RELIAS MODULES EXAMS 2025-2026 FULLY COMPREHENSIVE QUESTIONS BANK WITH 100% CORRECT ANSWERS ALREADY GRADED A+
1/1655
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1656 Terms
Which of the following is an example of positive punishment?
Telling someone "no" when they are about to run into the street
Which of the following is an example of a motivating operation?
Jan is hungry, so she works harder to get crackers as a reward.
Differential reinforcement works by:
Reinforcing only the behaviors that should be increased while removing reinforcement from behaviors that should be decreased.
Spontaneous recovery refers to:
Sudden reoccurrence of behavior that was extinguished
Extinction works by:
Abruptly stopping reinforcement for problem behavior
What is the difference between differential reinforcement of alternative behavior (DRA) and differential reinforcement of incompatible behavior (DRI)?
The replacement behavior selected in DRA does not have to be incompatible with the problem behavior.
Which of the following is an example of overcorrection?
Marty had to clean the bathroom wall because she wrote on it.
At what point should a behavior reduction plan be considered?
When environmental variables for behavior are ruled out
Which of the following functions of behavior involves avoiding a task or interaction?
Escape
Differential reinforcement of other behavior (DRO) involves:
Setting an interval for the problem behavior not to be displayed and reinforcing if it is not displayed
Which of the following is an example of negative punishment?
Paying a speeding ticket
Which of the following could ensure that an intervention involving the use of punishment is effective?
Collecting and reviewing intervention data
Extinction of behavior maintained by positive reinforcement works by:
Taking away the reinforcer for problem behavior
Which of the following best explains the primary purpose of the BACB's RBT Ethics Code?
The purpose of the RBT Ethics Code is to provide guidelines for certified and credentialed individuals to follow when they are providing behavior analysis services.
If an RBT is unknowingly assigned to work with a relative, which of the following is the best course of action for the RBT to take?
Inform the supervisor and ask not to work with the client.
Which of the following statements is the best way to describe this particular behavioral intervention to a parent of a child receiving the intervention?
After John has written 3 letters of his name, give him a small piece of crunchy cereal.
According to the RBT Ethics Code, clients and their families have a right to:
Your background check and credentials
When is it acceptable to videotape a client receiving an intervention?
If the client and family provide informed consent, which means they know why the videotaping is occurring.
Before a behavior change plan can be developed, what has to happen?
An assessment of the client's skills and needs must be conducted.
Which of the following is an example of an issue related to boundaries of competence?
Jenny was told to use non-contingent reinforcement with Annie and she does not know what that is.
Which of the following is an example of an exploitive relationships?
A BCBA agreeing to take a child on his caseload if the parent of the child receiving services will agree to give a discount on power tools at his hardware store
Any reinforcer that has the potential to affect the health of the client adversely if used inappropriately or in excess is called a:
Harmful reinforcer
Sarah works as an RBT in the local school system. She was at a party, drank one too many drinks and was arrested for driving while intoxicated. The Monday after the incident, she:
She informed her supervisor and the BACB what had happened.
If an RBT puts a picture of herself and the clients she works with on a social media site, she is:
Violating the client's right to confidentiality
According to the BACB, a client's record should be:
all of the above
If an intervention is implemented with a "high degree of fidelity," it is:
Implemented consistently and accurately
You are working with a young client in a clinic setting and are implementing a toilet training protocol. Which of the following should you do to make sure that this client's dignity is protected?
Make sure that the bathroom door is shut when the client is using the toilet.
Your supervisor tells you to use a strategy you have no idea how to use. What is the best response to the request?
Tell the supervisor immediately that you do not know how to use the strategy and ask for them to demonstrate it.
What percentage of births are affected by OB hemorrhage?
OBH is responsible for how many pregnancy related deaths worldwide?
11% of births
25% of pregnancy deaths worldwide, 10.7% in the US
4 domains of care?
- Readiness (hemorrhage cart, training, protocols)
- Recognition/prevention (risk assessment, accurate EBL)
- Response (standard plan)
- Reporting (debriefs/reviews)
OB Hemorrhage protocols have been shown to decrease maternal death rate by ___ and maternal morbidity by ___.
OB Hemorrhage protocols have been shown to decrease maternal death rate by 50% and maternal morbidity by 21%.
