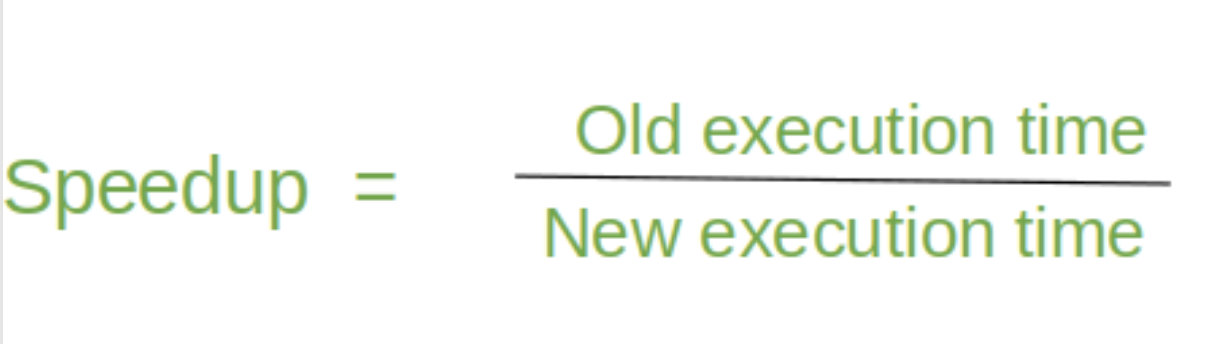code.org csp vocab
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Binary
A way of representing information using only two options.
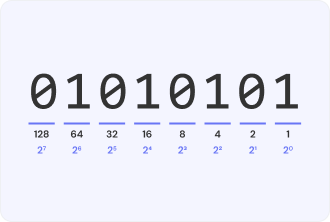
Decimal
A way of representing information using ten options.
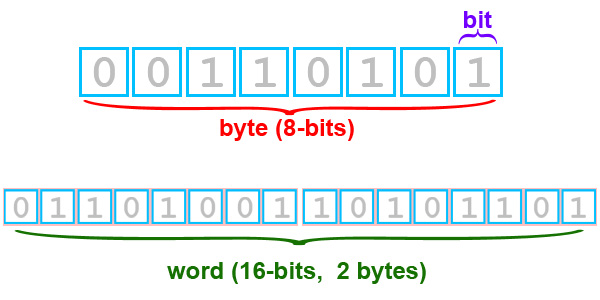
Bit
A contraction of Binary Digit; the single unit of information in a computer, typically represented as a 0 or 1

Byte
8 bits
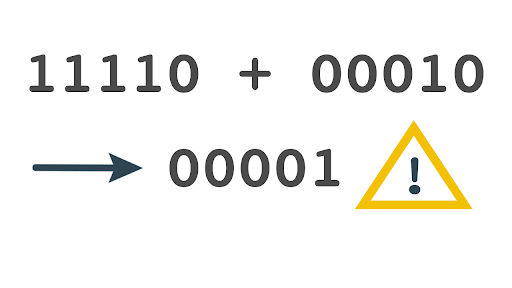
Overflow Error
Error from attempting to represent a number that is too large.
Round-off Error
Error from attempting to represent a number that is too precise. The value is rounded. EX: 1/3 = 0.333333 (repeating)
Analog Data
Data with values that change continuously, or smoothly, over time.
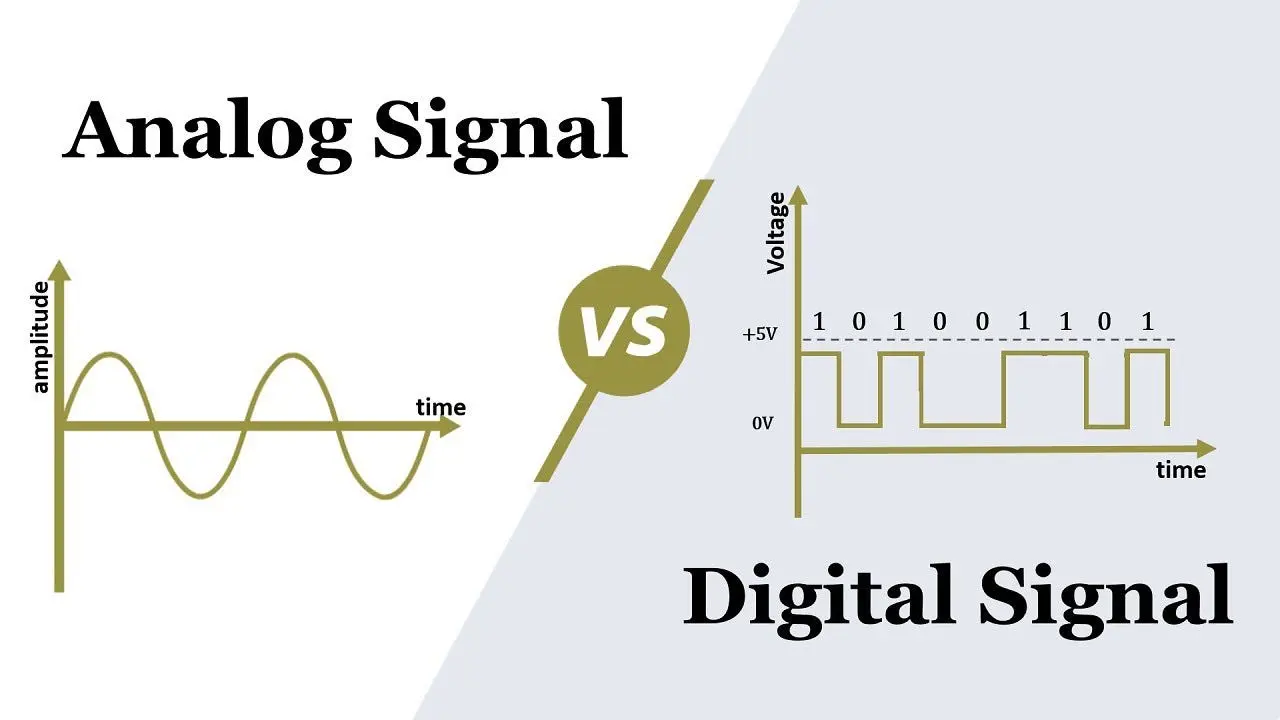
Digital Data
Data that changes discretely through a finite set of possible values
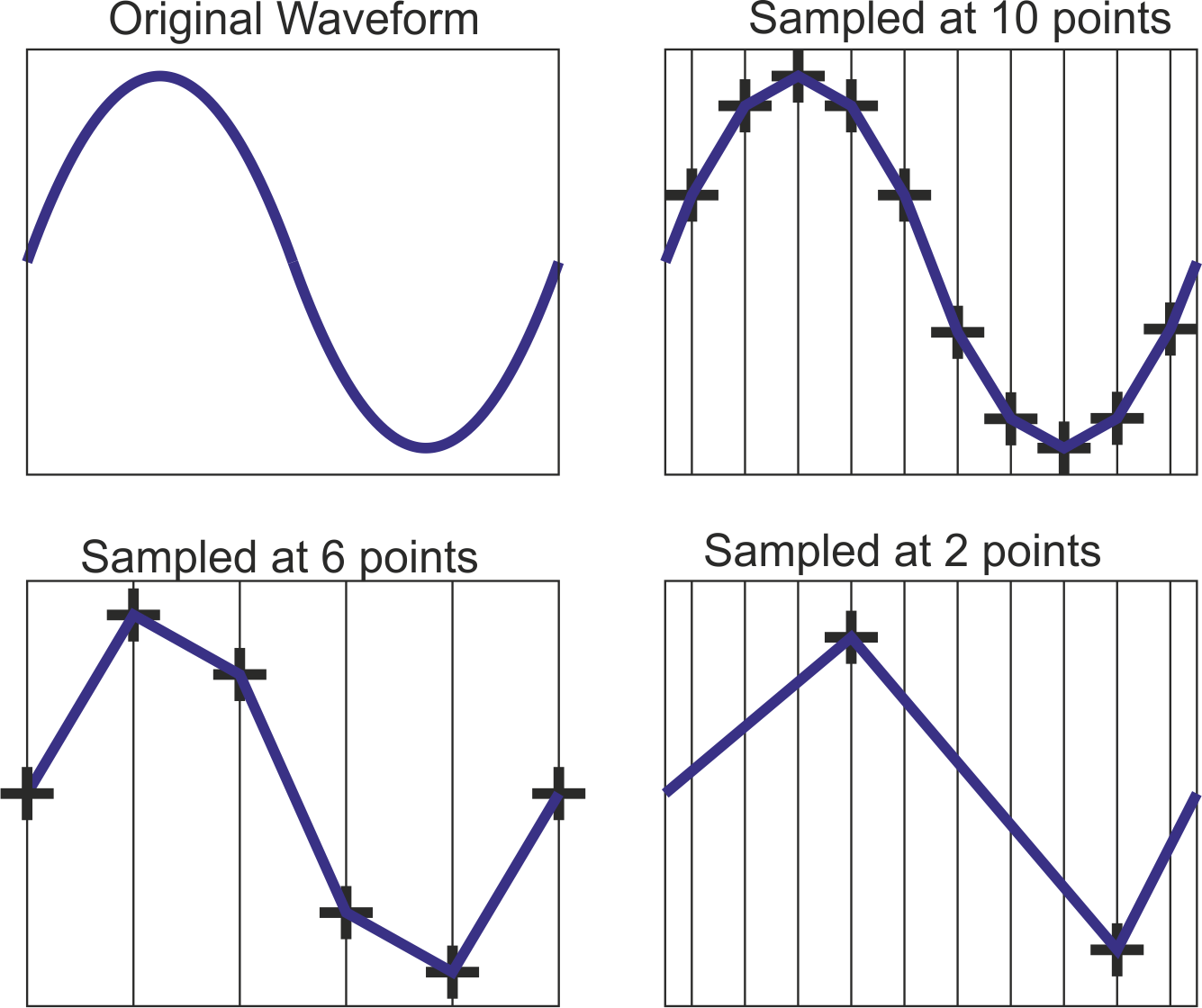
Sampling
A process for creating a digital representation of analog data by measuring the analog data at regular intervals called samples.
Lossless Compression
A process for reducing the number of bits needed to represent something without losing any information. This process is reversible.
Lossy Compression
A process for reducing the number of bits needed to represent something in which some information is lost or thrown away. This process is not reversible.
Intellectual Property
A work or invention that is the result of creativity, such as a piece of writing or a design, to which one has rights and for which one may apply for a patent, copyright, trademark, etc.

