Chapter 18: Cell Organization & Movement II: Microtubules Flashcards
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
unstable
αβ-Tubulin assembles into dynamically _________ and polarized microtubules with (+) and (-) ends and 13, 13+10, and 13+10+10 protofilament walls
GTP
Assembled tubulin hydrolyzes ________
MAPs
__________ mediate the assembly, dynamics, and function of microtubules
microtubules
All ________________ are nucleated from microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs), and many remain anchored by their (−) ends
microtubule organizing centers
what does MTOC stand for
centrosome
________________ MTOCs consist of two centrioles and the surrounding pericentriolar material
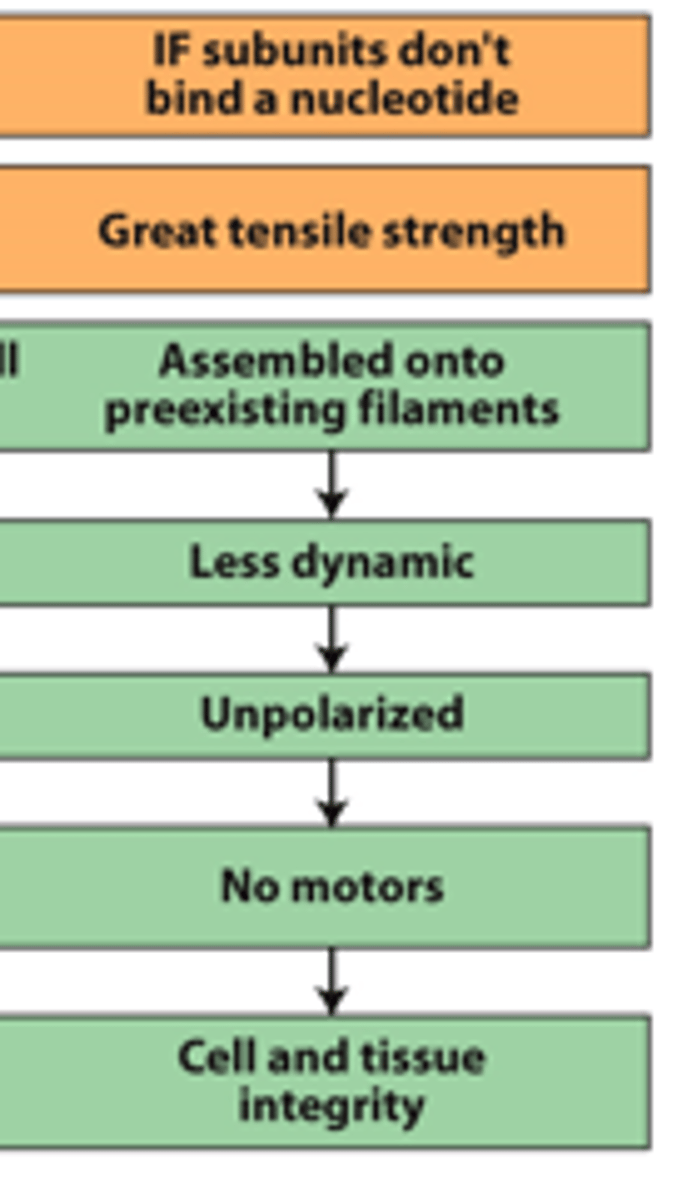
intermediate
________________ ________________ cytokeratins (red) connected to desmosomes (yellow) in epithelial cells. Intermediate filaments also line the inner surface of the nucleus
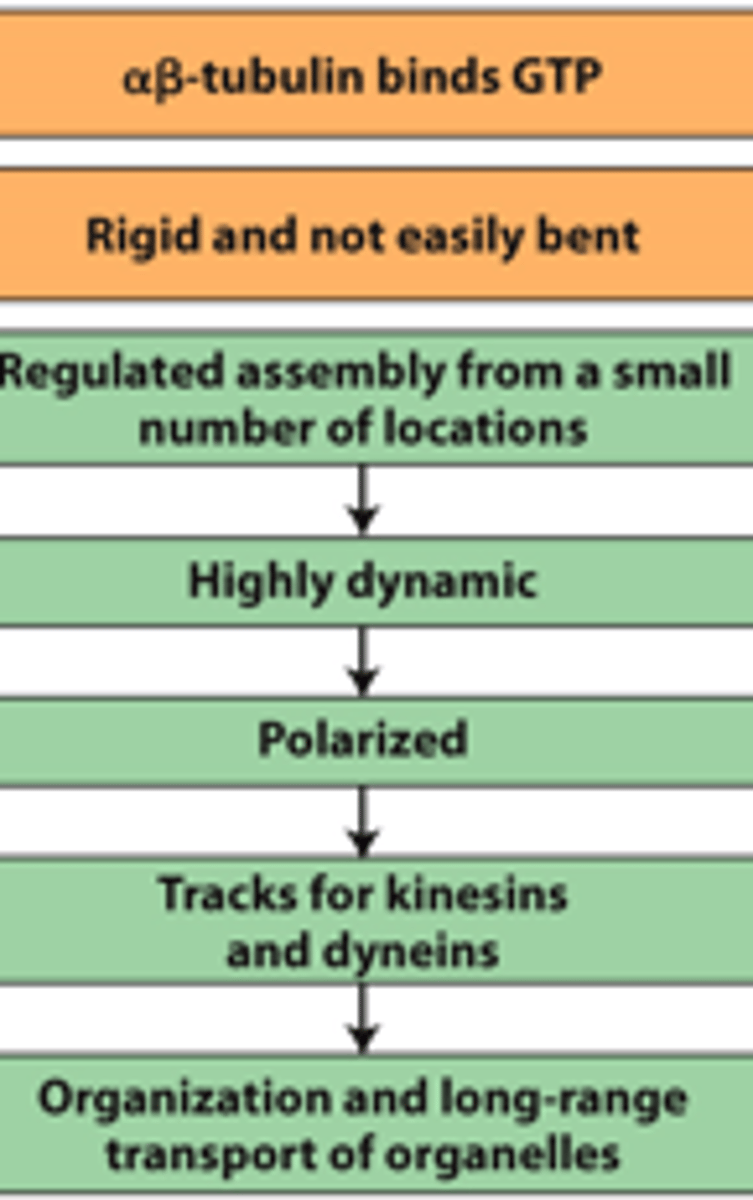
