Biomechanics of the Upper Extremity
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Shoulder Complex
permits upper extremity movement and weight bearing
Very mobile, relies on muscle for stability
Sternoclavicular Joint
True joint
saddle-shaped, synovial joint
connects the clavicle to the manubrium
only connection of the UE to the axial skeleton
where most movement happens
Full arm abduction and elevation
closed pack position of the sternoclavicular joint
1st Principle
Elevation and Depression of the SC joint
2nd Principle
Protraction and Retraction of the SC joint
Acromioclavicular Joint
True joint
Connects the clavicle and scapula
Serves as the fine-tuning of the SC joint
Transmission of forces from UE to axial skeleton
Plane Synovial Joint
Anterior-posterior tilting of AC
happens when the clavicle is depressed/elevated
happens with the same action of the SC
Internal-External rotation of AC
occurs when the clavicle is protracted/retracted
Upward-downward rotation of AC
occurs during abduction/flexion or adduction/extension
the clavicle also moves posteriorly and anteriorly rotates
Scapulothoracic Joint
False joint
Provides shoulder region stability
aligns the fossa and glenohumeral head
Maintains the length tensions relationship of the deltoid muscle
Increases the ROM of the shoulder
Permits elevation of the body
Glenohumeral Joint
True joint
Connects the scapula and humerus
Most freely moving joint, little bony stability
Ball-and-socket joint
External rotation of humerus
happens with full shoulder abduction
Internal rotation of humerus
happens with full flexion
Scaption
shoulder abduction that happens in the 30°-40°
Most functional shoulder abduction motion occur in the scapular plane
Full abduction + Full External rotation
Closed-pack position of the GH Joint
20-30° horizontal adduction + 55° flexion
Open-packed position of the GH Joint
Bursa, Supraspinatus, Biceps tendon
What are the contents of the subacromial space?
Scapulohumeral Rhythm
GH motion + scapular rotation, which permits higher shoulder flexion/abduction with elevation reaching 150-180°
2(GH):1(S) variable
First 30°, GH
Deltoid
the muscle that pulls upward in the Deltoid-Rotator Cuff Mechanism
Supraspinatus
muscle that pulls to keep the humerus in the glenoid fossa, in the Deltoid-Rotator Cuff Mechanism
Infraspinatus, Teres Minor, Subscapularis
muscle that pulls downward for a good roll and slide for abduction in the Deltoid-Rotator Cuff Mechanism
Proximal Radio-Ulnar Joint
motion is pronation/supination
part of the forearm complex
Elbow Joint
humeroulnar + humeroradial joint
uniaxial hinge joint (flexion and extension)
145° (120-160°)
ROM of elbow in flexion
30-130°
functional range of elbow flexion
Radioulnar Joint
proximal + distal radioulnar joints
one degree of freedom (pronation/supination)
90°
ROM of forearm supination
Firm end-feel
80-90°
ROM of forearm pronation
Hard/Firm end-feel
Ulna
the rigid base for forearma and wrist function
stays stationary
Ulnar deviation and supination
What is the coupling motion when the wrist flexes?
Radial deviation
What is the coupling motion when the wrist extends?
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris and Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Flexor Carpi Radialis and Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Antagonist muscle for Flexion/Extension
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris and Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
Synergists for ulnar deviation
Flexor Carpi Radialis and Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Synergists for radial deviation
5th
most mobile digit
3rd
least mobile digit
Tenodesis
wrist extension = finger flexion
wrist flexion = finger extension
provides grasping mechanism
Wrist flexion
has twice the work capacity than its counterpart movement
30-40°
there is 3x more grip in this ROM of the wrist extension, compared to 40° flexion
Radial Deviation
has slightly higher work capacity than its counterpart movement
20° extension, 10° ulnar deviation
Wrist at the functional hand position
45° MCP flexion, 30-45° PIP flexion, 10-20° DIP flexion
Hand at the functional hand position
Intrinsic-plus position
MCP flexion
IP extension
interossei and lumbricals at shortest
caused by muscle contracture (rheumatoid arthritis)
Intrinsic-minus position
claw hand
IP flexion
MCP extension
Paralysis in the lumbricals and interossei
Power Grips
uses entire hand to hold
Full-hand Prehension
partially flexed fingers and palm.
