Positive Psychology: Optimism, Hope, Wisdom, and Courage
Optimism
^^One’s expectancy that good things rather than bad will happen^^
When a goals is of sufficient value, the individual would produce an expectancy about attaining that goal
Stable trait independent form self-efficacy
Attribution: the process by which individuals explain the causes of behavior and events
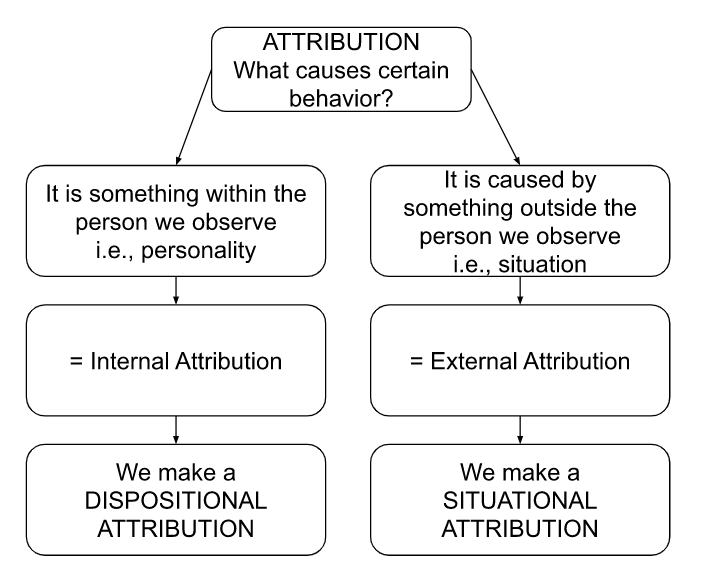
The optimist uses adaptive causal attributions to explain negative experiences/events
Makes ^^external, variable, and specific attributions^^ for failure-like events rather than internal, stable, and global attributes
Childhood Antecedents of Optimism
- There is a ^^genetic basis^^ of optimism
- Optimism can stem from ^^childhood experiences^^ that foster trust and secure attachments to parental figures
Measures of Optimism
- Life Optimism Test (LOT)
- Index of Optimism
- self-mastery, self-esteem
- can predict outcomes related to coping and adjustment
What can Optimism Predict?
- staring college
- performing in work situations
- caring for Alzheimer’s patients
- coping with cancer
- coping in general
Hope
- defined as a ^^goal-directed thinking^^ in which the person utilizes pathways of thinking (the capacity to find ways to desired goals) and agency thinking (motivations to use these ways)
- If there’s a will, there’s a way.
Childhood Antecedents of Hope
- Hope has no hereditary contribution but rather a learned cognitive set about ^^goal-directed thinking^^
- inherent part of parenting
- components of hopeful that are in place by the age of 2
- strong attachment to caregivers is crucial for imparting hope
Can Hope be Measured?
- Hope Scale
- Children’s Hope Scale
- State Hope Scale
Hope can predict…
- academics, sports, physical health, adjustment, psychotherapy
Collective Hope
- level of goal-directed thinking of a large group of people
- it is operative when several people join together to tackle a goal that would be impossible for any one person
Wisdom and Courage: 2 Universal Virtues
Wisdom
- involves an integration of k^^nowledge, experience, and deep understanding^^ that incorporates tolerance for the uncertainties of life as well as its ups and downs
Baltes Model of Wisdom
- Wisdom as Expert Knowledge
- ^^factual knowledge^^ in fundamental pragmatics of life
- knowledge in ^^contexts^^ of life and societal change
- knowledge which considers ^^uncertainties^^ of life
- ^^procedural knowledge^^ in fundamental pragmatics of life
- knowledge which considers ^^relativism^^ values and goals
- Definition of Wisdom: good judgment and advice in important but uncertain areas of life
Wisdom
- found in persons seeking contemplative life (Sophia)
- practical nature (Phronesis)
- scientific understanding (Episteme)
- process used to ^^balance personal interests^^ with ^^environmental context^^ to achieve a common good
- this involves using ^^tacit knowledge and personal values^^ to form a judgment of or resolution for competing interests
Developing Wisdom
- resolving conflicts leads to enhanced discernment and judgment
- wisdom builds on knowledge, cognitive skill and personality characteristics
- exposure to wise role-models
- fluid intelligence, creativity, openness to experience, psychological mindedness, and general life-experiences orchestrate to produce wisdom
Characteristics of Wise People
- Sage: the carrier of wisdom
- Age: timeless and universal knowledge of wisdom
- includes the understanding of affect in problem-solving
- professional specialization does play a role in the manifestation of wisdom
Measurement of Wisdom
- Values in Action Classification of Strengths
- Wisdom Development Scale
- self-knowledge
- altruism
- judgment
- life knowledge/ life skills
- emotional management
Courage
- defined as ^^behavioral approach despite the experience of fear^^, in an effort to better understand its relationship with anxiety, fear, and behavior
- the planning and execution of great and expansive projects by putting forth ample and splendid effort of the mind
- Confidence, with these projects, the mind self-confidently collects itself with sure hope
- Patience, the voluntary and lengthy insurance of arduous and difficult things, which are honorable and useful
- Perseverance, ongoing persistence in a well-considered plan
Types of Courage
- Moral Courage: behavioral expression of authenticity in the face of discomfort, disapproval or rejection
- Physical Courage: maintenance of societal good by expression of physical behavior
- Vital Courage: perseverance through a disease or disability even when outcome is ambiguous
- Physiological Courage: strength in facing destructive habits
- Civil Courage: brave behaviors accompanied by anger and indignation that intends to reinforce societal and ethical norms without considering own social cost
Measures of Courage
- Woodard-Pury Courage Scale
- one’s job or self-interest
- one’s beliefs
- individual social and/or moral situations
- situations relevant to family
- Values in Action Inventory of Strengths