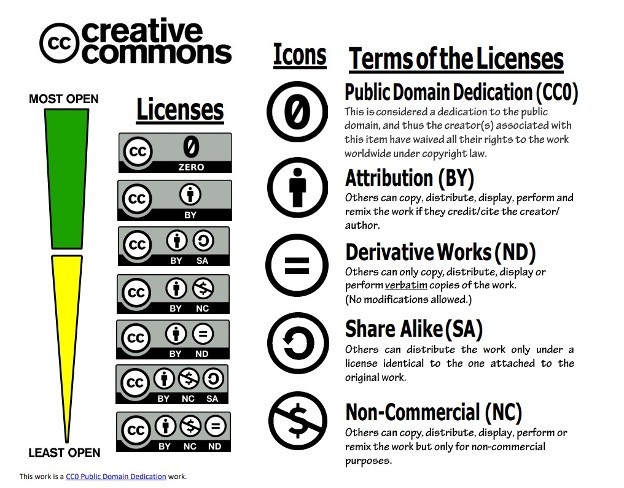
Creative Commons
A collection of public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted work, used when an author wants to give people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that they have created.
Computing Device
a machine that can run a program, including computers, tablets, servers, routers, and smart sensors

Computing System
a group of computing devices and programs working together for a common purpose

Computing Network
a group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending or receiving data.
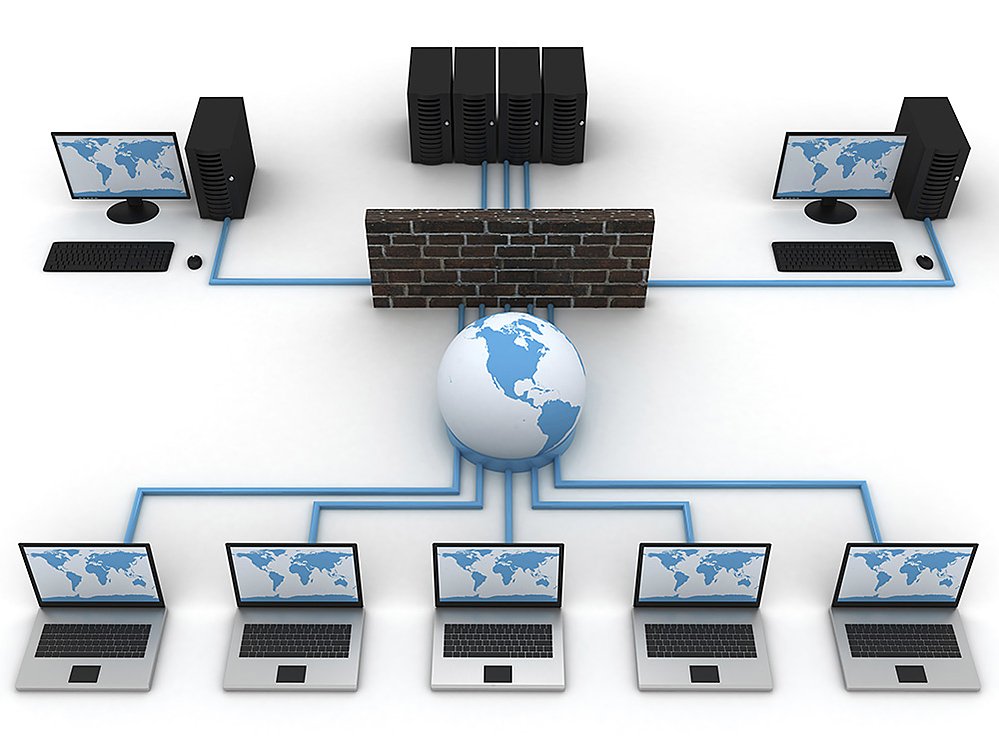
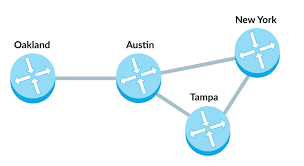
Path
the series of connections between computing devices on a network starting with a sender and ending with a receiver.
Bandwidth
the maximum amount of data that can be sent in a fixed amount of time, usually measured in bits per second.
Protocol
An agreed-upon set of rules that specify the behavior of some system

