Pharm 107 - Electrolytes Pt. 1
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Coverage: Body Fluids, Extra- and Intracellular Ions, Physiological Acid-Base Balance
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Total Body Water (TBW)
Represents ~60% (avg of 45%-75%) of adult body weight.
Divided into Intracellular and Extracellular fluid compartments.
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
~2/3 of TBW (~40% of body weight).
Fluid inside cells; primary cations: K⁺ and Mg²⁺; primary anion: phosphate (PO₄³⁻).
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
~1/3 of TBW (~20% of body weight).
Divided into:
Interstitial Fluid
Vascular/Intravascular Fluid
Interstitial Fluid
Fluid found in the spaces around the cells.
~75% of ECF; 12-15% TBW
Vascular Fluid
Also called plasma, refers to the liquid component of your blood.
~25% of ECF; 4-5% TBW
Solid Body Mass
Around 40% of the body weight (proteins, lipids, minerals).
Liquid Body Mass
Around 60% of the body weight (TBW).
Water Content by Demographics
Men: ~60% TBW.
Women: ~50–55% (due to higher fat content).
Infants: Up to 75% TBW.
Elderly: Lower TBW due to reduced muscle mass.
Water Gain (Input)
Metabolic Water: ~200 mL/day from cellular respiration.
Ingested Liquids: ~1,600 mL/day.
Moist Food: ~700 mL/day.
Water Loss (Output)
Urine: ~1,500 mL/day (main source).
Skin (sweat/evaporation): ~600 mL/day.
Lungs (exhalation): ~300 mL/day.
Feces: ~100 mL/day.
Fluid Balance
Homeostasis between water gain and water loss.
Maintained via thirst, kidney function, hormonal regulation (ADH, aldosterone, ANP).
Membranes
Separates compartments from each other.
Permeable to H2O and many other organic and inorganic solutes.
Selectively permeable to Na+, K+, Mg2+ but impermeable to macromolecules.
Osmosis
Passive water movement through a semipermeable membrane from low to high solute concentration.
Osmolality
Osmoles/kg of water (more clinically relevant).
Osmolarity
Osmoles/L of solution.
Tonicity
Effect of a solution on cell volume:
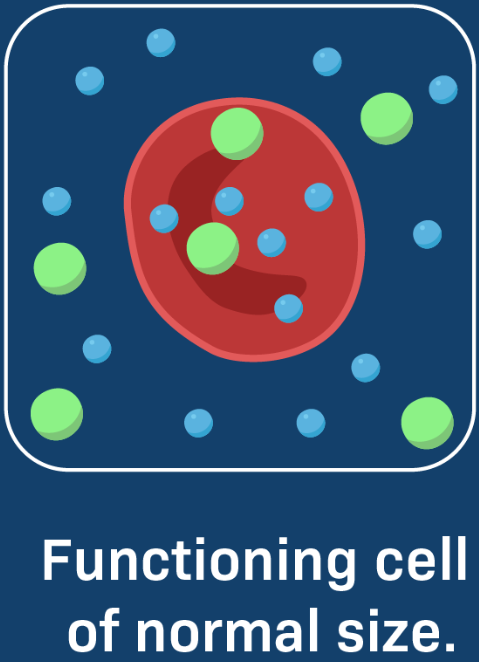
Isotonic: No net water movement.
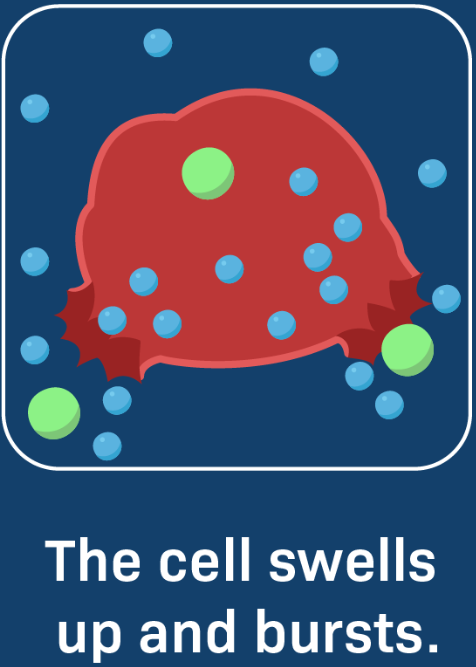
Hypotonic: Water moves into cells (cell swells).
