CM Cardio Diagnostic Tools (EKG, Echo, Stress Tests, Biomarkers)
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
What are the indications for EKG?
- Evaluation of R&R
- Identifying active cardiac ischemia
- Identifying pericarditis
- Identifying cardiac remodeling as part of chronic disease
- Identifying electrolyte derangements
- Identifying drug exposure/toxicity
What does EKG tell us about the mechanical functions of the heart (ie. blood flow)?
Nothing, electrical info only
True/False: it is possible to have a normal EKG while in cardiac arrest
True
What are the 4 basic things required for an EKG?
1. patient
2. Recording electrodes in contact with patient's skin
3. Wires to connect the recording electrodes to the recording device
4. Recording device that converts electrical signals to visible signal
What is an electrode?
A paper or foam-backed adhesive pad with conductive gel that is attached to the patient
What is the difference between a Lead and a lead?
Lead: combination of a positive and negative electrode used to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart along a single one-dimensional axis
lead: a wire that connects an electrode to the recording machine
How many leads does a standard EKG use? How many Leads?
leads: 10
Leads: 12
Where are the black, red, and white leads placed for a 3-lead EKG?
White on right, smoke over fire
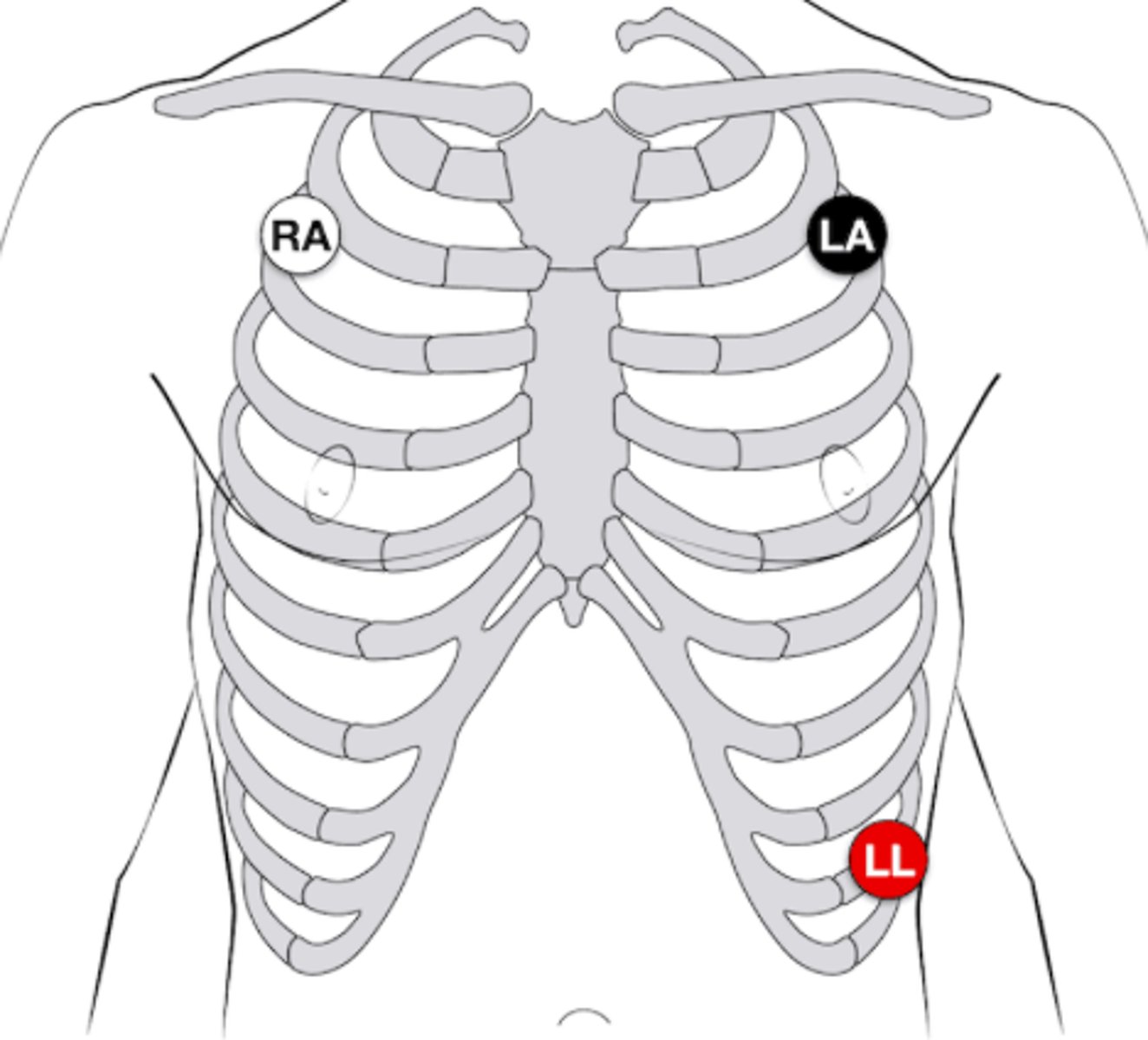
Why are the Right Arm (RA), Left Arm (LA), and Left Leg (LL) leads typically placed on the torso?