IP Address
The unique number assigned to each device on the Internet.
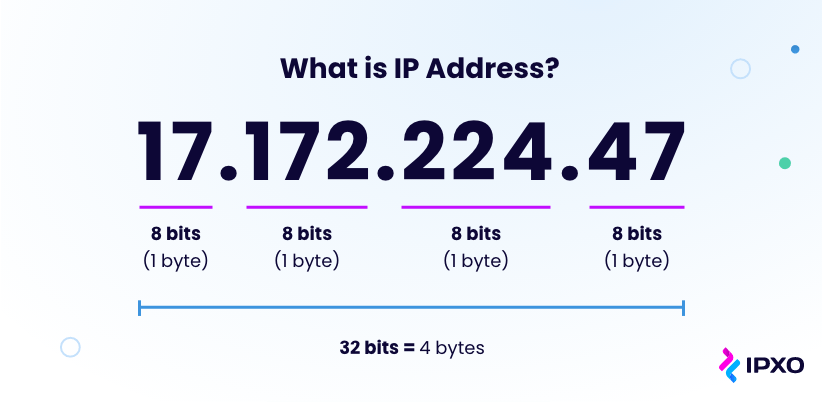
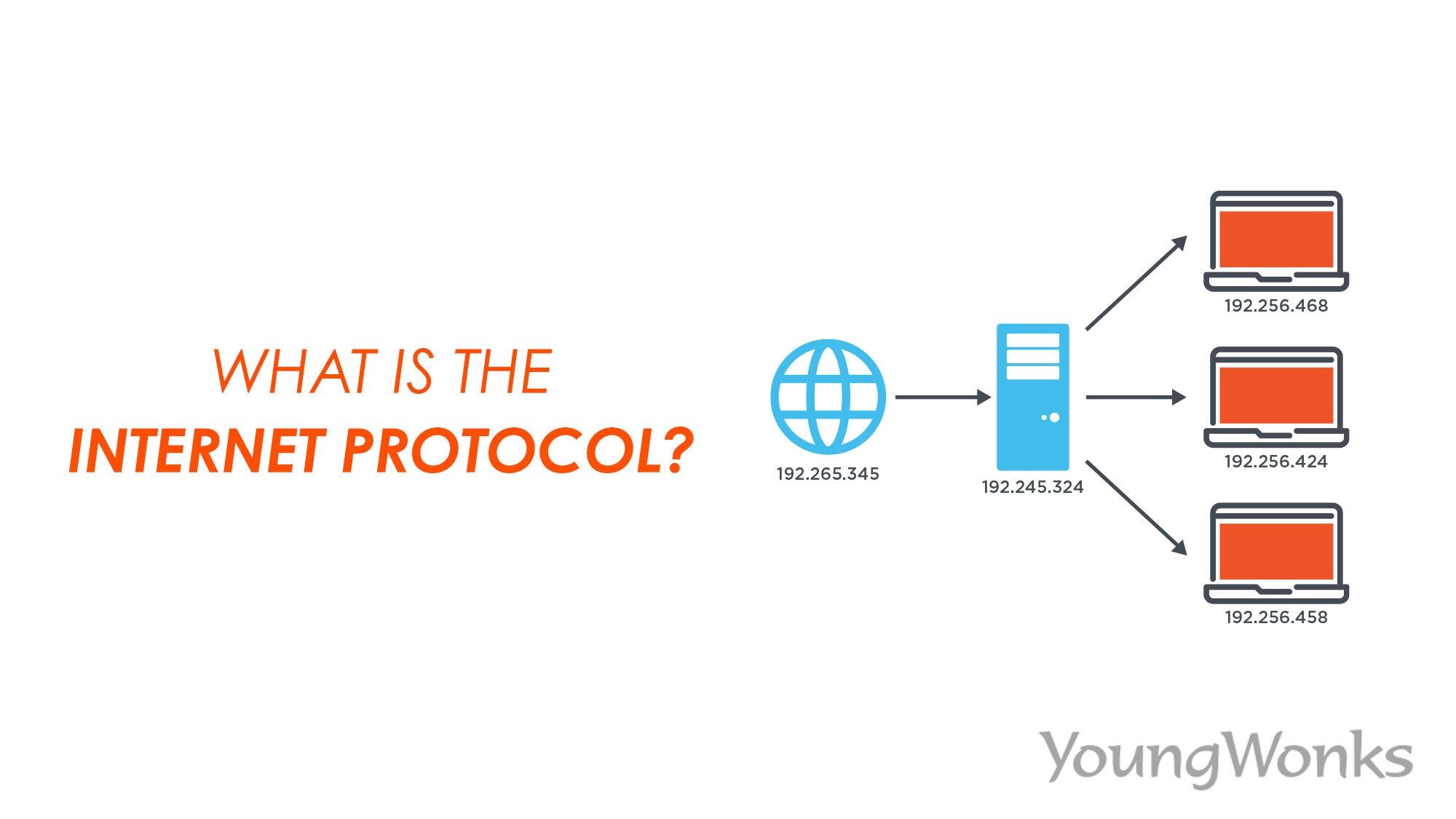
Internet Protocol (IP)
a protocol for sending data across the Internet that assigns unique numbers (IP addresses) to each connected device
Router
A type of computer that forwards data across a network
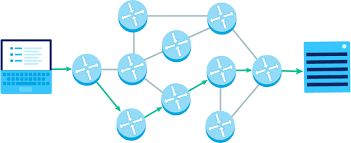
Packet
A chunk of data sent over a network. Larger messages are divided into packets that may arrive at the destination in order, out-of-order, or not at all.

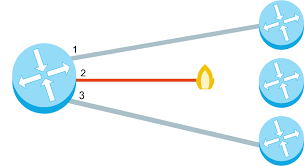
Redundancy
the inclusion of extra components so that a system can continue to work even if individual components fail. EX: having more than one path between any two connected devices in a network.
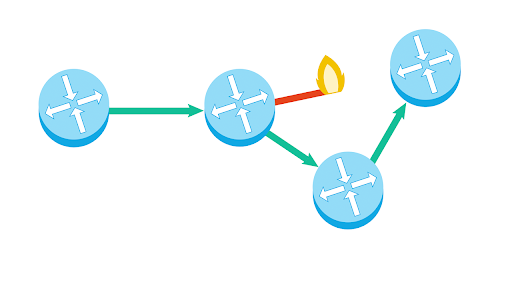
Fault Tolerant
Can continue to function even in the event of individual component failures.
HTTP
HyperText Transfer Protocol - the protocol used for transmitting web pages over the Internet
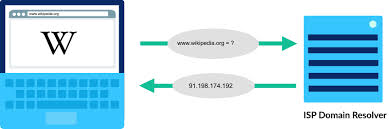
Domain Name System (DNS)
the system responsible for translating domain names like example.com into IP addresses
Internet
a computer network consisting of interconnected networks that use standardized, open (nonproprietary) communication protocols.

