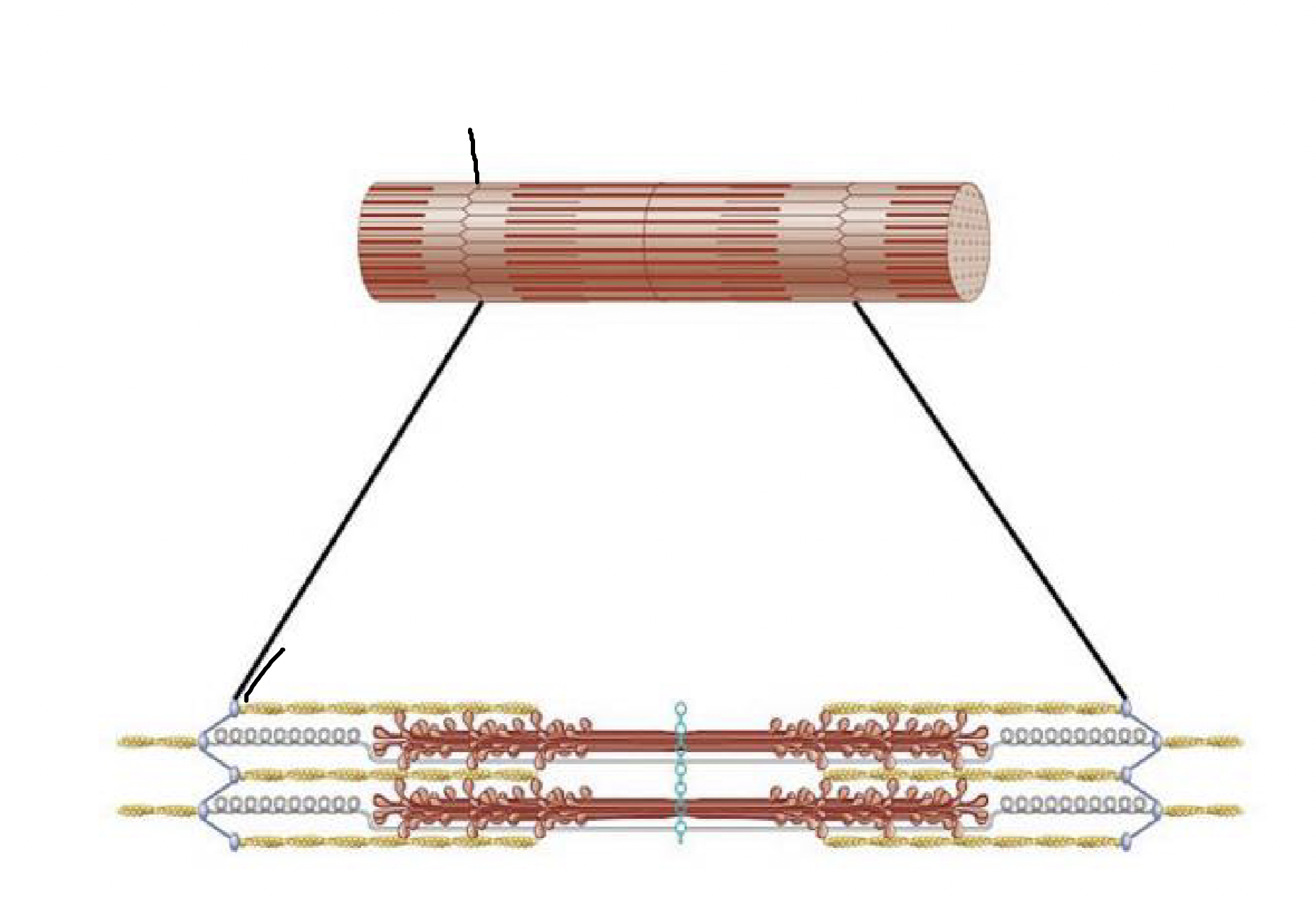
what muscle feature is this?!
Z-disc
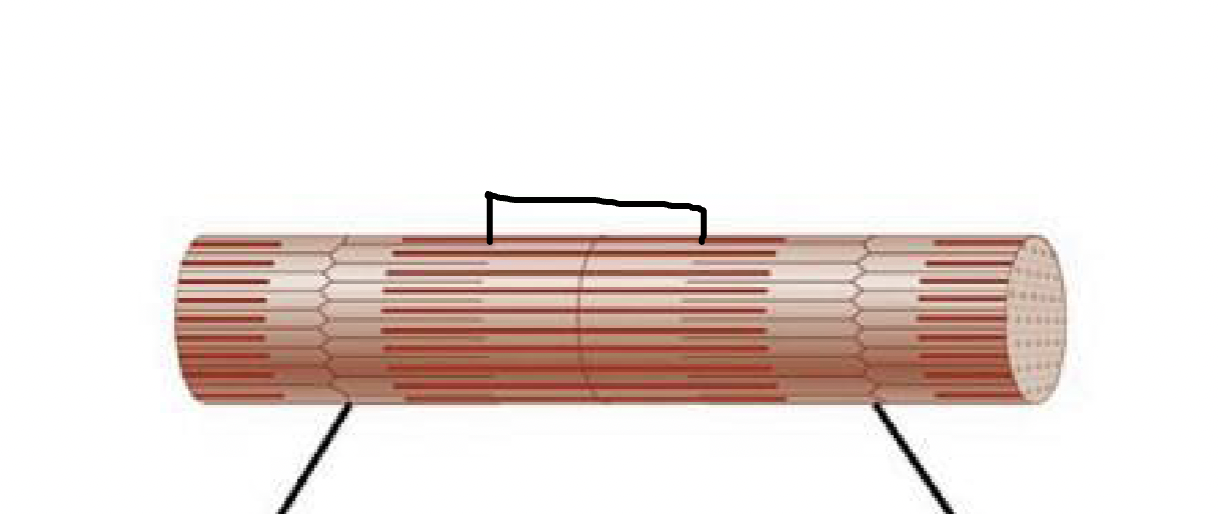
what muscle feature is this?!
