Topic 7 - Fields
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What is a field?
a region in space in which a non-contact force is exerted on an object
How can a field be described?
- a diagram showing field lines that indicate the direction of the field
- a mathematical expression to calculate the magnitude of the field
What is Coulomb's law?
The force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
What is Coulomb's Law?
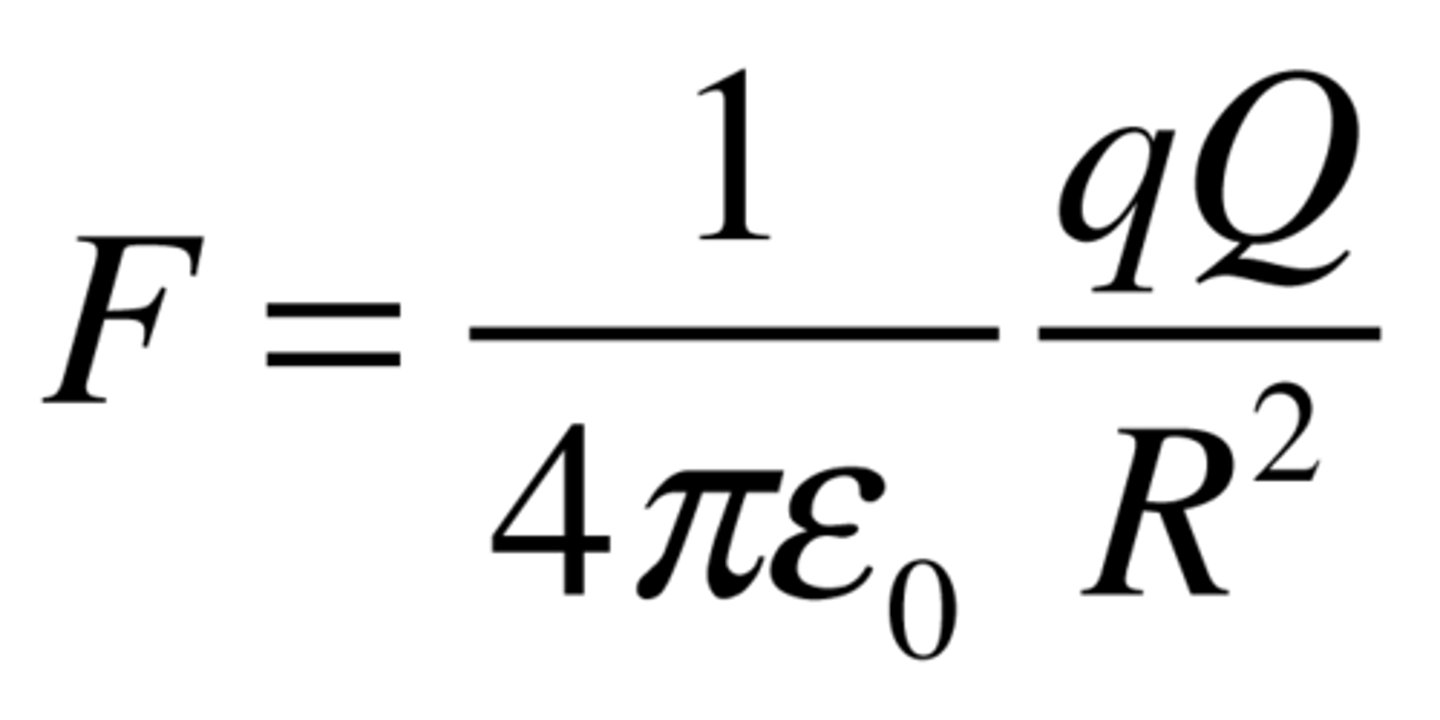
What is an electric field?
The region of space in which a an electrostatic force is exerted on a charged object.
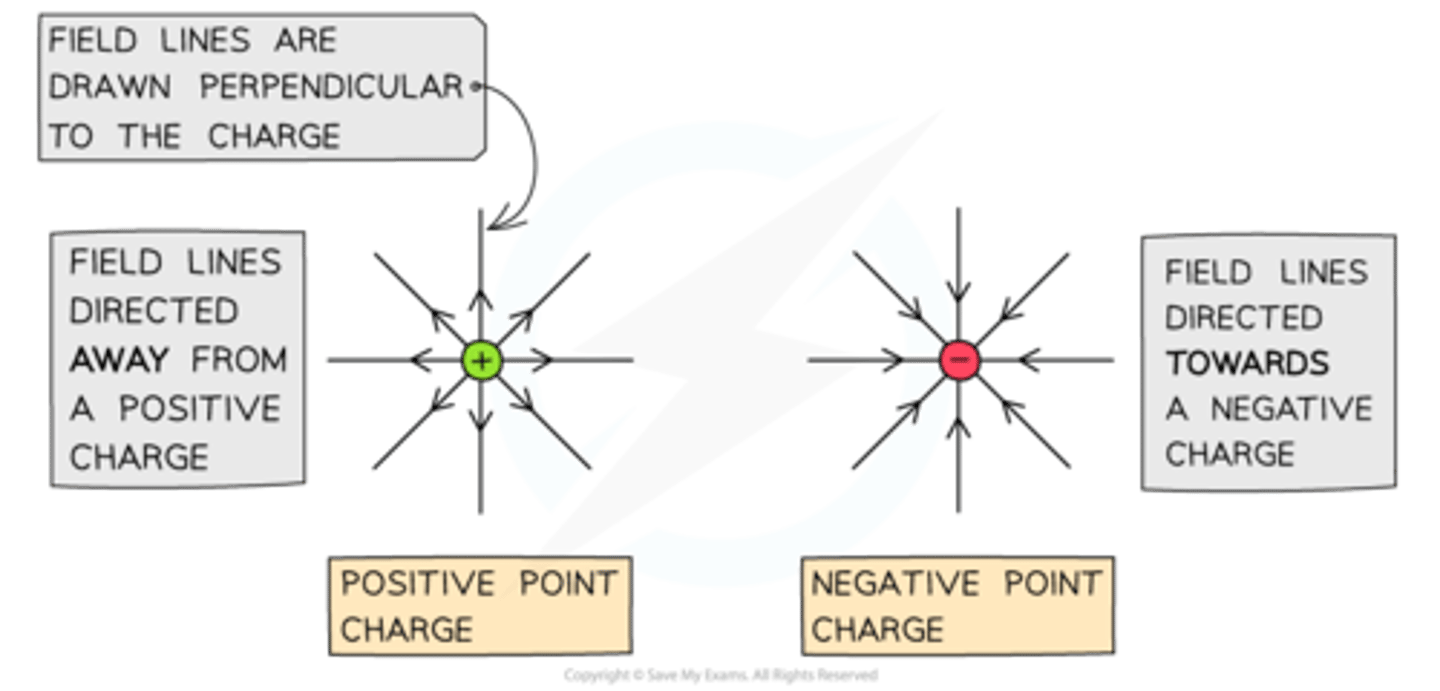
Draw an electric field around a point
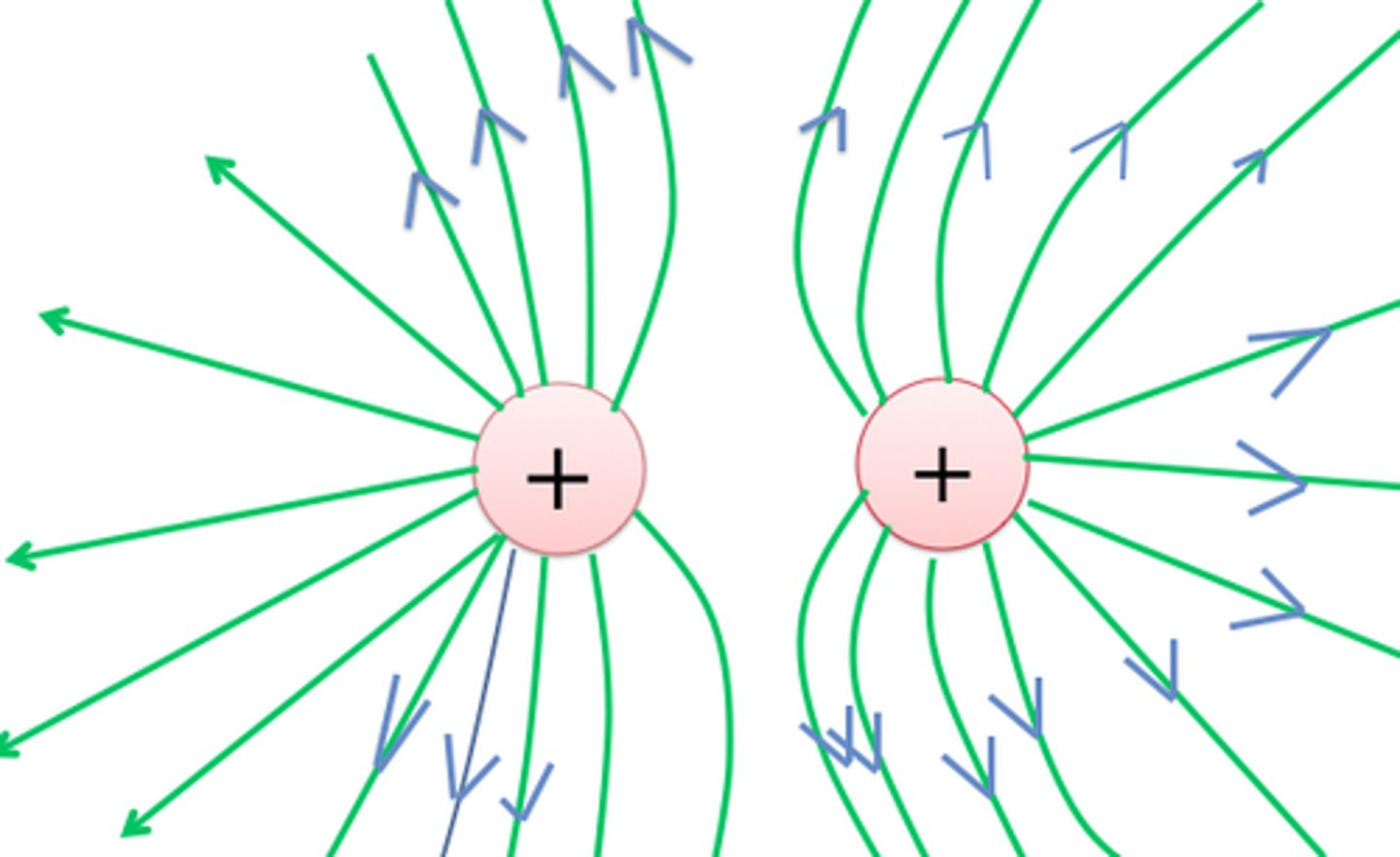
Draw the electric field between two like charges
Draw the electric field between two opposite charges

Draw the electric field between two parallel plates of opposite charge
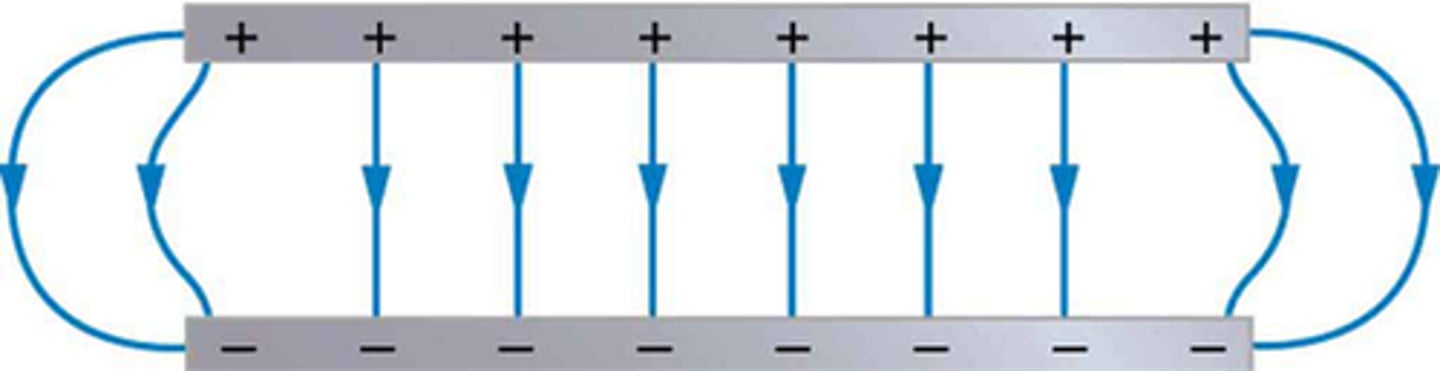
What is meant by a uniform field?
One where the field lines are show as being parallel and evenly spaced
What is electric field strength (E) ? Formula?
the force on unit positive charge placed at that point in the field
E = F/Q
What is the formula for electric field strenght for a radial field around a point charge or spherical object?
E = 1/(4πε0) x (Q/r^2)
where ε0 is the permittivity of free space
What is electric potential?
The work done on moving unit positive charge from infinity to that point. It is a scalar, but can be positive or negative.
What is the formula for electric field strength for a uniform field?
E = V/d (d = distance between plates, V = potential difference, E = electric field strength)
What are the units for electric field strength?
NC^-1 or Vm^-1
Describe Milikan's Oil Drop Experiment
- oil drops become statically charged
- one drop can be held stationary in an electric field when the upwards force due to the field balances the weight acting downwards
- the weight can be determined by measuring the size of the drop and its terminal velocity
EQ = mg
Describe a beam of electrons in a uniform field?
- electrons are deflected towards the positive plate
- the force is constant because there is a uniform field
- F = EQ so if the field is uniform, the force is constant
- a = F/m, so the acceleration is constant.