World Wide Web
a system of linked pages, programs, and files.

Digital Divide
differing access to computing devices and the Internet, based on socioeconomic, geographic, or demographic characteristics
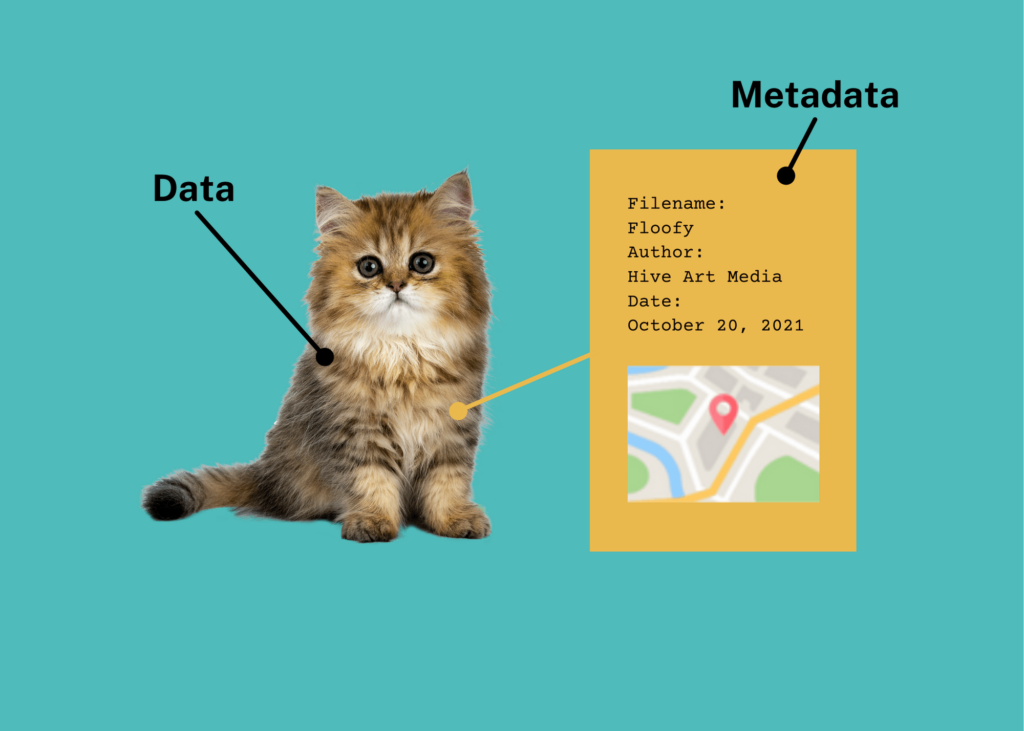
Metadata
data about data (ex: metadata of a photo could be its file size or the time it was taken)
Citizen Science
scientific research conducted in whole or part by distributed individuals, many of whom may not be scientists, who contribute relevant data to research using their own computing devices.

Cleaning Data
a process that makes the data uniform without changing its meaning

Correlation
a relationship between two pieces of data, typically referring to the amount that one varies in relation to the other.
Crowdsourcing
the practice of obtaining input or information from a large number of people via the Internet.

Information
the collection of facts and patterns extracted from data
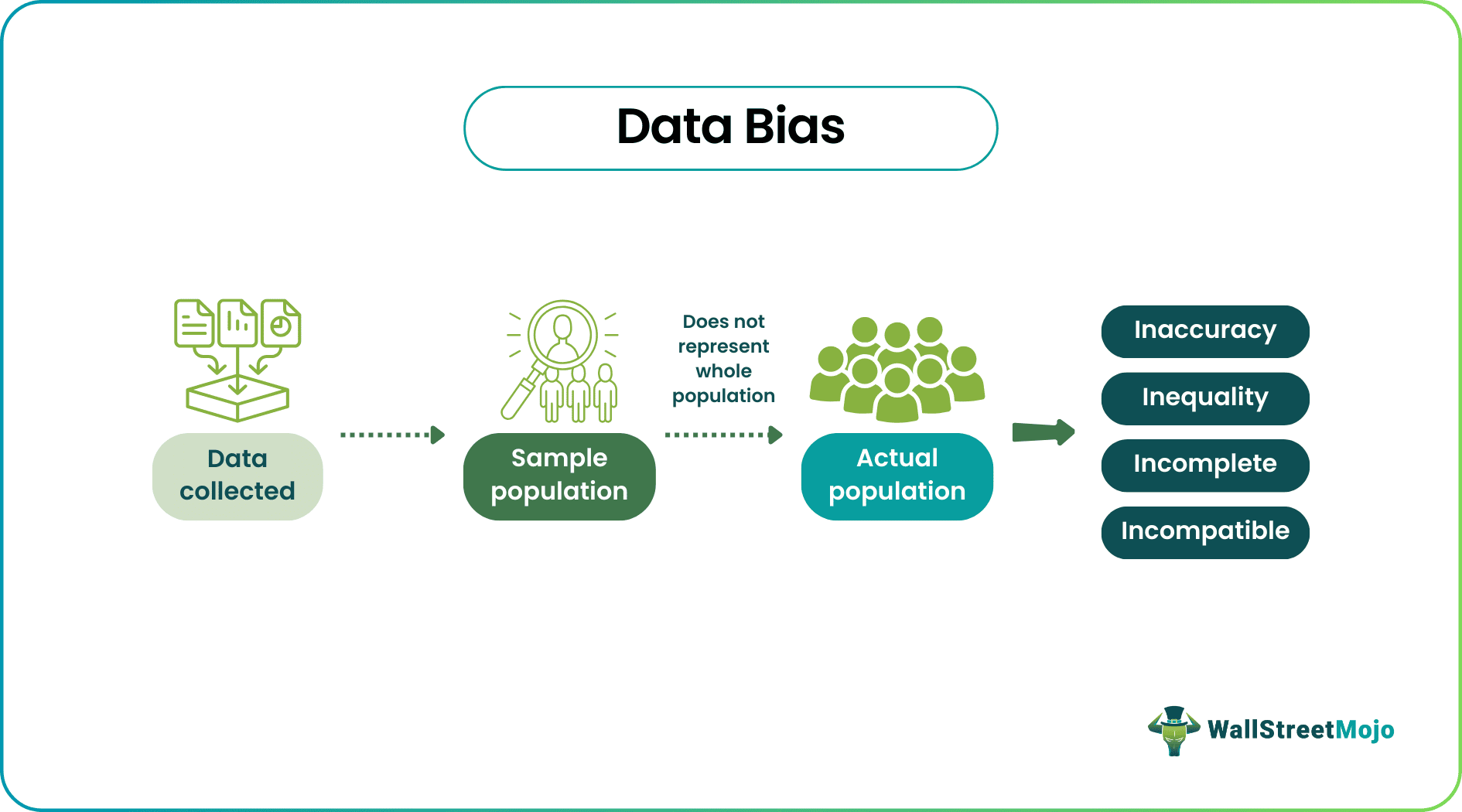
Data bias
data that does not accurately reflect the full population or phenomenon being studied
Data filtering
choosing a smaller subset of a data set to use for analysis

Computing Innovation
includes a program as an integral part of its function. Can be physical (e.g. self-driving car), non-physical computing software (e.g. picture editing software), or non-physical computing concepts (e.g., e-commerce).
Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
information about an individual that identifies, links, relates, or describes them.
Phishing
a technique that attempts to trick a user into providing personal information.