H-zone
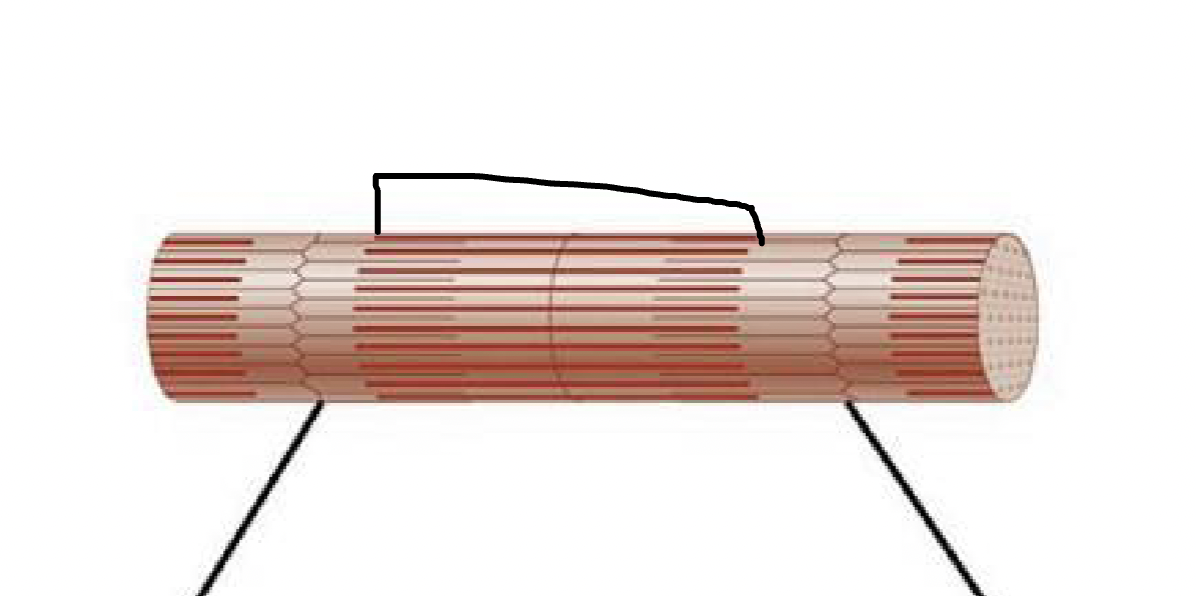
what muscle feature is this?!
A-band
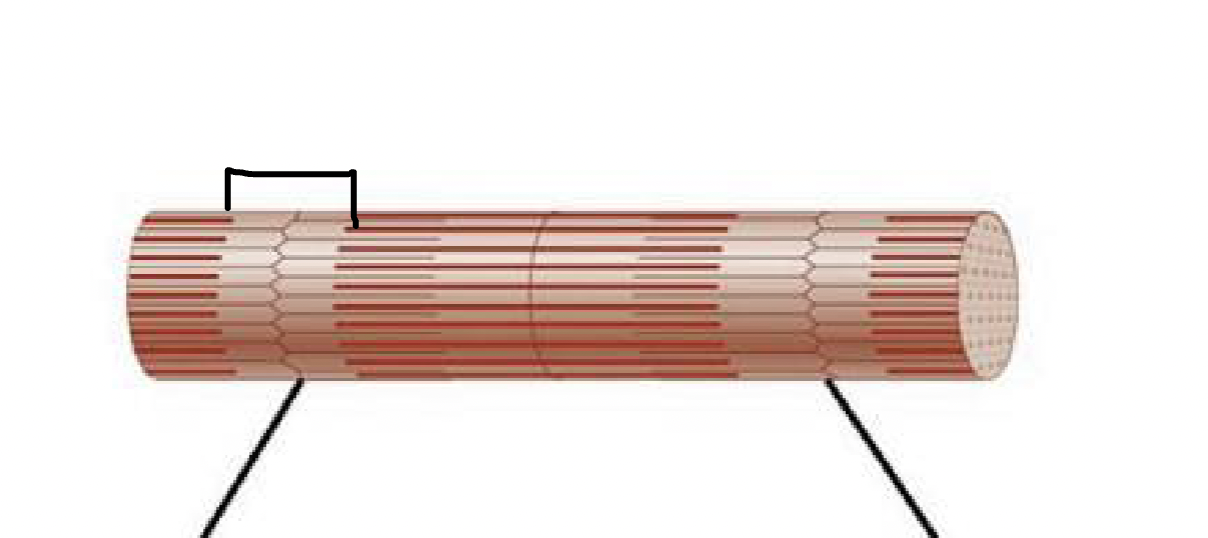
what muscle feature is this?!
