6 NSAIDs, steroids, and small molecules
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
what is the target enzyme of NSAIDs
COX 1 and COX2
what is the difference b/w selective and non-selective NSAIDs?
Nonselective target COX 1 and COX2
Selective tend to target COX 2
Which NSAIDs are non-selective?
-naproxen
-aspirin
-ibuprofen
Not Individual Antagonizers
Which NSAIDs are selective? Which enzyme are they selective for?
COX 2 selective:
-celecoxib
-rofecoxib
-tylenol (not an NSAID but still)
which COX enzyme is chiefly responsible for analgesia, anti-inflammation, and fever reduction?
COX 2
nonselective NSAIDs block COX1 and COX 2, and tend to block peripheral COX 2 more than Tylenol, which is why Tylenol doesn't have as much of an anti-inflammatory effect. Don't need to know this, but this helps make sense that COX 2 blockade is responsible for anti-inflammation, yet Tylenol is not very anti-inflammatory
do selective or non-selective drugs have more side effects in general?
non selective (duh)
AEs of NSAIDs
-GI upset / bleeding
-renal impairment
-liver disorders
how does inhibiting COX produce anti-inflammatory properties?
COX 2 is mostly responsible for inflammatory response. Inhibiting this enzyme will reduce production of inflammatory mediators
nonselective NSAIDs block COX1 and COX 2, and tend to block peripheral COX 2 more than Tylenol, which is why Tylenol doesn't have as much of an anti-inflammatory effect.
MOA of aspirin
nonselective COX inhibitor
Indications for aspirin
-pain
-fever
-inflammation
-heart attack risk reduction
AEs of aspirin
-GI upset/ bleeding
-renal impairment
-poisoning in OD
MOA of ibuprofen
non selective COX inhibitor
indications for ibuprofen
-pain
-fever
-inflammation
-painful menstruation
potency of aspirin vs ibuprofen
same
AEs of ibuprofen
-GI upset / bleeding
-renal impairment
-dizziness
relative incidence of AEs in ibuprofen vs aspirin