Keylogging
the use of a program to record every keystroke made by a computer user in order to gain fraudulent access to passwords and other confidential information

Malware
software intended to damage a computing system or to take partial control over its operation
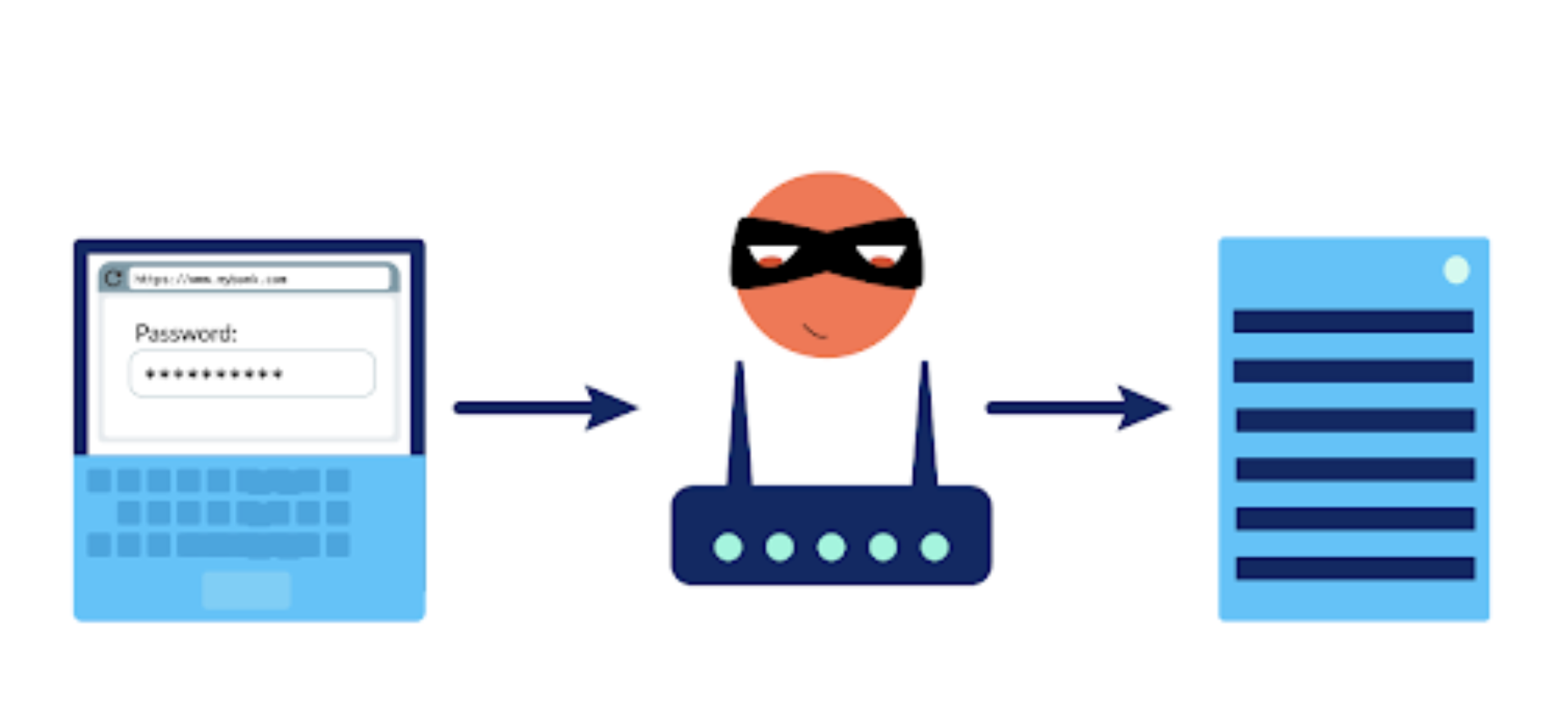
Rogue Access Point
a wireless access point that gives unauthorized access to secure networks.
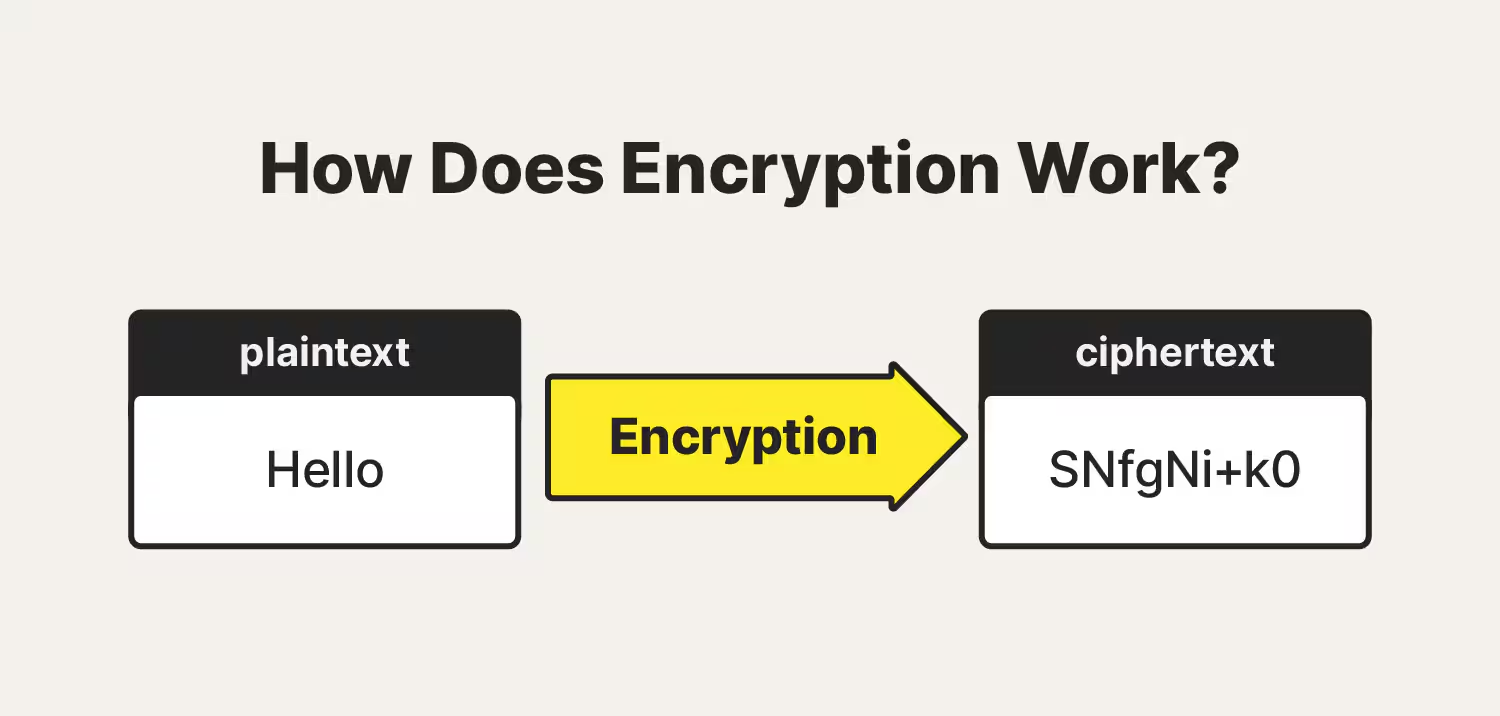
Encryption
a process of encoding messages to keep them secret, so only 'authorized' parties can read it.
Decryption
a process that reverses encryption, taking a secret message and reproducing the original plain text.