I-band
A Band
composed of overlapping thin and thick filaments except in the H zone (just thick)
-bisected by M-line
I band
composed of thin filaments
bisected by Z-line
What are thick filaments made of? describe the orientation
made of myosin
myosin dimerizes and each has a globular head and long fibrous tail
the myosin head stick out of the filament everywhere except the H-zone, ready to bind to actin
What are thin filaments made of? describe the orientation
made of actin, troponin, and tropomyosin
actin is the main globular protein that looks like a pearl necklace
has an active site for myosin
troponin has a binding site for calcium
when attached, rolls tropomyosin off of actin active side to initiate contraction
tropomyosin blocks the actin active site
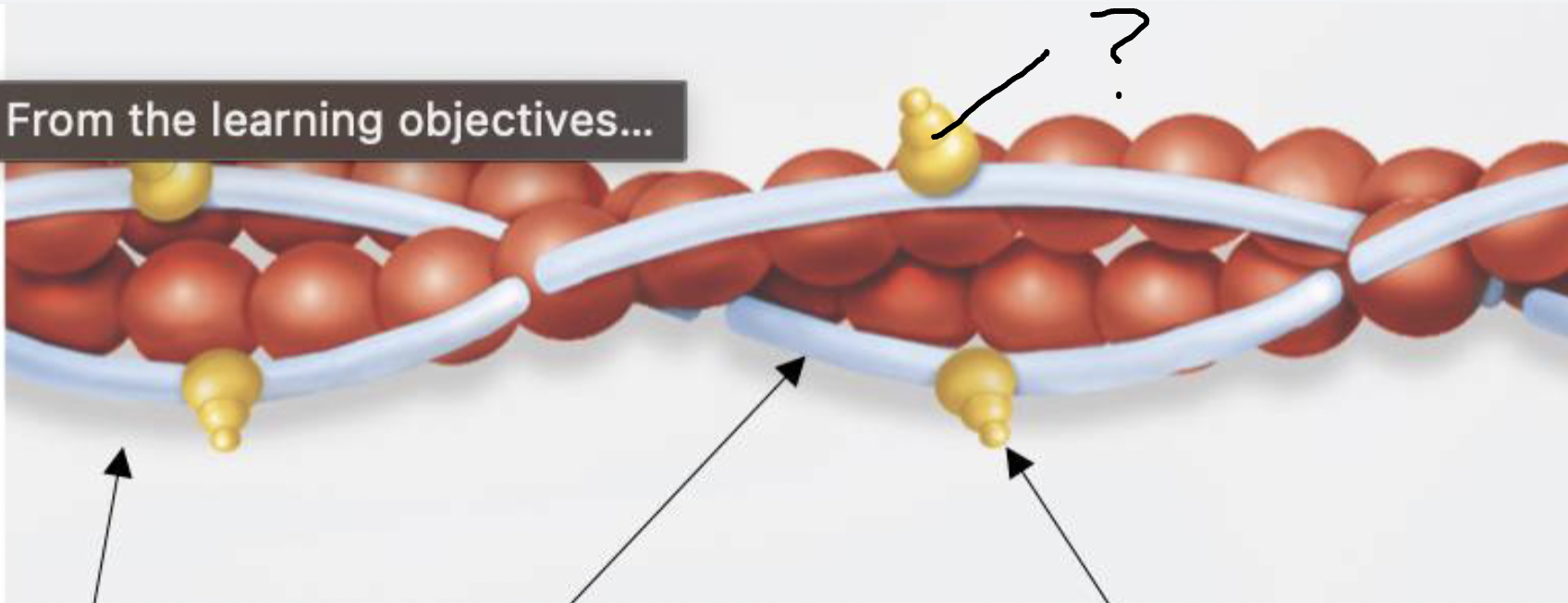
what is this?
troponin of thin filament
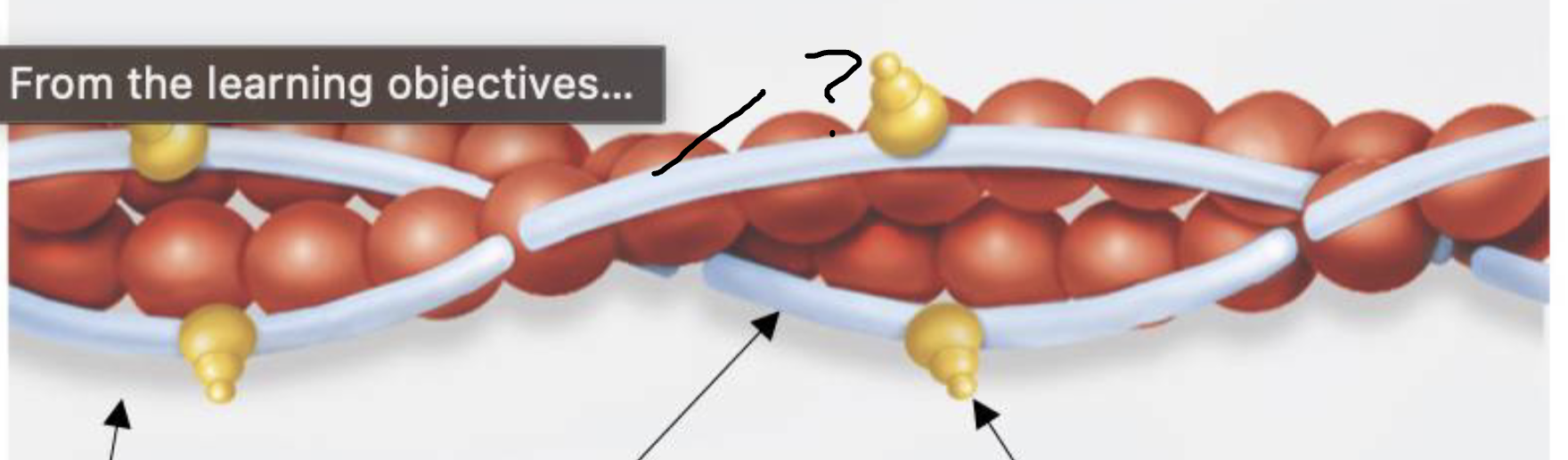
what is this?
tropomyosin of thin filament
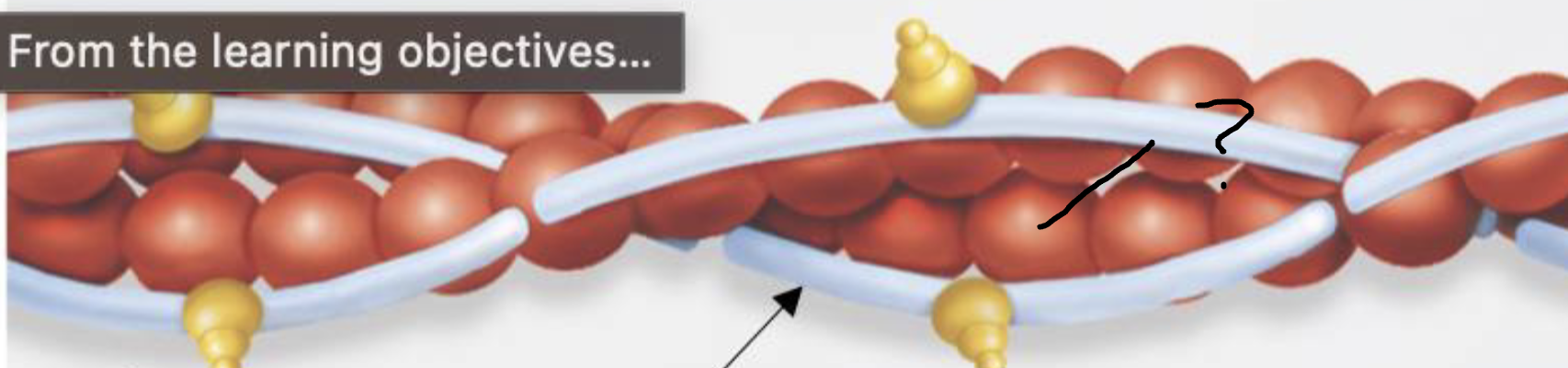
what is this?
