Youth Culture in a Digital World - begrippen hoorcollege
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
culture
geographical: culture of a country
social: group you want to belong to
temporal: age and generation
youth culture
shared beliefs, behaviors, practices, and values of young people within a particular society or subculture.
the ways in which young individuals express themselves, interact with one another, and distinguish themselves from older generations.
social presence theory
sense of being toghether (lower in digital media)
social information theory
how people process and react to social information
channel expansion theory
users with experience will strive to develop necessary skills
uses and gratification theory
What purposes or functions does media offer for active users/receivers?
Zij kiezen media niet zomaar, maar om specifieke behoeften te bevredigen (gratifications).
4 main reasons to use media BEFORE
surveillence of the environment
affective need
cultural transmission
entertainment
→ now: self-promotion, maintaining existing relationships, escapism, expressing opinions
developmental tasks approach
Volgens deze benadering doorloopt ieder mens een hiërarchische lijst van biologische en sociale uitdagingen die op een specifieke leeftijd succesvol afgerond moeten worden, wat in de mediawetenschap betekent dat de effecten van media sterk afhangen van de ontwikkelingsfase (leeftijd) waarin de gebruiker zich bevindt.
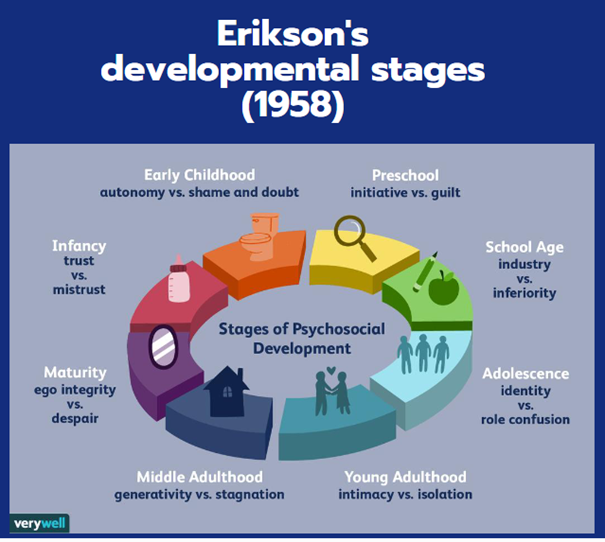
risk and resilience approach
Deze benadering richt zich op de verschillen in levenservaringen tussen mensen en verklaart waarom bepaalde risicofactoren bij de ene persoon leiden tot negatieve media-effecten, terwijl anderen juist veerkracht tonen en beschermd worden door positieve invloeden in hun omgeving of karakter.
key developmental tasks of adolescence
learning to build intimate and committed friendships/relationships
adjustment to pubertal changes
transition to secondary schooling
developing strong and coherent personal identity
examples for children
<12 parents
>12 influencers
turnaround model
a group who starts of with a high media use can decline overtime because of new protective factors such as hanging with peers)
Bronnfenbrenner ecological system
micro: how do parents monitor and regulate their children’s media use
exo: is school offering classes online safety and social media policies (smartphone bann)
macro: what do we believe and valiue regarding social media (dangerous vs entertainment)
asynchrony
communicating at your convenience, breaking time and space constraints (whatsapp, being able to respond when you want, no pressure)
Payne fund studies
studies that investigated the effects of movies on the behavior of children and adolescents (se, romance, crime)
legacy of fear
anything in media can have negative impact and we shouldn’t expose our children to it
Magic bullet / Hypodermic Needle Perspective
Deze theorie stelt dat media-boodschappen als een "magische kogel" of een "onderhuidse injectienaald" rechtstreeks en onmiddellijk in een passief publiek worden geschoten, waarbij iedereen op exact dezelfde manier wordt beïnvloed zonder erover na te denken.
two step flow of communication
media komt via 2 stappen bij ons binnen, het gaat eerst langs bijv journalisten
evergreen theories
theories that resisted the test of time, those that are still relavant
cultivation theory
This theory suggests that long-term exposure to media, especially television, gradually shapes a person’s perception of reality to match the "media world," such as believing the real world is more dangerous than it actually is (Mean World Syndrome).
o 1st order: how often do you think something happens?
o 2nd order: how do you perceive real life?
o 3rd order: what happens in your behaviour?
agenda-setting theory
Agenda-setting role of the media = ability to influence the salience (opvallendheid) of topics on the public agenda
- First level: object → Op dit eerste niveau bepalen de media welke onderwerpen belangrijk zijn
- Second level: attributes → Op het tweede niveau beïnvloeden de media hoe we over een onderwerp denken door specifieke kenmerken (attributes) te benadrukken. Dit lijkt op framing.
- Third level: network → Het derde niveau gaat over de combinaties van onderwerpen. De media kunnen verschillende onderwerpen of kenmerken aan elkaar koppelen in de hoofden van het publiek.
framing theory
This theory focuses on how media organizes and presents information within a specific context or "frame," thereby influencing how the audience interprets and evaluates a particular social issue or event.
spiral of silence
This theory states that individuals are less likely to express their opinions if they perceive themselves to be in the minority, out of a fear of social isolation, which causes the dominant viewpoint to seem even more prevalent than it might be
social comparison theory
This theory explains that individuals have an innate drive to evaluate their own lives, abilities, and appearance by comparing themselves to others, often leading to "upward" or "downward" comparisons that affect self-esteem.
social cognitive/learning theory (bandura)
This theory posits that people learn new behaviors, values, and attitudes by observing and imitating the actions of "models" in their environment or in the media, especially when those behaviors are seen to be rewarded.
