BIOC 3021 - Exam 1, things to memorize
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
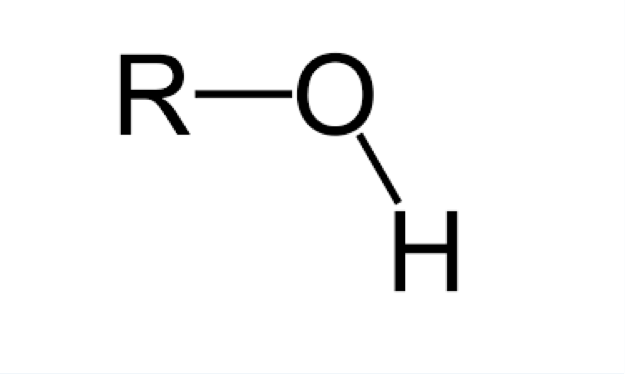
alcohol
hydroxyl group attached to carbon, ending “-ol”; if on ring, ending “phenol”
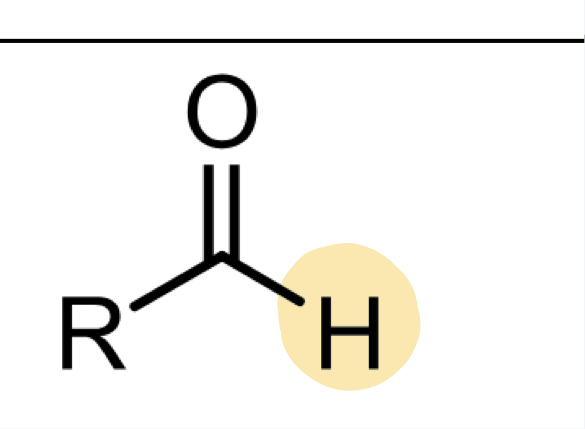
aldehyde
C O DOUBLE bond, attached to one carbon with hydrogen and connected to rest of structure. ending “-al”
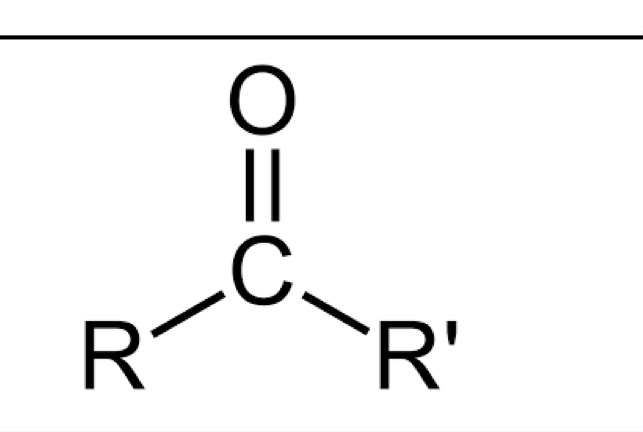
ketone
C O double bond attached to carbon which is bonded to TWO OTHER CARBONS. ending “-one”