microtubules
________________ (green) and the Golgi complex (yellow), which is centrally located by transport along microtubules
microfilaments
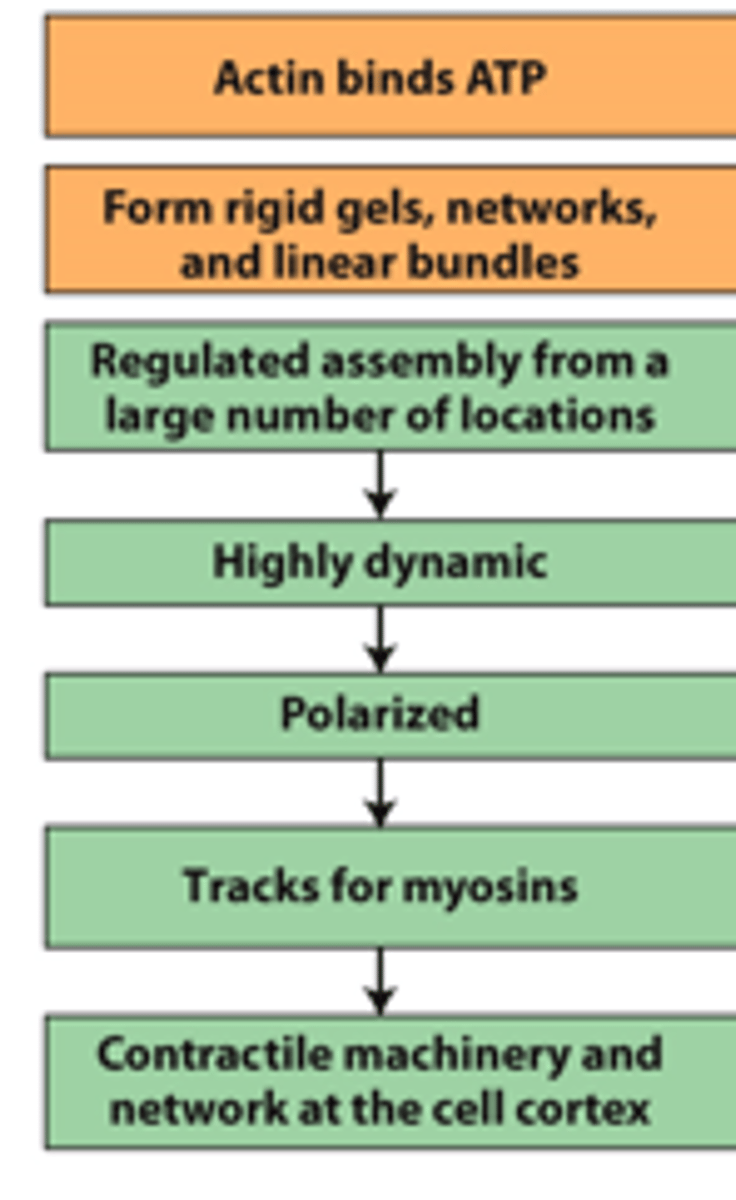
microtubules
intermediate filaments
cilia
__________ projecting from the surface of the ciliated epithelium lining a rabbit oviduct. Each cilium contains a core motile MT structure, which beats to propel eggs down the oviduct
tracks
Microtubules and intermediate filaments in a nerve axon provide __________ for intracellular vesicle motility and axon structural stability, respectively
microtubule
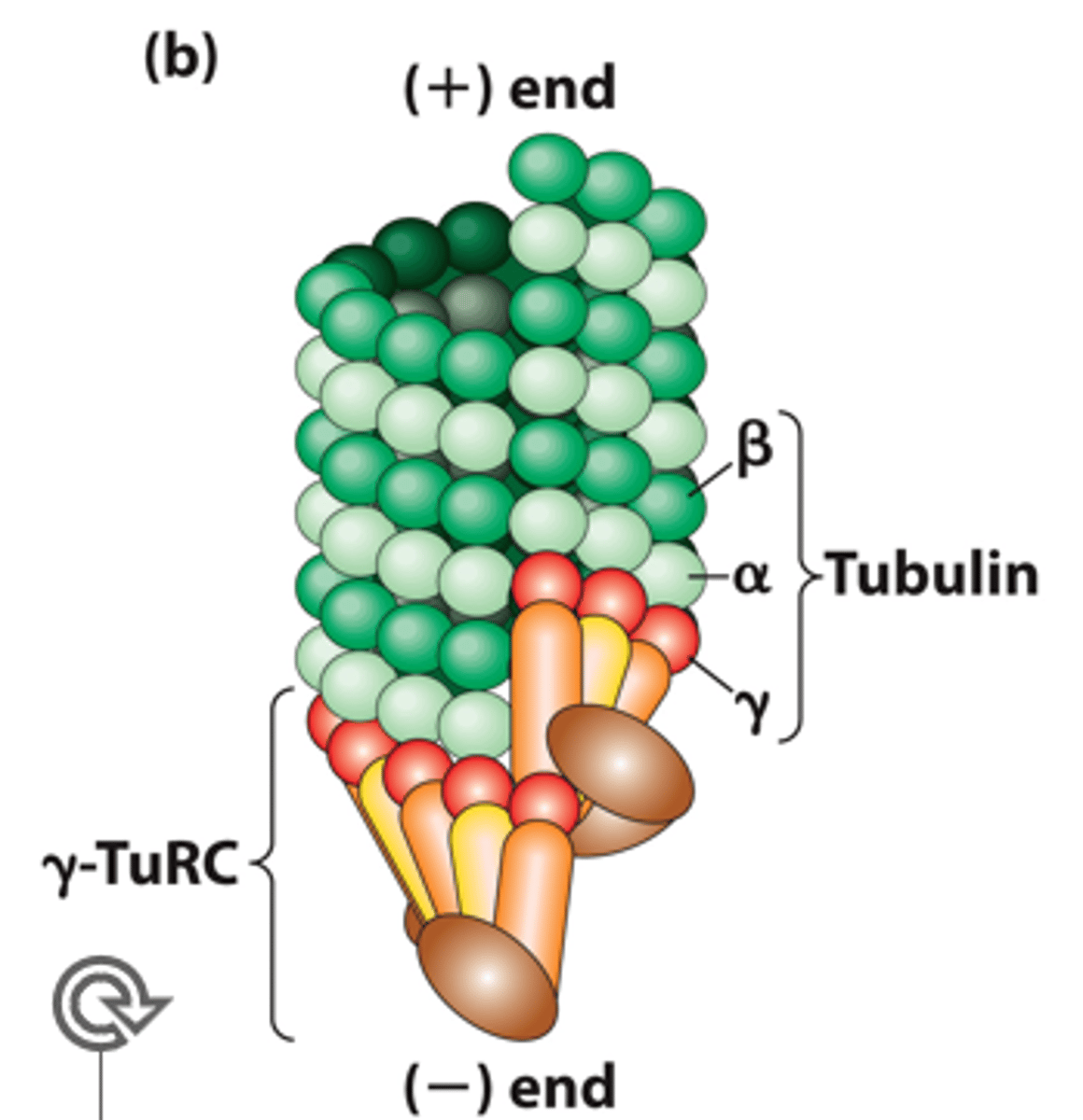
______________ cross section showing ends of the 13 protofilaments that form the MT wall.
tubulin dimer
•omposed of stably associated, highly conserved (in eukaryote), and structurally similar α-tubulin and β-tubulin monomers (55kDa MW).
