ASL 13. Neck; Face
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
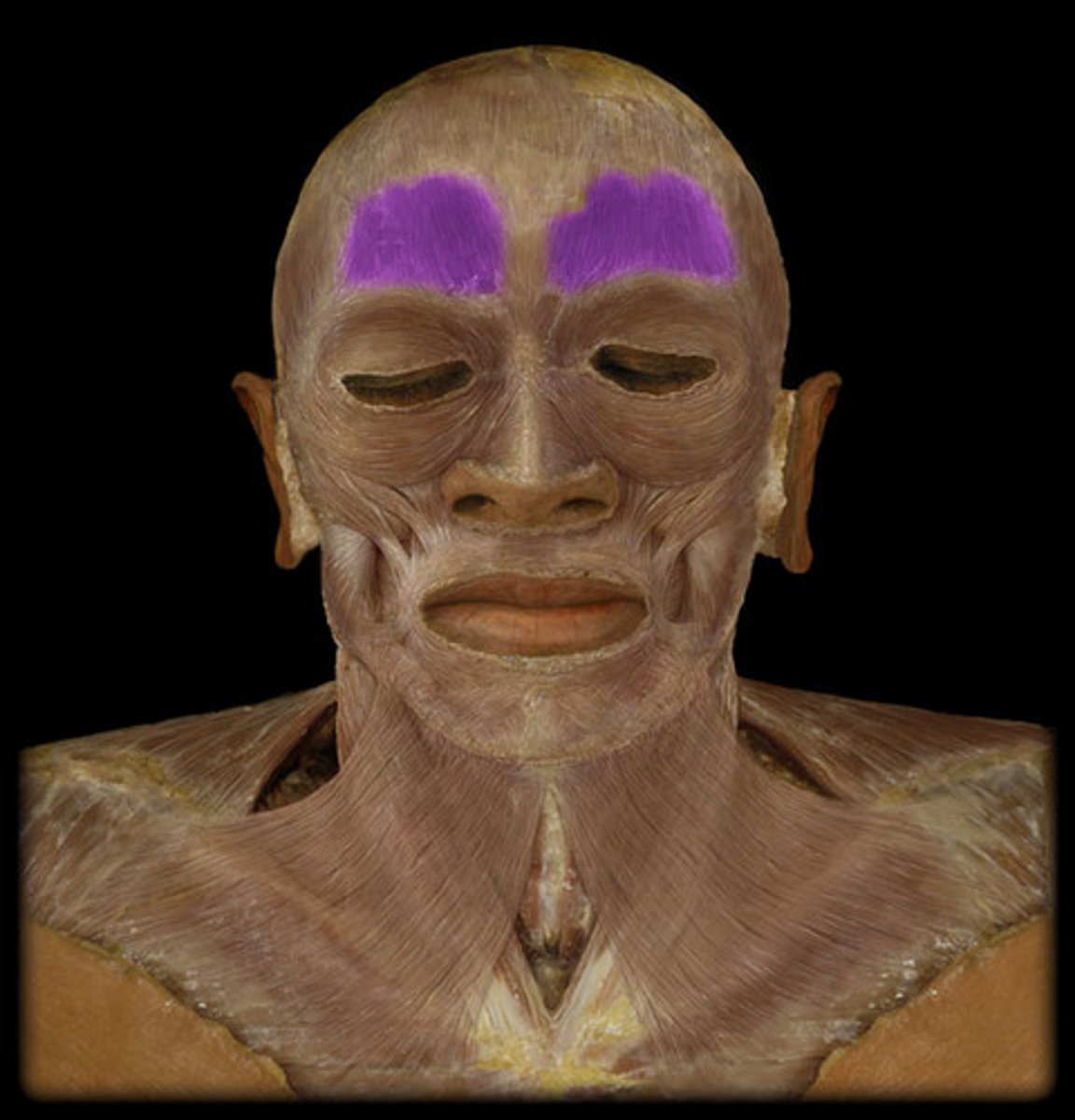
Frontalis m.
draws scalp anteriorly, raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
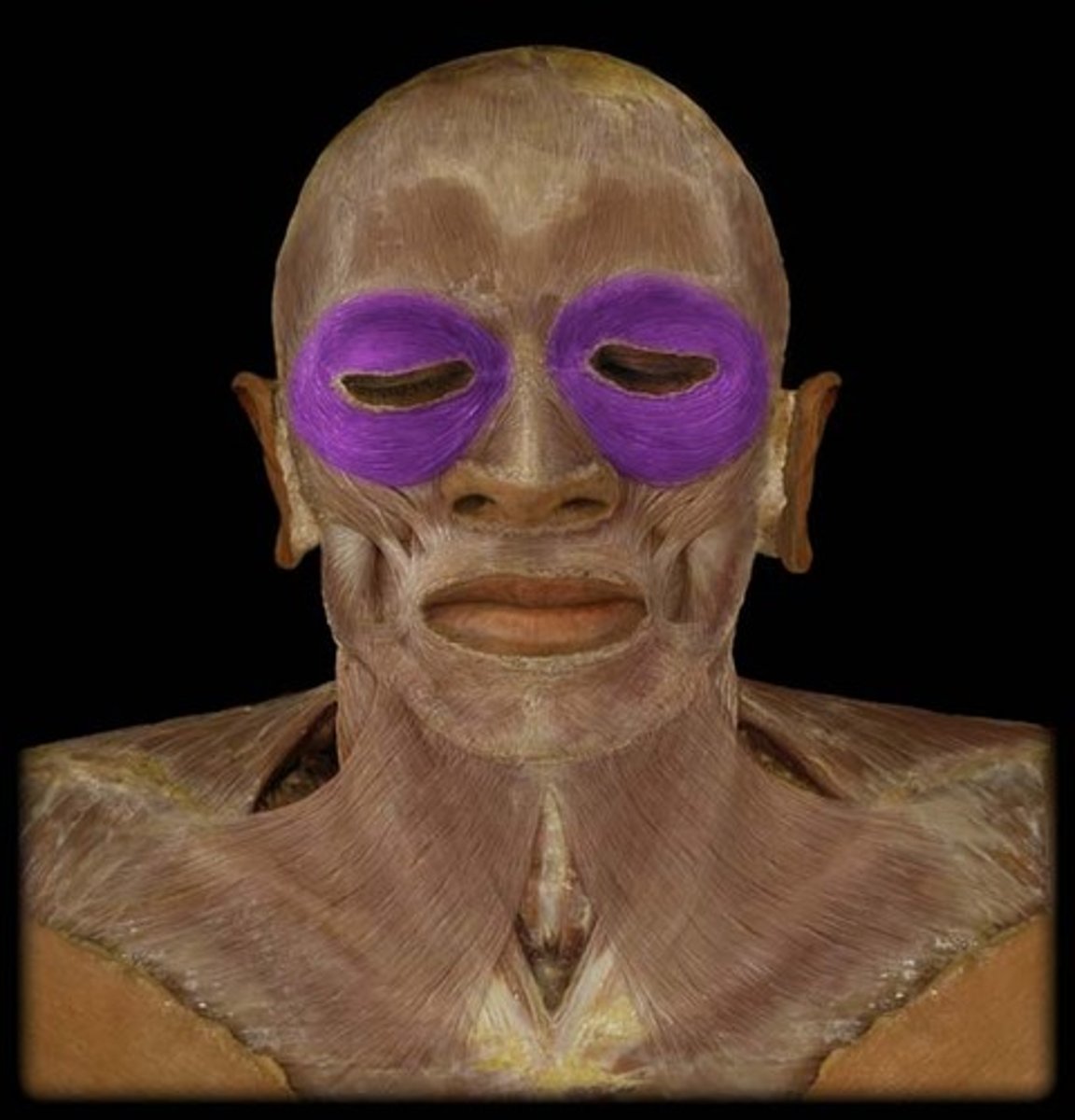
Orbicularis oculi m.
closes the eyelids or presses them together
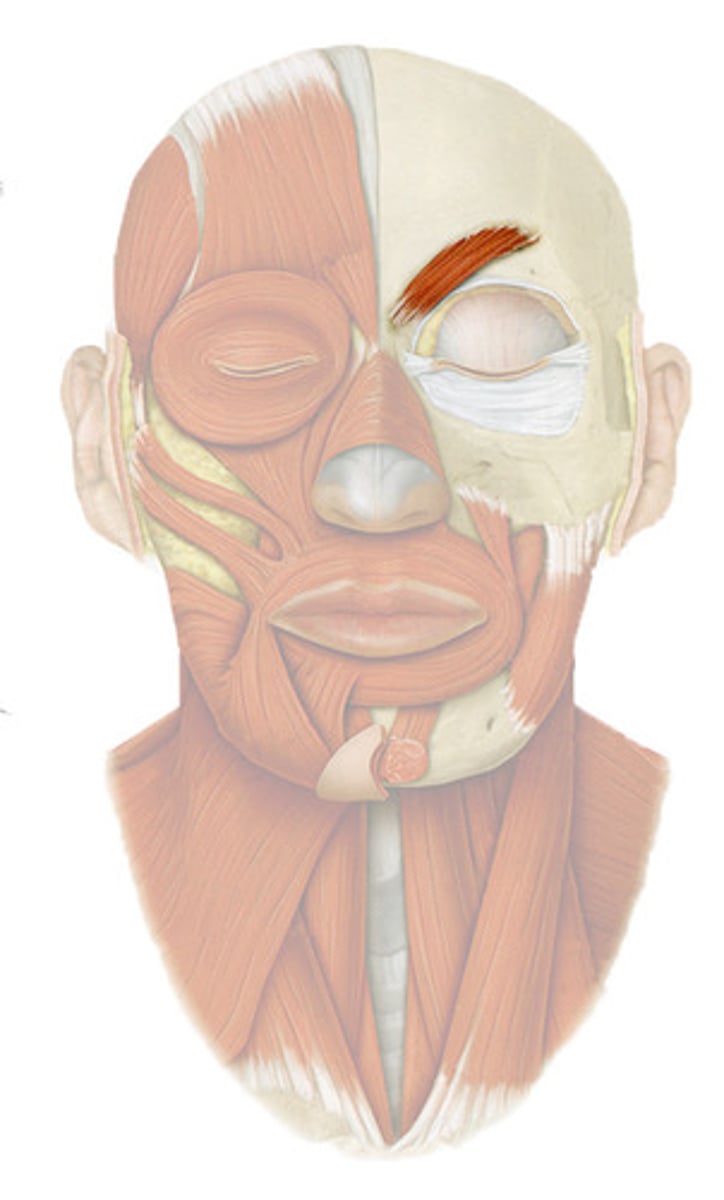
Corrugator supercilii m.
draws eyebrows downward and medially
Levator labii superioris m.
elevates upper lip and flares nares
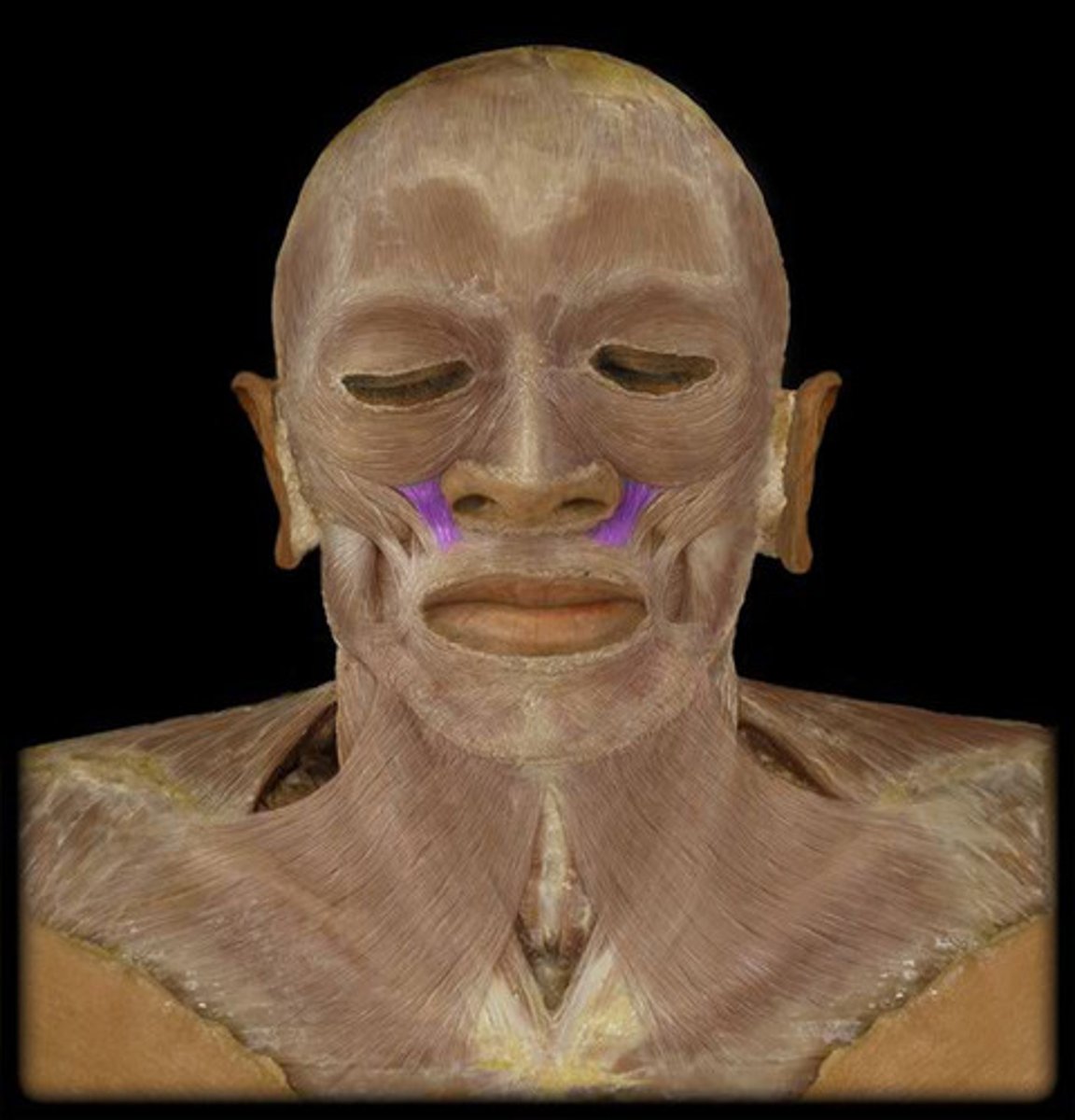
Zygomaticus major m.
smiling
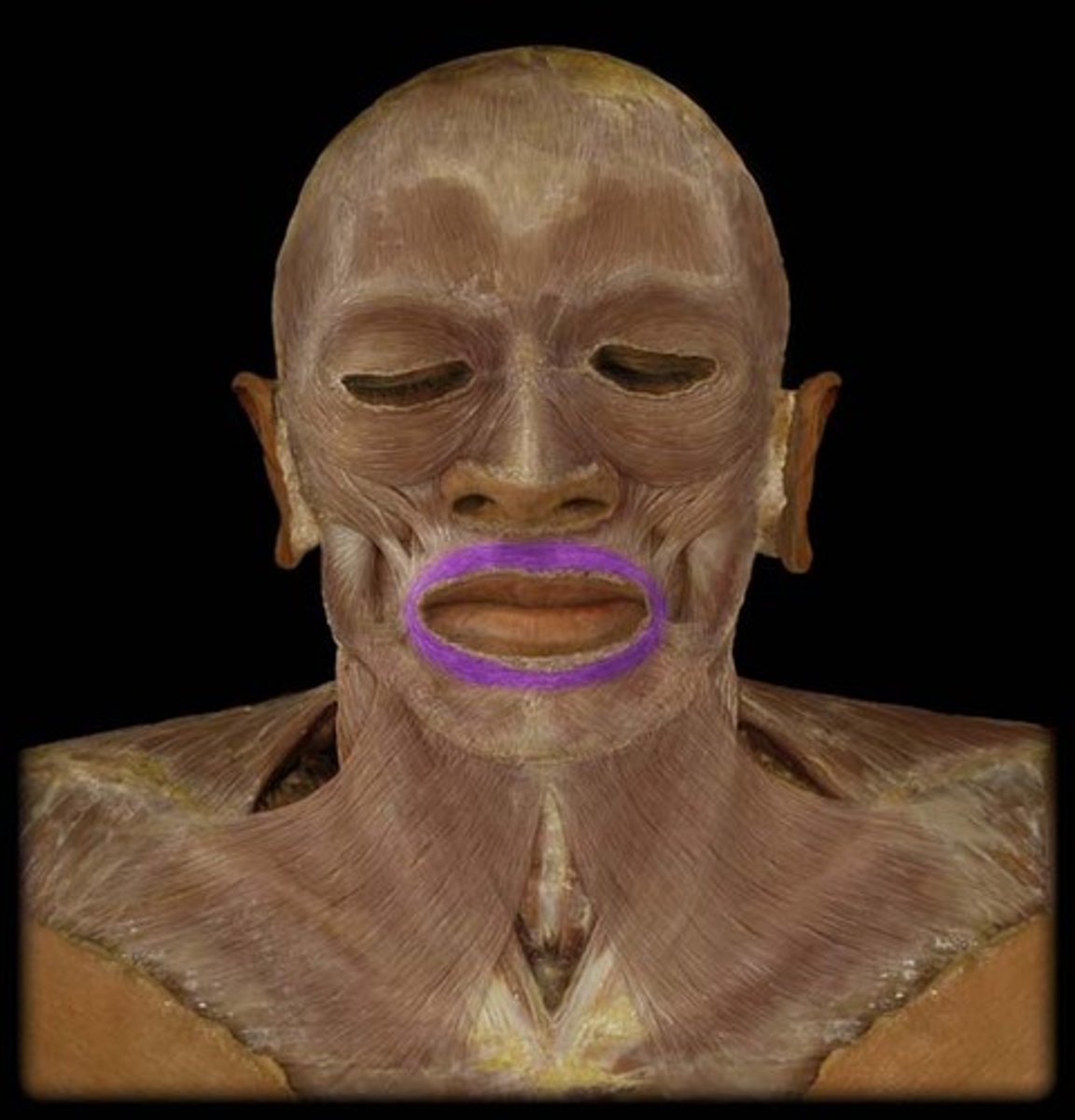
Orbicularis oris m.
closes and protrudes lips
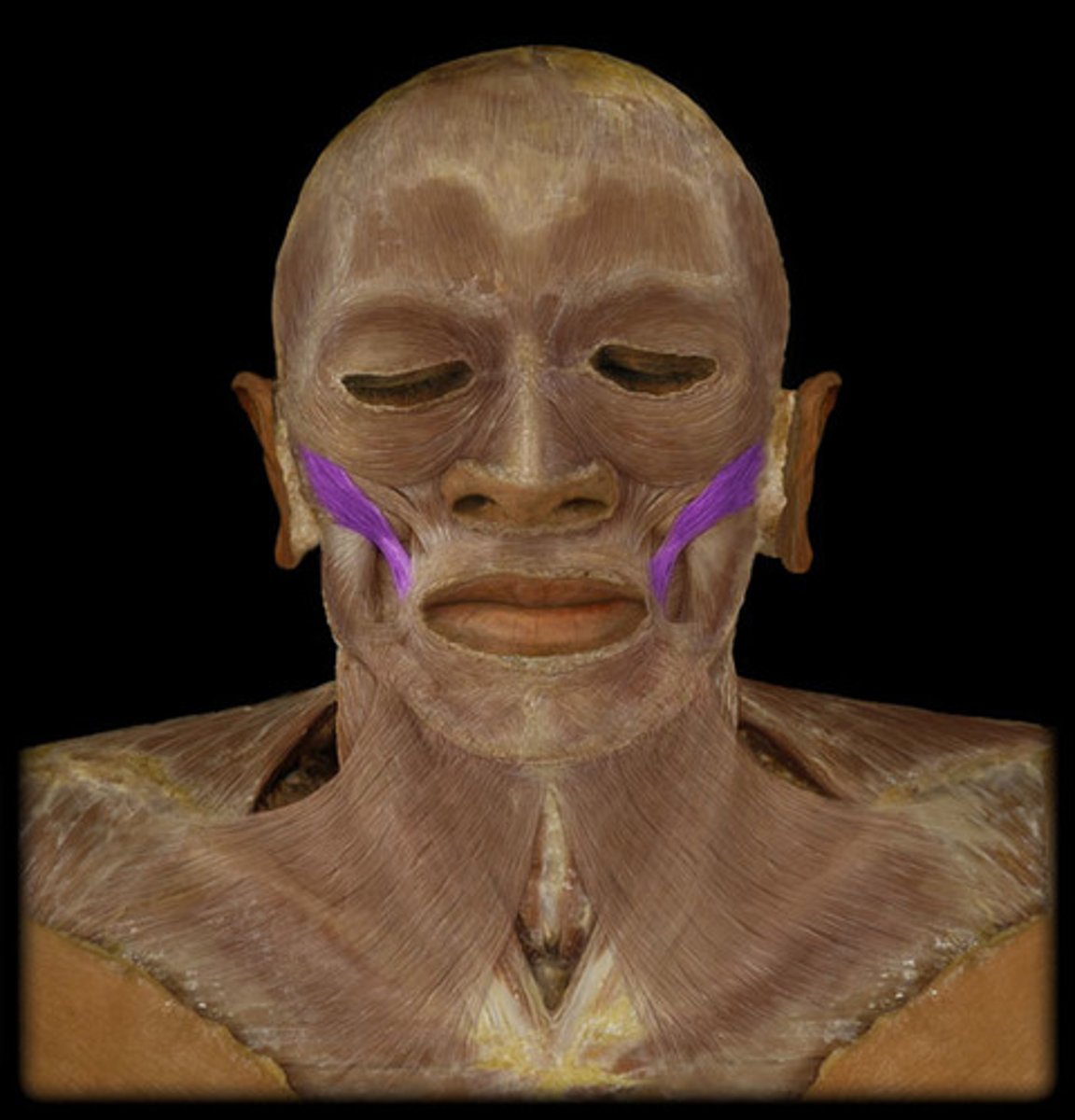
Buccinator m.
Compresses cheeks against teeth, aids in mastication, sucking and blowing
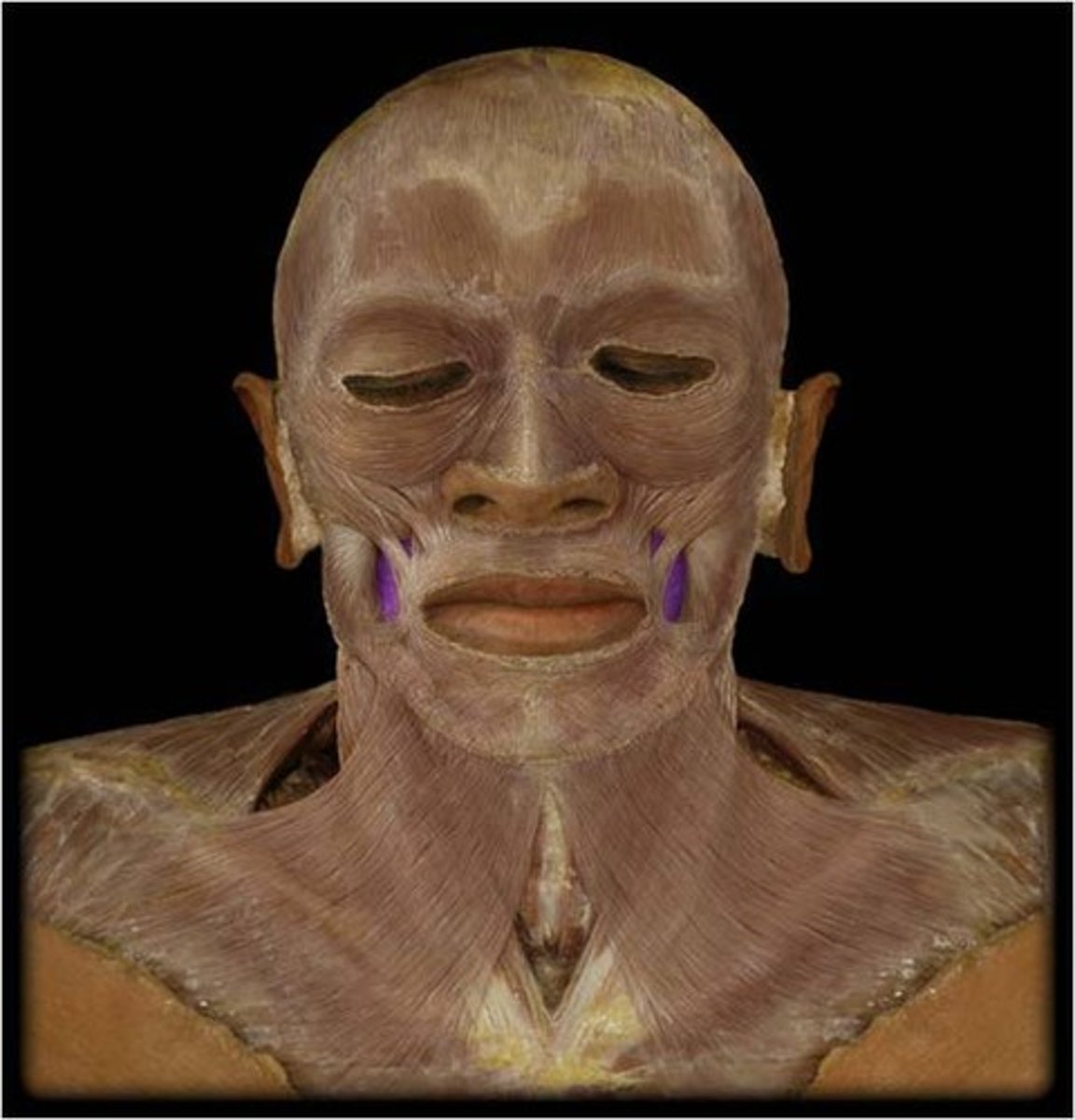
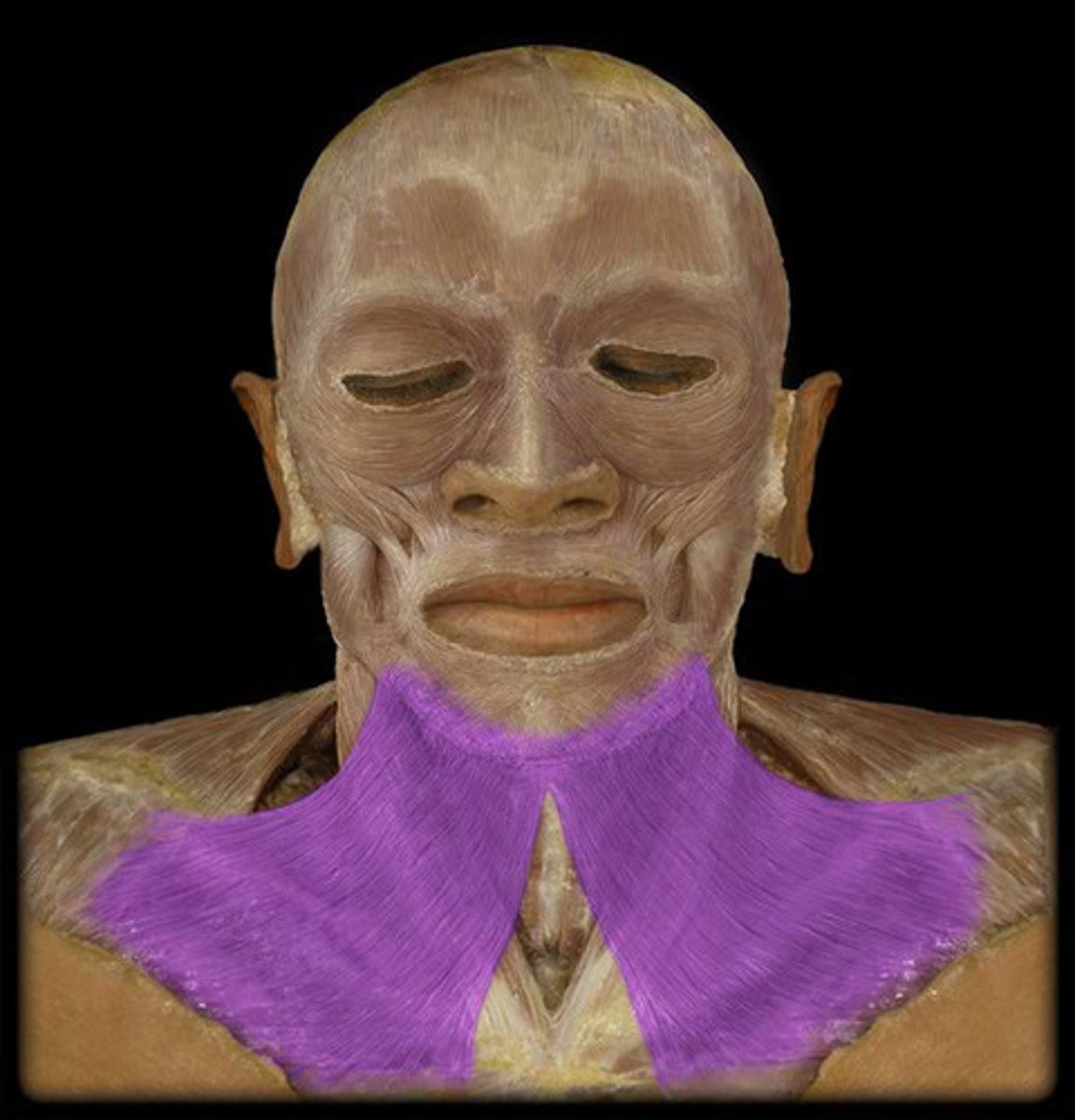
Platysma m.
draws out part of lower lip inferiorly and posteriorly as in pouting; tenses skin of neck
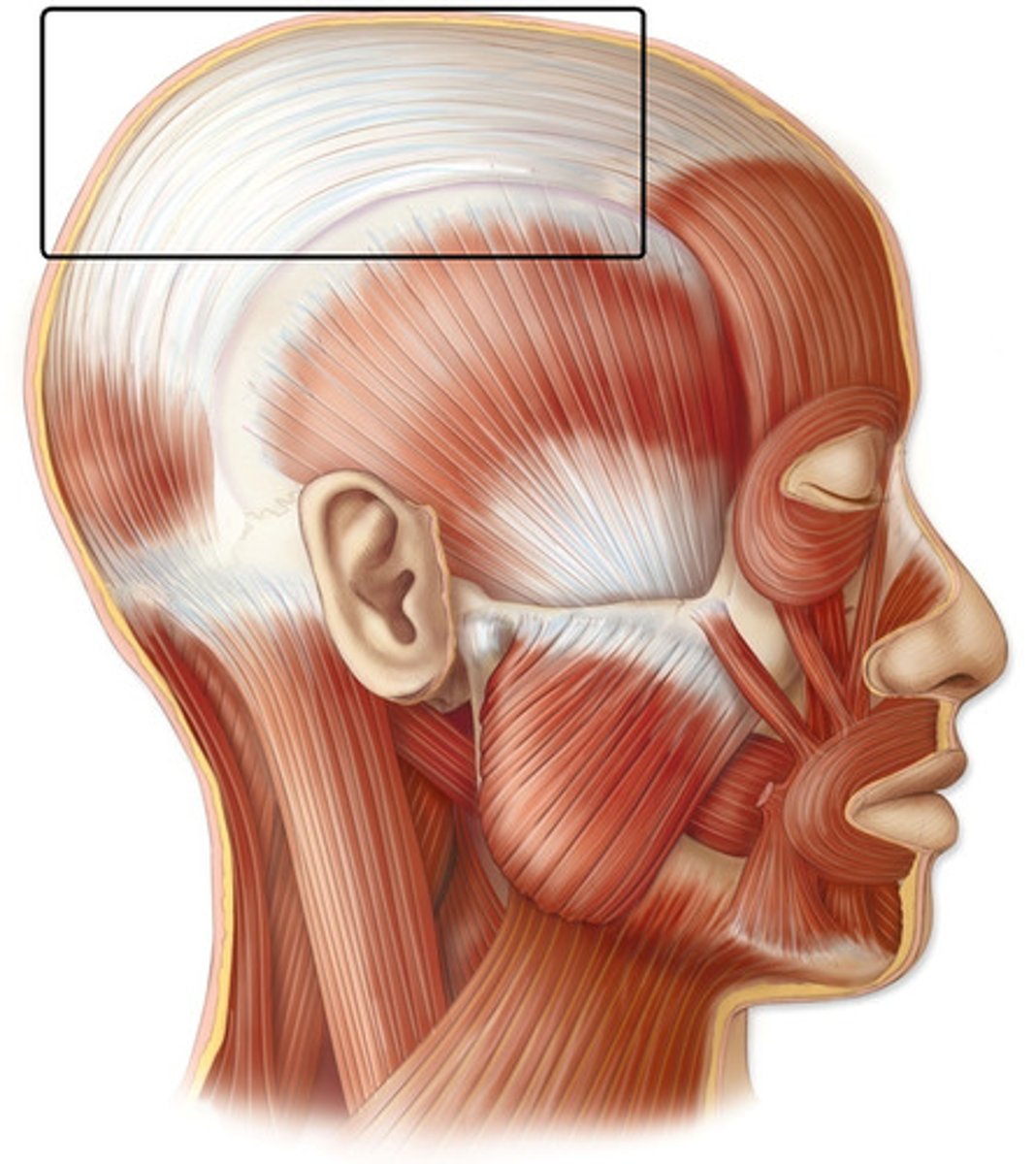
Epicranial aponeurosis (galea aponeurotica)
Aponeurosis that covers the skull
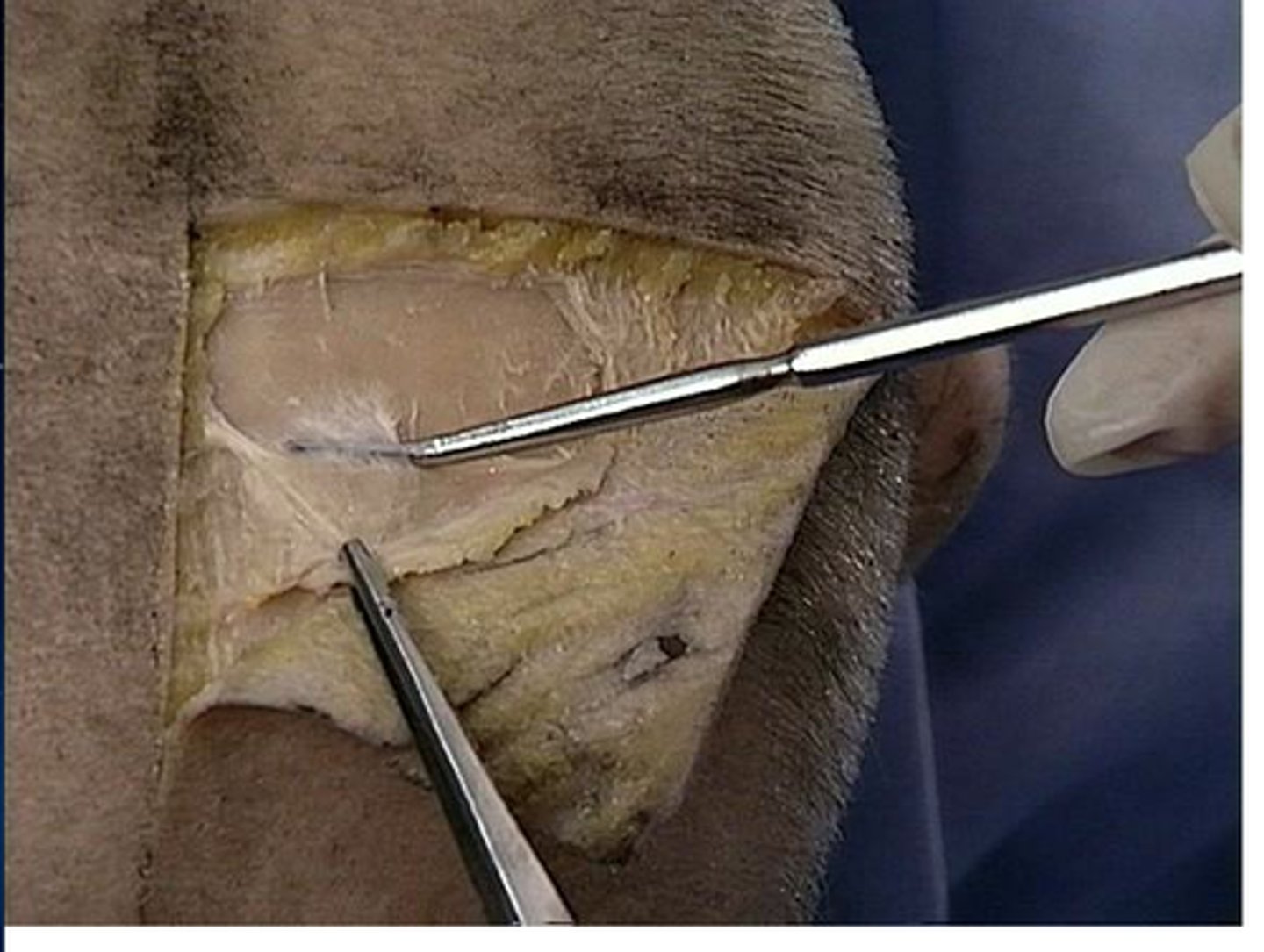
Pericranium (external cranial periosteum)
the external membrane that covers the outer surface of the skull
Superficial temporal a.