- it's kind of like projectile motion
Define electric potential
the electric potential at a point is the work done in moving unit positive charge from infinity to that point
it is a scalar; + or - signs are important not to show direction, but because it can be positive or negative
What is the formula for electric potential energy?
QV
What is the formula for electric potential around a point charge?
V = 1/4πε0 x Q/r
What are the units of potential?
JC^-1 or V
Define potential difference
the pd between two points is the energy needed to move unit charge between the points
Describe an equipotential surface.
- all points have the same potential so there is no p.d. between 2 points on the surface
- equipotential surfaces are always perpendicular to field lines
- around a point charge equipotential surface are concentric spheres, but appear as concentric circles on a 2D diagram
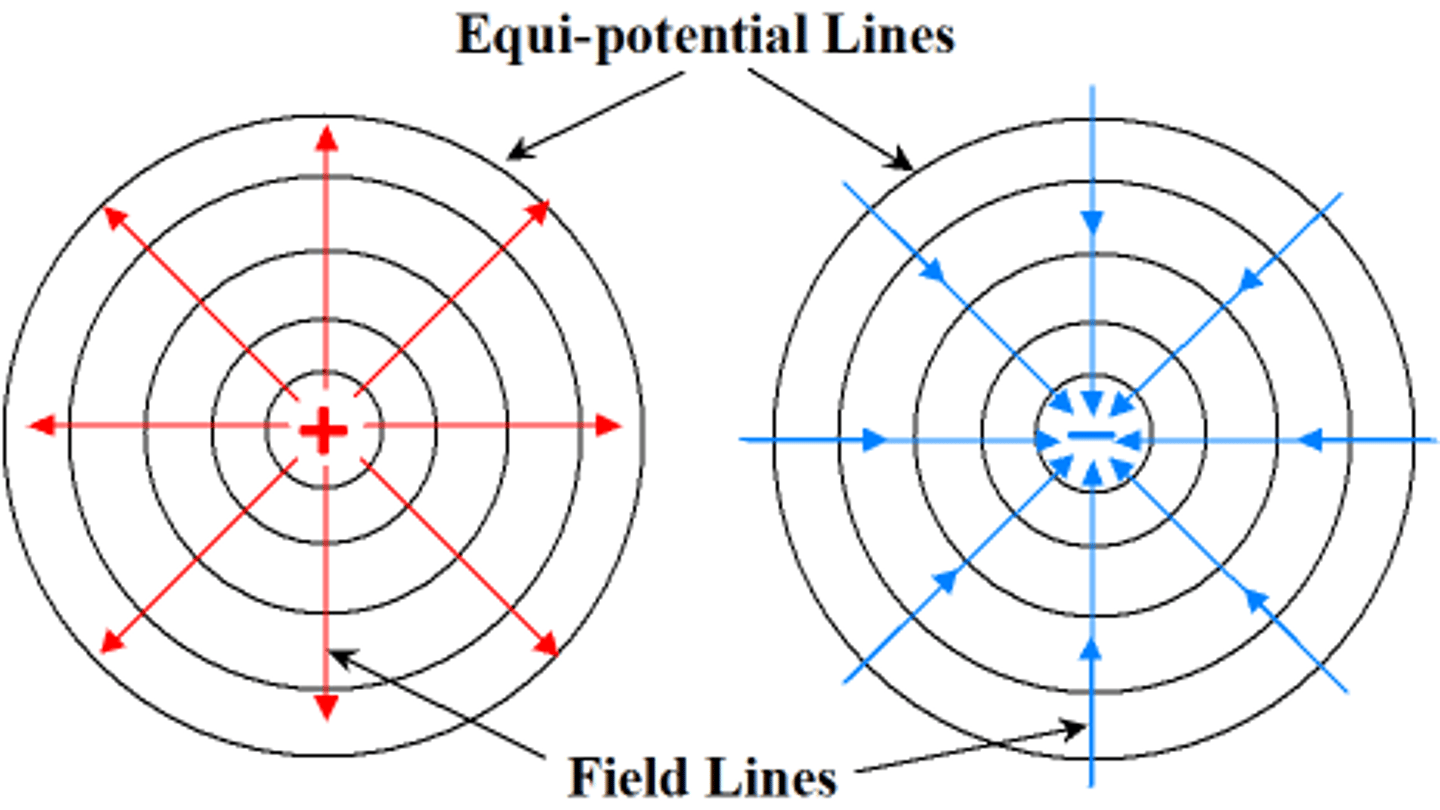
Formula for magnitude of field strength?
E = ∆V/ ∆r
On a graph of potential against distance, how can you find E?
negative the gradient
On a graph of E against d, how can you find the change in potential?
the area under the graph
What is a capacitor?
A capacitor consists of two metal plates separated by a dielectric.
What is capacitance?
the amount of charge stored on the capacitator for every 1.0V of potential difference.
What are the units for capacitance?
Farads (F)
What happens to a capacitor when connected across the terminals of a battery?
One side gains a positive charge and the other side gains a negative charge.
What is a dielectric?
An insulating material placed between the capacitor plates
What is the purpose of a dielectric?
To increase the capacitance of a capacitor
How does using a dielectric increase capacitance?
- between the oppositely charged plates there is an electric field
- we know E = V/d, and so V=Ed, where V is the potential difference across the capacitor and d is the distance between the plates
- dielectrics reduce the magnitude of the field, thus reducing the p.d. between the plates
- this increases capacitance as C = Q/V
How do dielectrics reduce the magnitude of the field between capacitor plates?
- the polar molecules in the dielectric rotate so the positive side is towards the -ve plate and vice versa.