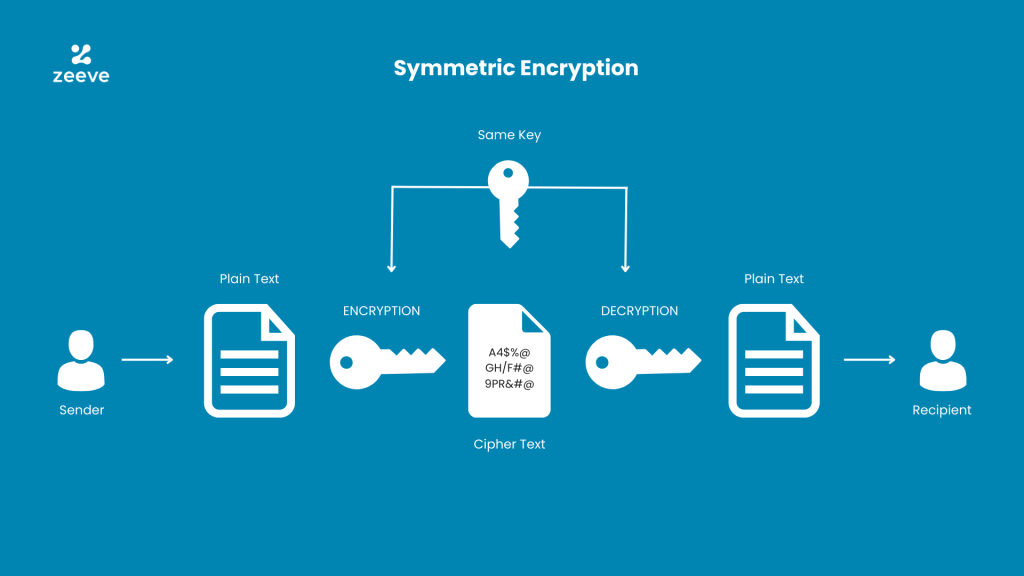
Symmetric Key Encryption
involves one key for both encryption and decryption.
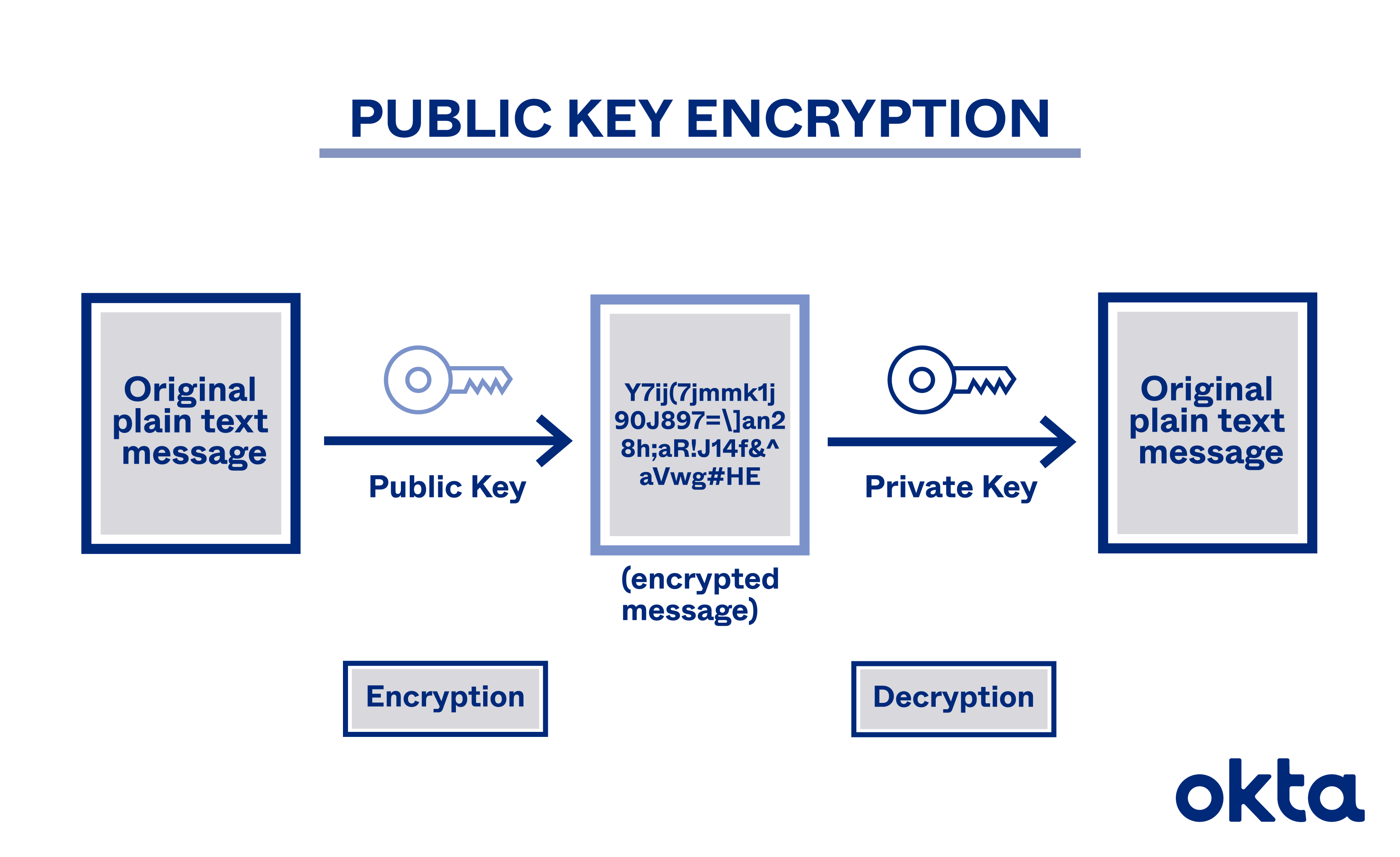
Public Key Encryption
pairs a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The sender does not need the receiver’s private key to encrypt a message, but the receiver’s private key is required to decrypt the message
Multi-factor Authentication
a system that requires at least two steps to unlock protected information; each step adds a new layer of security that must be broken to gain unauthorized access

Computer Virus Scanning Software
protects a computing system against infection.