genes
Most eukaryotes have several ___________ encoding both dimers and additional genes encoding a gamma-tubulin subunit, which is involved in MT assembly
alpha tubulin
tubulin dimer: GTP is never hydrolyzed and nonexchangeable
beta tubulin
tubulin dimer: GDP is exchangeable with GTP, which can be hydrolyzed in the site
tube
Tubulin subunit organization in a microtubule: forms a structurally polarized _________
protofilaments
Dimers are aligned end-to-end in the same orientation into _______________
polarity
Protofilaments pack side by side with the same subunit ____________ to form the wall of the microtubule
staggered
Protofilaments are slightly _________________ so that α-tubulin in one protofilament is in contact with α-tubulin in the neighboring protofilaments, except at the seam, where an α-subunit contacts a β-subunit.
microtubule
Dimer alignment provides structural polarity to the __________________
positive
Subunits are added preferentially at the ___________ end where β-tubulin monomers are exposed
singlet
_____________ microtubule: 13 protofilaments - most cytoplasmic MTs
cytoplasm
where are the singlet microtubules located?
cilia, flagella
where are the doublet microtubules located?
basal bodies, centrioles
where are the triplet microtubules located?
doublet microtubule
an additional wall of 10 protofilaments forms a second tubule (B) in cilia/flagellar outer doublets
triplet microtubule
two 10-protofilament walls (B) and (C) on the 13-protofilament (A) microtubule in centriole and basal body microtubule organizing centers
microtubules
_______________ are assembled from MTOCs to generate diverse configurations
interphase, mitosis
MT distribution: immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to tubulin
