Chemistry Finals
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
**Study Daily
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Who created the Atomic Theory?
Dalton
What was found in the Atomic Theory?
all matter is made of atoms
Who created the Cathode Ray experiment?
Thompson
What was found in the Cathode Ray experiment?
Electrons are negatively charged. E/M, charge - mass ratio
Who created the Oil Drop experiment?
Millikan
What was found in the Oil Drop experiment?
Electron charge mass (it was an addition to the plum pudding model)
What was the model included in the Atomic Theory?
Atomic Model
What was the model included in the Cathode Ray experiment?
Plum Pudding Model
Who created the Gold Foil experiment?
Rutherford
What was found in the Gold Foil experiment?
the proton, it is small with a dense positively charged nucleus. the atom is mostly empty
What was the model included in the Gold Foil experiment?
Nuclear Model
Who created the Beryllium Bombardment Alpha Particle experiment?
Chadwick
What did they find in the Beryllium Bombardment Alpha Particle experiment?
the neutron, it has no charge and a mass similar to the proton
What model was included in the Beryllium Bombardment Alpha Particle experiment?
it was an addition to the nuclear model
Who created the Black Body Energy Radiation theory?
Planck
What was found in the Black Body Energy Radiation theory?
energy is not emitted or absorbed continuously but rather in discrete packets called quanta
What model is included in the Black Body Energy Radiation theory?
it was an addition to the nuclear model
Who created the photoelectric effect?
Einstein
What was found in the photoelectric effect?
light behaves also as a particle
What model was included in the photoelectric effect?
it was an addition to the nuclear model
Who explained the atomic emission/ absorption spectra?
Bohr
What was found in the atomic emission/ absorption spectra?
Electrons orbit the nucleus like planets at specific energy levels & transitions emit energy as light
What model is included in the atomic emission/ absorption spectra?
Bohr Model
Who created the Double Slit experiment?
de Brogile Schrodange Heisenberg
What was found in the Double Slit experiment?
electrons have wave particle duality and exist in orbitals (probability clouds). uncertainty principle
What model is included in the Double Slit experiment?
it was an addition to the Bohr Model
What is the nucleus responsible for?
Stability
What is the neutron responsible for?
Stability
What is the protons responsibility?
Identity
What is the electrons responsibilty?
reactivity
proton mass
1.00727amu
neutron mass
1.0066amu
electron mass
0.00055amu
What are isotopes?
atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons
Average atomic mass equation
Σ(fractional aubundance x isotopic mass)
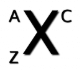
label each letter
a - mass #
z - atomic #
x - element
c - charge
% abundance equation
% abundance = (# of atoms of a specific isotope/total # of atoms of all isotopes) x 100
what is this: c
speed of light
what is this: lambda
wavelength
what is this: v
frequency
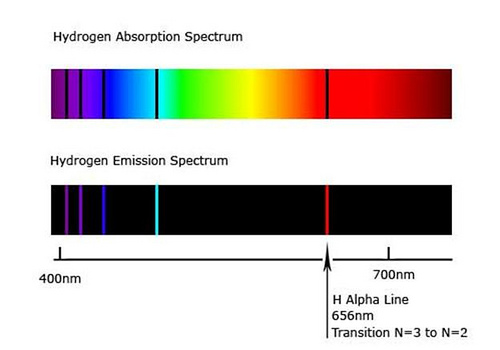
what is the emission spectrum
unique pattern of light emitted by an element when it transitions from a higher to lower energy state
what are the quantum numbers?
set of 4 numbers that describe the properties of an electron in an atom
what is the principle quantum number and what does it do?
n, represents the main energy level
what is the angular momentum quantum number and what does it do?
l, describes the shape of the electrons orbital
what is the magnetic quantum number and what does it do?
ml, specifies the orientation of the orbital in space
what is the spin quantum number and what does it do?
represents the spin of the electron
What is Hund’s Rule?
when electron orbitals are being filled, individual electrons will occupy separate orbitals within a subshell before pairing with the same orbital
how many elements were discovered by 1860?
60
what did Mendeleev do?
put together the periodic table in the order of its properties
how many elements did mendeleev predict would be discovered?
3
What did Mosely do?
rearranged the periodic table by proton charge
how is the periodic table organized?
atomic #
group 17 was added by -
Ramsey
what are lanthanides?
14 elements with atomic #’s from 58-71
what are actinides?
14 elements with atomic #’s from 90-103
why are noble gasses so stable?
they have special electron configurations and completely balanced electrons
what are valance electrons?
outermost electrons in an atom that help with chemical bonding
valance electrons in the s-block
number of ve corresponds to the group number and is on the outermost part of the last s orbital
valance electrons in the p-block
number of ve is determined by the last number in the group number (18=8), outermost s and p orbitals
valance electrons in the d-block
number of ve is very complex to determine (n-1)d, ve in their outermost s and d orbitals
valance electrons in the f-block
number of ve is always 2, ve on the outermost part of the s and f block
name of group 1
alkali metals
name of group 2
alkaline earth metals
name of group 3-12
transition metals
name of group 13
boron group
name of group 14
carbon group
name of group 15
nitrogen
name of group 16
oxygen group
name of group 17
halogens
name of group 18
noble gasses
what type is alkali metals
highly reactive & soft
what type is alkaline earth metals
highly reactive & silvery
what type is transition metals
metal, low reactivity
what type is boron group
metalloid, medium reactivity
what type is carbon group
non-metals, low reactivity
what type is nitrogen group
pnictogens, low reactivity
what type is oxygen group
chalcogens, pretty reactive
what type is halogens
non-metals, high reactivity
what type is noble gases
gases, low reactivity