supplies muscles and skin of frontal and temporal regions
Facial artery
supplies muscles and skin of face
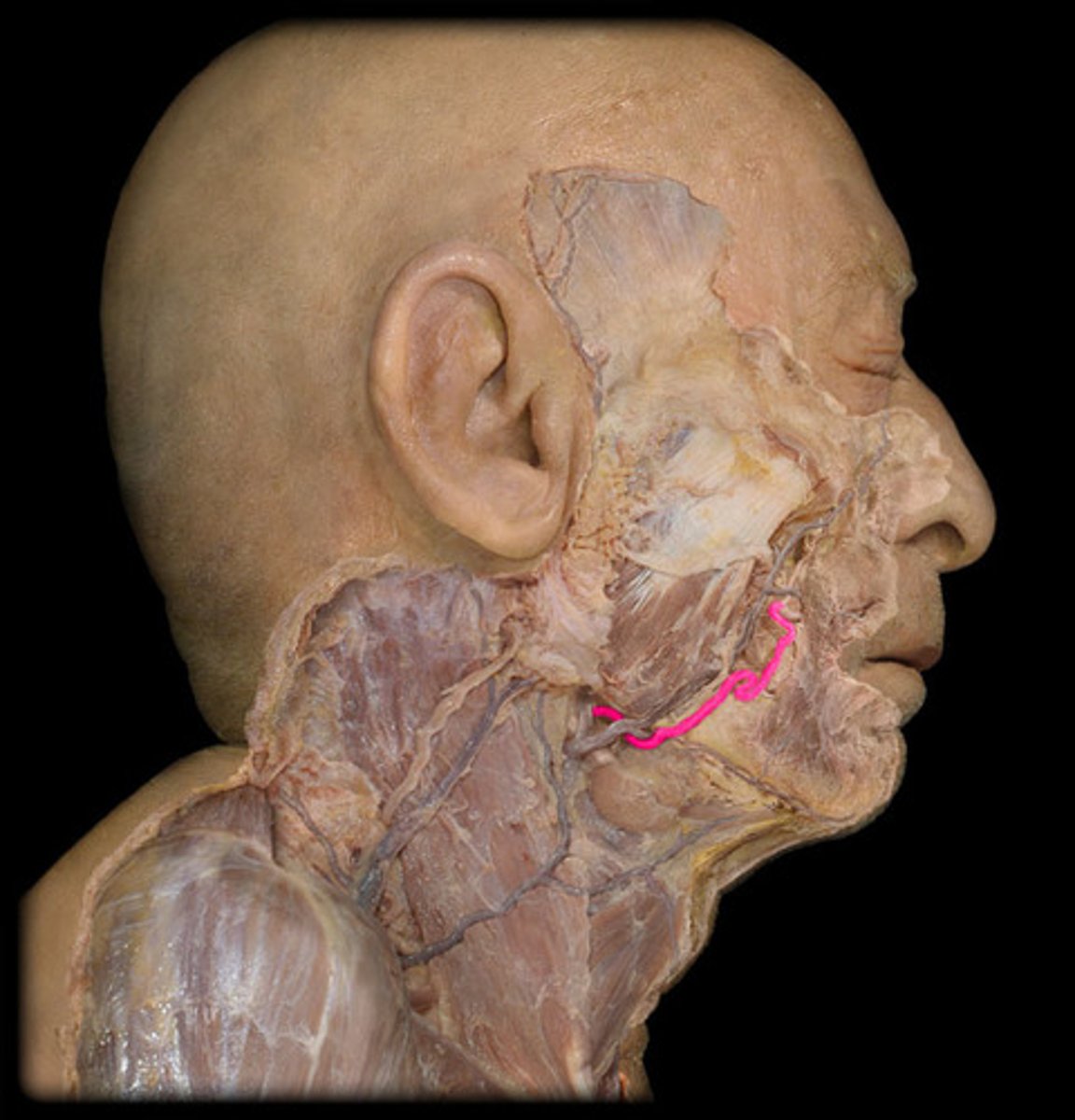
Inferior labial artery
lower lip and chin
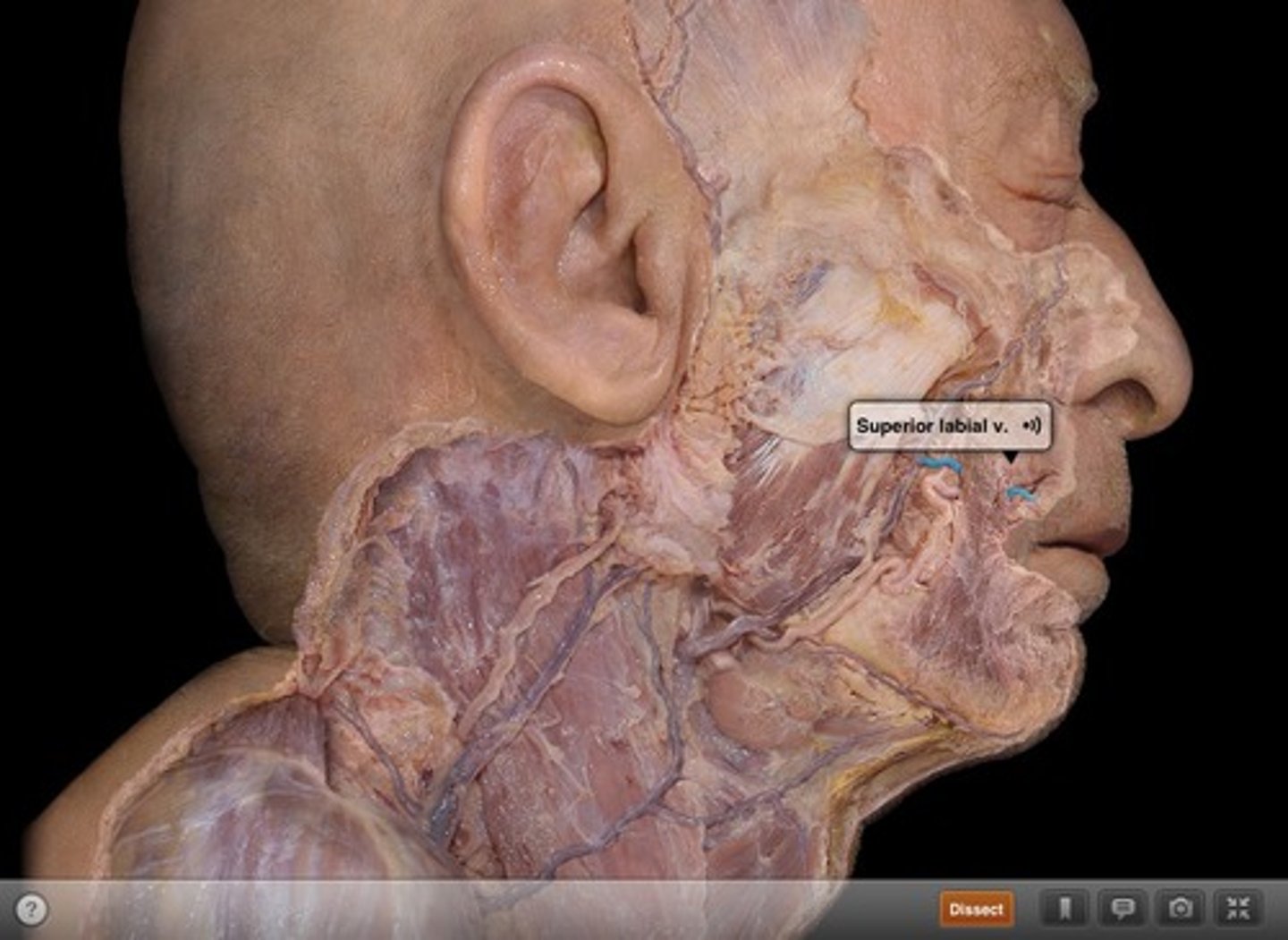
Superior labial artery
Upper lip & region of nose
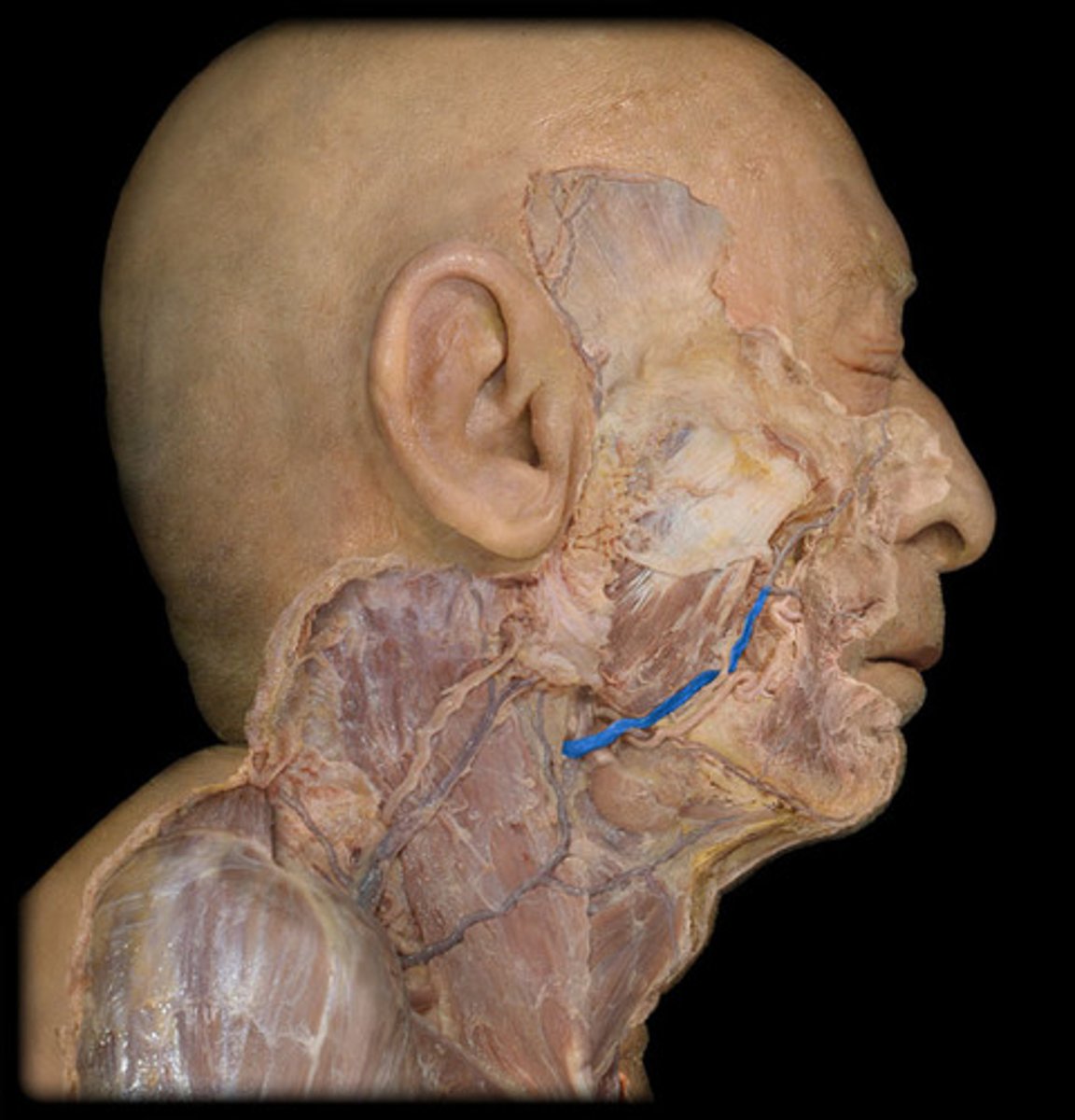
Facial vein
drains the facial structures beginning near the eye and descending toward the mandible
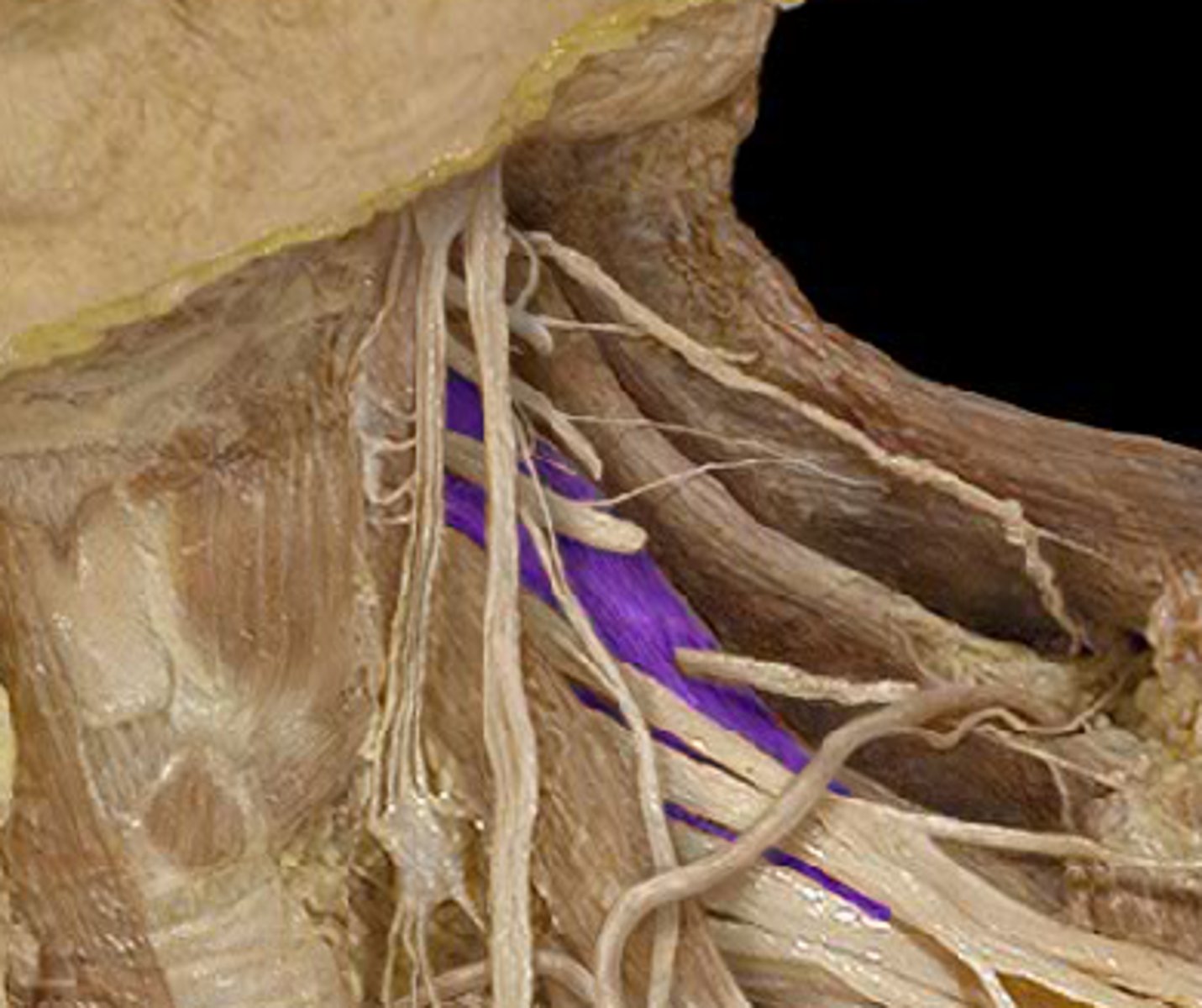
Facial nerve
Cranial nerve VII. Sensory and motor nerve. Sense of taste for the front of the tongue. Movement of the facial muscles and salivary and lacrimal glands.
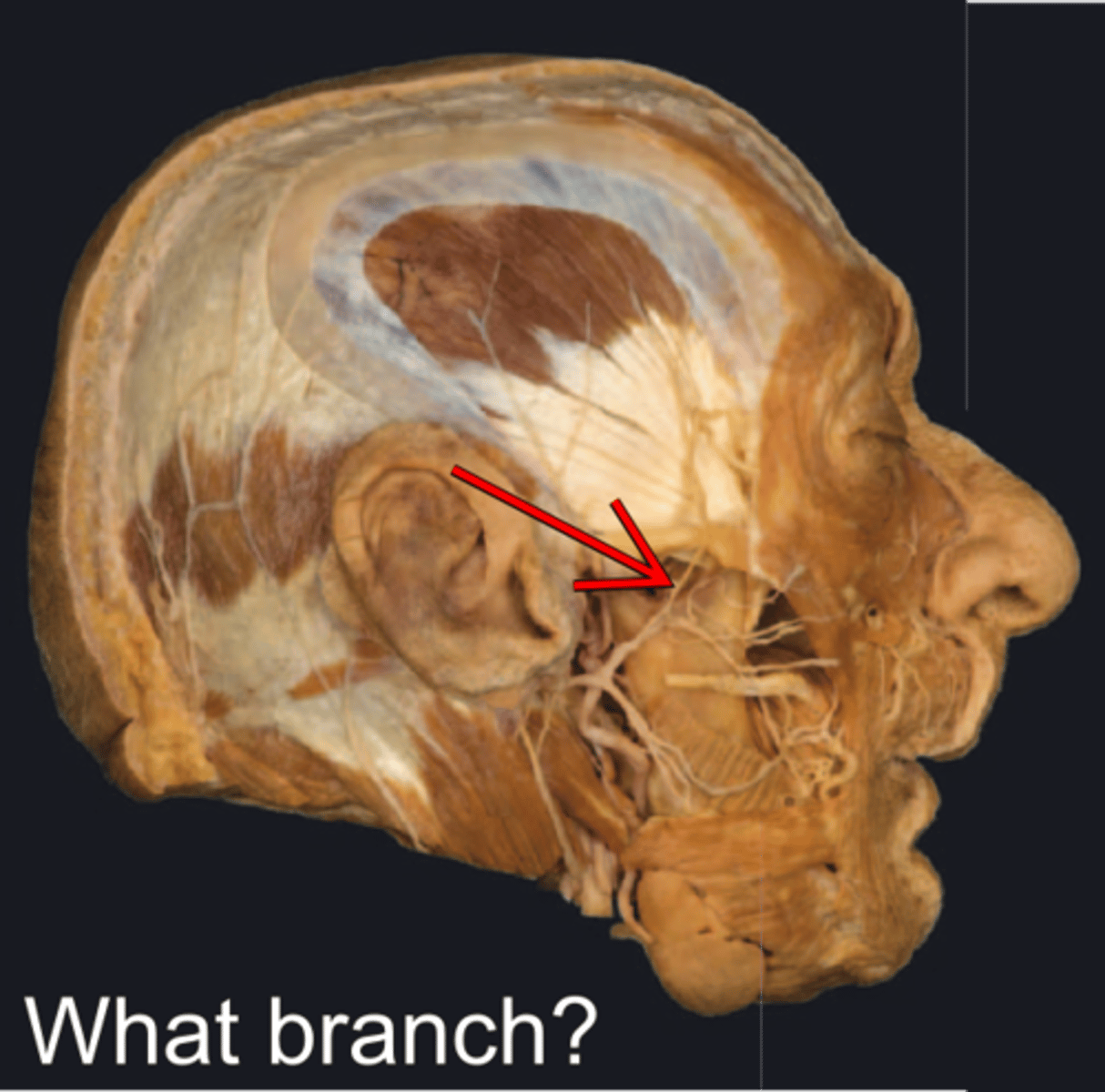
Temporal branch of facial n.
- crosses zygomatic arch
- Innervates auricularis superior and anterior, the frontal belly of occipitofrontalis and the superior part of orbicularis oculi mm.
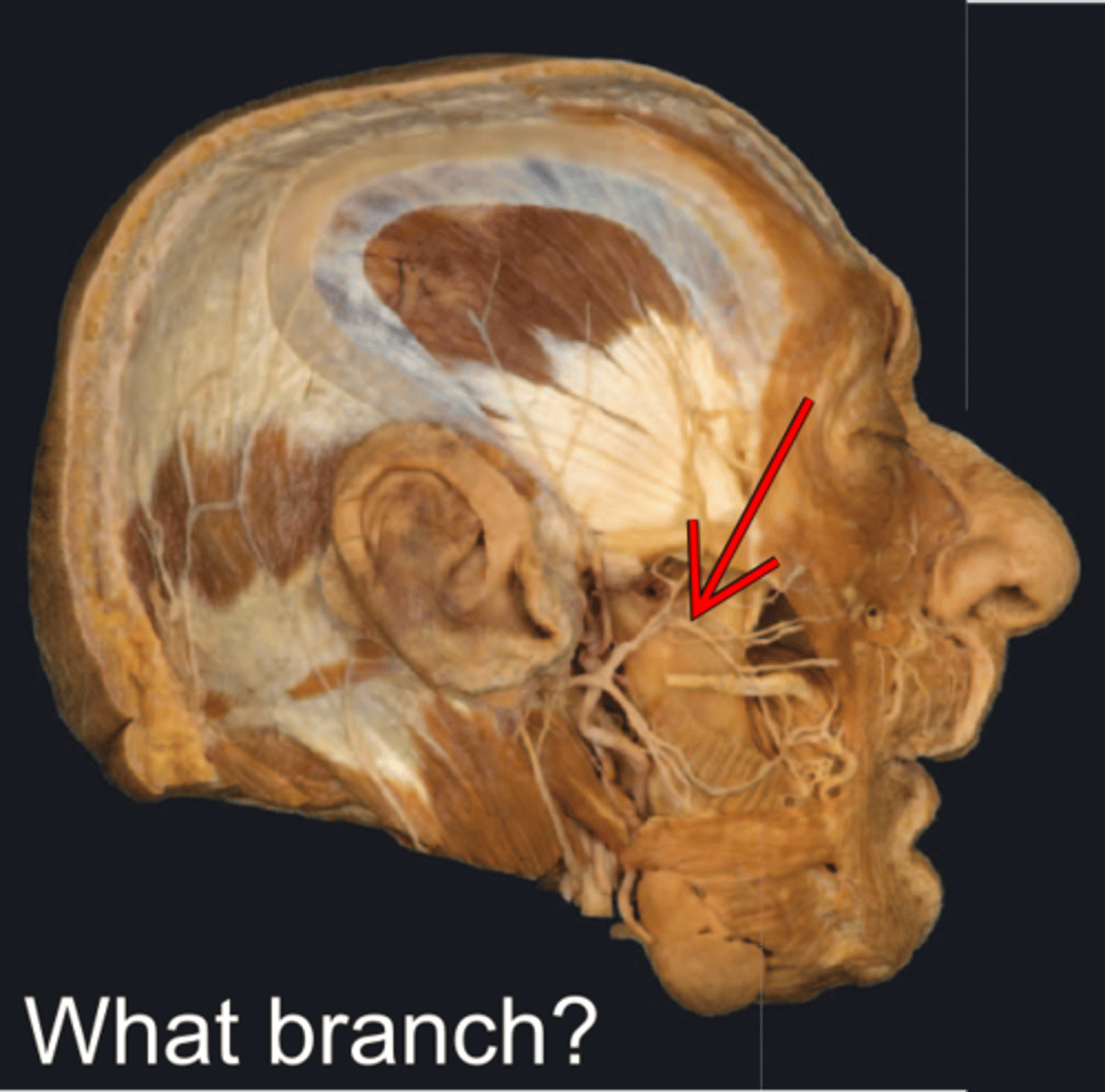
Zygomatic branch of facial n.
- has 2-3 main branches
- Innervates inferior part of orbicularis oculi and other facial mm. inferior to orbit
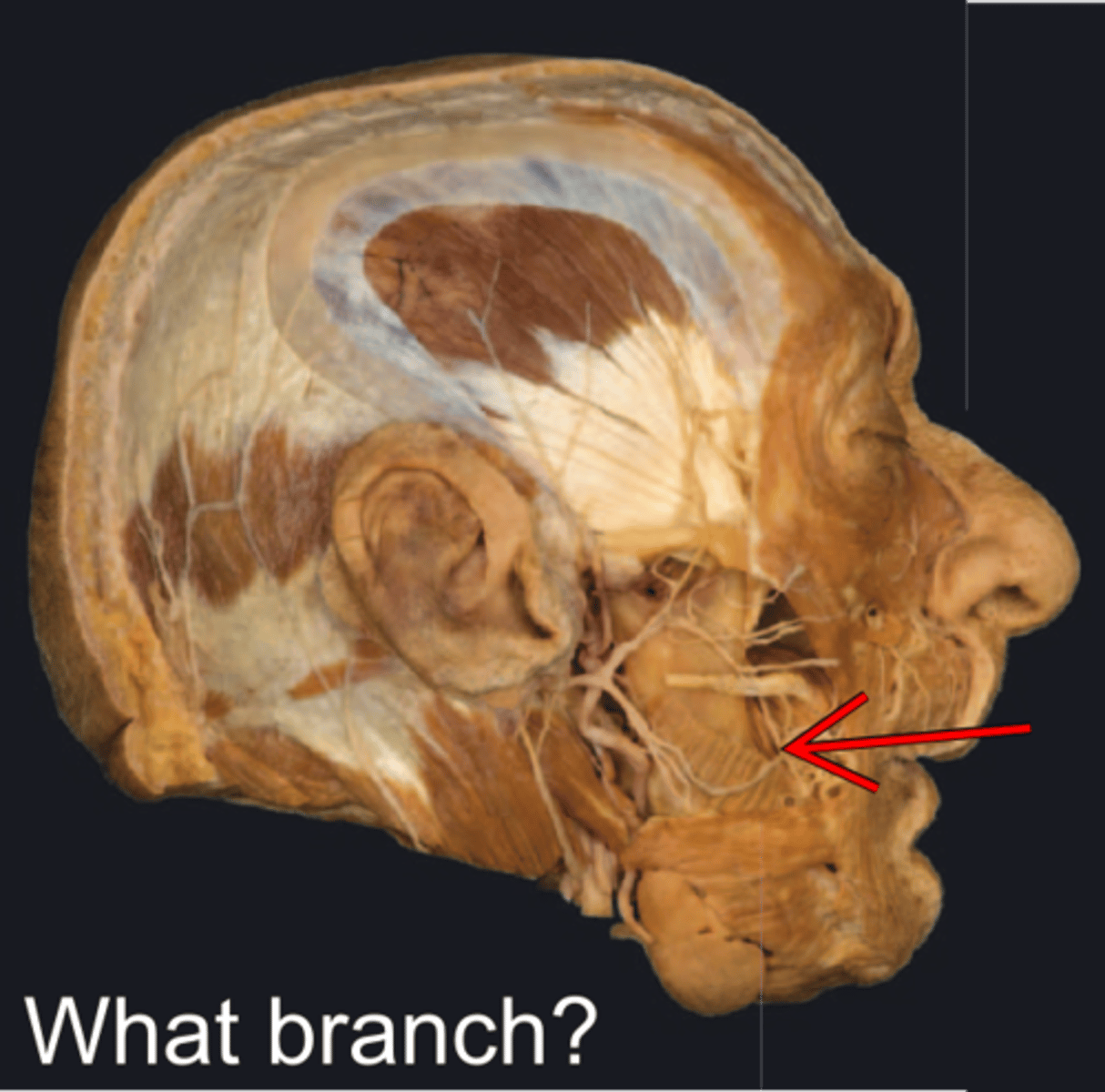
Buccal branch of facial n.
- external to buccinator m.
- Innervates buccinator, orbicularis oris and inferior levator labii superioris mm.
Mandibular branch of facial n.
innervation of mentalis
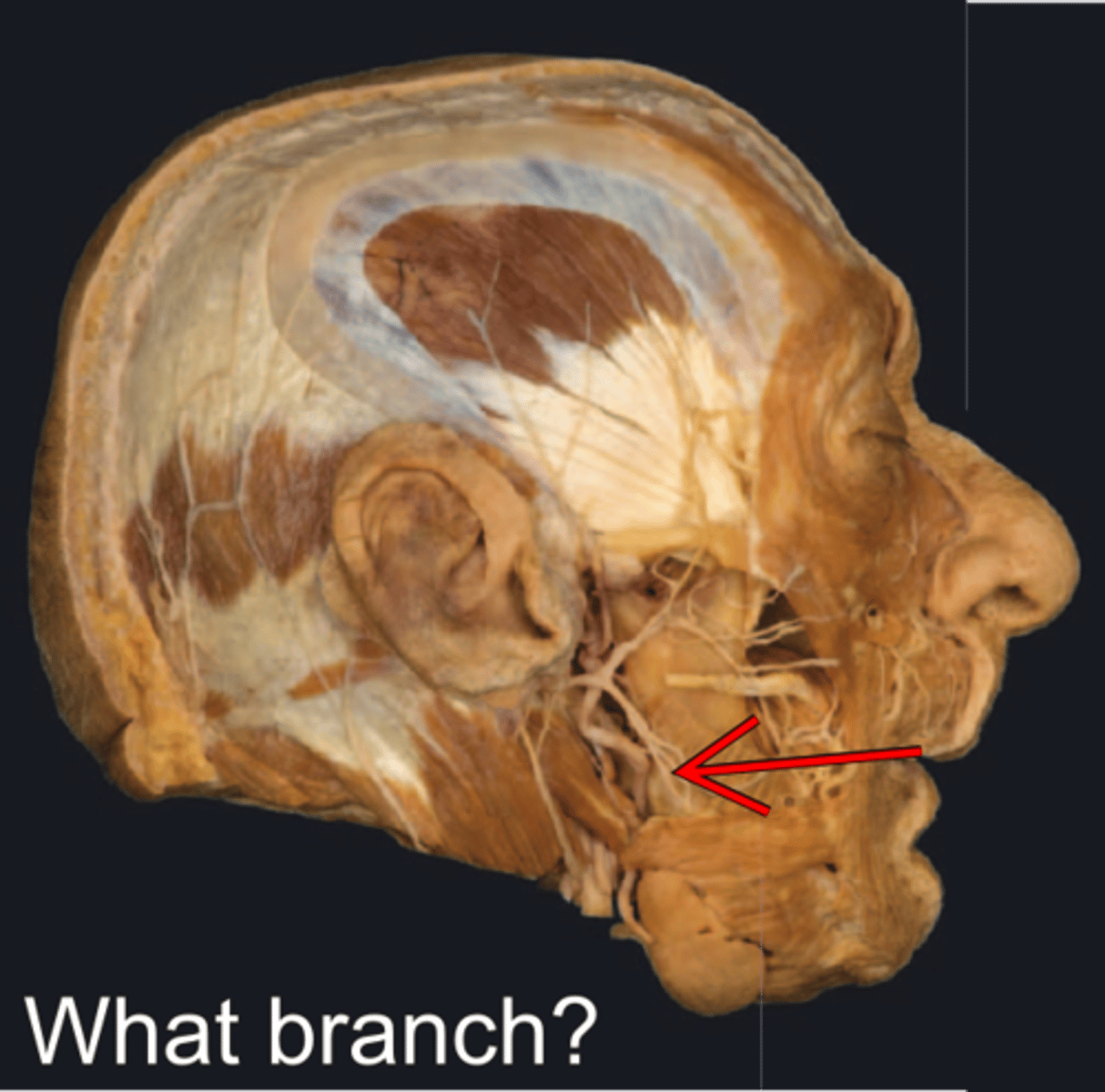
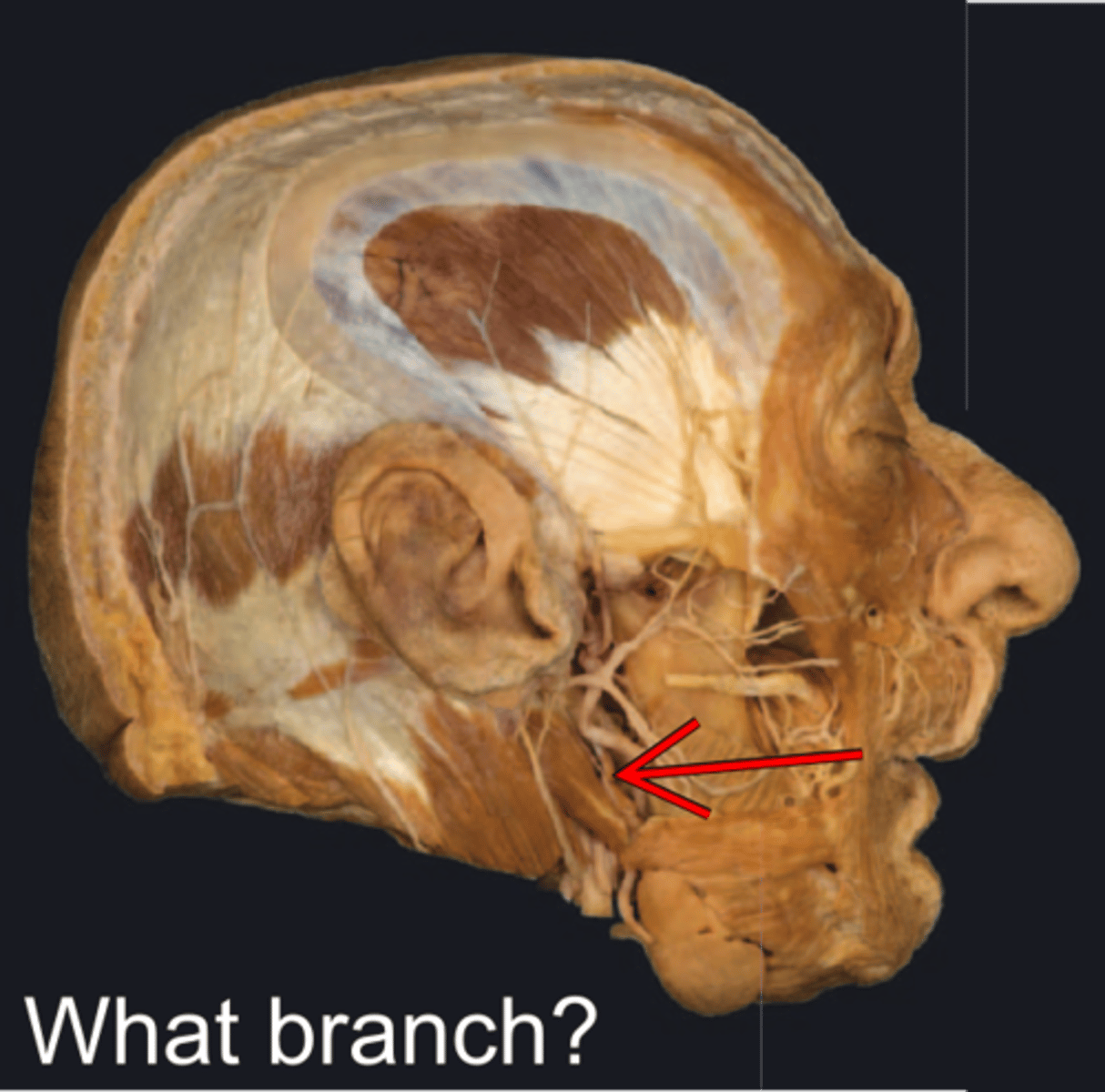
Cervical branch of facial n.
- runs posterior to mandible
- Innervates platysma m.
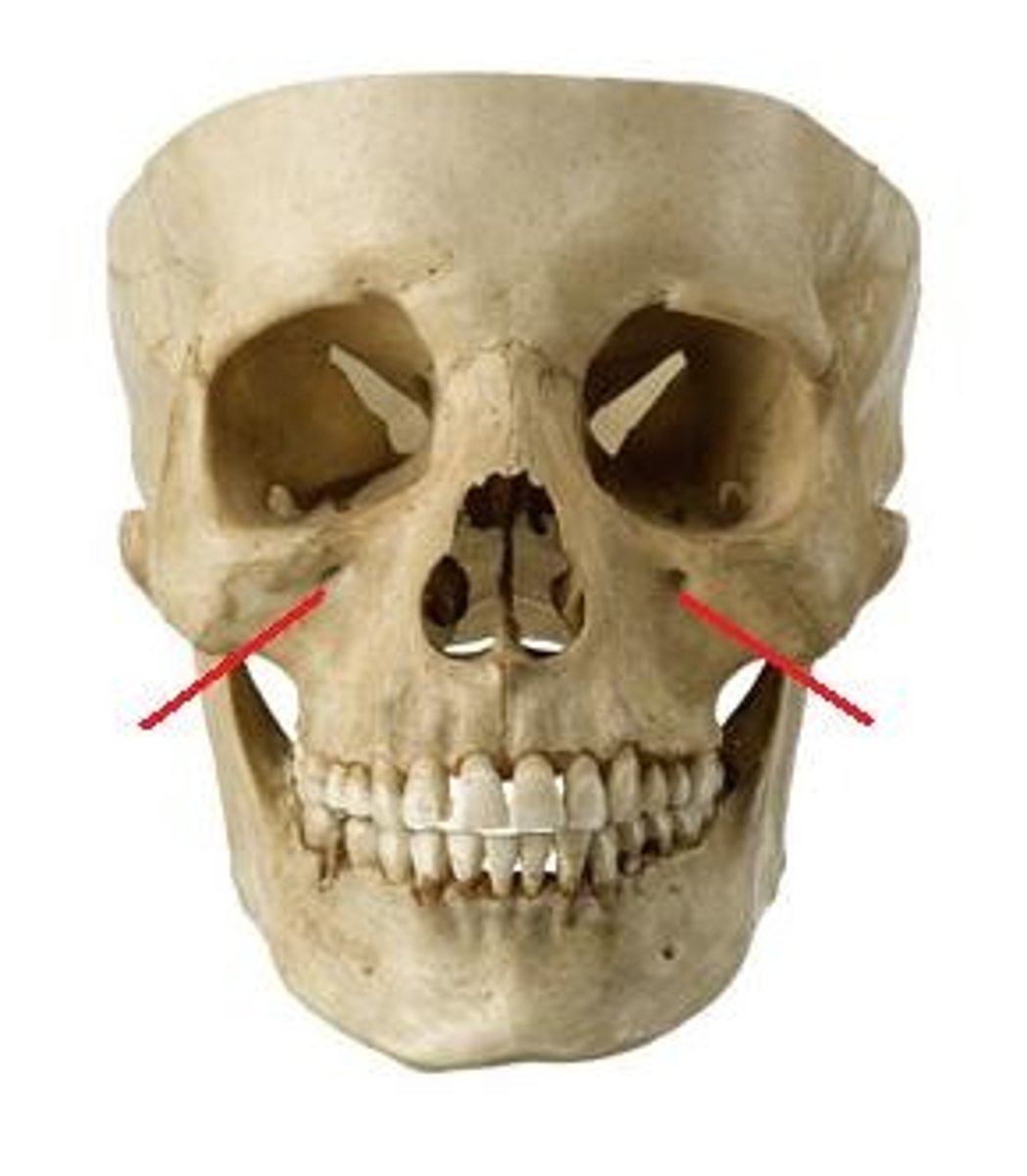
Supraorbital n.
an opening in the frontal bone above the eye orbit
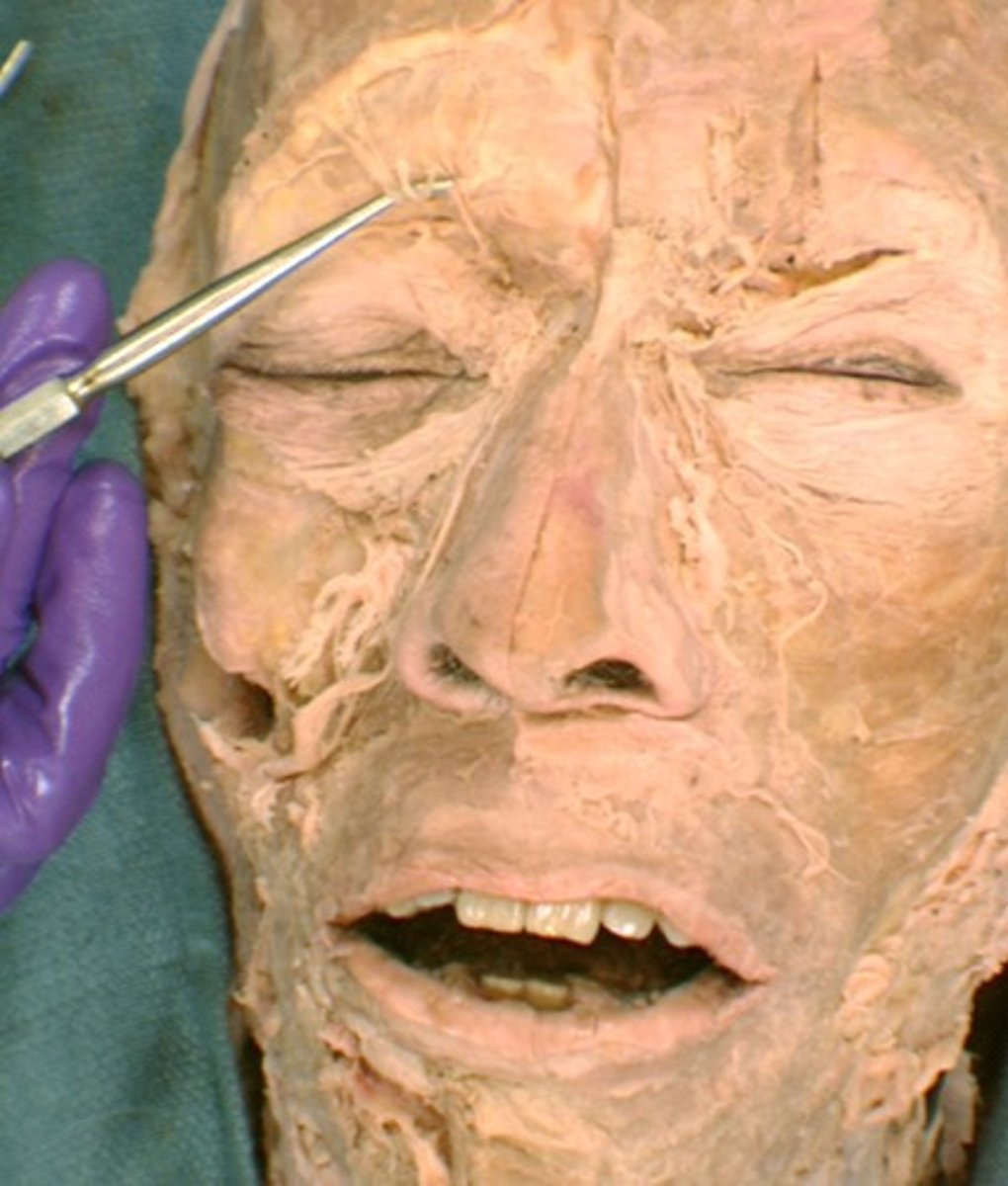
Infraorbital n.
pertaining to below the eye
Mental n.
