lab practical 1
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
simple squamous epithelium
-single layer of flattened cells -the typical preparation to show these cells are made from a cheek smear -the cells have a polyhedron shape from above & a flattened appearance when viewed from the side -another location where this is found is in the alveoli of lungs
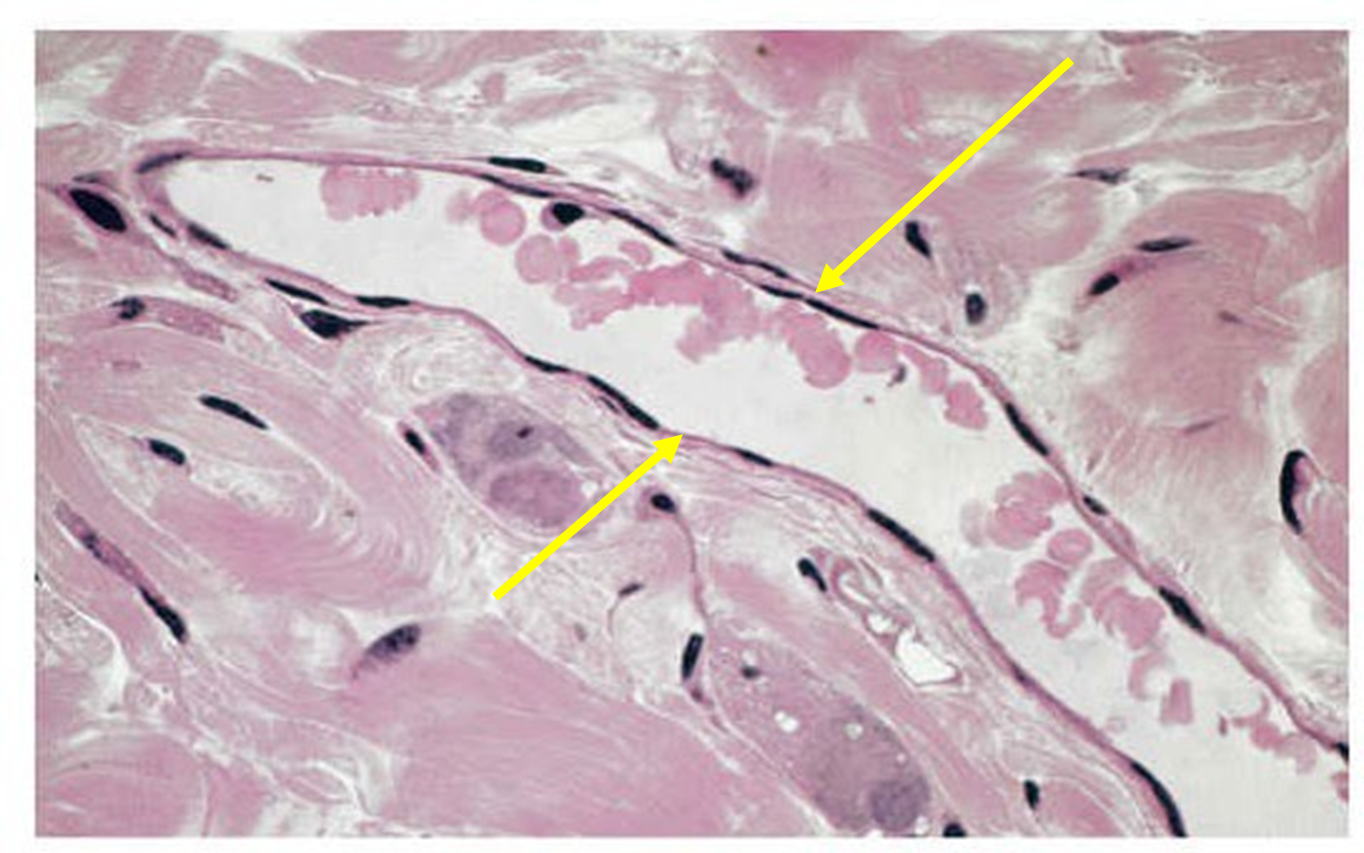
simple squamous epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube shaped epithelial cells -found in ducts of glands or sections of the kidneys showing the kidney tubules
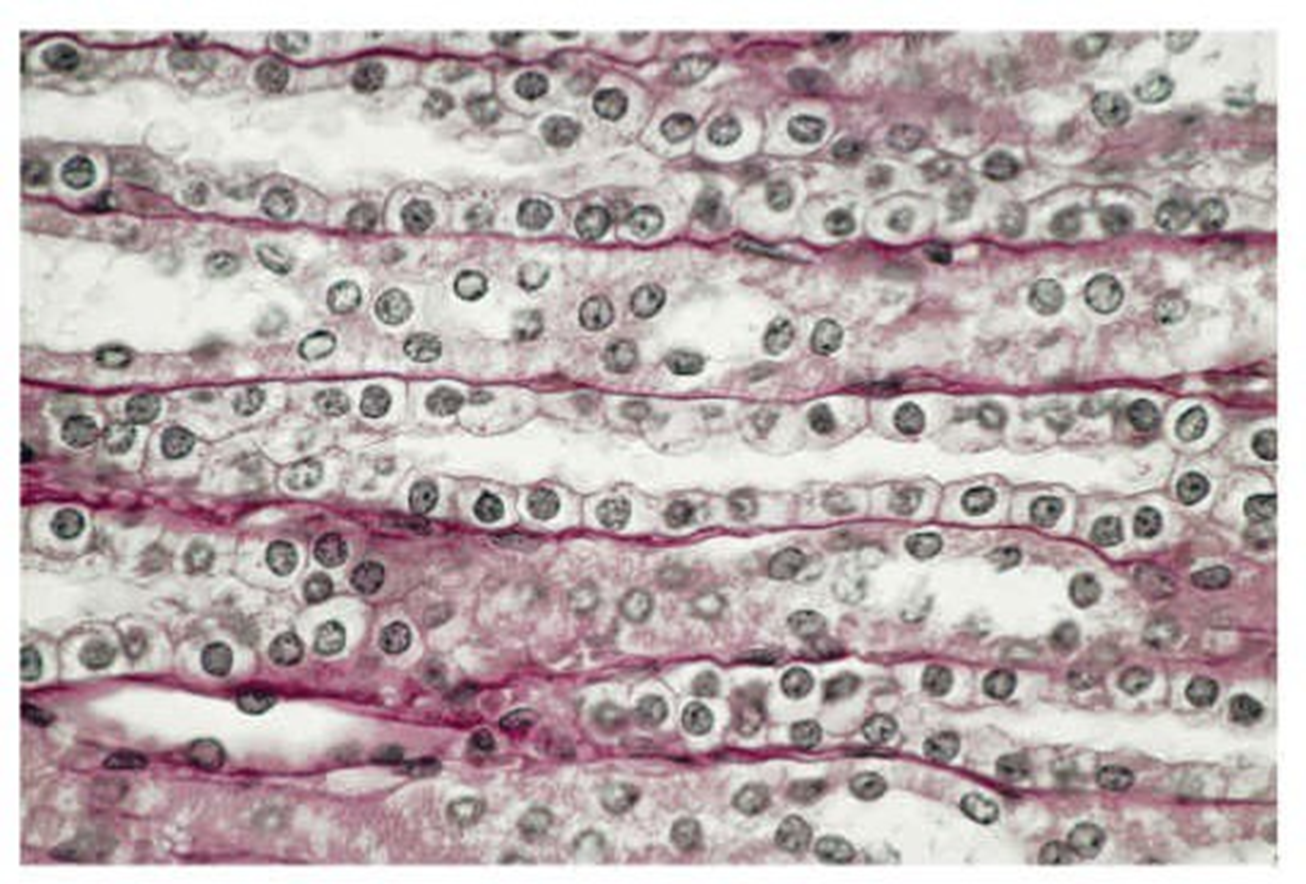