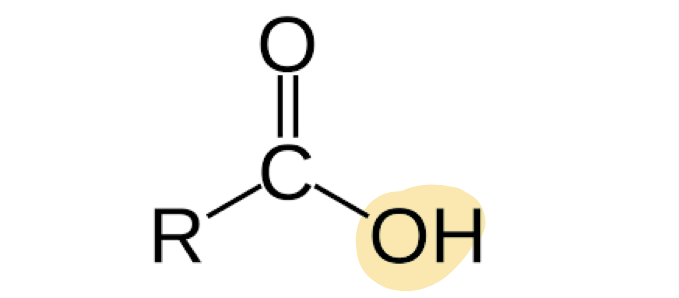
carboxylic acid
C double bond O with HYDROXYL group and connected to rest of structure. ends in “-oic”
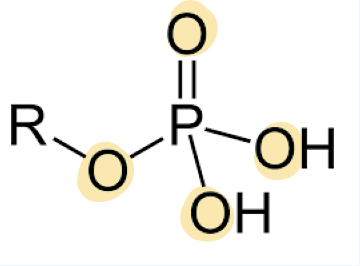
phosphate
phosphorous atom bonded to four oxygen atoms — one oxygen atom is attached to a carbon chain
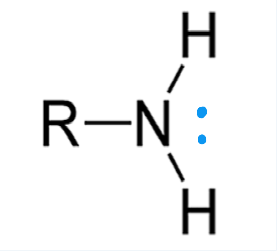
amine
nitrogen atom with lone pair of electrons attached to carbon chain. ends in “-amine”
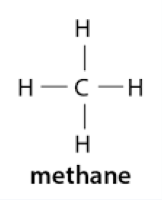
alkane
Formula: CₙH₂ₙ₊₂
