developmental psychology
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
monozygotic
identical twins
dizygotic
fertonal twin
similar personalities and characteristic
Monozygotic
intelligence
higher correlation in monozygotic
stages of development
Heredity genes passed down from of parents genes
variety
what changes across
Gregor Mendel described principles of Heredity (cross breeding)
Genes are not a blending of two traits
one copy of each trait from parents (dominant)
Heredity Mendel (Principle)
interaction of one trait from mom and dad's copy (not a blending)
Phendype
observable
Genotype
genes
Principle of dominants
Dominate (rolling tongue) vs recessive genes
Principle of segregation
Each copy of trait is Passed down separately as a unit
ex. moms copy is Segregated → blue eye egg will not attract Sprem with blue eye
Principle of Independent assortment
the different traits are independent of each other
Polygenic inheritance
some traits determined by multiple genes
Incomplete to dominance or Codominance
not all gens are entirely dominate or recessive
cell division
Transmission of this genetic material
Two types of cell division
meiosis-
mitosis
meiosis
- four cells with 1/2 chromosomes
egg and sperm must contain right amount of chromosomes for reproduction (one member of each 23 contain in in all other pairs of the body)
mitosis
two identical child cell
Chromosome (3 ine plus mes)
Adenine, cytosine, Thymes and guanine
Chromosome replication
double helix unzips
Gens nucleotides
specific sequences
Disorders (Dominant)
may not become active until passing to Offspring
Disorders: Huntington
nervous system degeneration uncontrollable movement, Mood shits and memory disturbances in adulthood (between 30-50)
disorder Recessive
typically dominant within particular people
Gene- Behavior Interaction
reaction range- expression of gene and phenotype might depend on environment
family Studies
Examine generation for traits believe to have genetic basis
ex similar environment, cultures, religion
family studies when genetics aren’t the cause
environment
Adoptive vs Biological
difference in genes same environment
Adoptive Studies: Schizophrenia and intelligence
strong biological correlations
Genetics become more important as the child deveps
environment has an effect more on early development
Twins Studies : Monozygotic
identical
Twins Studies Dizygotic
fraternal
Twins Studies: intelligence
higher correlation in mono than di
Twins Studies: characteristic
Monos more similar on personally characteristic than Dis
Prenatal Devolvement
_______ by meiosis Contain half of required genetic materials
dads sperms sperm and moms egg
Prenatal Devolvement: Conception
