Lifecycle of stars
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
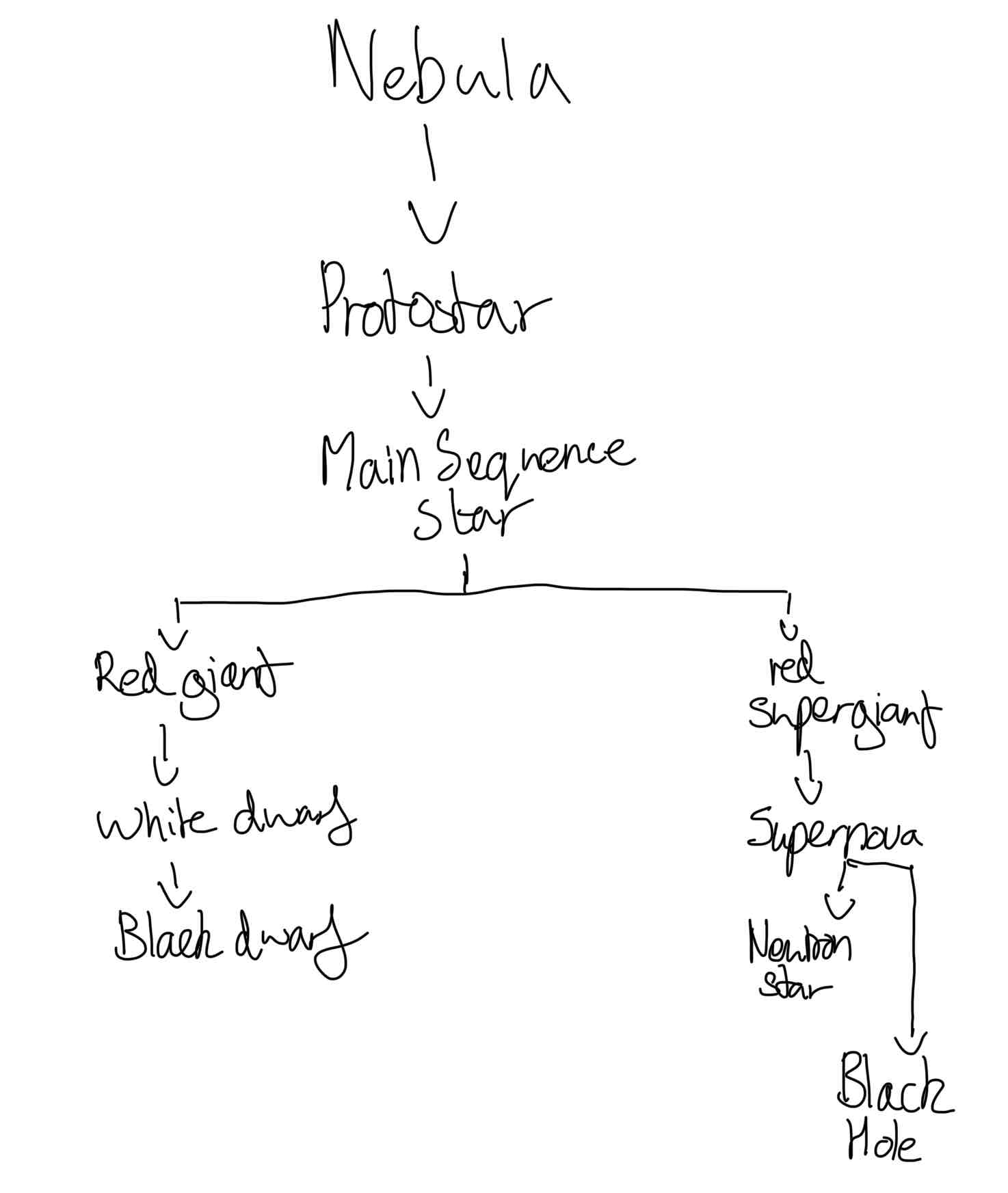
What is a nebula?
A large cloud of gas and dust
How is a protostar formed?
Gravitational attraction pulls gas and dust of nebula together. This collapses and the core of the nebula becomes very hot and turns into a protester which is hot and dense.
Describe nuclear fusion
Two light nuclei join together to form a heavier nucleus. Hydrogen nuclei joined together form helium nucleus, which releases energy that keeps the core of the star hot.
What is a main sequence star?
When the energy released by nuclear fusion causes an outward force and the star expands. The inward pressure and the outward pressure become equilibrium and the star becomes stable.
How is a red giant star formed?
Eventually, hydrogen will run out and the temperature will increase. This causes an increase in outward force. The star will expand and turn red. Inside the core, a fusion reaction begins to create heavier elements.
How is a white dwarf star formed?
The red giant becomes unstable and the outer layer is expelled. The remainder collapses due to gravity and leaves behind a smaller but very hot dense solid core. It appears white as it is very hot.
How is a black dwarf star formed?
When a white dwarf calls down it uses up the energy until it no longer has enough energy to emit light.
What happens to a red super giant star?
They begin to shine brightly again as they experience more nuclear fusion. After passing through several cycles of expansion and contraction, they eventually explode.
What happens in a supernova?
The red super giant will collapse rapidly and explode as it explodes, the extremely high temperature means that elements heavier than iron will be formed through fusion. The explosion distributes them throughout the universe.
How is a neutron star formed?
After a supernova, a very dense core remains which tends to spin very fast.
How is a black hole formed?
When a supernova collapses in on itself, the court is so dense that nothing can escape the black holes gravity not even electromagnetic radiation so there is no visible light.
State the life cycle of a star