straight chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms, no carbon-carbon double or triple bonds. ends in “-ane”
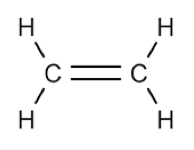
alkene
Formula: CₙH₂ₙ
unsaturated, carbon-carbon double bond. note cis and trans isomers. ends in “-ene”
Alanine
Ala, A
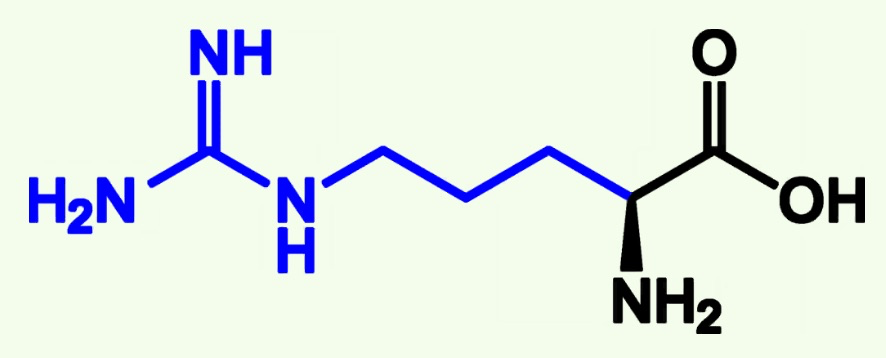
Arginine
Arg, R
asparagine
Asn, N
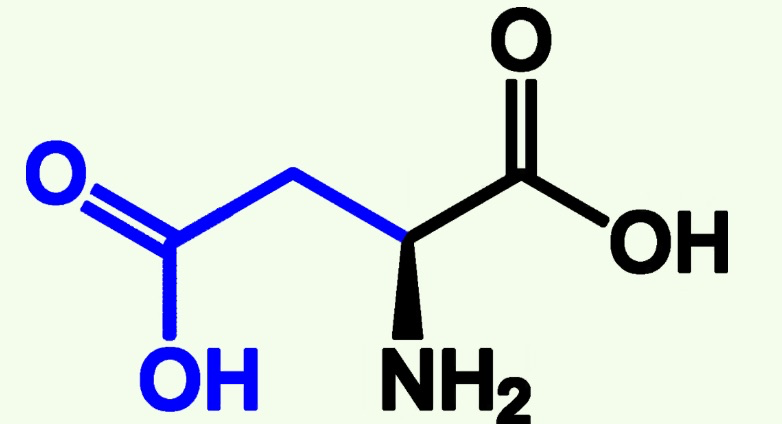
Aspartic Acid
Asp, D
cysteine
Cys, C
Glutamine
Gln, Q
Glutamic acid
Glu, E
Glycine
Gly, G
Histidine
His, H
Isoleucine
Ile, I
Leucine
Leu, L
lysine
Lys, K
Methionine
Met, M