- Reduces signal interference from motion
- Provides better patient mobility for long-term monitoring
In a 4-lead EKG, a Right Leg lead is added. What is its purpose?
Functions as a ground lead to improve signal quality
Where are the positive and negative electrodes placed for the bipolar Lead I?
Negative: Right arm
Positive: Left arm
Where are the positive and negative electrodes placed for the bipolar Lead II?
Negative: Right arm
Positive: Left leg
Where are the positive and negative electrodes placed for the bipolar Lead III?
Negative: Left arm
Positive: Left leg
What portion of the heart does Lead I "visualize"?
Top portion of lateral wall
What portion of the heart do Leads II & III "visualize"?
Inferior surface
Where is the negative electrode for augmented Leads?
It can be hypothetically thought that they have a negative electrode in the center of the heart
What portion of the heart does the aVL Lead "visualize"?
Upper lateral wall
What portion of the heart does the aVF Lead "visualize"?
Inferior surface
What portion of the heart does the aVR Lead "visualize"?
Not mapped to a specific area of the heart; "wild card" Lead
What Leads (I-III) will "augment" data with aVR?
I and II
What Leads (I-III) will "augment" data with aVL?
I and III
What Leads (I-III) will "augment" data with aVF?
II and III
Where are the precordial Lead electrodes placed?
V1 - right 4th intercostal next to sternum
V2 - left 4th intercostal next to sternum
V3 - midway between V2 and V4
V4 - left 5th intercostal, midclavicular line
V5 - left 5th intercostal, anterior axillary line
V6 - left 5th intercostal, midaxillary
What is the most anterior structure of the heart?
Right ventricle
What does the P wave represent?
Atrial depolarization
What does the PR interval represent?
Pause in electrical activity at the AV node that allows the ventricles time to fill
True/False: the PR interval includes conduction between the AV node and the ventricles
True: conducting tissue is very small and therefore does not produce a signal on the EKG. Once the ventricles contract, the QRS complex is produced
Is the rate of electrical conduction highest in the atrial muscle, ventricular muscle, or AV node? Where is it slowest?
Fastest: Ventricular muscle
Slowest: AV node
If the AV node did not pause electrical conduction, what would happen?
The ventricles would not fill sufficiently
What does the QRS complex represent?
Ventricular depolarization and atrial depolarization (masked by vent depolarization)
What does the Q wave represent?
Interventricular septum depolarization
What does the R wave represent?
Spreading of depolarization down the septum and into the myocardium (upslope) and through the distal portions of ventricles toward base (downslope)
What does the S wave represent?
Conduction through the left ventricular wall with vector directed toward left shoulder
What does the ST segment represent?
ventricular depolarization has completed, heart continues to contract but there is no electrical conduction
What does the T wave represent?
Ventricular repolarization
True/False: the ventricles repolarize while the heart continues to contract
True
What is the standard speed of EKG paper?
25 mm/s
How much time does 1 small box represent?
0.04 sec or 40 ms
How much time does 1 large box represent?
0.2 sec or 200 ms
What should be your first step in analyzing an EKG?
Determine the HR
True/False: the block method can be used to calculate the rate of regular and irregular rhythms
False: regular only
What is the first step in the block method to calculate HR?
Find a QRS complex that falls on a thick line
If a subsequent QRS complex falls on the 2nd thick line from the first, what is the HR? 3rd? 4th? 5th? 6th?
2nd: 150
3rd: 100
4th: 75
5th: 60
6th: 50
What is the equation to calculate HR based on # of large squares between QRS complexes?
HR = 300/# of large squares
What is the equation to calculate HR based on # of small squares between QRS complexes?
HR = 1500/# of small squares
How to calculate HR based on 6-second markings?
Count number of QRS complexes inside of a 6 second rhythm strip and multiply by 10
What is the only method that can be used to calculate HR with an irregular rhythm?