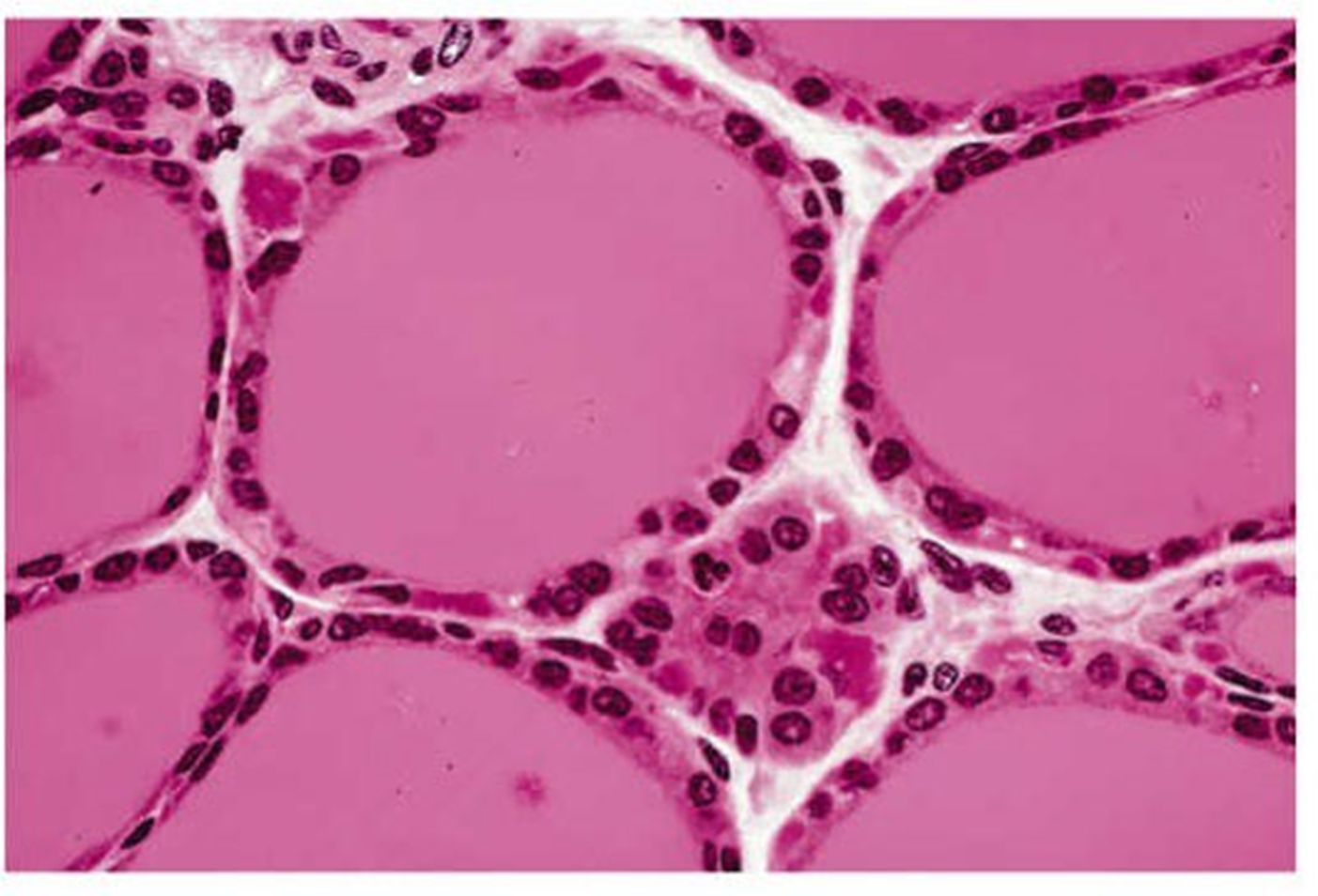
simple cuboidal epithelium
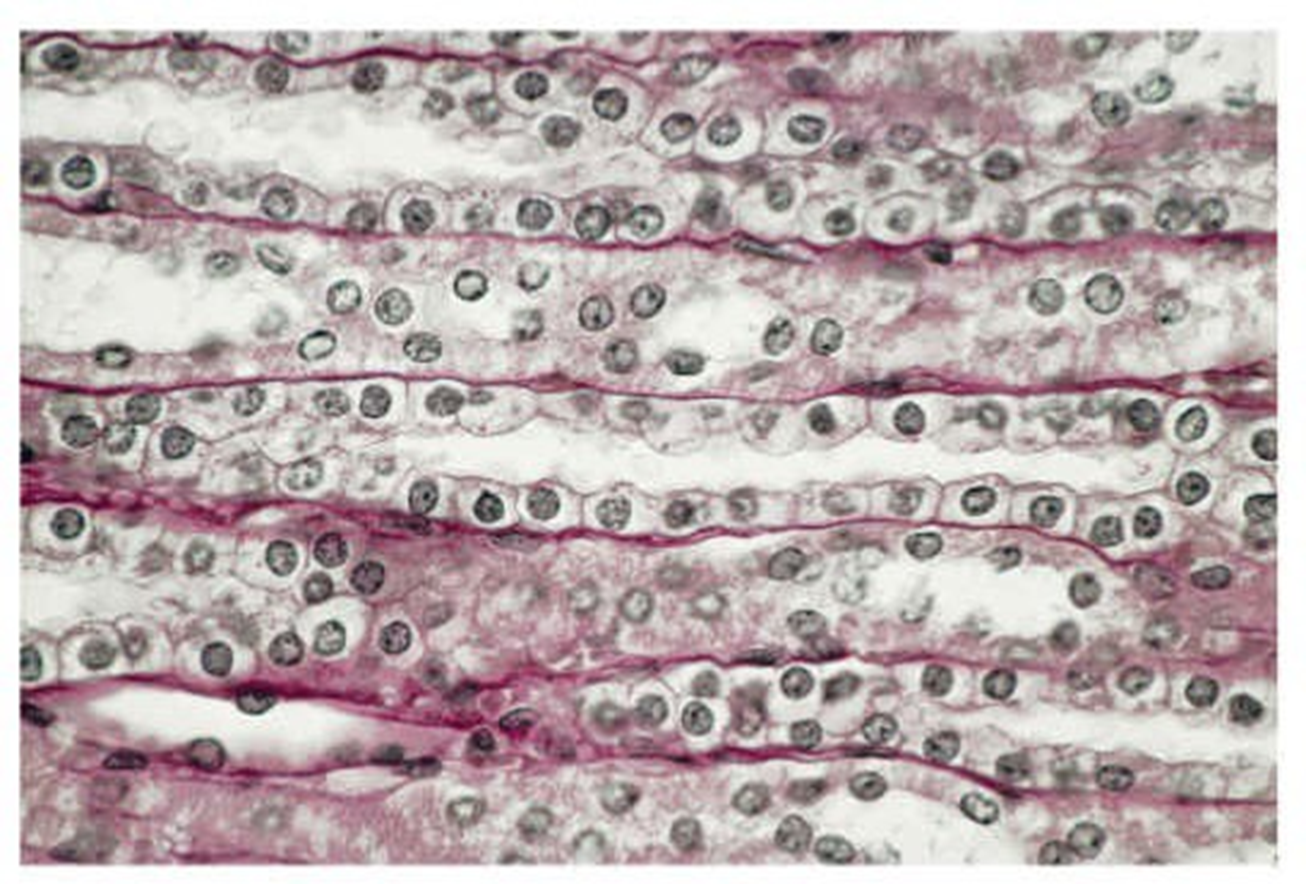

simple columnar epithelium
single layer of column shaped epithelial cells. cells are longer than they are wider. found in the lining of the intestinal tract and fallopian tubes
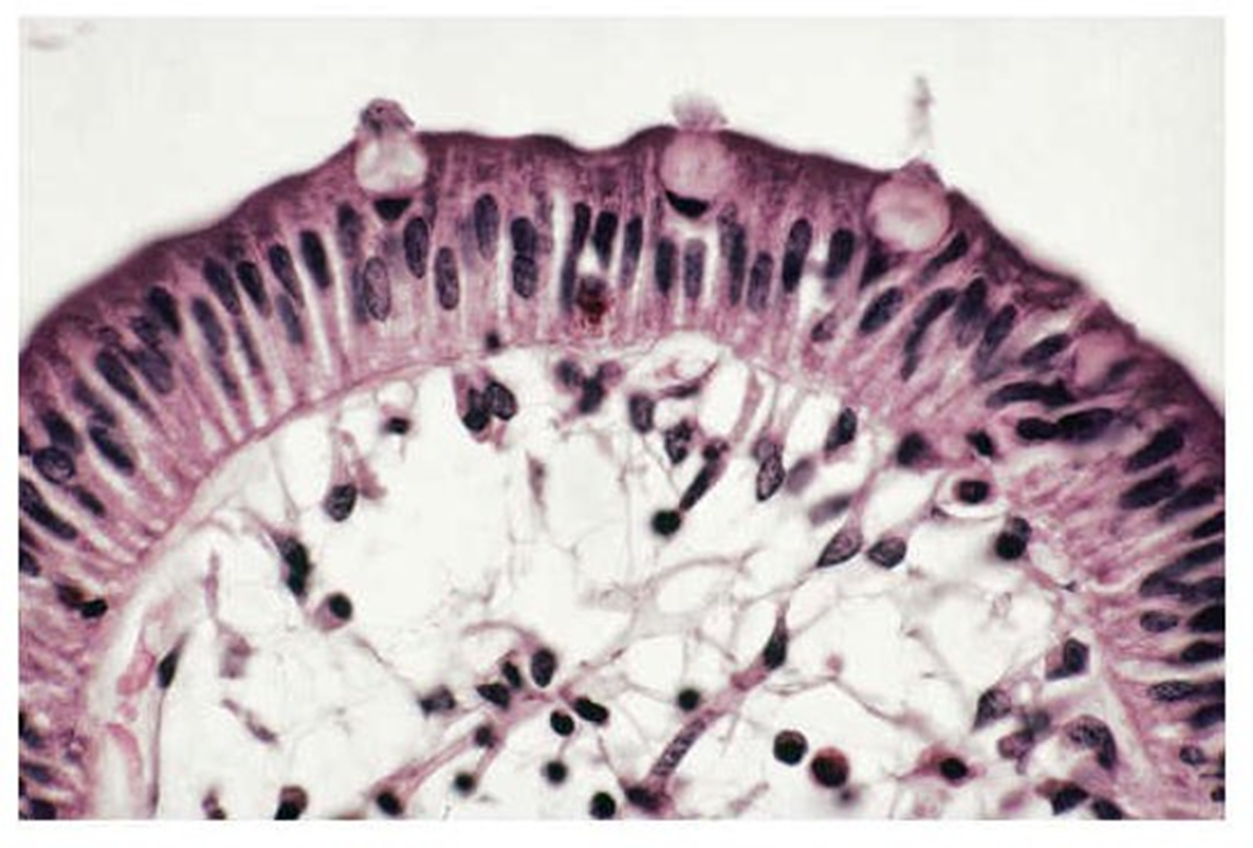