Phenylalanine
Phe, F
Proline
Pro, P
Serine
Ser, S
Threonine
Thr, T
Tryptophan
Trp, W
Tyrosine
Tyr, Y
Valine
Val, V
Asparagine or aspartic acid
Asx, B
Glutamine or glutamic acid
Glx, Z
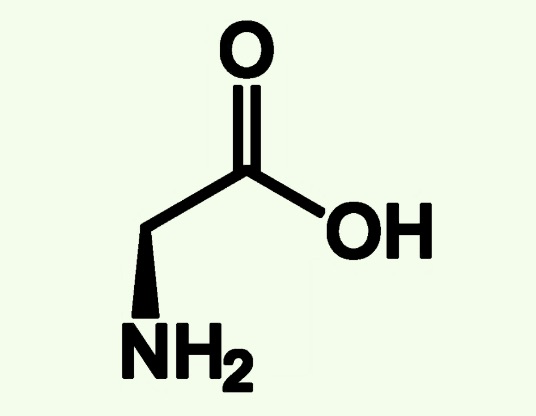
simplest amino acid, glycine
H as R group, can occupy any position. No chiral center
polar amino acids
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Aspartic acid, glutamic acid, asparagine, glutamine, tyrosine, histidine, lysine, arginine
Hydrophilic, on exterior face of protein
