urine crystals
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
find in urine sediment?
crystals
sperm
casts
bacteria
white blood cells
red blood cells
dirt
yeast
normal red blood cells on sediment slide
<5RBCs/ field
normal white blood cells in sediment
<5WBCs / field
pyuria - inflammation, infection, trauma, neoplasia. More then 5.
presence can be contamination of the sample.
normally seen with bacteria
epithelial cells in urine sediment
transitional epithelial cells - lines the urethra and bladder -common grainy cytoplasm, central nucleus
squamous epithelial cells - free-catch/ expressed - off skin
neoplastic epithelial cells - transitional cell carcinoma
neoplastic squamous cells- squamous cell carcinoma - look weird as dividing quick.
NEOPLASTIC = INDICATES CANCER
Casts in sediment
mucoproteins
hyaline - parallel sides, rounded ends, few is normal.
epithelial - entrapment of sloughed cells.
granular - degenerated epithelial cellular casts, few is normal.
waxy - degeneration of granular.
RBC and WBC casts - always abnormal
fatty - diabetes mellitus
Lots of casts =
renal damage
can be a sign a toxin has damaged the tubular cells in kidney badly and that they have fallen off and formed casts.
If bacteria in a cysto sample
infection
Bacteria in a free-catch sample
contamination?
common bacteria in urine
rods and cocci
confirm with gram stain or aerobic culture
Yeasts
contamination usually
round/ oval
colourless
infection - cysto
seen if log term antibiotics and immunosuppression
poor immune system
fungal hyphae
commonly due to contaminants overgrowth
very rare
parasitic ova
contaminant from rectum
capillaria plica - in UTI system - rare signs - confirm with cysto
lipids
common
white ring around
common in cats
sperm
males/ recently bred females
move on slide
plant material
debris in voided samples
Struvite
very common
dogs, cats and ruminants
low levels are normal in SA
ALKALINE
long rectangular crystals
caused by bacterial infections
can form in storage
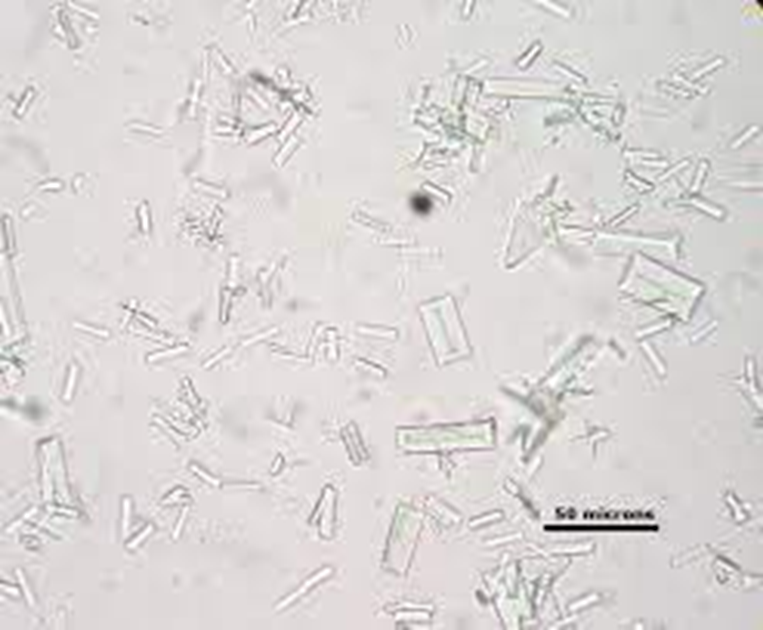

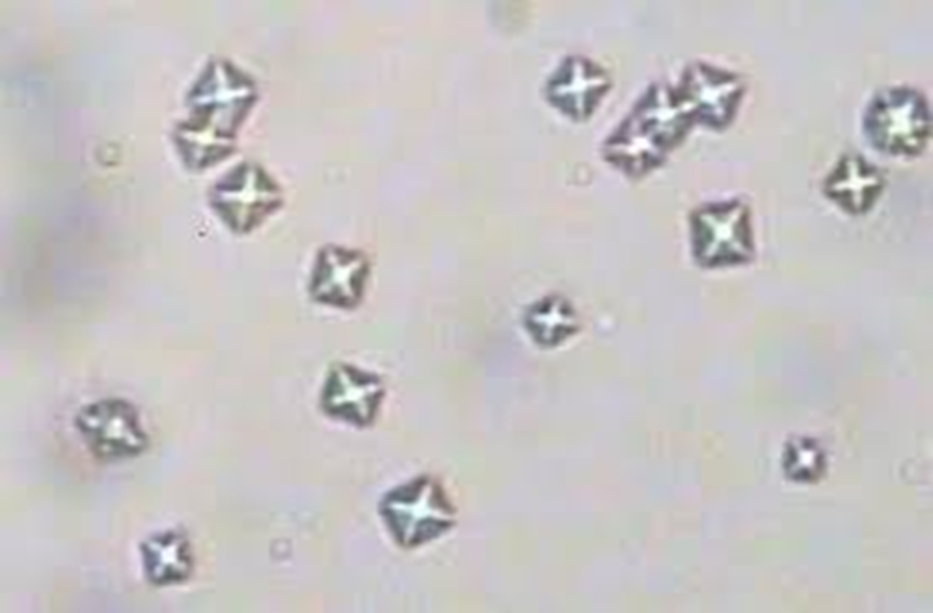
calcium oxalate
less common
dogs and horses (common in healthy horses)
ACIDIC
forms when animals have inadequate fluid intake
effected by cold
affected by time - can develop over time.