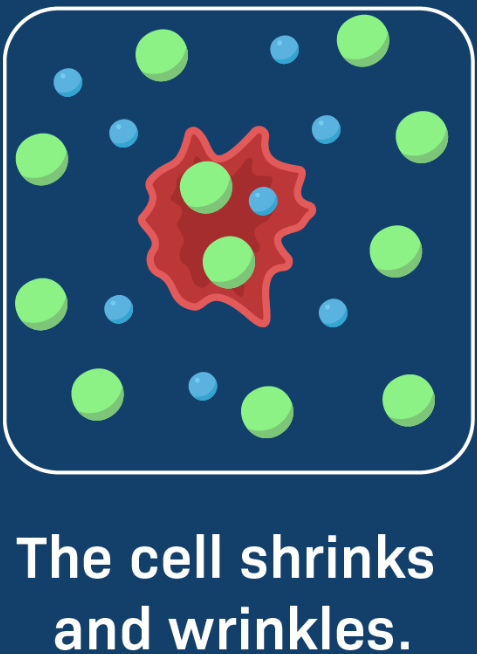
Hypertonic: Water moves out (cell shrinks).
Isotonic Cell
Hypotonic Cell
Hypertonic Cell
Hypothalamus
Thirst Center of the Body.
Activity is triggered by increased plasma osmolality or decreased blood volume and flow of saliva.
RAA System
Stands for the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system.
Hormone system that plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance in the body.
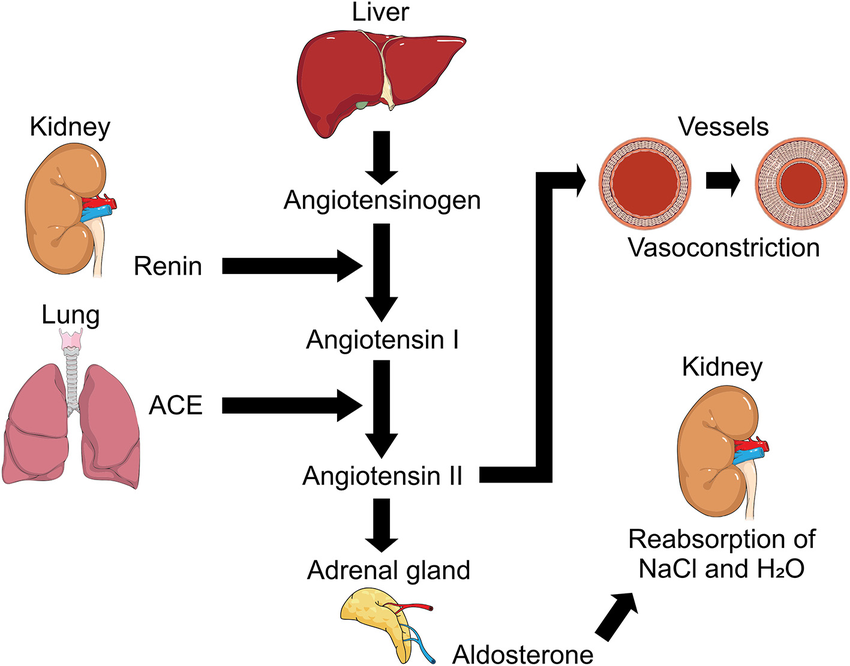
Hormonal Regulation of Fluids
Angiotensin II
Aldosterone
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH or Vasopressin)
Angiotensin II
Created by the synthesis of Angiotensin I through the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme.
Tightens the blood vessels and stimulates adrenal glands, the latter of which signals the production of aldosterone.
Effect of Angiotensin II
Reduces loss of water in urine.
Increases blood pressure.
Aldosterone
Promotes urinary Na⁺ and Cl- reabsorption and increases water reabsorption via osmosis.
Promotes the excretion of K+.
Effect of Aldosterone
Reduces loss of water in urine.
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Promotes natriuresis, which is the increase in excretion of Na⁺ and Cl-, accompanied by water.
Leads to a decrease of blood volume.
Effect of ANP
Increases loss of water in urine.
Decreased blood volume.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Also called vasopressin.
Promotes insertion of water-channel proteins (aquaporin-2) into apical ducts of kidneys.
Results to increased water permeability of cells and more water reabsorption.
Effect of Vasopressin
Reduces loss of water in urine via renal water reabsorption.
Goal if Dehydrated
Decrease urine output.
Increase angiotensin II, aldosterone, ADH, and thirst center activity.
Goal if Increased NaCl
Natriuresis
Increase atrial natriuretic peptide and more natriuretic activity.
Hypernatremia
Happens if the body has too little water and too much sodium.
Common when dehydrated.
Hyponatremia
Happens when sodium content in blood is abnormally low.
Common when overhydrated.