Unit 5: Kinetics
Rate Law Using Initial Concentrations
- The rate law of a reaction is based on the initial concentrations of the reactants, the rate at disappearance of products and appearance of product, and requires experimental data. Arrhenius constant, k, is based on the activation energy for a reaction and the temperature.
How to do it
- A+ 2B + C → D
| experiment | initial [A] (M) | initial [B] (M) | initial [C] (M) | initial rate of formation of D (M/sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | .1 | .1 | .1 | .01 |
| 2 | .1 | .1 | .2 | .01 |
| 3 | .1 | .2 | .1 | .02 |
| 4 | .2 | .2 | .1 | .08 |
- Rate = k[A]^x[B]^y[C]^x
- The value of the exponent is based on how the reactants affect the rate. Larger exponent means the reactant concentration changes more. To find the exponent value, find what happens when a concentration is doubled.
For [A]
- Use experiment 3 and 4 values for [A] because no other reactant value changes. The rate changes from .02 to .08 by quadrupling. The value of the exponent x is found by doubling the concentration and setting it equal to the value of the rate changes (4).
- (2)^x = 4, so x=2.
- Now the rate is Rate = k[A]^2[B]^y[C]^x or second order with respect to A.
For [B]
- Use experiment 1 and 3. it doubles the rate from .01 to .02.
- (2)^y=2, so y=1
- The rate is now Rate = k[A]^2[B]^1[C]^x or first order with respect to B
For [C]
