eye diseases
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what does the eye detect
different wavelength and patterns of light
what does light entering the eye trigger
photochemical reaction in rods and cones at back of retina
what determines the pattern of vision loss
the faulty region/ cell type in the retina
different causes of blindness
diabetic retinopathy, residual causes of vision loss, glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, cataract, undercorrected refractive error, degeneration macular and posterior pole
What is age related macular degeneration
multifactorial disease with demographic environmental, and genetic risk factors contributing to disease development
what does age-related macular degeneration vision look like

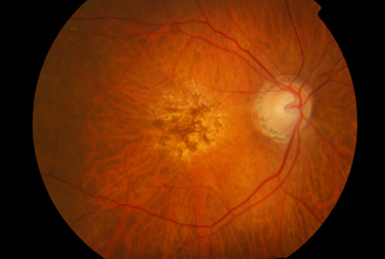
what does retinitis pigmentosa vision look like
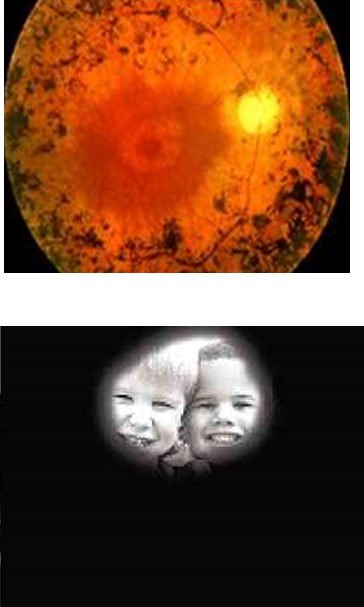
what does acquire trauma vision look like
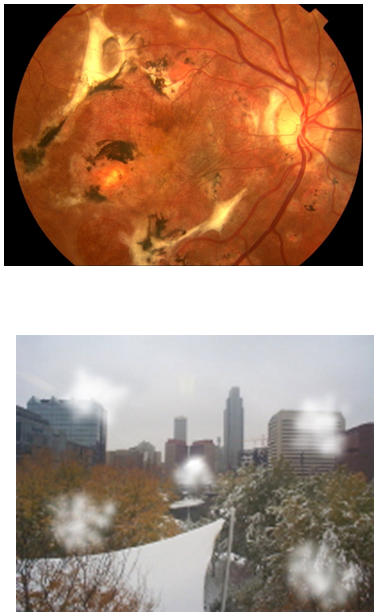
risk factors of AMD
age, smoking, diet and exercise
what does early AMD imaging include
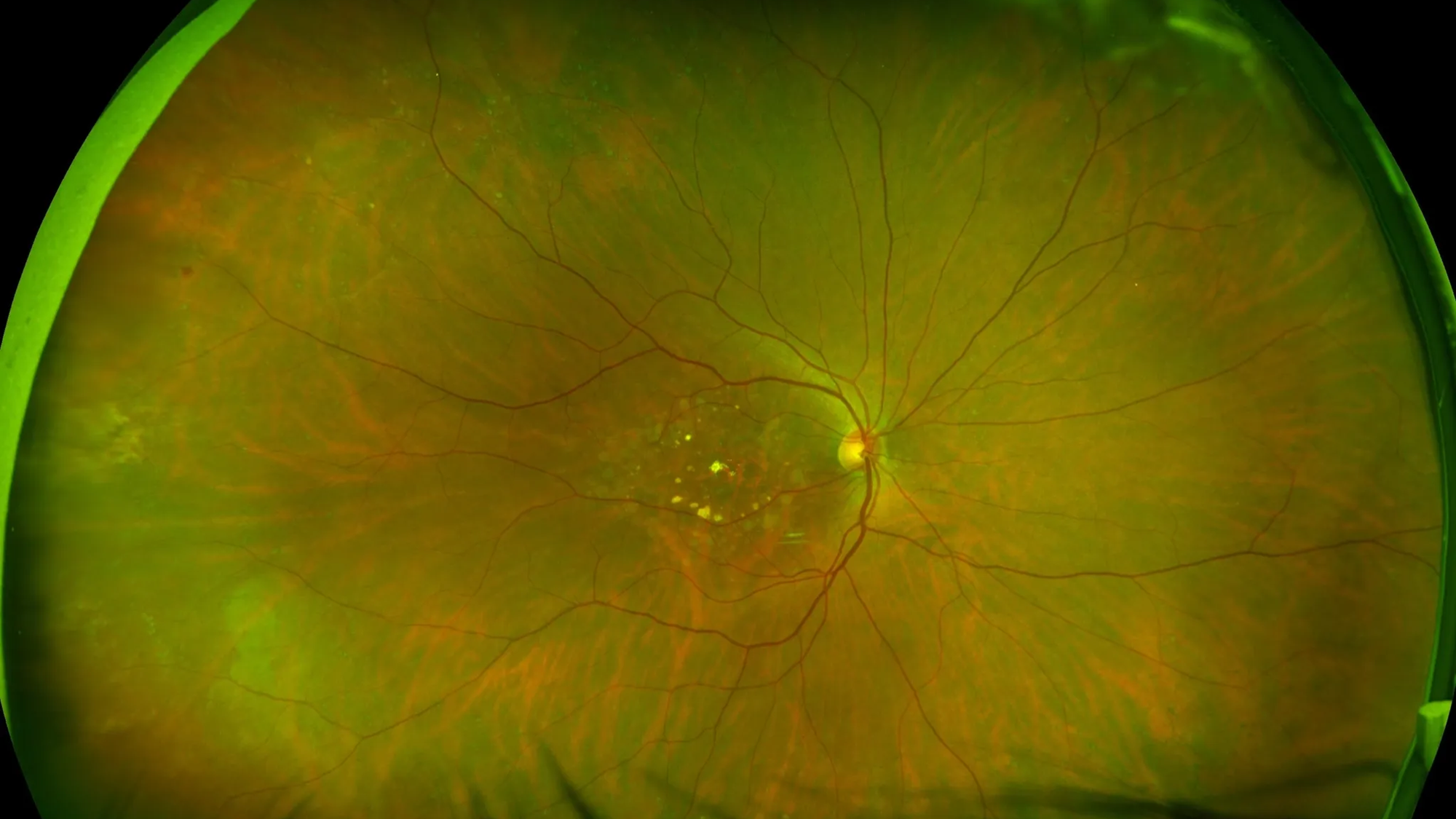
yellow spots- lipids, hypopigmented-scarring, peripheral degeneration
what is drusen
focal deposits of extra-cellular debris (lipids), yellow-white mound-like elevations under the RPE
The size of drusens at intermediate AMD
(>125um) migrating retinal pigment epithelium cells and subretinal drusenoid deposits (reticular pseudodrusen)
Treatment for early/intermediate AMD
Current trials- AREDS…
•No direct evidence that patients with early AMD should take lutein / multivitamin supplementation
•Dietary advice: Plenty of fruit, leafy green vegetables
•For those with the following in at least one eye, consider supplementation with a preparation based on AREDS 2 study: •Extensive, intermediate-sized /large drusen
•Geographic atrophy
•Advanced AMD in either eye
Consideration of treatment
Is there definitely macular neovascularization present? (new vessels)
