OCR A 6.1.3 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
carboxylic acids solubility
-dissolve in polar solvents
-they can H bond with water molecules
-larger the hydrocarbon part less soluble
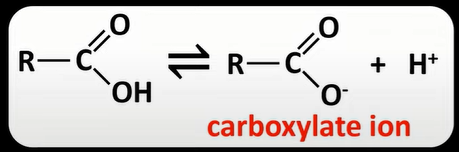
carboxylic acid dissociation
-weak acids: dissociate partially to form H+ ion and a carboxylate ion
carboxylic acid + carbonate
forms
-CO2
-H2O
-salt

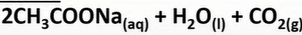
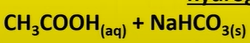
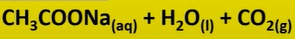
carboxylic acid + base
-salt and water
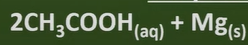
carboxylic acid +metal
-salt + hydrogen


carboxylic acid + metal oxide
water + salt



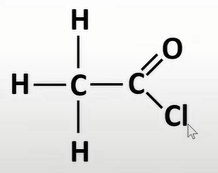
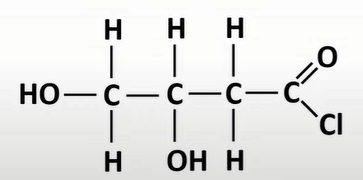
acyl chlorides
-func grp: -COCl
-oyl chloride


acyl chloride reactions
-when reacted Cl is replaced
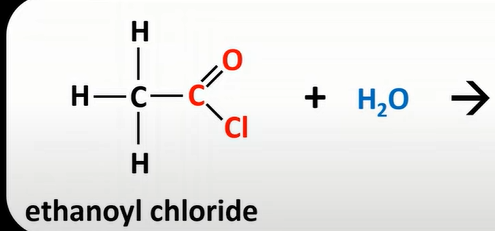
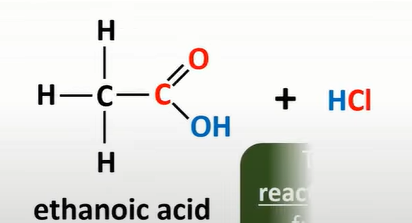
water + acyl chloride
HCl and acid
nucleophilic addition/elimination
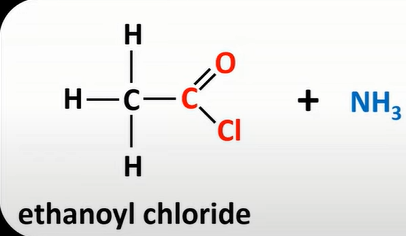
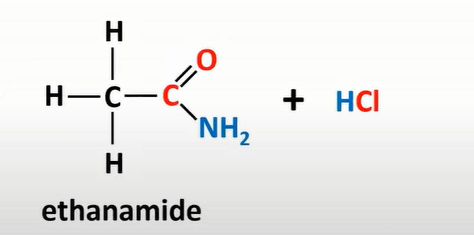
acyl chloride + ammonnia
amides +HCl
nucleophilic addition/elimination
acyl chloride + alcohol
produce esters + HCl
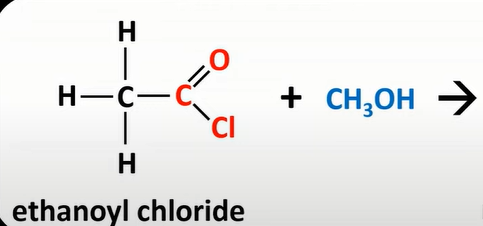
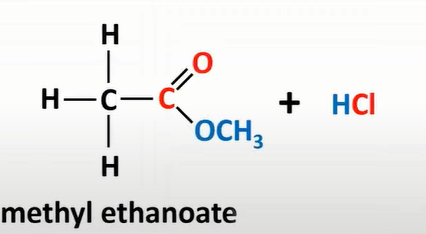
acyl chloride + primary amine
n-subd amides + HCl
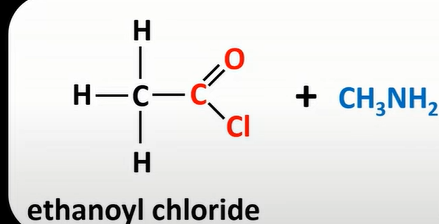
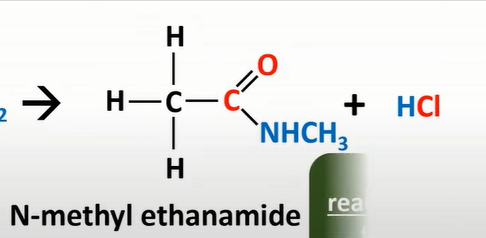
acid anhydrides
molecule made from 2 carboxylic acids that are same
naming acid anhydrides
from carboxylic acid - acid + anyhydride
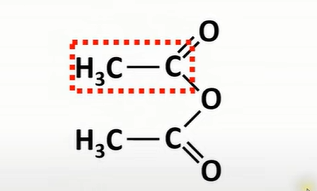
name