actin of thin filament
What part of sarcomere moves during contraction?
thin filaments
pulls Z-disc toward midline to shorten sarcomere
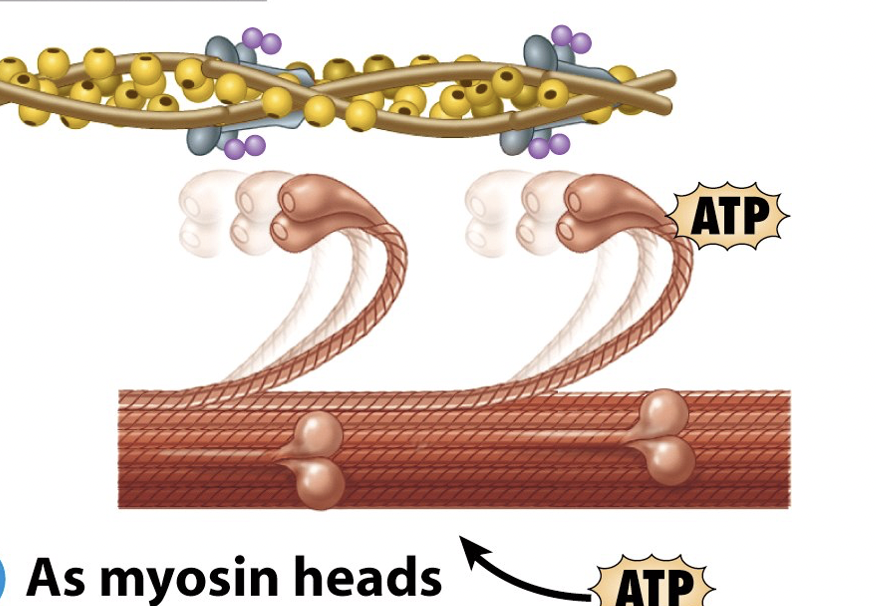
What is the first step of sliding filament theory?
Myosin heads hydrolyze ATP into ADP and P
heads pivot to enter high energy state
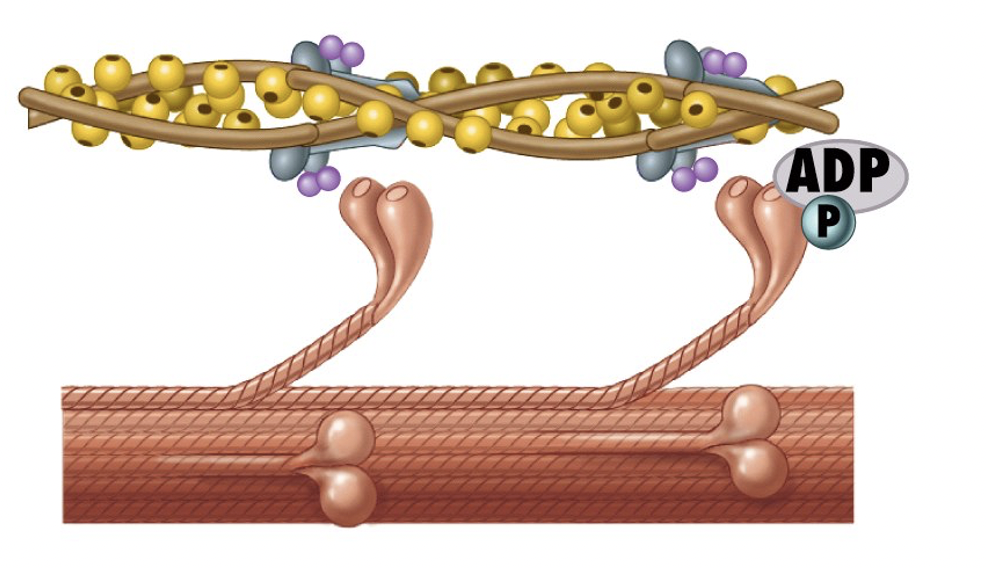
What is the second step of sliding filament theory?