•(a) _______________ cell
•(b) Cell in ______________
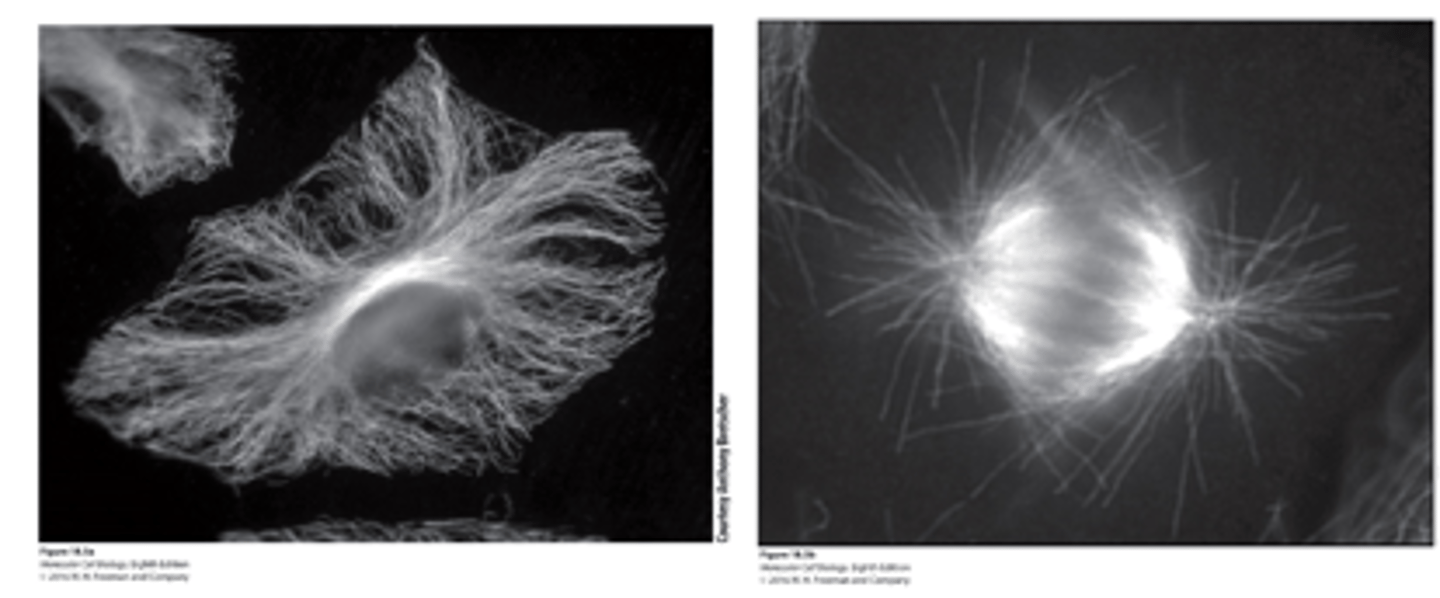
distribution
microtubule ________________ in various cells and structures - assembled from distinct MTOCs (Microtubule polarity is indicted by (+) and (−).)
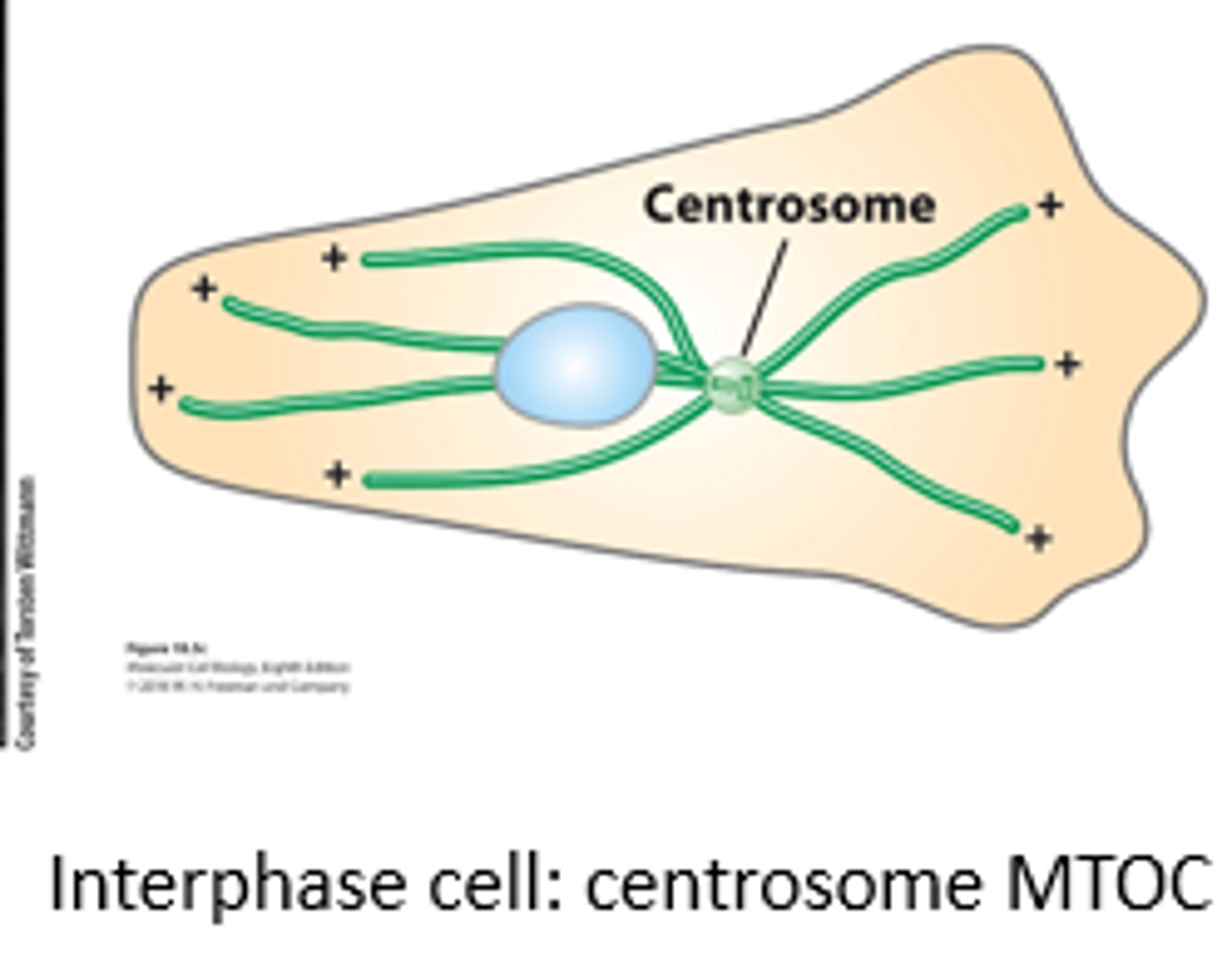
centrosome
microtubule, Interphase cell: _______________ MTOC
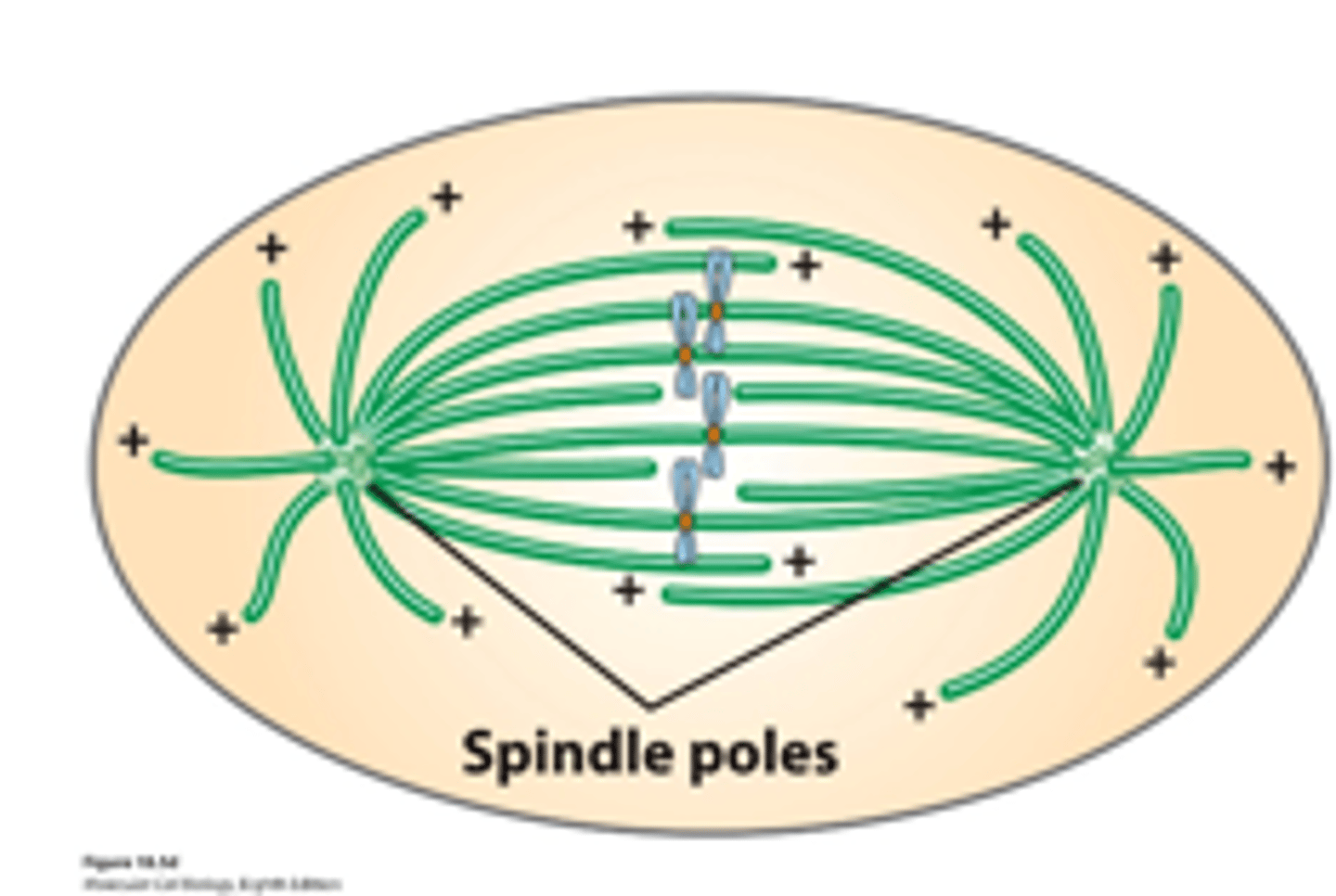
mitotic
microtubule, In a _________ cell: two spindle pole centrosome MTOCs organized two MT arrays
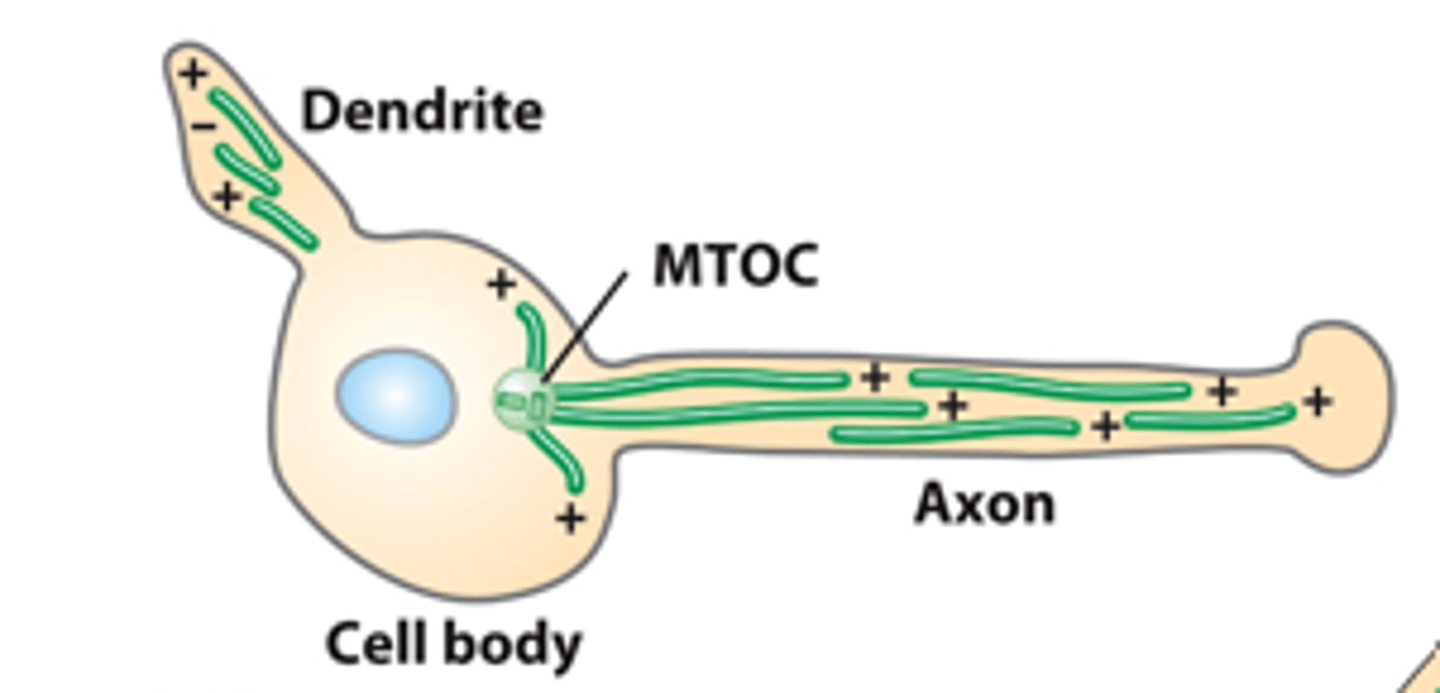
neuron
microtubule, ____________: microtubules in both axons and dendrites are assembled from an MTOC in the cell body and then released from it. Dendrite MTs have mixed orientation
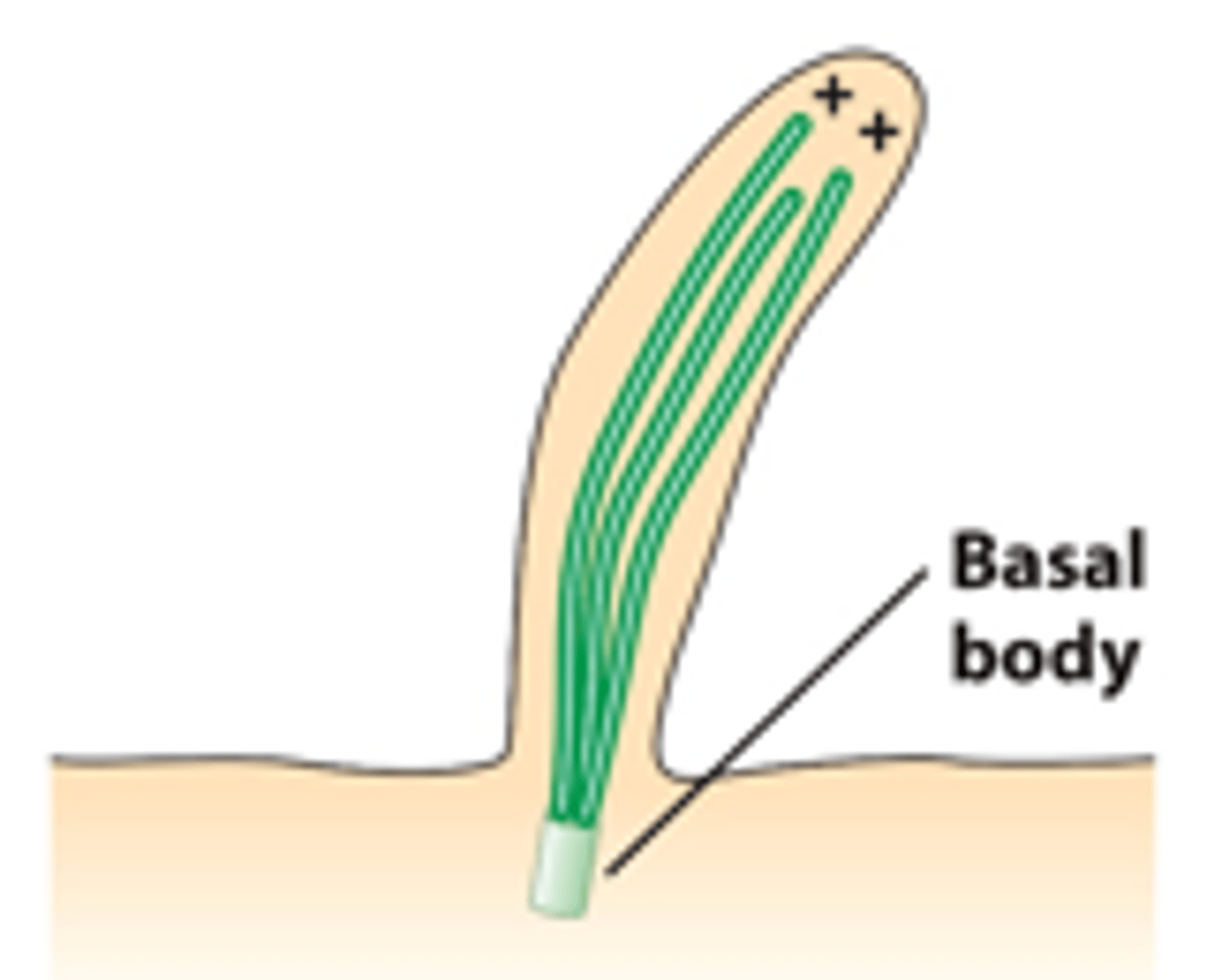
cilium, flagellum
microtubule, ____________/______________: microtubules are assembled on a basal body MTOC
dendrites