pertaining to the chin
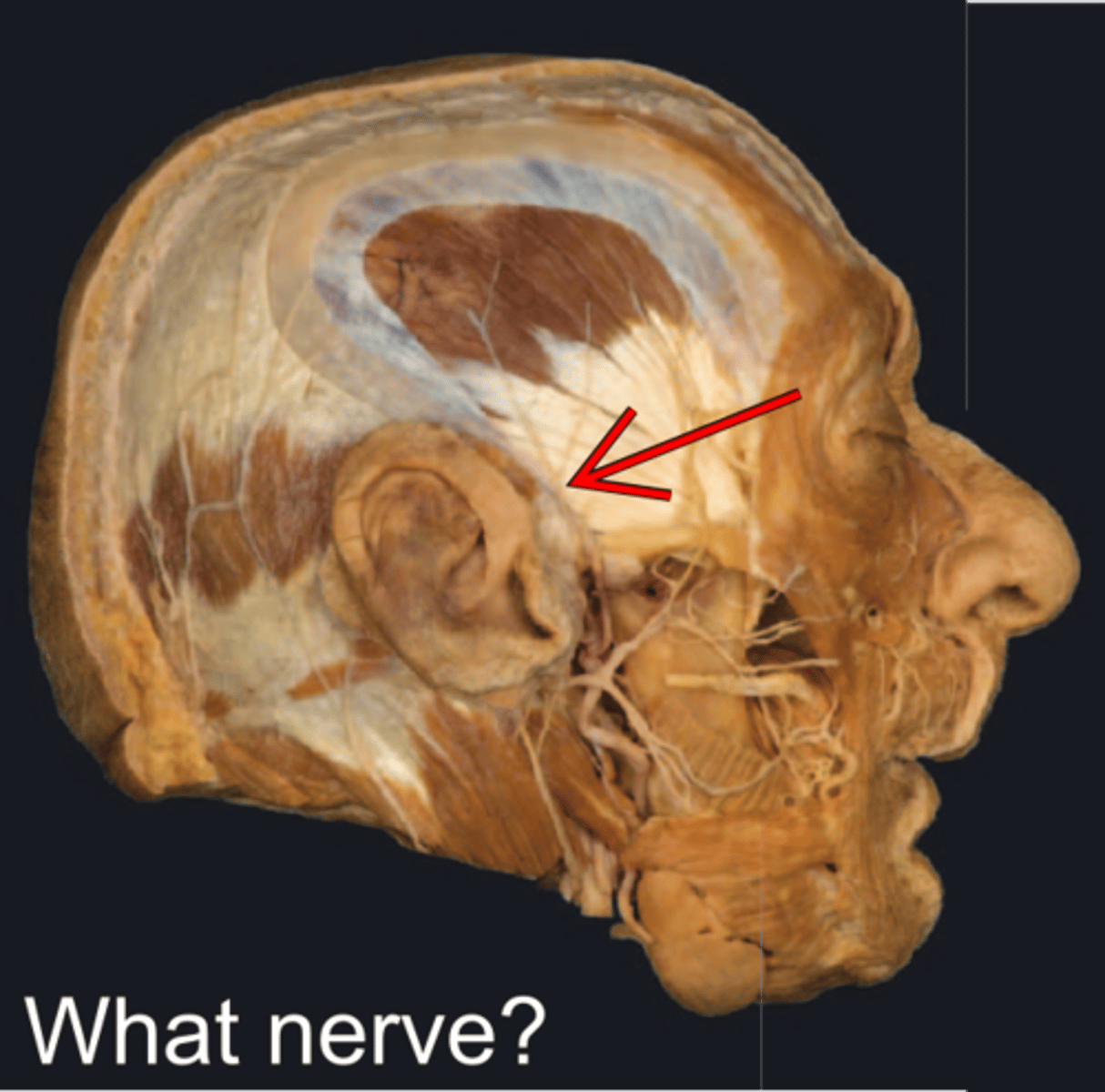
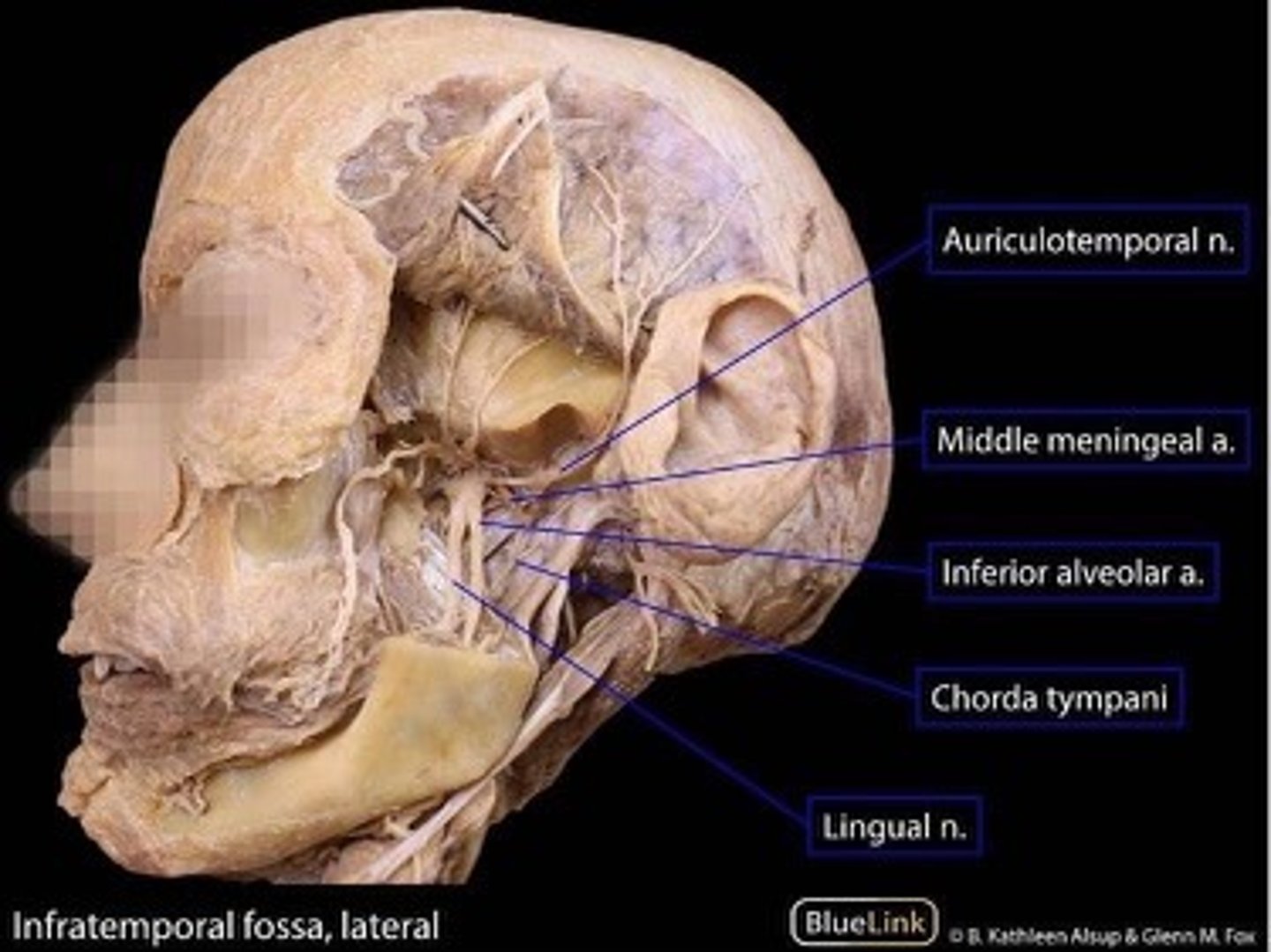
Auriculotemporal n.
pertaining to the ear and the temporal area of the skull
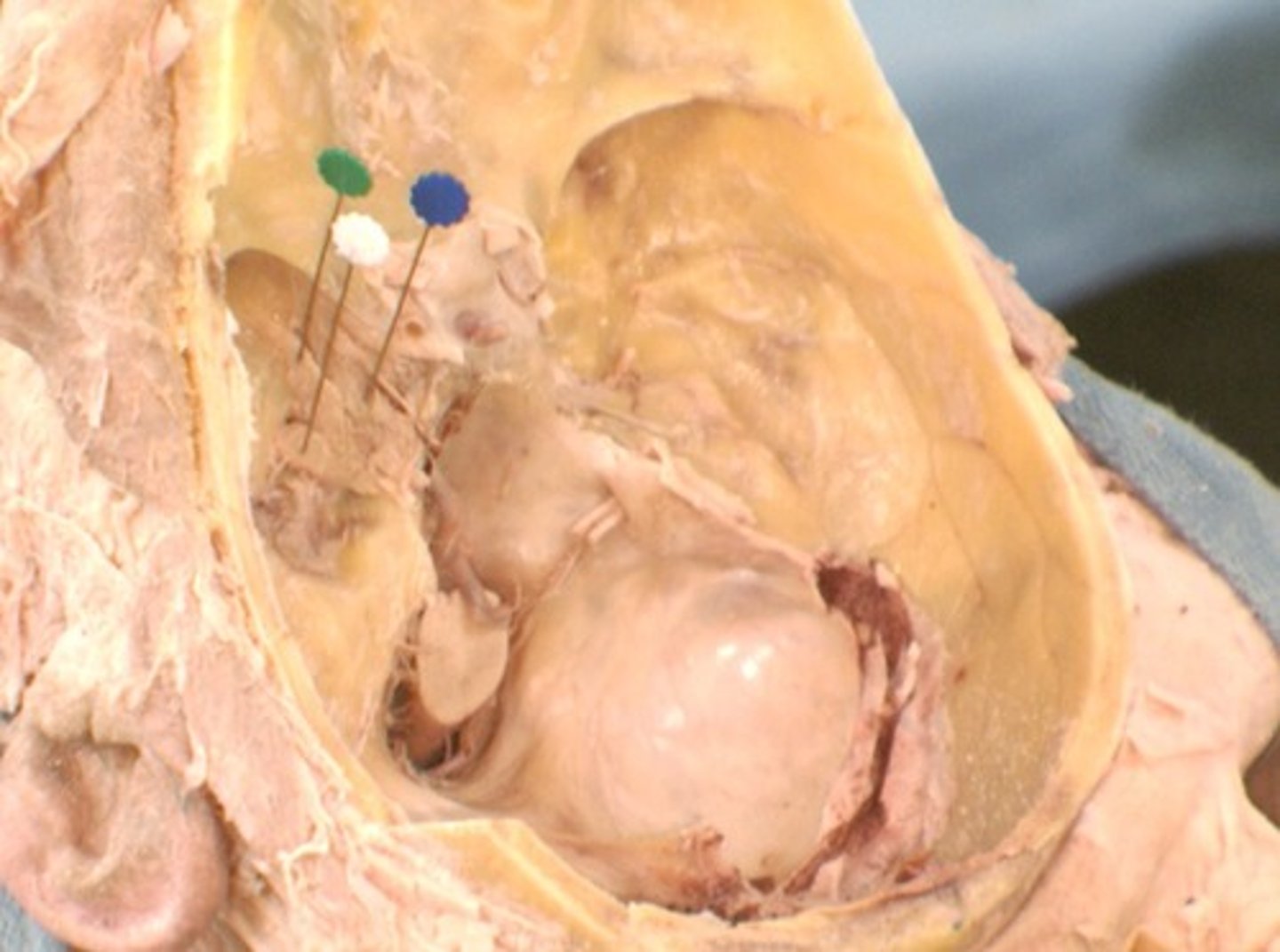
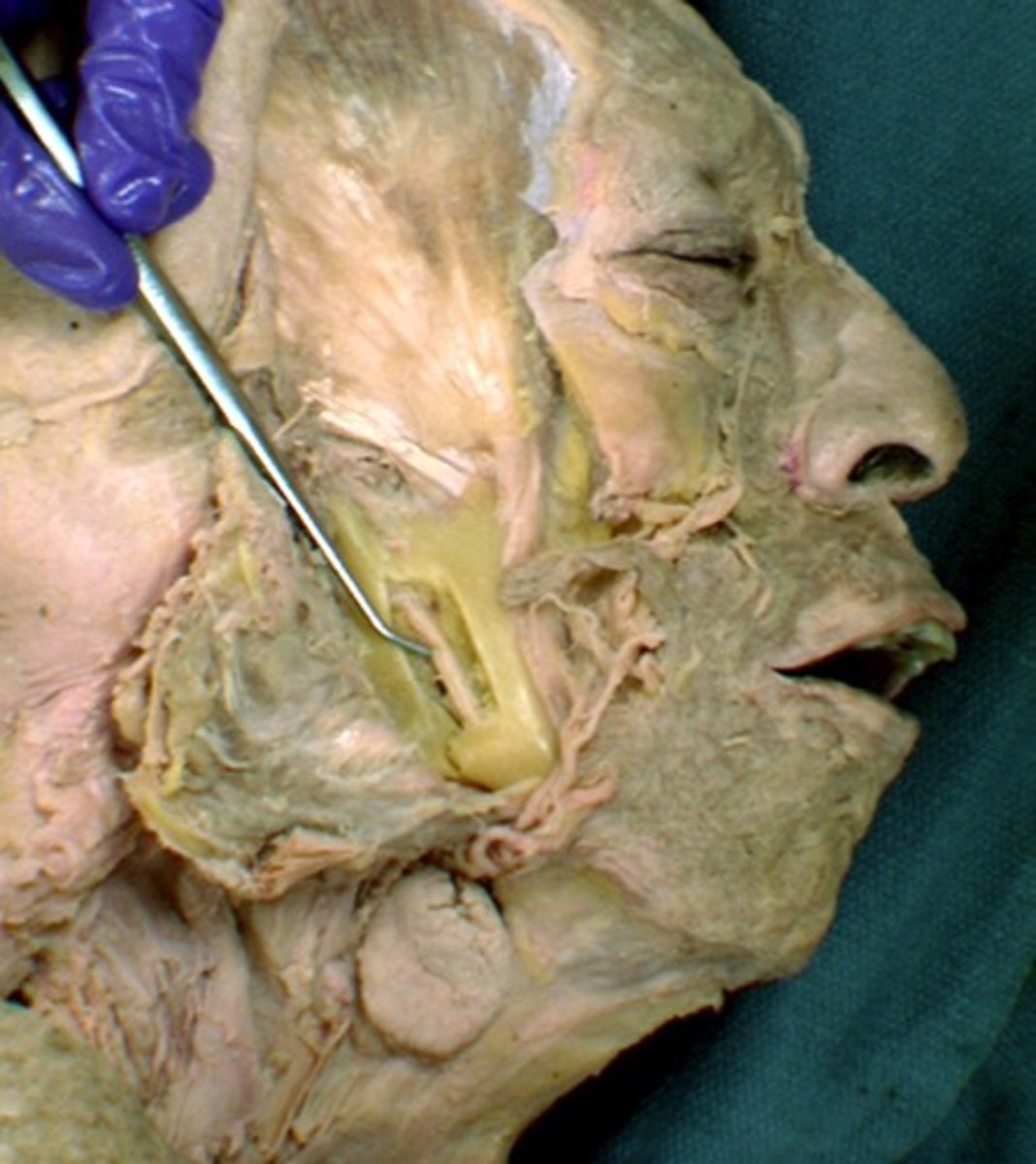
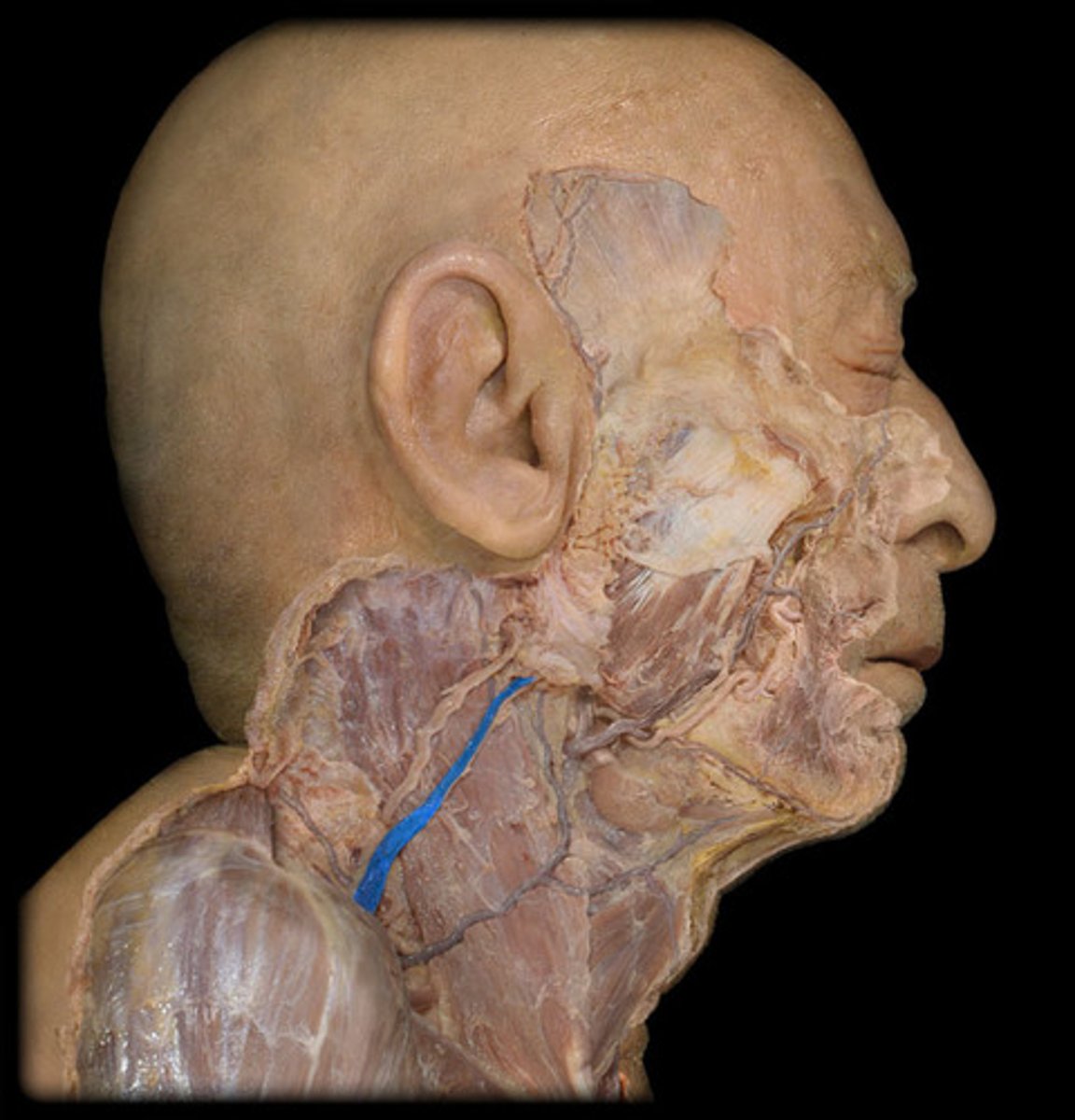
Parotid salivary gland
lies under the skin covering the lateral and posterior surface of the mandible
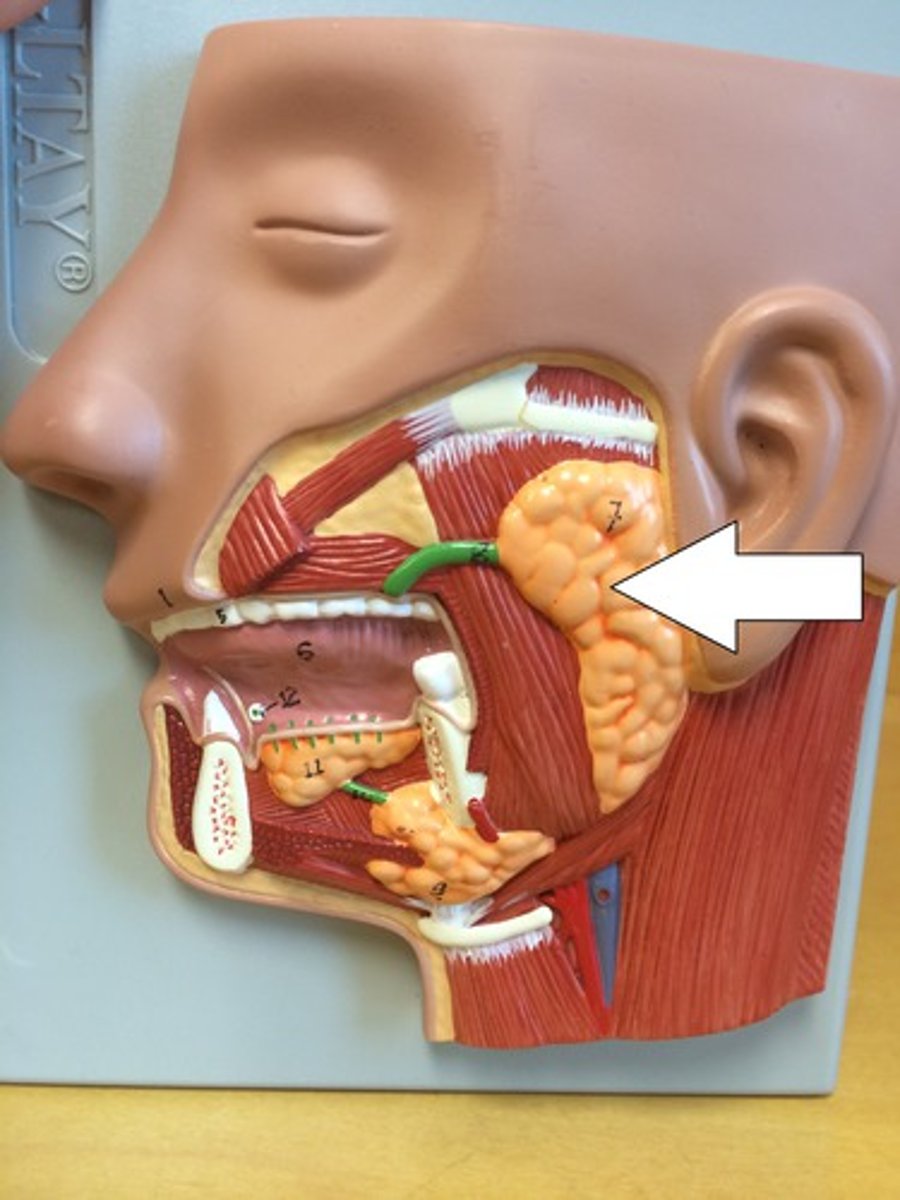
Parotid duct
Duct associated with the parotid salivary gland, which opens into the oral cavity at the parotid papilla.
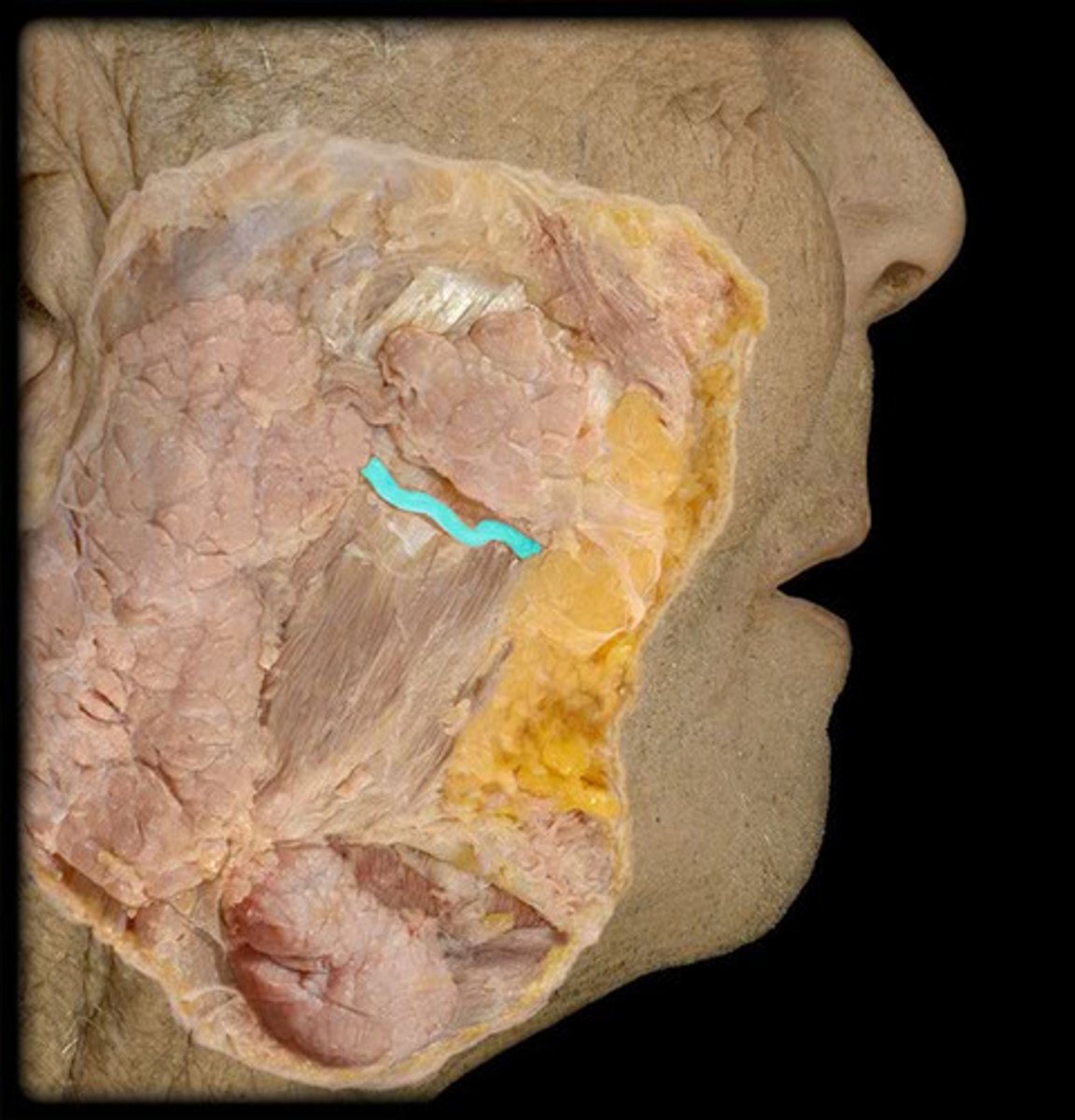
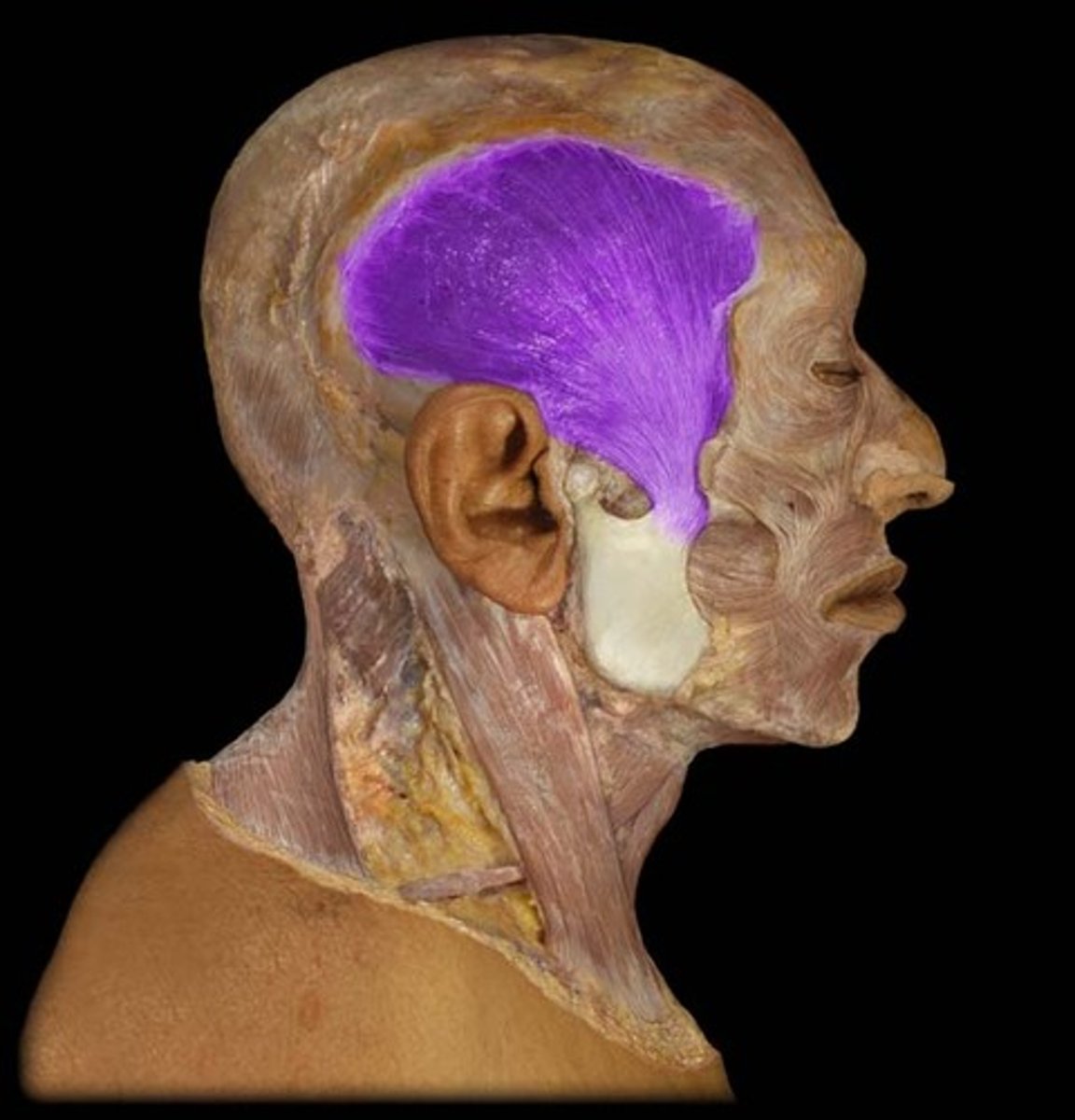
Temporalis m.
elevates and retracts the mandible; moves mandible laterally
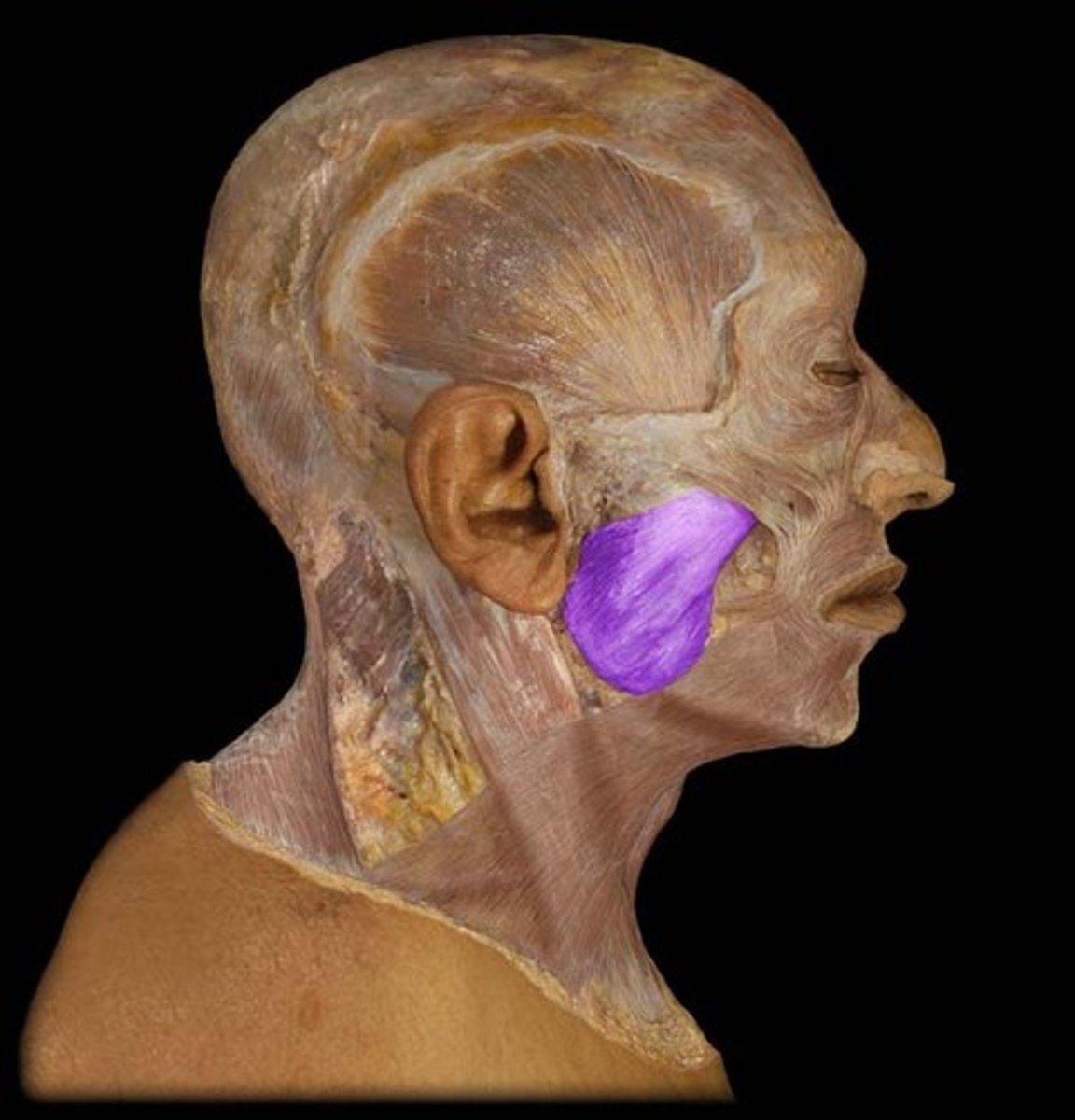
Masseter m.
elevates mandible to close the jaw (bite)
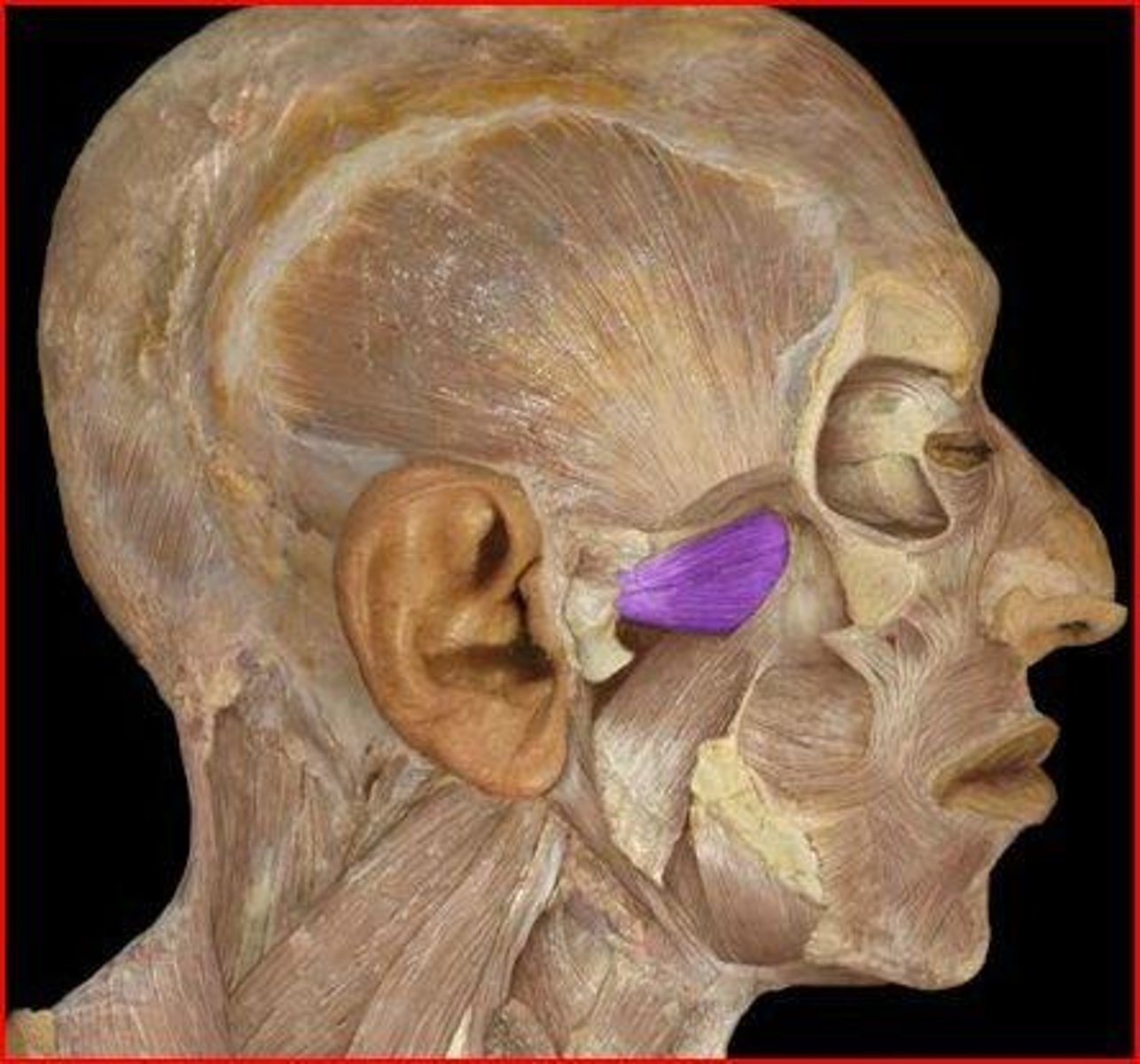
Medial pterygoid m.
elevates and protracts and moves mandible from side to side

Lateral pterygoid m.
depresses, protracts, moves the mandible from side to side
Temporomandibular joint
connection on either side of the head between the temporal bone of the skull and mandibular bone of the jaw
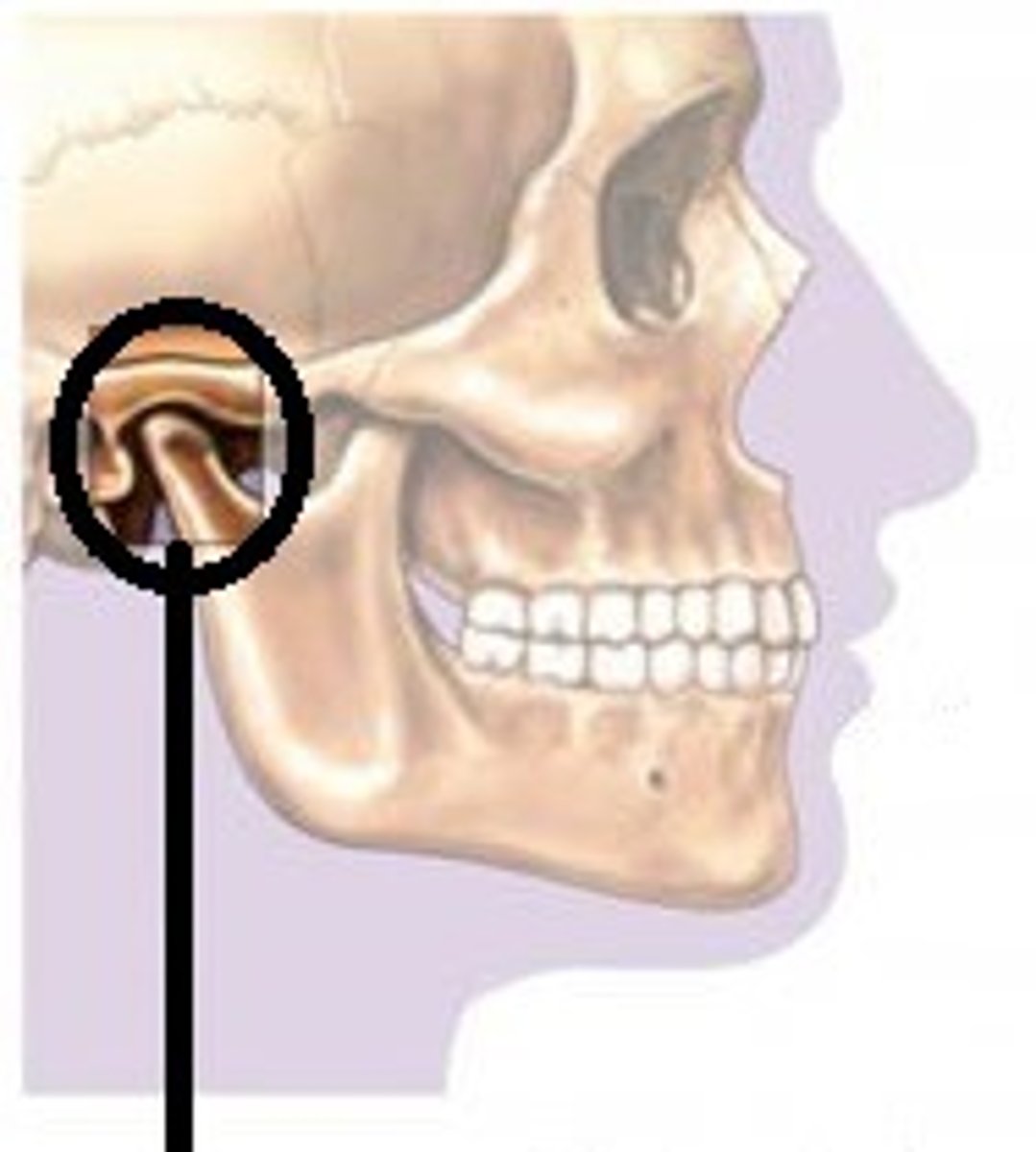
Articular disc of temporomandibular joint
The articular disc is a thin, oval plate made from fibrous connective tissue and found between the condyle of the mandible and the mandibular fossa.