- therefore, the polar molecules produce their own electric field in the opposite direction to the one between the capacitpr plates
- this field also has a smaller magnitude than the one between the capacitor plates
- therefore the resultant field between the plates is reduced
What is the increase in capacitance when a dielectric is added? (isolated capacitor)
The capacitance increases by factor εr, which is the relative permittivity of the dielectric.
There is no change in the charge stored, as the capacitator is not connected to a circuit.
What happens when a dielectric is added to a capacitor at a constant p.d.? (e.g. connected to a battery)
- capacitance increases
- charge will be transferred from the circuit to the capacitor since Q = CV and C has increased
- when C is increases, then V decreases
For a graph of Q against V, how can you find the energy stored in the capacitor?
the area under the graph
Why must work be done to remove a dielectric?
Because there is electrostatic attraction between the capacitor plates and the dielectric
What happens to energy stored on an isolated capacitor when the dielectric is removed?
- the capacitance decreases
- total charge stays the same bc it's isolated
- since E = Q^2/ 2C, the energy stored will increase by a factor εr.
- the p.d. increases by the same factor
What happens to the rate at which charge is lost as a capacitor discharges?
the rate decreases: it loses charge exponentially
Explain the decreasing rate of loss of charge for a capacitor?
- as current flows, the charge Q stored on the capacitor decreases from its inital value Q0
- as the charge decreases, so does p.d., as V = Q/C
- the current also decreases as I = V/R , and current is the rate of flow of charge.
Draw a graph of Q against t for a capacitor discharging, and for charging.
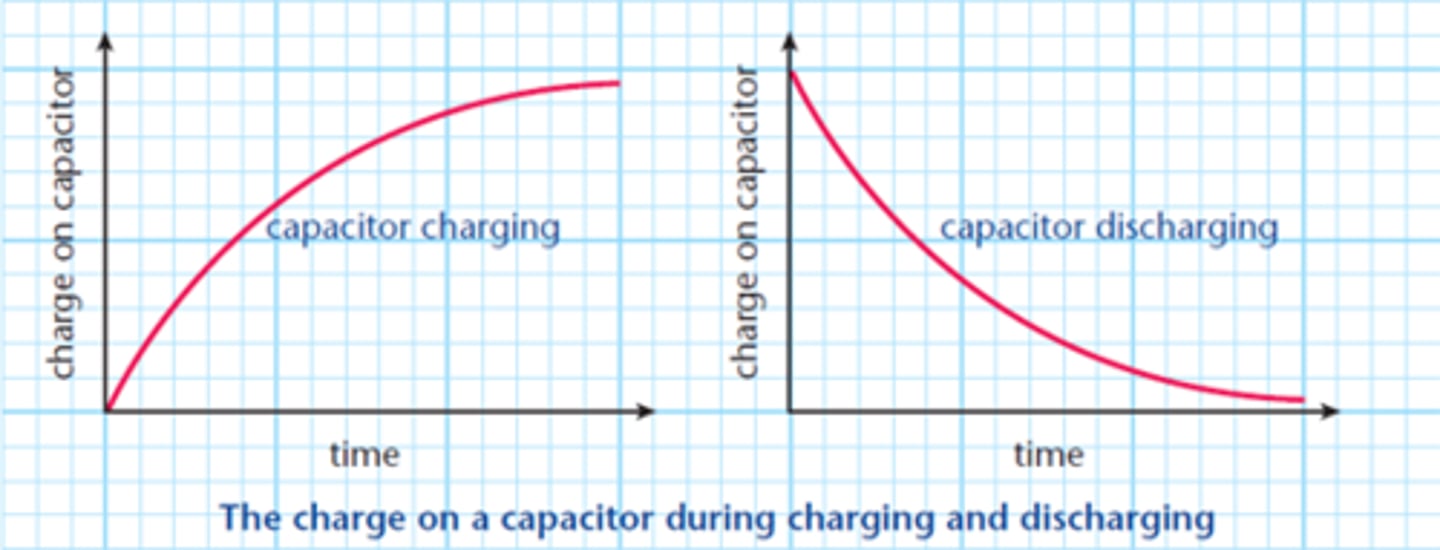
What is the gradient of a Q against t graph equal to?
the current: I = Q/t
What are the formulae for p.d. and current as a capacitor discharges?
V = V0 x e^(-t/RC)
where V0 = inital pd, R = resistance, t = time and C = capacitance
You can replace V and V0 with I and I0 respectively to get the equation for current
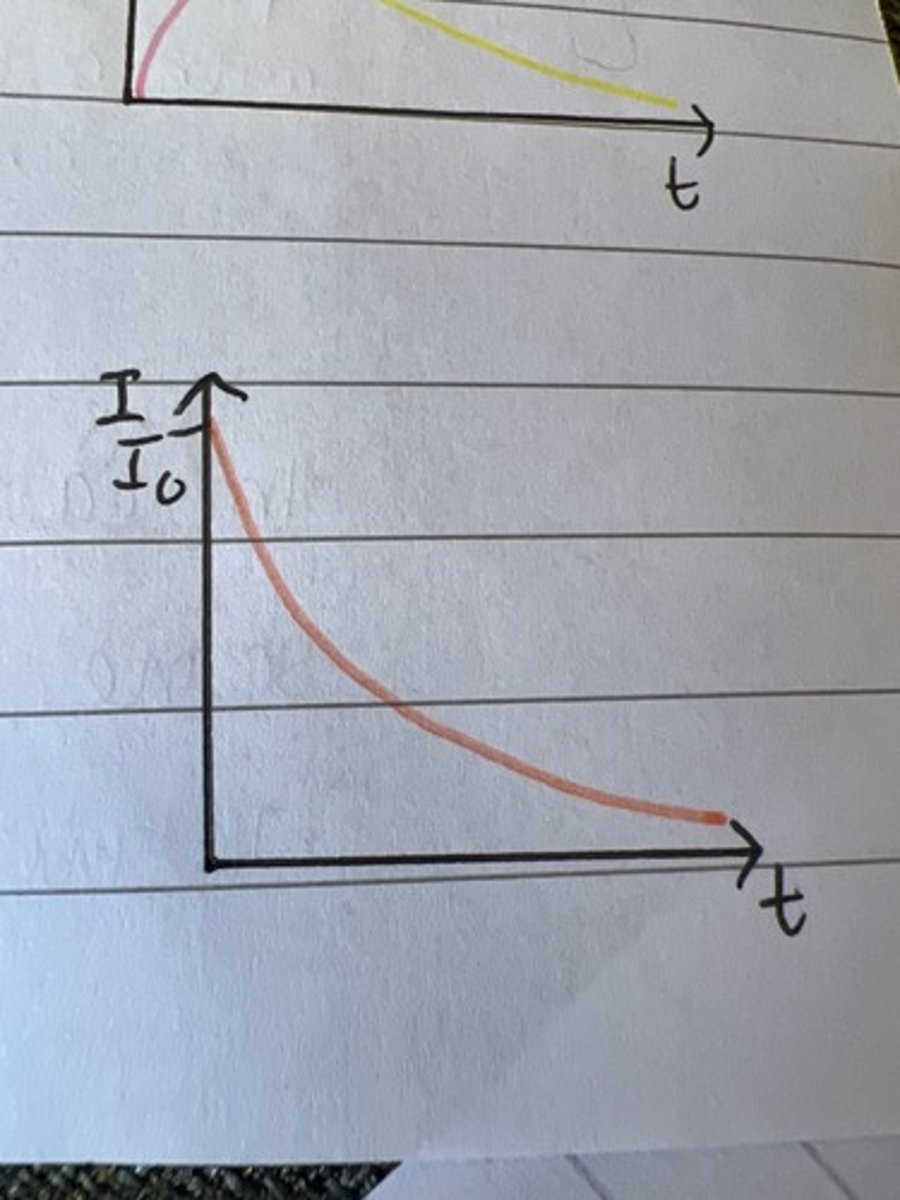
Draw the graphs for current and p.d. as a capacitor discharges.
they're the shape as the Q v t graph

What is the time constant?