Problem
a general description of a task that can (or cannot) be solved with an algorithm
Algorithm
a finite set of instructions that accomplish a task.
Sequencing
putting steps in an order.
Selection
deciding which steps to do next.
Iteration
doing some steps over and over

Efficiency
a measure of how many steps are needed to complete an algorithm
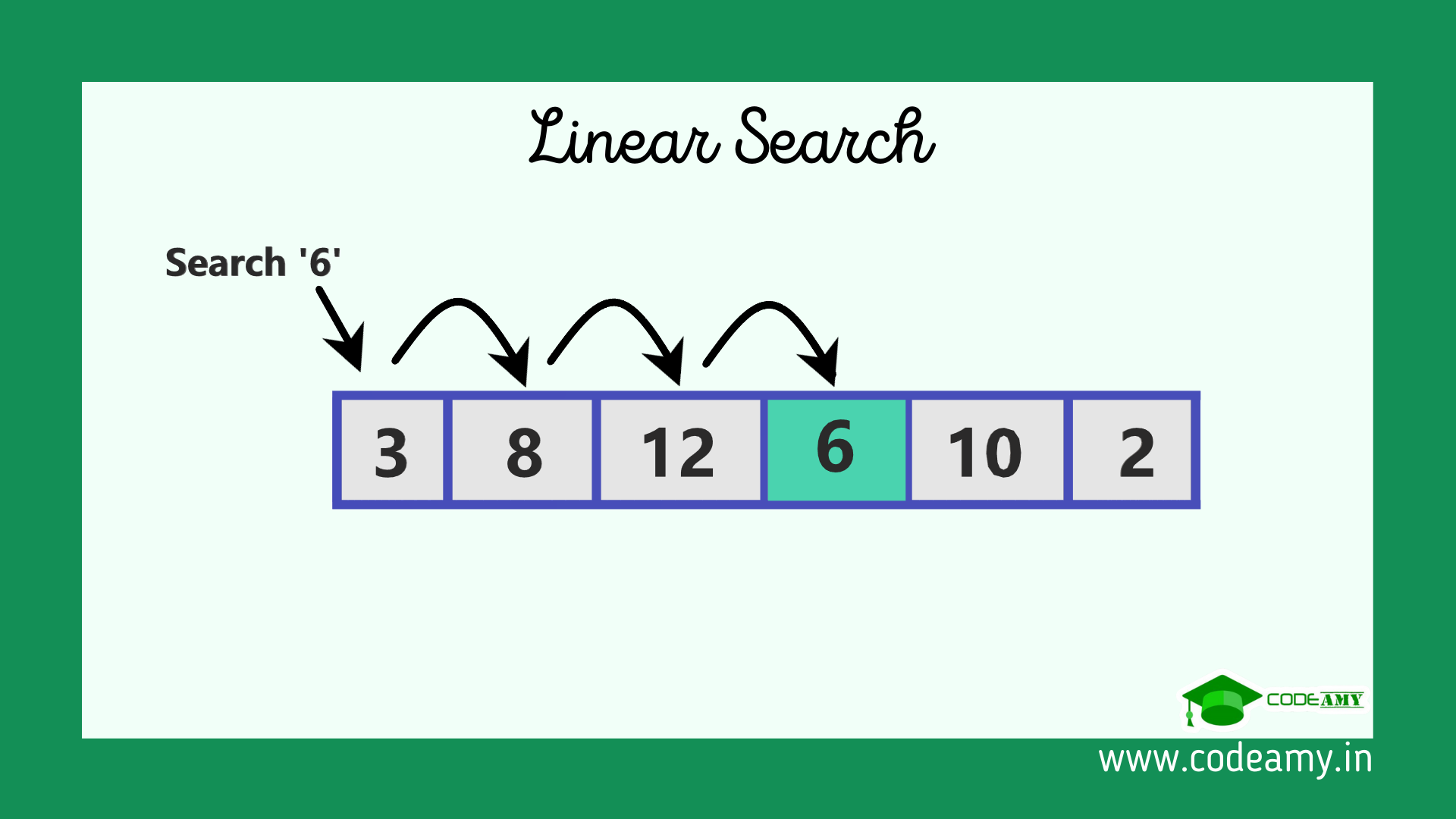
Linear Search
a search algorithm which checks each element of a list, in order, until the desired value is found or all elements in the list have been checked.
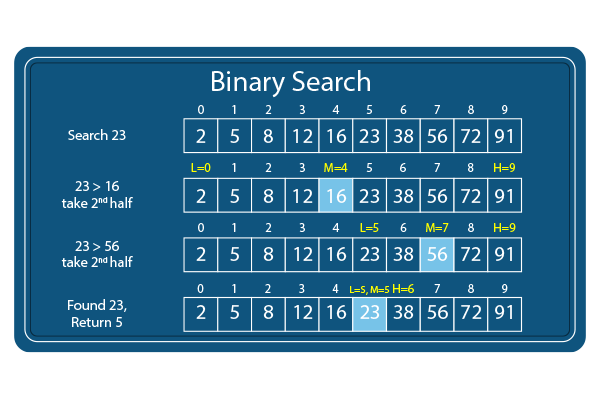
Binary Search
a search algorithm that starts at the middle of a sorted set of numbers and removes half of the data; this process repeats until the desired value is found or all elements have been eliminated.
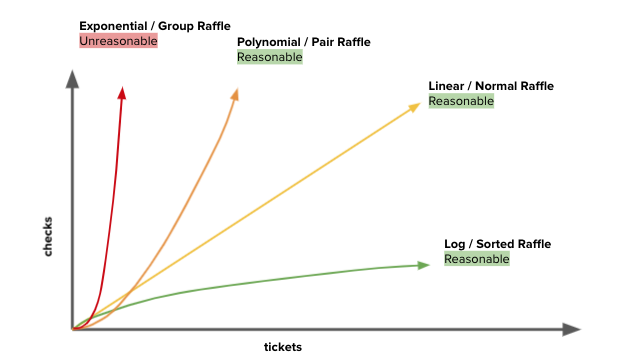
Reasonable Time
Algorithms with a polynomial efficiency or lower (constant, linear, square, cube, etc.) are said to run in a reasonable amount of time.
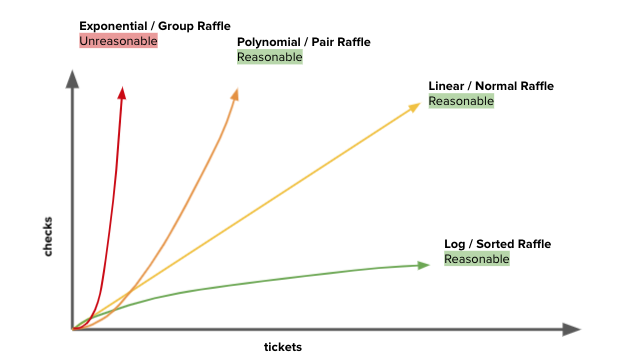
Unreasonable Time
Algorithms with exponential or factorial efficiencies are examples of algorithms that run in an unreasonable amount of time.
Heuristic
provides a 'good enough' solution to a problem when an actual solution is impractical or impossible
Decision Problem
a problem with a yes/no answer (e.g., is there a path from A to B?)