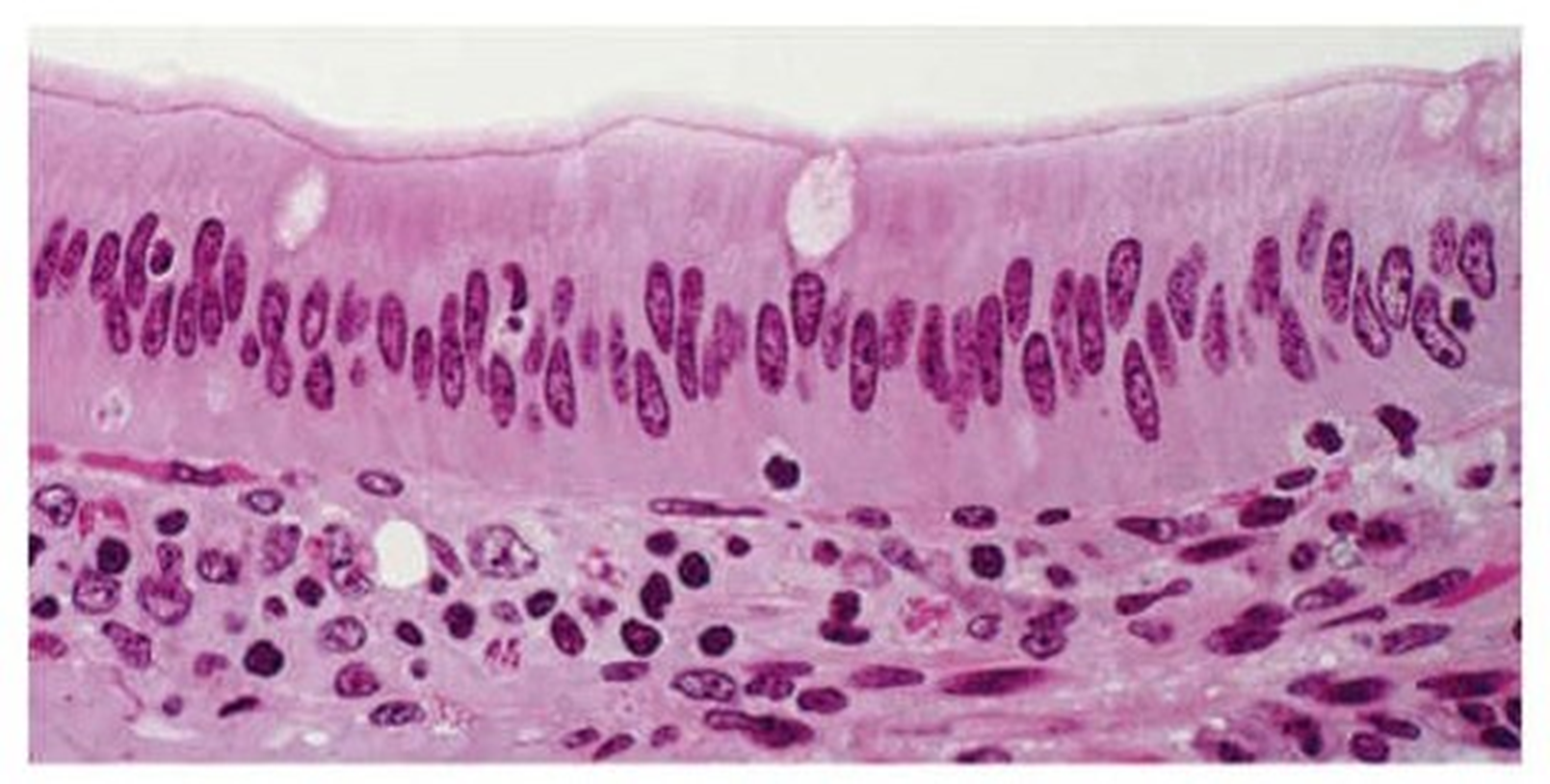
simple columnar epithelium


stratified squamous epithelium
multilayered tissue of squamous (squished) epithelial cells. the multiple layers provide protection such as in the epidermis of the skin. these cells may appear cuboidal but change to squamous as they reach the later.