egg and sperm come together to produce a single cell
Prenatal Devolvement: Zygote
all genetic material (23 pairs chromosomes)
Zygote embeds in uterine lining
51.3% of male newborns even though male fetuses susceptible to
spontaneous abortions
males more likely to experience fetal distress → lager circumference
Developmental Processes
zygote → embryo → fetus
Developmental Processes :
zygote divides into 2 full of genetic material → continues to multiple next 38 weeks
Developmental Processes : Cell migration
movement newly formed cells
Prenatal Devolvement: conception
egg and sperm come together to produce a single cell
gametes produce by meiosis, Contain half of required genetic materials
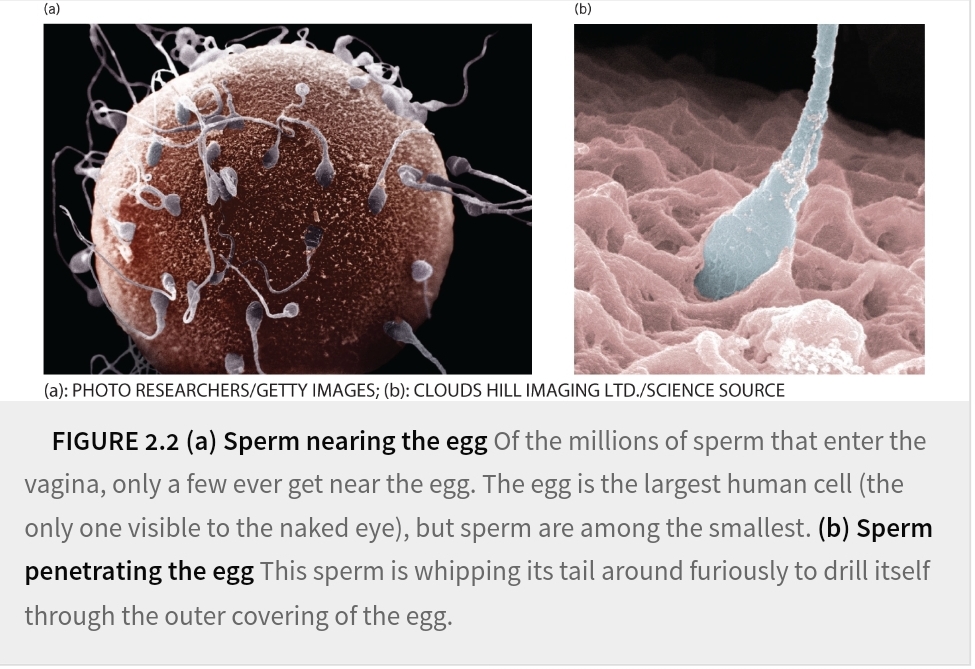
Prenatal Devolvement: gametes
gametes result of specialized cell from mom (egg) and dad’s (sperms)
Developmental Processes: prenatal devel
cell differentiation embryo cells (aka embryonic stem cells) starts specializing
regenerative medicine (stem cells)
apoptosis
death-apoptosis: programed death required for hands to form
Stage 1 : (conception-2 week)
implants in utero
cells multiples by mitosis
Stage 1 : (conception-2 week): amniotic sac, umbilical cord
Cells differentiate and specialize in to embryo and support cells for embryo
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks)
