Biology Midterm semester 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:46 PM on 12/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
Prokaryotic cell
a cell that does not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
* the only prokaryotes are bacteria
* Prokaryotic cells do have DNA ; DNA is not just in nucleus
* the only prokaryotes are bacteria
* Prokaryotic cells do have DNA ; DNA is not just in nucleus
2
New cards
Eukaryotic cell
a cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
* All organisms except bacteria are eukaryotes
* All organisms except bacteria are eukaryotes
3
New cards
plasma/cell membrane
the boundary between the cell and its environment
4
New cards
Selectively permeable
allows some molecules into the cell while keeping others out
5
New cards
phospholipids
The phospholipids form a bilayer, layer is arranged so tails point toward each other
6
New cards
proteins
some protists help self-identify each other. These proteins act as name tags
7
New cards
transport protiens
serves as a passageway into and out of a cell
* molecules unable to get through the phospholipid bilayer can sometimes enter through transport proteins
* molecules unable to get through the phospholipid bilayer can sometimes enter through transport proteins
8
New cards
Cholesterol
Helps stabilize the plasma membrane by preventing the tails of the phospholipids from sticking together
9
New cards
carbohydrate chains
work together with certain proteins to help cells identify each other
10
New cards
Cytoplasm
the clear, gelatinous fluid between the nucleus and the cell membrane
11
New cards
nucleus
the central membrane-bound organelle that manages cellular function and contains DNA
12
New cards
chromatin
DNA that is not tightly coiled; cell is not dividing
13
New cards
Chromosome
DNA is tightly coiled; cell is dividing
14
New cards
nucleolus
spherical organelle found inside the nucleus where ribosomes are made
15
New cards
Nuclear envelope
the membrane that surrounds the nucleus
16
New cards
nuclear pores
holes in a nuclear envelope through which substances can pass
17
New cards
ribosomes
* both prokaryotic and eukaryotic
* attatch to the rough ER or float freely
* NOT SURROUNDED by a membrane
* attatch to the rough ER or float freely
* NOT SURROUNDED by a membrane
18
New cards
Vacuole
sac like organelle that stores water food and waste
plants contain 1 large and animals have multiple smaller ones
provide plant w support
plants contain 1 large and animals have multiple smaller ones
provide plant w support
19
New cards
Lysosomes
Sac like organelle that contains digestive enzymes (Intracellular)
* can digest excess or worn out organelles and allow parts to be recycled
* can digest excess or worn out organelles and allow parts to be recycled
20
New cards
Chloroplasts
organelle that captures energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy in food
21
New cards
Mitochondria
Organelle that transforms the energy stored in food molecules to ATP, common in muscle cells
* provide energy the cell needs
* inner membrane is highly folded called cristae. Folding allows large surface area to fit
* provide energy the cell needs
* inner membrane is highly folded called cristae. Folding allows large surface area to fit
22
New cards
Allele
segment of DNA on a chromosome
23
New cards
Dominate alleles
an allele that masks another allele
24
New cards
recessive allele
an allele that can be masked by another allele
25
New cards
homozygous
Same
Dominate- DD
ressessive-dd
Dominate- DD
ressessive-dd
26
New cards
Heterozygous
different
Dd
Dd
27
New cards
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism
USE ALLELS TO REPRESENT
USE ALLELS TO REPRESENT
28
New cards
Phenotype
Physical make up of an organism
ex: Black, white, red
ex: Black, white, red
29
New cards
producers
autotrophs
make their own food
example- grass
make their own food
example- grass
30
New cards
Primary consumers
heterotrophs
herbivores
example- squirrel
herbivores
example- squirrel
31
New cards
secondary consumers
carnivores or omnivores
* snake
* snake
32
New cards
Tertiary consumer
carnivores or omnivores
* lion
* lion
33
New cards
10% rule of energy transfer
Only 10% of energy available at one level is passed on to the next
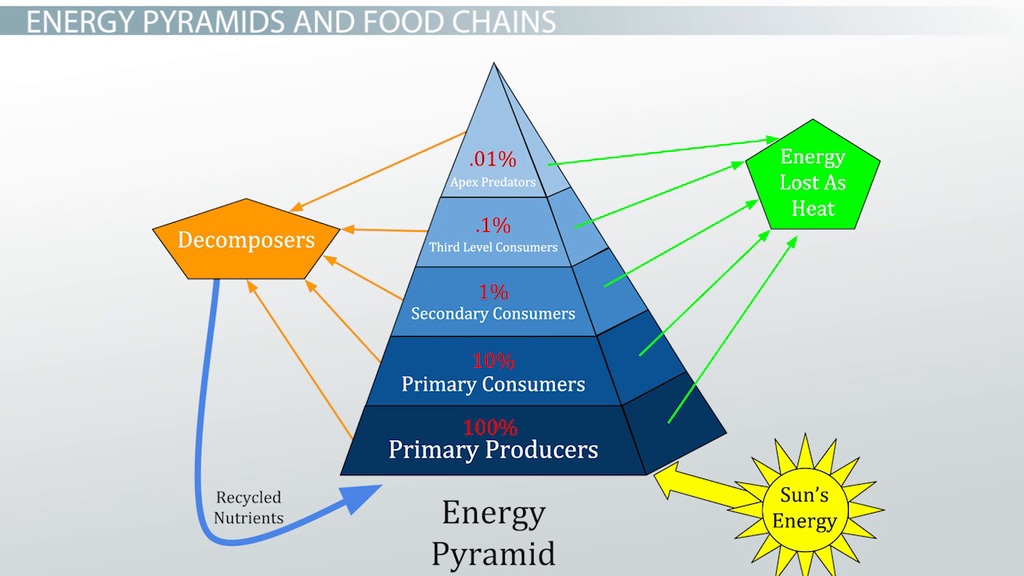
34
New cards
competition
the struggle among organisms for limited natural resources