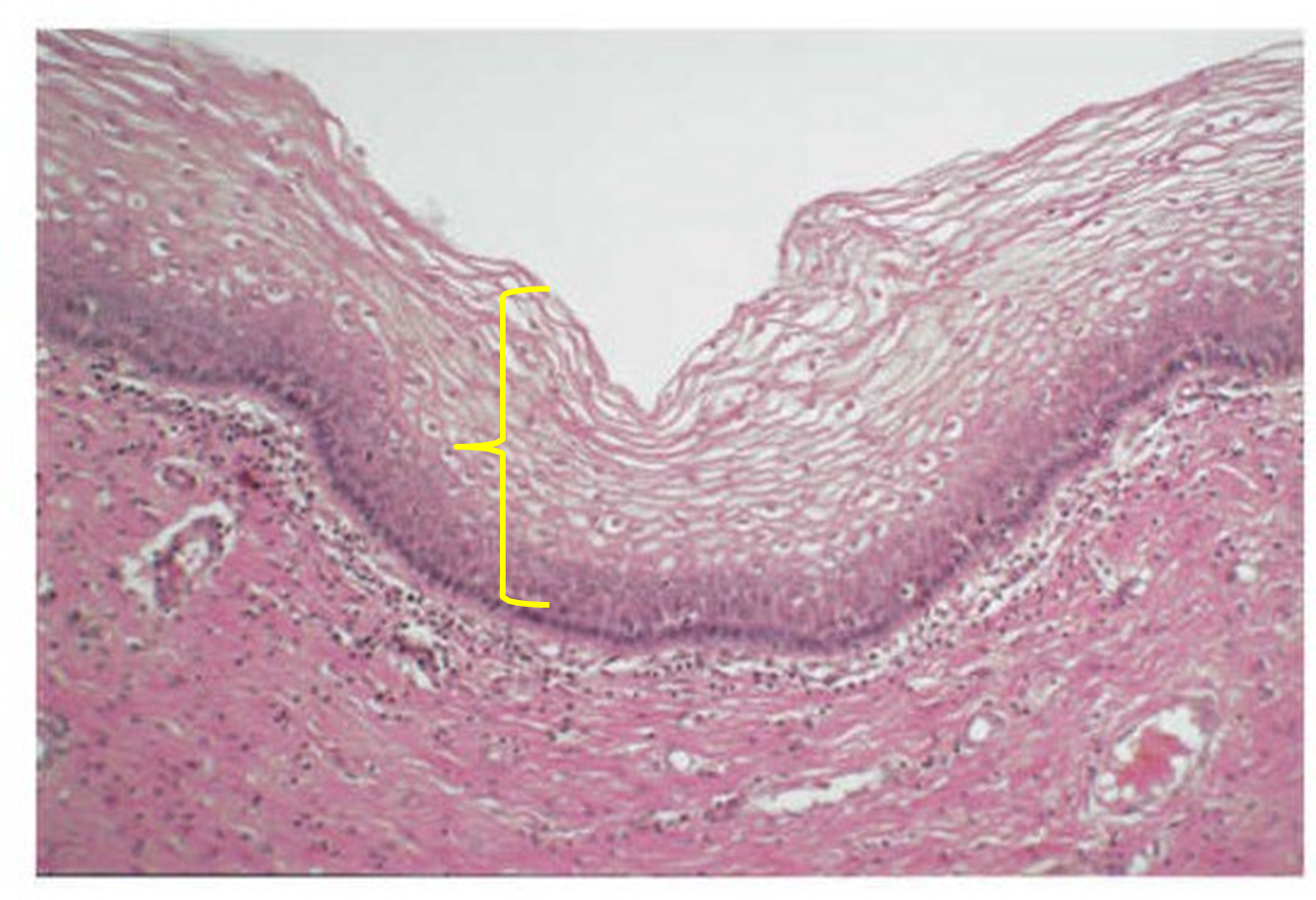
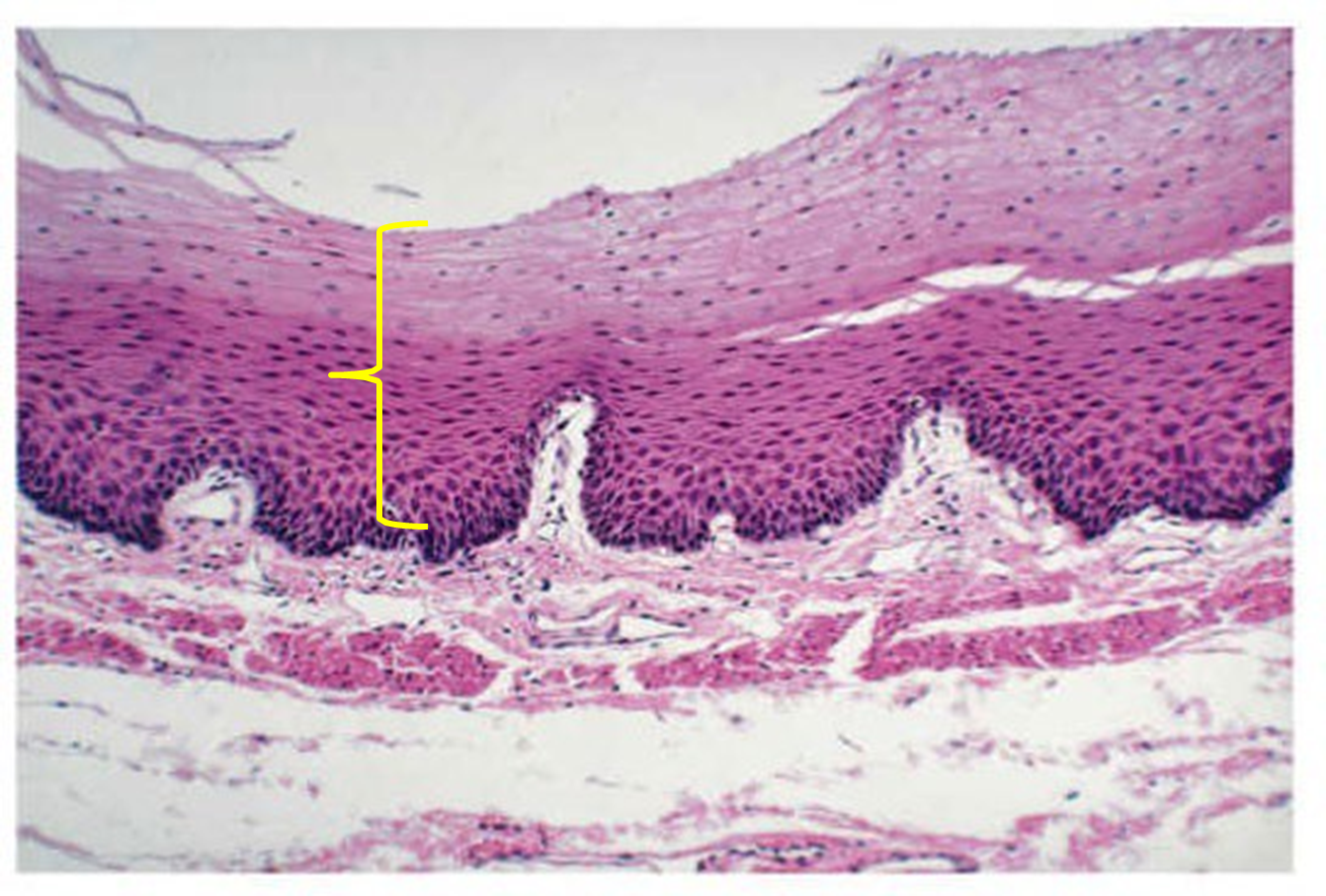
stratified squamous epithelium


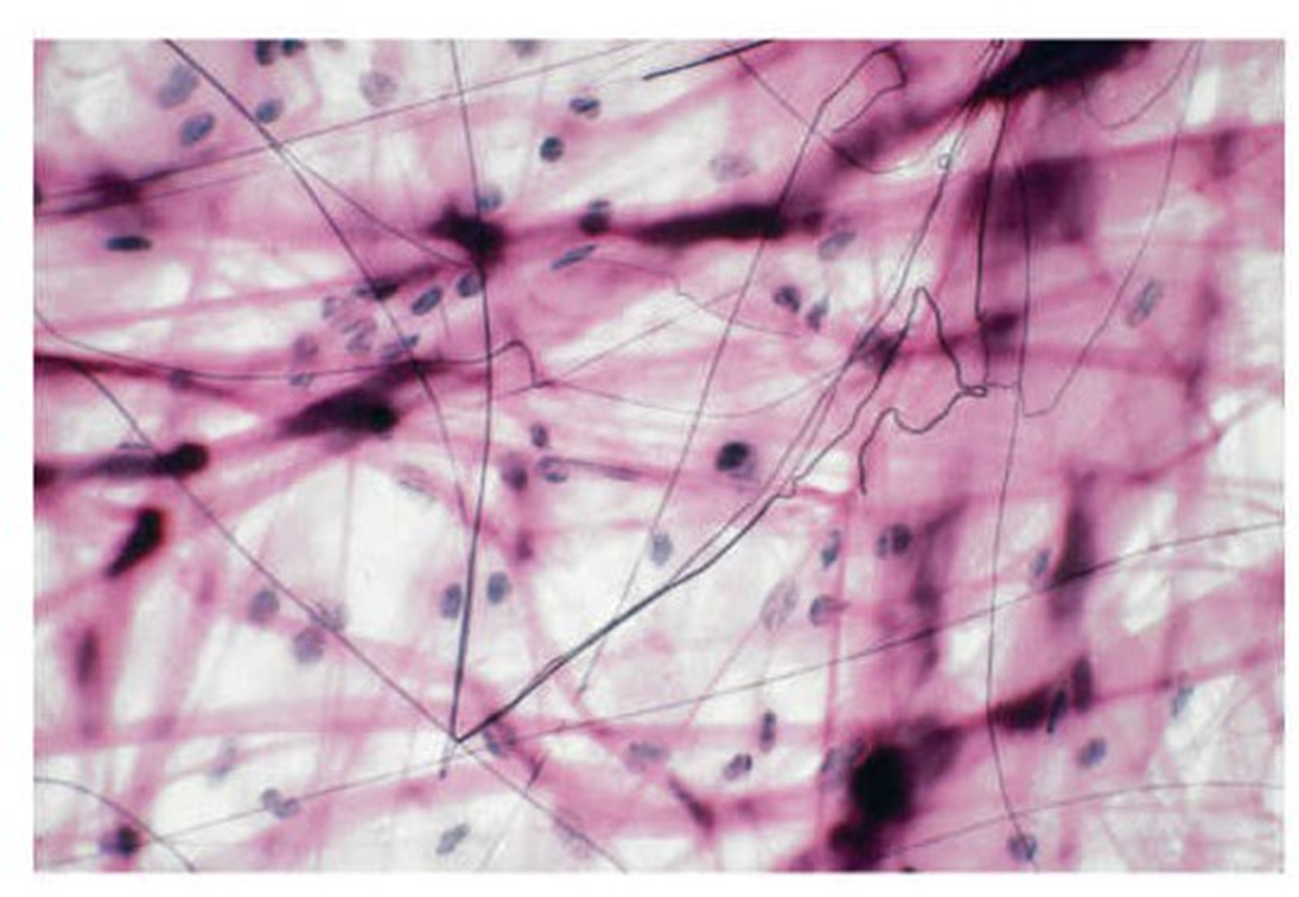
areolar connective tissue
loose connective tissue. found between organs and contains various types of fibers, cells and ground substance.