All major internal and external structures form
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): cell layers
Endodermal
Ectodermal
Mesodermal
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): Endodermal
internal organs
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): Ectodermal
nervous system, eyes, ears, skin
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): Mesodermal
muscles, bones, heart
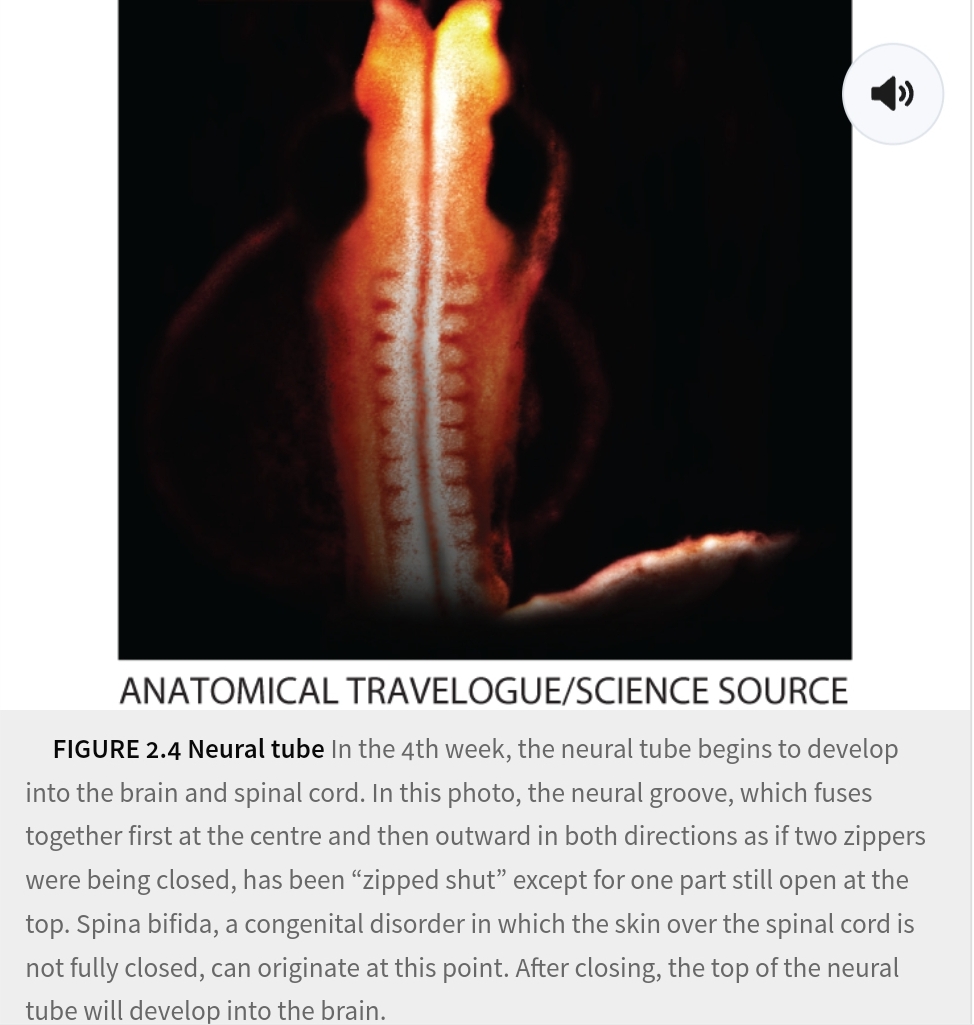
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): neural tubes
develop in brain rest spinal card (week 4)
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): Week 5
Major brain development
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): Week 6 & 7
differentiation of limbs
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): placenta
barrier exchange materials bloodstreams (don't mix)
Carbon dioxide removed from mother bloodstream
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): umbilical cord tube
umbilical cord tube containing blood vessels run to fetus
stage 2: Embryo (3-8 weeks): Cephalocaudal devel
Cephalocaudal devel → head before body, hands before feet
Stage 3: Fetus (9-38 weeks)
development of body so at Birth head mass 25%
Stage 3: Fetus (9-38 weeks):
Facial features
Nails and toes
Head hair grows
Stage 3: Fetus (9-38 weeks): 3 month