RC in the formula V = V0 x e^(-t/RC)
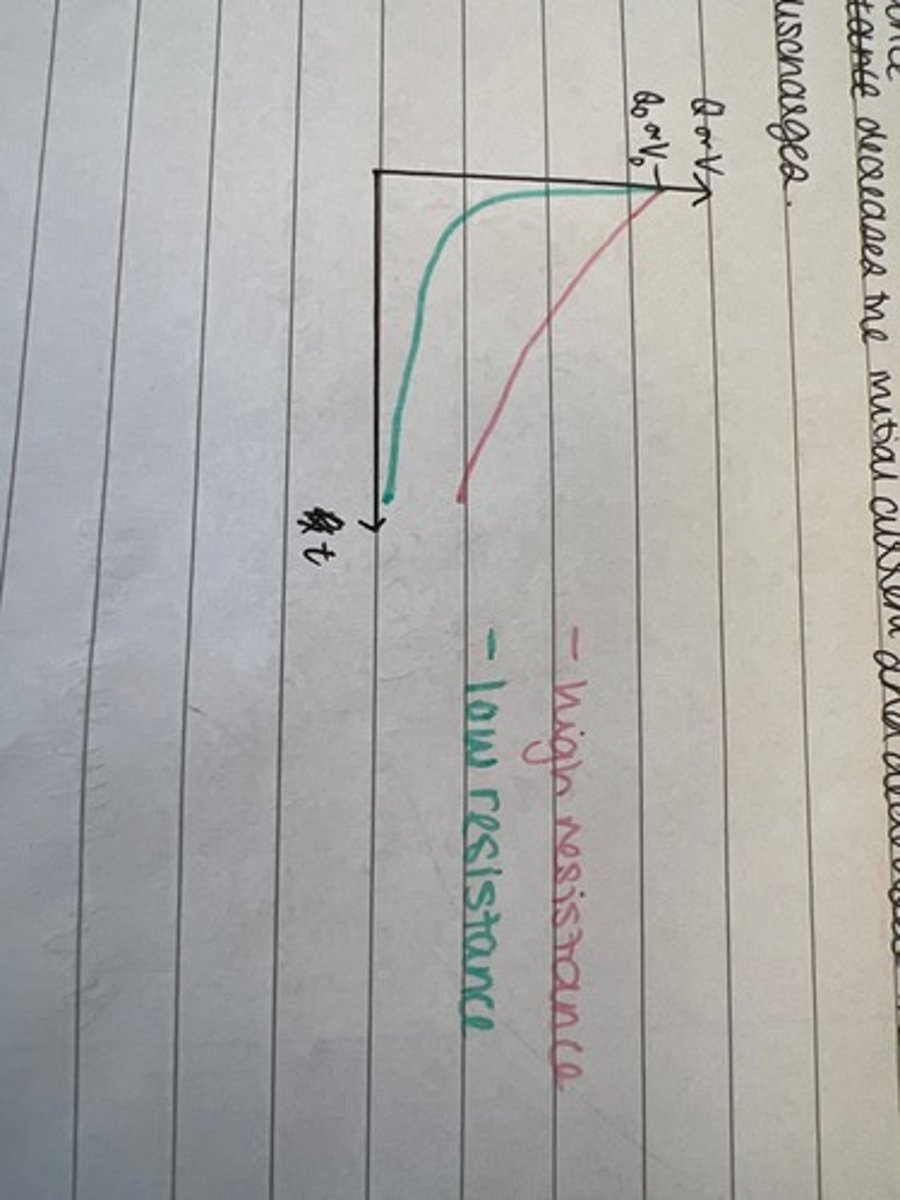
How does increasing resistance change discharging a capacitor? Draw a graph
- decreases the initial current
- decreases the rate at which the capacitor discharges.
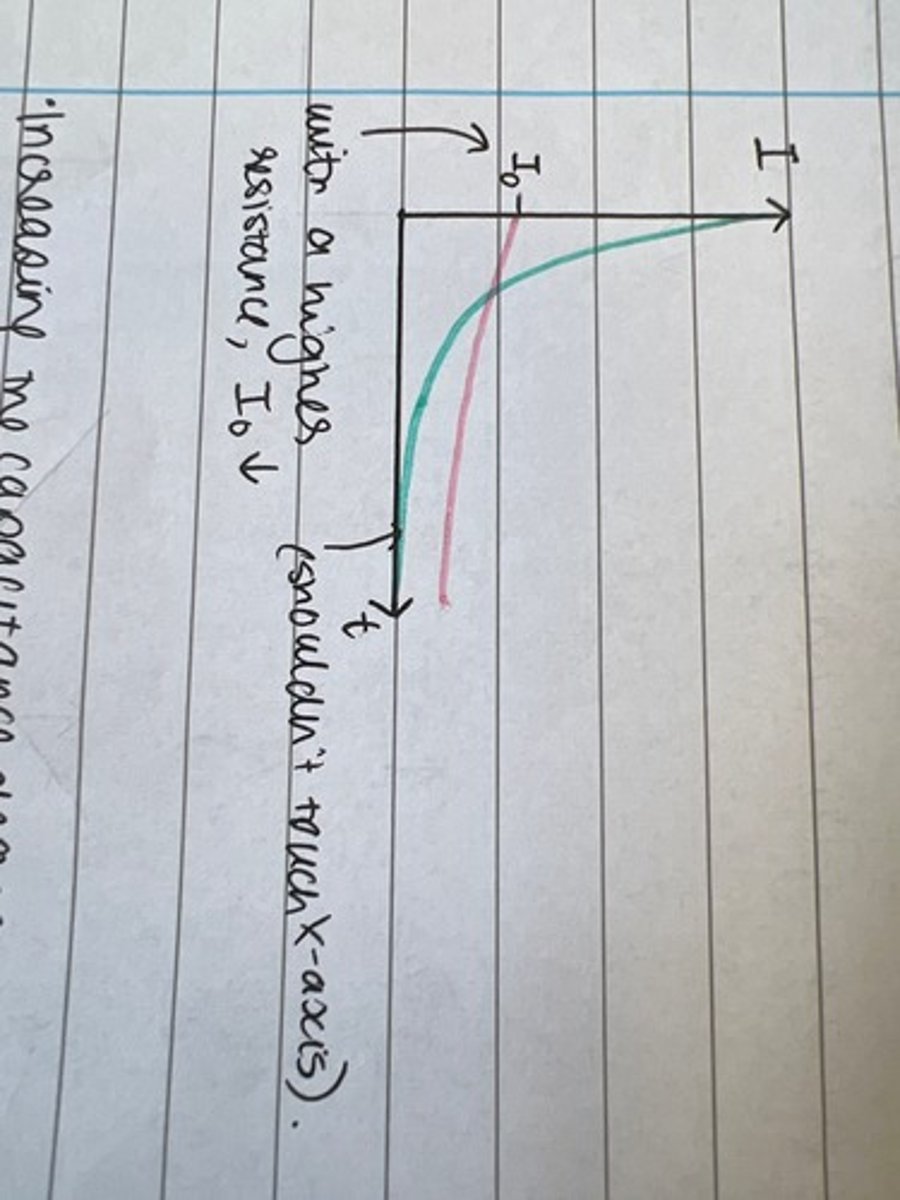
How does increasing capacitance change discharging a capacitor? Draw a graph
This decreases the rate at which the capacitor discharges so the current, charge and p.d. will all