after hydrolyzing ATP, myosin binds to actin to form crossbridges
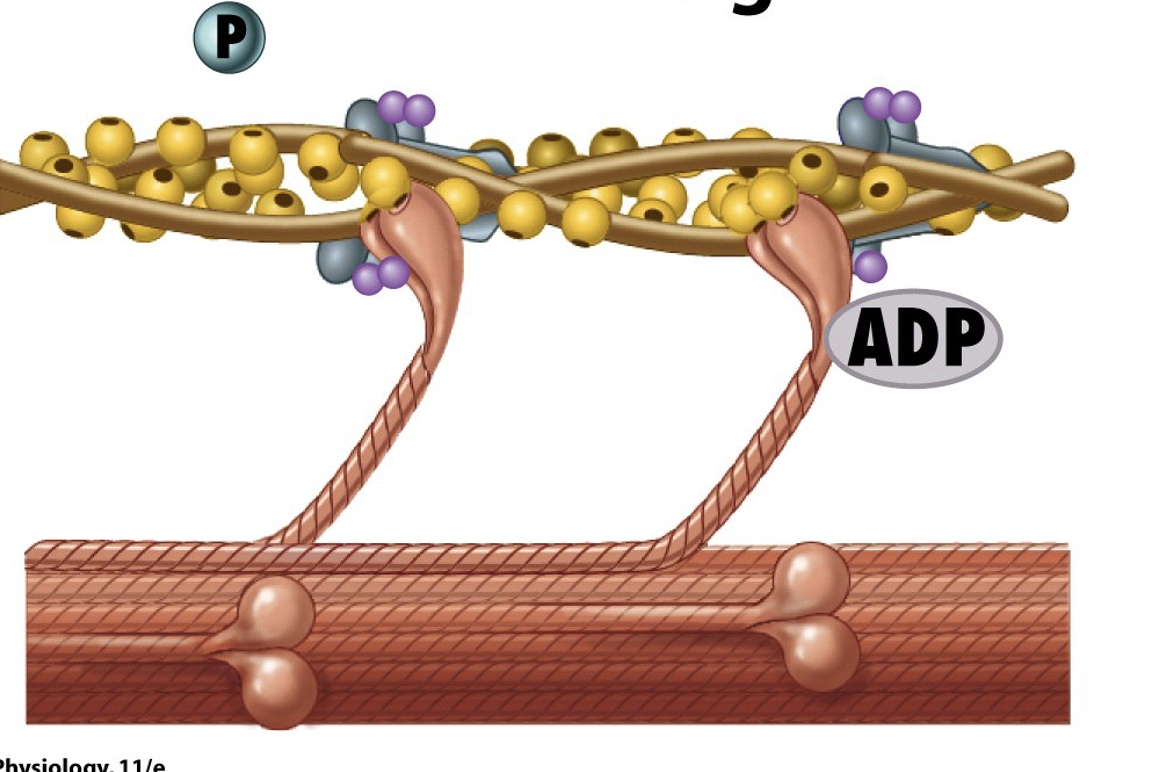
What is the third step of sliding filament theory?
myosin cross-bridges rotate toward the center of the sarcomere - called the power stroke
ADP and P are released
myosin rotates and pulls actin with it
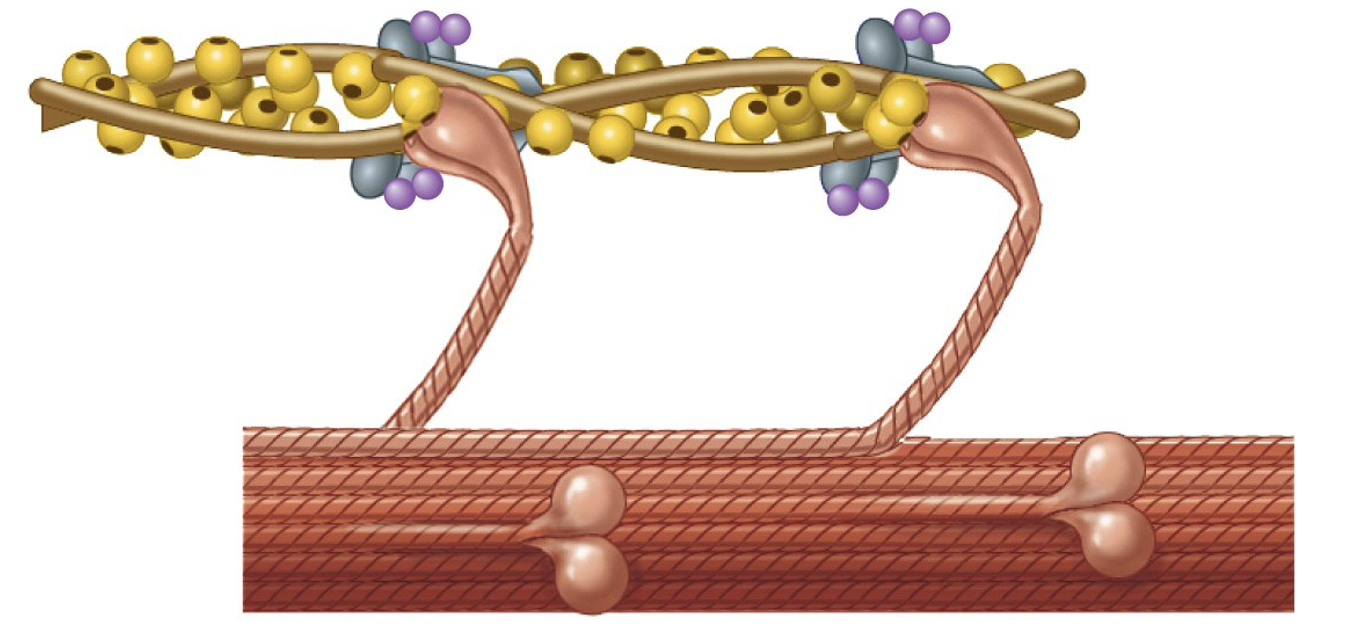
What is the fourth (final) step of sliding filament theory?
Myosin head binds to ATP and the cross-bridges detach from actin
Resting Membrane Potential
maintained by the sodium-potassium pump, it is the transmembrane potential when the cell is at rest
separation of charges where inside of the cell is more negative
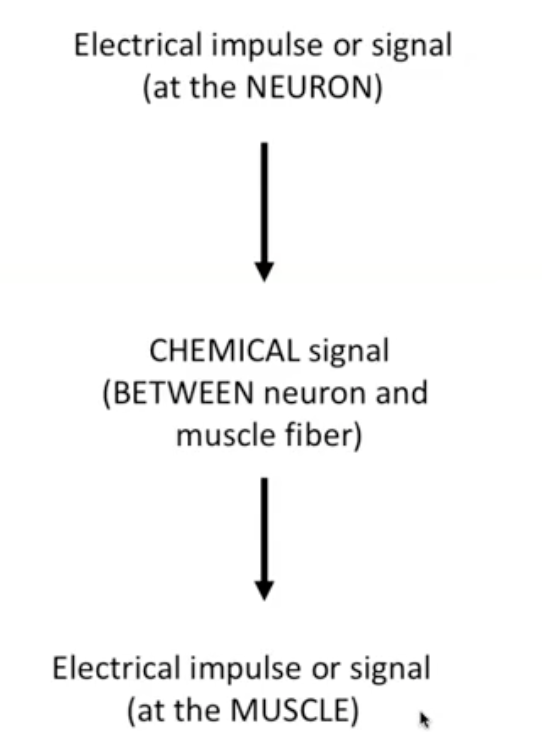
What tells myofibril to shorten?