brain differentiated into visual, auditory, cognitive centers
Stage 3: Fetus (9-38 weeks):
month 3 physical activity begins → fist forming and toe wiggling
Stage 3: Fetus (9-38 weeks): month 4
eyes sensitive to light
Stage 3: Fetus (9-38 weeks): month 5
→ Sounds cause reaction (kicking and turning)
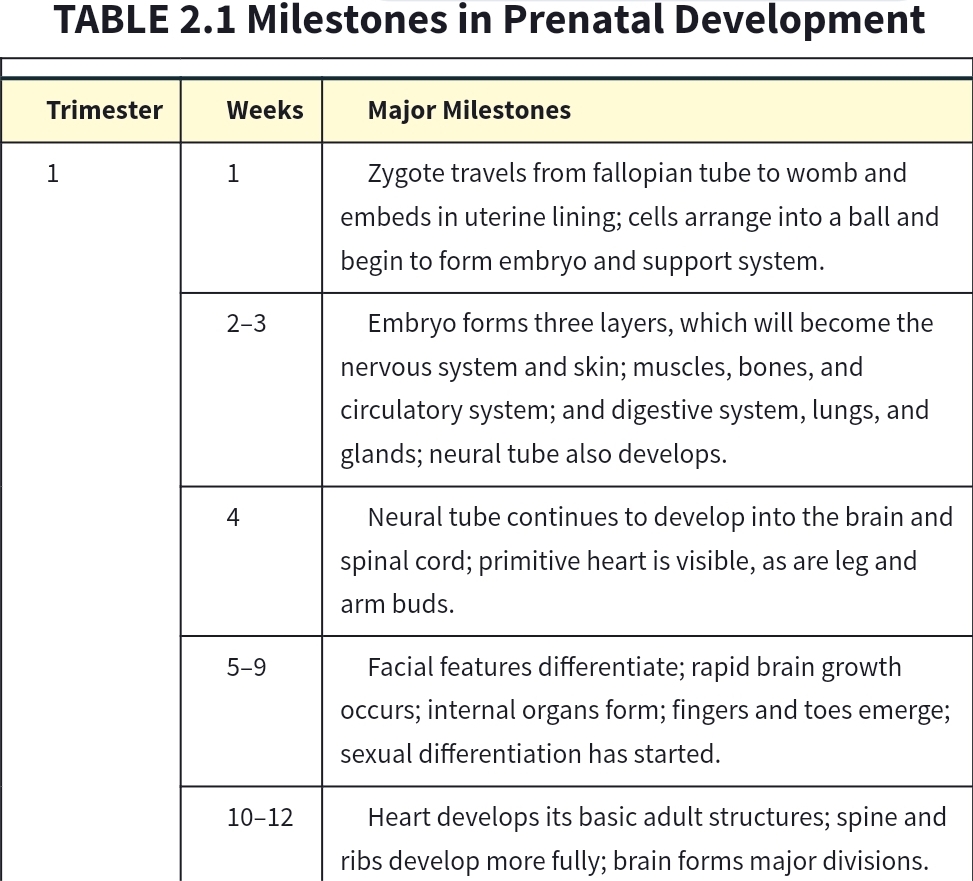
Trimester 1 (Discontinuity)
week 1: zyote
week 2-3: embryo layers- nervous, circulatory system, glands
week 4: neural tube- devels brain, spinal cord
week 5-9: facial features, internal organs, fingers, sexual differentiation
week 10-12: heart develops, spine, ribs, brain forms
Trimester 2 (Continuity)
weeks 13-24: external genitalia, fetal movement felt, basic expression
Discontinuity
Discontinuity refers to the view that development occurs in a series of distinct stages:
Three layers of cells of embryo
change over weeks→ zygote, embryo, fetus
Continuity
refers to the view that development is a gradual
Prenatal Learning: Discontinuity (five senses)
Movement: Swallowing amniotic fluid → helps digestive system mature properly
Touch: Contact of hand and mouth
Sight: Prefer to look towards face that are up right
Taste: amniotic fluid veriest in taste
Smell: amniotic fluid takes on the smell of what mothers eaten ( liquid transmission)
Hearing: mother bloods, voice and amniotic fluid