ibuprofen has less incidence of AEs in general
MOA of Tylenol
selective COX 2 inhibitor
indications for tylenol
-analgesia
-limited anti-inflammatory effect
AEs of tylenol
-liver damage in OD
-rare but fatal skin rxns
Major steps in Immune Response
Where in these steps will corticosteroids, cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus, MMF, and azathioprine function?
1) Ag presentation
2) IL-1 production and cell proliferation (steroids)
3) TCR activation and signaling
4) IL-2 and other cytokine expression (tacrolimus, cyclosporine)
5) T and B cell activation, differentiation, and proliferation (sirolimus, MMF, azathioprine)
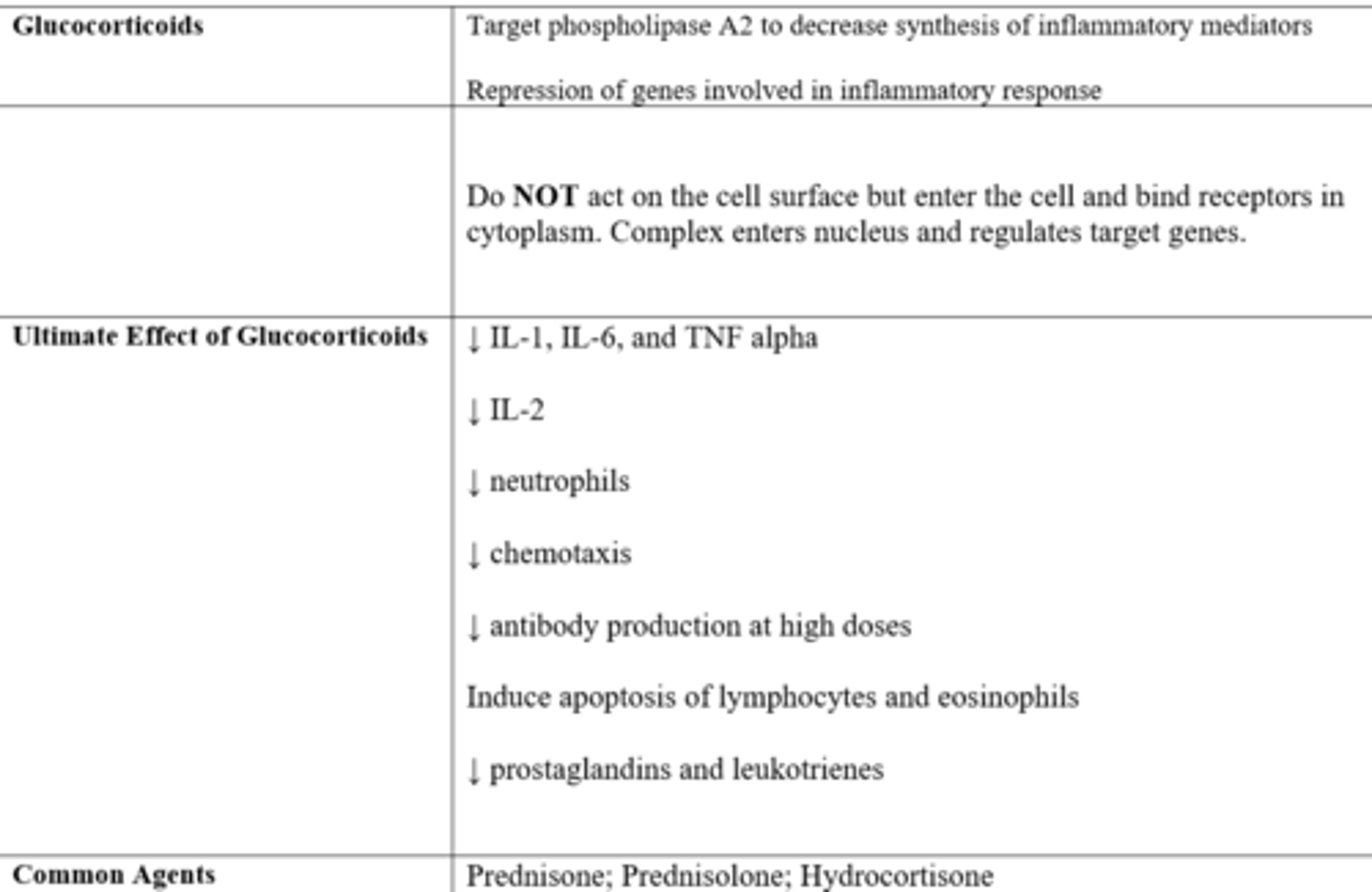
MOA of glucocorticoids, particularly in inflammation
-regulations of genes (e.g. NF-kB down-regulation → decreases T cells)
-repression of genes involved in inflammatory response
what is special about the MOA of glucocorticoids and their site of action
Do NOT act on the cell surface but enter the cell and bind receptors in cytoplasm. Complex enters nucleus and regulates target genes.
what is the ultimate effect of glucocorticoids as they relate to inflammatory mediators?
-↓ IL-1, IL-6, and TNF alpha
-↓ IL-2
-↓ neutrophils
-↓ chemotaxis
-↓ antibody production at high doses
-induce apoptosis of lymphocytes and eosinophils
-↓ prostaglandins and leukotrienes
what MOA contributes to the immunosuppressive functions of corticosteroids?
down-regulation of genes that are involved in T cell signaling
AEs of gluococorticoids
-cushing's w/ long term use of high doses
-adrenal insufficiency
-growth inhibition in children
-osteoporosis
-weight gain
-cataracts and glaucoma
-diabetes / glucose intolerance
-CV risk
-infection risk
-anxiety and personality changes
2 commonly used glucocorticoids
prednisone (prodrug)/ prednisolone
hydrocortisone
how does prednisone / prednisolone work as an immunosuppressive?
