AP Chemistry 9.1-9.6 Basic Overview
9.1- Introduction to Entropy
^^Entropy^^: dispersal of matter/energy in sample of matter
changes of entropy can be seen as how dispersed the matter/energy is
entropy increases when matter is more dispersed
- (ex. a phase change from solid to liquid, liquid to gas)
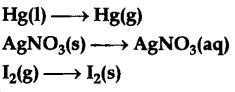
- (ex. a phase change from solid to liquid, liquid to gas)
individual particles at increased entropies are more free to move and occupy more space
With gases:
- entropy of gas increases when volume, increase because gas molecules are able to move in a larger space with same speed
- if total number of moles of gaseous products>total number of gaseous reactants, entropy increases
entropy also increases when energy is more dispersed
according to KMT, K.E among particles broadens when temperature increases
entropy increases when temperature increases
9.2- Absolute Entropy and Entropy Change
entropy change can be calculated from absolute entropies in individual species
- unit: J/K
most substances have a nonzero value for absolute entropy unlike enthalpy
when calculating, number of moles of each substance have to be considered
^^Find delta S with: ΔS=∑S(products)−∑S(reactants)^^
entropy is positive if : phase changes occur as, solid to liquid to gas or if number of moles increase from reactants to products
entropy is negative if: phase changers occur as, gas to liquid to solid
9.3- Gibbs Free Energy and Thermodynamic Favorability
^^Gibbs free energy:^^ △G describes if a reaction is thermodynamically favorable or unfavorable
^^Thermodynamically favorable:^^ equation proceeds to equilibrium with no outside factors
reminder! just because reaction is favorable does not mean it happens quickly
in Gibbs free energy all reactants and products are in standard states (pure substance, 1.0M, 1 atm)
^^Find delta G with: ΔG=∑G(products)−∑G(reactants)^^
thermodynamically favorable, G=negative
thermodynamically unfavorable, G=positive
G can be calculated from enthalpy and entropy with: ^^ΔG=ΔH-TΔS^^ * t=temperature
- if both enthalpy and entropy are favorable or both unfavorable, there is no need to find G to see if its favorable
9.4-Thermodynamic and Kinetic Control
- processes that are favorable but do not make products at measurable rate, are under kinetic control
- things under kinetic control usually have large activation energy (Ea), making the rate slow down
- a catalyst (ex. enzyme) can decrease Ea and increase reaction rate, but has no effect on favorability
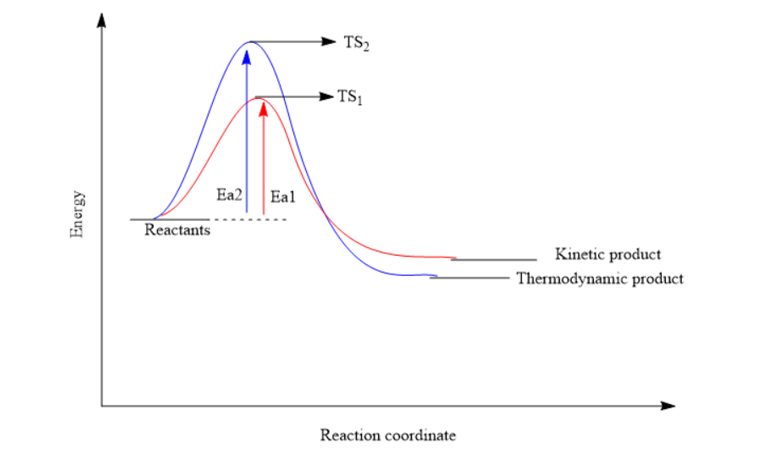
- even if the process doesn't happen at a noticeable rate, it does not mean it's at not equilibrium
9.5- Free Energy and Equilibrium
- thermodynamically favored (ΔG
- at equilibrium, no net change in concentration of reactants and products occurs
^^Find K with: K=e-GT/RT^^
Find Delta G with: ΔG° = -RTlnK *R = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1
- -when ΔG is neg, K>1, reaction favors products
- when ΔG is pos, K<1, reactions favors reactants
- when ΔG=0, reaction is at equilibrium
9.6-Coupled Reactions
- a process with positive ΔG is unfavorable
- different paths occurs to make process happen when the reaction is unfavorable
- paths can be external sources of energy (ex. sunlight, power source)
- or it can be coupled to another favorable reaction
^^Coupling:^^ when two reactions share an intermediate, they can be coupled, Hess’s law can be applied and the sum of the reactants’ ΔG values makes overall process favorable when added