electrical impulse in neuron → chemical signal at neuromuscular junction → electrical impulse travelling along sarcolemma
Action potential
all-or-nothing electrical signal produced by ion movements across the membrane of excitable tissues
causes excitation of muscle cell
Neuromuscular Junction
way of communicating between the nervous system and muscular system along the synaptic cleft
Acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) is released from neurons and exits in vesicles via exocytosis
binds to receptors on muscle cell → generating electrical signal that tells muscle to contract
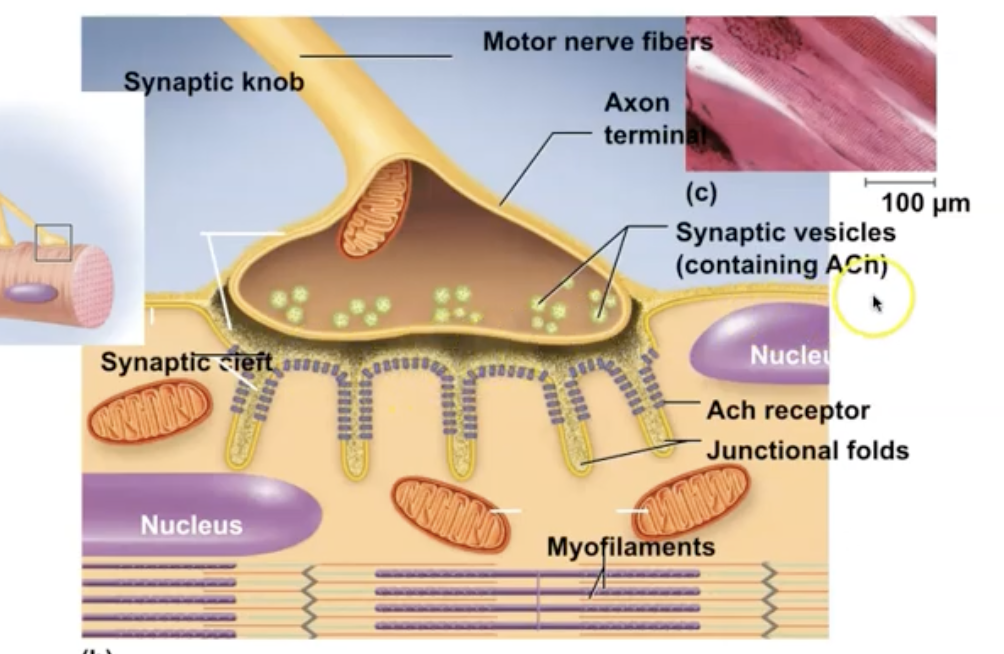
Acetylcholinesterase
an enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter ACh to terminate the signal that causes muscles to contract
Steps of Action Potential
start at resting potential
Na+ and K+ channels closed
Depolarization
Na+ channels open, Na+ enters the cell, K+ channels beginning to open
Depolarization ends, repolarization begins
Na+ channels closed, K+ channels fully open, K+ leaves the cell
Repolarization/ hyperpolarization
Na+channels closed, K+ channels closing
Threshold
voltage that must be reached to enact all or nothing action potential
Depolarization
membrane potential becomes very positive
opening of Na+ voltage-gated channel → Na+ rushes into the cell
Repolarization
membrane potential quickly decreases
K+ exits the cell when opening voltage-gated K+ channel
cell becomes more negative again
Hyperpolarization
voltage goes below resting membrane potential because potassium channels are slower to respond
eventually evens out to resting membrane potential
Absolute refractory period
can’t respond to any stimulus because channels are already open and responding to a different stimulus
during depolarization and repolariztion
Relative refractory period
could respond to a stimulus, but it has to be larger
during the hyperpolarization phase when voltage is more negative, it takes more to reach the threshold
Excitation-contraction coupling
sequence of events by which an electrical signal leads to sliding of microfilaments
How is AcH released during excitation?
exocytosis
What kind of receptor is acetylcholine receptors?
ligand-gated ion channels
-then, na+ flows in and K+ flows out at the same time to produce a local potential
How does the charge from an action potential get down into the cell?
t-tubules , Ca2+ then stored in SR→ diffused into cytoplasm
What is happening during relaxation of a muscle?
troponin holds tropomyosin in position to block myosin binding site on actin
Calcium channels are closed
What is happening during contraction of a muscle?