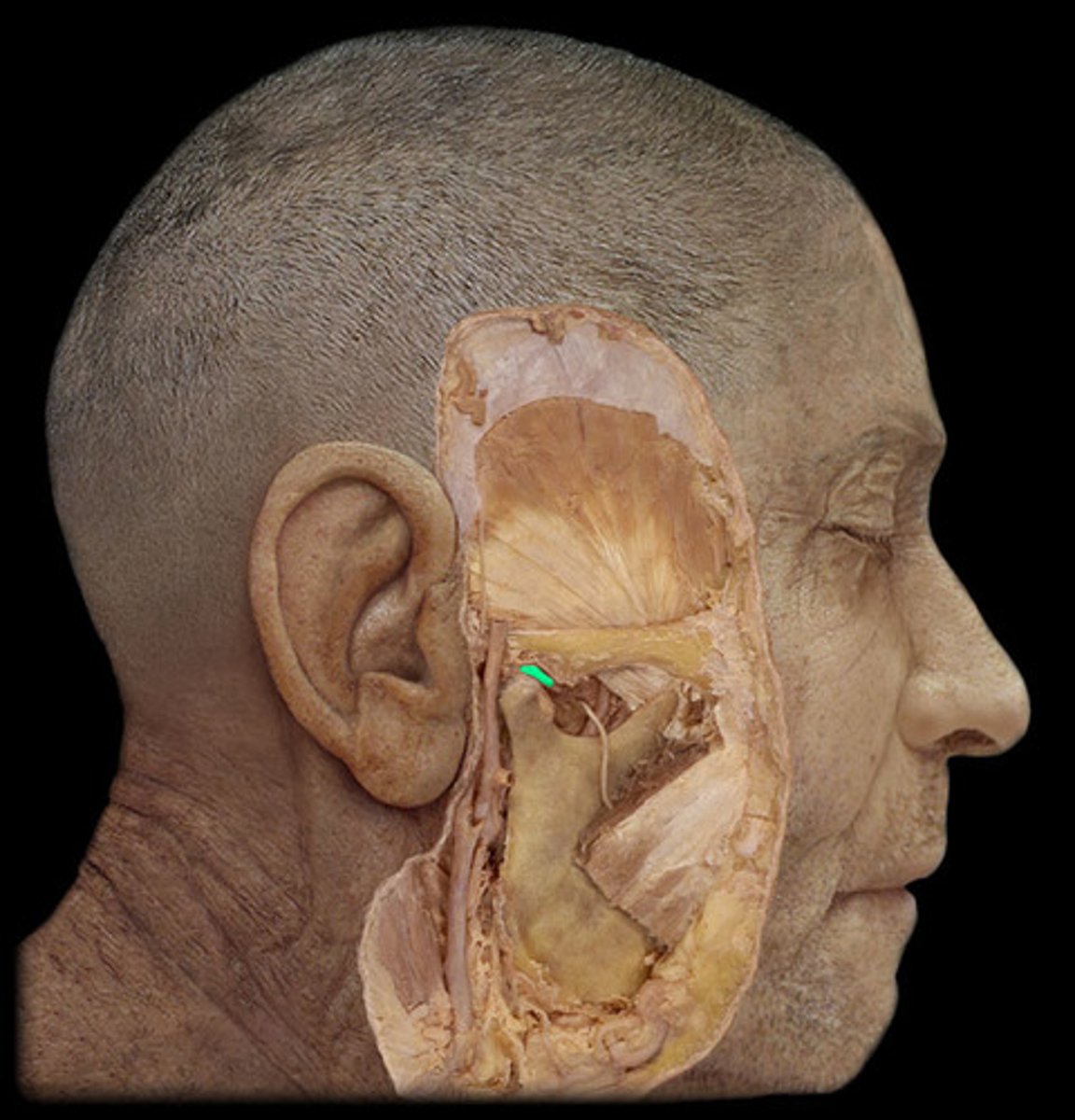
External carotid a.
Gives off many branches in the neck
Supplies external neck & face
Maxillary a.
supplies teeth, palate, and nasal cavity

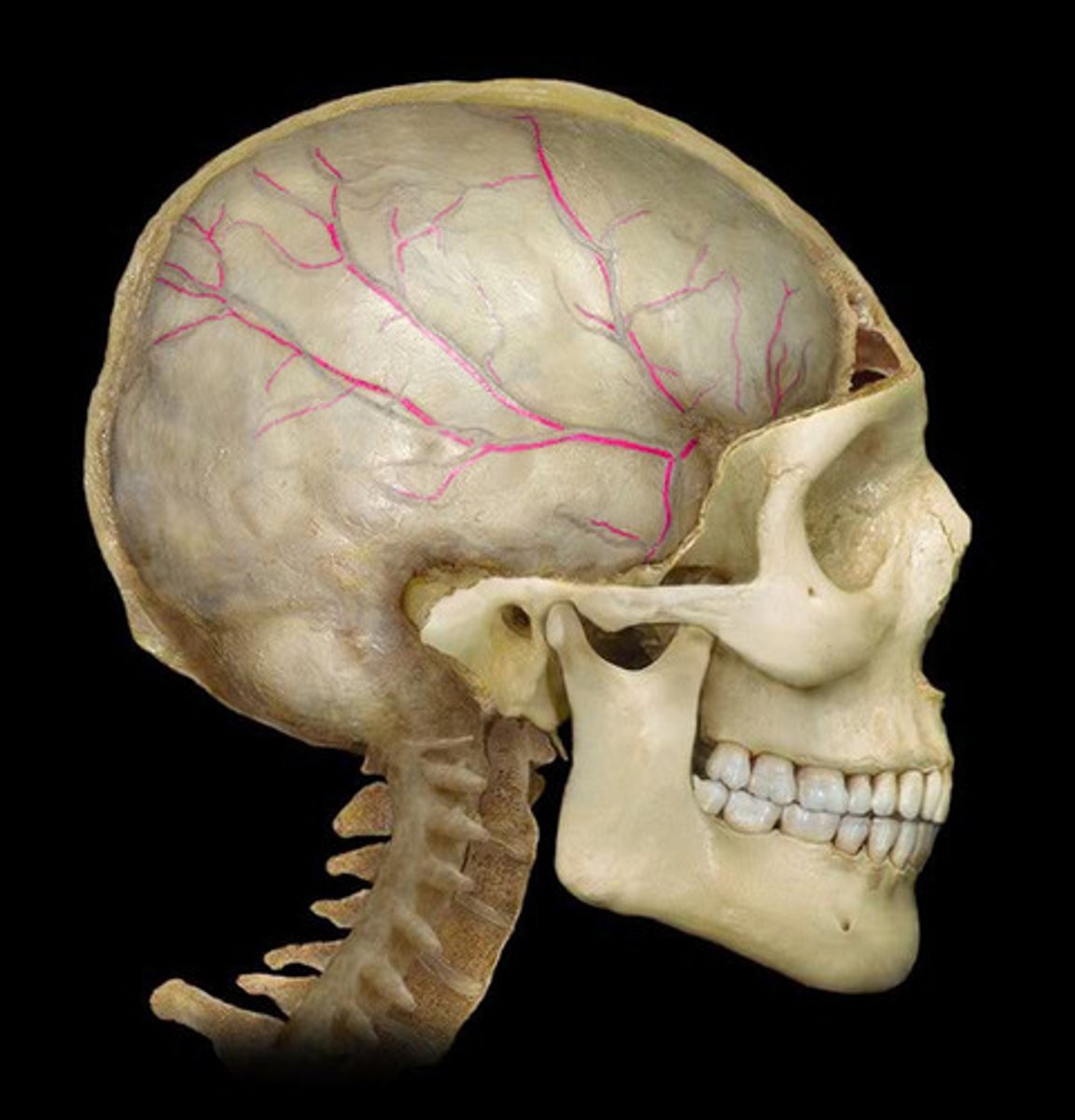
Middle meningeal a.
foramen spinosum
Inferior alveolar a.
Enters the mandibular foramen with the inferior alveolar n. and courses through the mandibular canal
S: branches to the roots of the teeth in the lower arcade
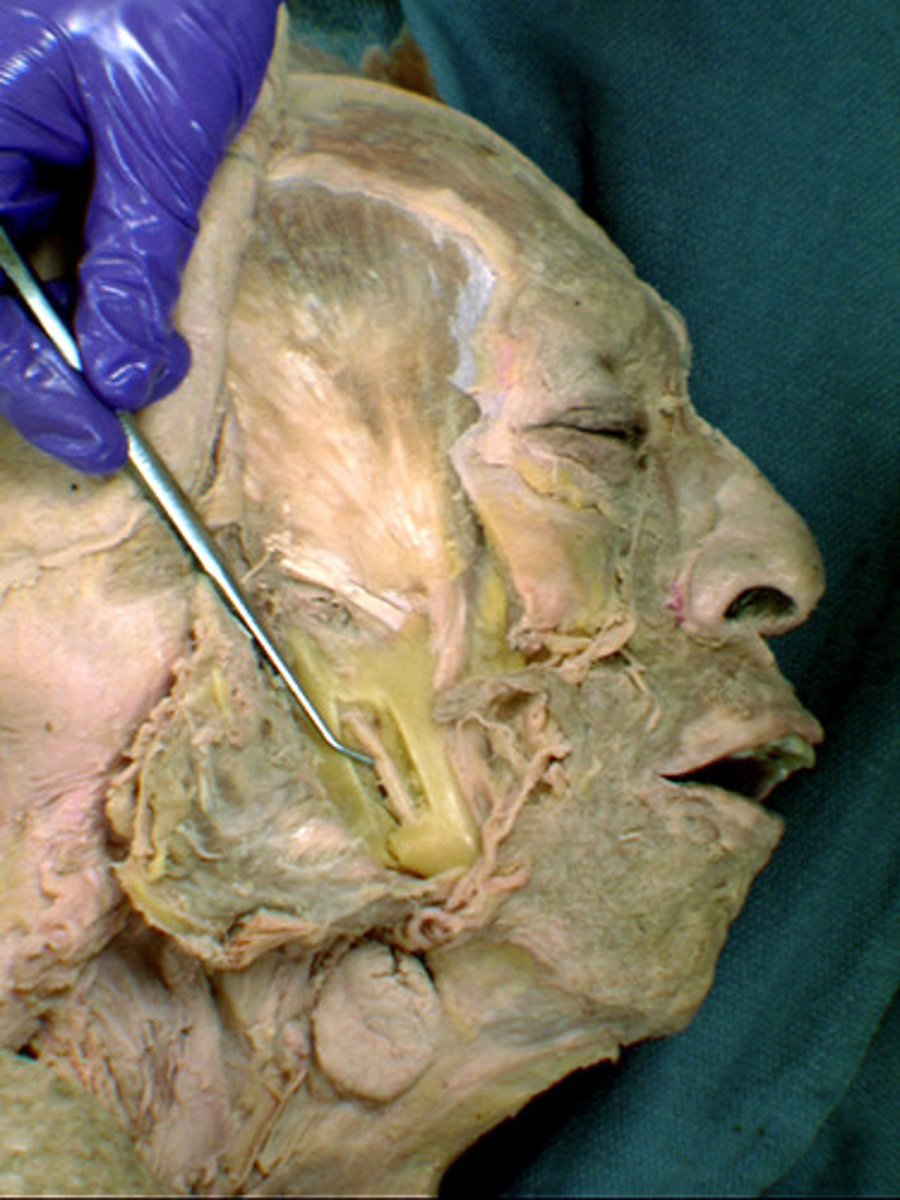
Mandibular division of trigeminal n.
sensory branches transmit impulses from the scalp behind ears, skin of jaw, lower teeth, lower gum, lower lip; the motor branches supply the muscles of mastication and floor of mouth
Lingual n.
towards the tongue
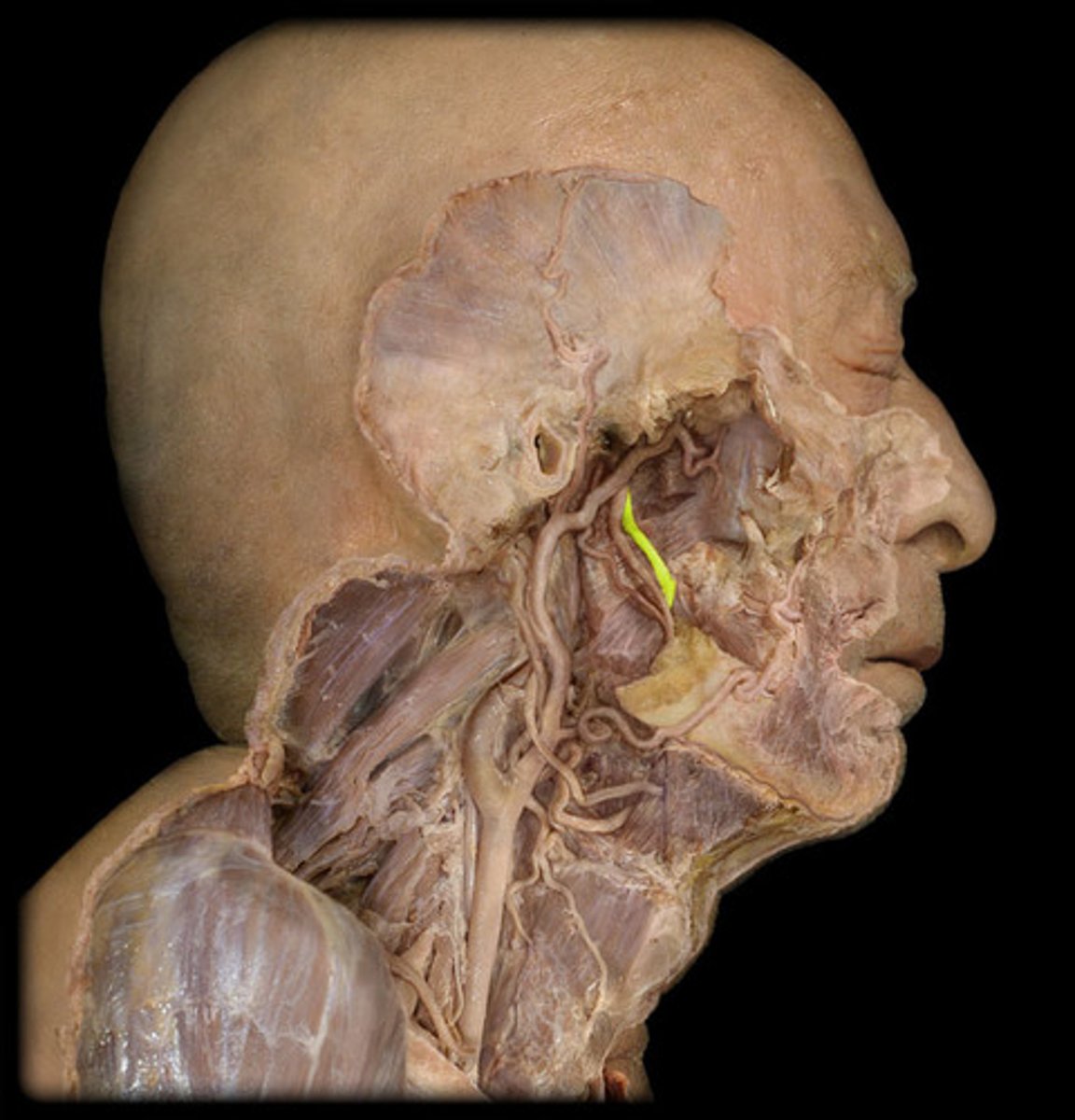
Inferior alveolar n.
carries sensation from the mandibular teeth and mucosa of the mouth floor and some tongue areas
Chorda tympani
Nerve that provides taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue
Cervical transverse process
transverse processes project laterally
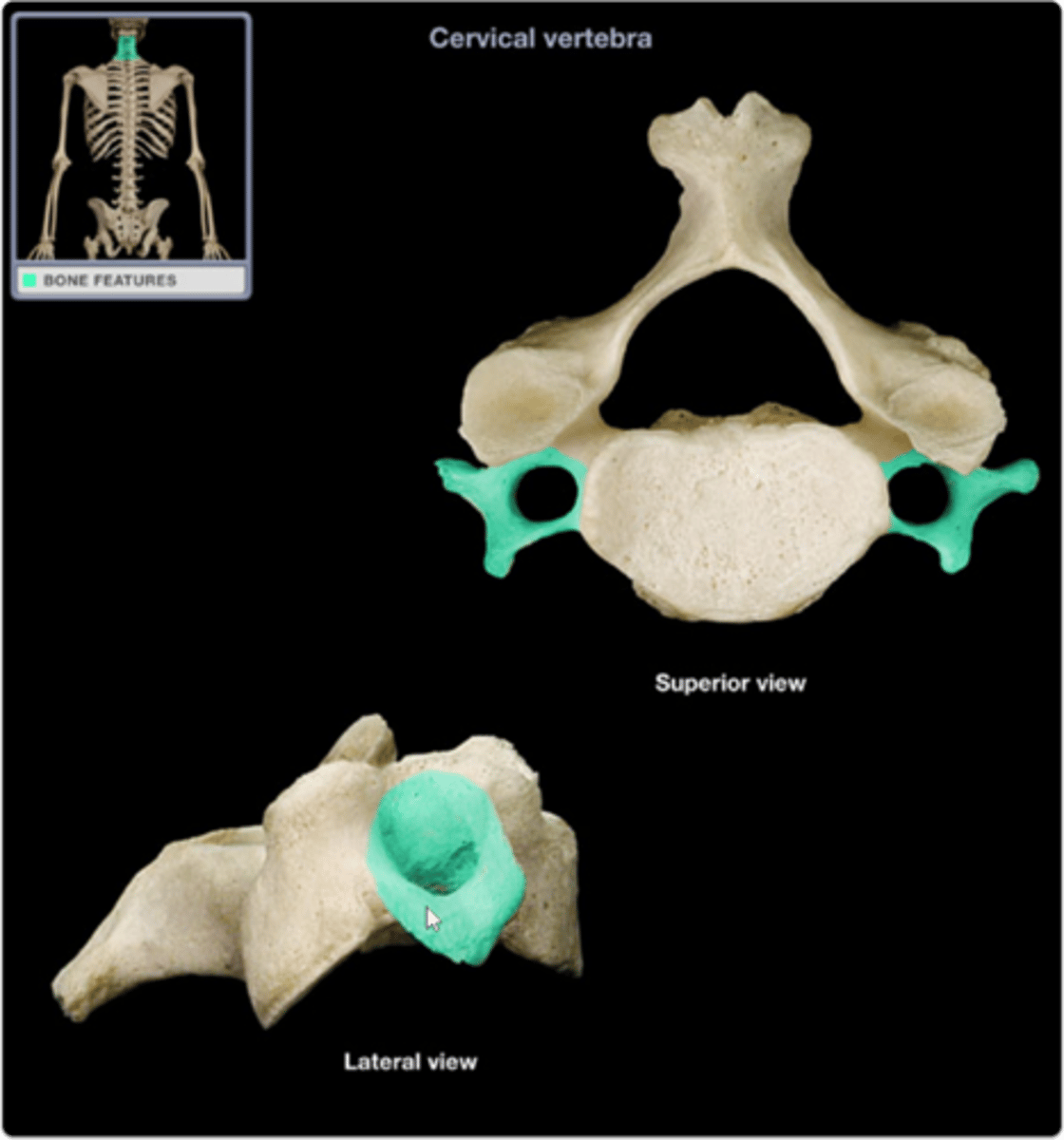
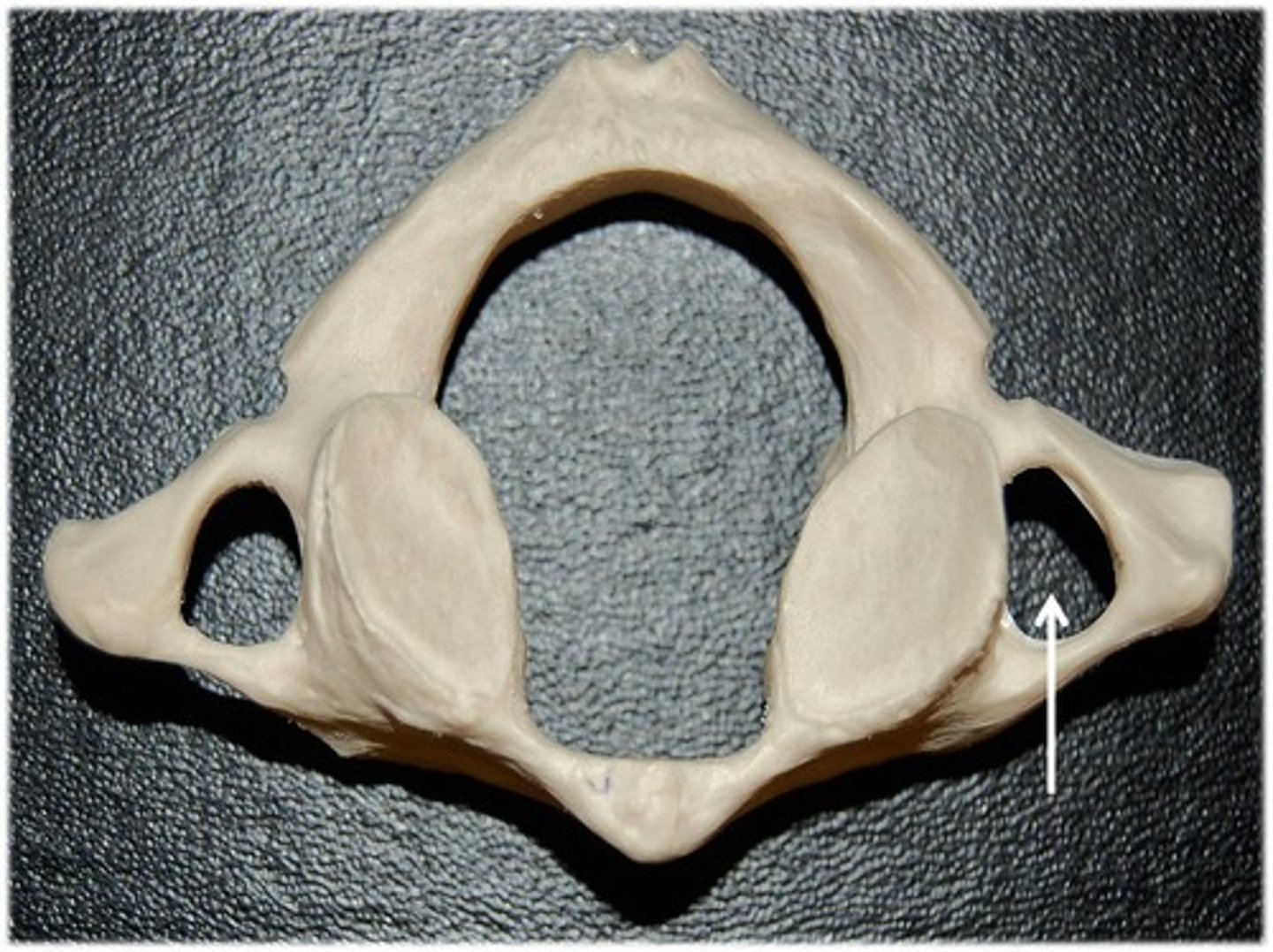
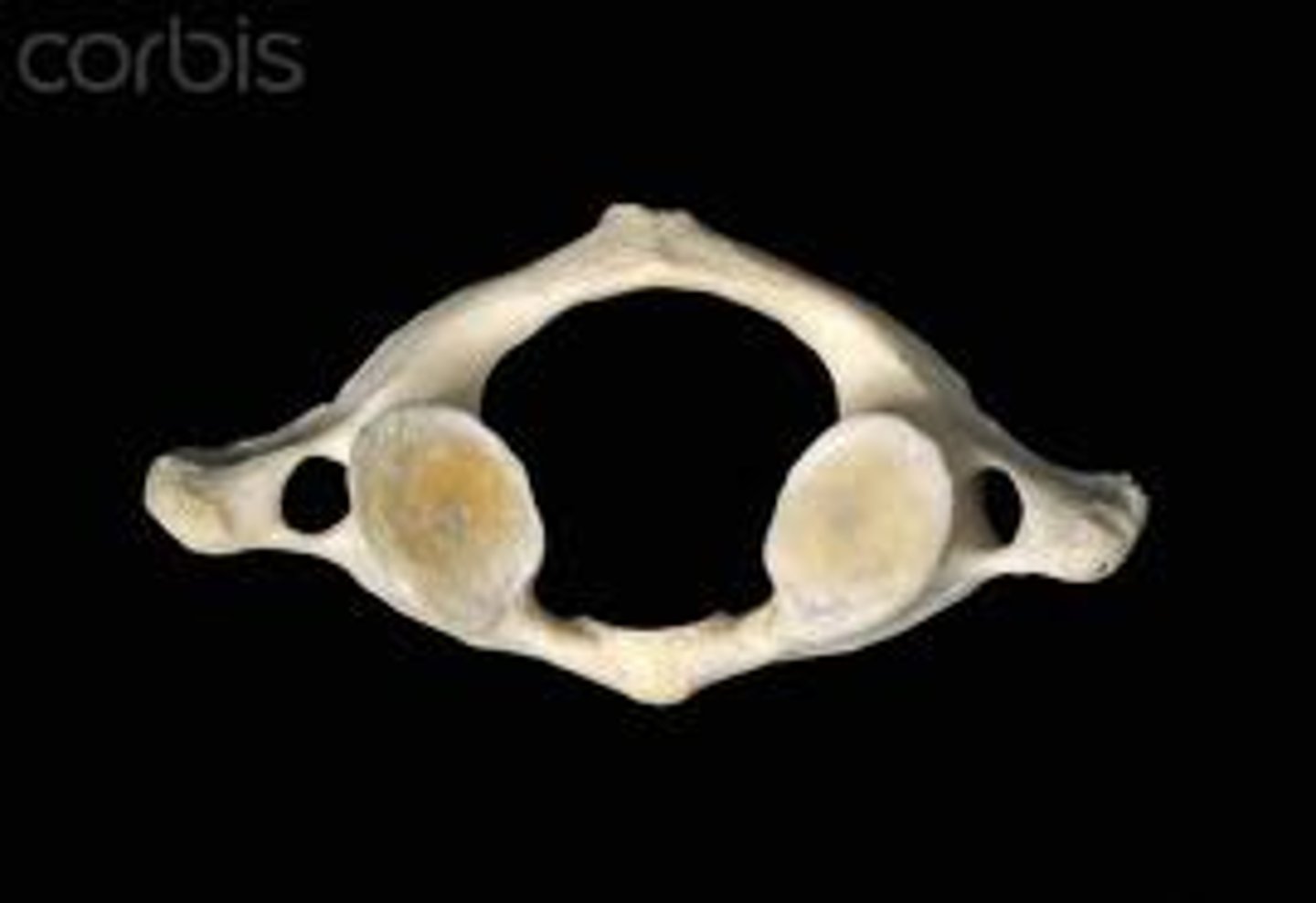
Transverse foramen
only found in the cervical vertebrae and allow passage of the vertabral artery, vein, and nerve
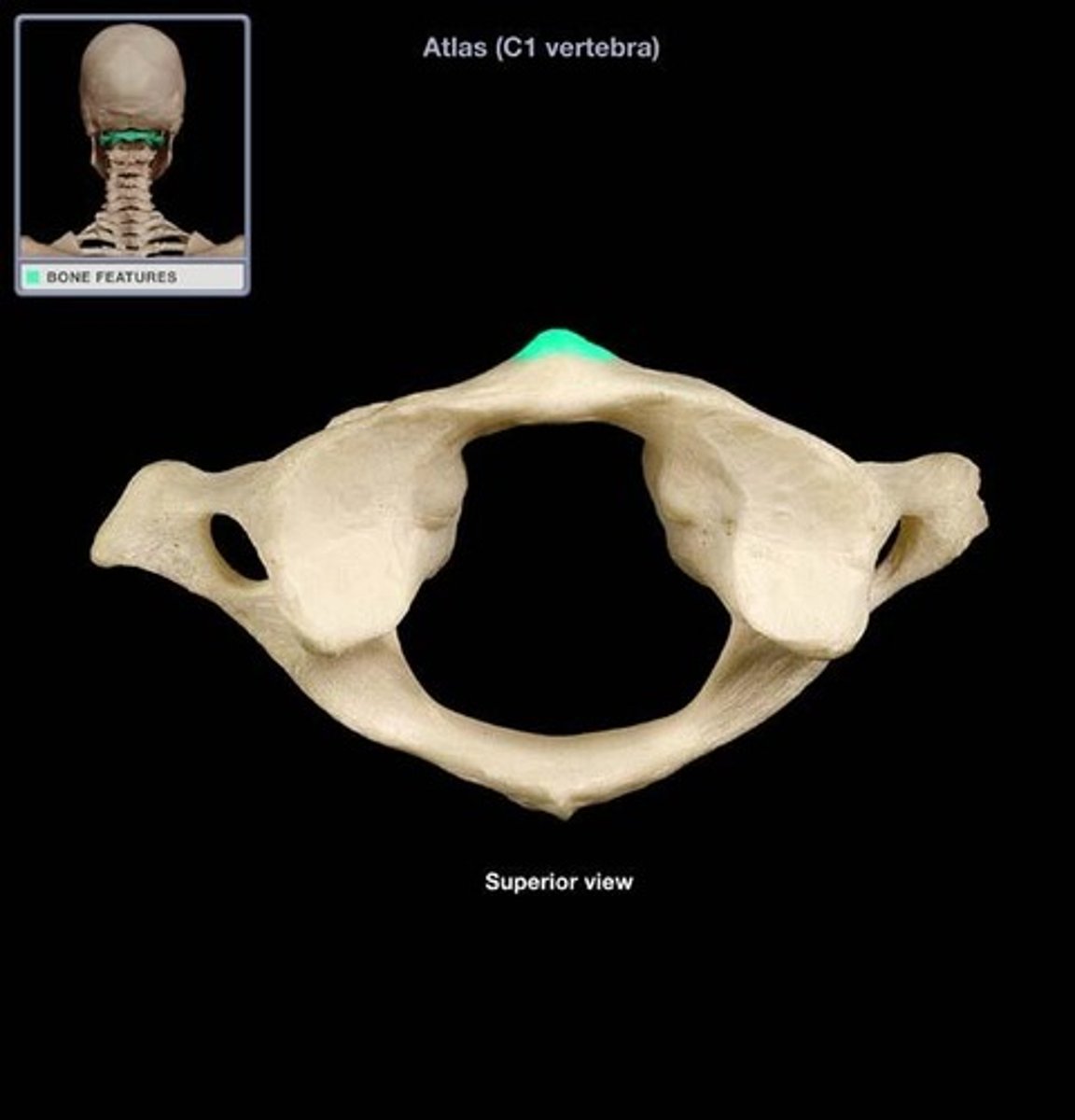
Atlas (C1 vertebra)
supports the head; allows a rocking motion in conjunction with the occipital condyles
Anterior arch of atlas
A small arch on the atlas that would be in the ventral most part of the body. Allows for a ventral articulation with the Dens.
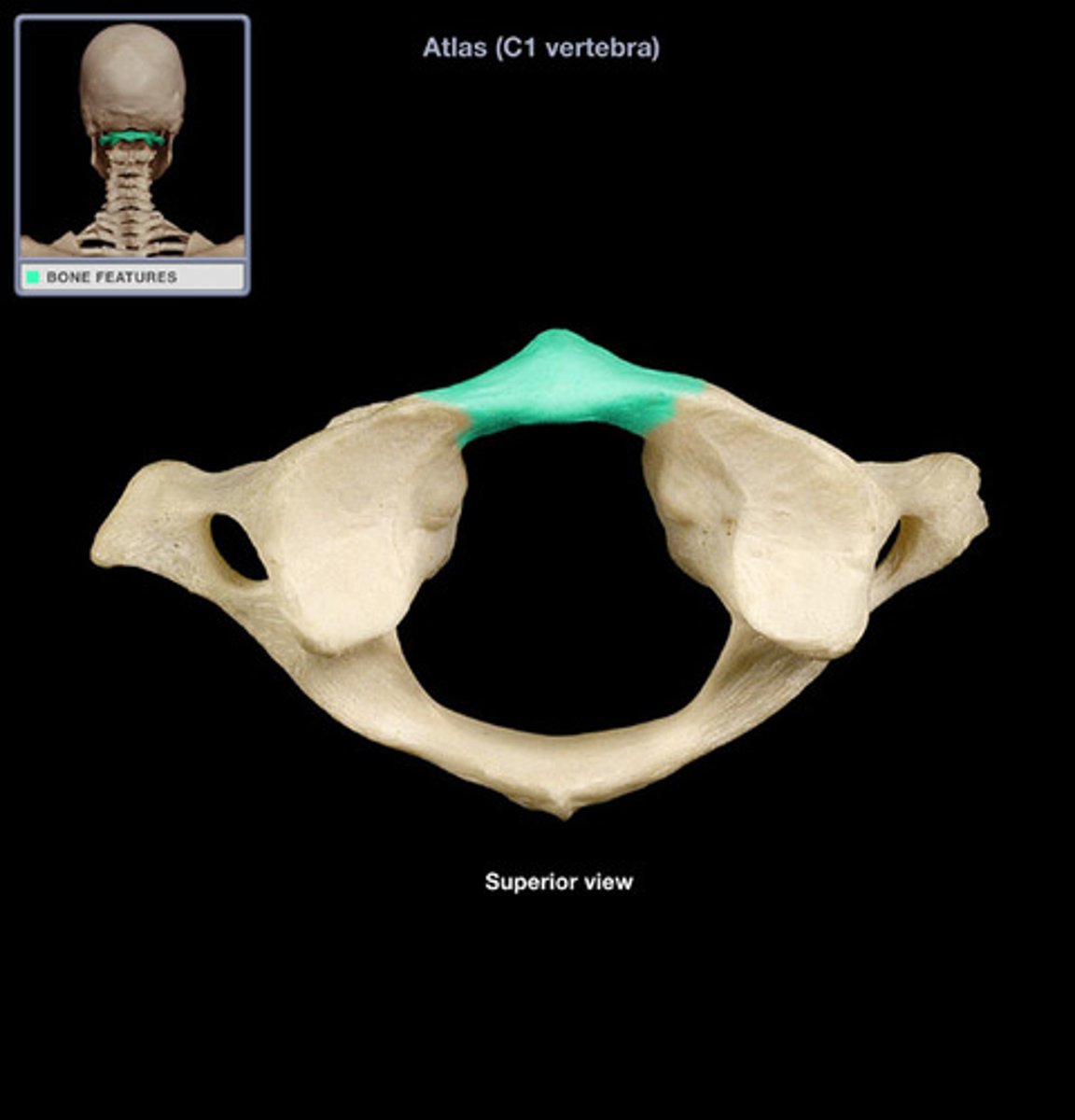
Anterior tubercle of atlas
serves as site of attachment for cervical ligaments and muscles
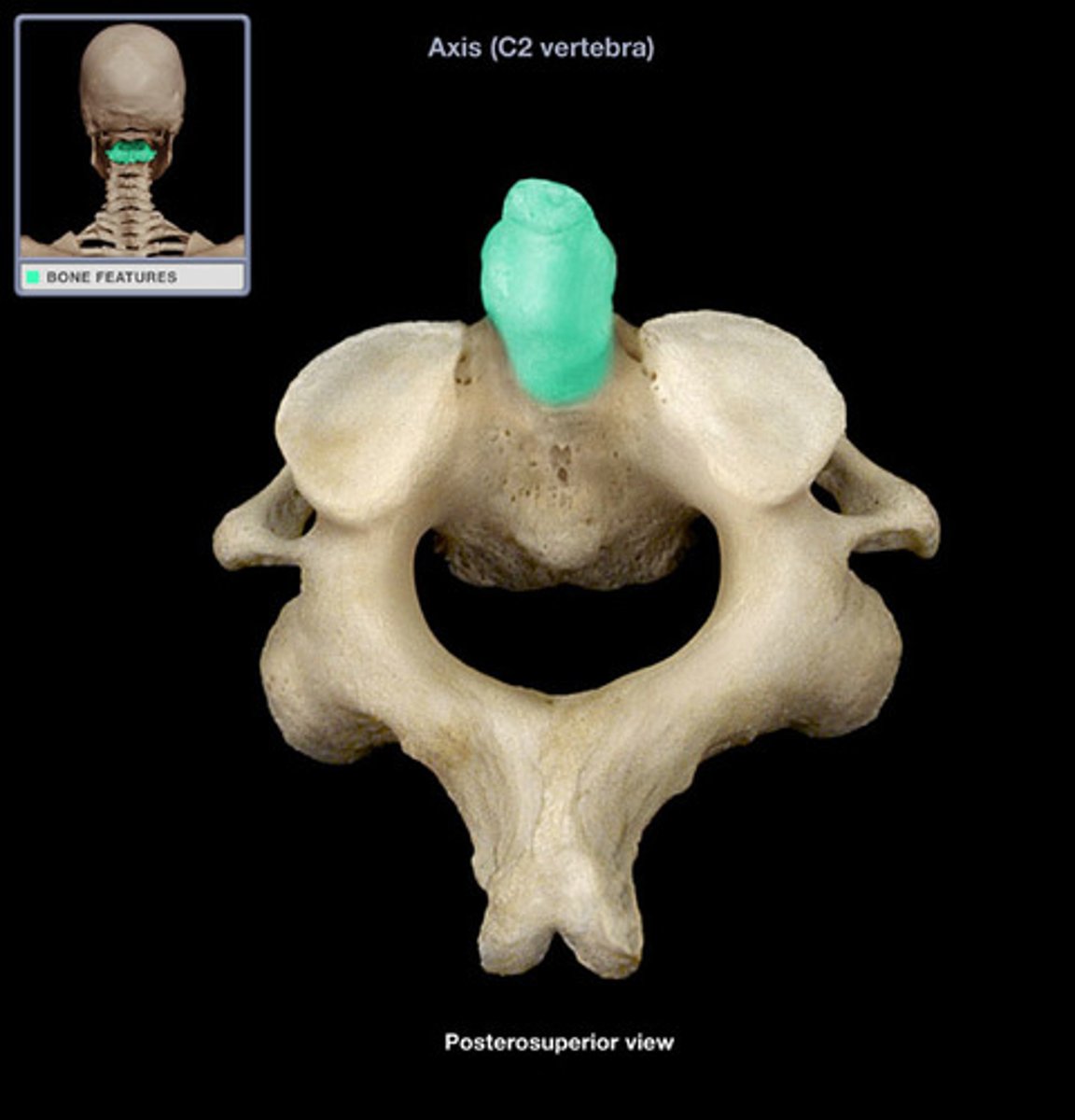
Axis (C2 vertebra)
Contains a body and a spinous process
Allows the head to shake side to side (no)
Dens
toothlike structure
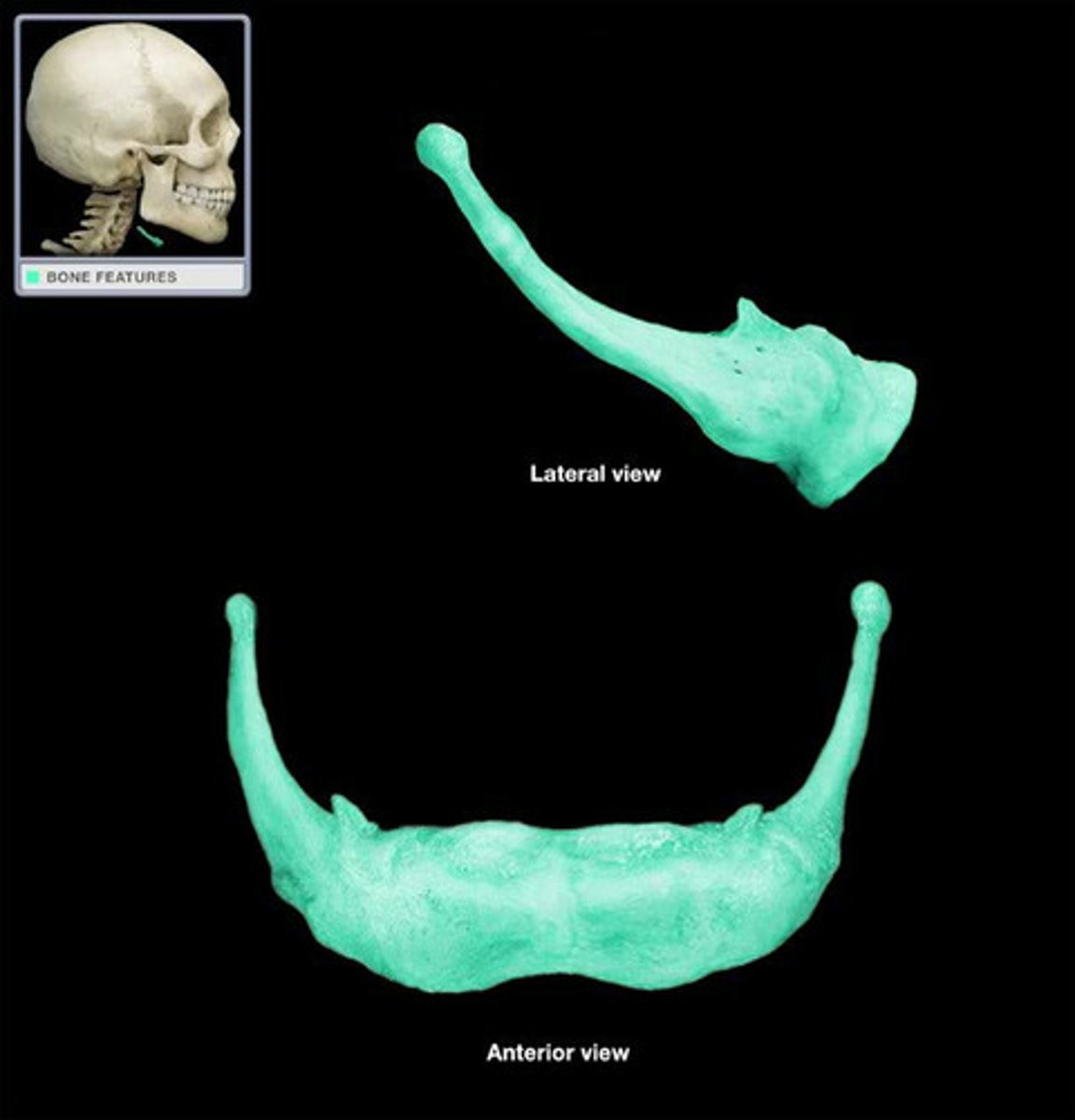
Hyoid bone
a U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
Thyroid cartilage
A firm prominence of cartilage that forms the upper part of the larynx; the Adam's apple.