decrease at a lower rate. The initial charge would be greater at the same value of V0.
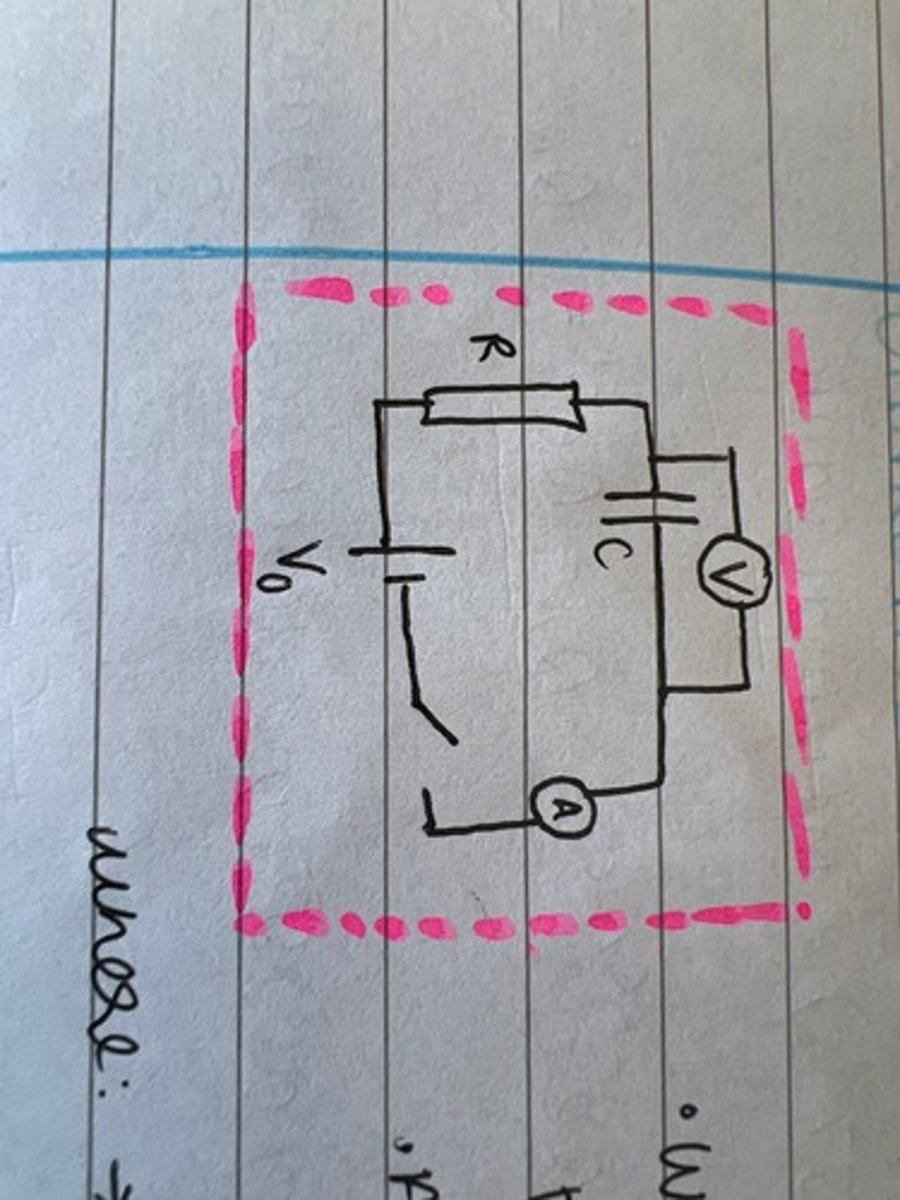
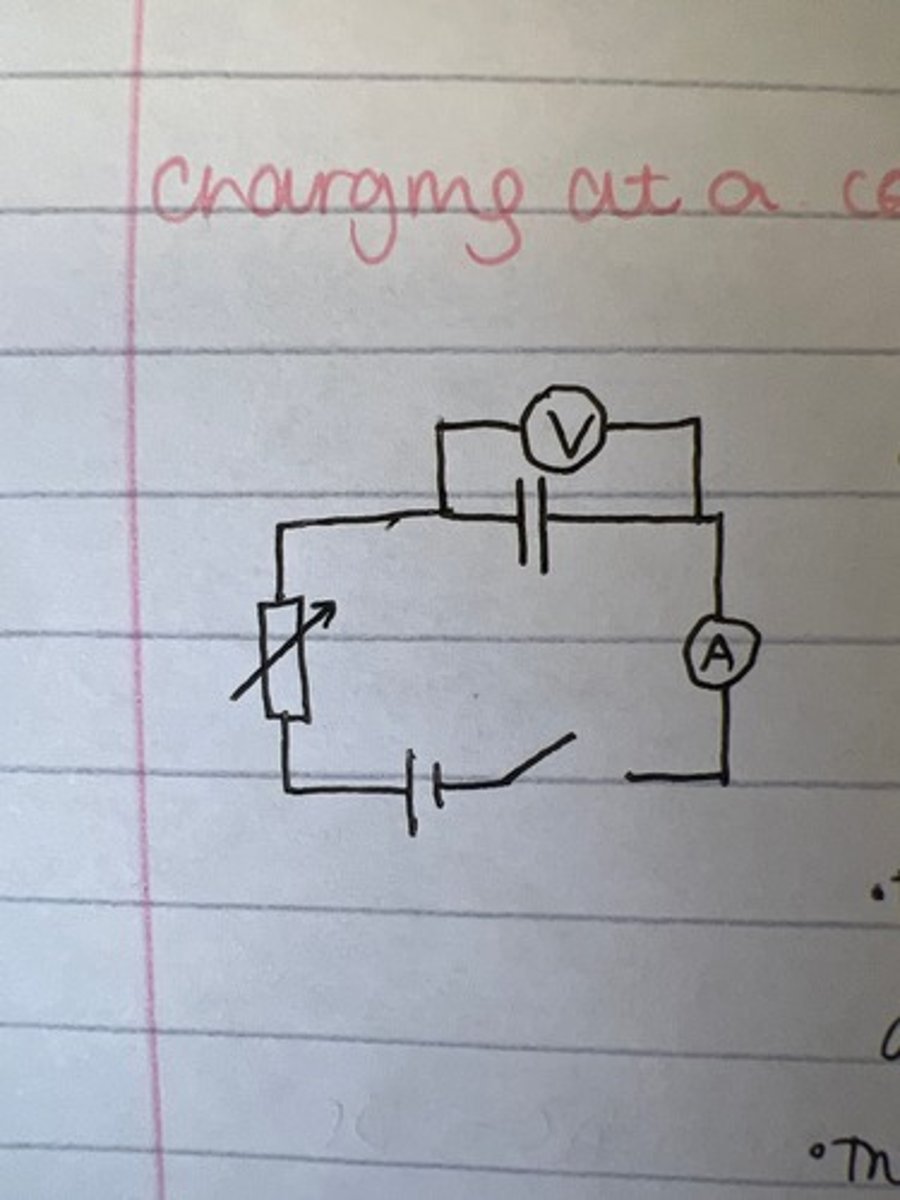
Draw the circuit for charging a capacitor?
Draw a graph for V against t for charging a capacitor.
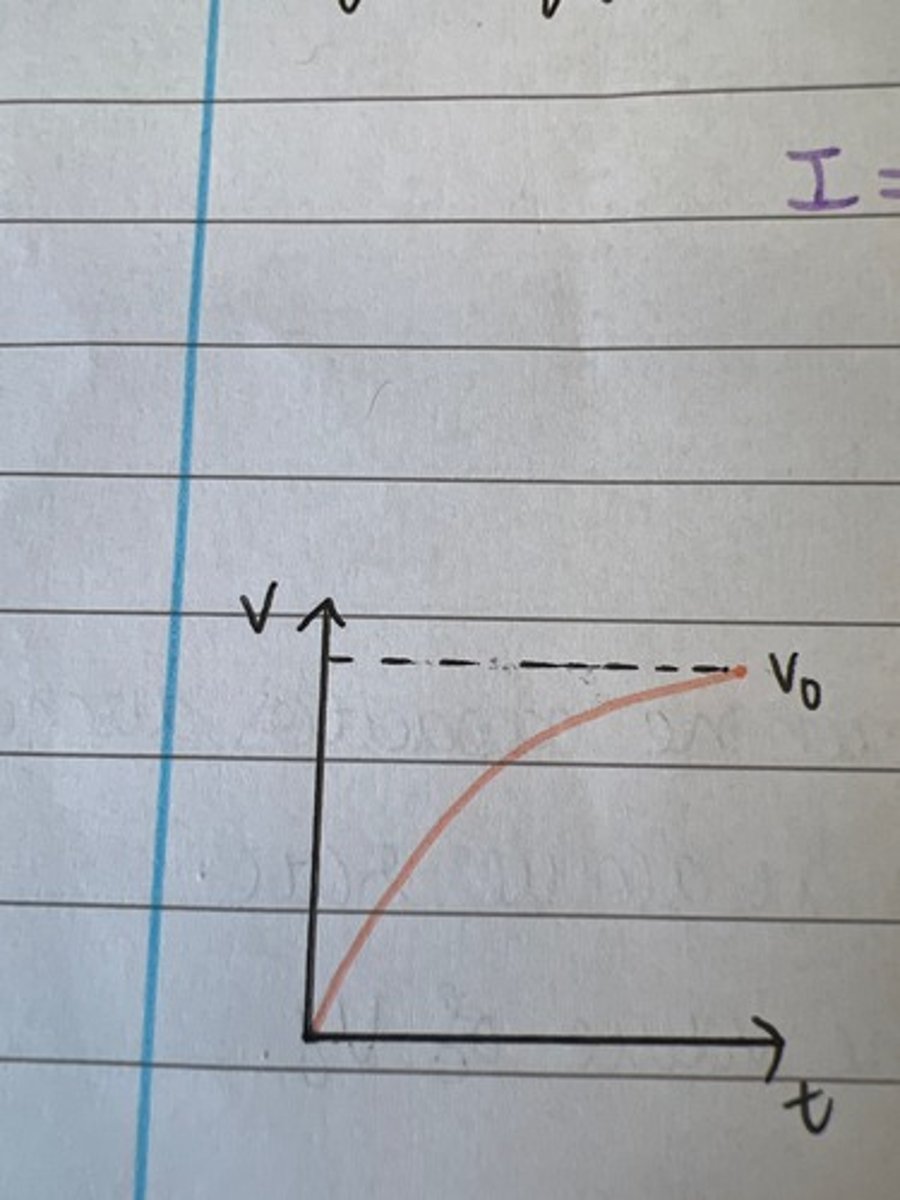
Draw a graph for Q against t for charging a capacitor.
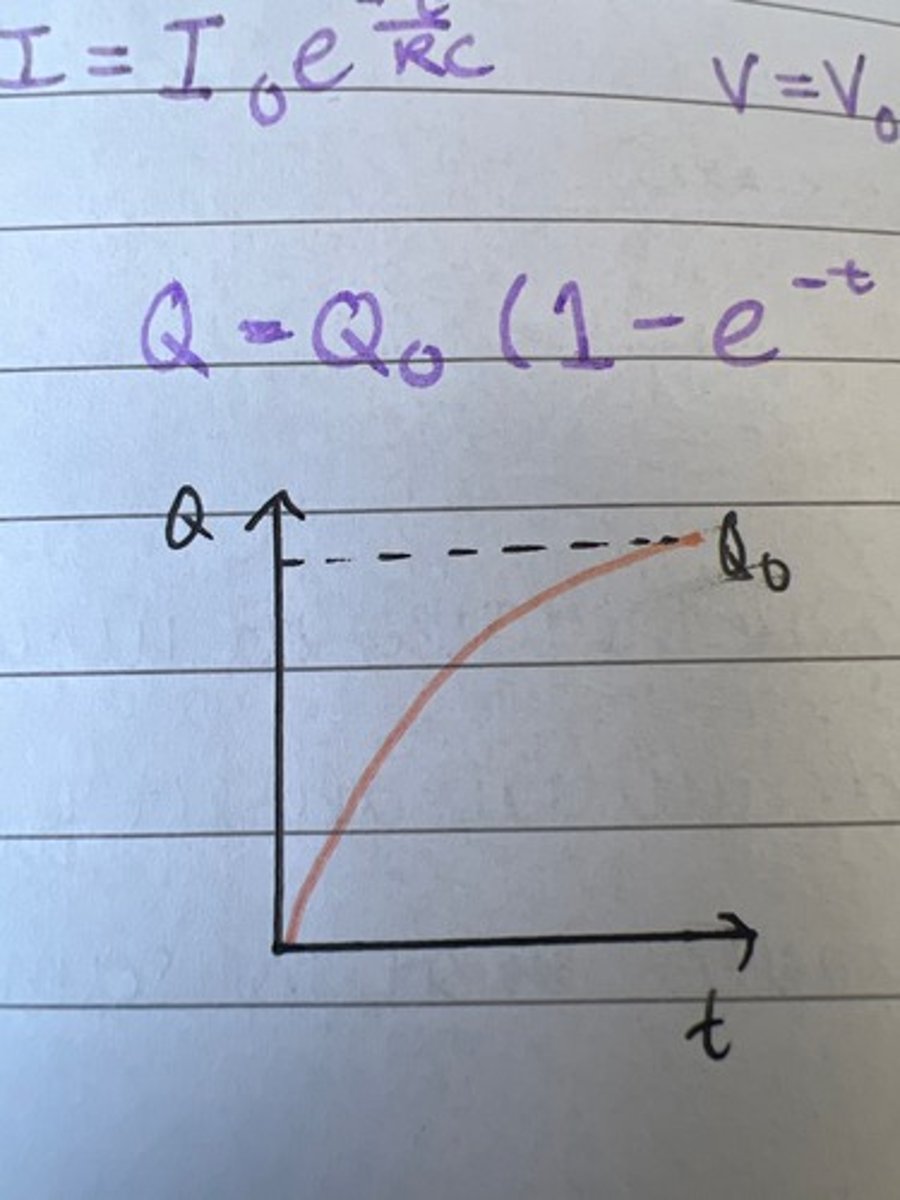
Draw a graph for I against t for charging a capacitor.