Prenatal Learning studies
infants suck pacifier to hear mother's voice over a stranger's
reading story during last 6 weeks pregnancy in fact prefers story read then (rhythm)
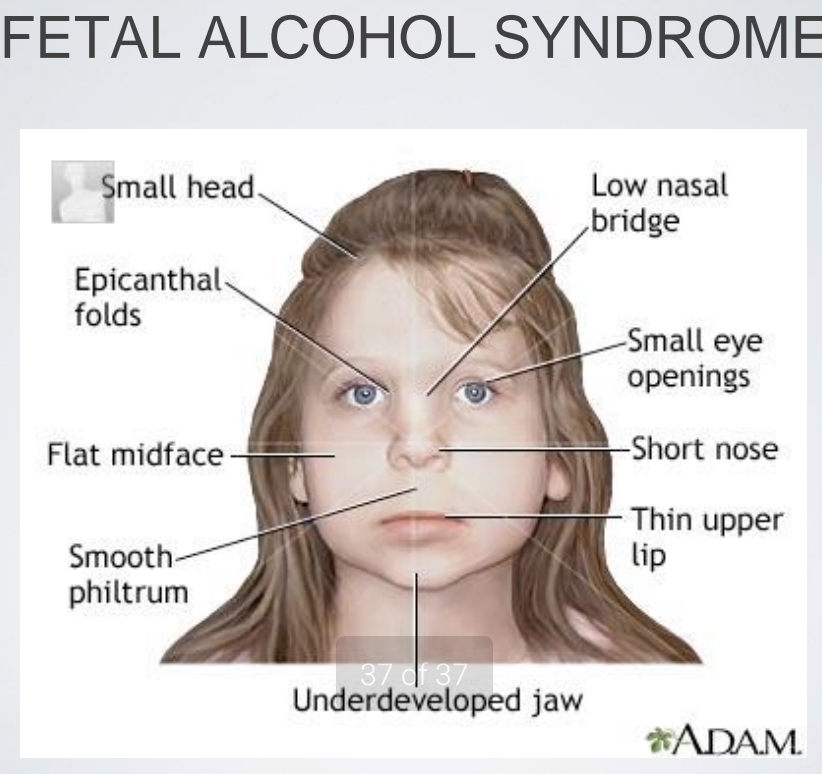
Teratology
nongenetic agents causes defects in embryo and fetus
Hazards to Prenatal Development
Thalidomide → cause limb devel (Second week)
dose -response relation → amount of exposure to teratogens
fetal programing →ajust to level Of nutrition deficiency doesn't rest
genetic susceptibility → predisposed
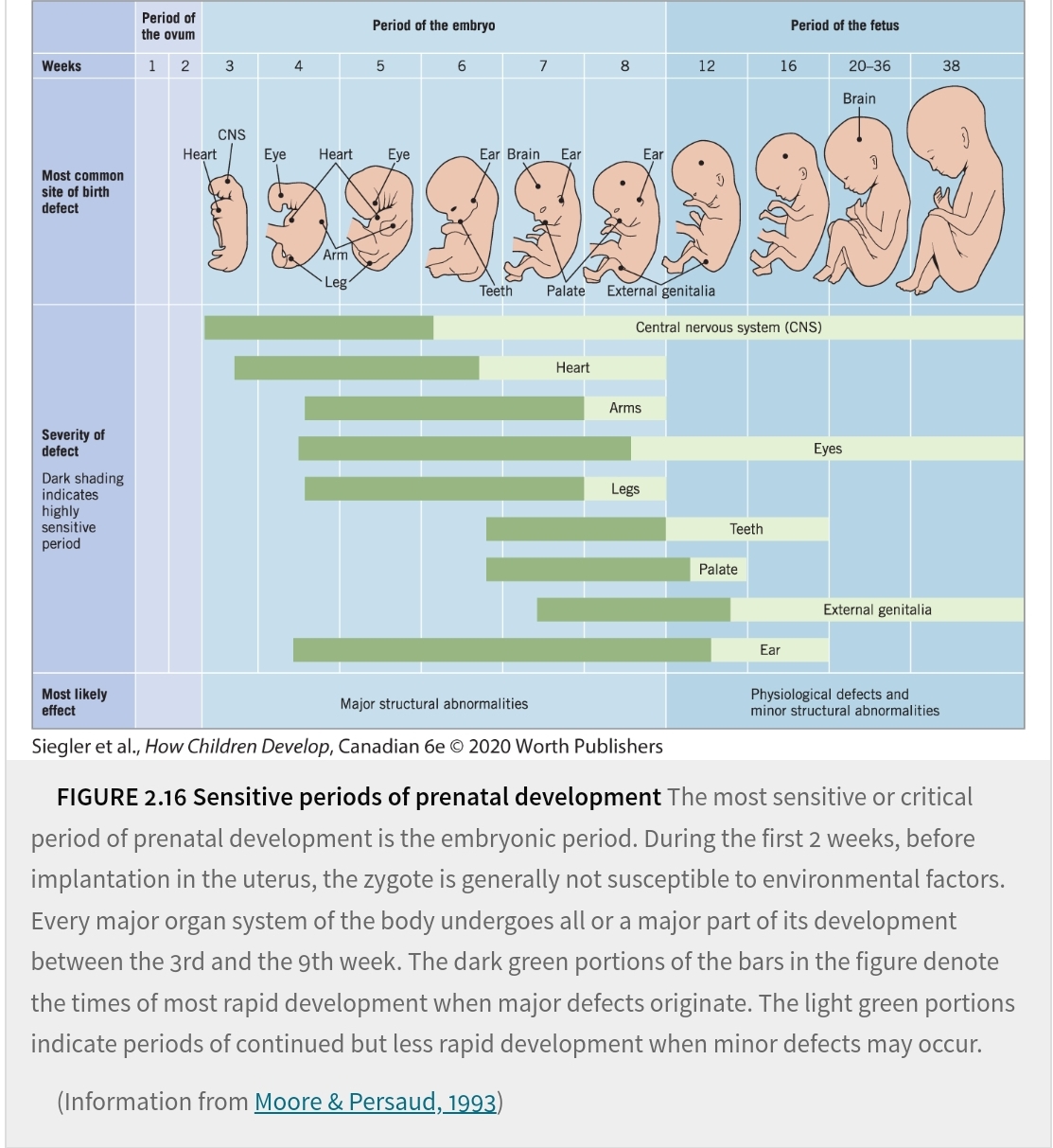
How Teratogens Act
Genetic sensitivity (species specific)
Temporal sensitivity
Effect specificity
How Teratogens Act: types
Rubella
Herpes →CNS
HIV → facial deformities, failure to smooth
syphilis & Gonorrhea→ prematurity, spontaneous abortion, eye infections
Malnutrition → spontaneous abortion, smallness, prematurity
Parental age → down's syndrome
Drugs → street drugs, caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, accutane, Opioids Neonatal abstinence syndrome (fetus withdrawal)
Marijuana → smallness, still birth, attention, learning and social problems
CAD 12% women smoke
Antidepressants → solulu therapy and mindfulness
SIDS accounts for 21.3% postneonatal deaths
limited access to oxygen and genetic mutation
How Teratogens Act: HIV