35
New cards
Competitive exclusion principal
two species cannot occupy the same niche at the same time and place
36
New cards
predation
when one organism feeds on another
37
New cards
predator adaptions
1. Fangs
2. teeth
3. stingers
4. camouflage
38
New cards
predator adaptations
Plants- produce toxins
Active- fight or flight
passive- hiding/ camoflauge
Active- fight or flight
passive- hiding/ camoflauge
39
New cards
Batesian mimicry
harmless but looks dangerous
40
New cards
Mullarian Mimicry
dangerous forms that look like eachother
41
New cards
Are virus’s living or nonliving
Missing key characteristics of living organisms
42
New cards
capsid
protein sheath that surrounds the nucleic acid in a virus
43
New cards
nucleic acid
genetic material
44
New cards
envelope
membrane- like layer that covers the capsid in some virus’s
* gives virus spherical shape
* gives virus spherical shape
45
New cards
glycoprotiens
proteins with attached carbohydrate molecules
* Help virus gain entry into the cell
* Help virus gain entry into the cell
46
New cards
Lytic Cycle
The cycle of viral infection and cell destruction
47
New cards
Lysogenic cycle
Virus becomes part of the host cell and hides
48
New cards
Viroid
an infectious, single strand of RNA
49
New cards
Domain Archea
Commonly found in extreme enviroments such as salt lakes and hot springs
* eukariotic cells
* eukariotic cells
50
New cards
Domain Bacteria
**Prokaryotes** are members of domain bacteria and are found everywhere
ex ecoli and c botulinum
ex ecoli and c botulinum
51
New cards
Bacillus
rod
52
New cards
coccus
sphere
53
New cards
spirillum
spiral
54
New cards
Thermoacidophiles
ocean vents
55
New cards
Methanogen
wet lands and digestive systems
56
New cards
Halophiles
salt/ salt lakes
57
New cards
Conjugation
occurs when two bacteria exchange genetic material by transferring plasmids
* can form antibiotic resistance
* can form antibiotic resistance
58
New cards
Gram +
Stain purple
Thick cell wall
Does not have extra cell membrane
Thick cell wall
Does not have extra cell membrane
59
New cards
Gram -
Stain Pink
Thin Cell wall
No extra cell membrane
Difficult to treat because cell membrane is to thin that they cannot trap the antibiotics
Thin Cell wall
No extra cell membrane
Difficult to treat because cell membrane is to thin that they cannot trap the antibiotics
60
New cards
endospore
some bacteria survive harsh conditions by forming thick walled structures
can survive: Boiling, radiation, acid
ex. anthrax
can survive: Boiling, radiation, acid
ex. anthrax
61
New cards
pathogen steps
1. Must find pathogen in animal w disease
2. Must isolate pathogen from sick animal in lab
3. Must inject pathogen in healthy animal
4. pathogen taken from 2nd animal must show same
62
New cards
Antibiotics
chemicals that inhibit the growth or kill microorgnaims
some cna become resistant
ex. TB and staph
some cna become resistant
ex. TB and staph
63
New cards
Emerging diseases
newly recognized
* Zika
* covid 19 NOT CORONA VIRUS
* Zika
* covid 19 NOT CORONA VIRUS
64
New cards
cilliates
\n unicellular \n cillia \n heterotroph \n animal-like \n hair-like \n reproduce through conjugation
65
New cards
Amoeboids
Unicellular \n Pseudopodia \n heterotroph \n animal like \n engulf food
66
New cards
Flagelletes
unicellular \n move by flagella \n heterotroph \n animal
67
New cards
Euglenioids
Unicellular \n move w flagella \n both auto troph and heterotroph \n plant like
68
New cards
Diatoms
unicellular \n DO NOT MOVE \n autotroph \n plant \n Great in cleaning agents and tooth paste
69
New cards
Slime molds
unicellular \n Move w cytoplasm \n heterotroph \n fungi \n form spores and absorb from soil \n decomposers
70
New cards
sexual reproduction in unicellular
1 haploid cell divides by binary fisson
2 gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote and zygospore
haploid cells break out of zygospore and grow into mature cells
2 gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote and zygospore
haploid cells break out of zygospore and grow into mature cells
71
New cards
Sexual reproduction multicellular
sporeophytes to spores to gametophytes to gametes to zygote
72
New cards
Giardiasis
Flagellete
caused by intestinal parasite
causes diarrhea
contaminated water
caused by intestinal parasite
causes diarrhea
contaminated water
73
New cards
Chagas disease
