Limbic System/Prefrontal Cortex
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Limbic System
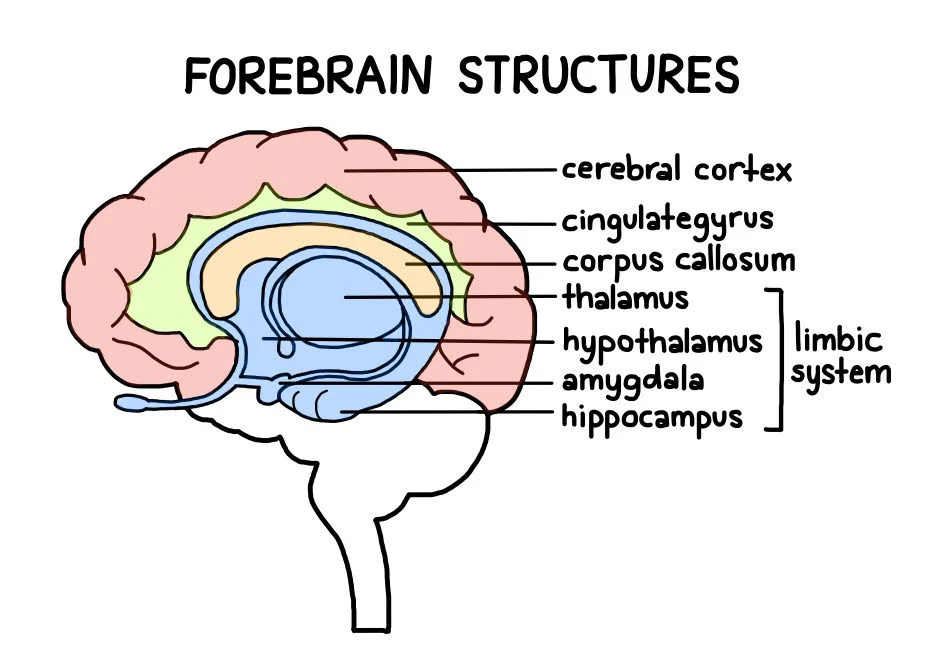
At the base of the forebrain, just above the thalamus and hypothalamus
Limbic means border (it is located around the edge of the center of the brain)
Includes such structures as the hippocampus (seahorse), cingulate gyrus (girdle), septum (partition), and amygdala
Helps regulate our emotional experiences and expressions and, to some extent, our ability to learn and to control our impulses
Also involved with the basic drives of sex, aggression, hunger, and thirst
Cerebral Cortex
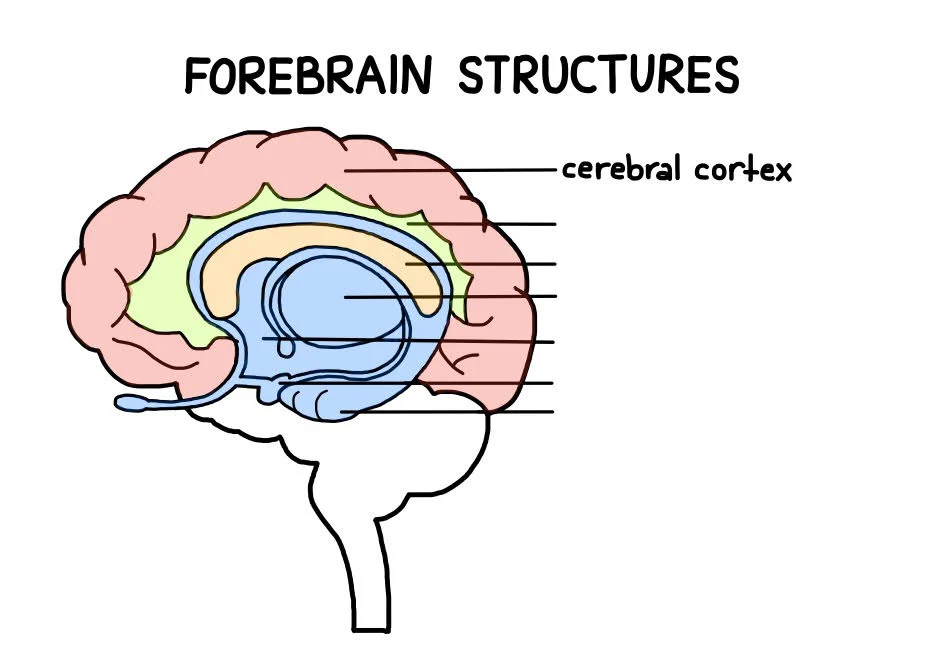