facial deformities, failure to smooth
How Teratogens Act: syphilis & Gonorrhea
prematurity, spontaneous abortion, eye infections
How Teratogens Act: Malnutrition
spontaneous abortion, smallness, prematurity
How Teratogens Act: Parental age
down's syndrome
How Teratogens Act: Drugs
street drugs, caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, accutane, Opioids Neonatal abstinence syndrome (fetus withdrawal)
Physical and Motor Development
Behavior's closely related to neurological mechanisms
To find infants at risk for later developmental issues
At Risk Infants:
Teratogens
Poverty
Teenage Mothers
unmarried Mothers
Mothers without high school Degrees
how Birth Weight Babies
Caesarean Section Babies
Low Birth weight:
Pre-term Infants; That is before the minus 2 weeks (point e.g 3-4 weeks )
Small for Gestational Age: smaller than they are supposed to be
complications to birth weight
trouble Breathing an Anoxia
Poor muscle Tone
Later Behavioural and Academic Problems
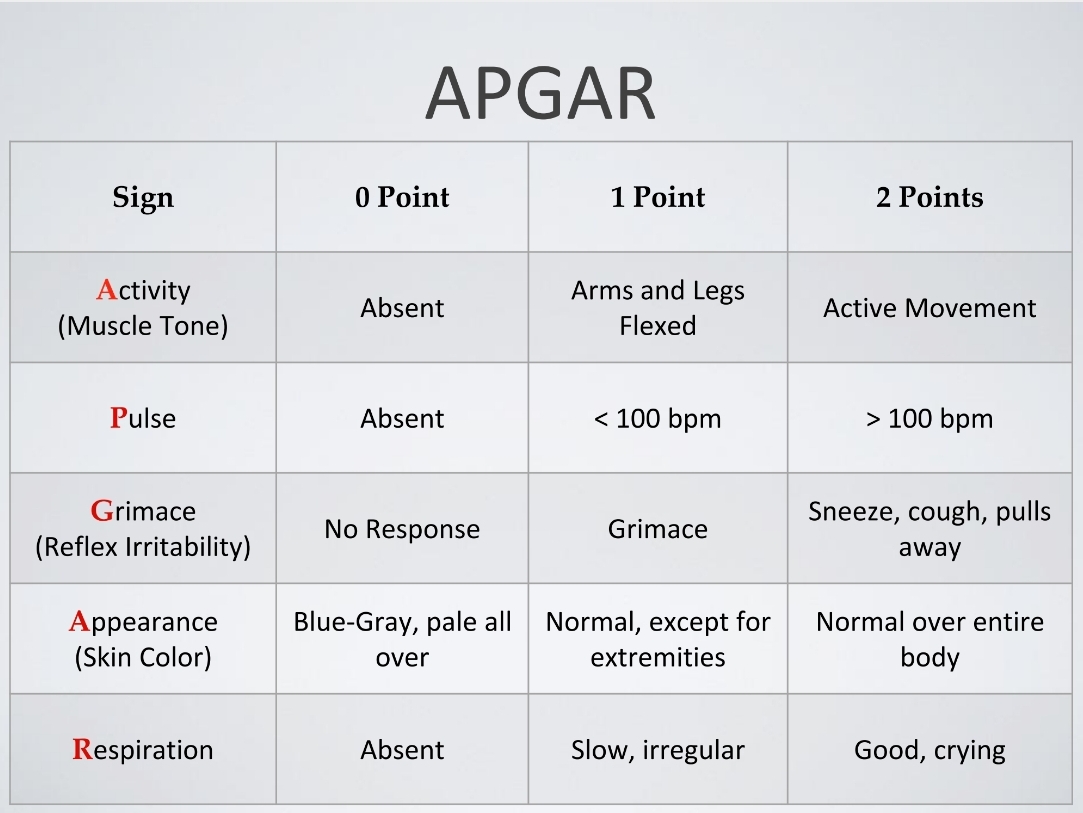
Newborn Assortment Methods: APGAR Exam
Measures heart rate, respiration, muscles tone, Skin color, and reaction to mild stimulus
Measures on a 0-10 scale
Assessed at birth, 5 minutes and sometimes at 20 minutes
infants with scores below 4 are consider "at risk”
Precht Test
Similar to APGAR but also assesses reflexes, facial expressions, alertness, etc