- Using experiment 1 and 2, the rate stays the same so x=0
- Rate = k[A]^2[ B]^1[C]^0 or Rate = k[A]^2[ B]^1 so the reaction is overall third order.
- Any experiment can be used to find k. Using experiment 3:
- k = (rate/[A]^2[B]) = (.02/(.1)^2(.2)) = 10 M^-2sec^-1
Rate Law Using Concentration and Time
- Rate law can be expressed using concentration changes over time. There are zero, first, and second order rate laws that each have the roan equation and graph.
Zero-Order Rate Laws
- In zero order, the rate is always the same at a given temperature and doesn't change based on reactant concentration.
- Rate = k
- The graph is a straight line equal to -k and concentration vs. time.
First- Order Rate Laws
First order rate law is based on the concentration of one reactant to the first power.
- Rate = k[A]
The graph is the natural log of [A] vs. Time. This creates a straight line with a slope of -k and y-interest of ln[A] at time 0.
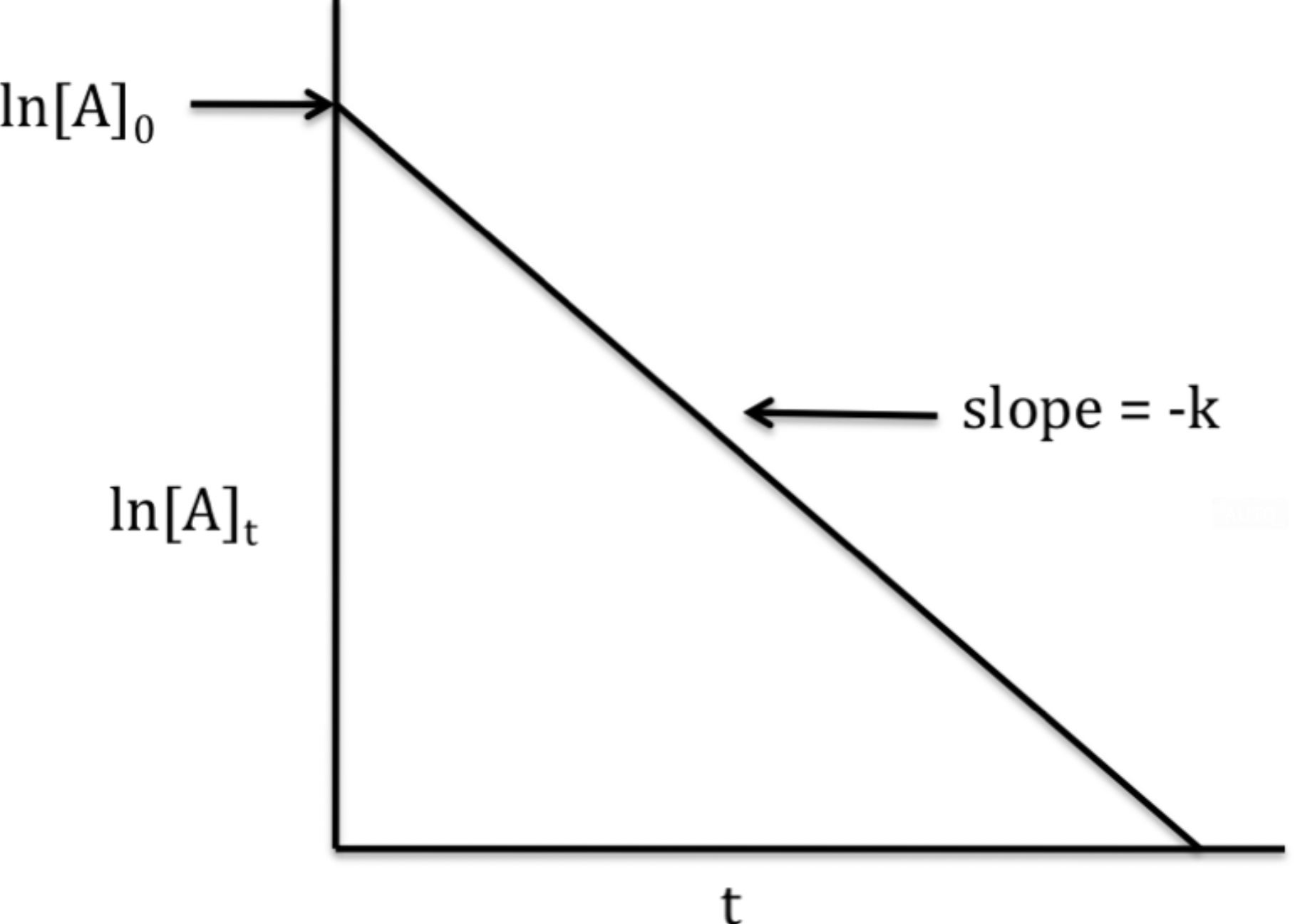
The rate law, using the slope-intercept formula, is

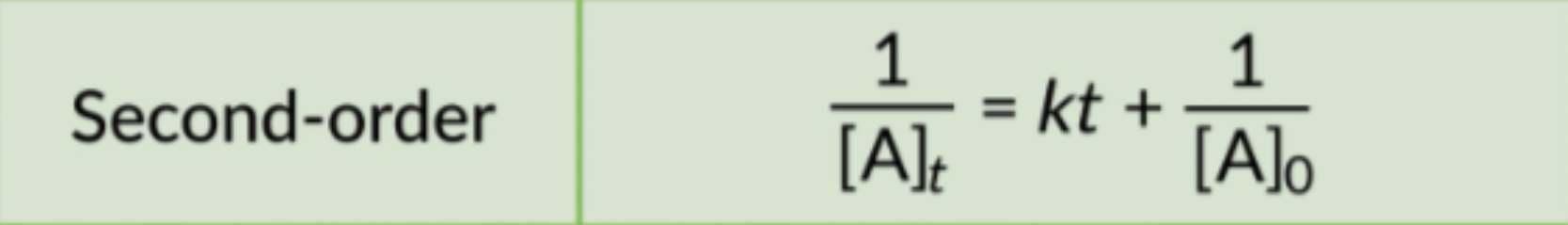
Second-Order Rate Law
Second-order rate depends On a reactant raised to the second power.
- Rate = k[A]^2
The rate law uses the inverse of concentrations.
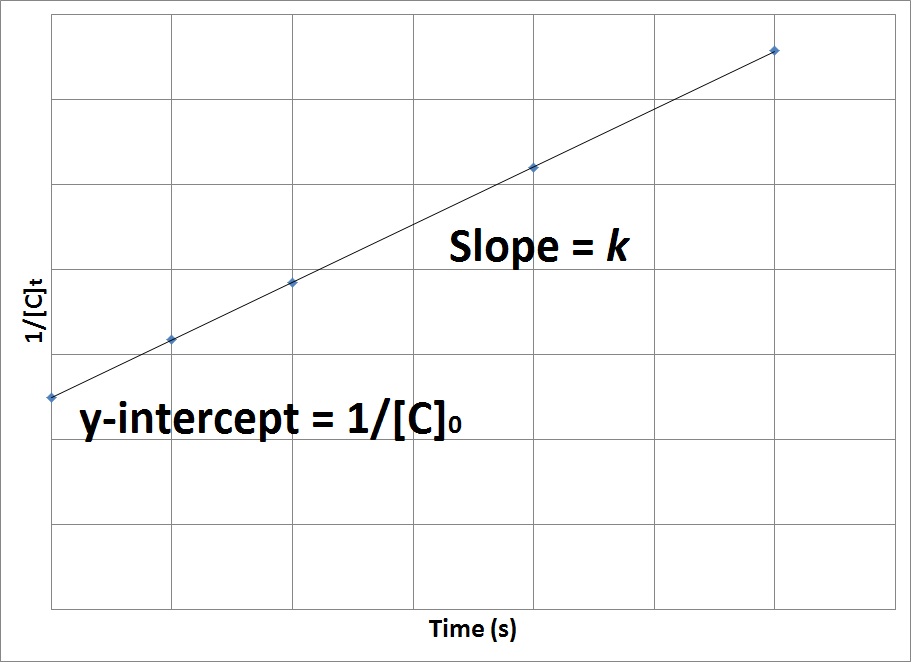
The inverse concentrations vs. time create a straight line, where the slope is k and y-intercept is (1/[A]) at time zero.