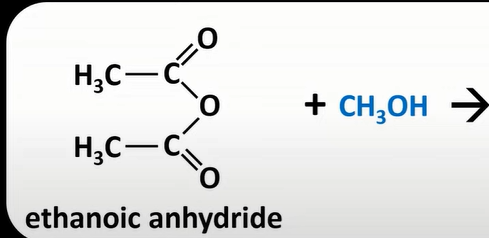
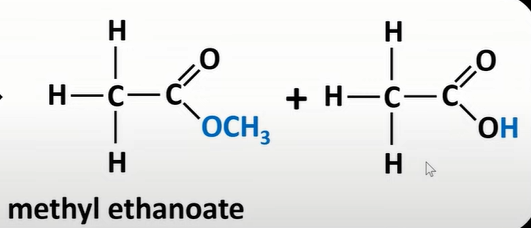
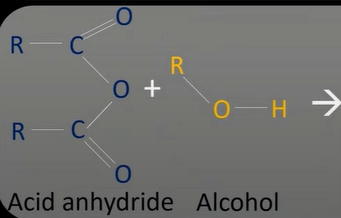
acid anhydrides + alcohol
esters + carboxylic acid
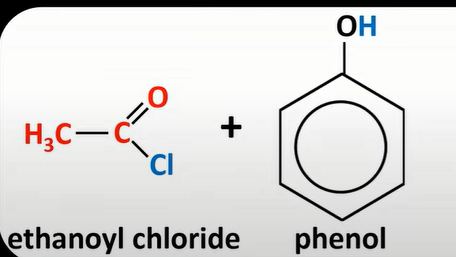
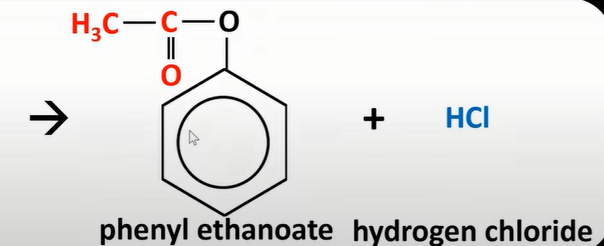
acyl chloride + phenol
ester + acylnoate
alcohol + carboxylic acid
ester
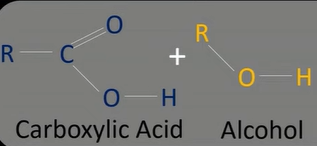
esterification
-carboxylic acid/acid anhydride + alcohol
-sulphuric acid catalyst
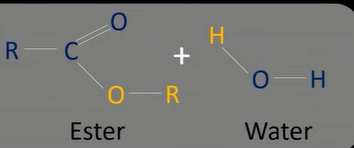
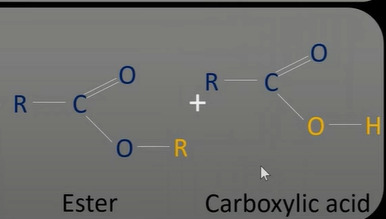
ester hydrolysis
-split using water
-sped up using an acid or base
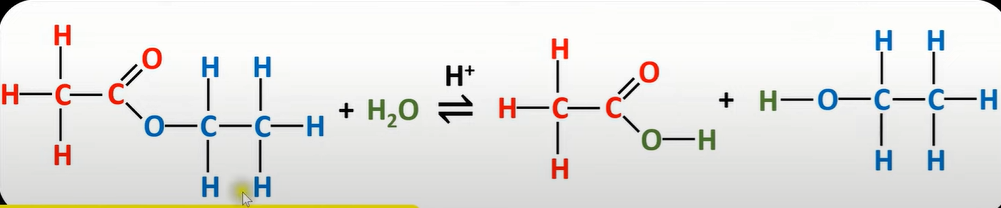
acid hydrolysis
-use dilute acid to split into alcohol and carboxylic acid
-use sulfuric/ hydrochloric acid
-under reflux
acid hydrolysis reaction
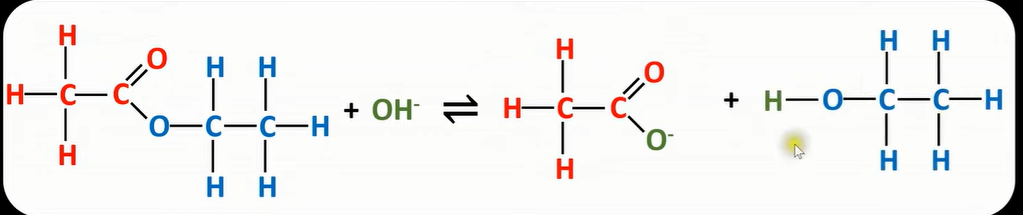
base hydrolysis
-use dilute base(sodium hydroxide)
-forms carboxylate ion & alcohol
-under reflux
base hydrolysis reaction