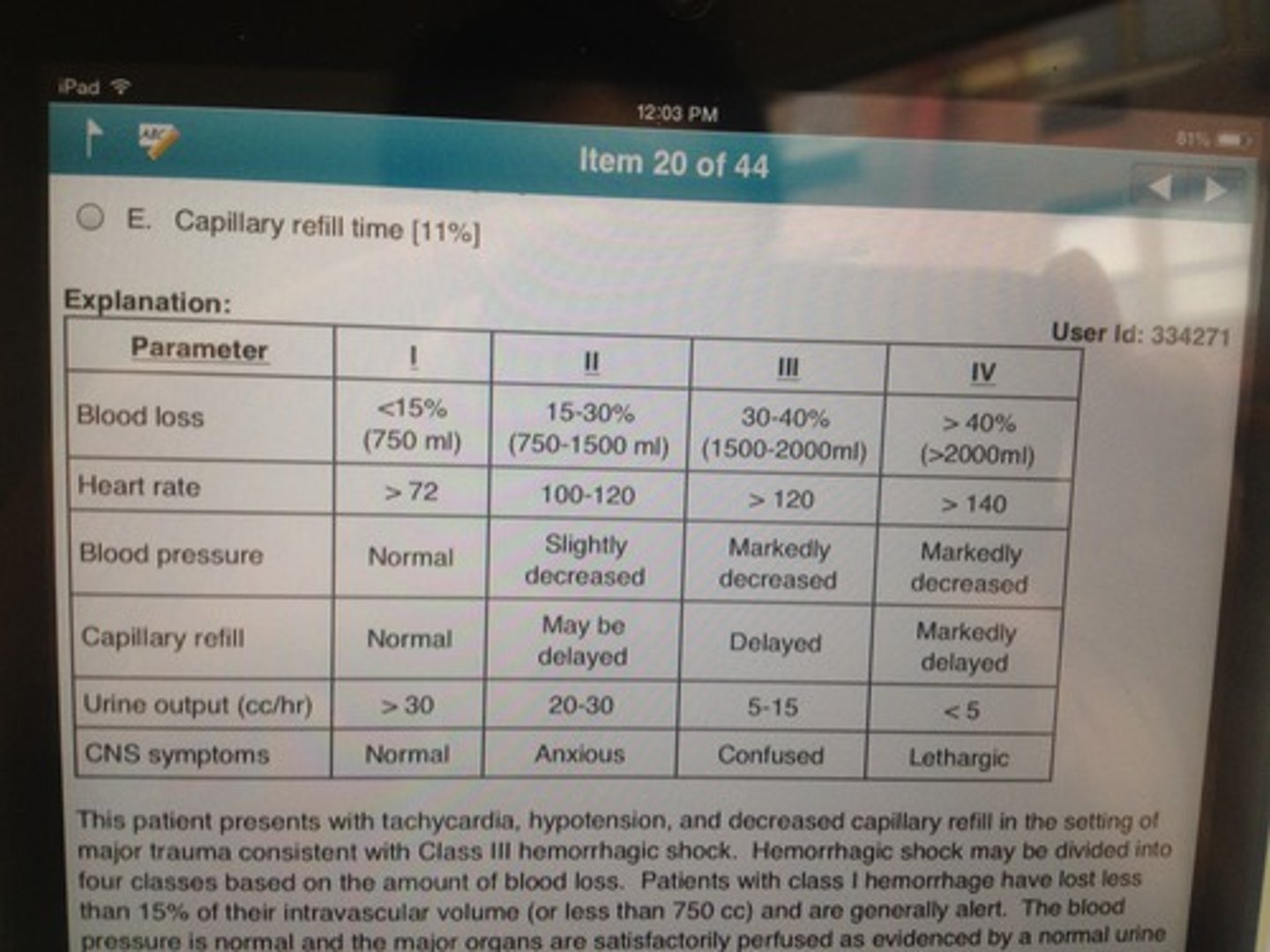
Stages of Hemorrhage
Stage 0 - active mgt 3rd stage
Stage 1 - >500 vaginal, >1000 CS: activate OBH protocol
Stage 2 - 1000 - 1500 QBL, advance through protocol sequentially
Stage 3 - >1500QBL: activate MTP, move to OR
Stage 4 - cardiovascular collapse
Uterotonics and dosages
TXA
Oxytocin: 10-40 units per 500-1000cc IV, or 10 units IM.
Methergine: 0.2mg IM q2-4h (avoid if HTN)
Carboprost: 0.25mg IM q15-90 min, no more than 8 doses =2mg. (avoid if significant asthma)
Misoprostol: 800mcg SL or PO x 1
TXA (not uterotonic): 1g (100mg/mL) infused over 10 min, can repeat at 30 min
Risk factors for OB Hemorrhage
-History of OBH
-Uterine overdistension (multiple gestation, large fibroids, macrosomia, polyhydramnios)
-Grand multiparity or Primiparity
-Obesity (inc atony)
-Prior CS / Uterine surgery
-Abnormal placentation
-Abruption
-Coagulopathy/ Bleeding Disorder
-Personal or FHx OBH in a 1st degree relative
Platelets <100k
-Prolonged or augmented labor
-Prolonged third stage
-Operative Delivery
-Connective tissue disorders
-Preeclampsia/HELLP
-Use of MgSO4
-Malpresentation (inc risk of trauma)
-General anesthesia
Recurrence risk of OBH?
ranges 8-28% depending on contributing factors
May be as high as 80% in patients with vWF disease
High risk factors for OBH include:
Previa/low lying placenta
Accreta spectrum
Hct <30 + other risk factor
Platelets <100k
Active bleeding on admission
Known bleeding d/o
Multiple lower level risk factors
TYPE AND CROSS these peeps
Signs/symptoms of hypovolemia and concealed hemorrhage to tell patients?
dizziness, rapid HR, fatigue, rectal or pelvic pressure, abdominal pain
Atony is the cause of OBH at delivery in about ___% of cases.