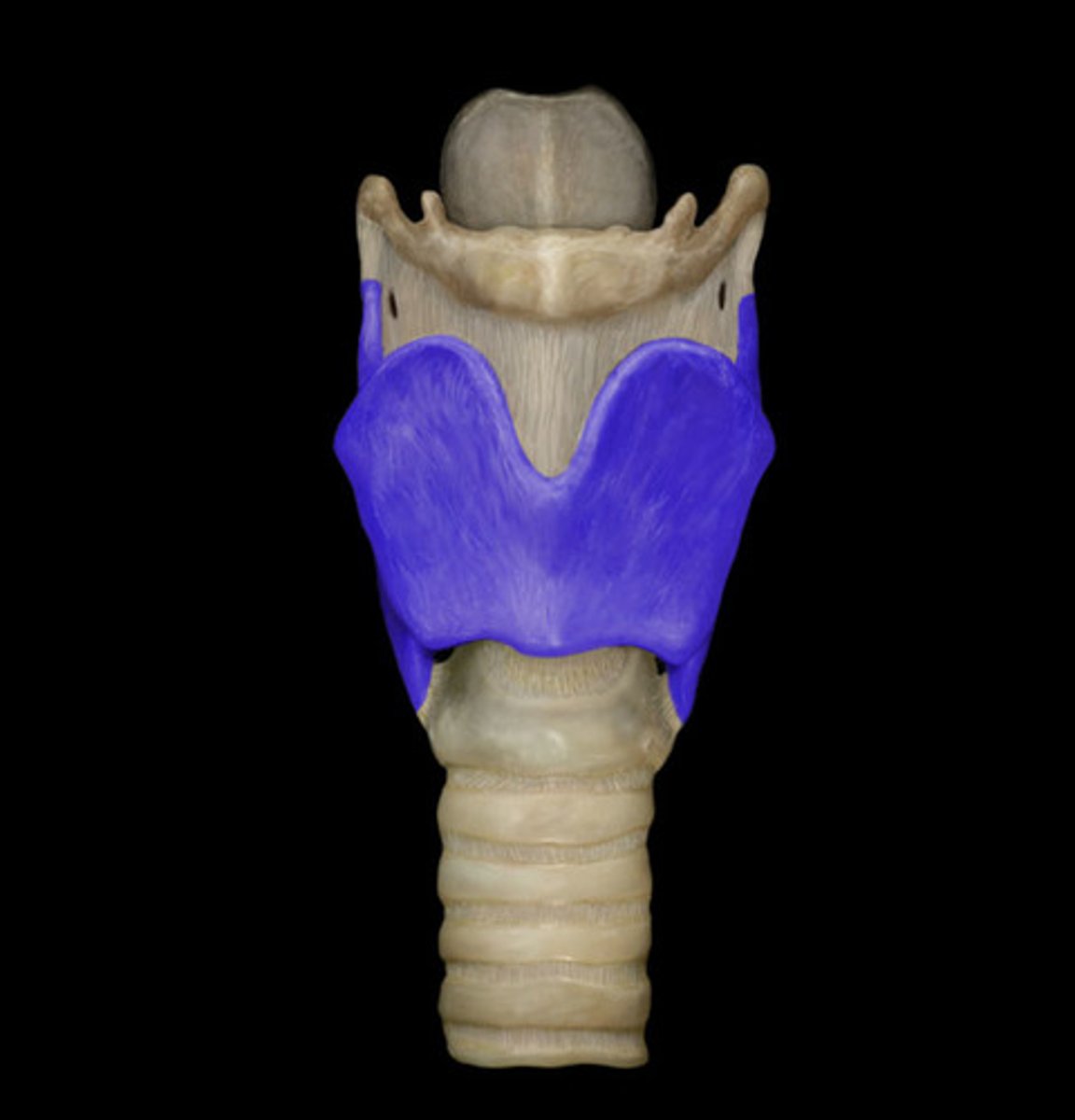
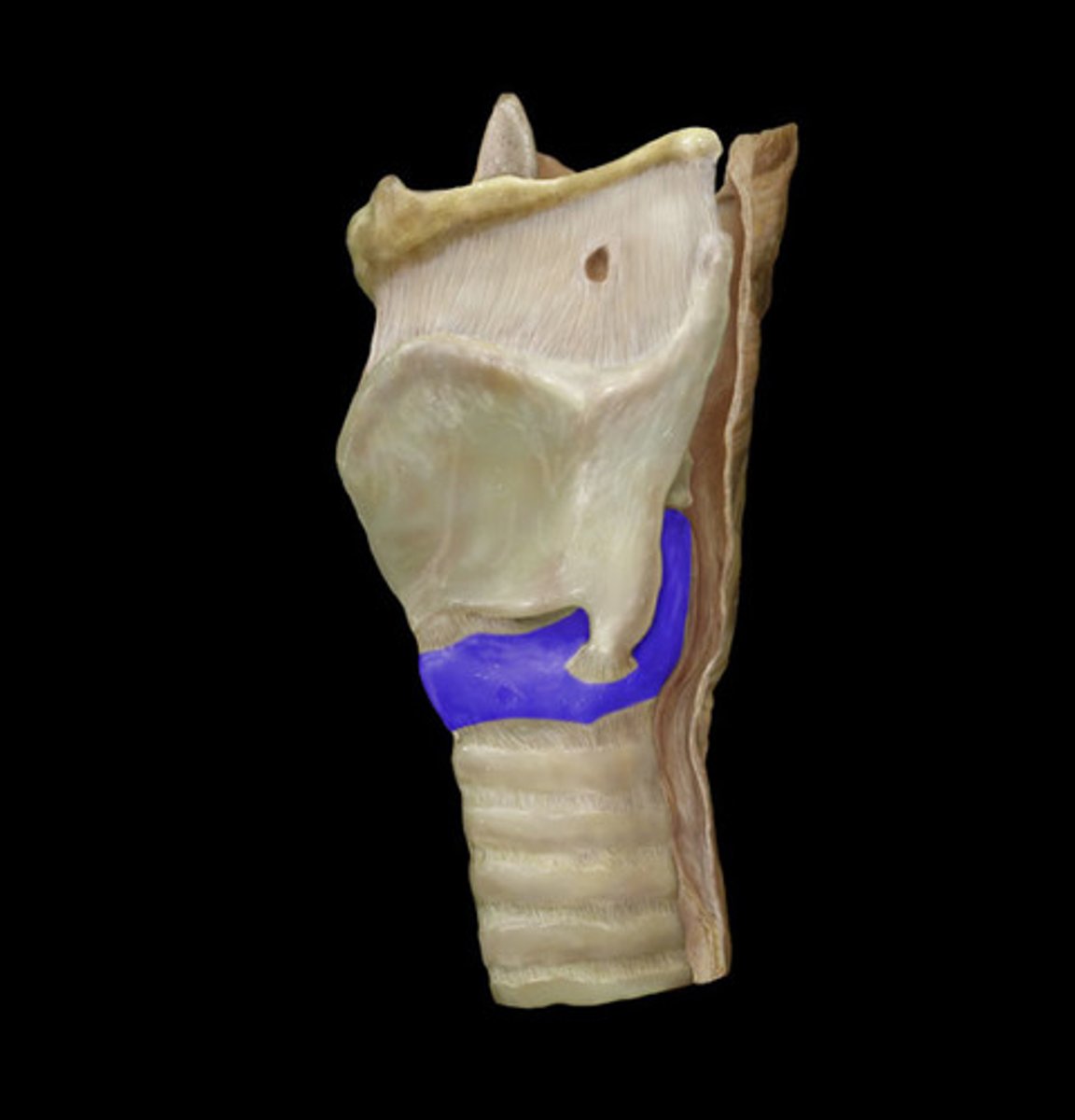
Cricothyroid ligament
soft piece of connective tissue between the thyroid cartilage and cricoid cartilage
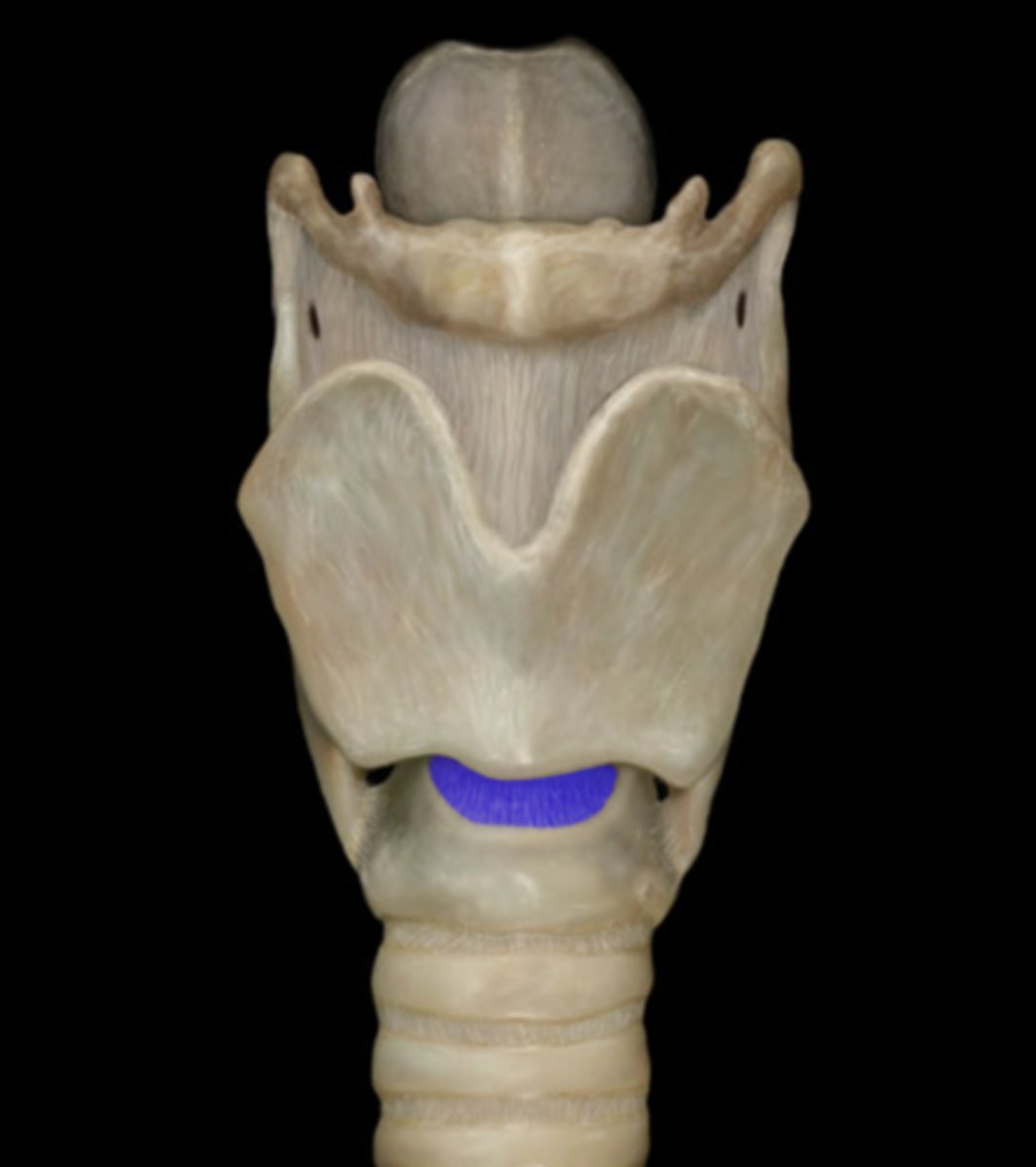
Cricoid cartilage
the ring-shaped structure that forms the lower portion of the larynx
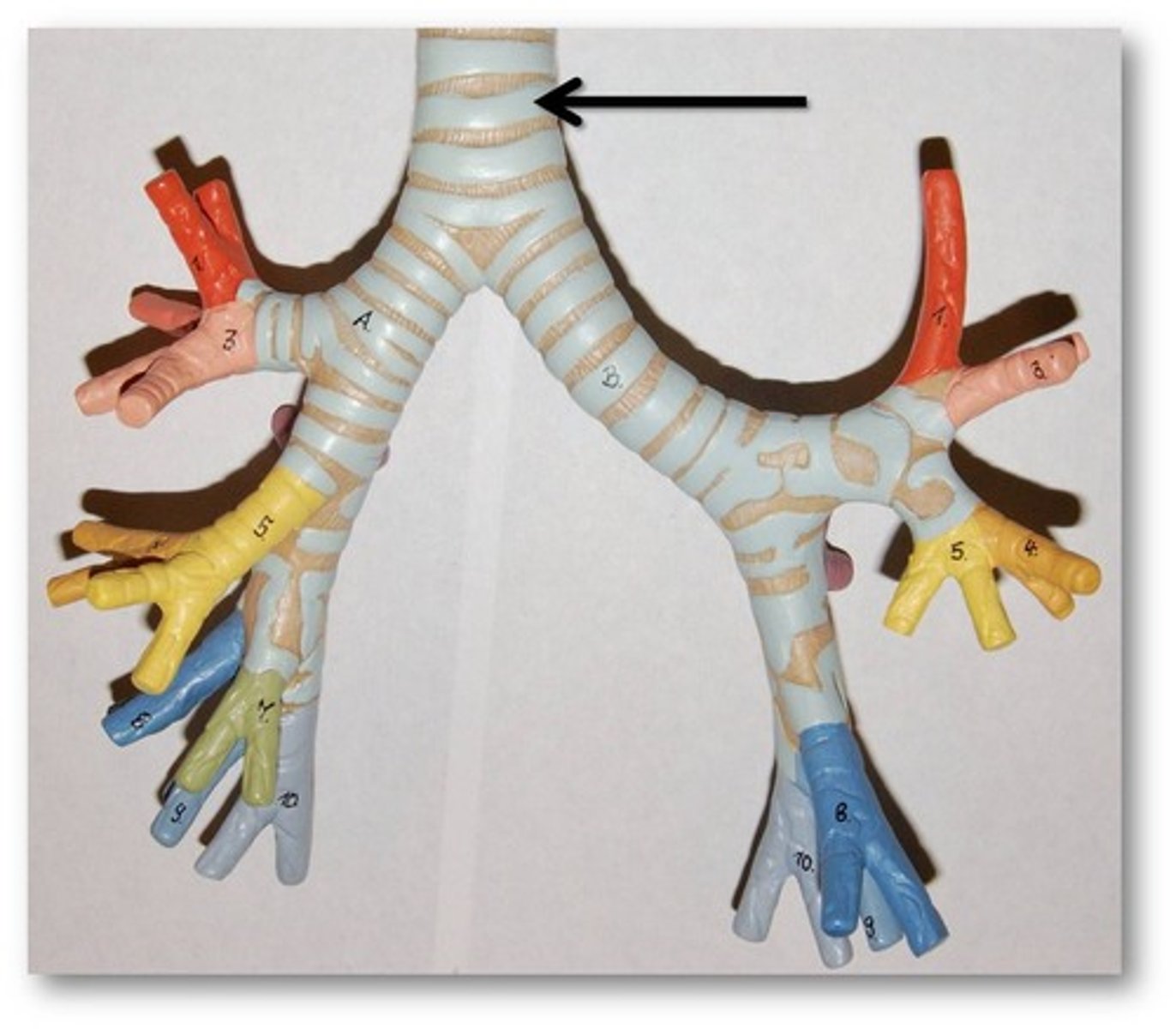
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs, windpipe
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
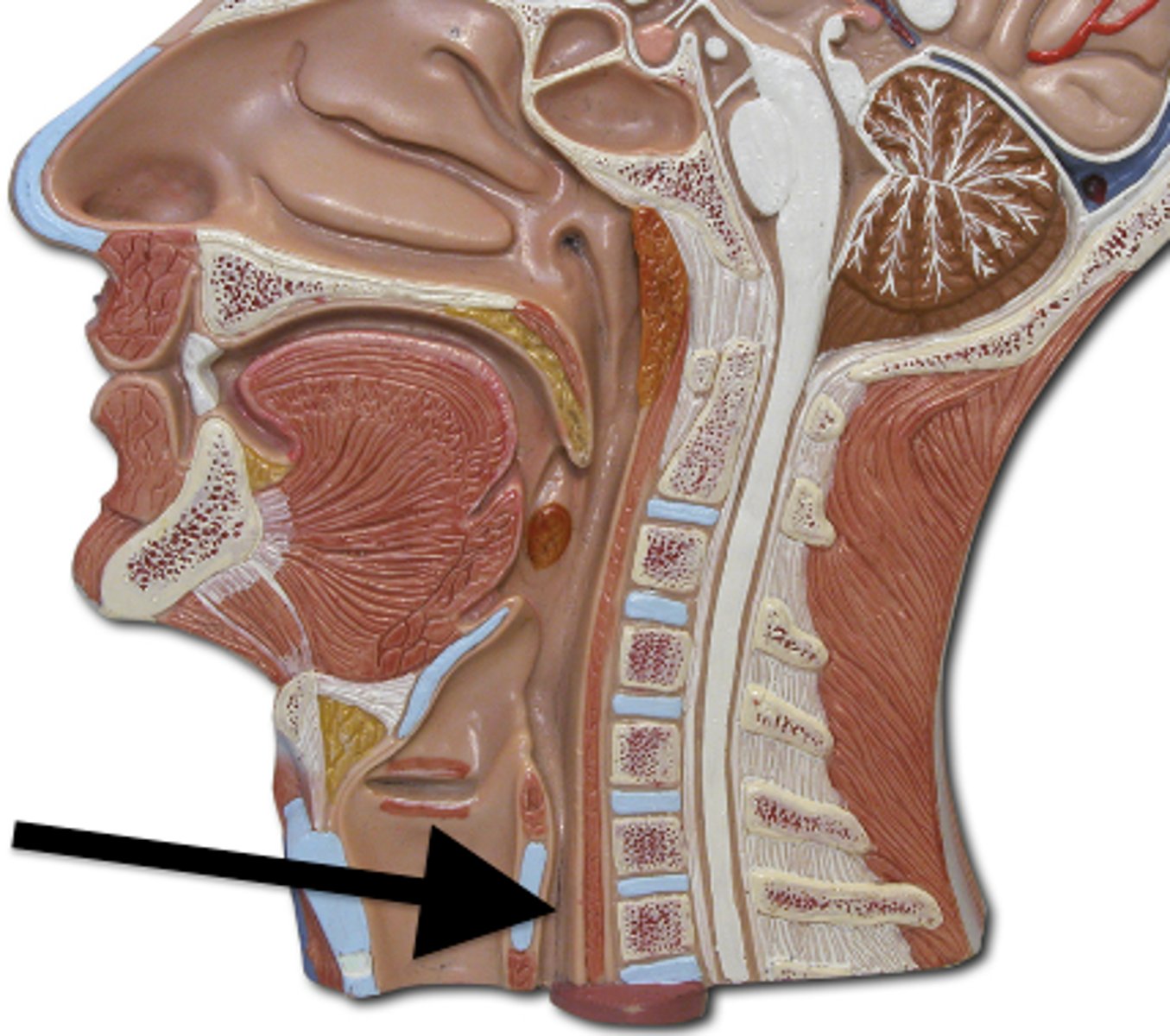
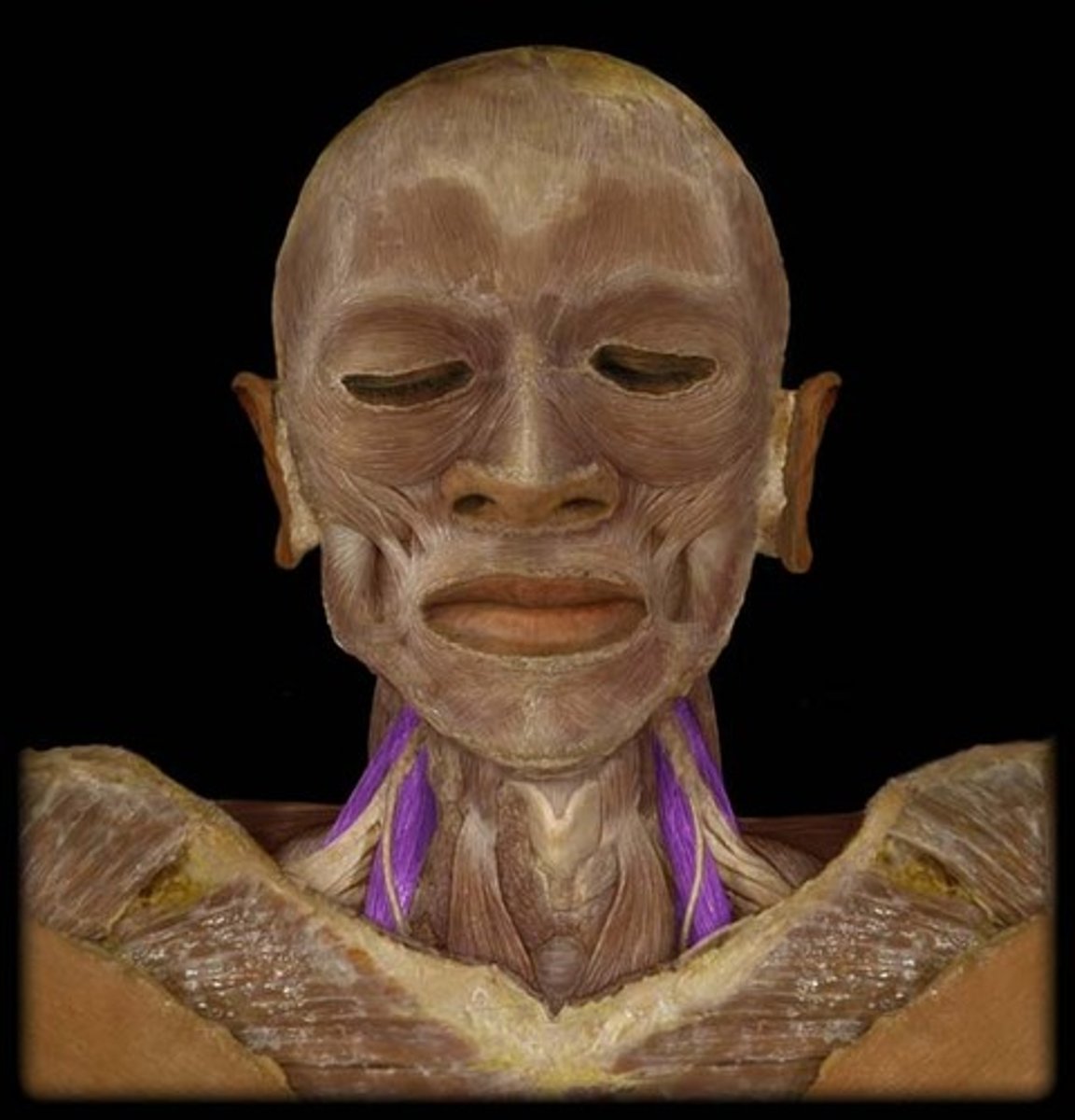
Sternocleidomastoid m.
Bilaterally, flexes cervical portion of vertebral column
Unilaterally, rotates head to the side opposite the contracting muscle
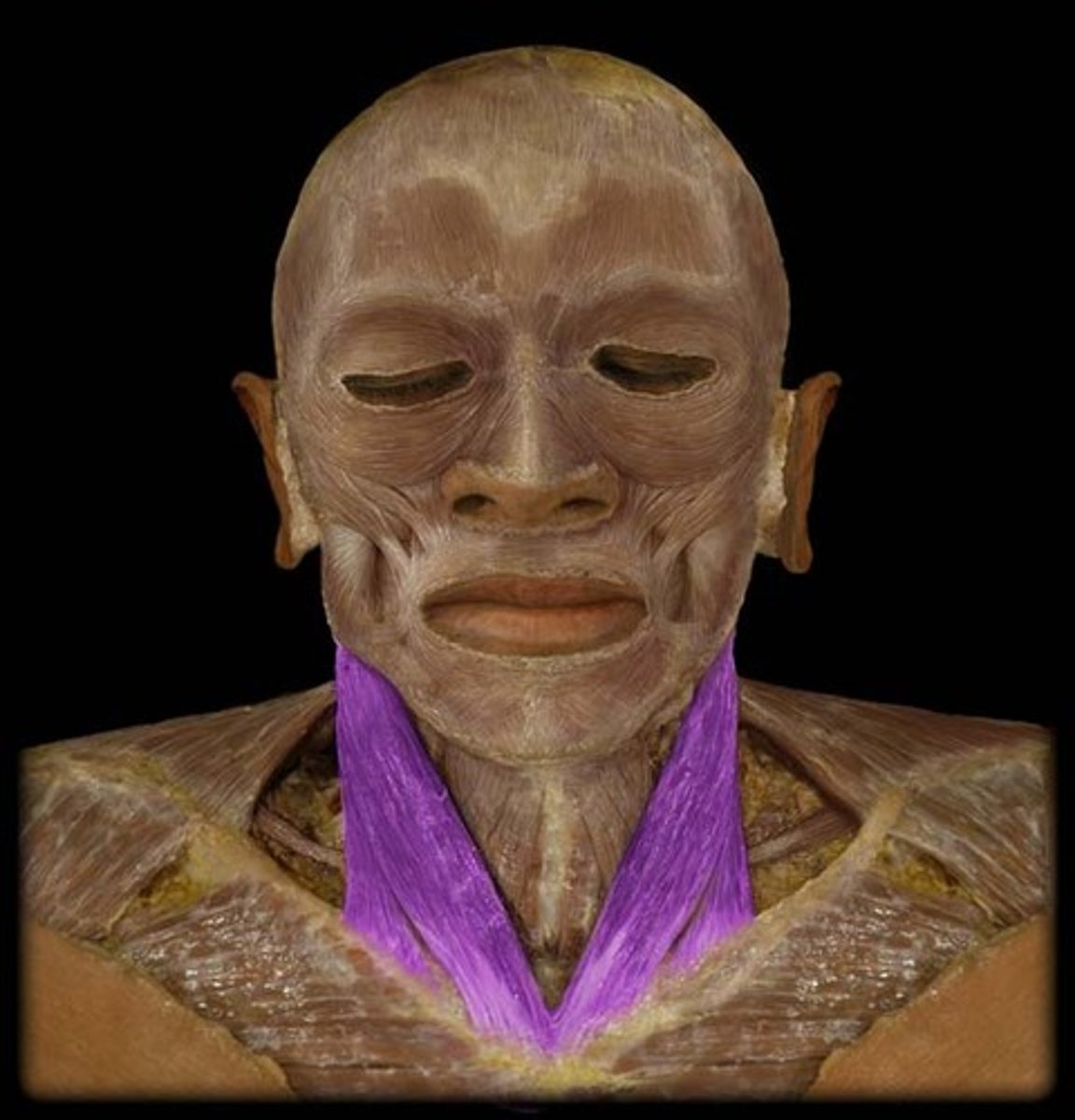
Anterior digastric muscle
Origin: Digastric fossa of mandible
Insertion: Intermediate tendon on the minor cornu of the hyoid bone
Action: Elevates the hyoid bone and depresses the mandible
Innervation: Nerve to the mylohyoid bone
Artery: Submental artery
mylohyoid muscle
hyoid elevation
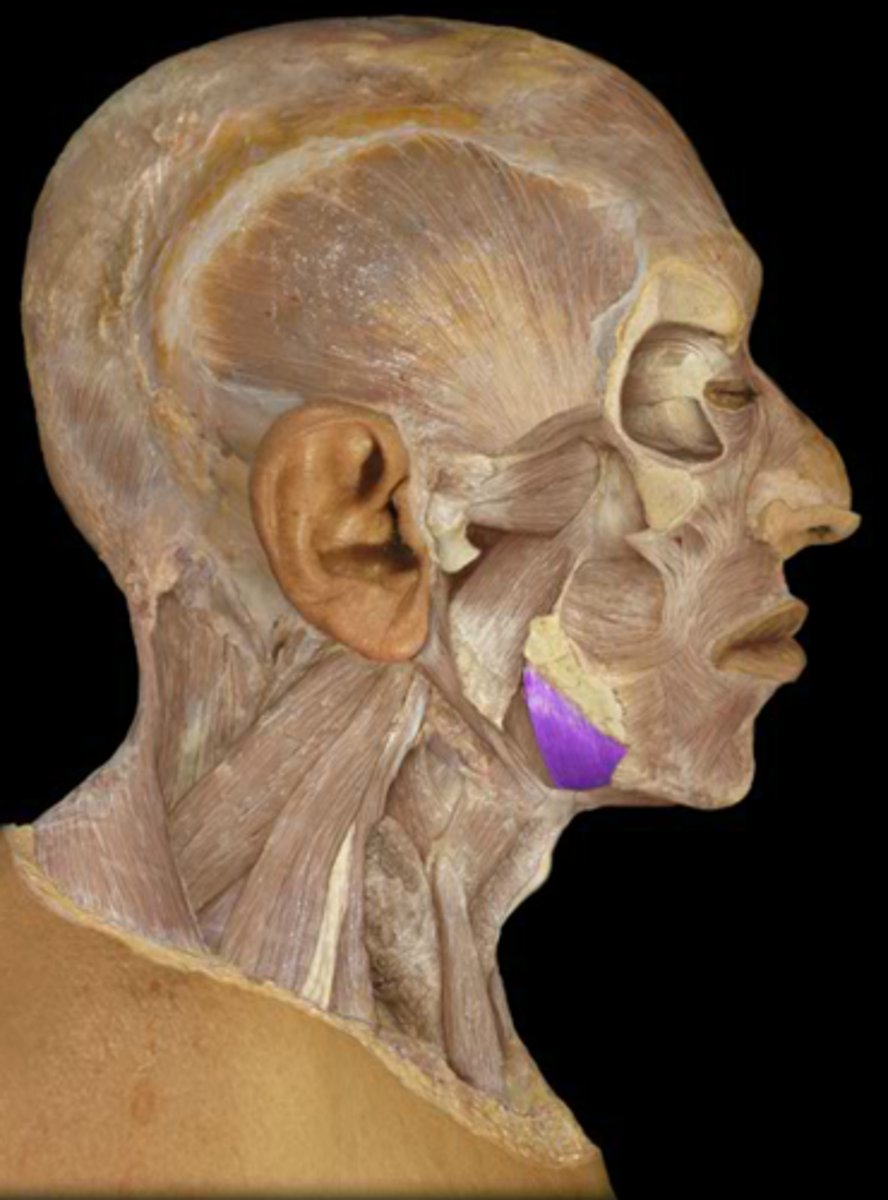
Posterior digastric muscle
Spans between hyoid bone and mastoid process, and parallels the stylohyoid muscle.
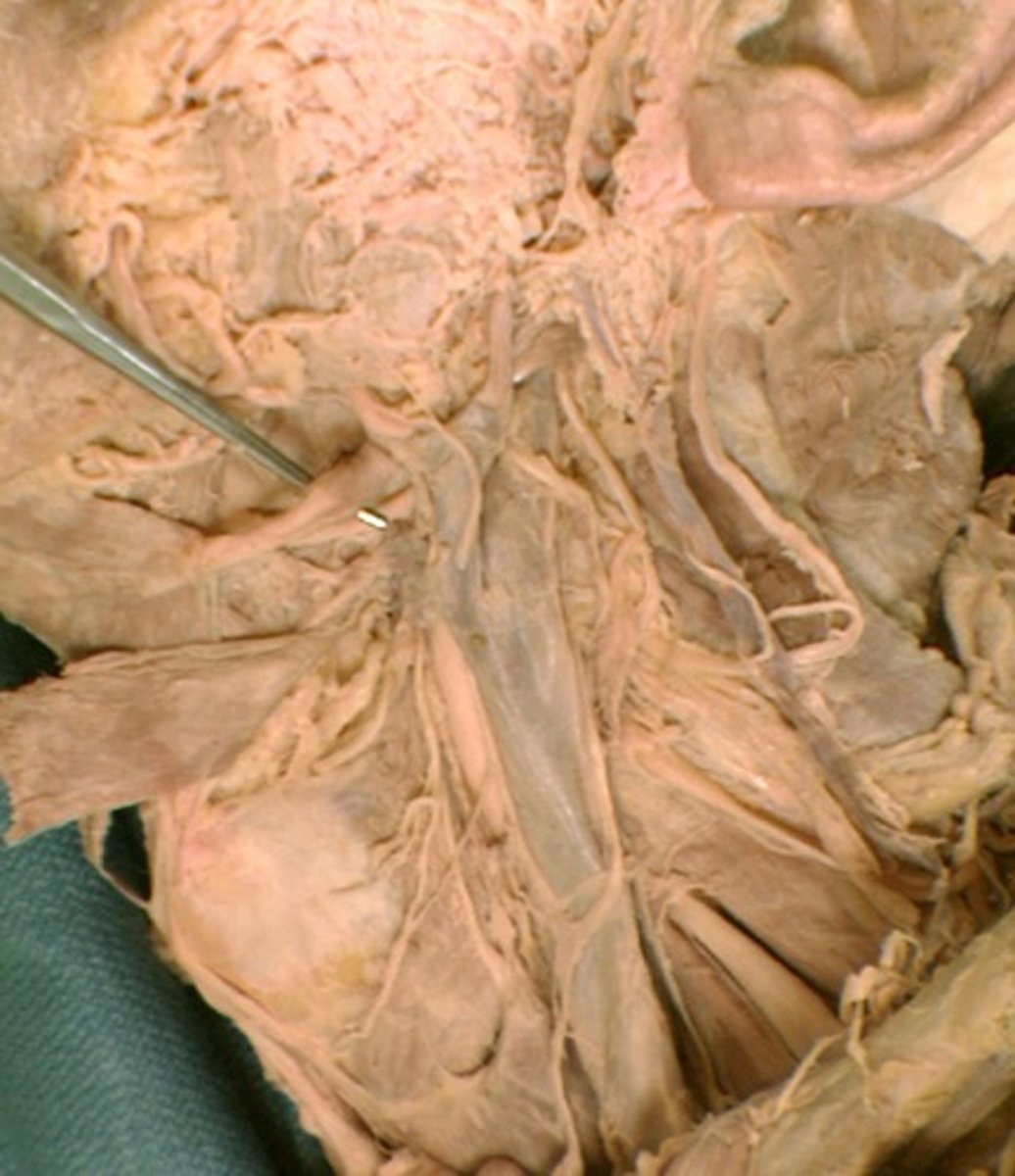
Stylohyoid m.
hyoid bone elevation and retraction
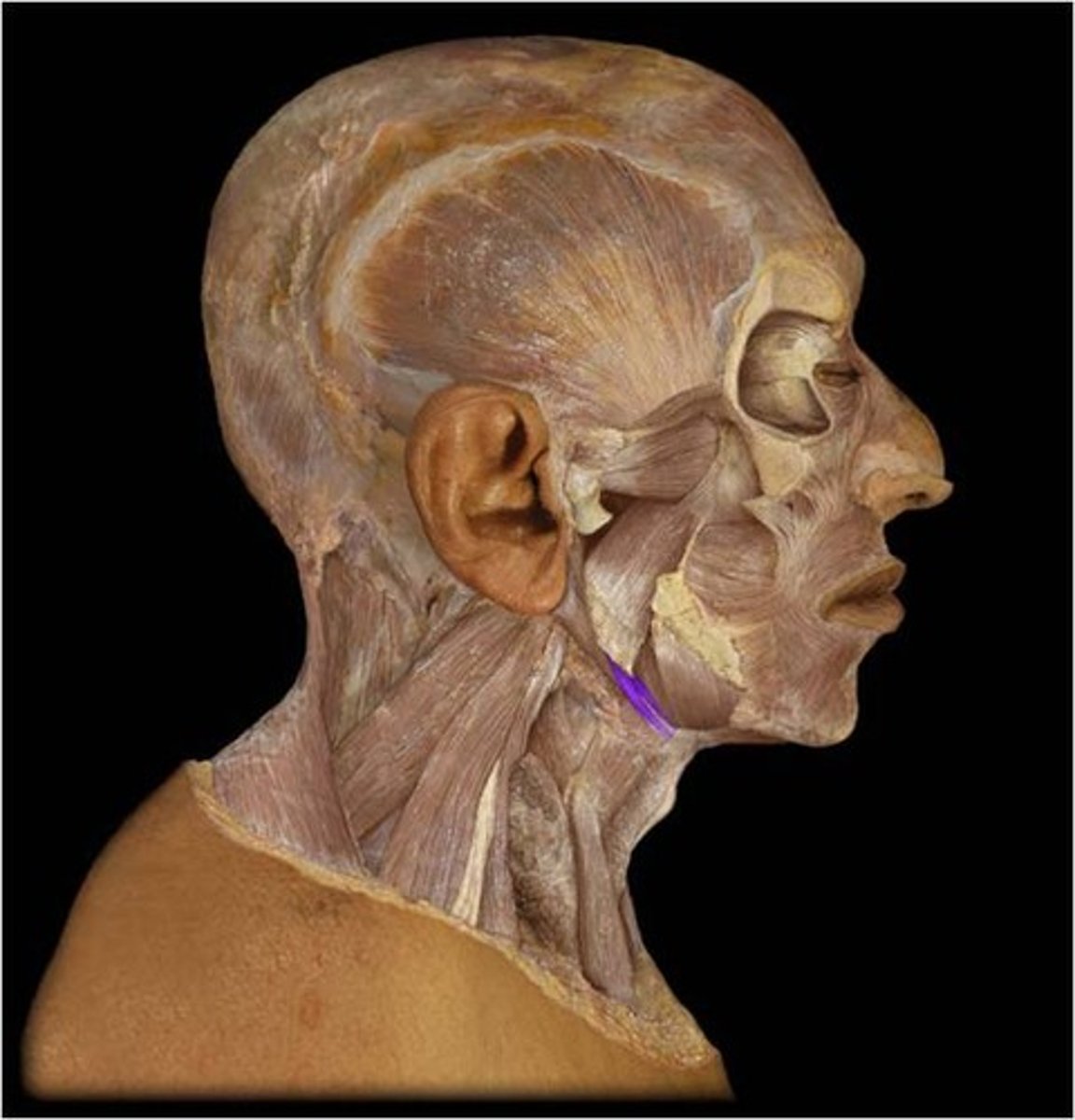
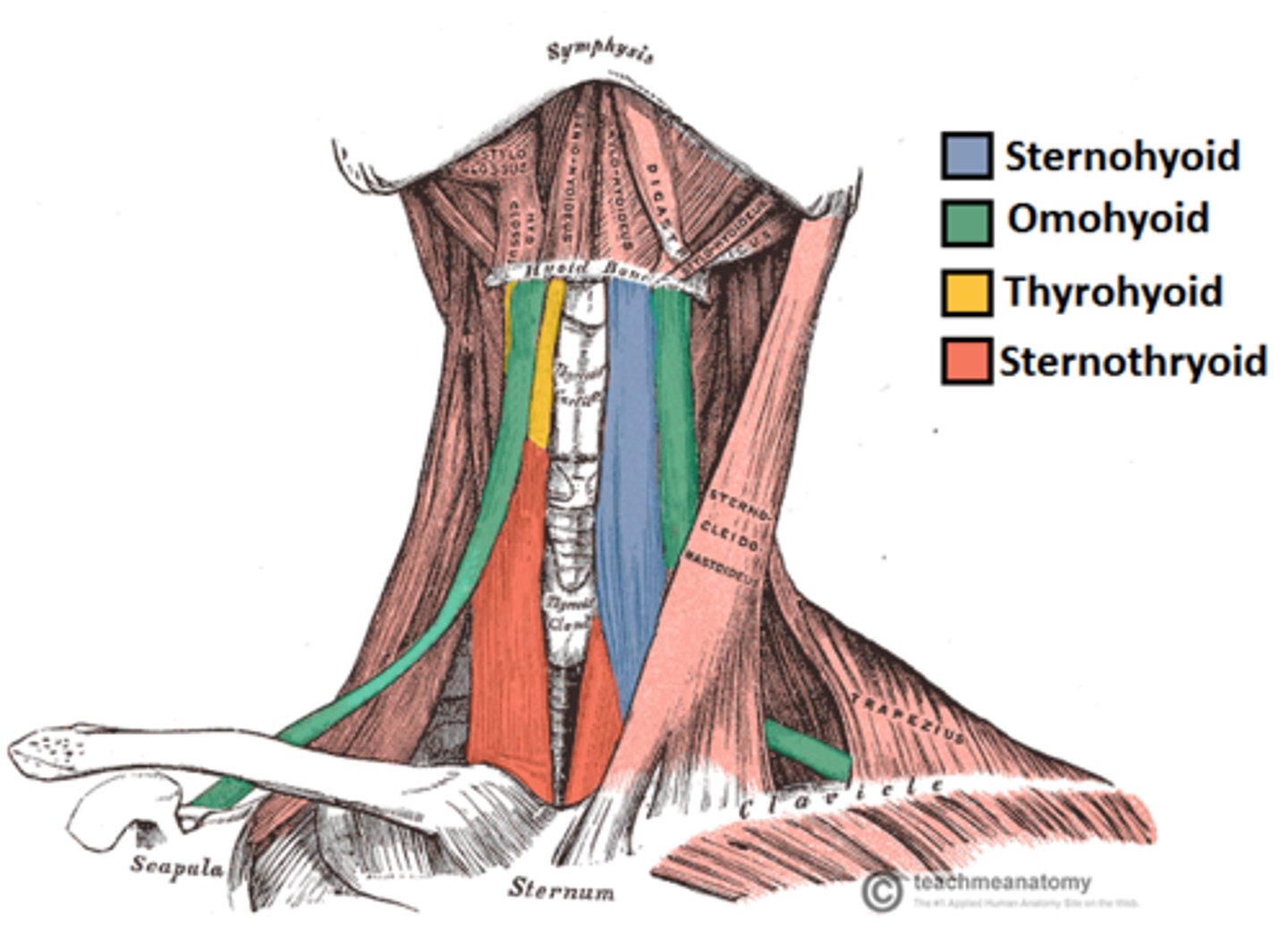
Infrahyoid mm.