# of QRS complexes in 6 seconds, multiplied by 10
How can you tell if the rhythm is regular on an EKG?
If the interval between QRS complexes is constant from one cardiac cycle to the next
What are the two suclassifications of irregular heart rhythm patterns on EKG?
Irregularly irregular and regularly irregular
What are the 4 conduction pathways that carry signals from the SA node to the rest of the heart?
3 are from sinus to AV node (internodal pathways; anterior, middle and posterior)
1 Bachmann's bundle (SA node to left atrium)
What does a normal P wave look like (in lead II)?
Upright, smooth, rounded, symmetric (bell-curve), 2.5 mm or less in height, 0.12 sec or less
What conduction pathways are included in the PR interval?
- Conduction from SA node to AV node
- Delay at AV node
- Conduction between AV node and ventricles
What is the normal duration of a PR interval?
0.12 - 0.2 sec (3-5 small boxes)
What are the 6 criteria for a normal sinus rhythm?
- Normal P wave
- 60-100 bpm
- Regular rhythm
- One P wave preceding each QRS complex
- One QRS complex following each P wave
- QRS complex <0.12 sec
What is the pathology of a sinus arrest?
Sinus node fails to fire, resulting in transient episode with no cardiac activity
What is the pathology of a sinus exit block?
The sinus node continues to fire, but impulses are blocked from exiting the node
Does a sinus arrest or sinus block result in a length of cardiac inactivity that is an exact multiple of the normal rate?
Sinus block
What is the pathology of a PAC?
Ectopic focus fires, causing one or more P waves to occur earlier than expected if the heart rhythm were to be regular. P and T waves often combine
What is an atrial bigeminy? Atrial trigeminy?
PACs every second beat or third beat
How is atrial tachycardia defined?
3 or more PACs in a row
If you see "irregulary irregular" in the absence of P waves, what are you thinking?
A-fib
True/False: rate must be tachy to be A-fib
False: can occur at any rate