Half-Life
- Half-life of a substance is how long it takes for half of the substance to react.
| Time | Sample |
|---|---|
| 0 half lives | 100% |
| 1 half life | 50% |
| 2 half lives | 25% |
| 3 half lives | 12.5% |
In first-order, half-life is constant. If after 30 sec 50% of a substance has decayed, in 30 more sec, 25% remains. 30 more sec, 12.5% remains, etc.
Half-life can be determined graphically
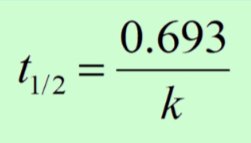
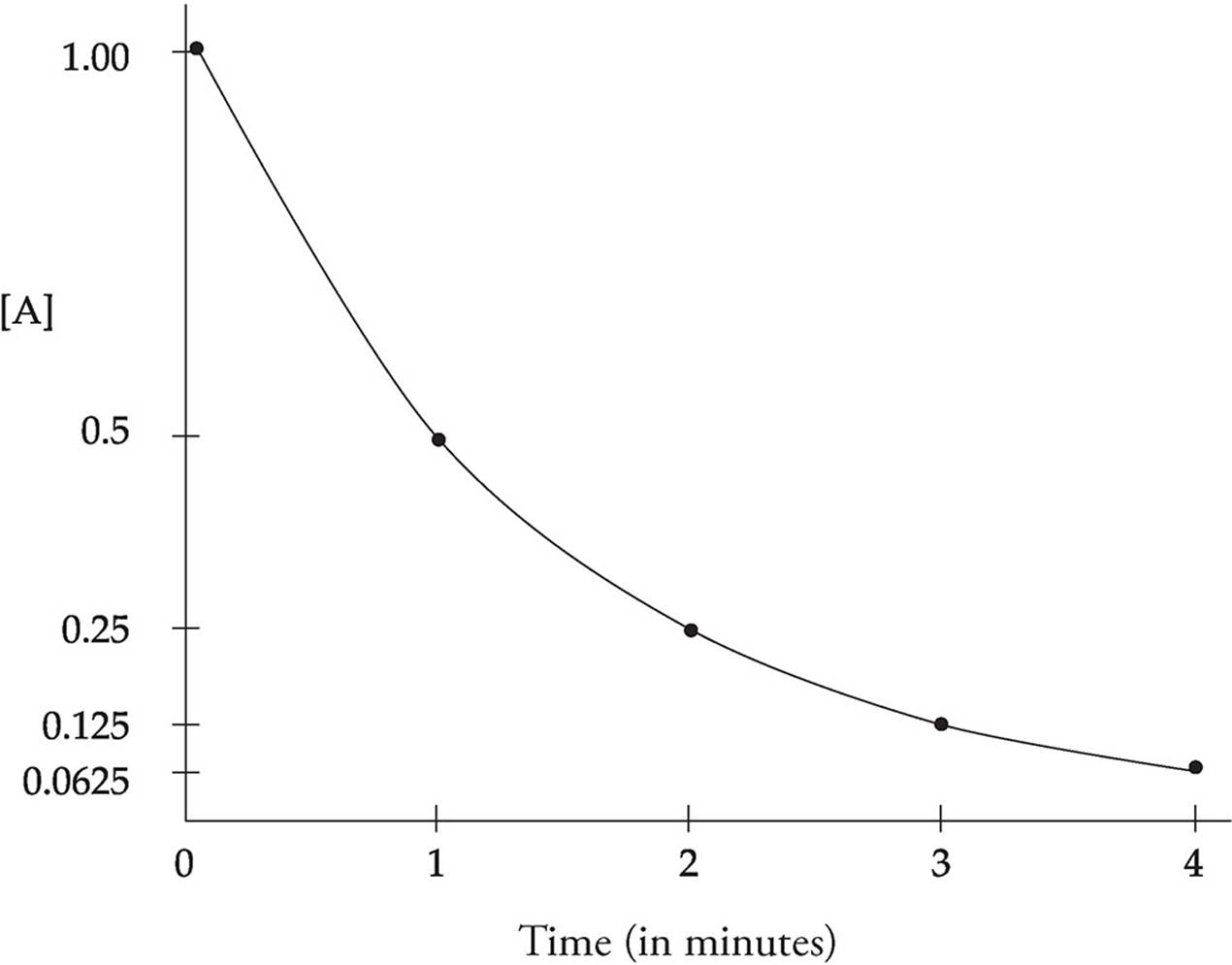
The half-life equation can only be used for first-order reactions because zero and second order do not decompose at the same rate and changes overtime
Collision Theory
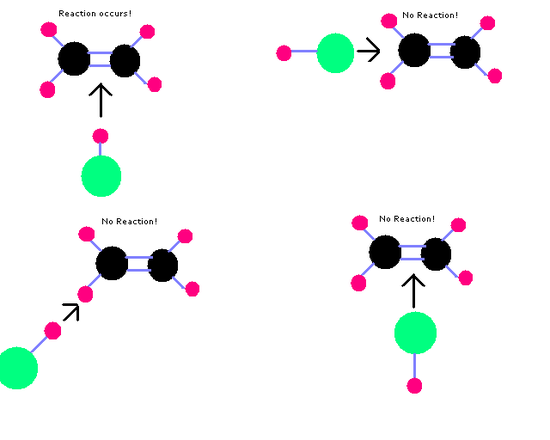
Collision theory states reactions only occur when chemicals collide with each other with sufficient energy (activation energy).