Thumb adducted or in position which provides counterpressure
Isometric contraction
Hook Grip
carry or support an object
does not use thumb
FDS and FDP
FDP for more distal load
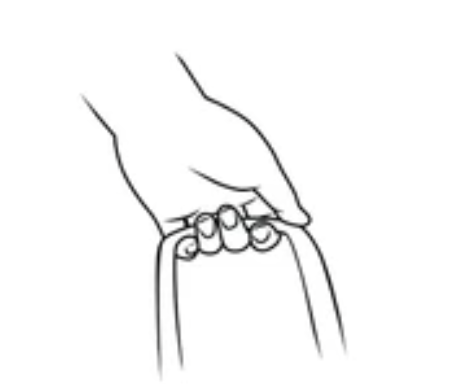
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
main muscle in hook grip
Cylindrical Grip
for cylindrical objects
fingers and palm flexed to grasp object
fingers are adjacent and parallel
thumb is usually flexed and adducted
Wrist in neutral or sometimes ulnar deviation
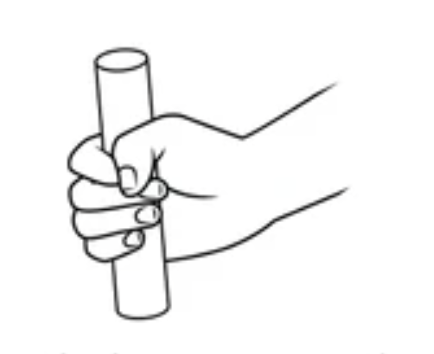
FDP, FDS, Interossei
muscle for cylindrical grip
Spherical Grasp
for round objects
greater spread of fingers
MCP abducted, partially flexed
Thumb in opposition and flexed at MCP or IP
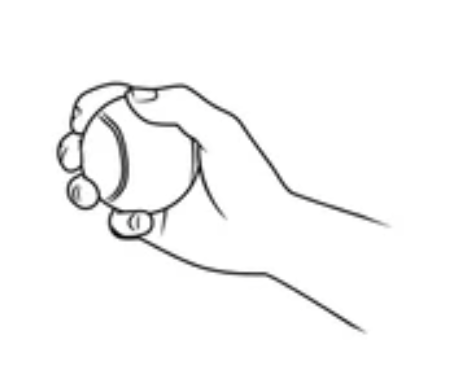
FDS, FDP, thenar muscles, interossei
muscles for spherical grip
extensor digitorum
during spherical grasp
contracts against flexor for controlled release of object
Fist Grip
Distal palmar prehension pattern
thumb is closer to the digits
closing a fist over a comparatively narrow object
fingers parallel to one another
thumb over and adducted against the object/in opposition to fingers
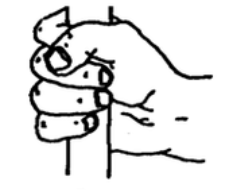
FDP, FDS
muscles for fist grip
Lateral Prehension
extensor muscle predominates
not powerful
not used in in-hand manipulation
object held in between extended fingers
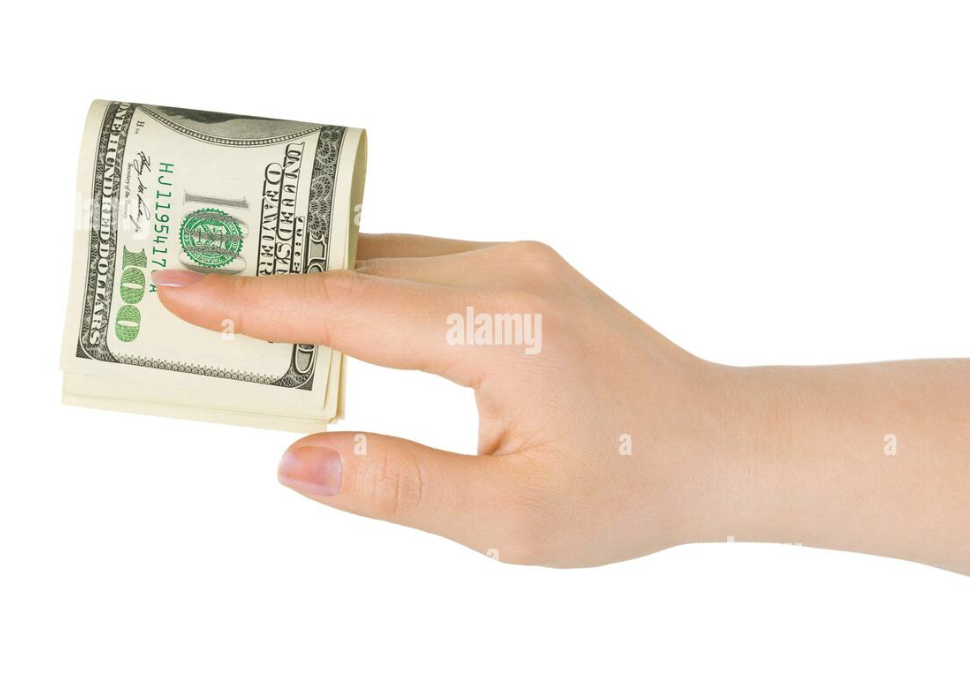

Precision Grips
accuracy and fine touch
Finger-thumb precision
on the flexor surface of the fingers
thumb adducted
Lateral Pinch Grip
key grip
contact between thumb pad and radial index finger
least precise
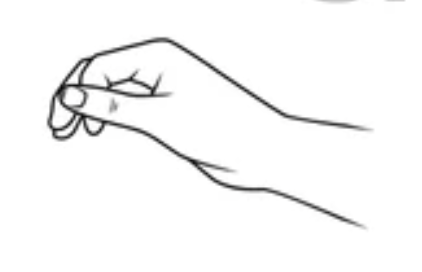
FDP, FDS, 1st dorsal interossei, FPL, FPB, AdP
muscles for lateral pinch grip
Three-prong Chuck
pad-to-pad/palmar prehension
thumb opposes distal pads of digits
joint of thumb and fingers are relatively extended
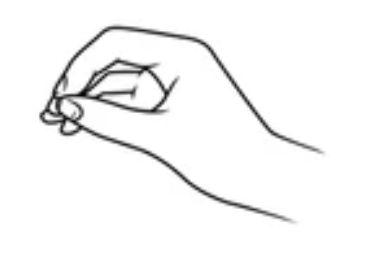
FDS, FDP, interossei, thenar muscles
muscles for three-prong chuck
Tip Prehension Grip
tip-to-tip grip
most precise but most easily disturbed
small objects
thumb nearly full flexion and opposing finger MCP joint to UD
allows fingertips to meet thumb facing radial
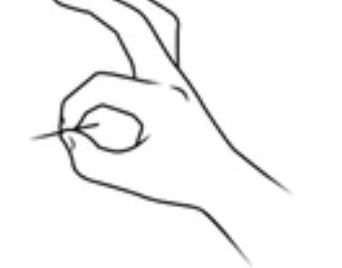
FDP, FPL, interossei
muscle for tip prehension grip