In all but _______________, the MT (-) end is attached to or oriented toward the MTOC
animal
___________-cell centrosome: two centrioles at right angles to each other, surrounded by pericentriolar material (arrows
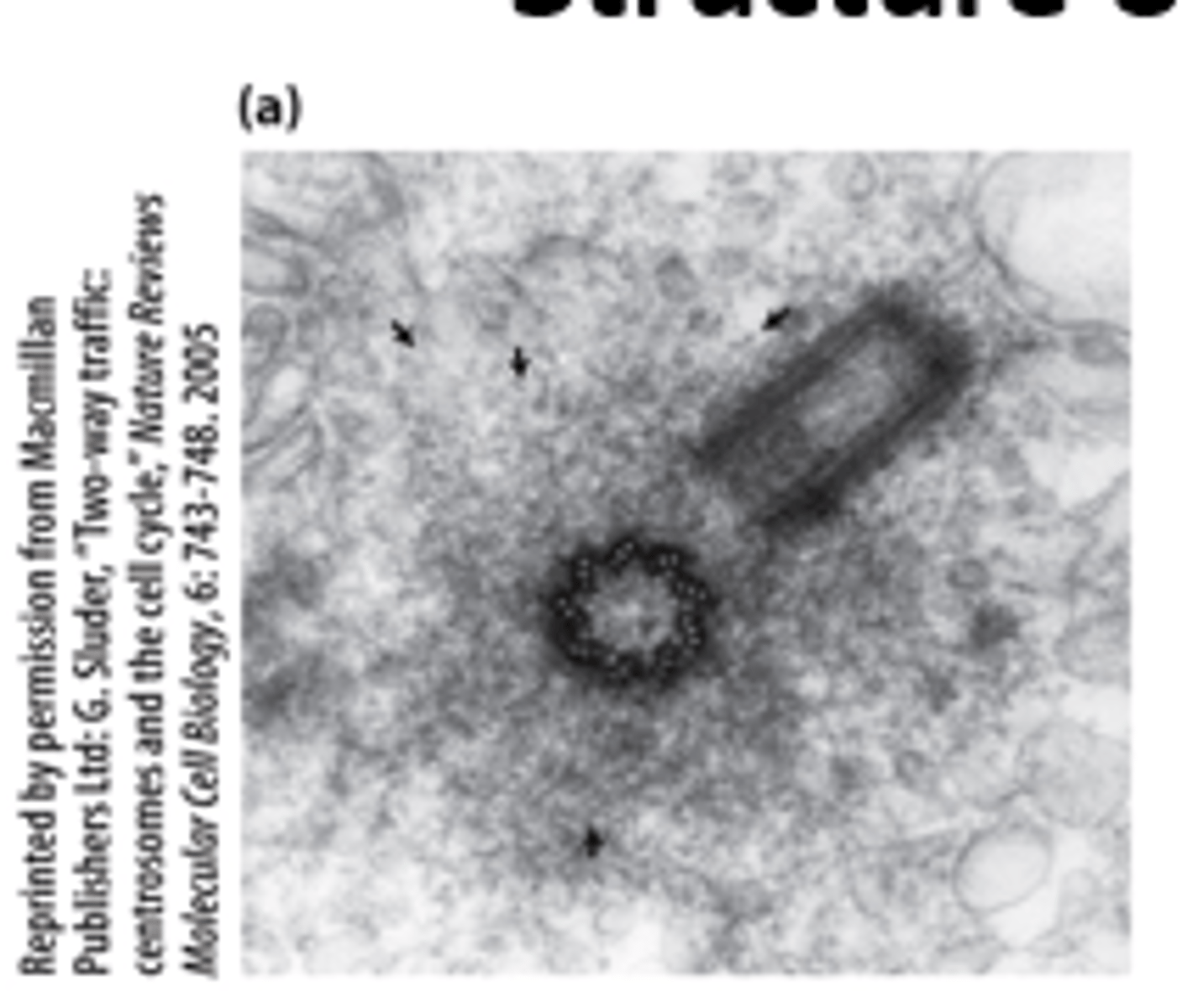
daughter
Mother, with distinctive distal appendages (blue spheres), and _____________ centrioles each consists of nine linked triplet microtubules
templated
The daughter centriole is _____________ by a nine-fold symmetric cartwheel structure that is later removed
plants
_________ do not have centrosomes and basal bodies, but use other mechanisms to nucleate the assembly of microtubules
negative
Microtubules assembled in vitro (green) with a γ-TuRC (red) at the ____________ end
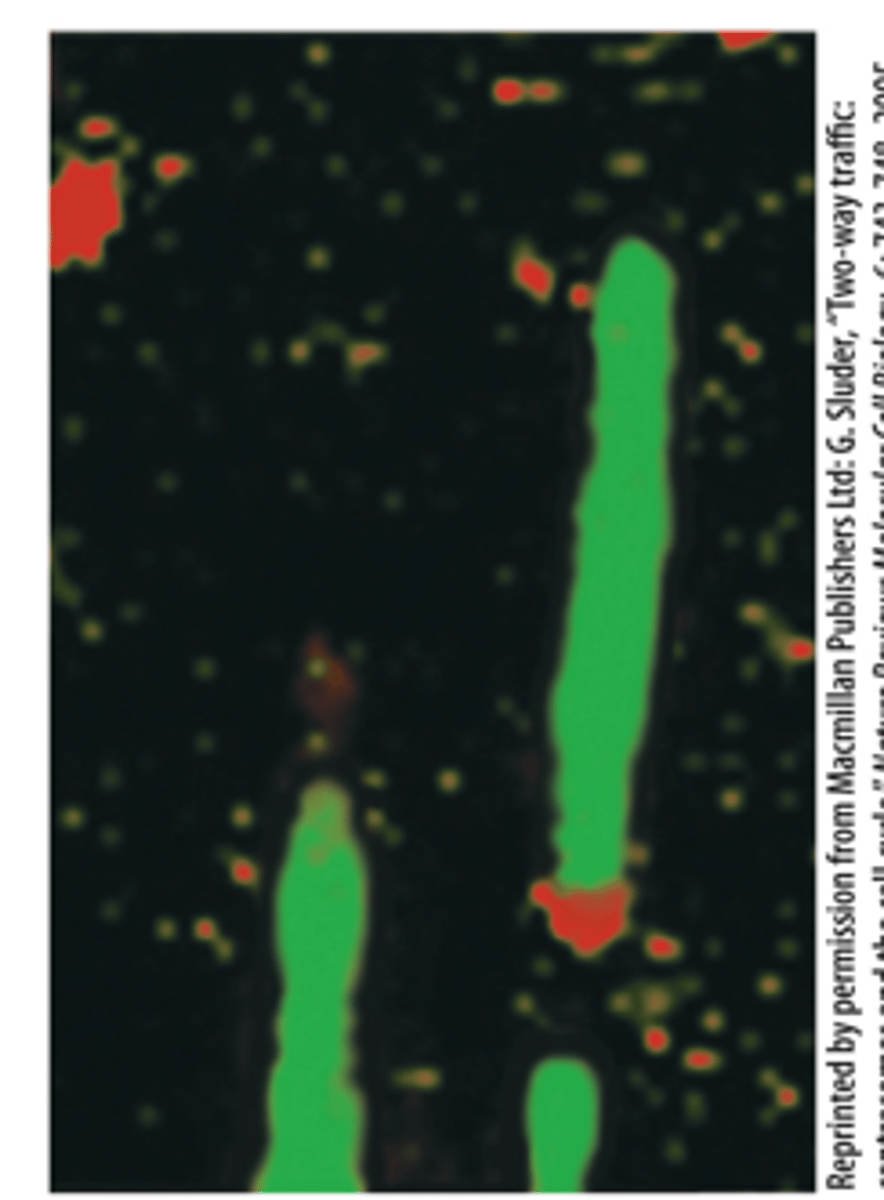
template
Model of γ-TuRC nucleation of microtubule assembly − forms a _______________ for the MT (−) end.