They can react more if there's a higher concentration of aqueous or gaseous substances, or a high surface area of a solid substance.
Stirring can sometimes speed up a reaction. If the mixture is heterogeneous, not all parts of a mixture is identical, then stirring will mix it more and speed it up. If the mixture is homogeneous, where the mixture is completely identical, then stirring will not help because it is already mixed and even.
Reaction rate increases with temperature because molecules are moving faster and have a higher likelihood to collide with other molecules at a sufficient speed.
Molecules will only react if they collide with the correct orientation.
Reaction Energy Profile
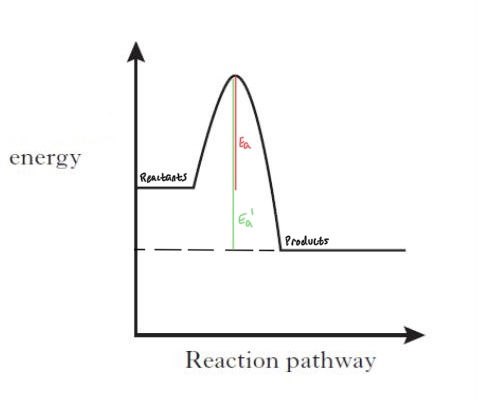
- The diagram shows a chemical reactions energy change. The red line is the activation energy, or how much energy is required for the reaction to occur. The green line is how much energy required for the reverse reaction.
Reaction Mechanisms
Some reactions occur in multiple steps rather than in one step and the overall balanced reaction is the sum. The in between steps are called elementary steps.
- Example: The rate for elementary steps can be determined by setting the concentration of a substance to the power of it’s coefficient
- I. A + A ⇌ X (fast) Rate=k[A]^2
- II. X + B → C + Y (slow) Rate=k[X][B]
- III. Y + B → D (fast) Rate=k[Y][B]
- X and Y are intermediates, they are created in one step and consumed in another, so they cancel out.
- If an elementary step has only one reactant, it is unimolecular. If it has two reactants (even if they are the same reactant, like in step l), it is considered bimolecular.
- The slowest step is considered the rate-determining step because the speed of the reaction cannot exceed the slowest step. This step determines the rate law for the entire reaction.
- Step II has an intermediate, which is not written in the reaction, and it is produced in step I, so X can be replaced with [A]^2. The rate law for step two and the overall reaction becomes Rate=k[A]^2[B].
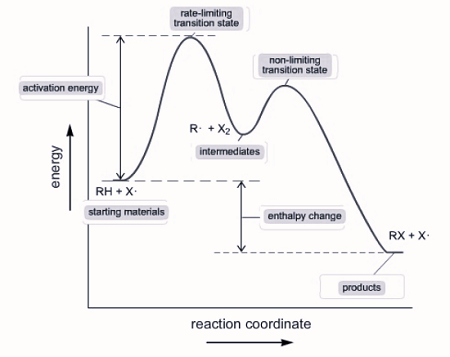
a multi - step reaction can be written as a reaction energy profile diagram
Catalysts
- Catalysts are added to a reaction to speed it up without being consumed. Catalysts are present in the beginning and end of elementary steps and cancel out.
- For the steps in the reaction A + B → C
- I. A+ X→ Y
- II. B + Y → C + X
- In this reaction, x is the catalyst and Y is the intermediate