APGAR' Links and Predictions
Prenatal Drug Exposure →Lower Scores
Caesarean Section → lower Scores
disclaimer: Lower Scores do Not predict physical growth and development at 6 months
Predictive:
low score predicts physical growth and ability at 4.5 years
Sleeping and Sids ( Sudden/ Death Syndrome)
Most vulnerable is between 2 and 4 months
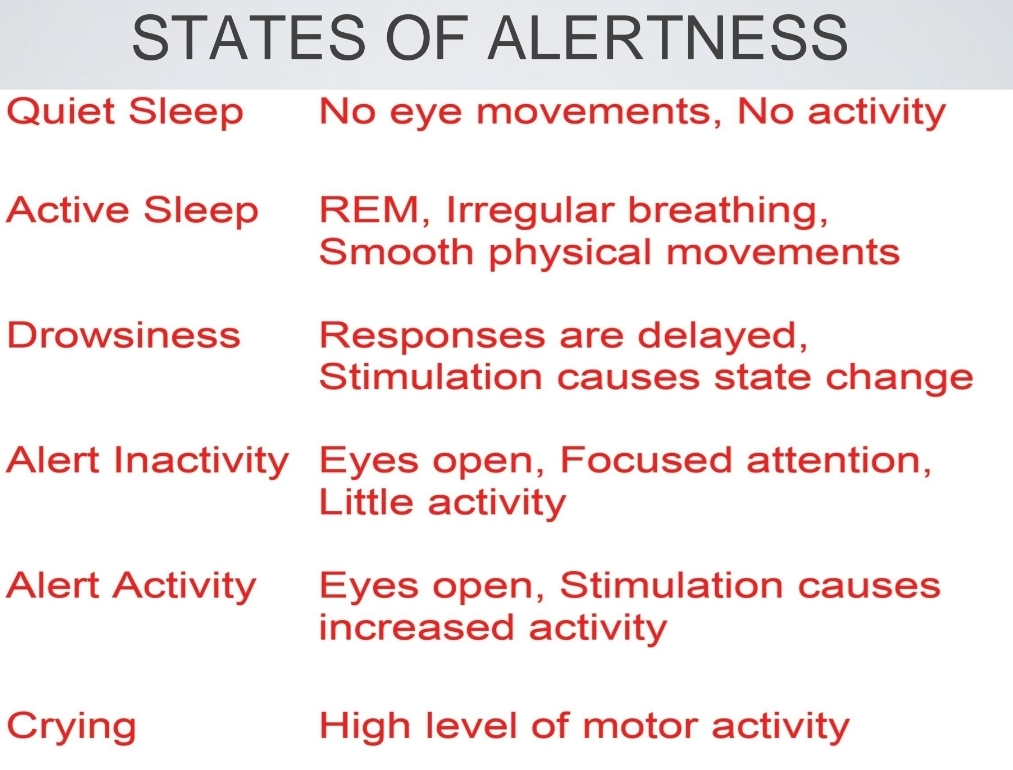
Sleep sids cause
thoughts they sleep face down breathing in CO2, general Suffocation
sleep side factors
Sleep position
soft bedding and overheating
Maternal smoking
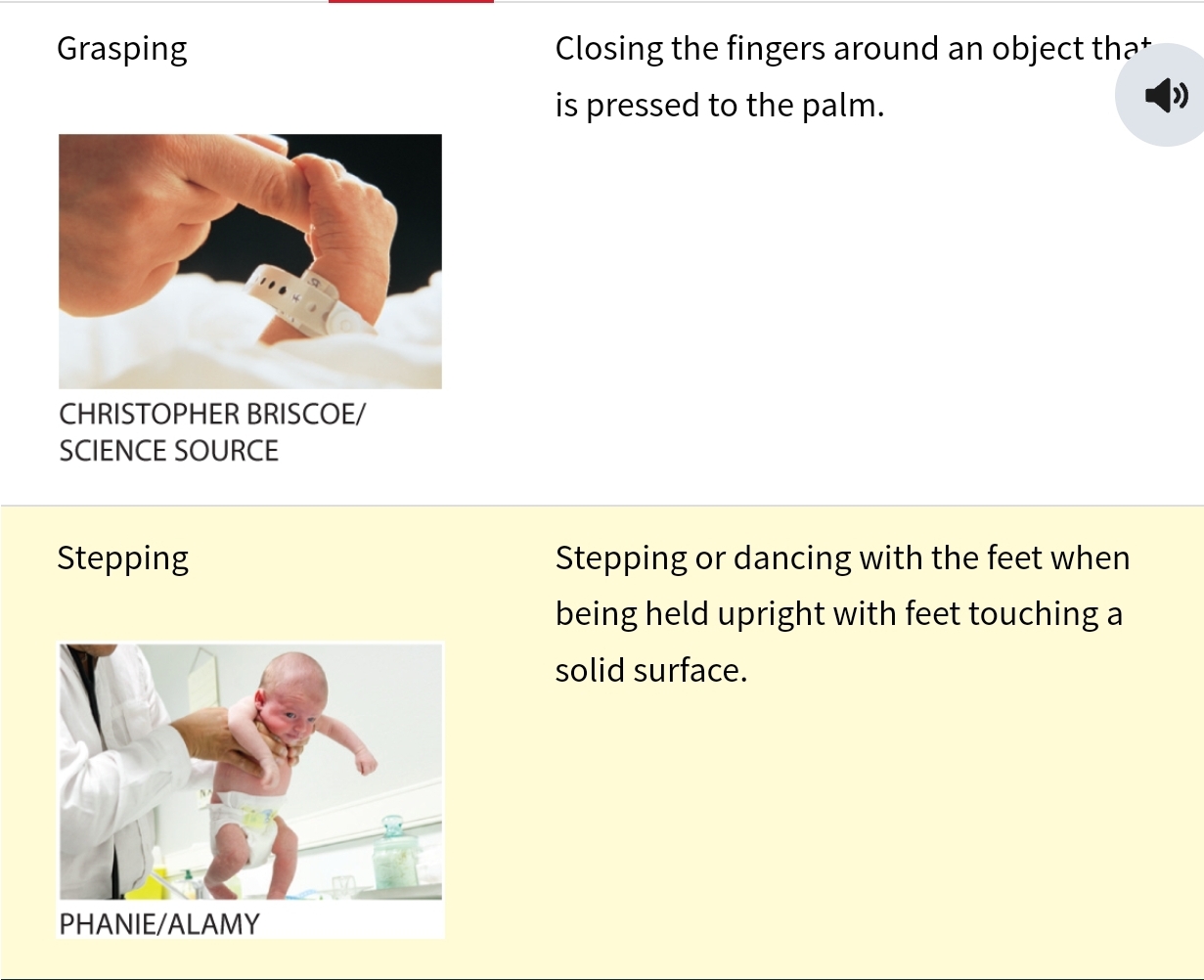
Reflex definition
tightly organized patterns → can have adaptive values others not so much
major Newborn reflexes include
grasping
rooting
sucking
swallowing
grasping
→ Close fingers around anything pressed into palm of hand
rooting reflex
→ stroke cheek turn head in direction to touch and open mouth (breastfeeding)
Sucking
→ oral contact with nipple
Swallowing
→ increases chance of nourishment and surviving

reflexes not fully automatic →
more likely to occur when infant is hungry
Motor Development
Locomotion
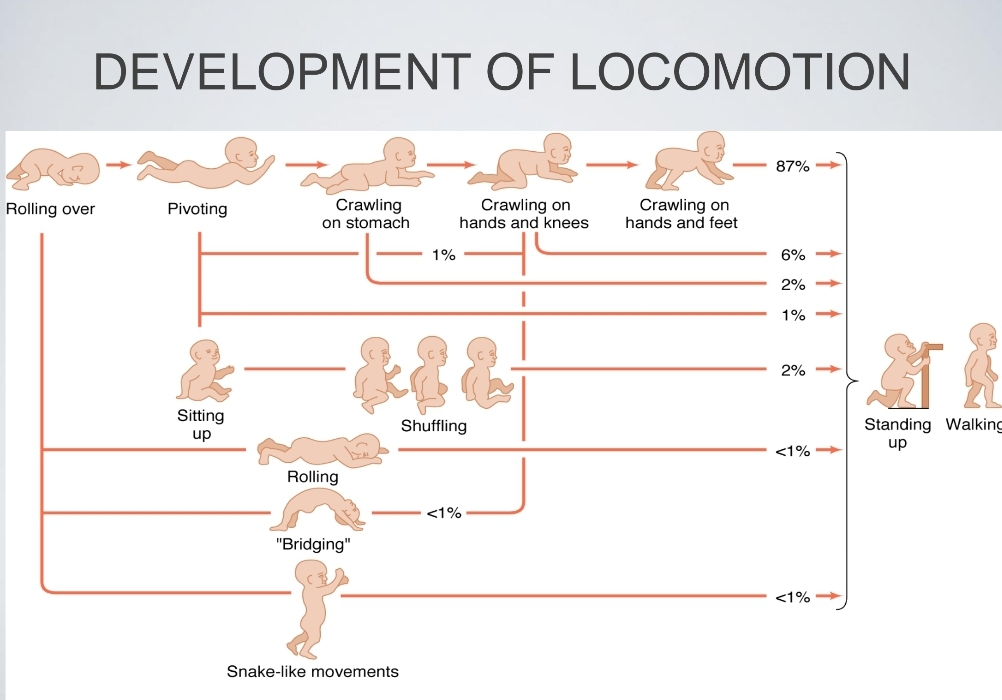
Individual and Cultural differences
context in which infants are developing matter to their progress
Exercises for limb manipulation
Use of diapers impact on walking pattern