-lysis of Ag-activated cells
-suppression and sequestration of T cells
-reduce IL-2
-reduce T cell response to IL-1
Uses for prednisone / prednisolone
-transplant rejection
-autoimmune disorders
-asthma
AEs of prednisone / prednisolone
-cushings
-osteoporosis
-infection
-glucose intolerance
-myopathy
-edema
-cataracts / glaucoma
main uses of hydrocortisone
used as anti-inflammatory for dermatologic disorders
how does hydrocortisone work as an immunosuppressive agent
-decreases synthesis of inflammatory mediators
-suppresses phagocytes
-reduces swelling, redness, pain
AEs of hydrocortisone
-thinning of skin
-easy bruising
-local hemorrhage
-acne with long term use
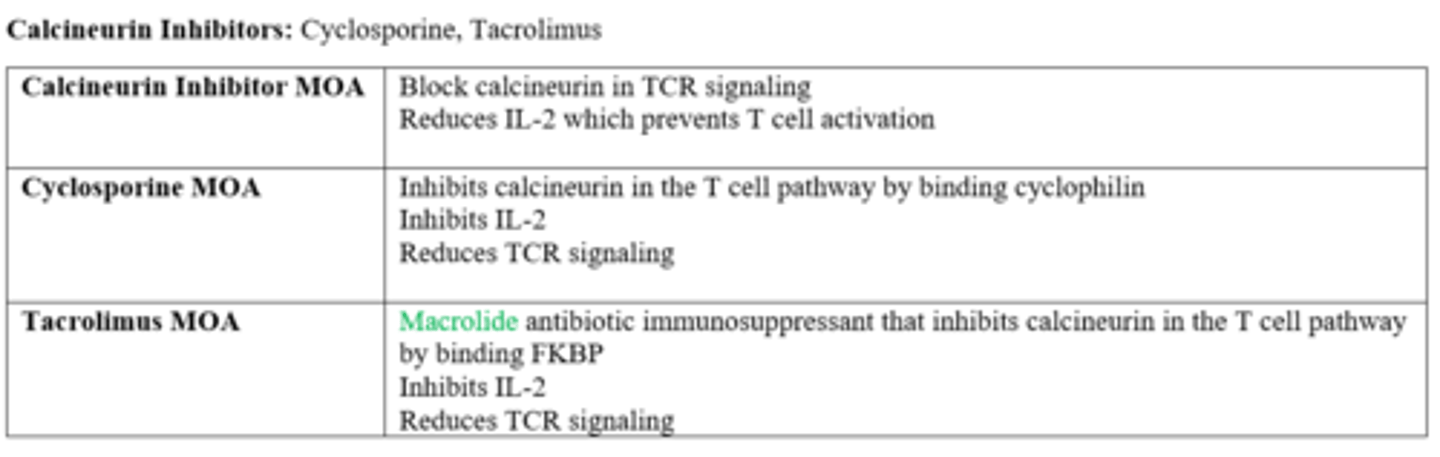
which drugs are calcineurin inhibitors
-cyclosporine
-tacrolimus
MOA of calcineurin inhibitors
block calcineurin in TCR signaling
reduces IL-2, which prevents T cell activation
what pathway is inhibited by calcineurin inhibitors?
TCR (T cell receptor) pathway mediated by IL-2, which ultimately reduces T and B cell immune responses (and granulocytes) via inhibition of CD4 T cells
difference in the MOA of cyclosporine and tacrolimus
Both inhibit calcineurin in the T cell pathway:
-tacrolimus binds FKBP
-cyclosporine binds cyclophilin
drug class of tacrolimus
macrolide antibiotic immunosuppressant
drug class (structure) of cyclosporine
cyclic, lipophilic peptide
is tacrolimus or cyclosporine more potent?