Optimization Problem
a problem with the goal of finding the 'best' solution among many (e.g., what is the shortest path from A to B?)
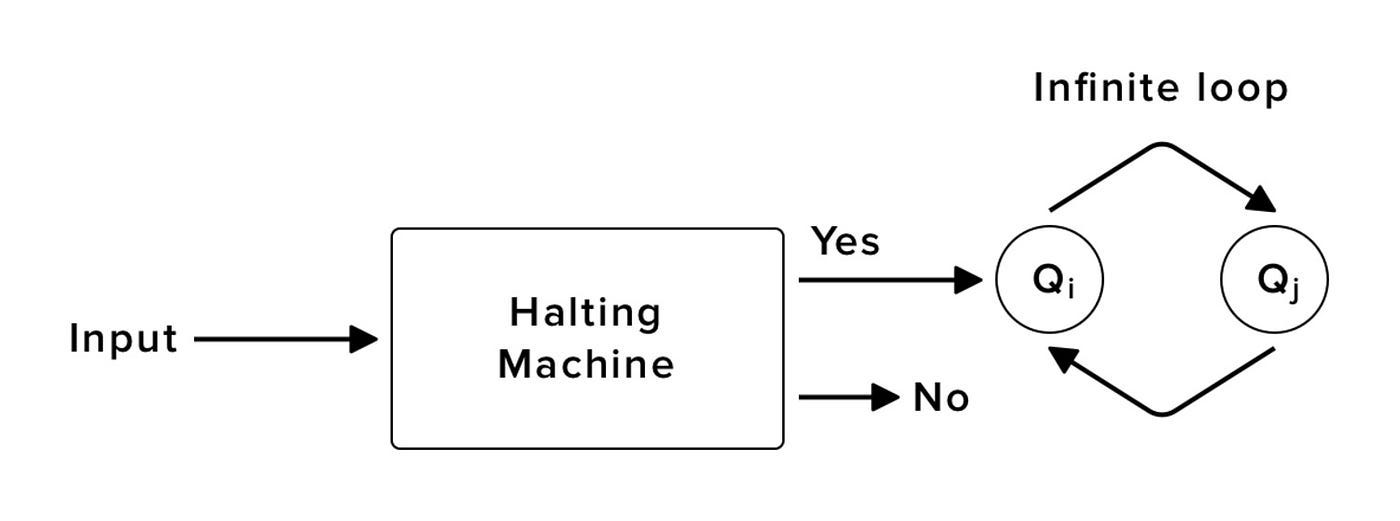
Undecidable Problem
a problem for which no algorithm can be constructed that is always capable of providing a correct yes-or-no answer
Sequential Computing
a model in which programs run in order, one command at a time.
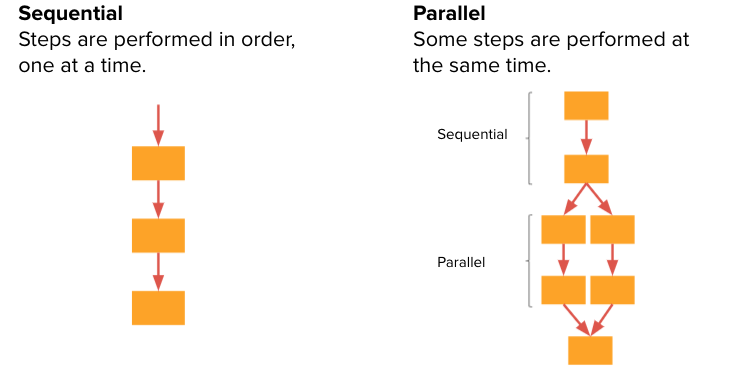
Parallel Computing
a model in which programs are broken into small pieces, some of which are run simultaneously
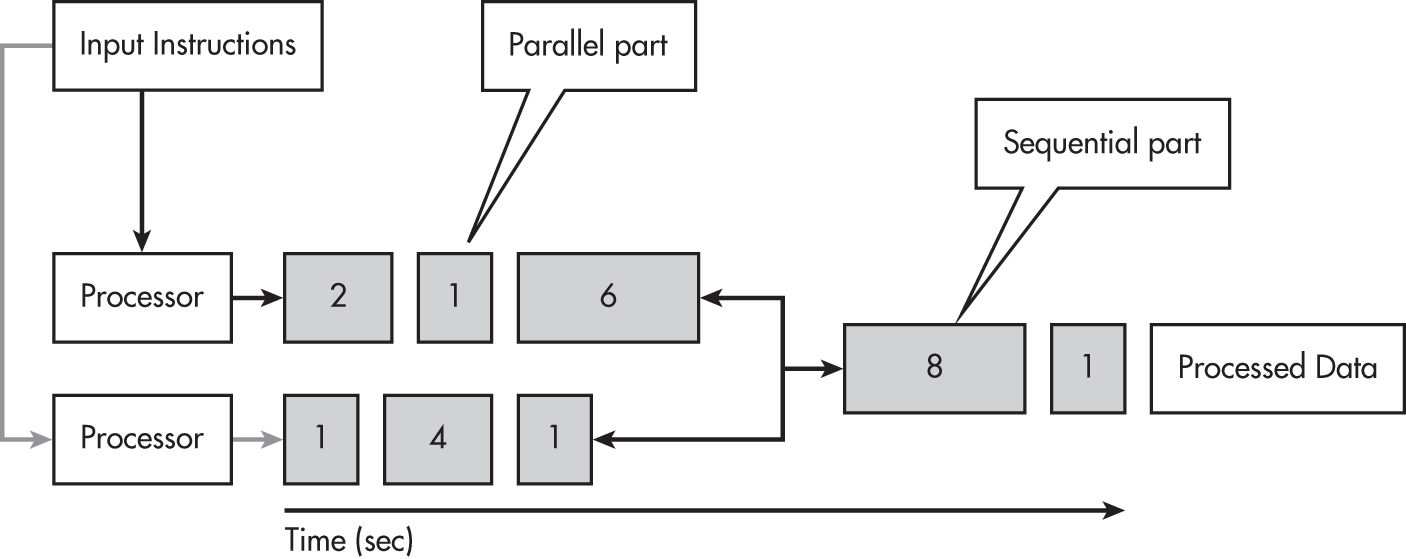
Distributed Computing
a model in which programs are run by multiple devices
Speedup
the time used to complete a task sequentially divided by the time to complete a task in parallel