About ____% of OBH is secondary (late).
80% atony
1-3%, rarely atony
When does primary and secondary hemorrhage occur?
Primary (early): within 24h of delivery
Secondary (late): 24h - 12 weeks after delivery
Women who deliver by primary CS have a ___% chance of subsequent CS.
90%
Women over 40 statistics:
2x as likely as moms <20yo to have a CS.
death rate 81.9 per 100k births
7.7x more likely to die of pregnancy than women <25yo
Physiologic cardiovascular changes of pregnancy peak at ___weeks.
Plasma volume expands by ____% while red cell volume increases by ____%, resulting in maternal ______.
Physiologic cardiovascular changes of pregnancy peak at 32 weeks.
Plasma volume expands by 40-50% while red cell volume increases by 20-30%, resulting in maternal anemia.
Clinical signs of maternal blood loss such as tachycardia and hypotension may not appear until _____% of circulating blood volume is lost.
Tachycardia: 15-20%
(1000-1500cc)
Hypotension w/tachycardia: 25-40%
(>2000cc)
What is the rate of uterine blood flow at term?
up to 750cc/min
(10-15% of maternal cardiac output)
3 mechanisms that control uterine bleeding at delivery:
-Contractions compress blood vessels
- Tissue factor is released from the decidua (combines with FVIIa to initiate the extrinsic clotting cascade)
- Circulating clotting factors including platelets, fibrinogen form clots at the uterine blood supply
What factors increase clotting?
What factors decrease clotting?
Increase: 5,7,8,9 and thrombin
Decrease: C, S, plasmin, antifactor Xa, antithrombin 3
What makes pregnancy a hypercoagulable state?
Increased clotting factors
Decreased anti-clotting factors
What is the shock index and its relevant cutoff?
Shock index = HR/SBP
Sensitive indicator of blood loss
>=1.4 requires urgent intervention
What is the lethal triad of excessive hemorrhage?
Hypothermia (halts coagulation)
Coagulopathy (increases lactic acidosis)
Acidosis (decreases myocardial performance)
Calcium, lactate, base deficit, temperature goals?
Ca >2
Lactate <2
Base Deficit <3
T 96.8-99.5
1 cc blood weighs ___.
1 cc blood = 1 gm
Types of peripartum hematoma?
Risk factors for developing?
Vulvar, vulvovaginal, paravaginal, retroperitoneal
Risks: nulliparity, episiotomy, forceps delivery
What are the processes in DIC?
Consumptive coagulopathy:
- Triggering event releases TF (thromboplastin), activating clotting cascade
- Platelets and clotting factors are used up > Bleeding
- Intravascular clots cause end-organ damage
Amniotic fluid embolism is also called ______.
What is the cause?
What is the maternal triad?
What are the two phases?
AFE = ASP (Anaphylactoid syndrome of pregnancy)
- maternal immunologic reaction to fetal antigens entering maternal circulation during labor/delivery, causing release of excessive catecholamines
Triad: hypovolemia, hypotension, coagulopathy
Phase 1 - cardiopulmonary phase
Phase 2 - late hemorrhagic phase (DIC)
How should oxytocin be used for active management of the third stage?
Give 10 units within 30 min (can be diluted in IVF or given IM)
Continue at 10 units per hour for 4 hours
Can give 10 - 40 units in 1000 mL saline
Up to 80 units in 1000mL can be given, but no extra benefit is shown
What is the mechanism of methergine?
Dosing?
Contraindications?
Alpha-adrenergic agonist that causes vasoconstriction
IM - 0.2mg, 2-5 min effect
PO - 0.2mg, 5-10 min effect
Intrauterine (can be transabominal) - 0.2mg, 2-5 min
AVOID IF: preeclampsia/HTN, Raynauds, scleroderma, CAD, or on protease inhibitors
What is the mechanism of prostaglandin F2-alpha?
Dosing?
AKA Hemabate / carboprost
IM or Intrauterine - 0.25mg
Given every 15 - 90 min to a max of 2 mg (up to 8 doses)
Must be refrigerated
AVOID if active asthma requiring treatments
What is the mechanism of prostaglandin E1?
Dosing?