Largest part of the forebrain
Contains more than 80% of all neurons in the central nervous system
Provides us with our distinctly human qualities (allowing us to look to the future and plan, to reason, and to create)
Divided into two hemispheres:
Each hemisphere consists of four separate areas, or lobes: temporal, parietal, occipital, and frontal
Cingulate Gyrus
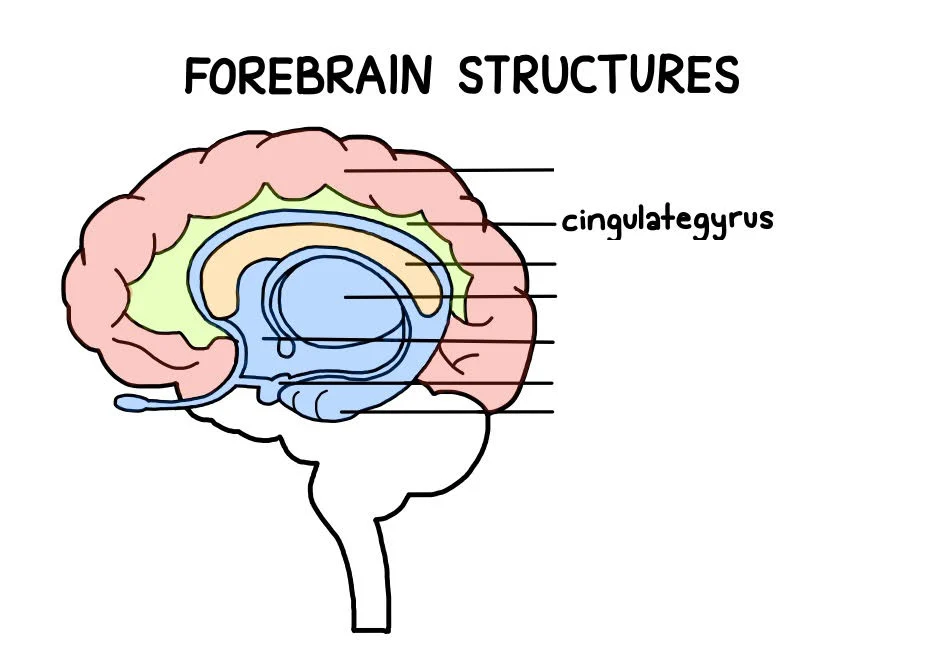
an arch-shaped convolution situated just above the corpus callosum, helps regulate emotions and pain. It is also involved in predicting and avoiding negative consequences
Corpus Callosum
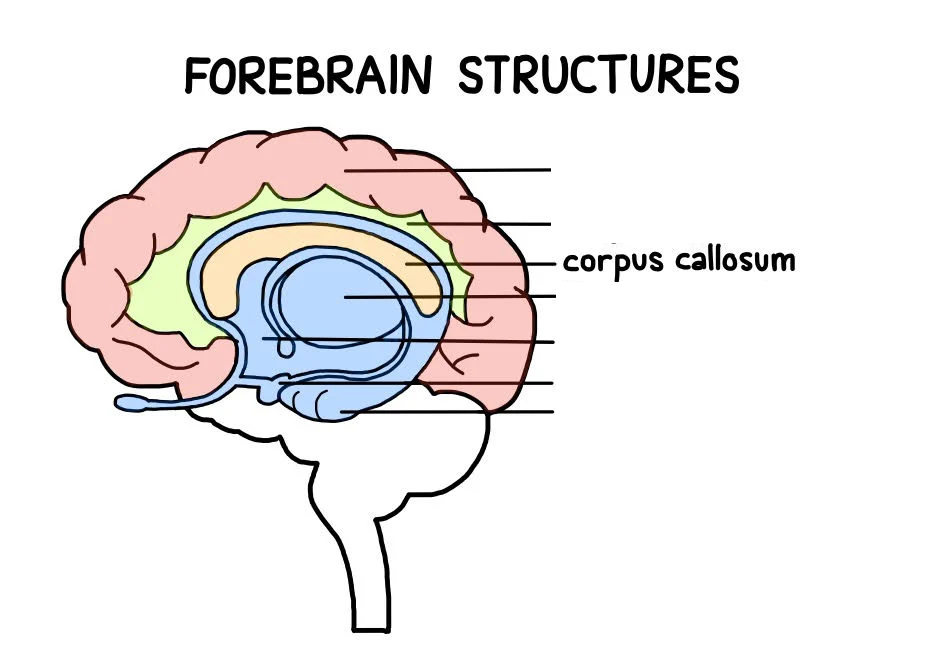