Non polar amino acids
Alanine, Valine, Leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline, phenylalanine, tryptophan
Hydrophobic, clusters on the inside of proteins
Proline properties
Imino group, causes bends and turns in proteins due to being incompatible with alpha helices or beta sheets
phenylalanine and tryptophan
contain aromatic phenyl rings, can absorb UV
valine structure
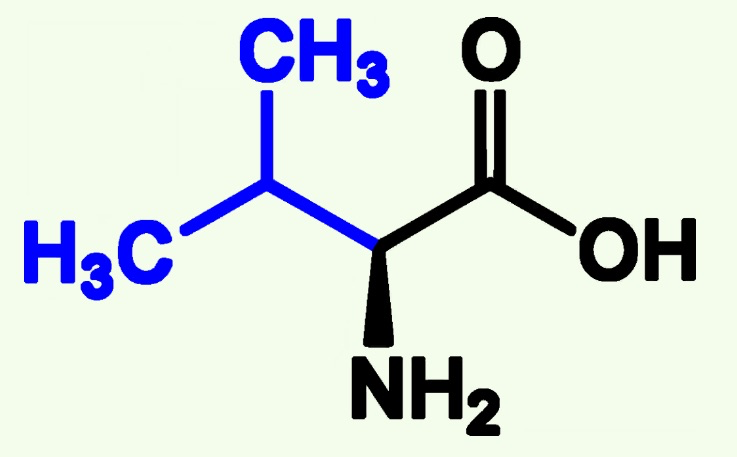
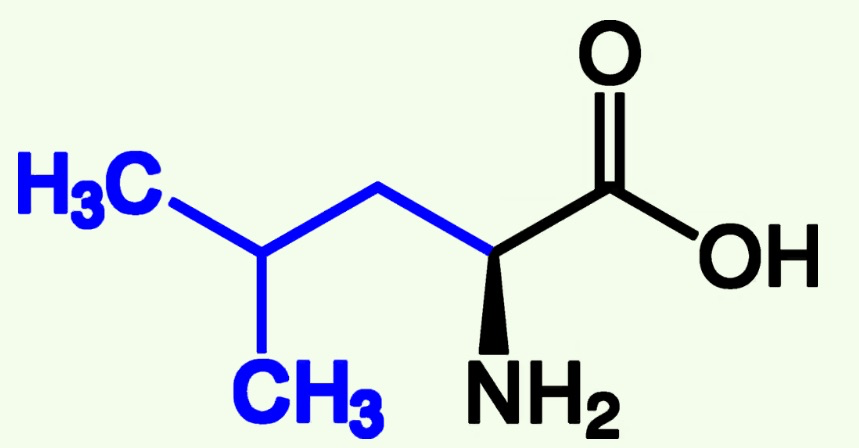
leucine structure
arginine structure
aspartic acid structure