tacrolimus is 10-100 times more potent
MOA of tacrolimus
-binds FKBP and inhibits calcineurin
-inhibits IL-2
-reduces TCR signaling
MOA of cyclosporine
-binds cyclophilin and inhibits calcineurin
-inhibits IL-2
-reduces TCR signaling
indications for tacrolimus
-organ transplant
-dermatologic disorders
indications for cyclosporine
-organ transplant
-RA
-IBD
-psoriasis
AEs of tacrolimus
-nephrotoxic
-cancer risk
-hyperglycemia
-GI
-HTN
-neurotoxic
-infection risk
AEs of cyclosporine
-nephrotoxic
-hepatotoxic
-hirsuitism
-neurotoxic
-HTN
-hyperlipidemia
which drugs are mTOR inhibitors
Sirolimus
Everolimus
MOA of sirolimus
-inhibits mTOR
-binds FKBP
-inhibits IL-2 signaling→ T cell inhibition
-selective blockade of cytokine signal transduction
compare sirolimus and tacrolimus MOA
both bind FKBP; sirolimus is also an mTOR inhibitor though, and tacrolimus is also a calcineurin inhibitor
what are mTOR inhibitors classified as and why?
anti-proliferative drugs because they inhibit T cell division and proliferation via IL-2 inhibition
AEs of sirolimus
-anemia
-leukopenia
-GI
-fever
-cancer
-infection
which drugs from this lecture are macrolides?
-tacrolimus
-sirolimus
indications for sirolimus
-organ transplant rejection
-graft vs host disease in stem cell transplant
-dermatologic disorders
Which drugs are cytotoxic drugs?
-azathioprine
-mycophenolate mofetil
indications for cytotoxic drugs (azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil)
-organ transplant rejection
-autoimmune diseases
MOA of cytotoxic drugs (azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil)
-suppress cell-mediated immunity (ie/ inhibits B and T cell proliferation)
-block DNA synthesis
azathioprine MOA
-prodrug
-purine analog that inhibits purine (adenine, guanine) synthesis, and thus inhibits DNA synthesis
-inhibits cell division and proliferation, specifically actively dividing T and B cells
indications for azathioprine
-organ transplant rejection
-RA
-IBD
-MS
-Systemic lupus erythematosis
AEs of azathioprine
-GI
-bone marrow suppression
-infection risk
-cancer risk
mycophenolate MOA
-prodrug
-inhibits important enzymes in DNA synthesis (inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase)
-inhibits guanine synthesis
-selectively inhibits T and B cell proliferation
indications for mycophenolate
-transplant rejection
-immune rejection
AEs of mycophenolate
-reversible bone marrow suppression (neutropenia, anemia)
-risk of infection
-risk of lymphoma
Which 2 drugs from this lecture are super contraindicated to being used together?
mycophenolate and azathioprine
what biologic process is inhibited by cytotoxic drugs?
-MMF inhibits enzymes in DNA synthesis
-Azathioprine inhibits purine synthesis to inhibit DNA synthesis
both decrease division of lymphocytes
class AEs of cytotoxic drugs
-cancer risk
-GI
-leukopenia and infection risk
-hepatotoxic
Which of the following statement is TRUE about NSAIDs?
a. NSAIDs exert their effects by inhibiting COX (cyclooxygenase), thus blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins, the major inflammatory mediators.
b. NSAIDs exert their effects by inhibiting mast cell degranulation, thus blocking the release of histamine, a major inflammatory mediator.
c. NSAIDs exert their effects by inhibiting mTOR, a protein kinase in the IL-2 signaling that is important for T cell activation.
d. NSAIDs exert their effects by inhibiting calcineurin, an important phosphatase in the T cell receptor signaling that is important for T cell activation.
a. NSAIDs exert their effects by inhibiting COX (cyclooxygenase), thus blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins, the major inflammatory mediators.