AKA Cytotec / misoprostol
SL, PO, Rectal - 400-800mcg
How does TXA work? Dosing?
inhibits fibrinolysis by competitively blocking plasminogen activation on the surface of fibrin (clots can't break down)
Opposite of tPA, which activates plasmin from plasminogen
1g in 100mL over 10 min, can give another 1g after 30 min
What is a uterine tourniquet?
A method to reduce blood loss at the time of laparotomy
A foley catheter is tied tightly around the lower uterine segment for vascular occlusion
What is a good indicator that uterine compression sutures will be effective?
If manual compression of the uterus slows bleeding
What is an O'Leary stitch?
Compresses the uterine artery to the uterine wall just above the level of the cervix
What is a pelvic pressure pack?
A sterile tamponade device used after hysterectomy in the setting of coagulopathy, placed into the general pelvis through the open vaginal cuff
What vital signs criteria are used to transfuse prior to return of labs?
QBL 1000cc or more
HR 110 or more
BP < 85/45
Ongoing bleeding with a negative clot tube
Unstable vitals
What is the transfusion Hb level for a patient who has STOPPED bleeding?
8 mg/dL
What does the INR tell you about clotting factors?
INR 1.6 suggests that clotting factors are at 30% of their normal level, and FFP may be needed
3-6 units of FFP required to increase clotting factors by 20%
1 unit FFP raises fibrinogen 10mg/dL
What is the usual dosing of cryoprecipitate?
1 unit per 10kg body weight
Criteria for activating MTP?
Stage 3 cumulative blood loss >1500cc
2u PRBC given with persistent hemodynamic instability
Coagulopathy
Anticipated EBL 50% or more of total blood volume in 2h
Persistent bleeding after 4u PRBC
Uncontrolled bleeding with maternal hypovolemia
What is ANH?
Acute normovolemic hemodilution
1L blood drawn immediately before surgery and replaced with 1L crystalloid
Person's own blood transfused back after surgery
Point is to reduce loss of RBCs by diluting
Escape extinction works by
Not allowing the individual to escape what they were trying to avoid
An example of positive punishment
Telling someone "no" when they are about to run into the street
Punishment is the result of a stimulus following a behavior that serves to
Reduce the behavior
Differential reinforcement of other behavior (DRO) involves
Setting an interval for the problem behavior not to be displayed & reinforcing if it is not displayed
What functions of behavior involves avoiding a task or interaction?
Escape
What is the best course of action to take in the event of an extinction burst?
Continue the intervention
An example of a motivating operation
Jan is hungry, so she works harder to get crackers as a reward
Extinction of behavior maintained by positive reinforcement works by
Taking away the reinforcer for problem behavior
Spontaneous recovery refers to
Sudden reoccurrence of behavior that was extinguished
The quote "All behavior has a communicative intent" (Carr, 1977) can be best explained by the statement
Behavior always serves a purpose for the person engaging in the behavior
In which situations are differential reinforcement of low rates of behavior (DRL) used?
Behaviors that are acceptable at low rates
Differential reinforcement works by
Reinforcing only the behaviors that should be increased while removing reinforcement from behaviors that should be decreased
Extinction works by
Abruptly stopping reinforcement for problem behavior
What could ensure that an intervention involving the use of punishment is effective
Collecting & reviewing intervention data
An example of overcorrection
Marty had to clean the bathroom wall because she wrote on it
Type 1 Punishment involves
Adding a condition to reduce a behavior
An example of negative punishment
Paying a speeding ticket
What is the difference between differential reinforcement of alternative behavior (DRA) & differential reinforcement of incompatible behavior (DRI)?
The reinforcement behavior selected in DRA does not have to be incompatible with the problem behavior
An example of type 1 punishment
When Austin hits his sister, his mother reprimands him & he doesn't hit her anymore
What are common reasons or "functions" of behaviors?
Gain attention, gain items, escape, & sensory stimulation
Variables that play a role in the frequency & intensity of behavior or the effectiveness of reinforcement for behaviors are called
Motivating Operations
An example of a behavior that could be placed on a differential reinforcement of incompatible behavior (DRI) plan?
Rosa sings instead of screaming
What is extinction?
Is a behavior reduction procedure that works by abruptly stopping reinforcement for a previously rewarded behavior
An example of escape extinction
When the individual refuses to do a task, the task is kept near him until he attempts it
A definitive diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease can be made by:
Examining brain tissue on autopsy.
Dementia cause by Alzheimer's disease is:
Irreversible.
Which condition, if treated, could reverse the course of dementia?
Depression.
Which of the following would be an early sign of dementia?
Forgetting a conversation from earlier in the day
True or False: The FDA has NOT approved any medications for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
False.
When should antipsychotic medications be used in a patient with dementia?
When symptoms are severe or cause the patient distress
One sign of typical aging is:
A slowing in the learning of new information.