Flagellete \n kissing bug \n chronic stage can result heart disease
74
New cards
Malaria
Sporozoan \n Spread by mosquito
kills 3 million each yr
kills 3 million each yr
75
New cards
cryptosporidiosis
sporozoan \n causes severe diarreah
contaminated water
contaminated water
76
New cards
oxygen production in protists
* plantlike protists along w cyanobacteria produce at least 1/2 of earth's oxygen and consume carbon dioxide
* many protists are important decomposers contribute to recycling of carbon and nitrogen
* many protists are important decomposers contribute to recycling of carbon and nitrogen
77
New cards
Agar
produced by algae
78
New cards
diatamasous earth
made by diatoms, fertilizer
79
New cards
Algal blooms
rapid increase in the population of algae in an aquatic ecosystem
80
New cards
symbiosis
protists supply coral w nutrients, coral provide a stable environment, nitrogen and minerals
81
New cards
Animal Like protists
amoeboids \n ciliates \n Flagellates \n sporozoans
82
New cards
saprobe
feed on dead organisms
example- Cytrid
example- Cytrid
83
New cards
parasite
Fungi that absorb nutrients from living hosts
84
New cards
How do Fungi gain their nutrients
* get nutrients through enzymes
* digest outside of their bodies
* suck the nutrients back up and absorb it across cell walls
* digest outside of their bodies
* suck the nutrients back up and absorb it across cell walls
85
New cards
Hypahe
Thread like strands throughout the fungus body
86
New cards
chitin
tough carbohydrate that is also found in covering of insects
87
New cards
ascus
sac like reproductive structure that produces spores
88
New cards
basidia
club shaped cells under the basidiocarp
89
New cards
Ascomycetes
* name for sac-like ascus that produces spores
* ascocarp forms when 2 hyphae from different mating types meet (Sexual reproduction)
* Each ascus produces 8 spores
* conidiophores in the group form conidia during asexual reproduction
* Have dikaryotic cells that form ascocarp
* ASEXUAL is more common than sexual
* ascocarp forms when 2 hyphae from different mating types meet (Sexual reproduction)
* Each ascus produces 8 spores
* conidiophores in the group form conidia during asexual reproduction
* Have dikaryotic cells that form ascocarp
* ASEXUAL is more common than sexual
90
New cards
Club Fungi Aka BAsidiomycetes
* Asexual reproduction is rare
* basidiocarp forms when 2 hyphae from different mating tupes meet
* name for cells called basidia that produce spores
* Puffballs
* shiitake mushrooms
* bracket fungi
* fairy rings
* toxic mushrooms (death cap)
* basidiocarp forms when 2 hyphae from different mating tupes meet
* name for cells called basidia that produce spores
* Puffballs
* shiitake mushrooms
* bracket fungi
* fairy rings
* toxic mushrooms (death cap)
91
New cards
zygote fungi
* name for sexual reproductive structures that produce zygotes in tough capsule
* reproduction occur when hyphae from two mating types come together
* not male or female, + and -
* example- bread mold
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IS MOST COMMON
* reproduction occur when hyphae from two mating types come together
* not male or female, + and -
* example- bread mold
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IS MOST COMMON
92
New cards
economic importance of fungi
Used for foods, medicines, research alternative foods and pest control
93
New cards
yeast
fungi that exists in primarlily unicellular state
* used in baking, brewing etc
* used in baking, brewing etc
94
New cards
Lichen
an association between a fungus and a photosynthetic partner, such as a cyanobacteria
95
New cards
Mycorrhizae
the hyphae transfer phosphorus and other minerals from the soil to roots
plants supplies carbohydrates to the fungus
plants supplies carbohydrates to the fungus
96
New cards
symptoms of fungal toxins
Diarreah, vomiting, liver damage and death
97
New cards
Alfatoxins
a type of fungus that contaminates corn, peanuts, and cottonseed produces alfatoxins that causes liver cancer
98
New cards
ergot
fungus that infects grain- led to Salem witch trials
\
**Fungus that causes severe reactions when ingested, such as hallucinations, muscle spasms, and confusion**
\
**Fungus that causes severe reactions when ingested, such as hallucinations, muscle spasms, and confusion**
99
New cards
Septa
partial cell walls
100
New cards
caps
allow cytoplasm and nutrients through