If you see a strip that looks like normal sinus rhythm but there is a constant rate of 150, what are you thinking?
Atrial flutter
Does atrial flutter have a regular or irregular rhythm?
Either
If there is a 2:1 atrial conduction and there are two flutter waves per QRS complex, what is the ventricular rate?
150
What is the distinguishing (and required) feature of wandering atrial pacemaker (WAP)?
3 or more different P wave morphologies
What differentiates WAP from MAT (multifocal atrial tachycardia)?
MAT has a rate >100
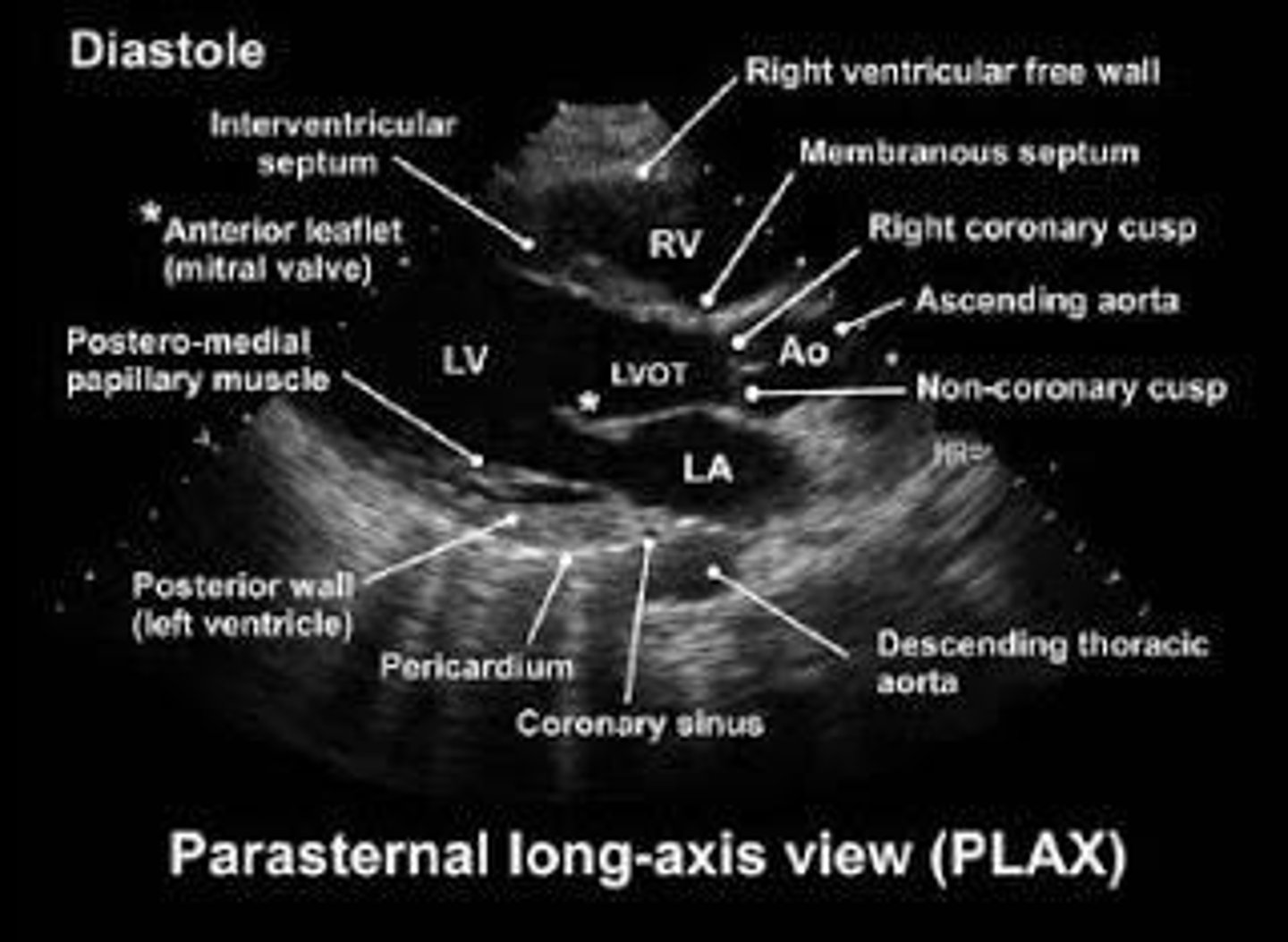
What structures can we see in parasternal long axis view on echo?
LV, LA, RV, AAo, Mitral valve, aortic valve
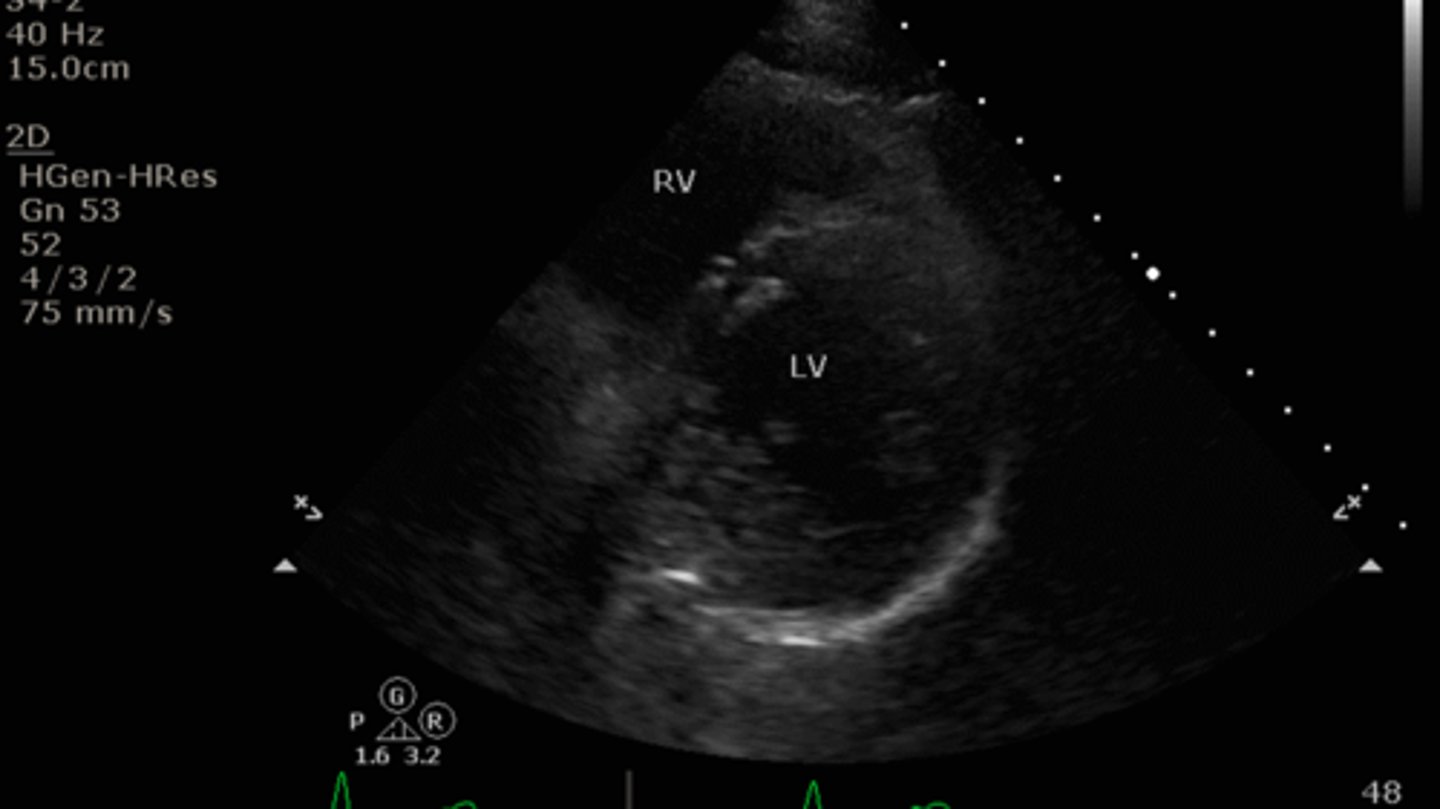
What structures can we see in parasternal short axis mid-ventricle view on echo?
LV, RV, IS, papillary muscles
What structures can we see in parasternal short axis mitral valve view on echo?
RV, LV, IS, mitral valve
How can you differentiate anterior and posterior mitral valve leaflets in a parasternal short axis mitral valve view on echo?
Anterior leaflet is closer to the IVS wall
What structures can we see in parasternal short axis aortic valve view on echo?
RV, RA, LA, aortic valve, tricuspid valve
How do you turn the probe to get from apical position to an apical 2 chamber view?
Rotate 60 deg counterclockwise
How do you turn the probe to get from apical position to an apical 3 chamber view?
Rotate 120 deg clockwise
What structures can we see in apical 2 chamber view on echo?
LV and LA and mitral valve
What structures can we see in apical 3 chamber view on echo?
LV, LA, RV, and aorta
How does the orientation of an apical 3 chamber view differ from parasternal short axis views, or other apical views?
Right-sided structures will appear on the right side of the monitor
What echo plane do we use to measure EF of the LV?
Parasternal long axis
How is EF of the LV calculated?
(EDV - ESV) / EDV
Use disc volumes to estimate LV volume; pi x r^2 x height
What is a normal EF?
55-70%
What does FAC measure?