How can current be held at a constant value as a capacitor charges?
If the resistance of the variable resistor is gradually decreased as the capacitor charges, the current could be held at a constant value.
What are the uses of a capacitor?
to store charge (defribrilator/ camera flash)
to "smoothing out" bc current when converted from AC to DC
What is the strength of a gravitational field?
The force per unit mass on a small test mass placed in the field
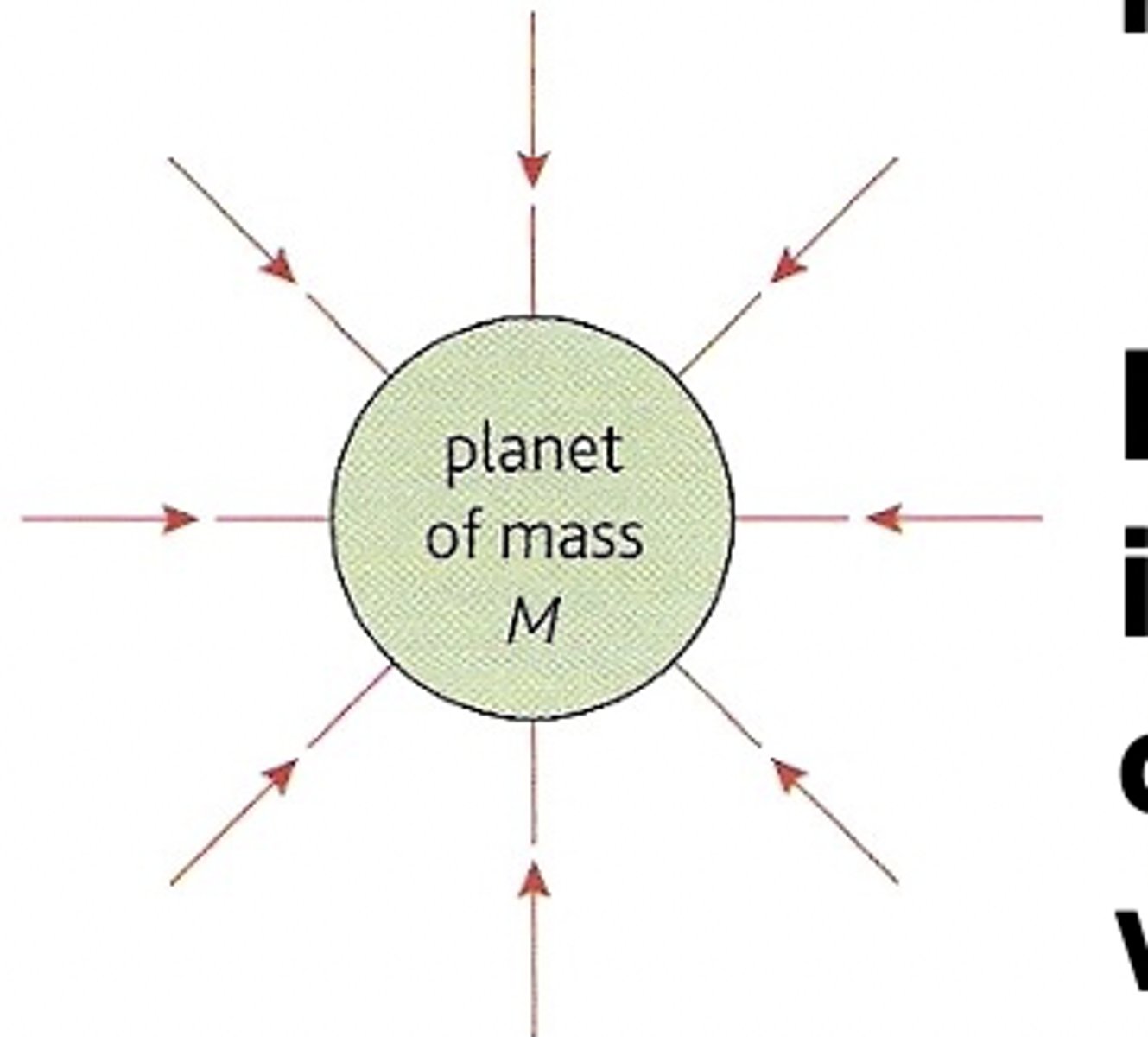
Draw a radial gravitational field.
What is gravitational potential energy?
the energy of an object due to its position in a gravitational field. The position for zero gpe is at infinity.
Define gravitiational potential?
The gravitational potential, V at a point is the work done to move unit mass from infinity to that point.
What is the unit of gravitational potential?
Jkg^-1
Why is gravitational potential always negative?
gravitational force is always attractive so work must be done to move mass from any point in a gravitational field to infinity.
Draw a graph of gravitational potential energy against distance (r) from a planet.
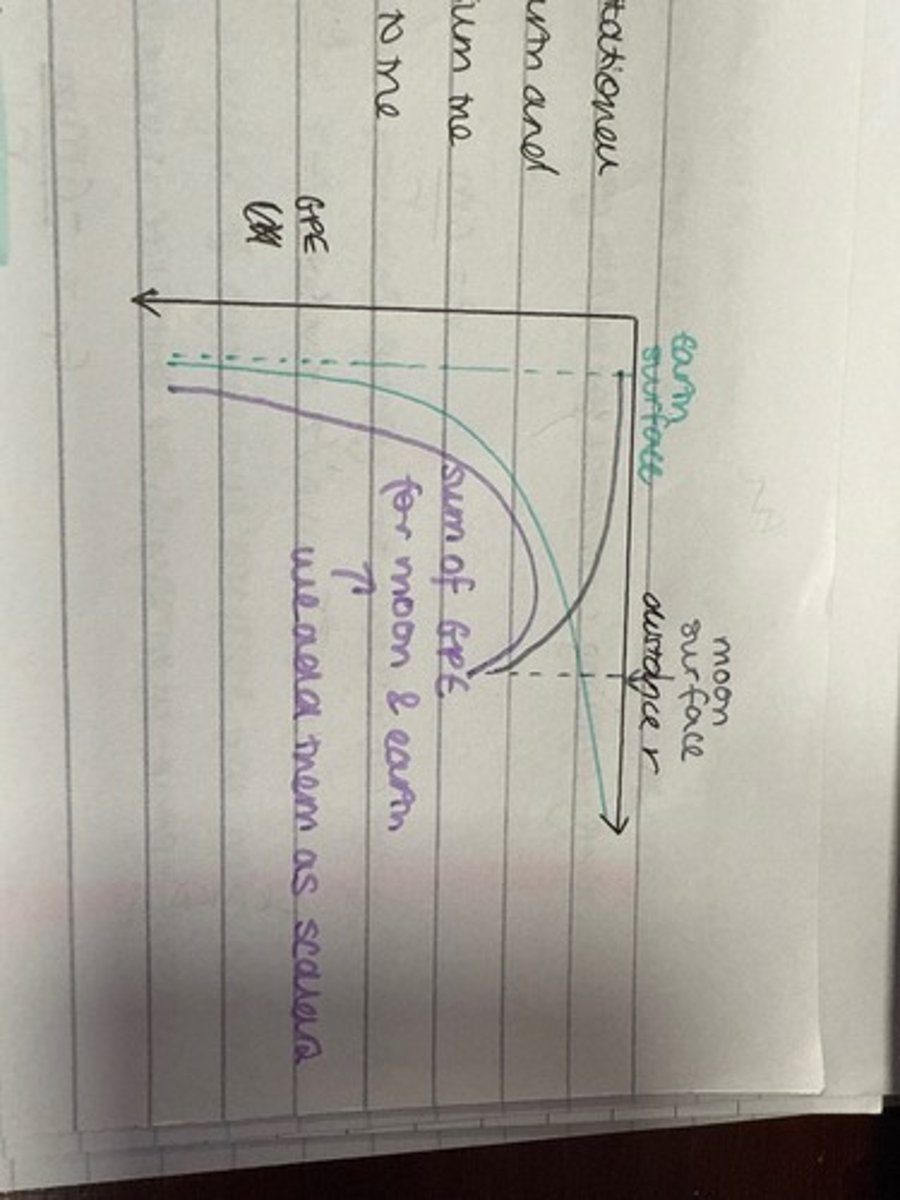
Draw a graph of gravitational potential against distance (r) from a planet.