mainstreaming
blurring, bending, and blending information for viewers → goal is to develop a common outlook on the world through constant exposure to the same images
resonance
influence of tv is different for subgroups based on interests and experiences
Kritiek op boek ‘The Anxious Generation
Cherry picking
Panic over smartphones only makes things worse
Niet zeker of het een juiste causaal verband is of juist andersom
no attention for individual differences
possible problems in research
maybe non-linear
maybe only cross-sectional designs
maybe no difference between active/passive media use
maybe there is a confounder
maybe the relationship differs largely between individuals
three ways of parental influence
parental modelling (bandura)
behaviour-specific parenting
general parenting
parental mediation theory
active mediation = talking with your child about the content they saw on television or other media
restrictive mediation = setting rules and regulations about children's television viewing and other access to online devices
reactive rules
regels die in het moment zelf bedacht worden (telefoon afpakken)
How often do your parents tell you to put away your laptop/tablet/smartphone?
restrictive rules
voorafgestelde regels
are you allowed to bring your smartphone to your bedroom when your going to sleep?
co-viewing
watching media together with parent
self-determination theory
stelt dat mensen een aangeboren groeimindset hebben en optimaal functioneren wanneer aan drie psychologische basisbehoeften — autonomie, competentie en verbondenheid — wordt voldaan, wat leidt tot intrinsieke motivatie en welzijn
parental phubbing
picking up phone in presence of child → Increases risk for problematic social media use later
still face experiment
playing with baby but when hearing cellphone buzz and ignoring baby, looking away the child responds with crying and when trying to reassure the baby, it takes a long time, it eventually creates feelings of rejection in parent-child relationships
rotten apple theory
one bad kid in the class will influence the rest
social bond theory
when having strong ties in society, you have less reasons to be in crime, when these bonds break you are more eligible to crime
o Social media will weaken these ties
o Bonds entail: friends, parents, school
parasocial bonds
not reciprocal (wederzijds) like influencers
relative deprivation
the feeling of discontent or injustice that arises when individuals compare their own situation to others and perceive that they are unfairly lacking the resources, status, or successes that they believe they deserve.
strain theory
social structures may pressure citizens to commit crimes when they experience a "strain" or gap between socially encouraged goals—like financial wealth—and the legitimate means available to achieve them.
connection gaming to Skinner
connecite game verslaving met Skinner en Pavlov
Skinner: The uncertainty of loot box contents makes the behavior harder to stop than a predictable reward.
Pavlov: The lights and sounds of the "opening ceremony" trigger a physical craving before you even see the prize.
types of rewards
- Random rewards (finding a valuable sword)
- Contingencies rewards (log-in bonus)
- Social rewards (teamplay/building guilds/clan)
Meta-achievements (leaderboard scores)
algorithmes als ‘echo chamber’
het algoritme is de architect die de kamer bouwt, en de echo chamber is het resultaat van wie er in die kamer worden toegelaten
Dit is het sociale/psychologische effect. Het is de overtuiging dat jouw wereldbeeld het enige juiste is, omdat je alleen gelijkgestemden ontmoet.
algoritmes als filter bubbels
Dit is het technische proces. Het algoritme filtert de informatie onzichtbaar voor je (het is de "bubbel" waar je in zit).
algorithmic imagination
‘the way in which people imagine, perceive and experience algorithms and what these imaginations make possible
critical evaluation
Critical evaluation of the influence algorithms over us as individuals, as well as what impact they have on our society
algorithmic power
How users actively influence the algorithmic workings of platforms to engage in conscious, instrumental interactions with algorithms, or in other words, how they ‘game the system
foreclosed identity
Je neemt de waarden en keuzes van je ouders of andere autoriteiten simpelweg over zonder zelf alternatieven te onderzoeken.
identity diffusion
Je hebt nog geen idee wie je bent en doet ook geen moeite om dat te ontdekken, waardoor je makkelijk met de massa meeloopt
moratorium
Je bent volop aan het experimenteren en verschillende paden aan het verkennen, maar je hebt nog geen definitieve keuzes durven maken.
identity achievement
Je hebt na een periode van actief zoeken en uitproberen eindelijk keuzes gemaakt die echt bij je passen, wat zorgt voor een sterk en stabiel zelfbeeld.
jingle-jangle problem
verschillende termen worden gebruikt voor dezelfde processen en vice versa. Bijvoorbeeld, de term "sociale media" kan verwijzen naar Facebook, Instagram of LinkedIn, terwijl "well-being" kan verwijzen naar depressie of levensvrede.
Mean World Syndrome
mensen die veel naar geweld op televisie of in het nieuws kijken, de wereld als gevaarlijker, gemener en vijandiger gaan zien dan deze statistisch gezien werkelijk is.
negativity bias
Mensen (en de media) hebben de neiging om zwaarder te tillen aan negatieve verhalen (zoals cyberpesten) dan aan de positieve kanten van digitale verbinding, wat het beeld van sociale media vertekent.
Situational Action Theory
stelt dat moreel grensoverschrijdend gedrag ontstaat door de directe interactie tussen iemands persoonlijke morele neiging (propensity) en de specifieke blootstelling aan een omgeving (exposure).
bonding social capital
het versterken van diepe banden binnen je eigen vertrouwde kring (zoals familie)
bridging social capital
het leggen van nieuwe, lossere contacten buiten je eigen bubbel (zoals kennissen of netwerken).
agency vs structure
debat over de mate waarin wij als mensen vrij zijn in onze keuzes, of dat ons gedrag wordt bepaald door de wereld om ons heen.
digital divide
digitale ongelijkheid: niet in toegang tot technologie, maar in de mate waarin je begrijpt hoe de onzichtbare krachten (algoritmes) je wereldbeeld vormen.
conversion
want change
reinforcement
on your existing opinions
differential association theory
Criminal behavior is learned through social interaction and association with others who hold favourable attitudes toward crime