Which of the following drugs is most likely to preferentially suppress adaptive immune response, without causing profound suppression of the innate immune response?
a. prednisone
b. tacrolimus
c. infliximab
d. aspirin
b. tacrolimus
this is because tacrolimus inactivates TCR signaling, and TCRs are involved in adaptive immunity

What is the mechanism of action of Tacrolimus?
a. repression of genes involved in inflammatory response
b. inhibits mTOR by binding FKBP
c. calcineurin inhibitor that blocks T cell receptor signaling
c. calcineurin inhibitor that blocks T cell receptor signaling
A is the MOA of glucocorticoids in general
B is the MOA of Sirolimus
Your preceptor gives you a list of medications that Mr. Johnson is currently taking and asks you to review it. One of the drugs Mr. Johnson is taking to suppress organ rejection was Azathioprine. Which of the following describes its mechanism of action?
a. inhibits mTOR by binding FKBP through selective blockade of cytokine signal transduction
b. conversion to 6-mercaptopurine, a purine antimetabolite that blocks purine synthesis
c. Inhibits important enzymes in DNA synthesis (inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase)
d. Target phospholipase A2 to decrease synthesis of inflammatory mediators by not acting on cell surface
b. conversion to 6-mercaptopurine, a purine antimetabolite that blocks purine synthesis
A is the MOA of Sirolimus
C is the MOA of mycophenolate which is also a cytotoxic drug like Azathioprine
D is the general MOA of glucocorticoids
The maintenance dose of this immunosuppressant drug is typically tapered down over the first year of therapy because it can cause serious side effects such as weight gain, cataracts, hypertension, and osteoporosis as well as growth retardation in children. This agent is:
a. tacrolimus
b. azathioprine
c. cyclosporine
d. prednisone
d. prednisone
enzyme targeted by steroids to reduce inflammation:
phospholipase A2
how do steroids affect cytokines, which cytokines are affected, and what is the result?
↓ Nf-kB → apoptosis of activated cells
↓IL-1, IL-6, and TNF alpha
↓IL-2 → ↓ T cell activation and ↓CTL cells

what is the function of mTOR?
compare the end-outcome of mTOR and calcineurin inhibitors
-mTOR = involved in IL-2 signaling
-both mTOR inhibitors and calcineurin inhibitors decrease T cell activation
T/F; "T and B cells cannot recognize a pathogen directly".
TRUE
Remember this! There was confusion in the study guide where it said B cells can recognize a pathogen.