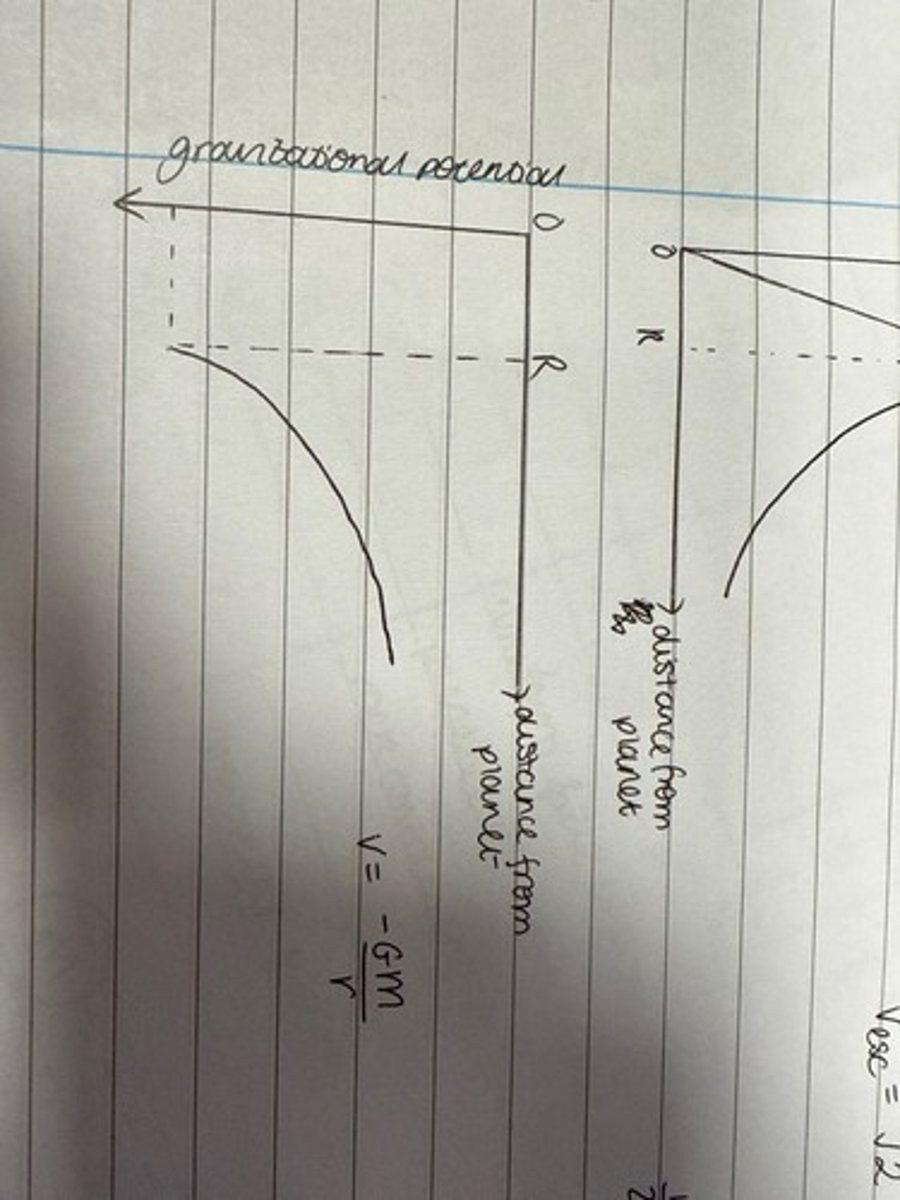
Draw a graph of gravitational field strength against distance from a planet with radius R.
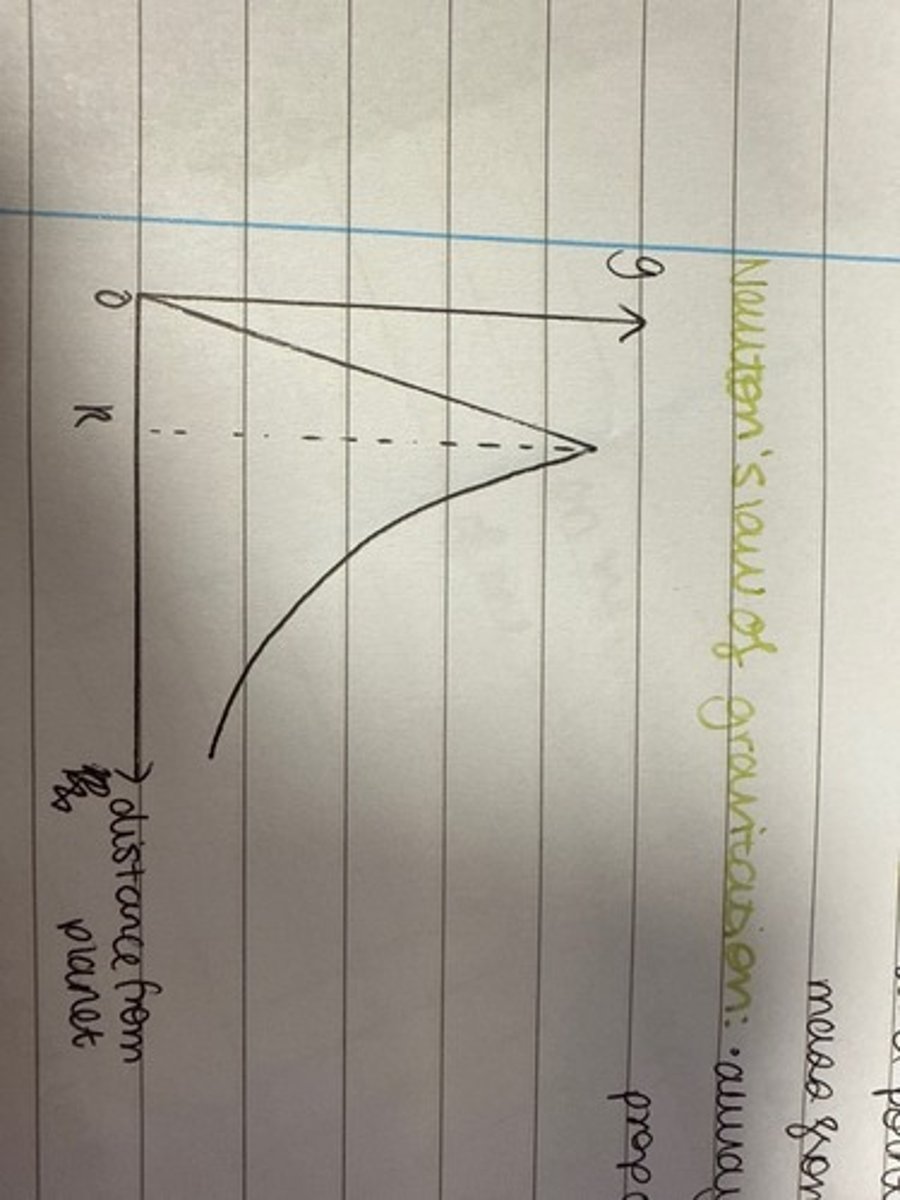
Show T^2 is proportional to R^3.
(T is the period)

Derive an equation to show speed of a satellite as radius of orbit increases

What is the equation for total energy of a satellite. (derive it) NEED TO LEARN

What is the formula for escape velocity?
v = √(2GM/r)
Describe the orbits of weather-monitoring satellites.
They have low height polar orbits. They have a smaller radius, hence a higher velocity, and so a shorter period.
This means they orbit the earth many times in a 24hr period so cover the full surface of the Earth as it orbits beneath them.
What is a synchronous satellite?
Period of exactly 24hrs so its period of rotation is exactly the same as that of Earth about its own axis.
What is a geostationary satellite?
One that has a period of 24 hrs (so it is a type of synchronous satellite) and also has an equatorial orbit so it stays above exactly the same point of Earth.
Write the formula for change in gravitational potential.
-GM((1/R1) - (1/R2))
What is the area under the g-r graph equal to?
the change in potential.
What is the gradient of the V-r graph equal to?
gravitational field strength.
Define a magnetic field.
a region in space in which a force is exerted on a magnetic material
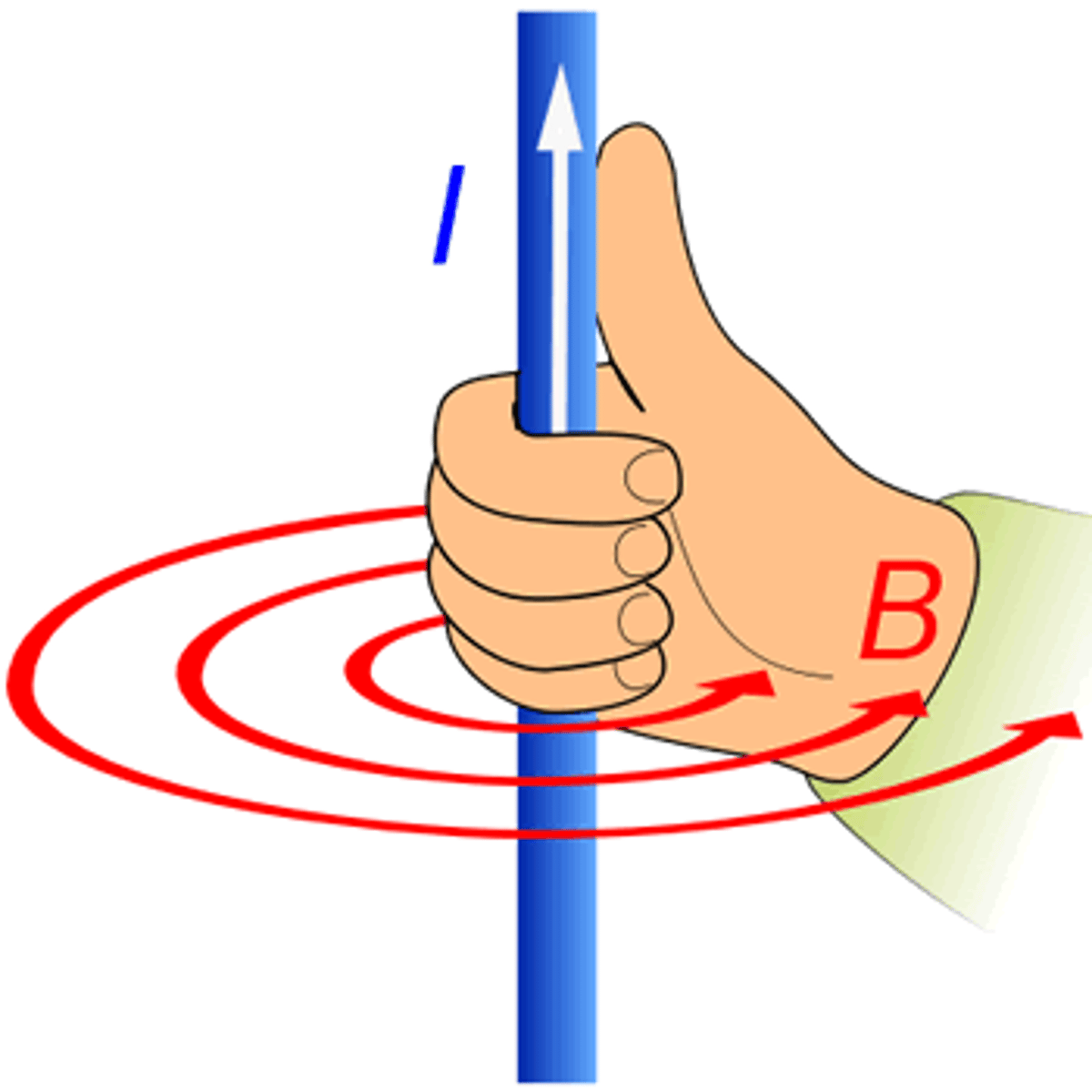
What is the right-hand rule?
