Geometry CONTENT EXAM
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Acute Angle
Vertex Connected by two rays
Obtuse Angle
Greater than 90 less than 180
Reflex angle
Greater than 180 but less than 360
Supplementary Angles
90 + 90
Complementary Angles
Two angles that sum up to 90
Adjacent Angles
Share 1 vertex
Corresponding Angle
Same position along the same parallel line
Vertical Pairs
angles are opposite each other and share the same vertex
Finding the sum of the interior angles of a polygon
180(n-2)
How many diangonals across a polygon formula
n(n-3)/2
Kite
2 pairs of congruent sides
Rhombus
all 4 sides are congruent
Regular Pentagon
All Sides are congruent
Apothem
Center to the opposite side
Finding the Area of a Pentagon
1/2 ap
Similar Triangles
Same shape and Proportional
Corresponding Angles are
Congruent
Trapezoids has
1 pair of parallel sides
Area of a Trapezoid
1/2h(b1+b2)
Area of an Isoceles Trapezoid (2 sides Congruent)
Mh
Area of Rhombus
1/2 D1D2
Parrallelgram
Parallel sides are congruent
Area of a Rectangle
l * w
Perimeter of a Rectangle
2w+2l
Area of a Triangle
1/2 bh
Fast Area of an Equilateral Triangle formula
S^2sqrt3/4
If you have no height and given all 3 sides, use the semiperimeter formula for the area of a triangle
sqrtS(S-a)(S-b)(S-c)
Altitude of a Triangle
a perpendicular line segment from a vertex to the opposite side
Orthocenter
Where all 3 altitudes meet
Obtuse Triangle
only 1 obtuse angle
Centroid
The point where all 3 medians of a triangle meet
Acute Triangle
where all 3 interior angles are less than 90
Pythagorean Theorem
a^2+b^2=c^2
What makes triangles congruent
SAS
ASA
AAS
SSS
HL
Concentrix Circle
Circles share the same center
Area of Circle
pi r^2
Circumference of a circle
Pi d
Circumscribed
Polygon inside a circle
Central Angle
Same angle inside then same on the out
Inscribed Angle is
2 times the angle
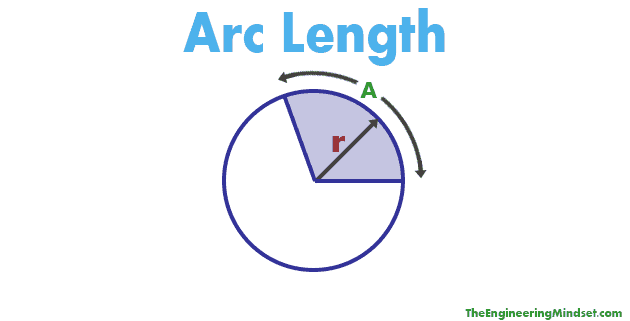
Arc length
outer angle/360 pi d
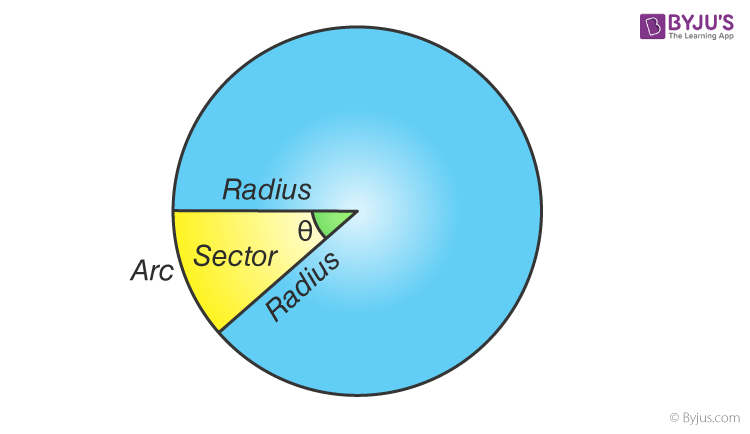
Area of a sector
angle/360 pi r^2
Right triangles inscribed in a semicircle are
always right
Chord Chord Angle Formula
1/2(arc 1 +arc2)
Secant Secant/Secant Tangent
1/2(difference in arc)
Tangent Tangent (snow cone angle)
180=x+angle
Volume of Sphere
4/3 pi r^3
Surface Area of Sphere
4 pi r^2
Volume of Cylinder
pi r^2 h
Surface Area of Cylinder
2pir^2+2pirh
Volume of any Prism
pi r^2h
Surface Area of any prism
2B+2Ph
Volume of a cone
1/3 pi r^2 h
Surface Area of a Pyramid
#T 1/2bh+B
Circumcenter
the point where the three perpendicular bisectors of a triangle's sides intersect
Incenter
Where all angles are bisected
Formula for an ellipse
x^2/a^2 + y^2/b^2=1
Find the FOCI
a^2-b^2=c^2
Diagonals of a square are
Perpendicular Bisectors
Diagonals on a rectangle are not
90 degrees
The dashed line on the parabola is called?
Directrix
If the parabola is facing upwards what is the point that the graph is “looking at”
Focal Point
Standard Formula for a parabola with vertical axis of symmetry and a vertex at
(x-h)²=4p(y-k)
Compound Events
2 or more independent events
Dependent Events
Rely on the outcome
Mutually exclusive
events that cannot occur at the same time
Theoretical Probrability
In theory you should get something
Objective Probability
Formulaic
Subjective
Based on your own interpretation
AUB
Bring together
A∩B
What do they share
P(AUB) =
P(A) + P(B) - P(A∩B)
P(A|B)
P(A∩B)/P(B)
Odds in Favor
number of times event will occur / number times event will not occur
Odds Against
Not occur/ will occur
Ordinal Data
numerical order
Nominal Data
You cant put them in numerical order
Quantitative
measurement
Qualitatitve
Cant be measured using numbers
Discrete Data
Scatter plot, specific values
Continous Data
any value in the given range ex: temperature
Primary Data
Raw Data
Secondary Data
analyzed Data
Population
group/or collection everything
mean
average
mode
most often
median
middle
Range
Largest - Smallest
Permutations
nPr
Combinations
nCr
Excentrix Formula
e=c/a
Elispe centered at the orgin
x²/a² + y²/b²=1
Hyperbola centered at the origin
x²/a²-y²/b²=1
Airtmetic Sequence
a_n=a_1+d(n-1)
Geometric
a_n=a_1( r)^{n-1}
vertical asymptote
set the denominator equal to zero
horizontal asymptote
compare the degrees of the numerator and denominator of a rational function
N<D: y= 0
N=D: Then the fraction
N>D: none
Percent Error
Actual-Find/Actual
Percent Change
Difference/Original *100
Compound Continous Fomrula
Pe^{rY}