NICE: Vision has to be worse than 6/12- but not as bad as 6/96 (governing body who determines who gets which treatment because of money)
Discussion with patient about risks/benefits and overall quality of life impact
The types of antiVEGF treatments available
ranibizumab, aflibercept, bevacizumab, farucimab and brolucizumab
How does Kd value affect receptor binding
The smaller the Kd value, the lower the concentration of drug required to achieve 50% receptor binding; therefore, the greater the binding affinity of the drug for its receptor
symptoms of wet AMD
distortion or sudden deterioration of vision
treatment of wet AMD
anti-VEGF
What is dry AMD (geographic atrophy)
no fluid at the end of the end, fibrosis, persistent scarring and atrophy of the retina. Nothing to perceive light. NO treatments. Loss of photoreceptors, retinal pigment, epithelium and choriocapilaris
What is unifocal
one spot of atrophy
Current complement therapies
Pegcetacoplan: blocks complement C3. Has FDA approval in USA since Feb 2023, awaiting EMA/NICE approval
Avacincaptad Pegol: blocks complement C5, USA FDA approval granted August 2023, awaiting EMA/NICE approval
Requirements for anti-complement therapies to reduce the rate of progression of GA
People needed to already have geographic atrophy at the start of the trials. They were not permitted to have had previous wet AMD in the treated eye.
What is the complement system
innate immunological network and helps with the detection and removal of pathogens
What part of the chromosome is responsible for AMD
1q31 which carries the gene for complement factor F (CFJ) and 10q26 which includes the ARMS2/HTRA1 genes
Which antiVEGF drug targets all VEGFR-1 ligands
afibercept
What does afilbercept target
VEGF and PIGF
what does VEGF and PIGF play a role in
in pathological vascular permeability, macular oedema, inflammation, and neovascularisation in retinal diseases