What is the size of the force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field?
- the size of the current
- length of the wire inside the field
- magnetic flux density, B in tesla
What is the definition of a Tesla?
the magnetic flux density that gives a force of 1N on 1m wire carrying a current of 1A at right angles to the magnetic field.
When is the force on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field the greatest?
when the wire and field are perpendicular.
Why do you need to change the direction of the current in a wire in a magnetic field to keep it rotating in the same direction?
- when the coil is parallel to the field there are no forces on the sides of the coil
- the force on each side remains vertical and of the same magnitude as the coil rotates, but the magnitude of the couple will decrease as the perpendicular distance between the force and axle decreases
- the direction of the current must be changed every half turn to keep the coil rotating in the same direction
Describe the force and field between two parallel current-carrying wires when the current is going in the same direction.
The field lines between the two wires cancel out, creating an inward force between the wires.
Describe the force and field between two parallel current-carrying wires when the current is going in opposite directions.
The field lines add together between the wires, creating a strong field between the two and an outward force on the wires.
Define magnetic flux.
Measure of the strength of the field formed around a magnet.
Φ=BAcosθ
θ is the angle between the normal to the coil and the field lines
What is magnetic flux linkage?
The product of the number of turns in a coil and the magnetic flux
What does moving a conductor through a magnetic field do?
induce an emf across the end of the conductor
What will increase the induced emf?
- number of turns on the coil
- speed of the motion
- strength of the magnetic field
the magnitude of the induced emf depends on the rate at which the lines of flux are cut
What is Faraday's law?
The induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage
What is the gradient of the flux-time graph equal to?
induced emf
What is the area under the emf-time equal to?
the change in flux over that time
How does EM induction occur?
- when a conductor moves through a magnetic field, its electrons will experience a force
- this means the electrons will accumulate at one end of the conductor, inducing an emf
When is a current produced?
when there is a complete circuit
What is Lenz's law?
the induced emf is in such a direction as to oppose the charge that produced it
Why does a magnet take more time to travel through a hollow copper tube than an unmagnetised piece of metal?
- unmagnetised metal will fall freely under gravity; no upwards force opposing motion
- the falling magnet creates a moving magnetic field
- copper tube is cutting through moving lines of flux so an emf is induced in the tube
- this emf produces currents in the copper, which produce a magnetic field
- the direction of induced field is opposing the motion, producing an upwards force on the magnet, reducing the downwards acceleration and increasing the fall time
There is coil around a metal rod. Either a split ring or a complete ring is placed above the coil when the current is switched on, the split ring remain stationary but the complete rings jump suddenly upwards. Why?
When the current flows a magnetic field is produced around the coil
The ring above the coil is cutting lines of flux
There is an EMF induced in both rings, but only the solid ring has a current flowing because the split ring is not a full circuit
The current induced and the complete ring is in such a direction that opposes the field that produced it
The field of the coil repel the induced field of the ring and the ring experiences and outputs force causing it to "jump" in the air
Describe how an AC generator functions.
- as the coil rotates, each side cuts through the field lines of the permanent magnets.
- one side is moving down while the other side is moving up
- every half turn, the direction of the current will switch, as the side that was moving up is now moving down
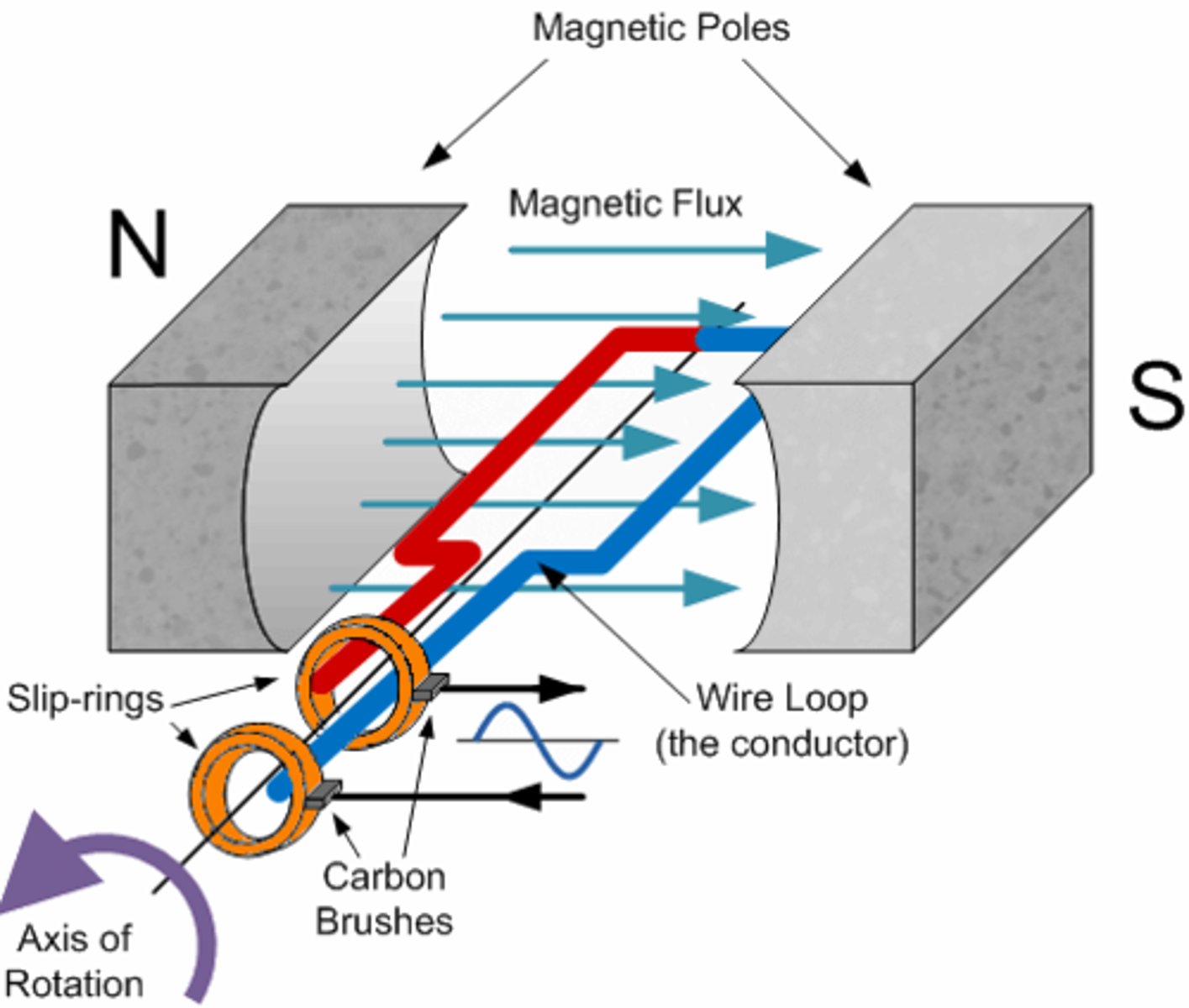
When is there an induced emf of zero for an AC generator?
when the plane of the coil is vertical, there is maximum flux linkage but zero emf as the two sides are moving parallel to the field lines.
When is there a maximum induced emf for an AC generator?
The plane of the coil is horizontal; there is zero flux linkage, but the emf is at a maximum because the sides of the coil are cutting through the field lines at maximum speed.
What happens to the graph of induced emf against time for an AC generator if the rotational speed of the coil increases?
the maximum amplitude increases, because there are more lines of flux cut in a given time (Faraday's law)
the time period increases, so the graph is squashed horizontally.
Describe the back emf in a a motor.
- an electric motor is a rotating coil inside a magnetic field, just like an AC generator
- this means we should expect an emf to be induced across the ends of the coil, since it is cutting through lines of flux (Faraday's law)
- the induced voltage across the coil in the motor is in the opposite direction to the driving voltage (Lenz's law)
- it is therefore known as a back emf and reduces the voltage across the coil
- at high speeds, a larger emf is induced in the coil and current is low
Describe the UK mains supply
50Hz
peak voltage of 325V
rms voltage of 230V
How does a transformer work?
- an AC through the primary coil produces an alternating magnetic flux in the iron core
- the role of the iron core is to link the changing flux from the primary to the secondary coil
- the flux travels through the iron core so the secondary coil, around the same core, is cutting through changing lines of flux
- an alternating emf is induced across the ends of the secondary coil
- the more turns on the secondary coil, the larger the number of lines of flux being cut per second and therefore the larger the induced emf.