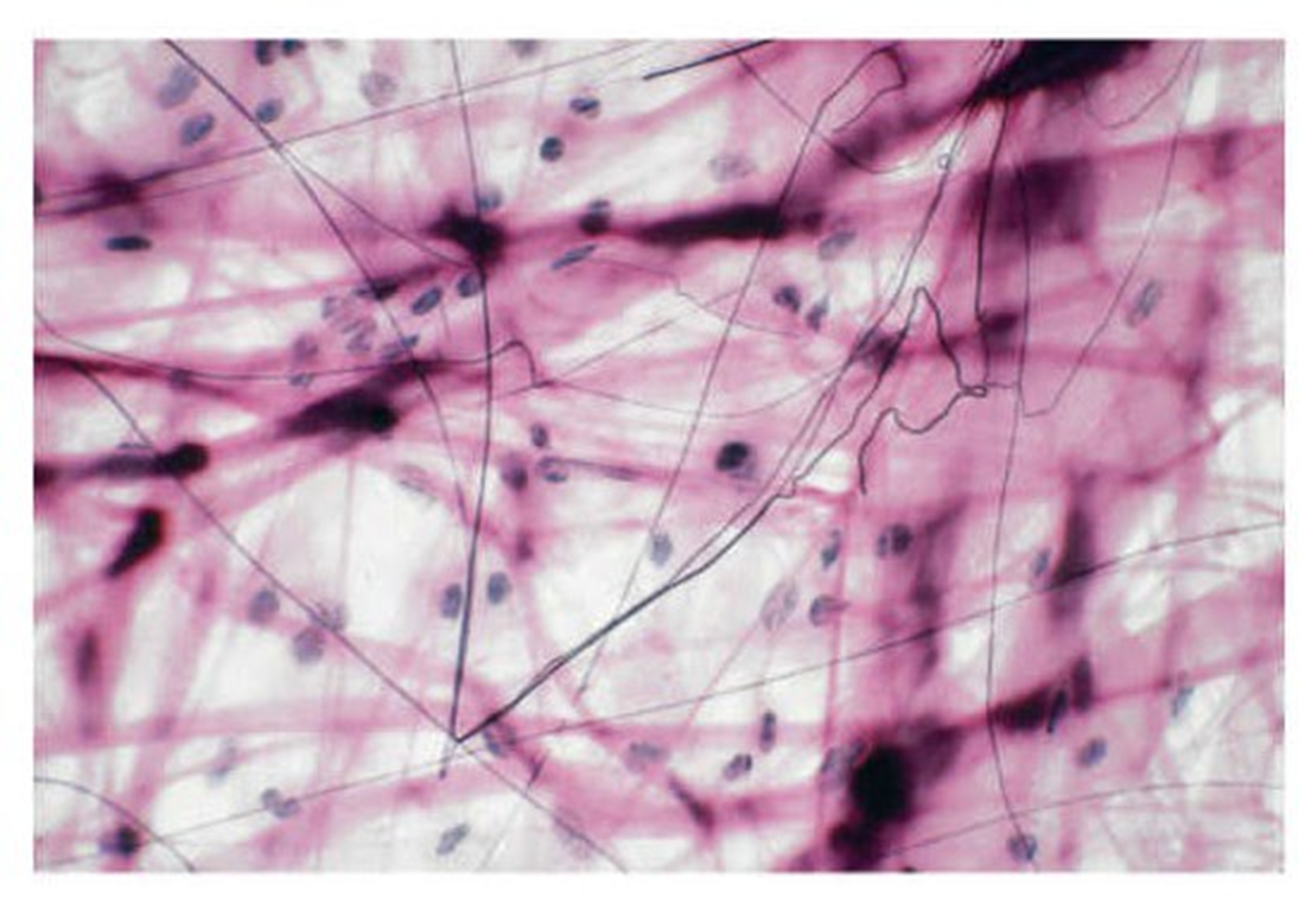
areolar connective tissue
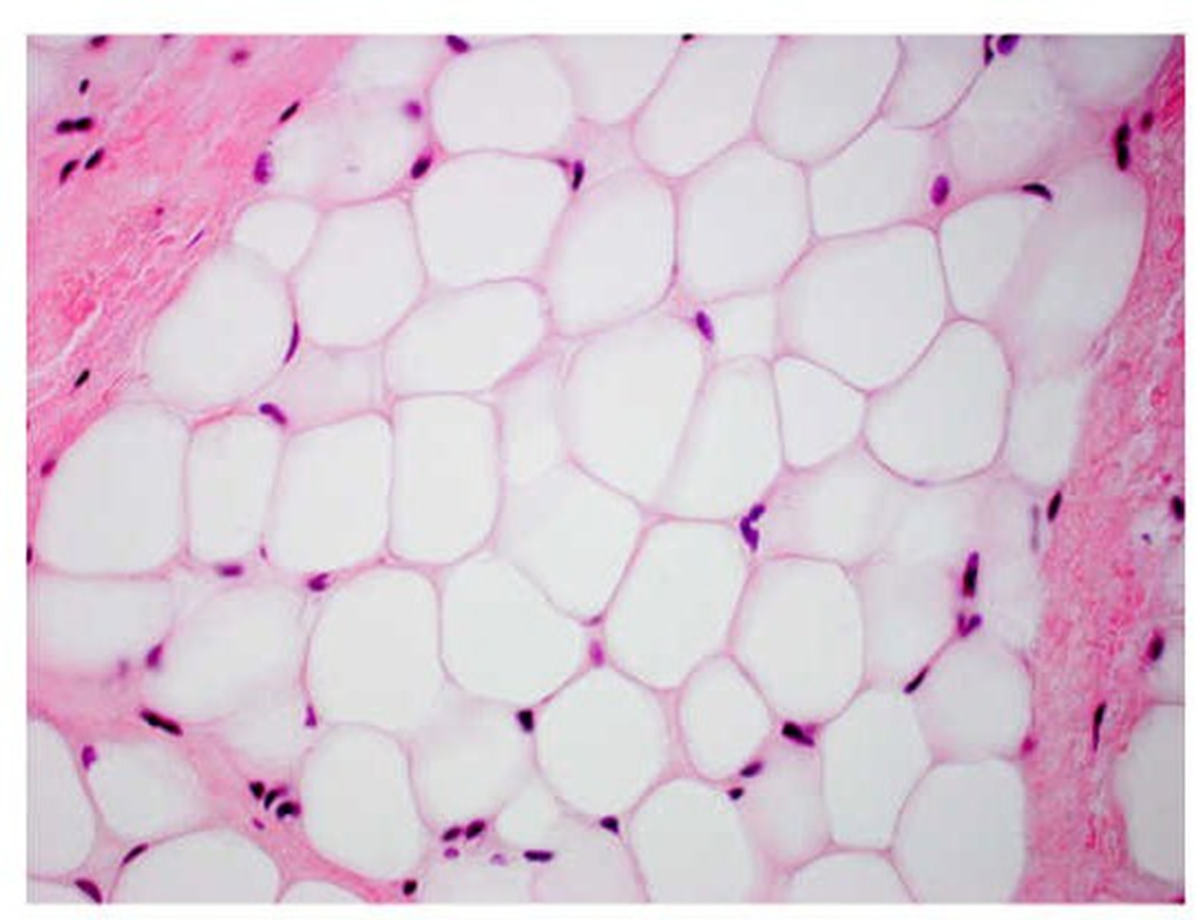
adipose tissue