Ca2+ binds to troponin which changes shape of the troponin-tropomyosin complex and uncovers myosin binding sites on actin
Ca2+ channels open
Length-tension relationship
length of the sarcomere at rest affects the amount of force generated by a muscle contraction
optimal length of 80-120 results in the highest tension
gives best overlap between thin filament and place where myosin heads are exposed
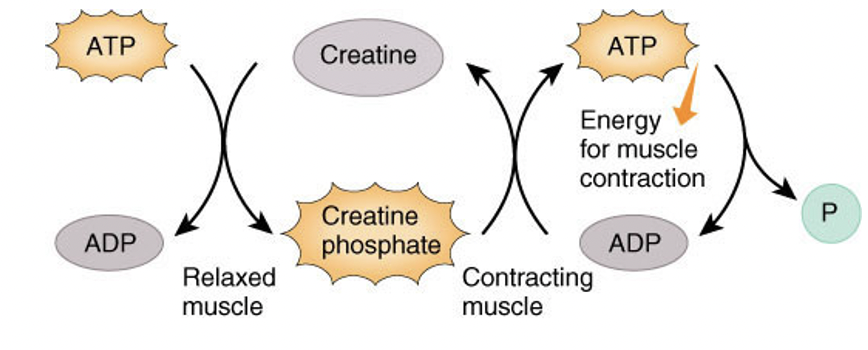
Creatine phosphate pathway
stores ATP as ADP and adds a phosphate (From creatine phosphate or ADP) back to ATP when energy is needed
quickest pathway, but very limited and short bursts
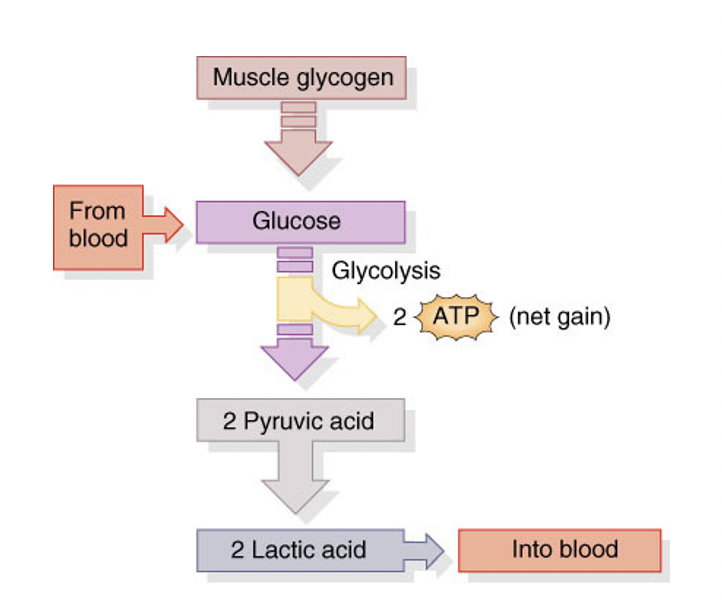
anaerobic respiration
generates ATP from a pathway that uses glucose for glycolysis, forming 2 ATP, lactic acid, and pyruvic acid
a lot of steps, very little product
used in the short-term
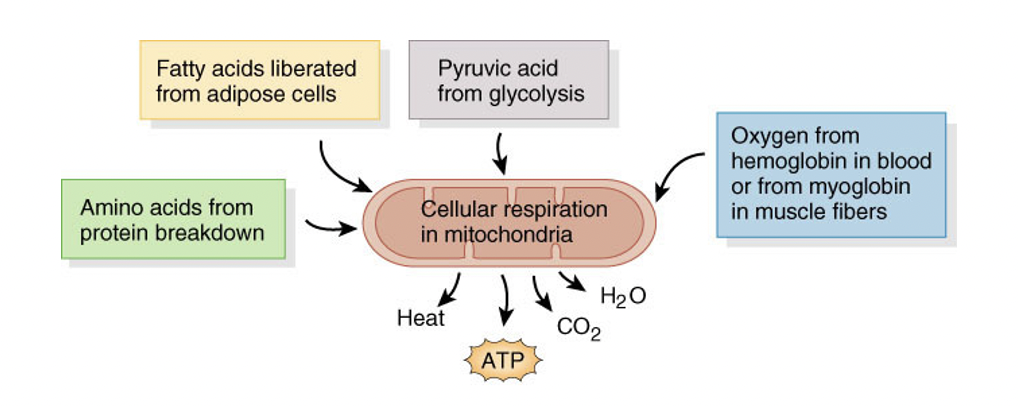
aerobic respiration
generates 34-36 ATP, along with heat, CO2,H20
can be other things rather that glucose going into pathway
requires oxygen to carry out cellular respiration in the mitochondria
motor unit
a motor neuron plus all muscle fibers innervated by it
twitch contraction
when all of motor unit contracts in response to single action in a neuron
Contraction period
Ca2+ binds to troponin
active sites exposed on actin
cross-bridges form
filaments slide toward the m-line
**The actual shortening of the muscle cell-
Relaxation period
decreased tension after contraction
Ca2+ removed from sarcpllasm and stored in the SR
troponin changes conformation
tropomyosin occludes active sites
cross bridges dissociate
filaments slide away from midline
Latent period
when the action potential depolarizes sarcolemma
tension formed
Ca2+ released from SR, and increases in sarcoplasm
wave summation
stimulation delivered to a muscle fiber before it is completely able to relax
no latent period because Ca+ is already i sarcoplasm and shortened elastic elements
results in more forceful contraction
Fused tetanus
during wave summation, if stimuli are frequent enough -results in a stable contraction force
unfused is the in between
Isotonic contractions
muscle retains the same amount of tension, but changes in length to maintain a load
aids in movement
two types are eccentric and concentric