instability
Individual microtubule (+) ends exhibit dynamic ______________ with alternating periods of growth and rapid disassembly (catastrophe), depending on GTP-cap or GDP-cap status
store
Assembling microtubules __________ energy derived from GTP hydrolysis in the microtubule lattice and can do work when disassembling.
cytoplasm
Dynamically unstable microtubules can "search" the ______________ and "capture" targeted structures or organelles
microtubules
dynamic structures that can assemble or disassemble rapidly at both ends
positive
Microtubules grow preferentially at the ____________ end
individual
____________ microtubules exhibit dynamic instability
lengths
Microtubule ___________ (observed with light microscopy) plotted over time exhibit dynamic instability
rapid
Assembly and disassembly of microtubules each proceed at uniform rates, but disassembly is much more ___________ (7 μm/min) than assembly (1 μm/min).
catastrophe, rescue
MT (+) ends make abrupt transitions from elongation to shrinking (______________) back to elongation (___________)
assembling
____________ MT: blunt end or curving sheet not yet closed at seam
disassembling
_______________ MT: splaying curled protofilaments
GTP-β-tubulin cap
lateral
GTP-β-tubulin cap: ___________ protofilament--protofilament interactions in the GTP-β-tubulin cap are sufficiently strong to prevent protofilament unpeeling at the MT end
end
GTP-β-tubulin cap: MT with GTP-β-tubulin on the ________ of each protofilament
assembly
GTP-β-tubulin cap: Strongly favors ___________ by adding more GTP-tubulins
protofilament
GDP-β-tubulin cap: MT with GDP-β-tubulin at the end of each _____________
disassembly
GDP-β-tubulin cap: Protofilaments curve and undergo rapid ______________
greater
switch from assembly to disassembly (catastrophe): rate of GTP hydrolysis (constant) is _______________ than rate of GTP-tubulin addition.
rescue
Switch from disassembly to assembly (___________): rate of GTP-tubulin addition is greater than rate of GTP hydrolysis
GTP beta tubulin islands
(detected with an antibody specific for GTP-β-tubulin) can persist along the length of an assembled microtubule. When a disassembling microtubule encounters a GTP-β-tubulin island, disassembly pauses and rescue may be initiated
GDP
Disassembled GDP-β-tubulin exchanges GTP for ___________ to become GTP-β-tubulin
stabilize
Side-binding MAPs _______________ microtubules
end
(+) ________-binding +TIPs can alter microtubule dynamic properties or attach cell components to the (+) end
catastrophe
Microtubule ends are destabilized by proteins such as the kinesin-13 family of proteins and Op18/stathmin, which enhance _________________ frequency
spacing
_____________ of microtubules depends on the length of the projection domains of microtubule associated proteins
space
MAP (long arm) and tau (short arm) side-binding proteins − stabilize and ___________ MTs
greater
MT spacing in MAP2-expressing cells is ______________ than in tau-expressing cells - enlarges caliber of cell
greater
MAP-MT associations: MT spacing in MAP2-expressing cells is ______________ than in tau-expressing cells - enlarges caliber of cell
stabilize
MAP-MT associations: Side associations with several monomers along protofilaments ______________ MTs and dampen dynamic instability
regulate
MAP-MT associations: MAP/tau phosphorylation can ____________ MT interactions
positive
+TIPs regulate the properties and functions of the microtubule _______________ end
antibodies
Cell stained with ______________ to tubulin (red) and the EB1 +TIP protein (green) enriched on MT (+) ends
kymograph
________________ (image slices over time) of EB3-GFP shows association only with growing MT end - binds only to straight GTP-capped ends and not to curved GDP-capped protofilaments on disassembling MTs
growth
EB1 and XMAP215 promote microtubule ______________ by enhancing polymerization at the (+) end
CLASPs
____________ reduce frequency of catastrophes
captured
A third class of +TIPs can become "____________" and stabilized by other proteins to link the microtubule (+) end to other cellular structures, such as the ER, F-actin in the cell cortex, and chromosomes during mitosis
kinesin 13
Enhances the disassembly of either a (+)/(-)-MT end
ATPase
_____________ activity dissociates Kinesin-13 from the αβ-tubulin dimer
dissociation
Op18/stathmin binds selectively to two dimers in curved protofilaments and enhances their _______________ from a MT end.
growth
Op18/stathmin binding: Activity is inhibited by phosphorylation, which is inhibited at a cell's leading edge, contributing to MT _____________ at front of cell.
organelles
The kinesin (+)end motor superfamily transports _____________ and slides antiparallel microtubules past each other.