Change in area of the RV between systole and diastole
What is an abnormal FAC value?
<35%
What does TAPSE measure?
Longitudinal displacement of the tricuspid valve annulus with systole (distance of minimum to maximum excursion of tricuspid valve)
What is an abnormal TAPSE value?
<17 mm
What does a TAPSE value <17 mm indicate?
Reduced right ventricular function
What mode of U/S is used for TAPSE?
M-mode: rapid, repeated images of the same area along a single line
Is doppler most accurate when the probe is parallel or perpindicular to the flow of blood?
Parallel
What is the modified Bernoulli equation to calculate pressure gradients across cardiac valves?
Delta P = 4v^2
What does continuous wave doppler measure?
Velocity of every RBC along a line of interest
What is continuous wave doppler best used to measure?
Very rapid velocities (aortic valve)
What is pulsed wave doppler best used to measure?
Low velocities (mitral valve) while minimizing noise from rapid velocities nearby
What does pulsed wave doppler measure?
Velocity at a sepcific intracardiac depth
Should continuous wave or pulsed wave doppler be used to measure aortic valve velocity?
Continuous
Should continuous wave or pulsed wave doppler be used to measure mitral valve velocity?
Pulsed wave
What does the E wave on mitral valve doppler represent?
Early diastolic filling
What does the A wave on mitral valve doppler represent?
Late diastolic filling (Atrial kick)
How would you tell apart a parasternal short axis aortic valve view from an apical 5 chamber view?
Apical 5 chamber will be oriented so RV and LV are closest to the probe
PSA Aortic Valve view will have RV most anterior, but the LV will not be visible
What does the apical 5 chamber view include that is not included in apical 4 chamber?
Ascending aorta
From apical 4 chamber view, do you turn the probe clockwise or counterclockwise to get to apical 2 and 3 chamber views?
Counterclockwise
What two chambers are seen in apical 2 chamber view?
LV and LA