Concentric contraction
type of isotonic
muscle shortens to lift load
ex. flexing bicep
Eccentric contraction
type of isotonic
muscle lengthens to lift load
ex. extending arm to put groceries on the counter
Isometric contraction
“same measure” - muscle stays the same length while developing tension
doesn’t actually move a load, but has stabilizing effect
ex. holding a yoga pose
Slow oxidative fibers
red fibers, slow fibers, slow-twitch fibers
contract/hydrolyze ATP more slowly through aerobic respiration
has blood vessels that contribute to red color
very fatigue resistant- prominent in marathon runner
Fast Glycolytic Fibers
white fibers. fast-twitch fibers
uses glycolysis to quickly generate ATP
no blood vessels to deliver oxygen → white
very fast contraction but not fatigue resistant - prominent in sprinters
Fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers
an intermediate
uses both glycolytic and oxidative pathways to generate ATP
pinkish color
fast AND fatigue resistant
Factors that affect tension
length of sarcomere befor contraction
frequency of stimulation
hydration status
temperature
fatigue
Compare the diameter of each fiber type
SO: smallest
FO: intermediate
FG: largest
Compare the fatigue resistance of each fiber type
SO: high
FO: intermediate
FG:low
compare the myoglobin content of each fiber type
SO: large amount
FO: large amount
FG: small amount
Compare the capillary supply of each fiber type
SO: many
FO: many
FG: few
same trend with mitochondria
name the structure of smooth muscle cell
intermediate filament
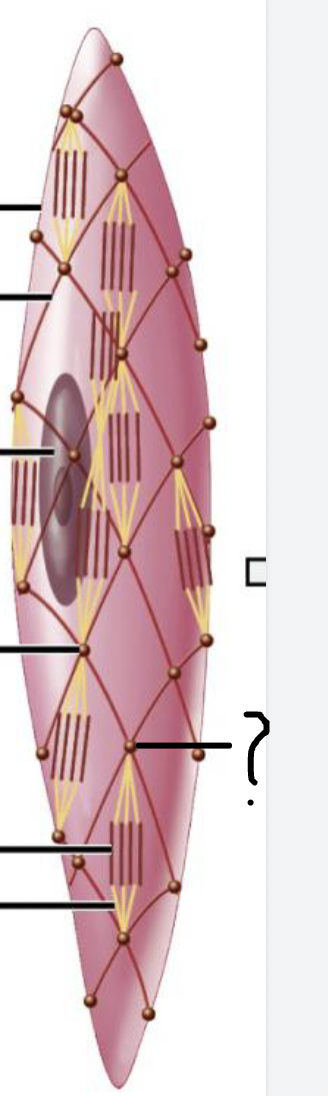
name the structure of smooth muscle cell
dense body
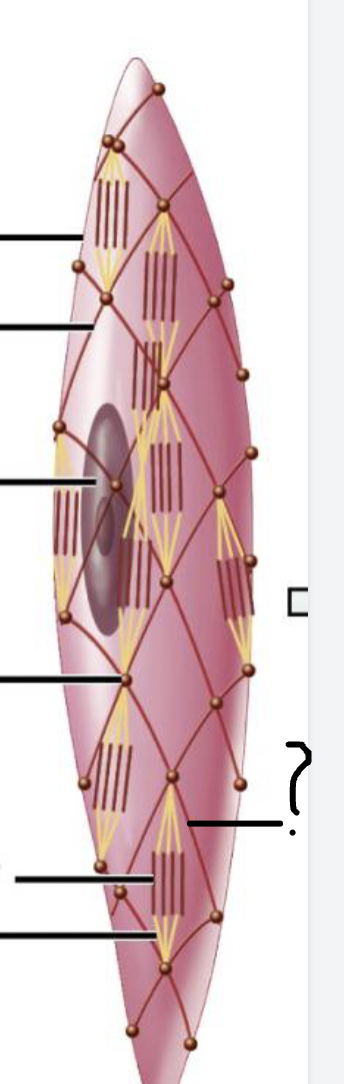
name the structure of smooth muscle cell
thin filament
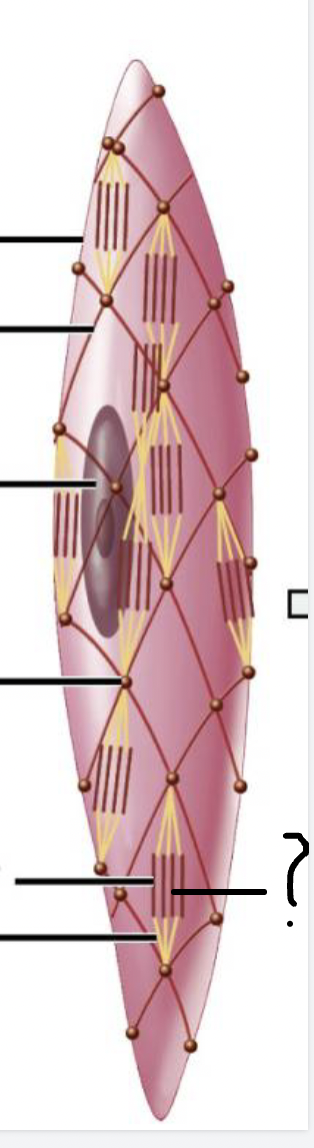
name the structure of smooth muscle cell
thick filament
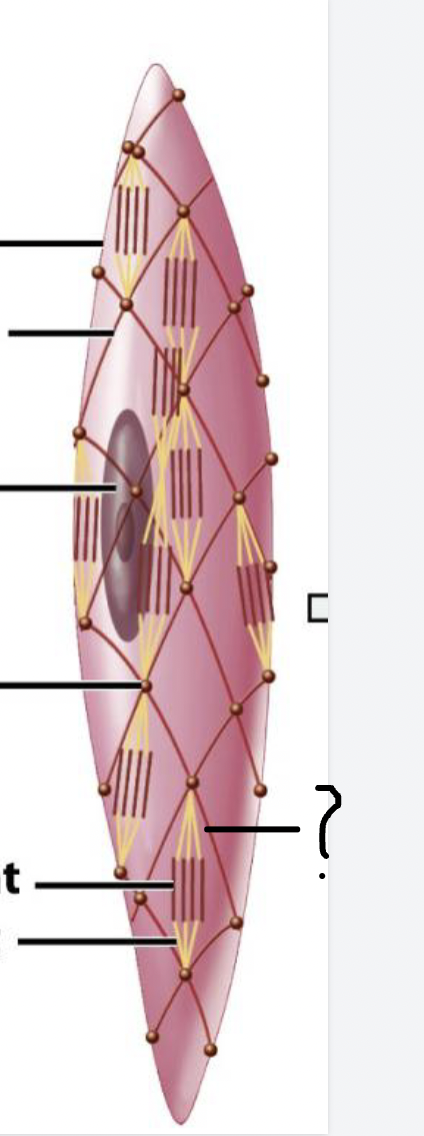
Features of a smooth muscle cell
single nucleus
- tapered fusiform shape
intermediate filaments connected by dense bodies
no striations
Role of dense bodies
connect thin filaments to intermediate filaments like a fishnet
similar to the Z-disc
Calmodulin
analogous to troponin in skeletal muscle
binds to Ca2+ to become activated
then activates myosin light chain kinase enzymes