a structure in the middle of your brain that connects the right and left hemispheres, to integrate and transfer information from both cerebral hemispheres to process sensory, motor, and high-level cognitive signals
Thalamus
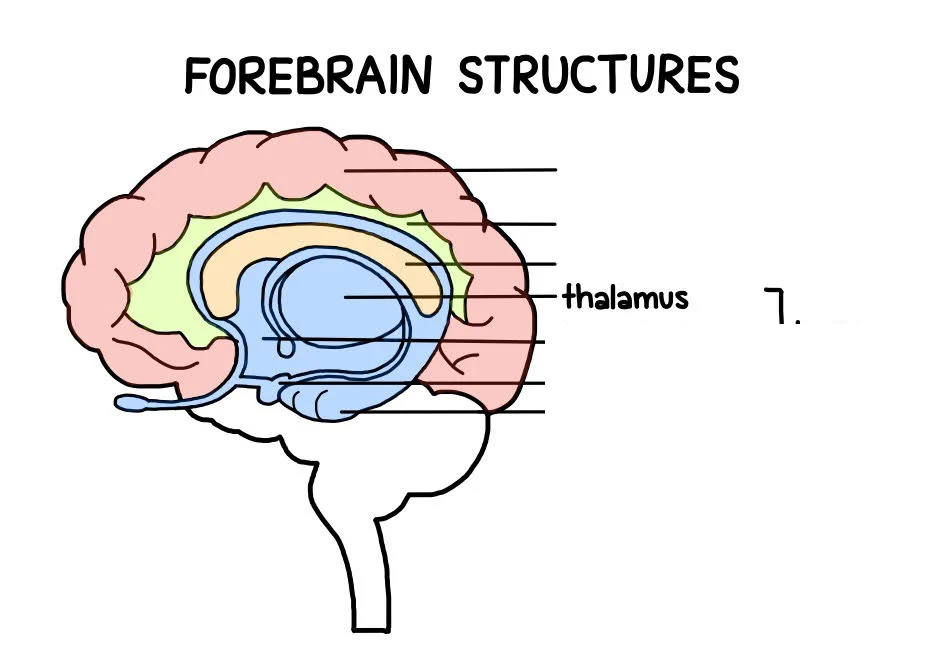
a mostly gray matter structure of the diencephalon that has many essential roles in human physiology. The thalamus is composed of different nuclei that each serve a unique role, ranging from relaying sensory and motor signals, as well as regulation of consciousness and alertness.
Hypothalamus
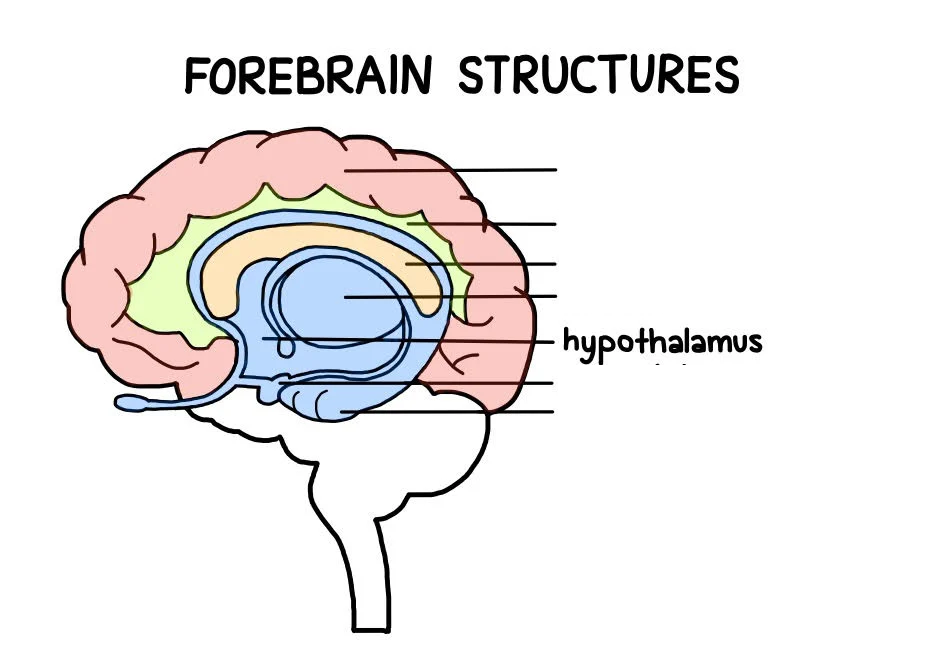
an area of the brain that produces hormones that control: Body temperature. Heart rate. Hunger. Mood.