glutamic acid structure
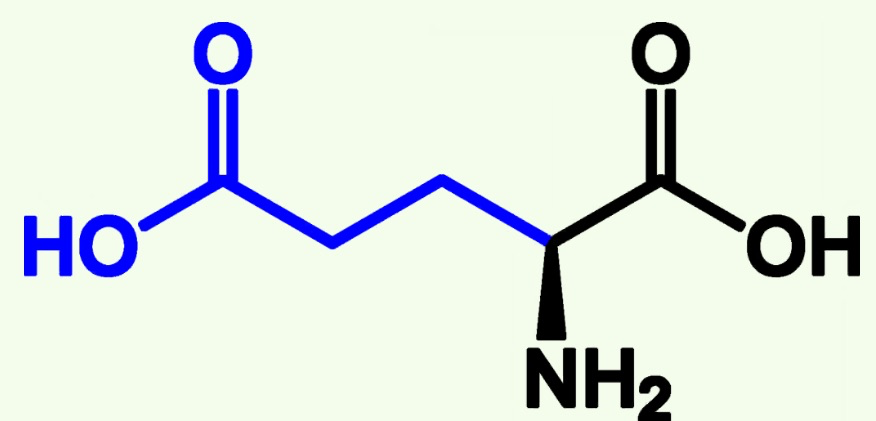
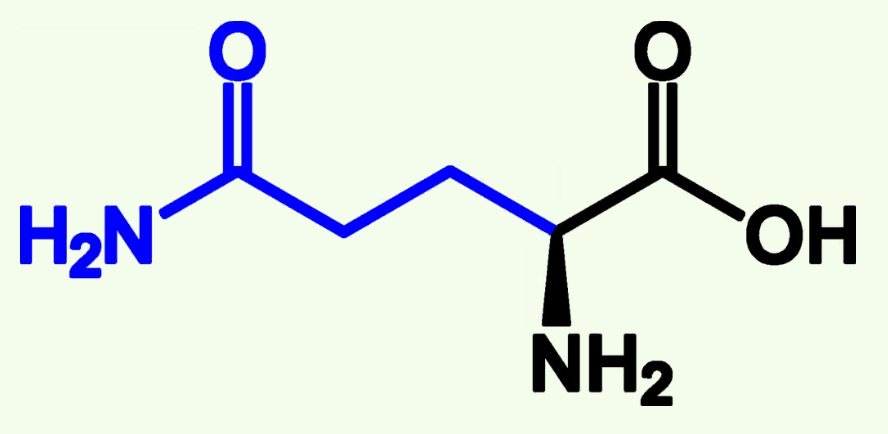
glutamine structure
glycine structure
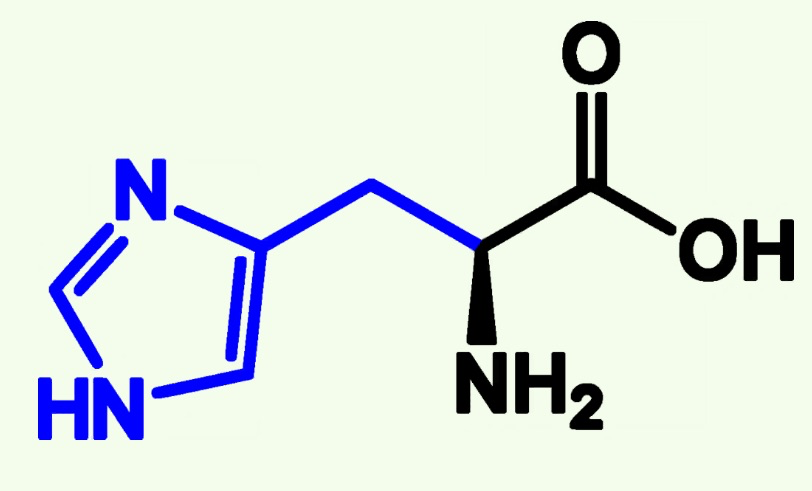
histidine structure
isoleucine structure
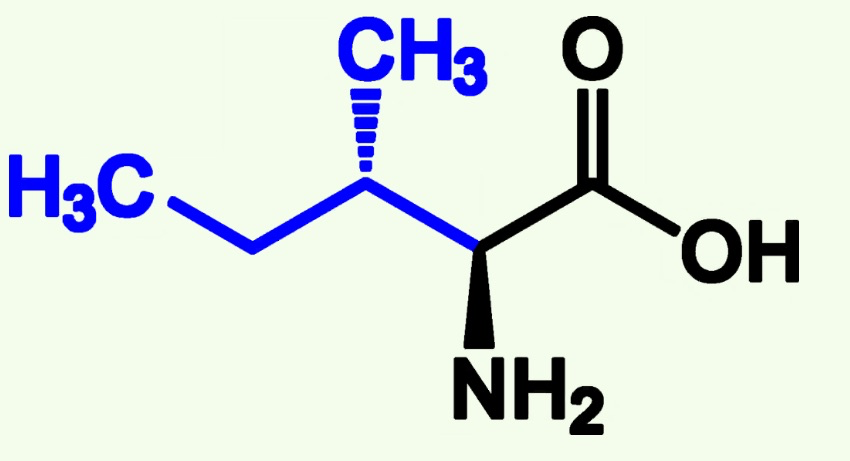
methionine structure
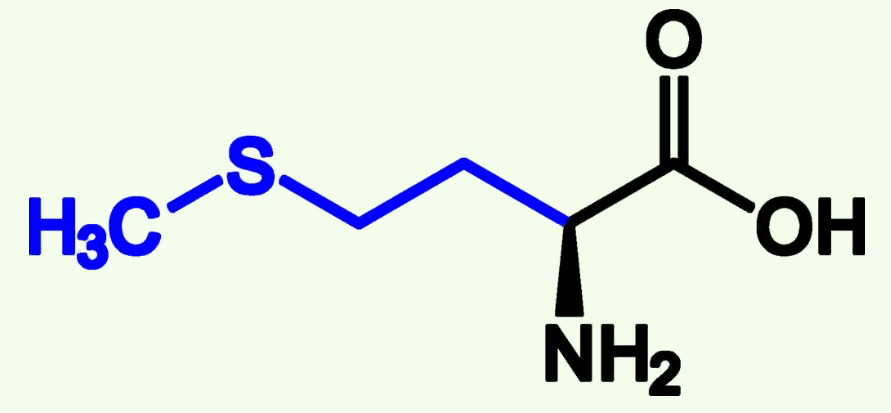
phenylalanine structure
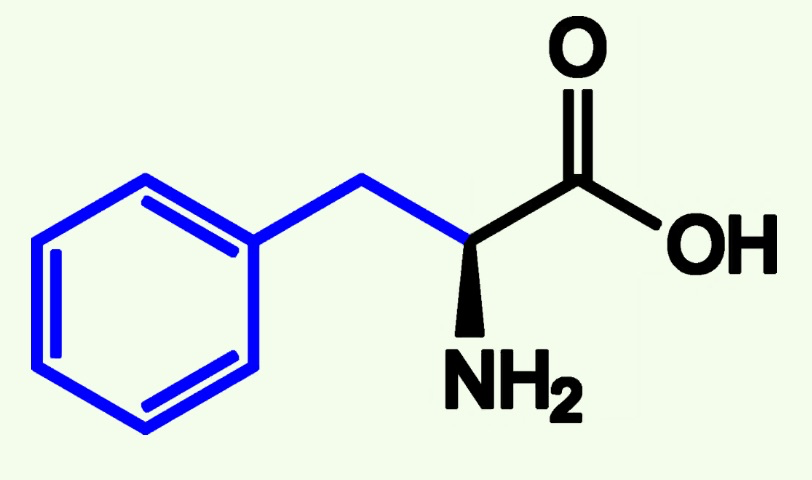
serine structure
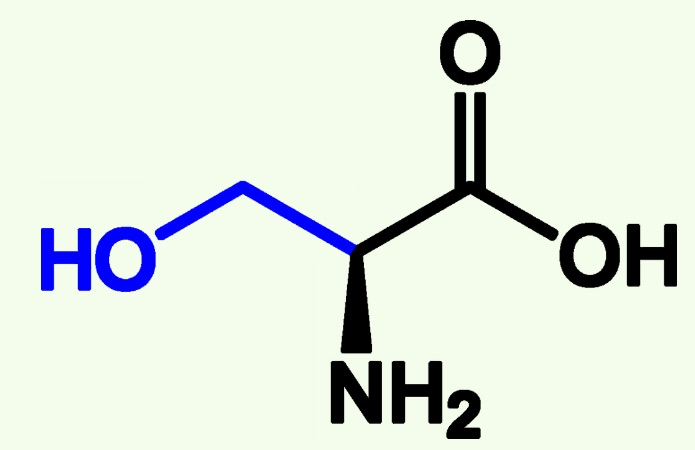
alanine structure
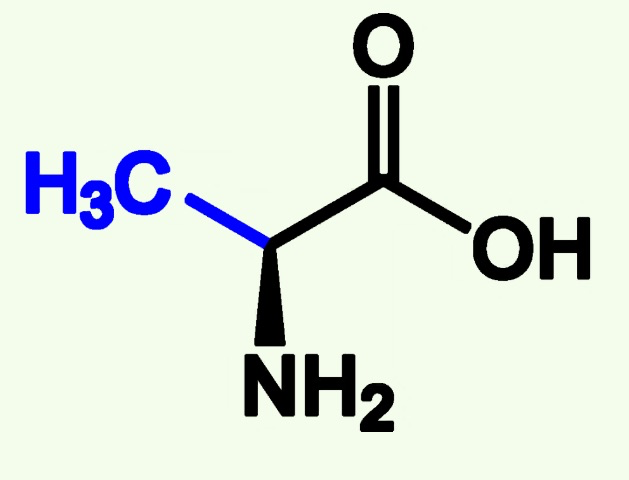