increased risk of uroliths
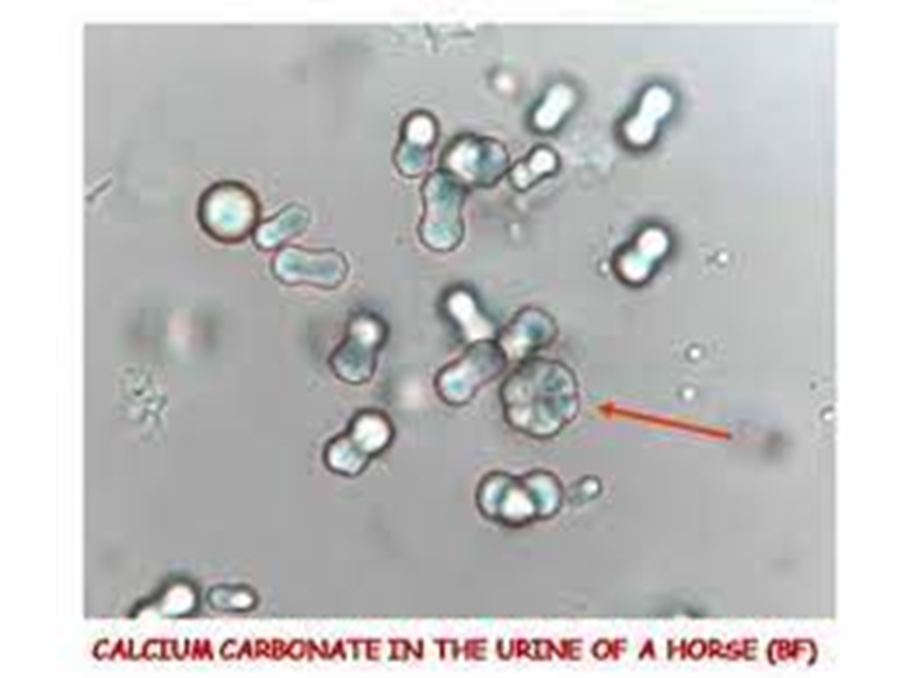
calcium carbonate
common in horses
ALKALINE
caused by prolongued urine retention and calcium in diet.
develop into uroliths
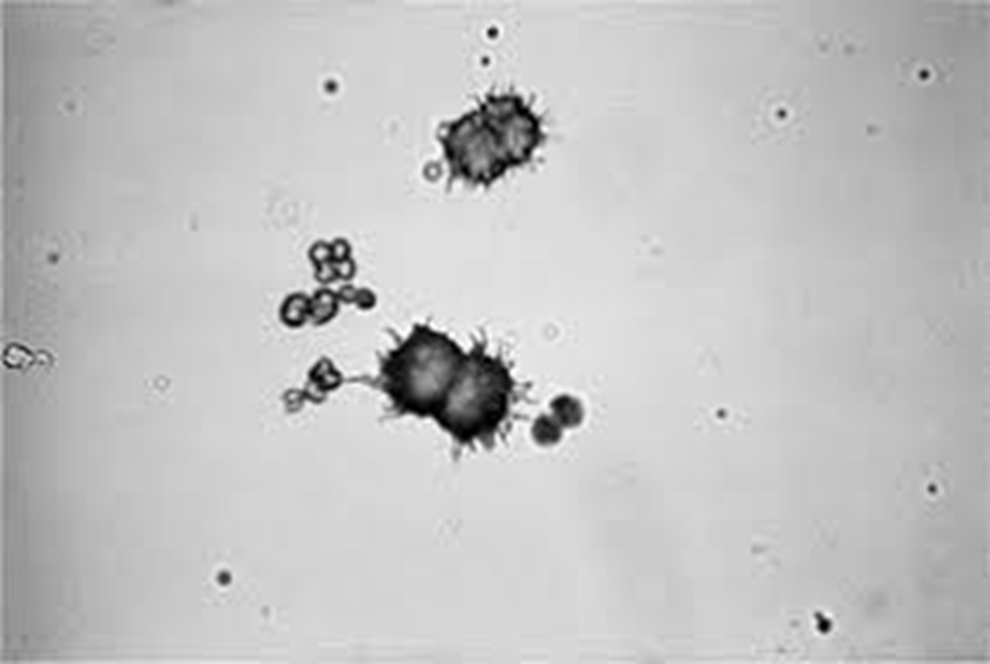
ammonium urate
common in canine and feline
normal in dalmatians
common in birds and reptiles
Liver disease
ACIDIC
Affected by hot temperatures
not effected by a delay
caused by increase in pH, liver disease, high protein in diet.
patients with porlo-systemic shunt.
uric acid
common in dalmations - can’t convert uric acid to allatoin
congential liver shunts
ACIDIC
abnormal
high temp = crystallisation, low temp= minerals suspended
don’t develop over time
cystine
ACIDIC
dogs, rarely cats
patients with renal dysfunction
not normal
managed through diet
proximal tubular defect in amino acid resorption
bilirubin
normal in dogs
bilirubinuria
never in cats
liver disease, haemolytic anaemia breaking down the RBC’s or bile duct blockage
not effected by temp or time
ACIDIC
struvite uroliths
associated with infection in dogs
more in male cats
calcium oxalate uroliths
monohydrate more common in Male and obese in dogs
dihydrate in male and obese in cats
urate crystals
uncommon, dogs treated with allopurinol
more male
cystine uroliths
male, young/ middle ages terriers
equine uroliths
calcium carbonate
crumble easily
increased risk - prolonged urine retention, increased calcium. uric acid
reduced risk - lower calcium in diet