TOSS
Thyrohyoid
Omohyoid
Sternohyoid
Sternothyroid
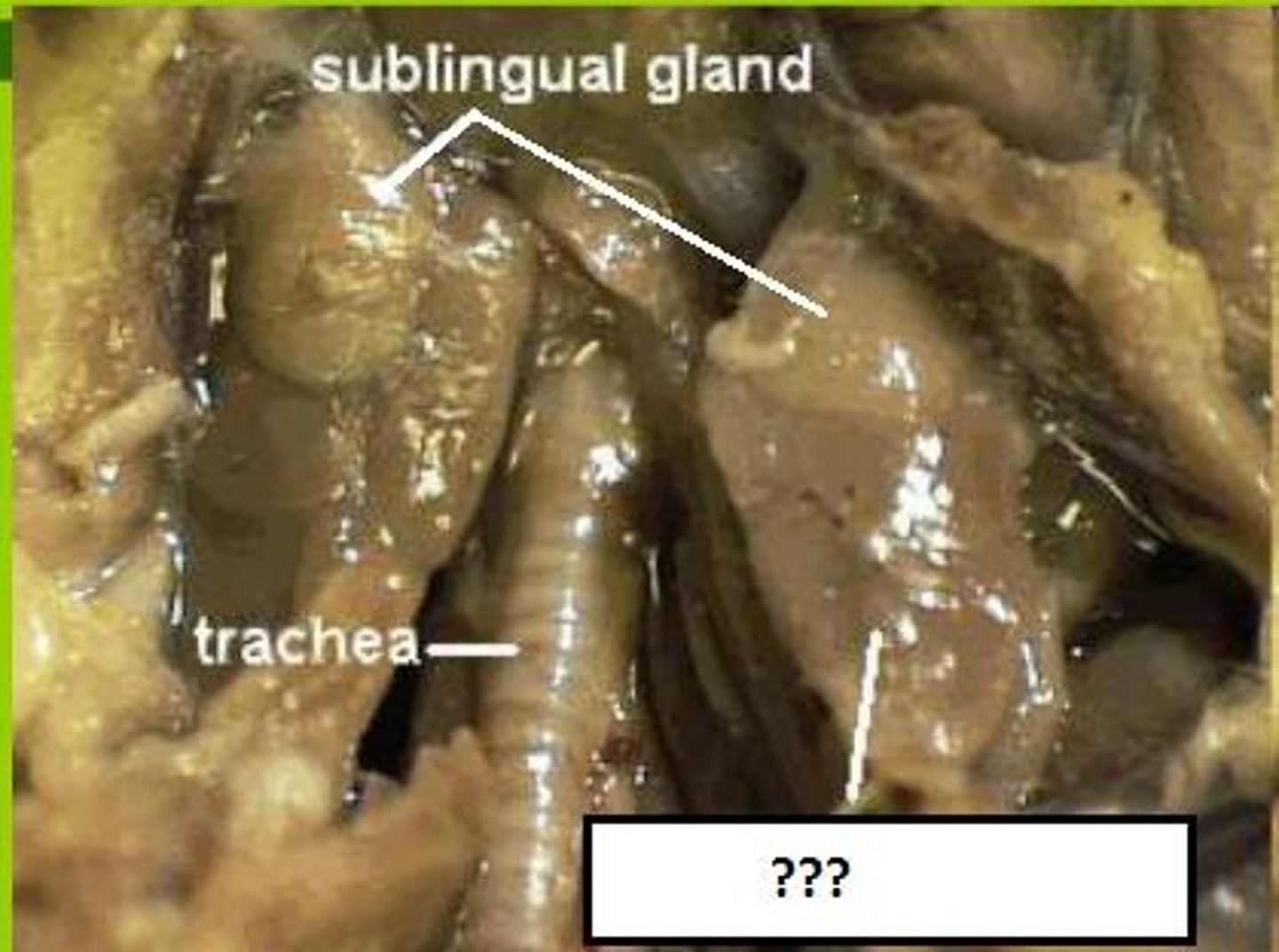
Submandibular salivary gland
a salivary gland inside the lower jaw on either side that produces most of the nocturnal saliva
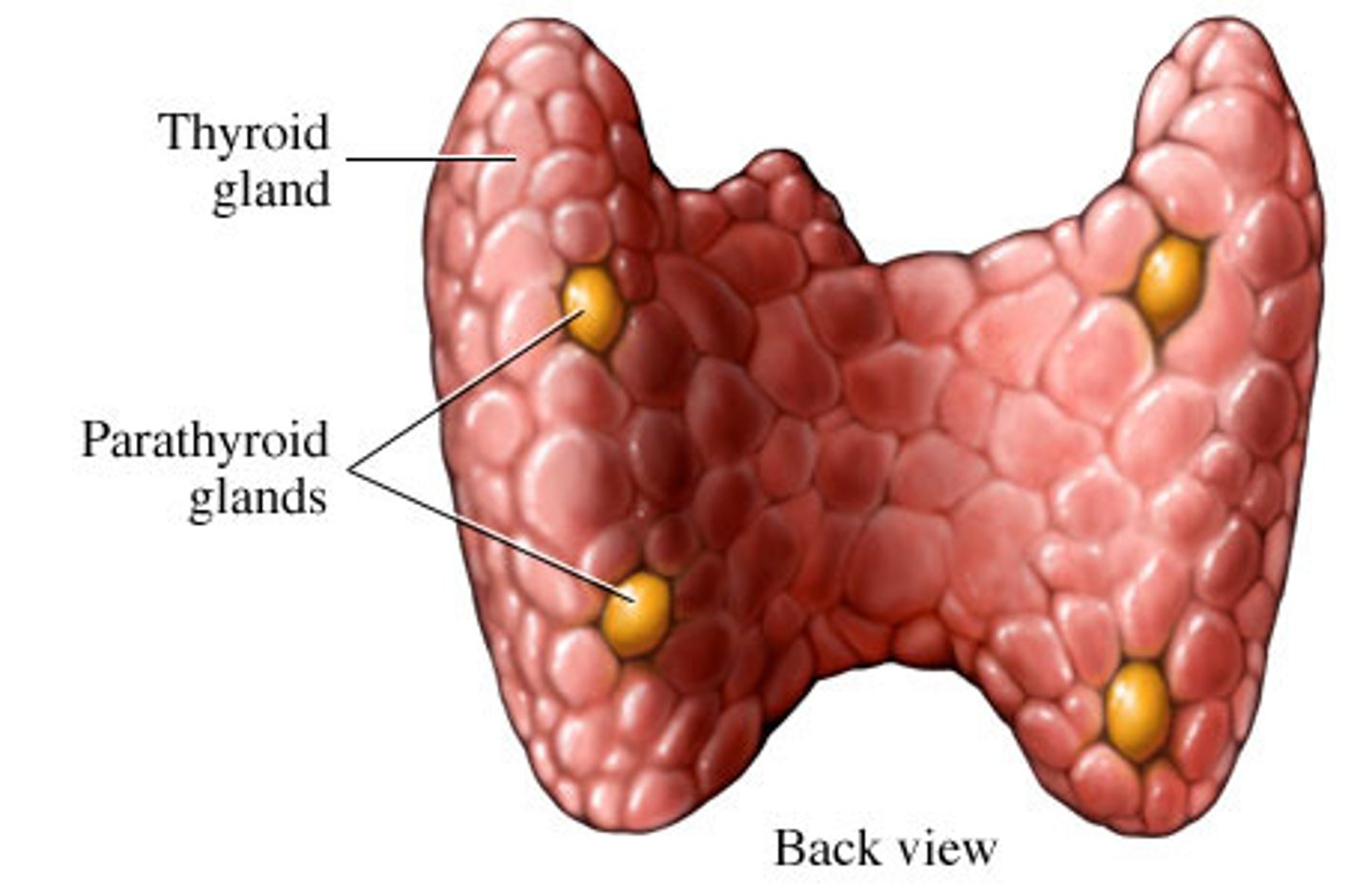
Thyroid gland
produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
Thyroid isthmus
connects the 2 lobes of the thyroid gland - lies over the 2nd and 3rd tracheal rings
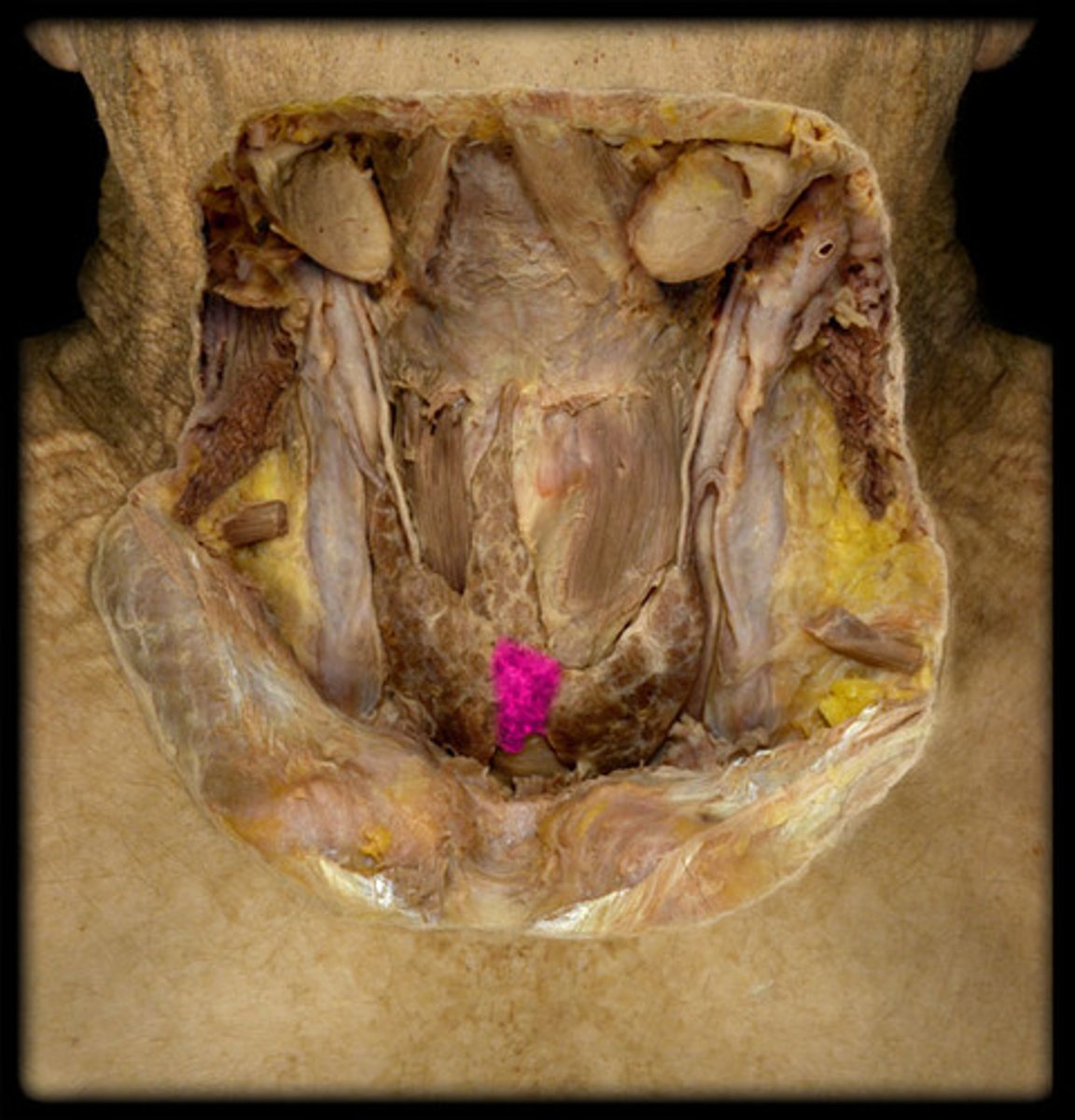
Parathyroid glands
small pea-like organs that regulate calcium and phosphate balance in blood, bones, and other tissues
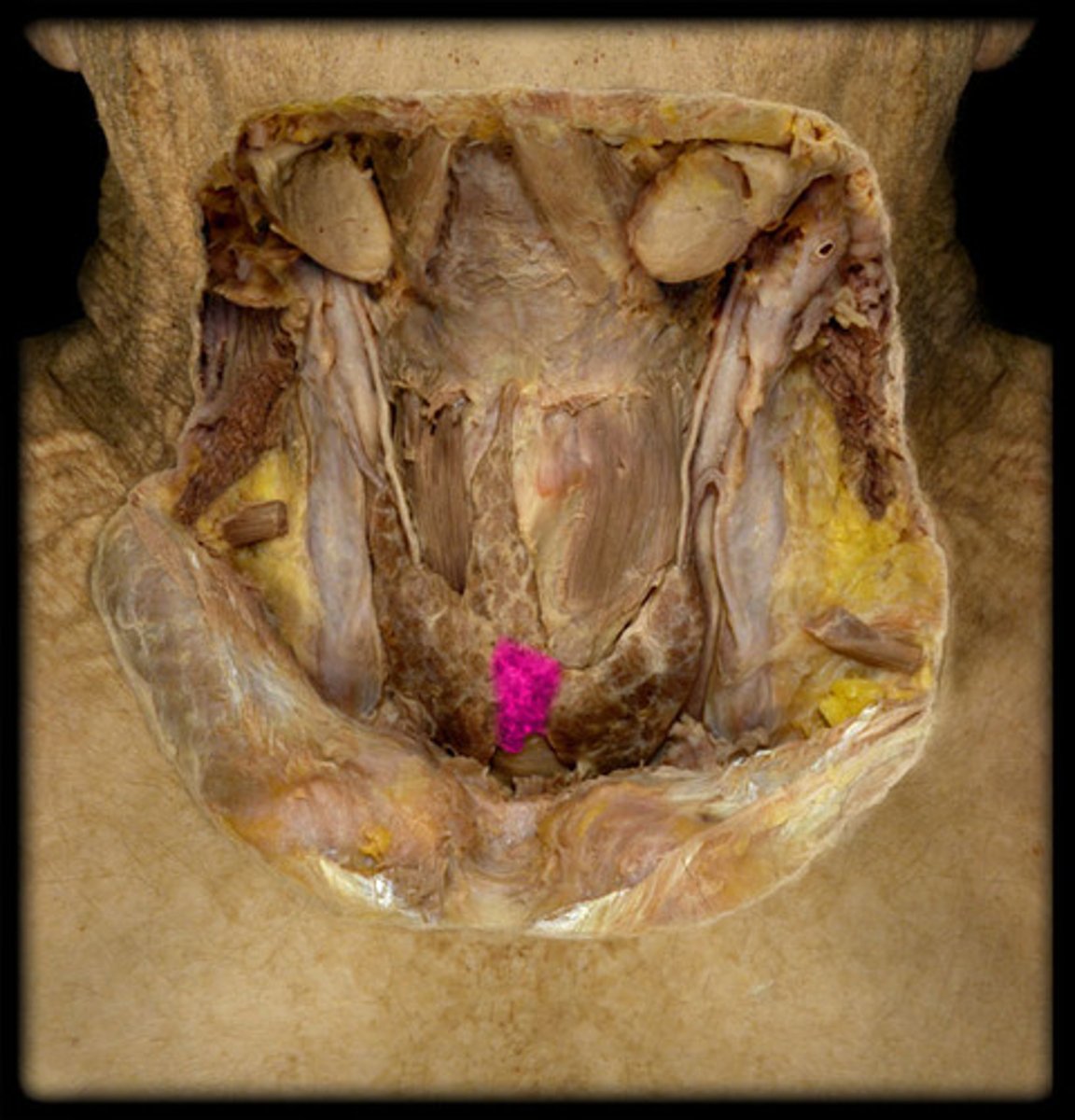
Carotid body
chemoreceptor located in the carotid artery that detects changes in oxygen, carbon dioxide, and blood acid levels
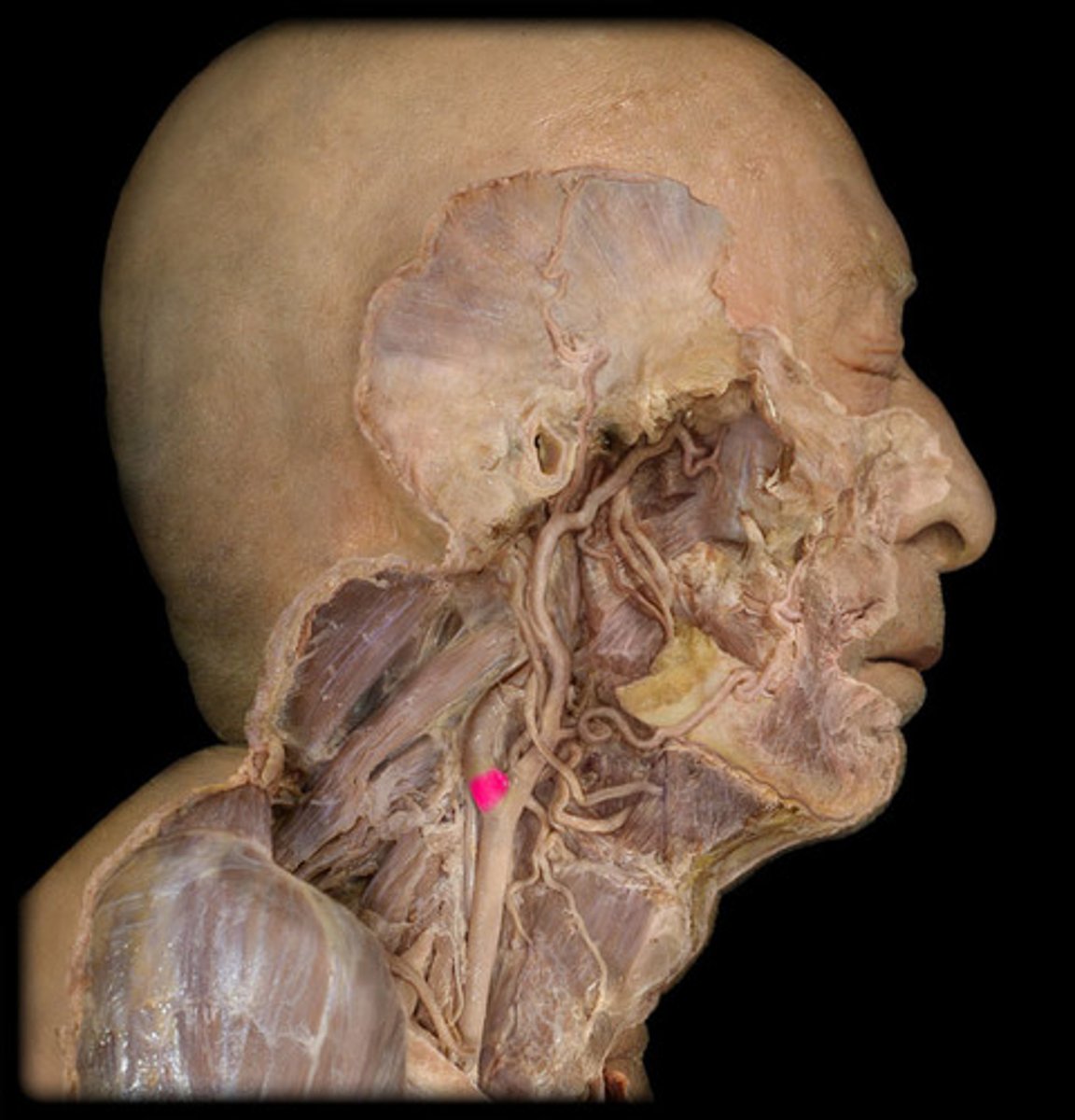
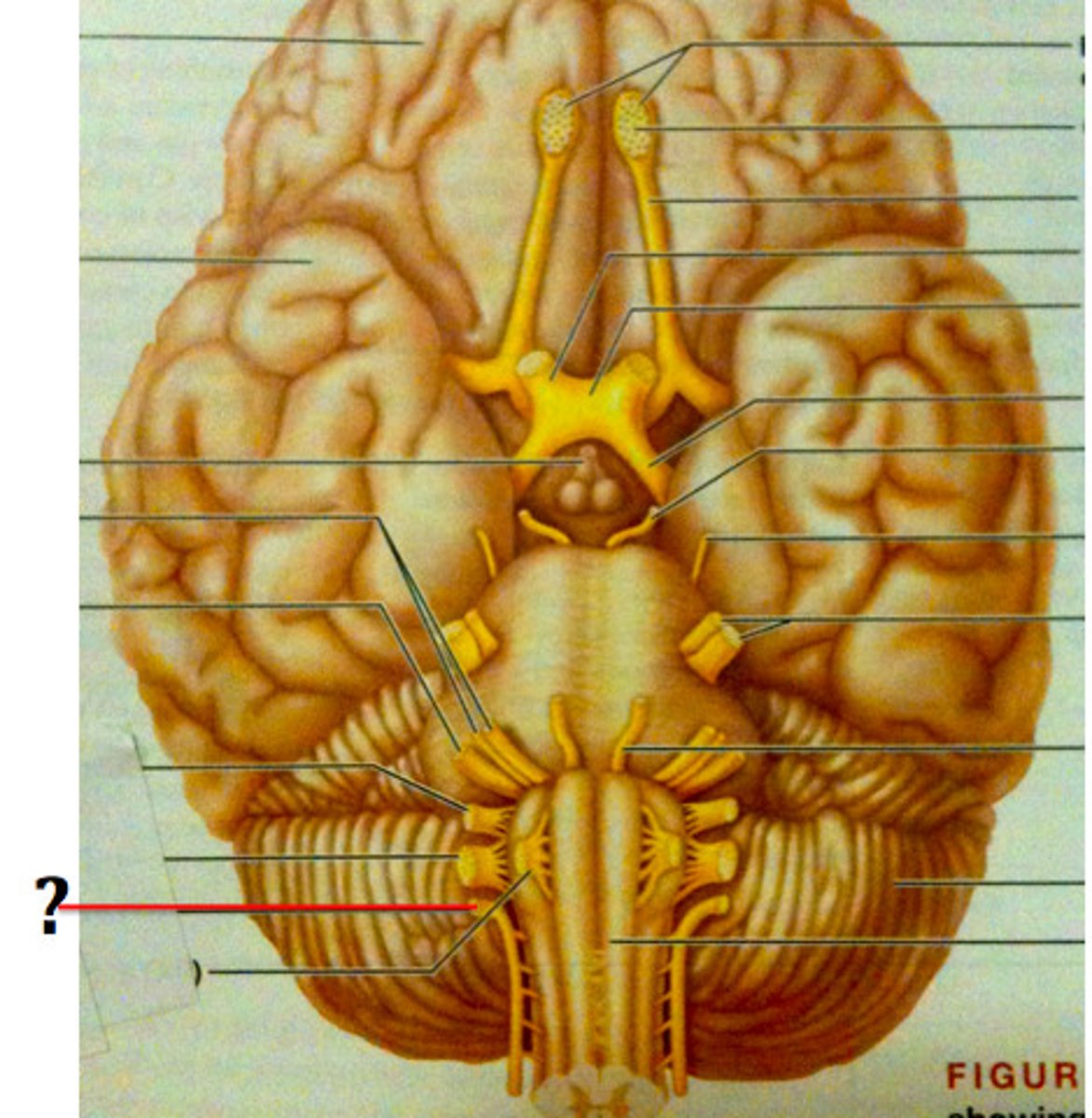
Hypoglossal nerve
CN XII; tongue movements for speech, food manipulation and swallowing (MOTOR)
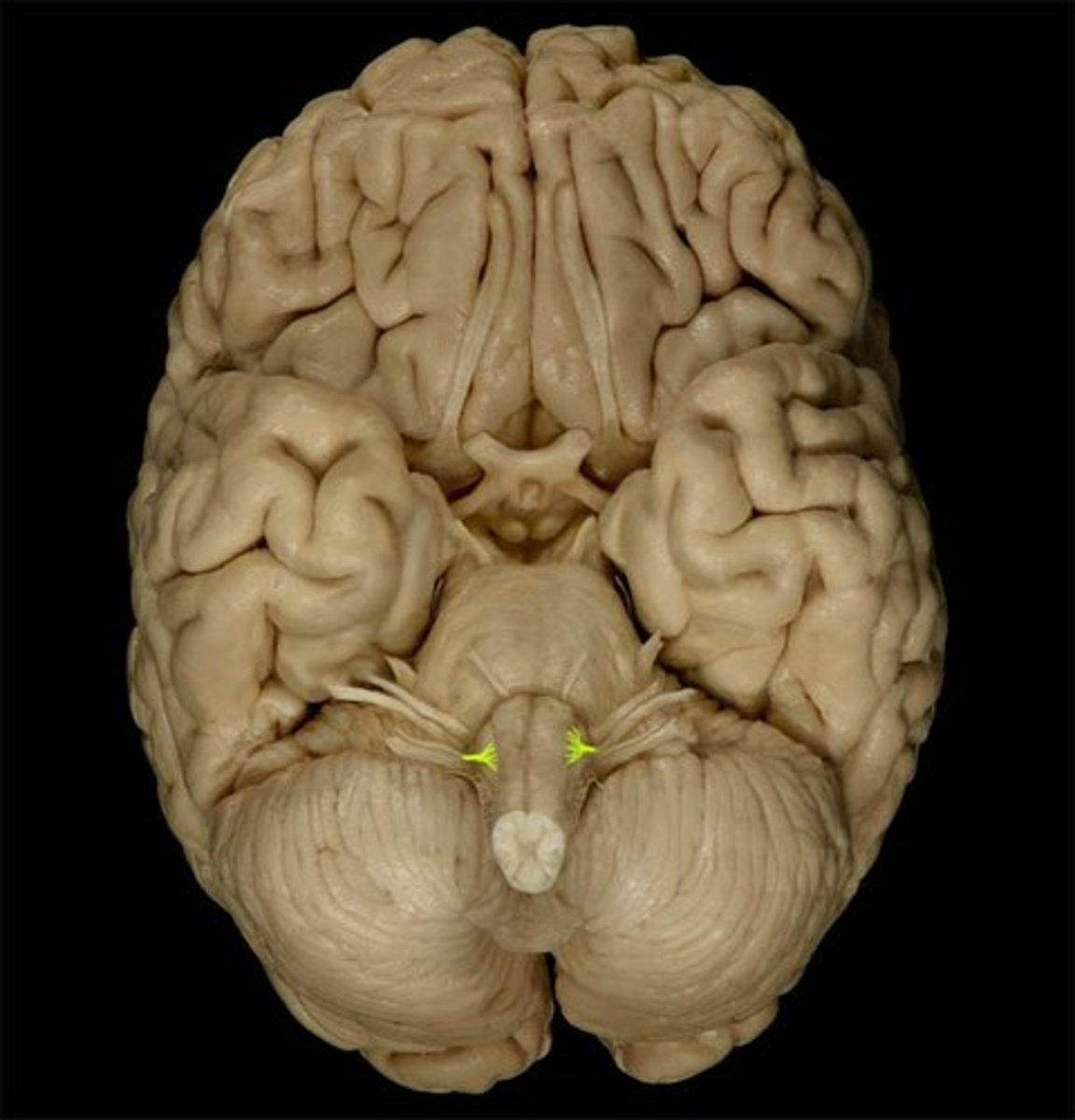
Vagus n.
Cranial nerve X, Both, Larynx, respiratory, cardiac and gastrointestinal systems
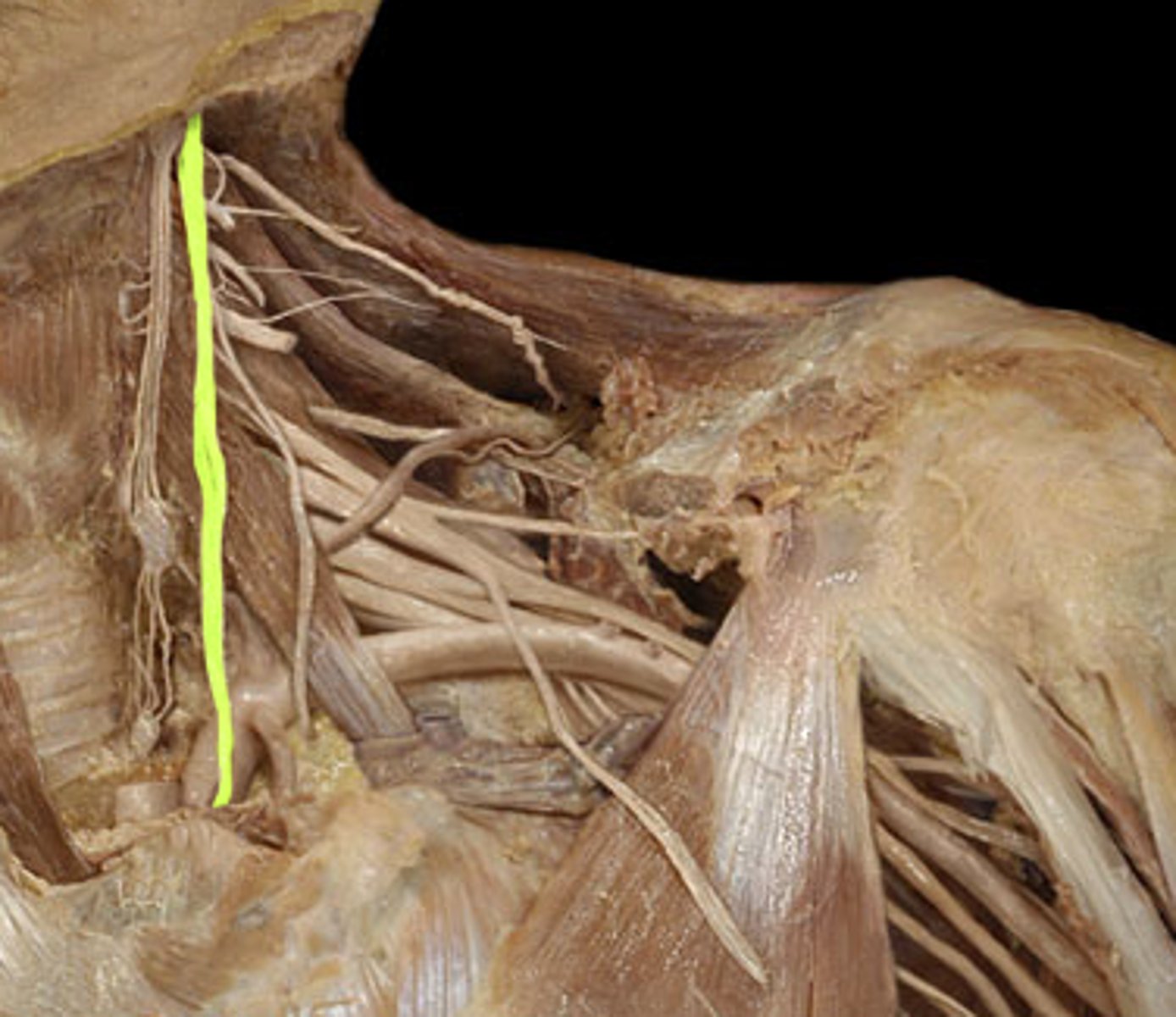
Superior laryngeal n.
The __________________ nerve of the X cranial nerve innervates the cricothyroid muscle
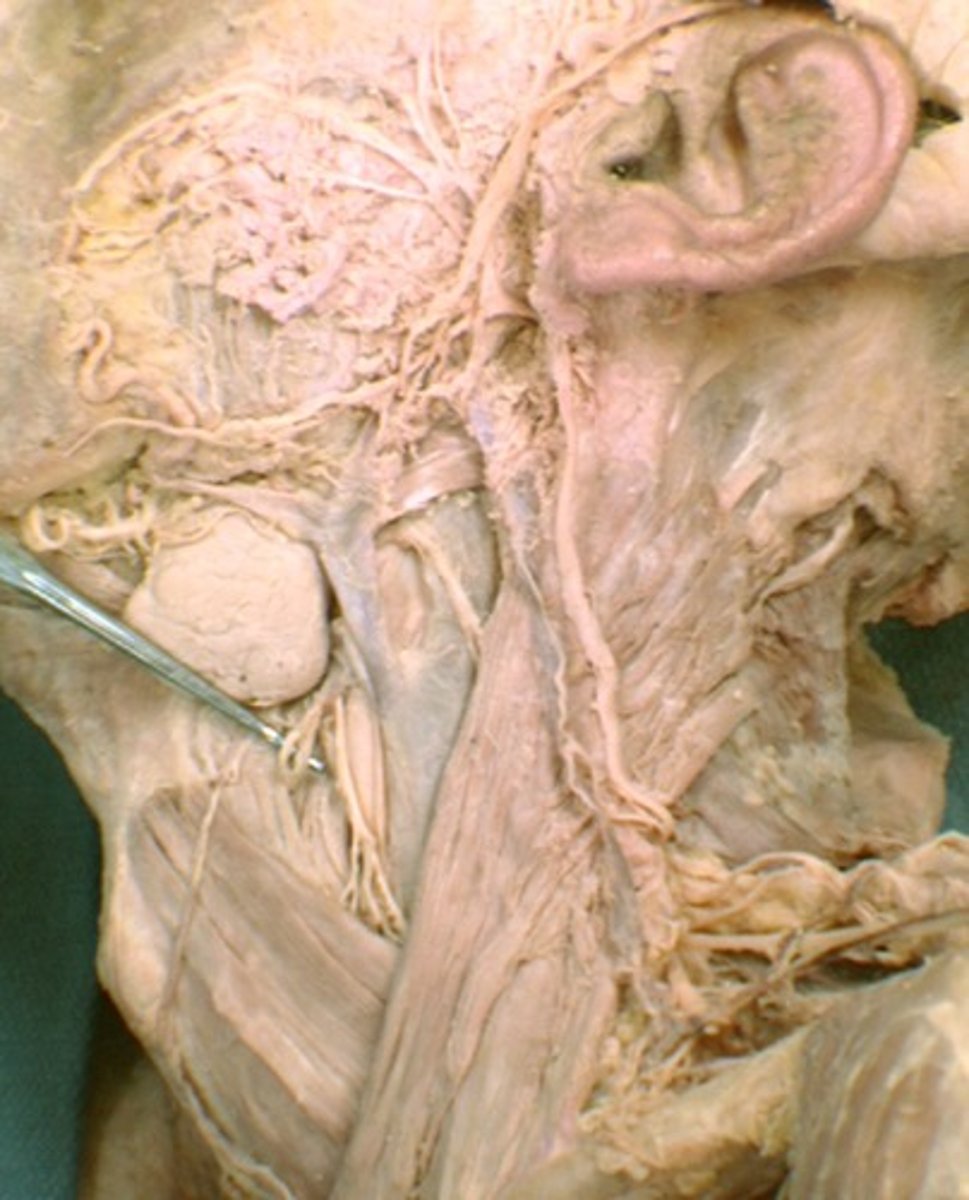
Internal laryngeal n.