lysine structure
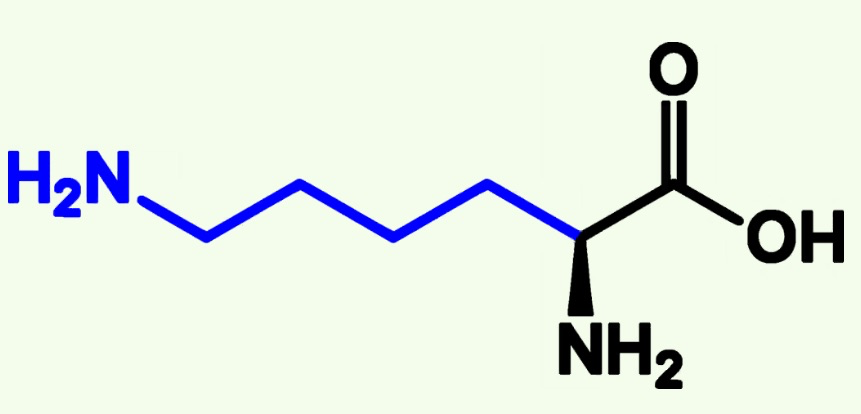
tyrosine structure
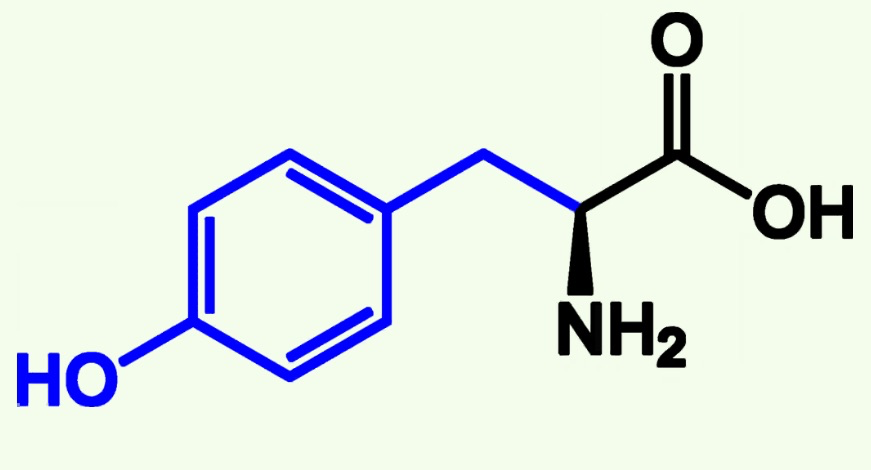
proline structure
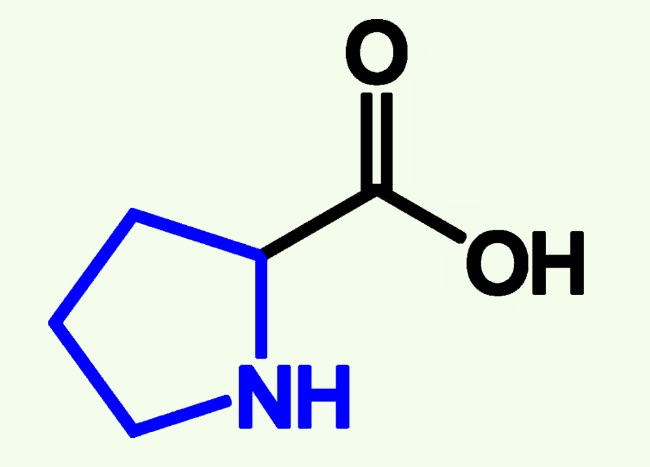
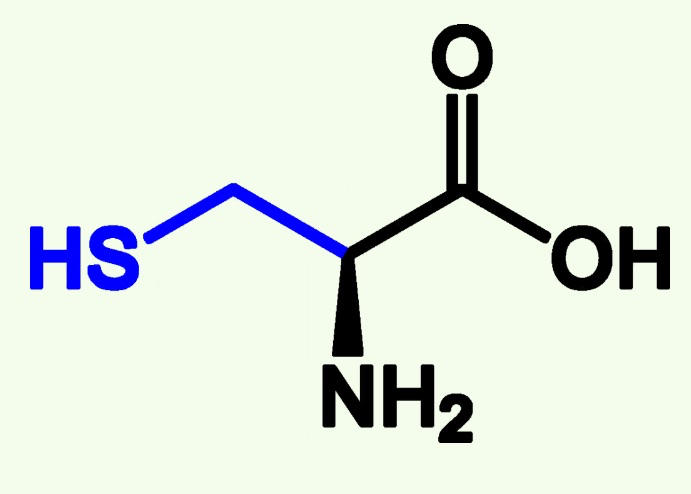
cysteine structure
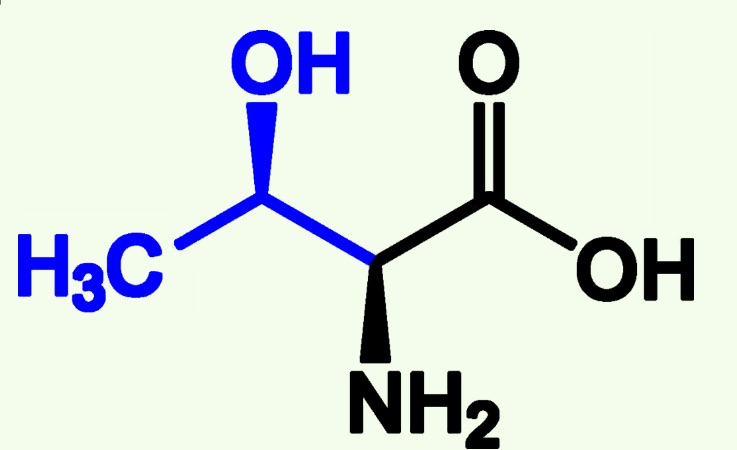
threonine structure
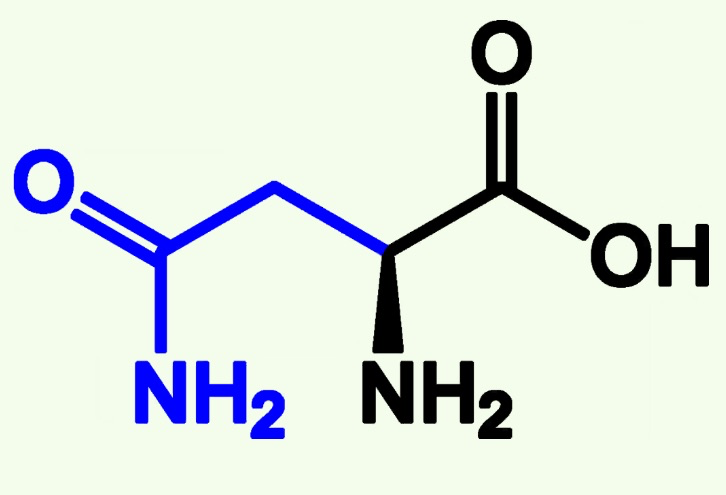
asparagine structure
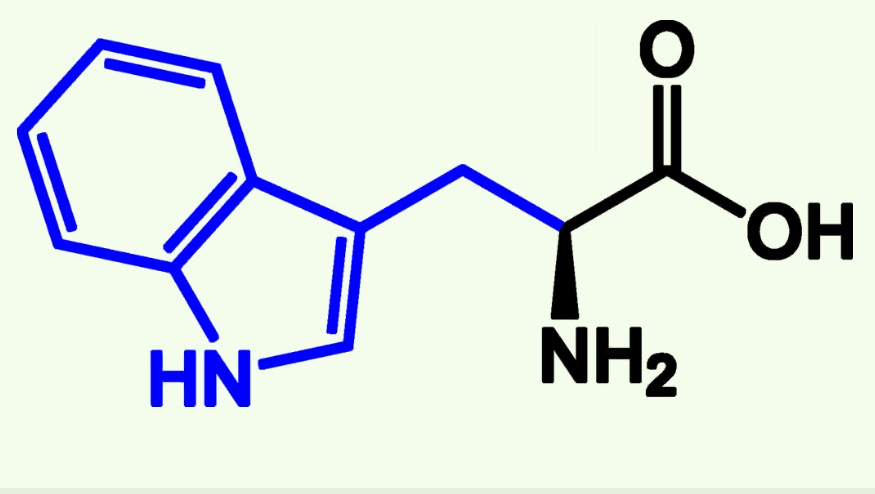
tryptophan structure
alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, proline, valine
aliphatic amino acids
phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine
aromatic amino acids
aspartic acid and glutamic acid
acidic amino acids
arginine, histidine, lysine
basic amino acids
serine and threonine
hydroxylic amino acids (has -OH group on R)
asparagine and glutamine
amidic amino acids (has amide group on R)
cysteine and methionine
sulfur containing amino acids
isoleucine, leucine, valine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, histidine, lysine, threonine, methionine
essential amino acids (must be in diet)