kinesin 1
__________-___ is a highly processive motor because it coordinates ATP hydrolysis by its two heads so that one head is always firmly bound to a microtubule
cytoplasmic dynein
_______________ ____________ is a (−)end motor that associates with the dynactin complex and cargo adapters to transport cargo
post translational
Tubulin __________-__________________ modifications stabilize microtubules and regulate ability to interact with motor
kinesin 1
___________-_____ powers vesicle movement down axons toward the (+) ends of microtubules
kinesin 1
homodimer of two identical heavy chains
head motor domain
kinesin 1, heavy chains: MT and ATP/ADP binding sites
flexible linker domain
kinesin 1, heavy chains: required for motor activity and connects head to the coiled-coil stalk
tail
kinesin 1: •Two light chains associated with the _______ of each heavy chain bind to receptors on vesicles
microtubule, nucleotide, linker
Kinesin head domains: _______________-binding site, ________________-binding sites (contains ADP), ___________ regions connect heads to stalks
surface
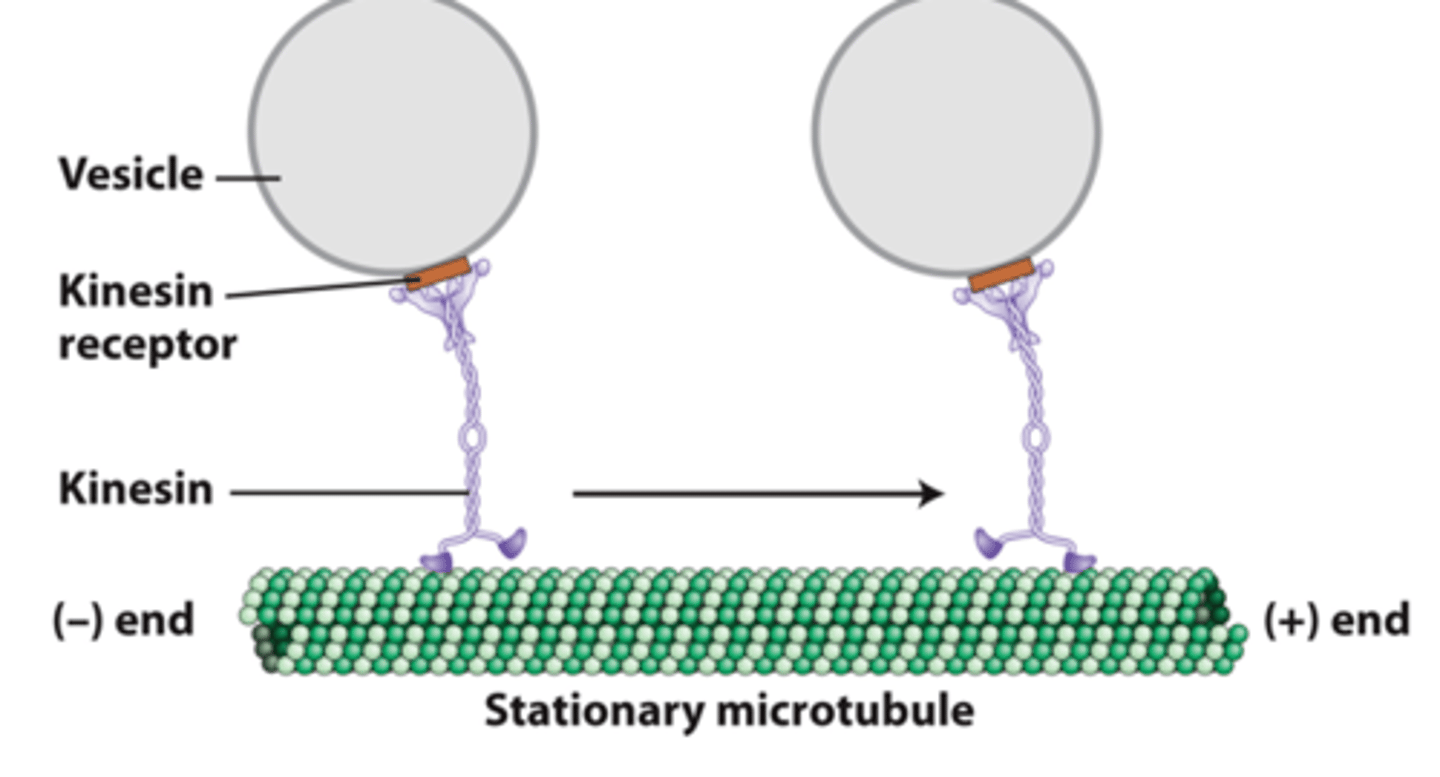
kinesin 1: Attaches to a vesicle __________ receptor
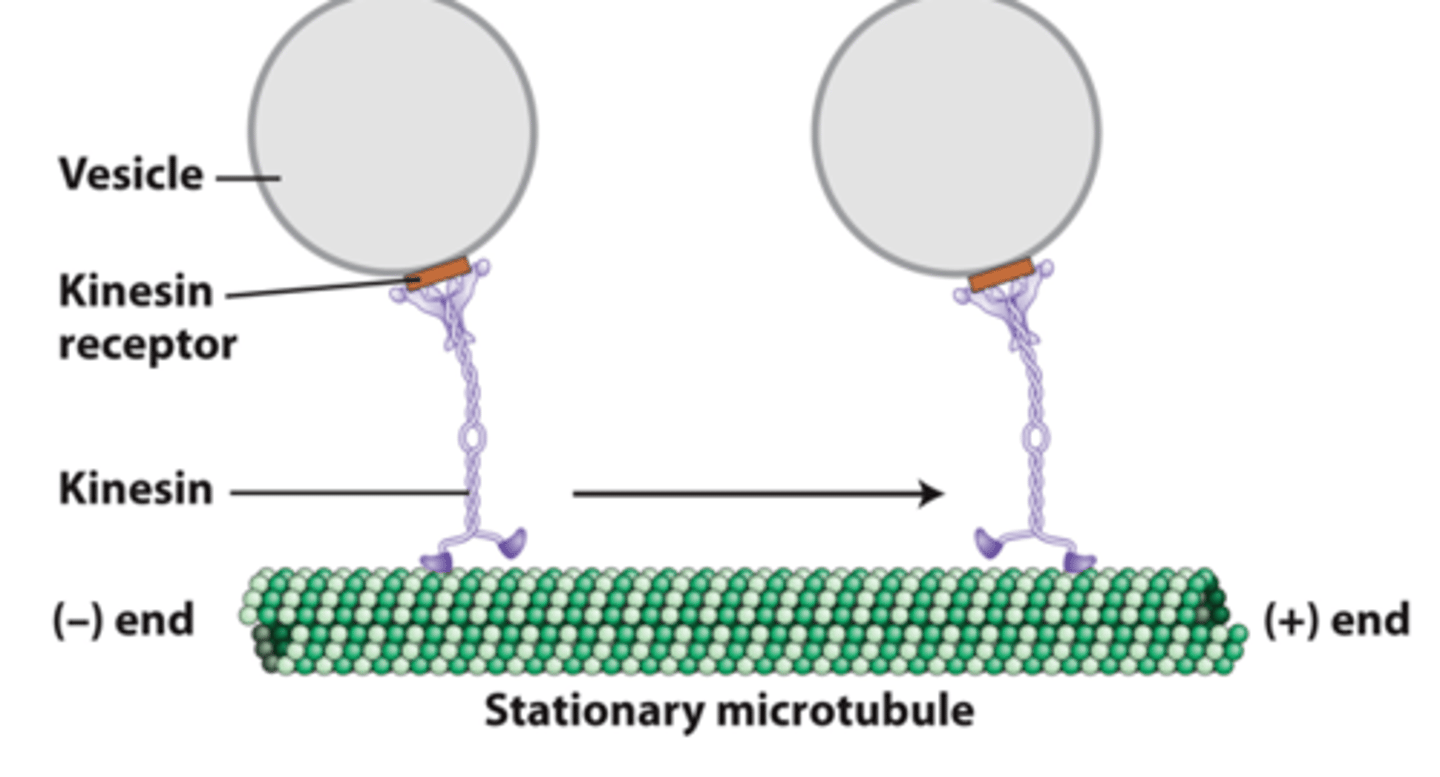
transports
kinesin 1: _______________ vesicles from the (−) end to the (+) end of a stationary microtubule
fourteen
______________ known classes of kinesins form a large protein superfamily with diverse functions. (45 kinesin genes in the human genome)
conserved
A ______________ motor domain is fused to a variety of class-specific nonmotor domains
transport
Kinesin-1: (+) end-directed microtubule motor involved in organelle ____________
vesicle
kinesin-2: (+) end-directed ___________ transport
heavy
kinesin-2: Family has two closely related but nonidentical ____________ chains and a third cargo-binding subunit