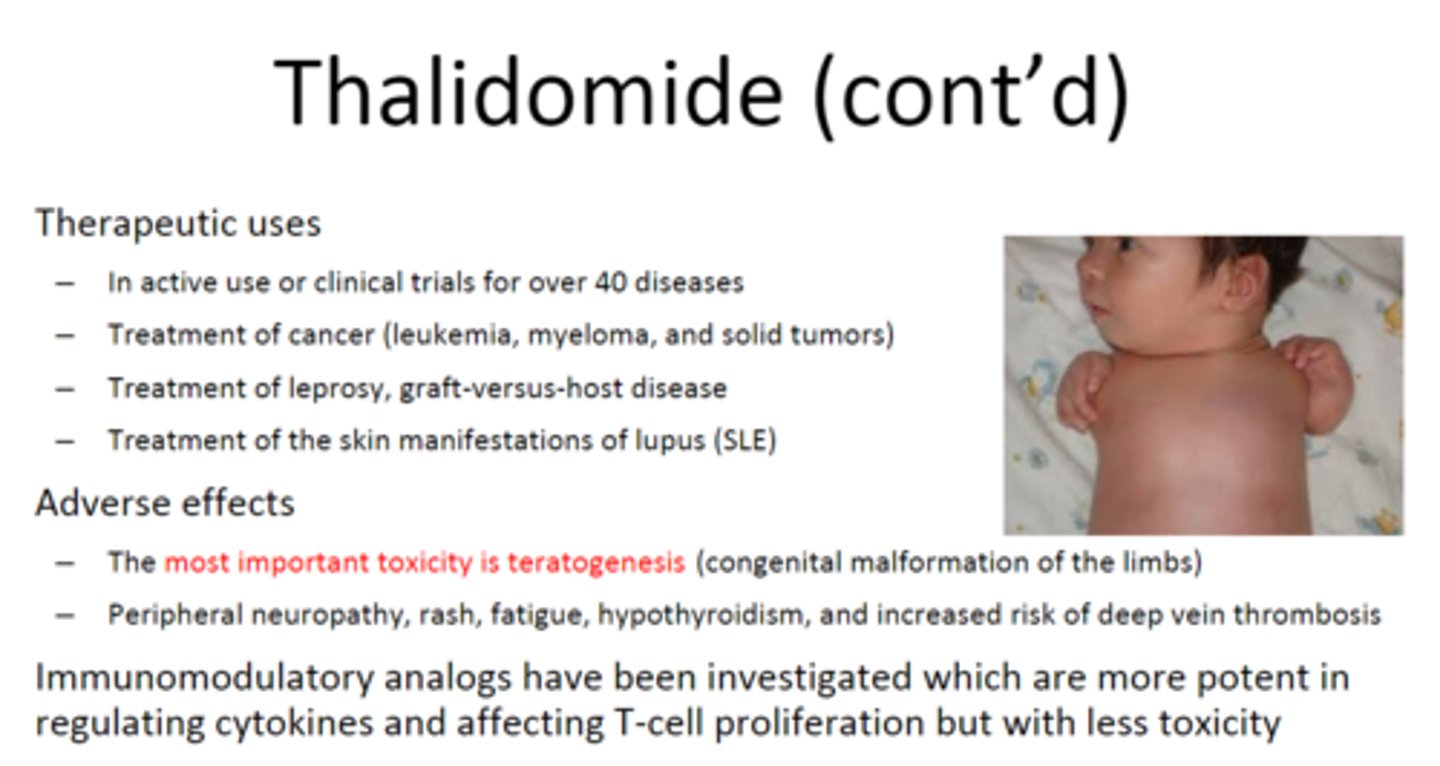
which drug is a highly teratogenic anti-inflammatory / immune modulator?
thalidomide
presence of what may help diagnose autoimmune hepatitis?
presence of ANA (antinuclear antibody test)
an ANA test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. If the test finds antinuclear antibodies in your blood, it may mean you have an autoimmune disorder. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake.
Which of the following is NOT involved in the regulation of hematopoiesis?
a. EPO
b. G-CSF/GM-CSF
c. IL-11
d. Leukemia inhibitory factor
d. Leukemia inhibitory factor
Which of the following is MOST likely to present in the lymph nodes of those with Hodgkin lymphoma?
a. merkel cell
b. schwann cell
c. reed sternberg cell
d. kupffer cell
c. reed sternberg cell
Which of the following is NOT true about innate immunity?
a. induced inflammatory response by recruiting inflammatory cells to site of infection
b. each time the body is exposed to an infection, the immune response improves
c. specificity and memory are not involved
b. each time the body is exposed to an infection, the immune response improves
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
a. neutrophils are the first cells at an infection
b. neutrophils are the last cells recruited
c. macrophages are longer-lived than neutrophils
d. macrophages are first to respond to invaders at the site of infection
b. neutrophils are the last cells recruited
make sure to know that D is true
naive CD8 T cells become activated and differentiate into what kind of cells?
CTL (cytotoxic T cells)
what cell types can CD4 T cells become?
Th1
Th2
Tregs
Which is the major player in poison ivy caused by immune reaction of contact dermatitis?
CD4 T helper cell
Which of the following characteristics are TRUE about Hashimoto?
a. hypothyroidism
b. autoimmune disease of the thyroid mediated by autoreactive T cells against thyroid cells
c. more prevalent in women
d. hyperthyroidism
A, B, C
T/F; NSAIDs block release of histamine from mast cells.
FALSE
They block COX to inhibit synthesis of NEW inflammatory mediators
Which of these will function together with a transcription factor to inhibit inflammation?
a. tacrolimus
b. MMF
c. prednisone
d. all of the above
c. Prednisone
Most NSAIDs reduce inflammation, pain, and fever by inhibition of which enzyme?
COX 2
Which cell type do calcineurin inhibitors primarily target?
T cells
Which signaling molecule is MOST important in the MOA of sirolimus?
IL-2