Sensory nerve to larynx superior to vocal cords
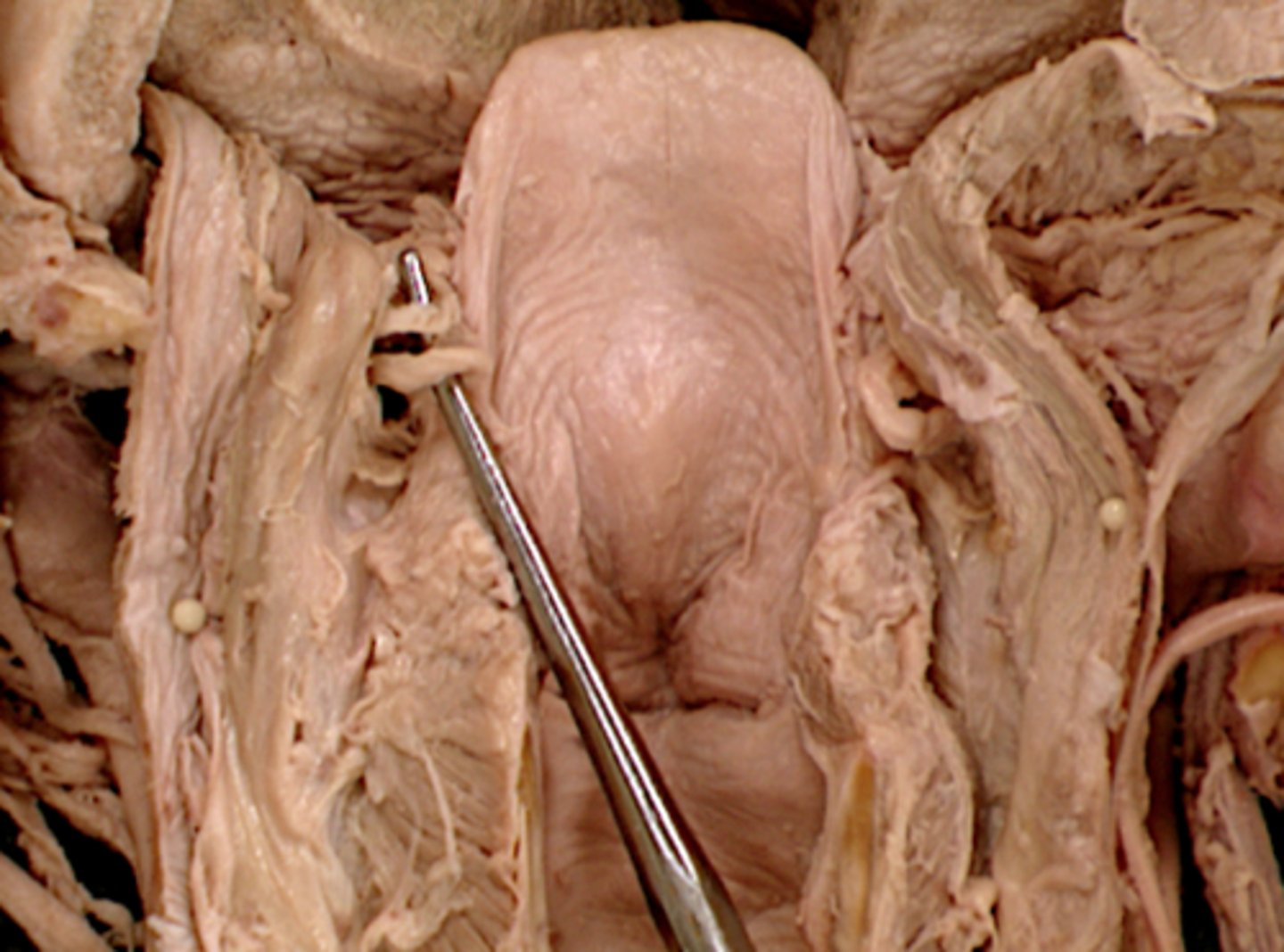
External laryngeal n.
motor to cricothyroid
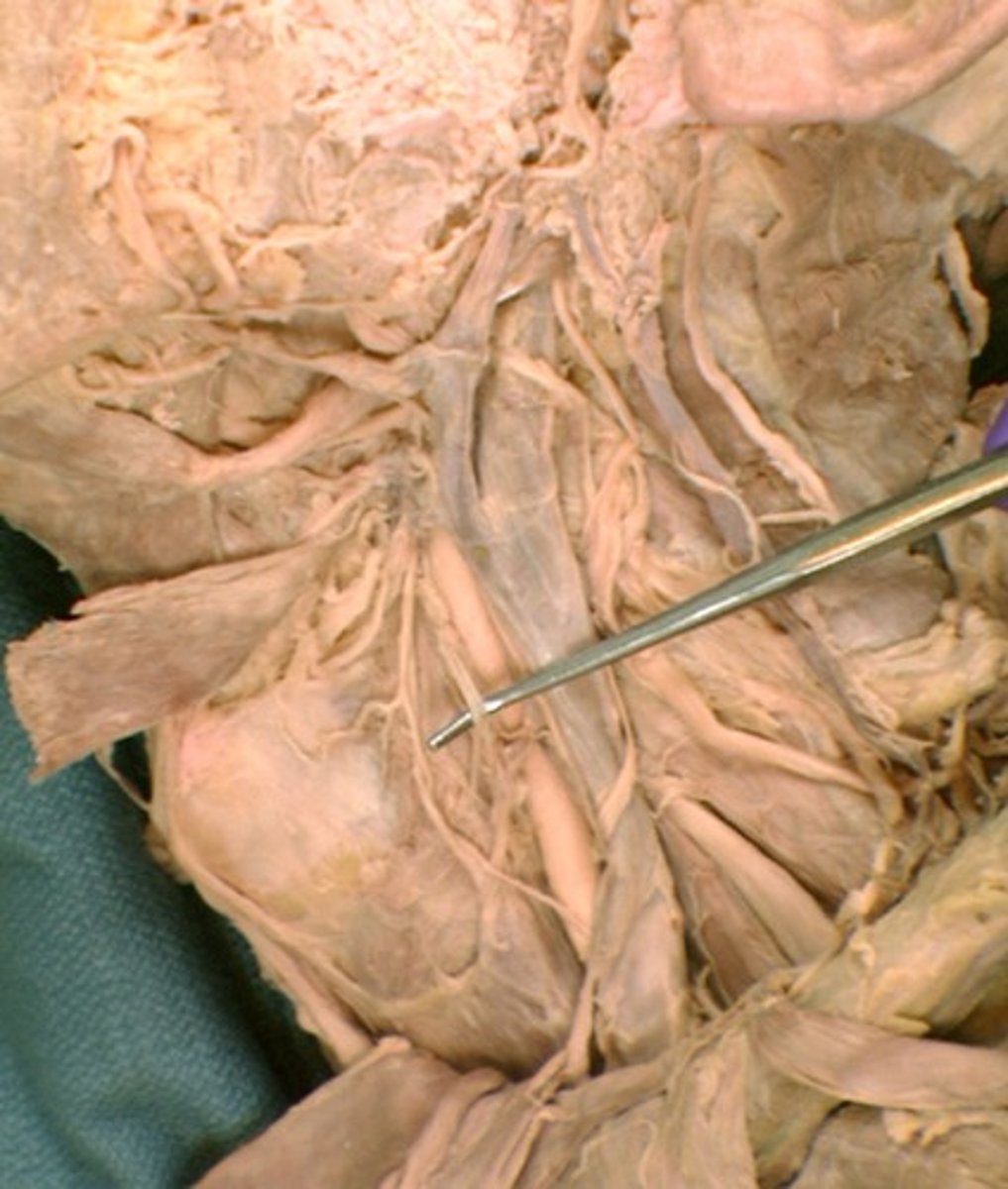
Accessory nerve
motor fibers to neck and upper back (11)
Ansa cervicalis
Innervation of omohyoid, sternohyoid and sternothyroid
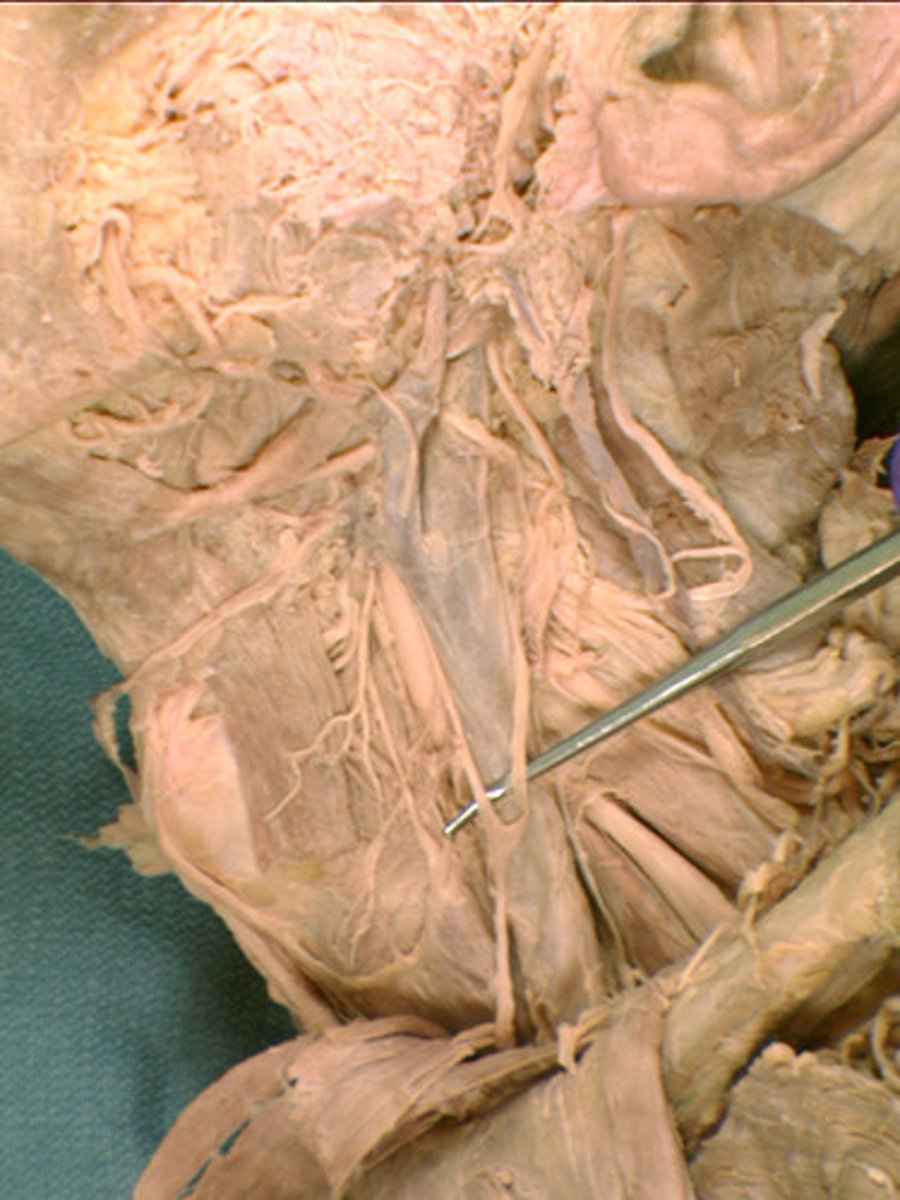
Carotid sheath
The deep fascia that covers the common carotid artery, vagosympathetic nerve trunk, internal jugular vein, and tracheal lymphatic trunk
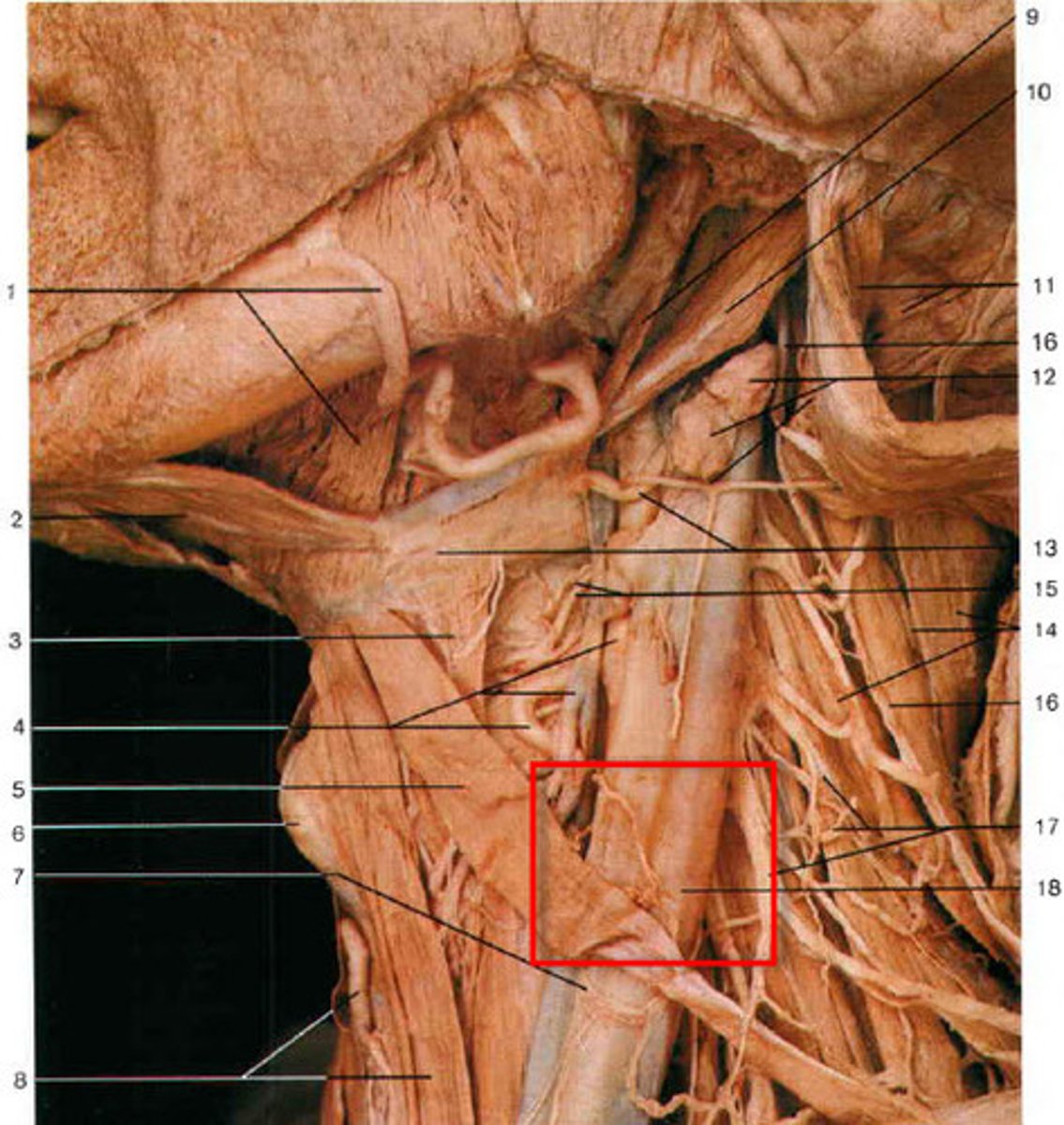
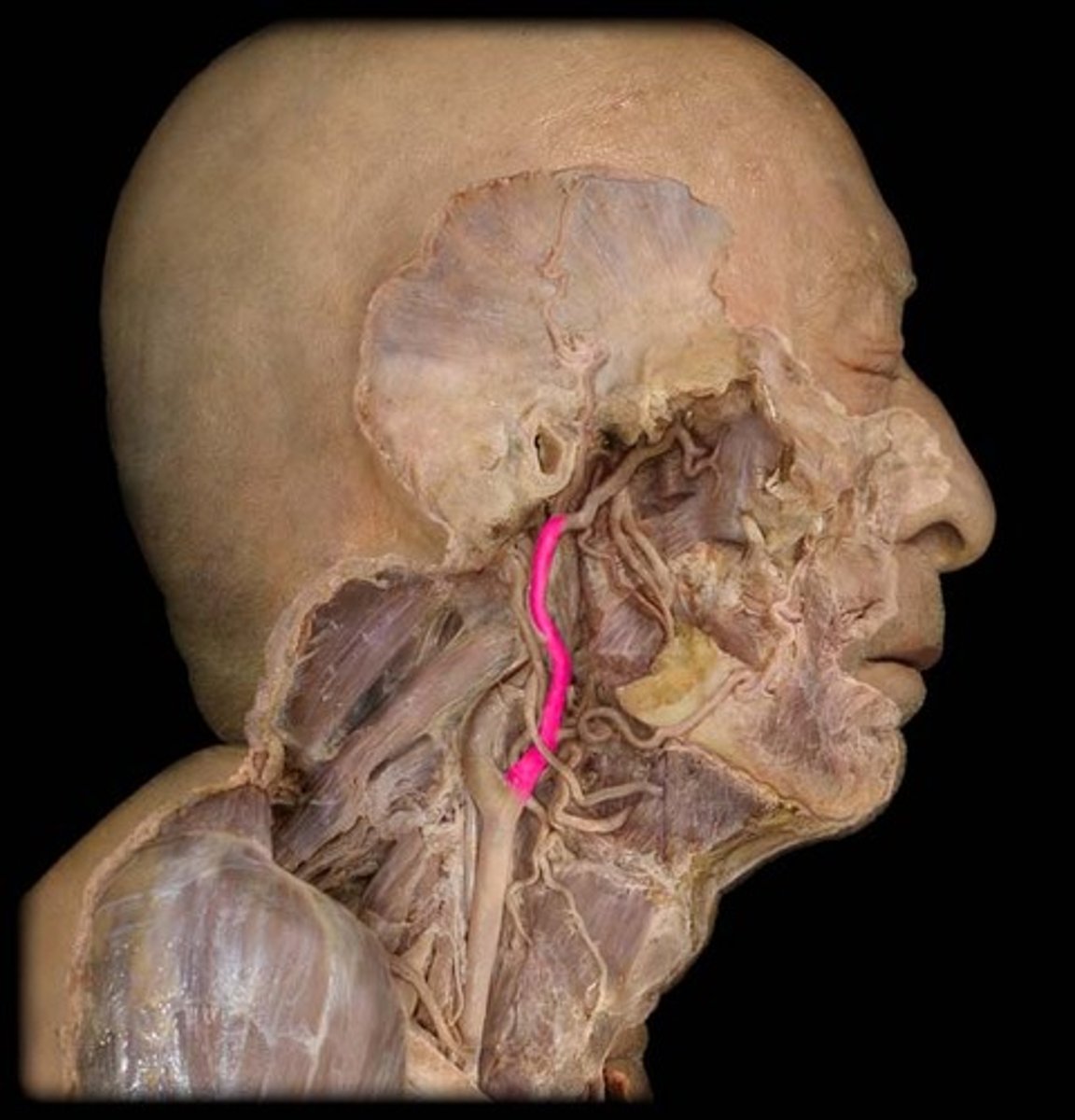
Common carotid a.
Bifurcates into the internal & external carotid aa.
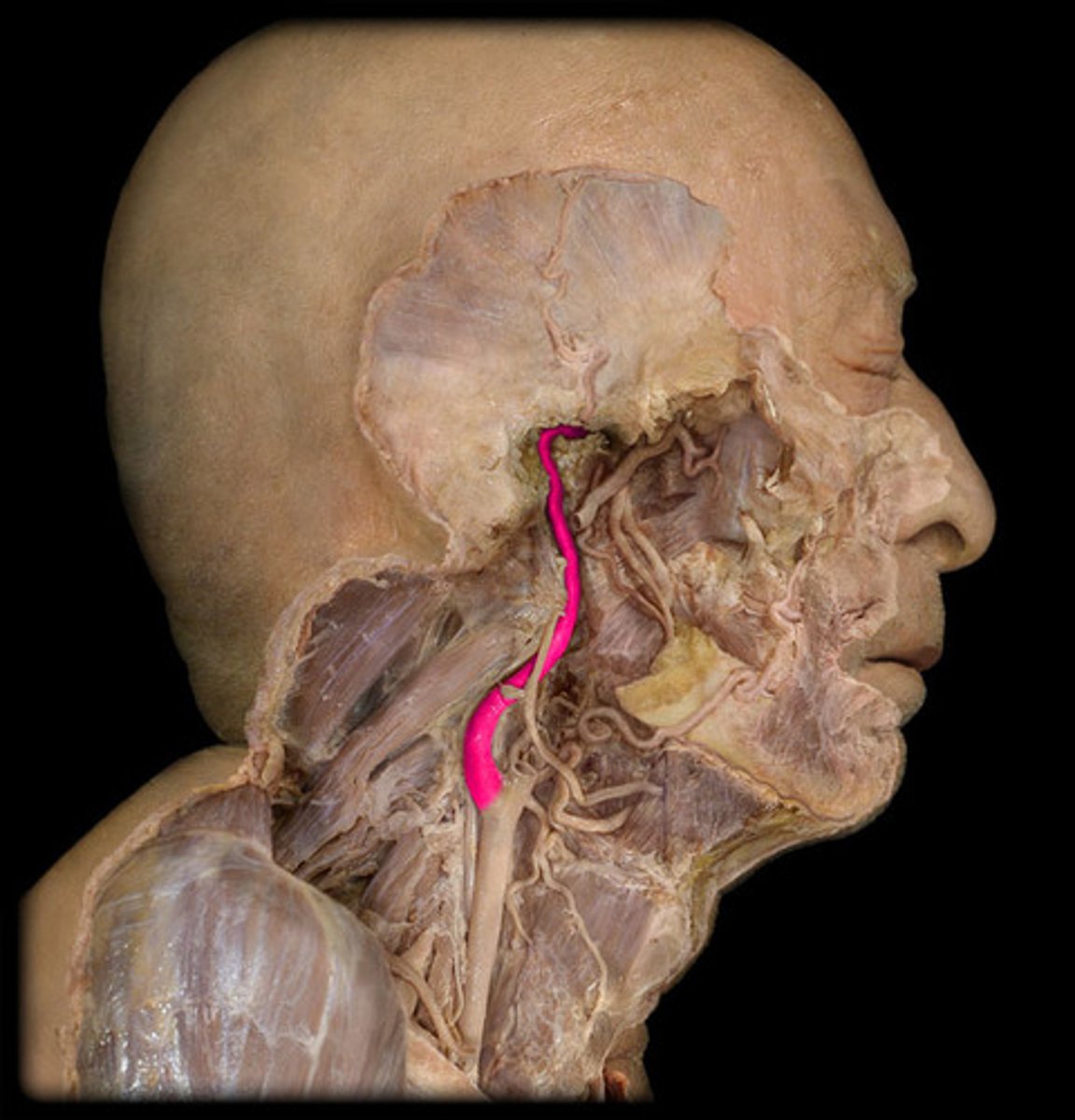
Carotid bifurcation
The point of division at which the common carotid artery branches at the angle of the mandible into the internal and external carotid arteries.
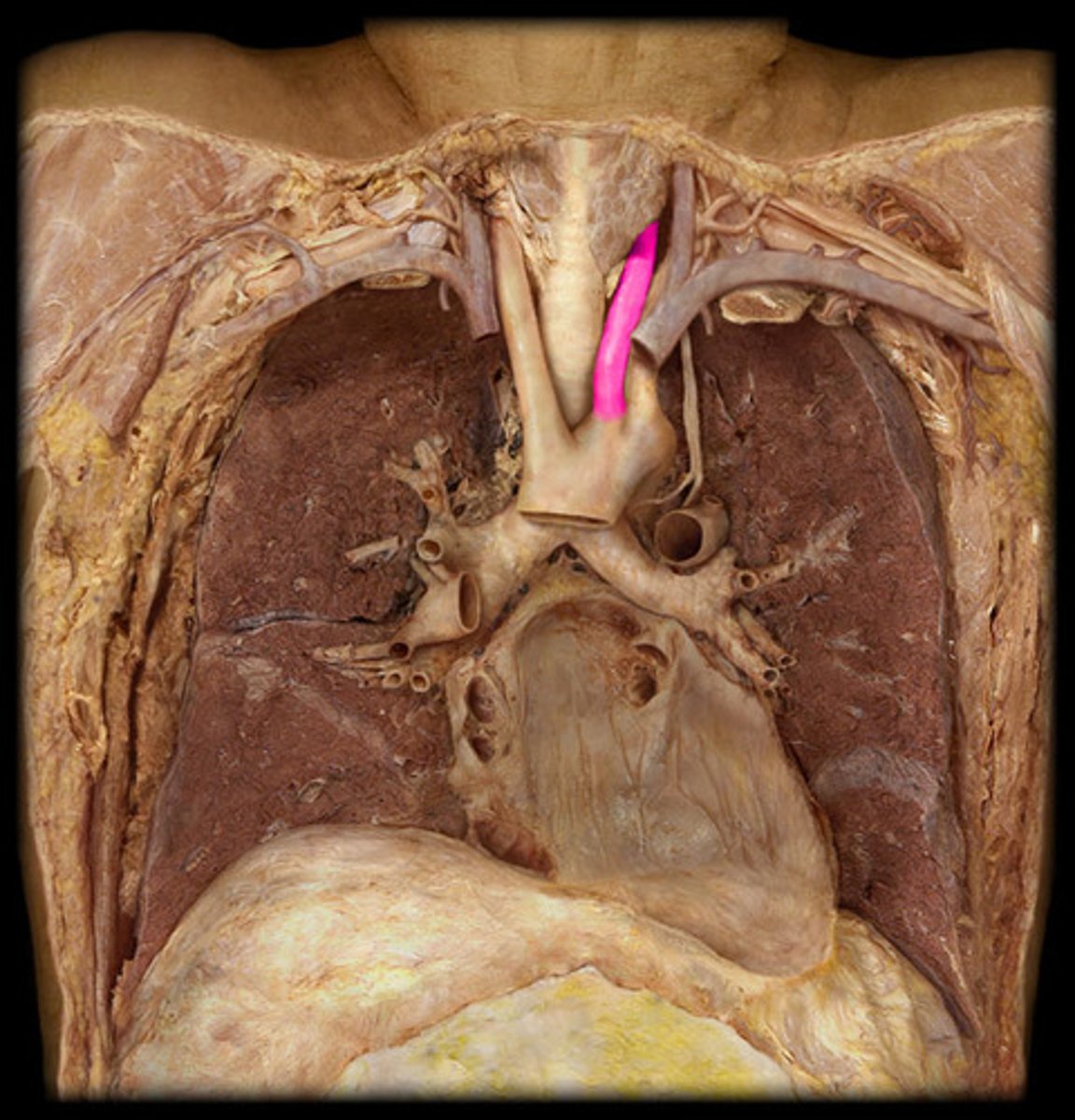
Internal carotid a.
supplies brain, eye, pituitary gland
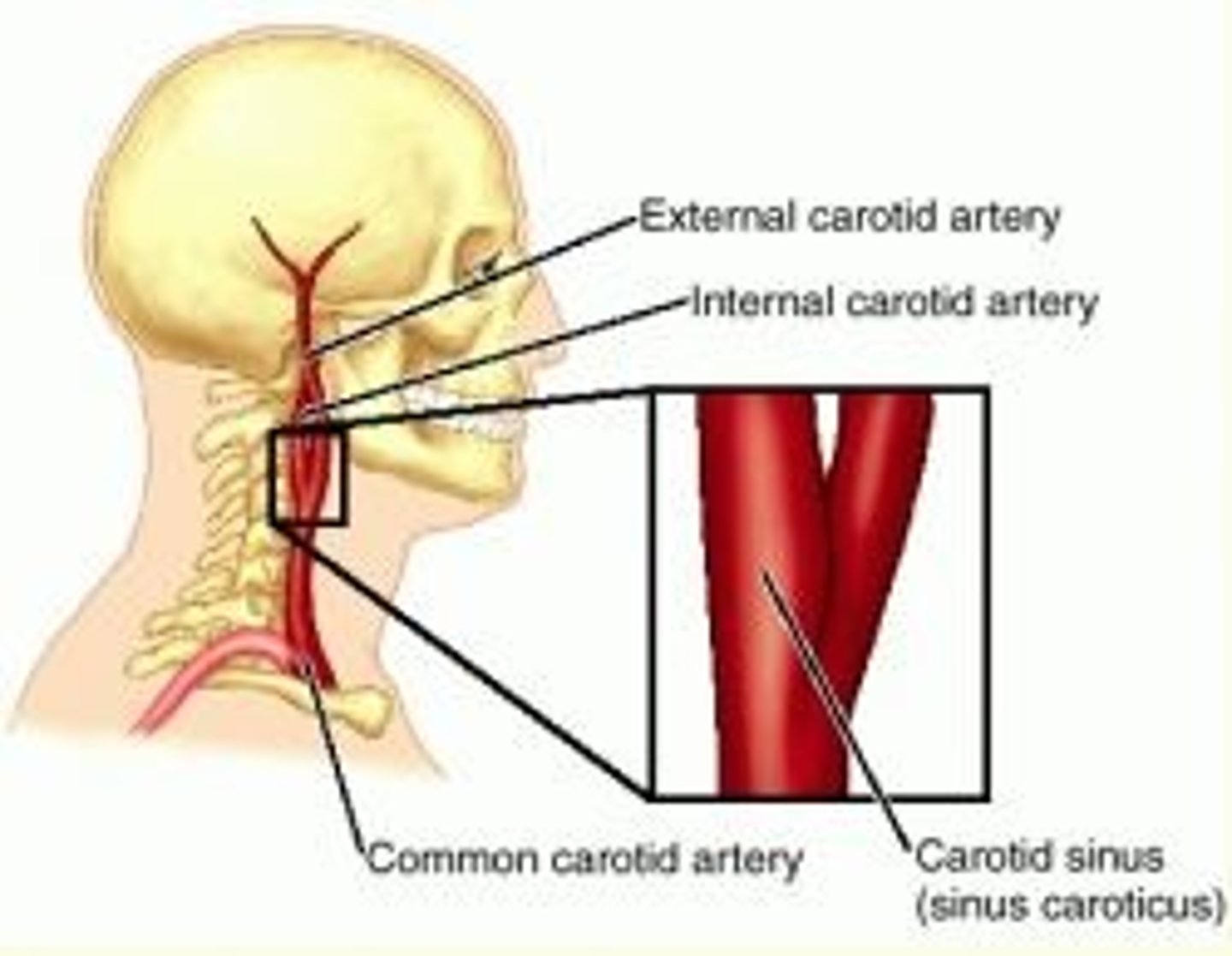
Carotid sinus
A dilation of a common carotid artery; involved in regulation of systemic blood pressure.
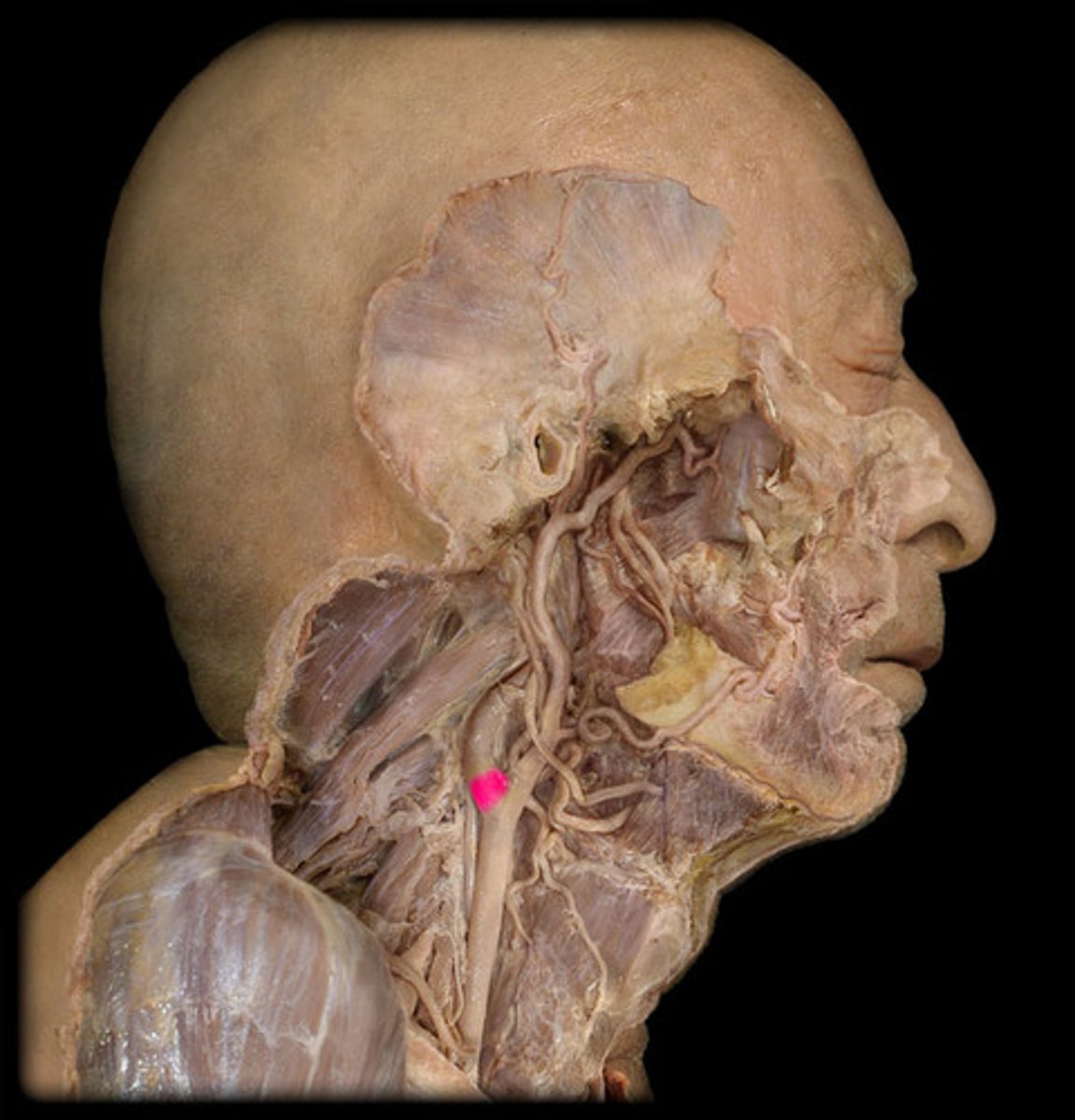
Superior thyroid a.
supplies thyroid gland
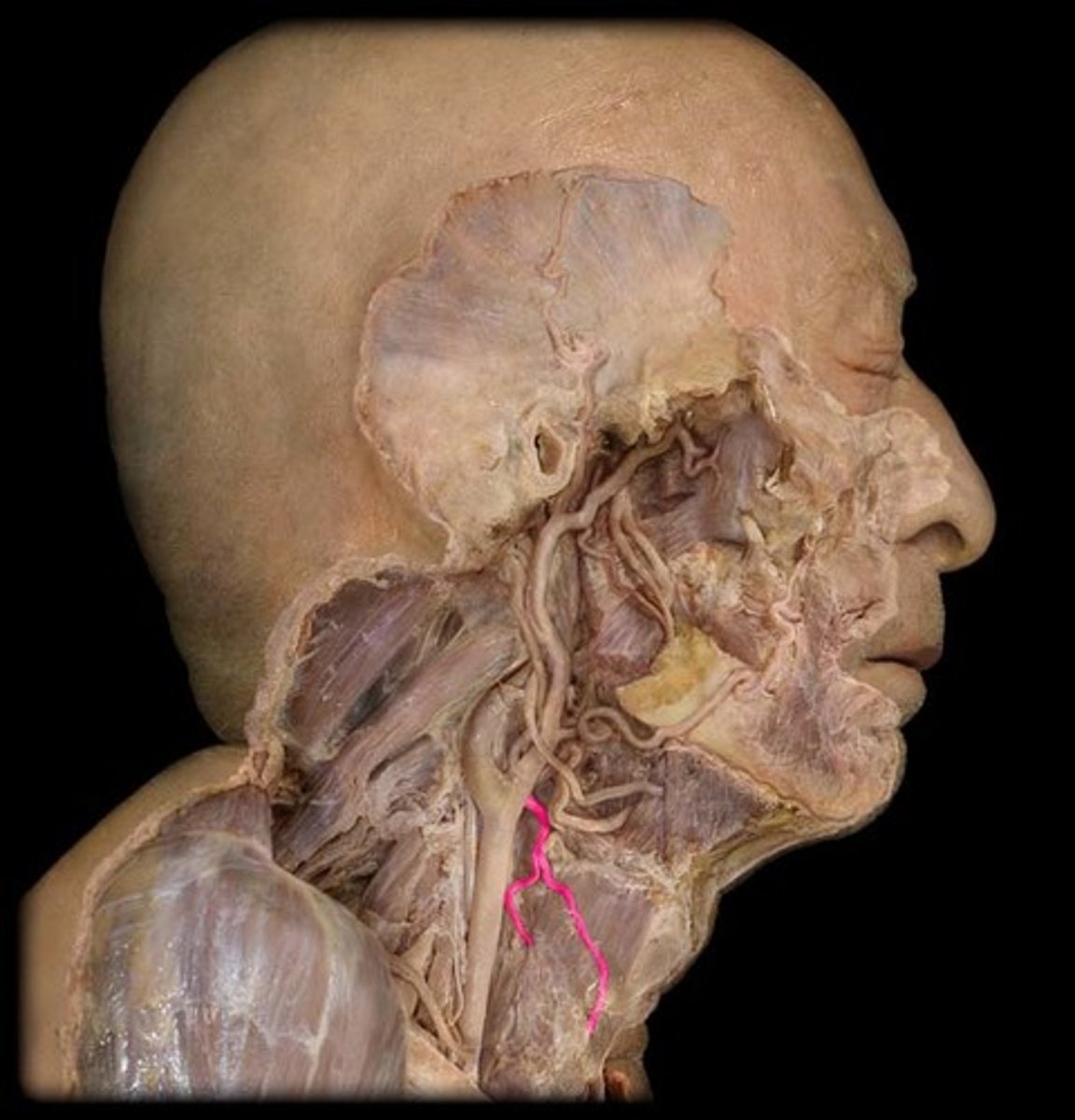
Lingual a.
supplies tongue
Occipital a.
supplies posterior scalp
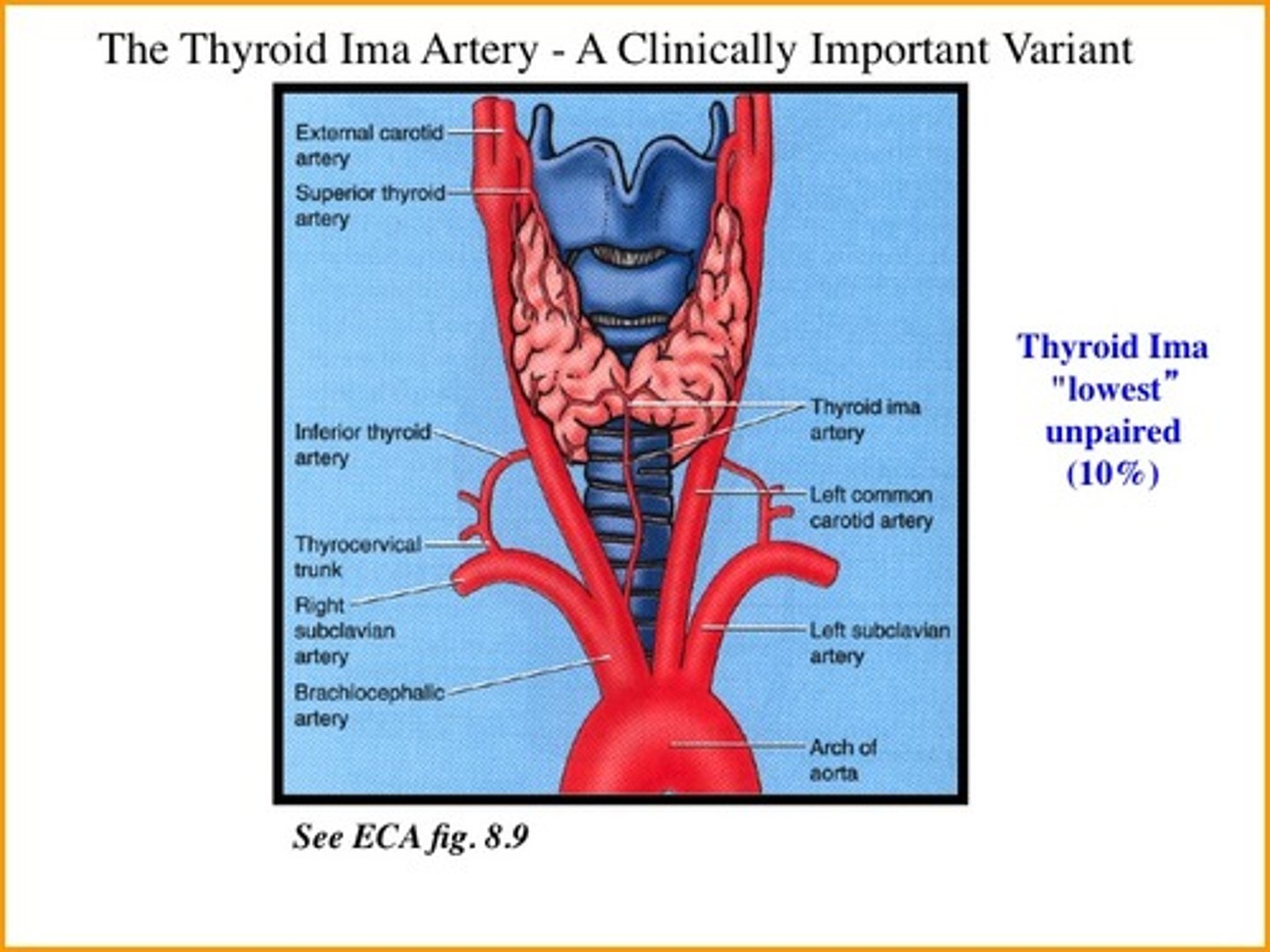
thyroid ima artery
• Ten percent of people, unpaired. Arises from brachiocephalic trunk, arch of aorta, right common carotid, sublavian, or internal thoracic arteries. Ascends on anterior surface of trachea to isthmus of thyroid, supplying both. Presence must be considered; potential source of bleeding.
Inferior thyroid veins
Arise in the venous plexus of the thyroid gland, communicate with the superior and middle thyroid veins, and empty into the left and right innominate veins.