Amygdala
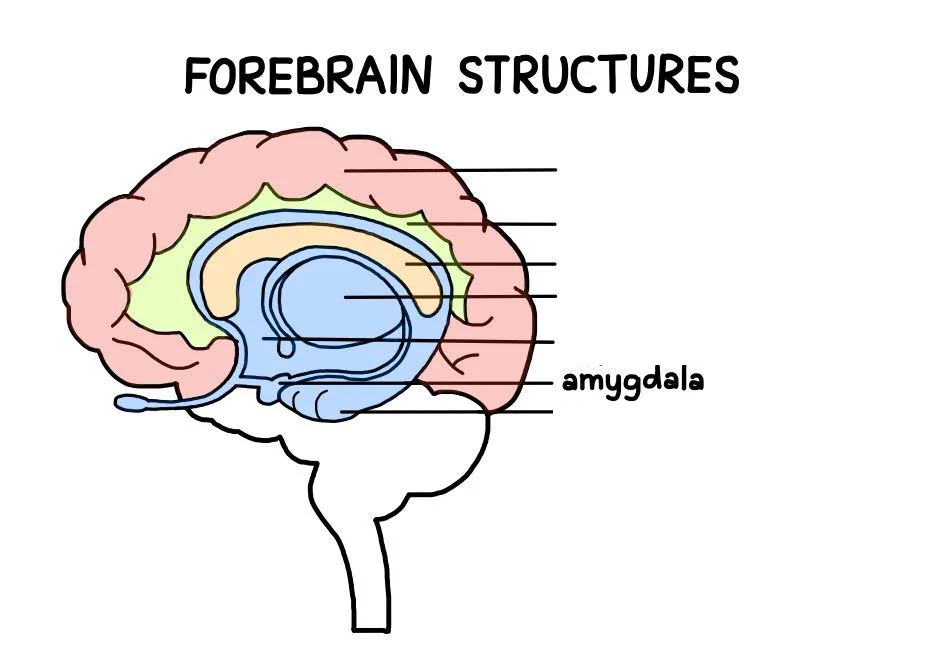
an almond-shaped mass of grey matter in the brain that is primarily responsible for emotional responses, especially in situations involving anxiety, fear, or rage
Hippocampus
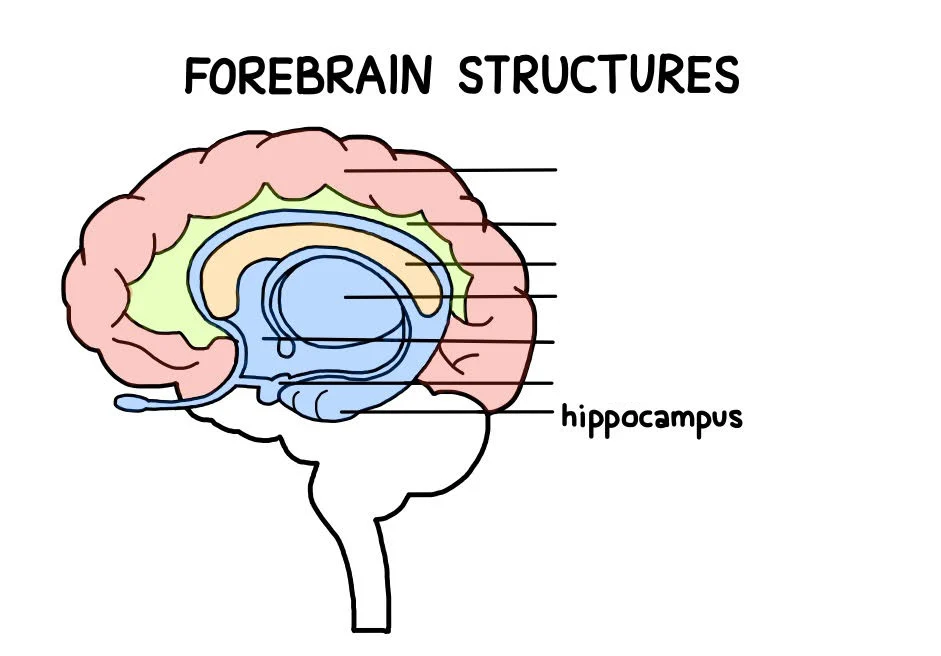
a group of brain structures that regulate your smells, emotions, memories and autonomic behaviors (such as heart rate, breathing, sweating, etc.)