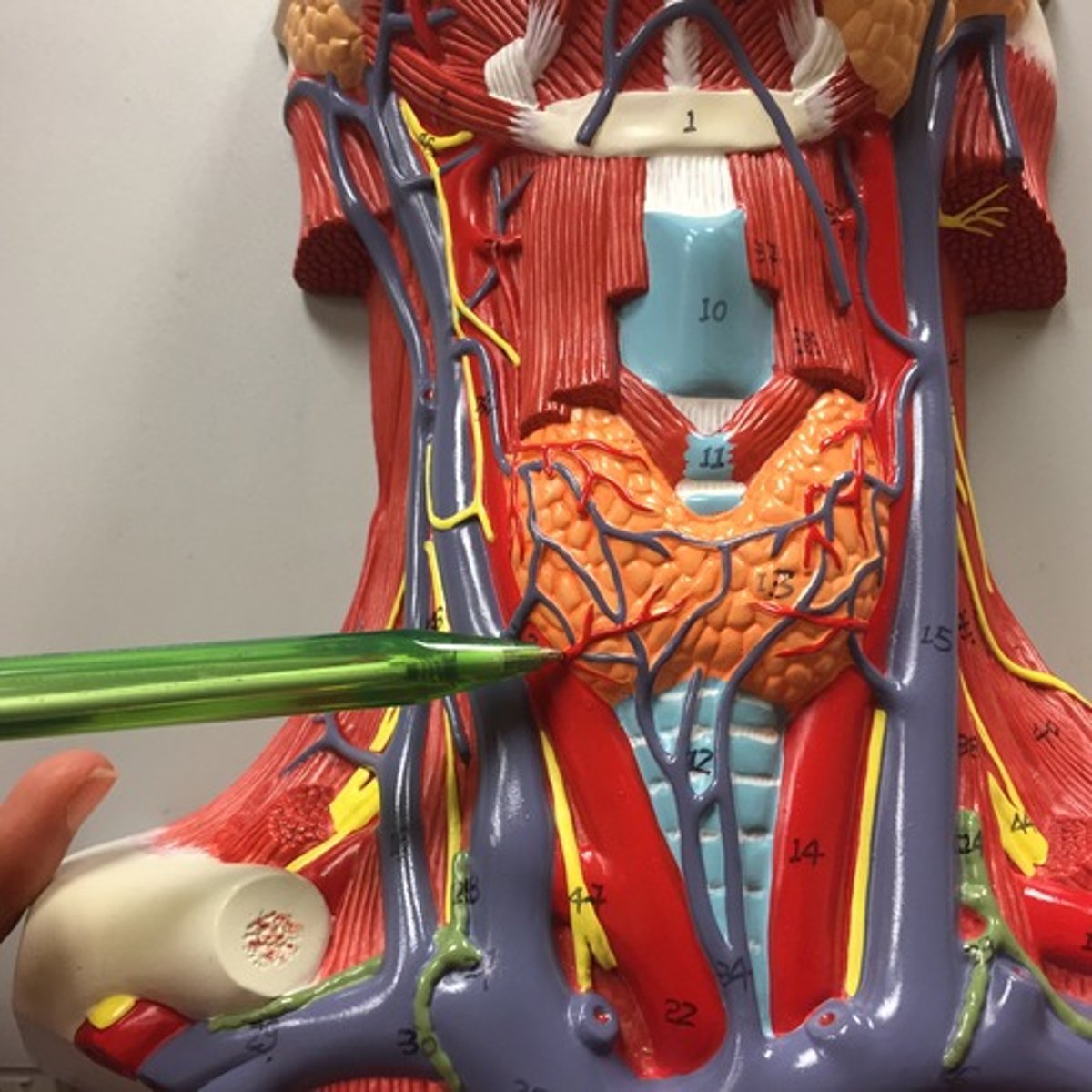
Internal jugular v.
either of the veins on each side of the throat close to the larynx that drain blood from the head; medial to the external version of this vein
Deep cervical lymph nodes
deep under the sternomastoid muscle and drains the soft palate, base of tongue, and max. 3rd molars,, posterior hard palate
Sympathetic trunk
nerve running along each side of the vertebral column
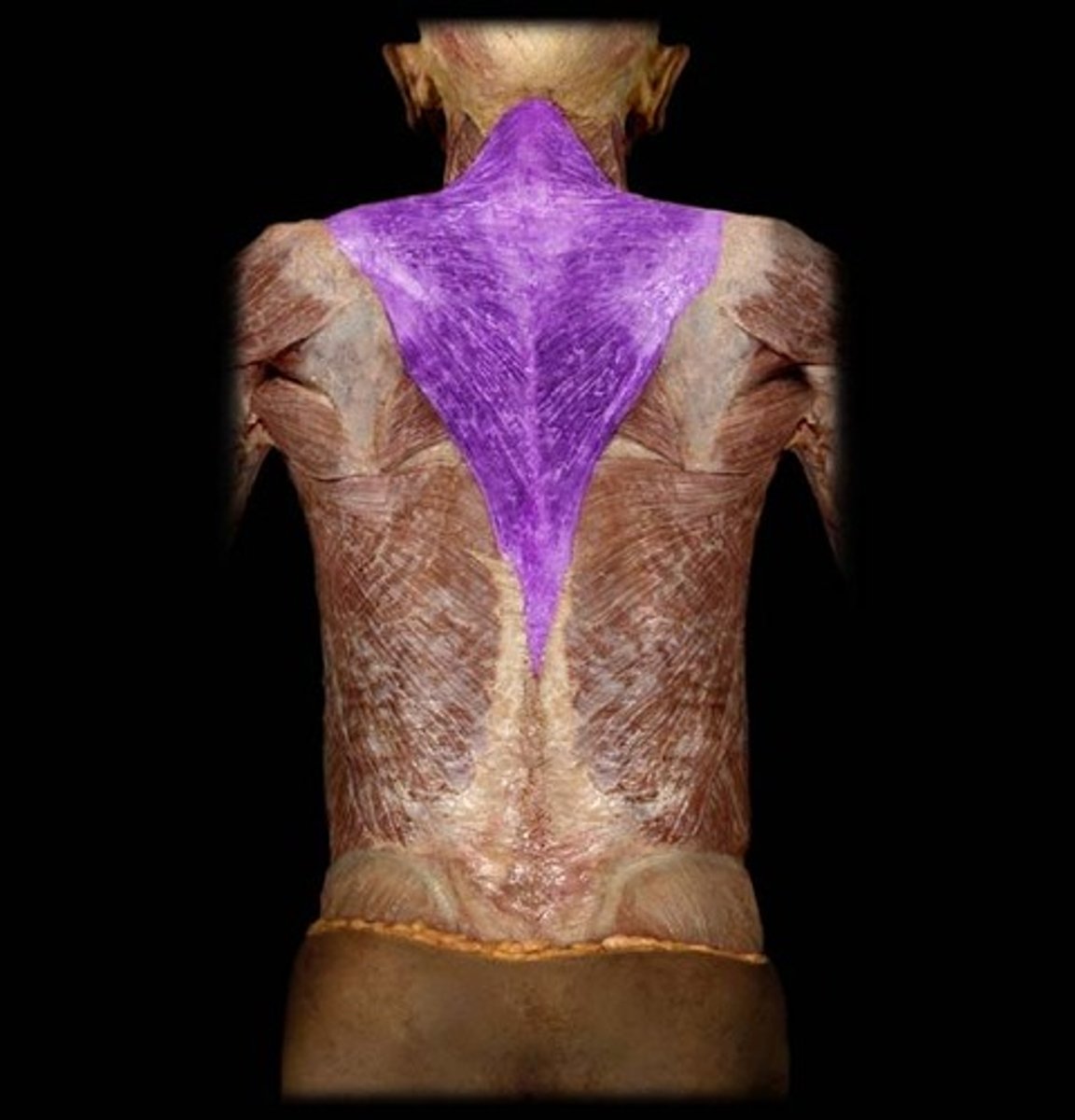
Trapezius m.
scapula elevation, depression, and retraction
Subclavian v.
below the clavicle = collar bone
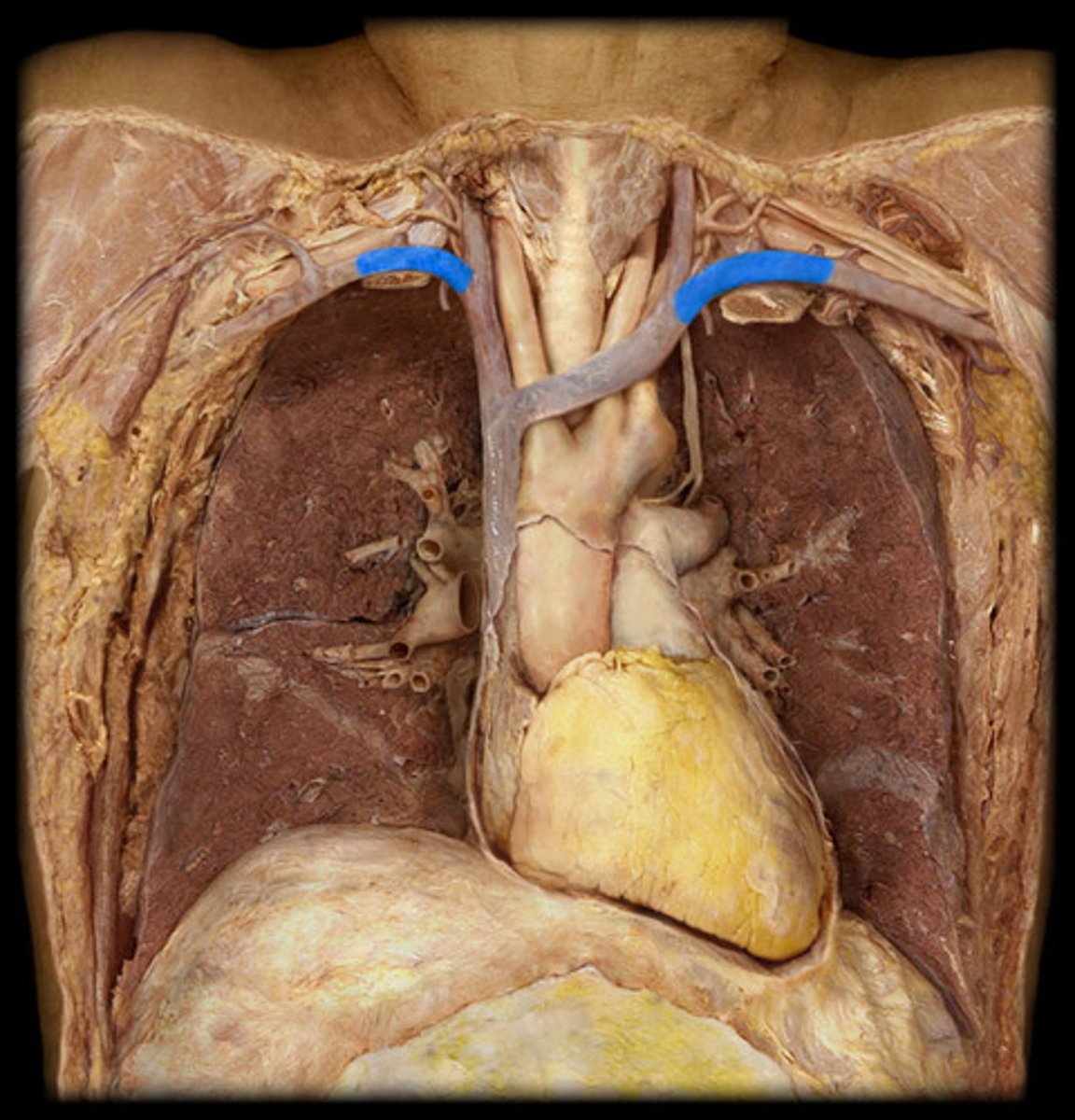
External jugular v.
either of the veins on each side of the throat that drain blood from the face and jaws; lateral to the internal version of this vein
Phrenic n.
pertaining to the diaphragm or pertaining to the mind

Anterior scalene m.
important anatomical landmark regarding the subclavian vasculature and brachial plexus
Subclavian a.
artery between the brachiocephalic trunk and axillary a.
located at first rib
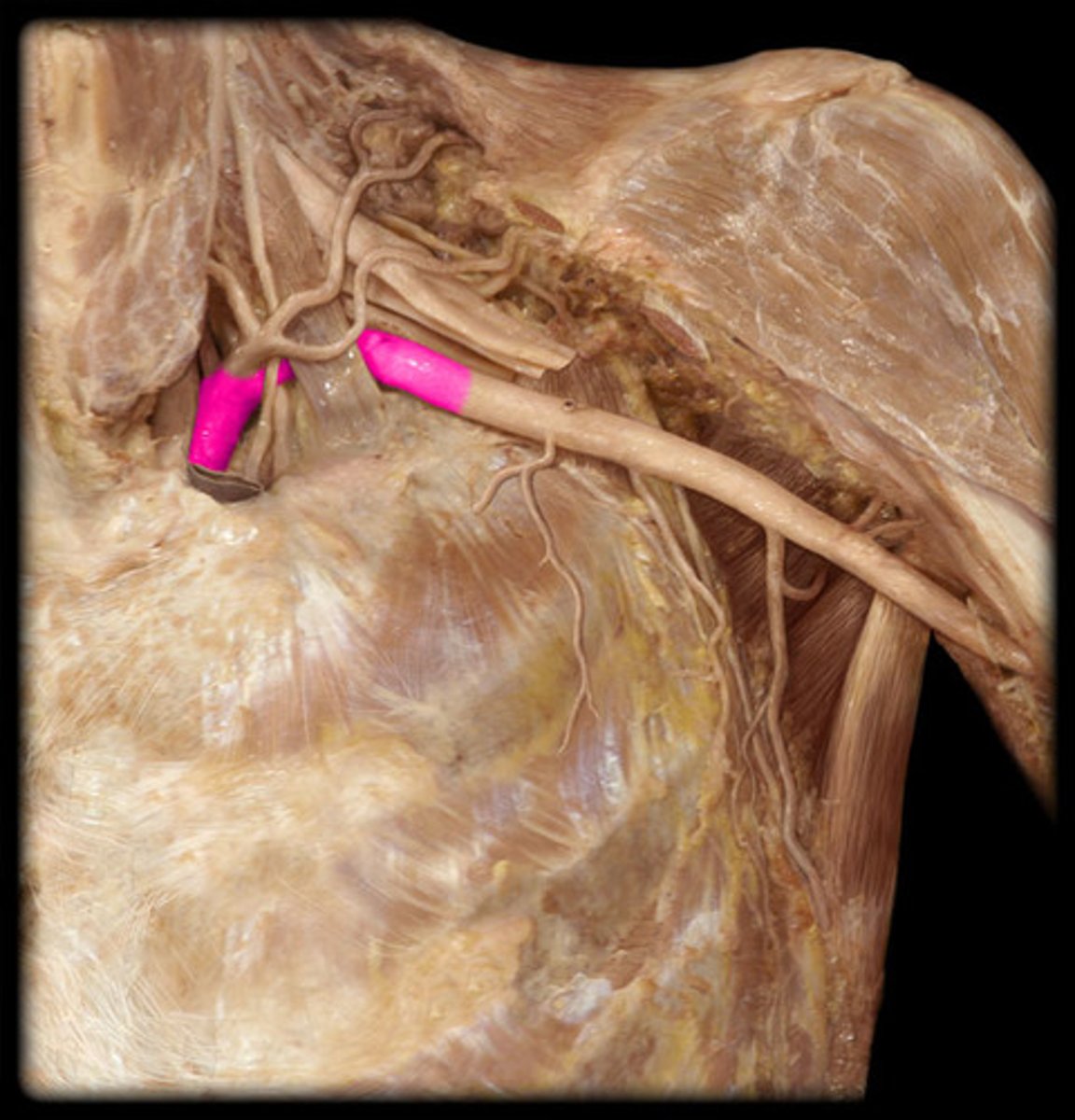
Vertebral a.
Branches off the subclavian aa.
Forms posterior circulation of the brain
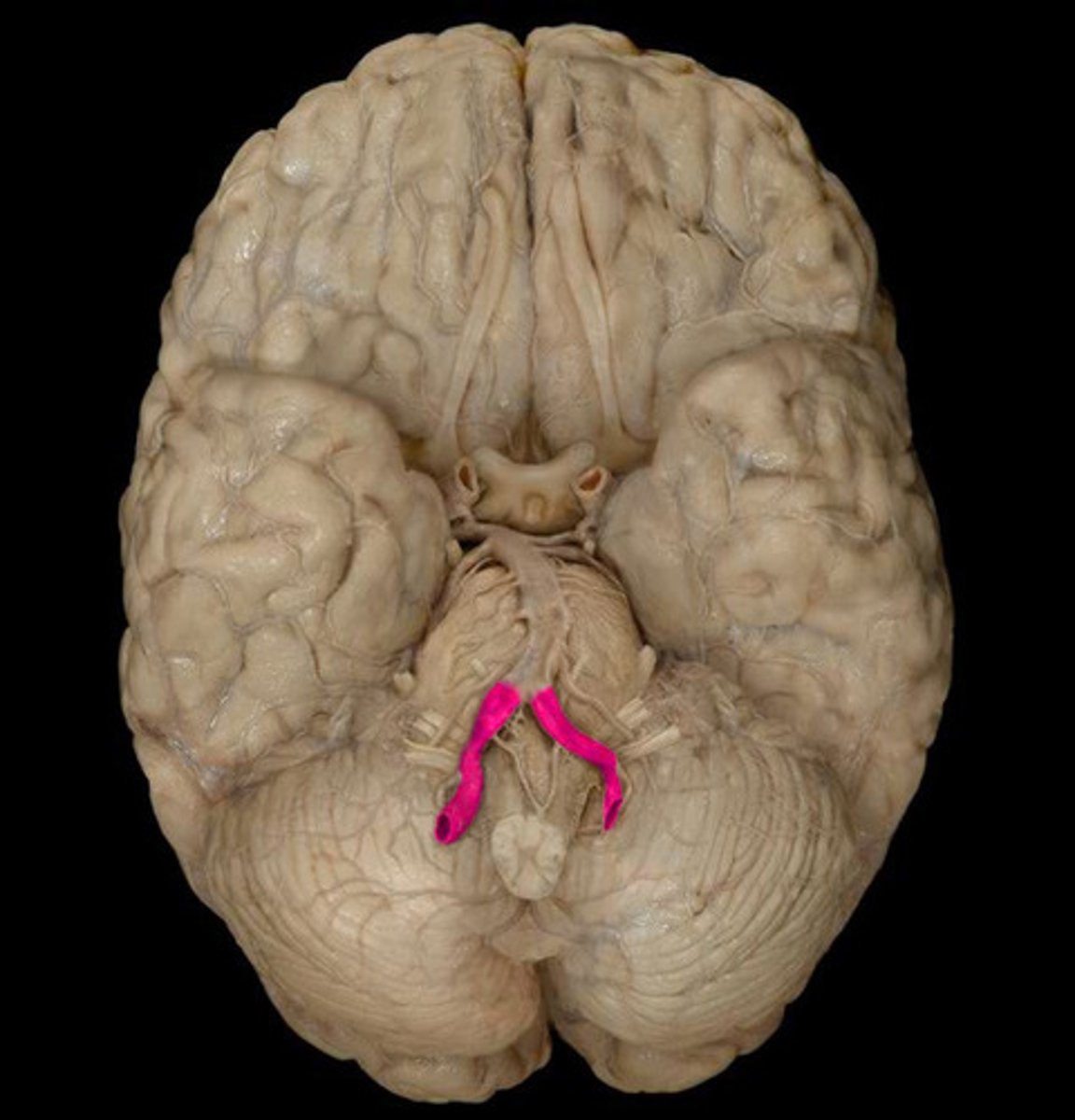
Internal thoracic a.
From: Subclavian a.
Serves: Pericardium, diaphragm, anterior thoracic wall
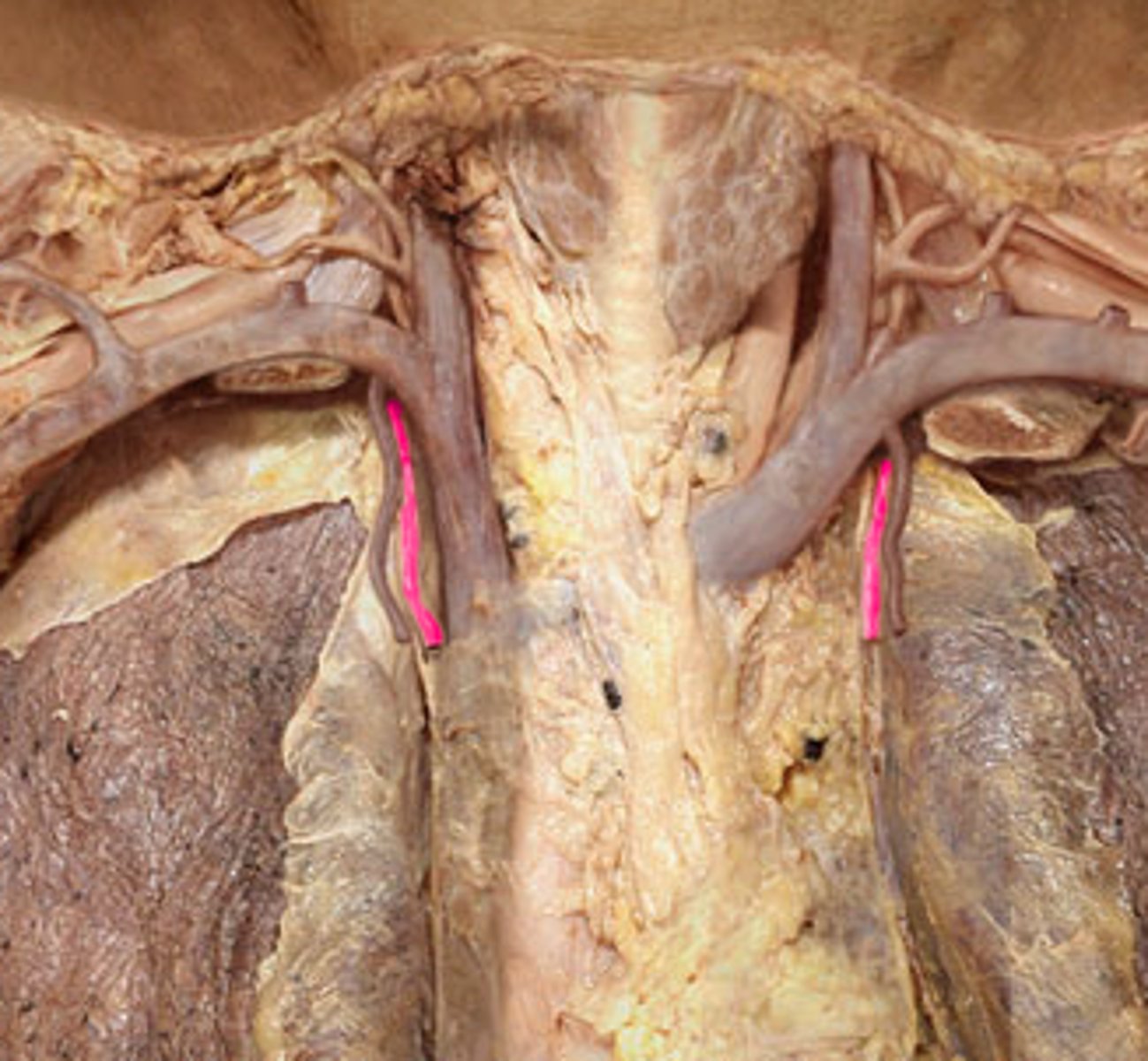
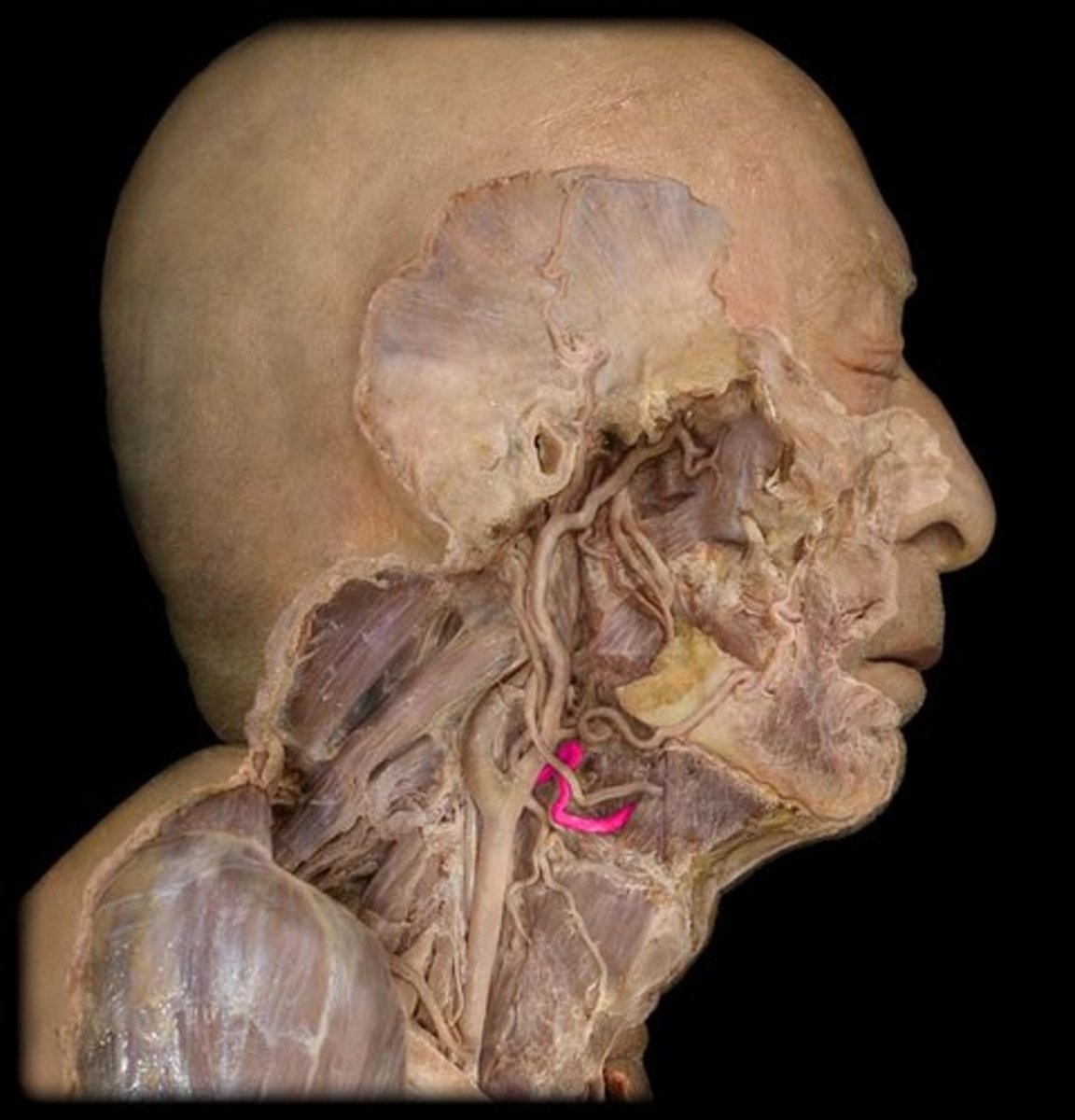
Thyrocervical trunk (a.)
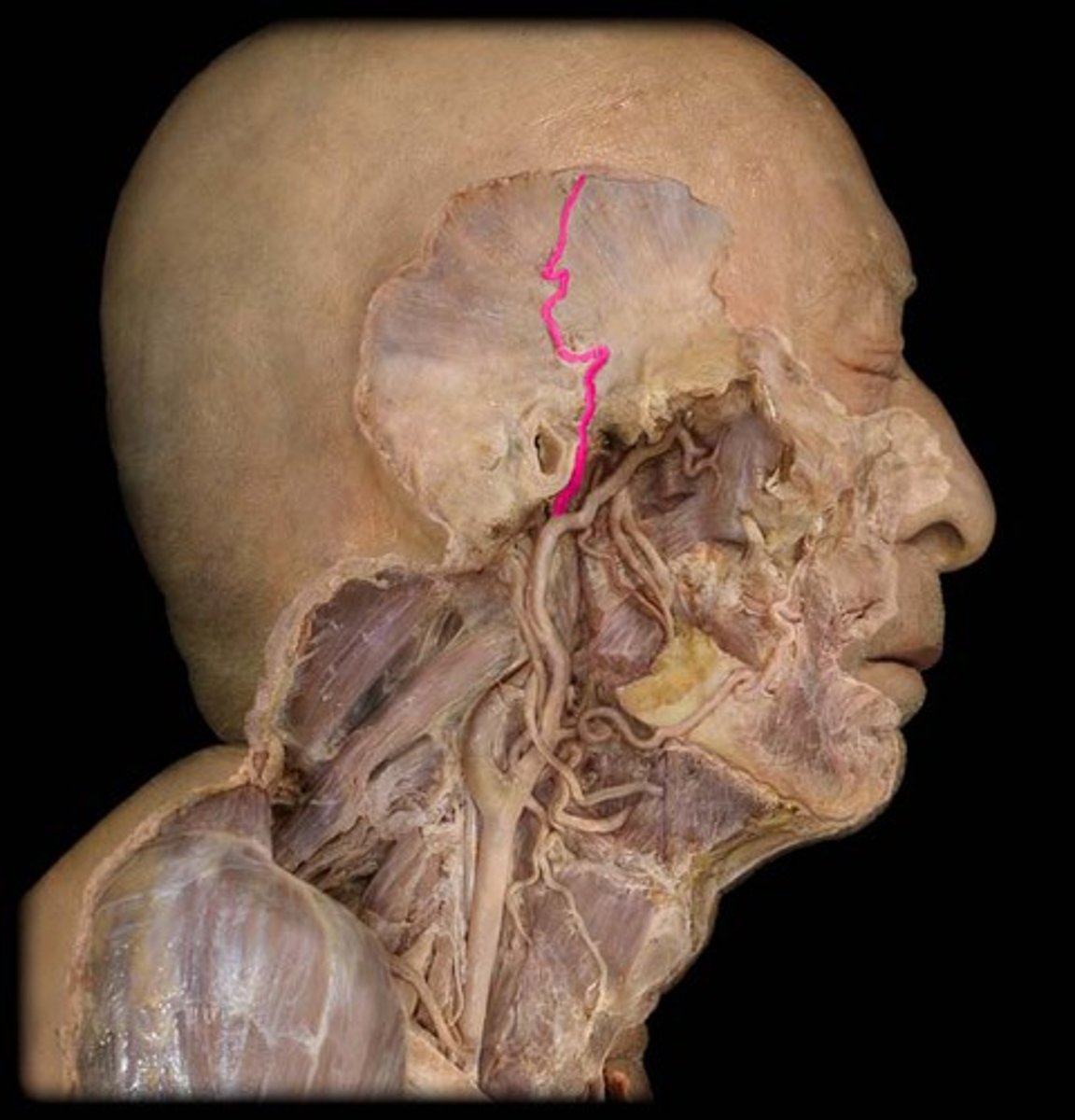
what structure is highlighted in pink?
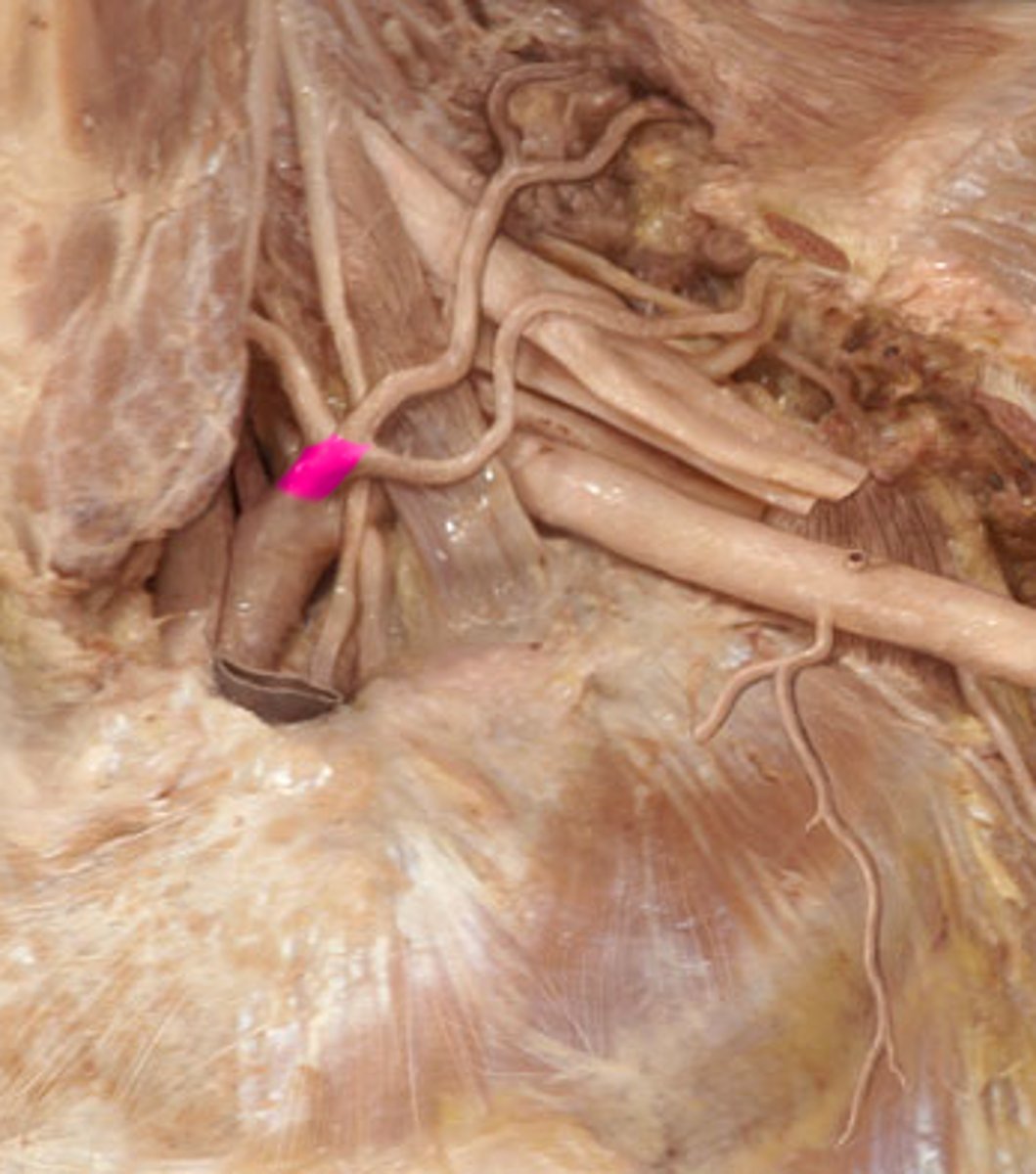
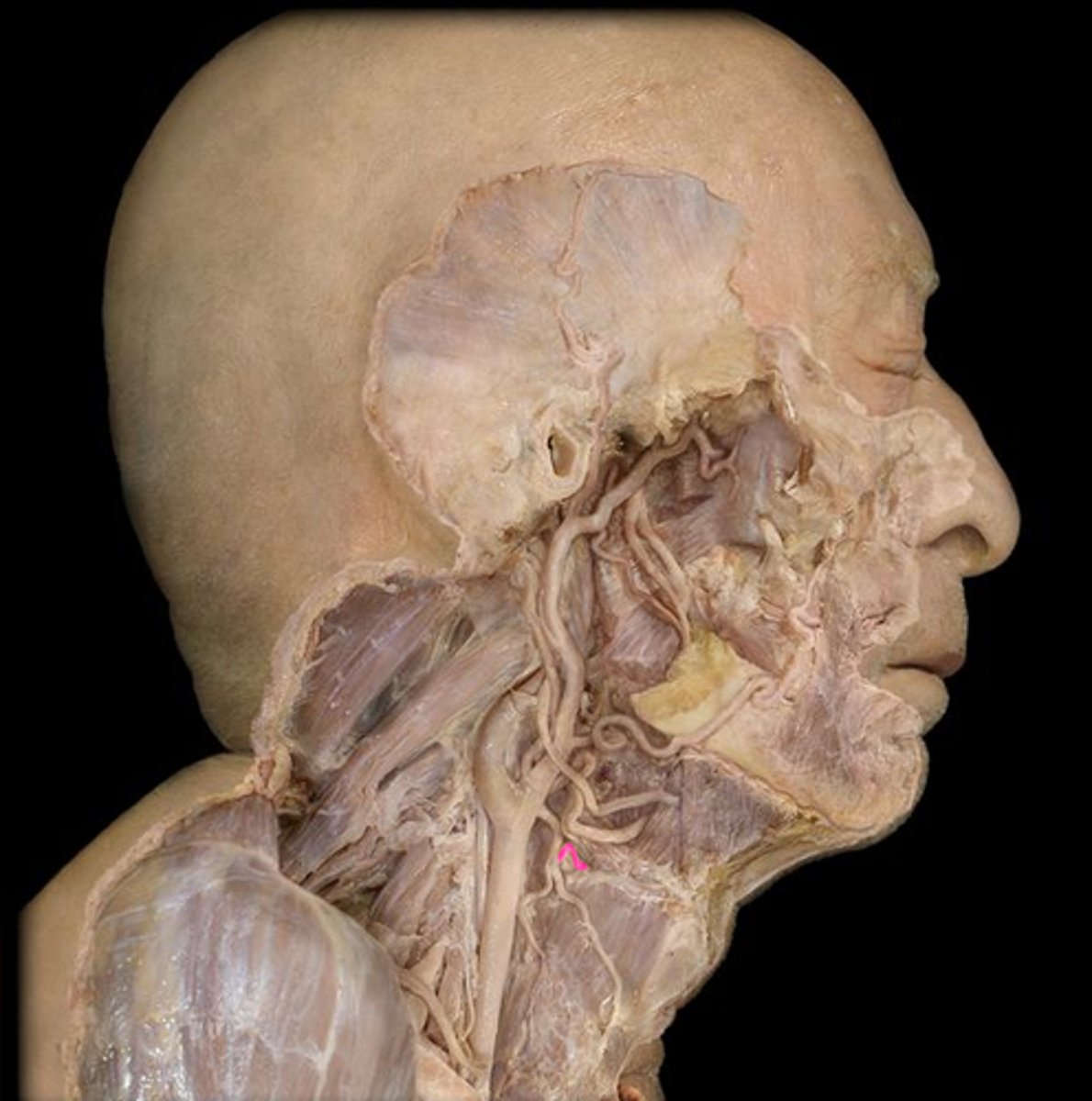
Inferior thyroid a.
supplies thyroid gland
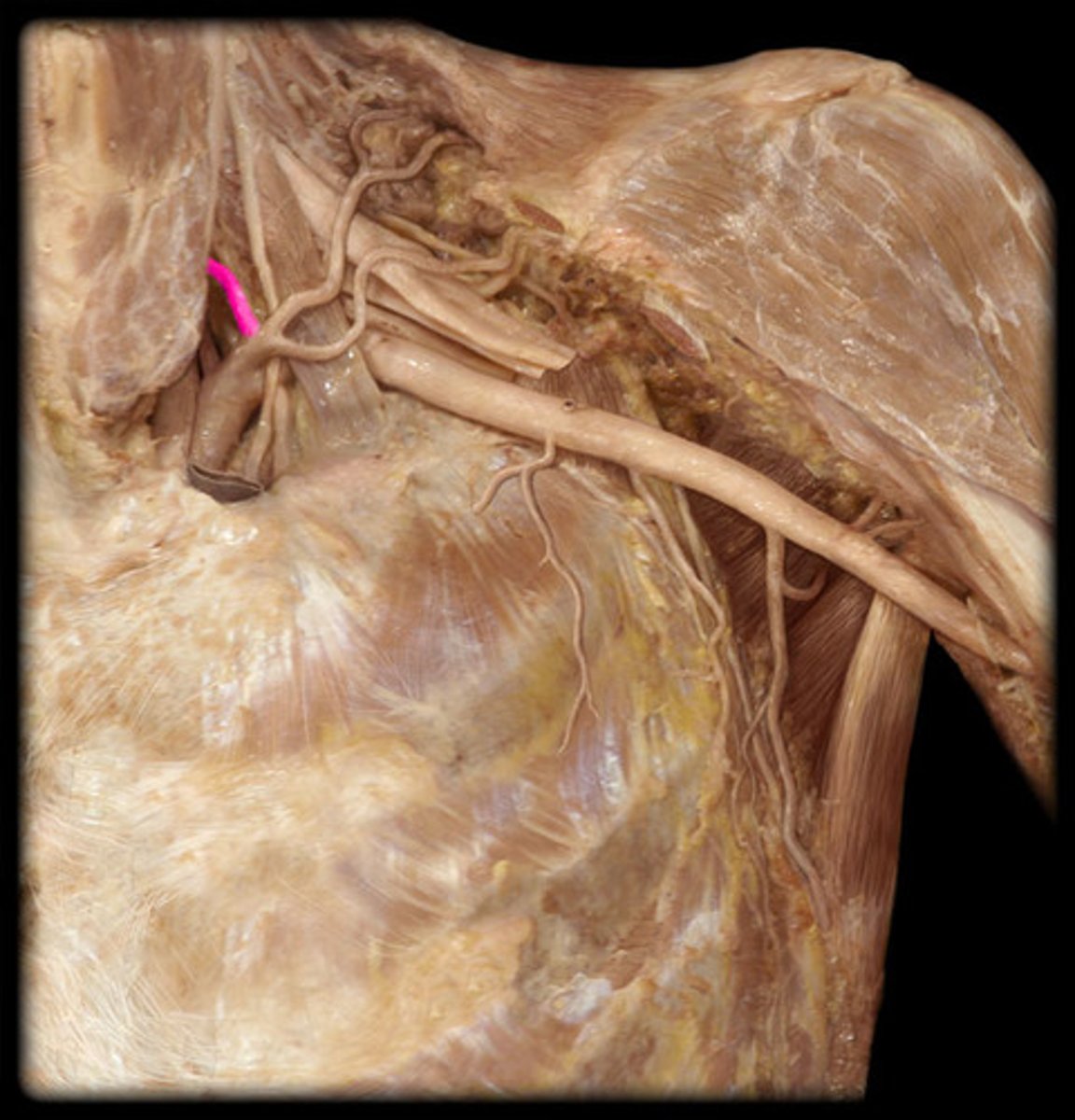
Brachial plexus
network of interlacing nerves found in the upper arm area

Thoracic duct
receives lymph from the left side of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, left arm, and lower extremities
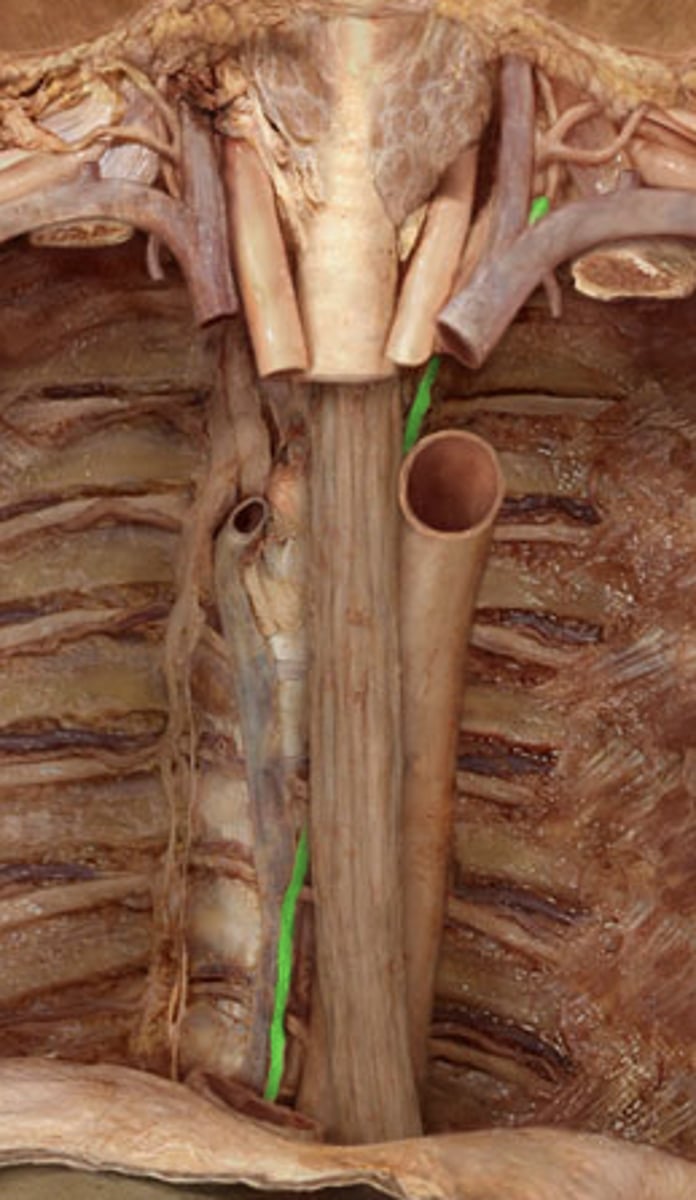
Middle scalene m.
O: transverse processes of C3-C6
I: scalene tubercle of first rib
N: brachial plexus
F: flexion of head/neck (bilateral contraction), lateral flexion of head/neck (unilateral contraction)