fat -fat droplet is center of the cell pushes the nucleus to the periphery of the cell
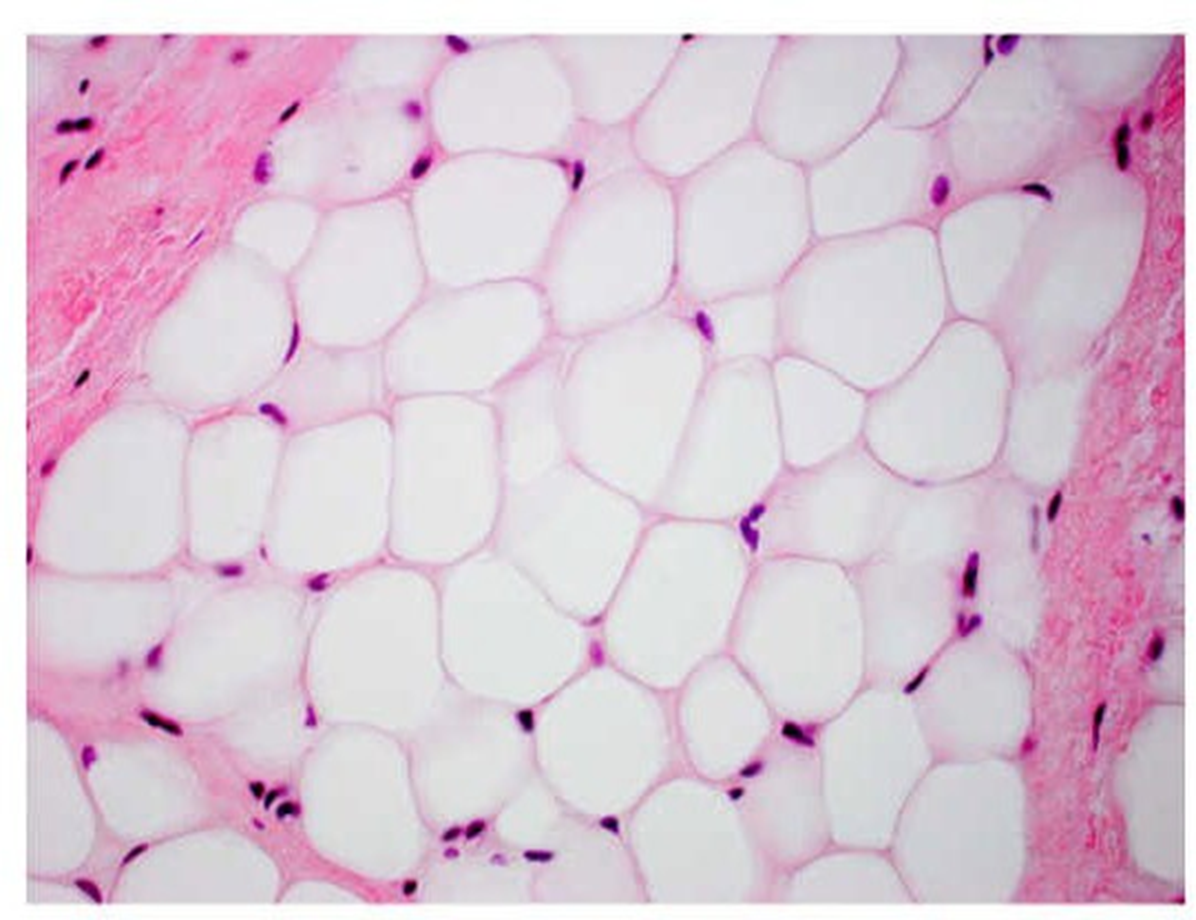
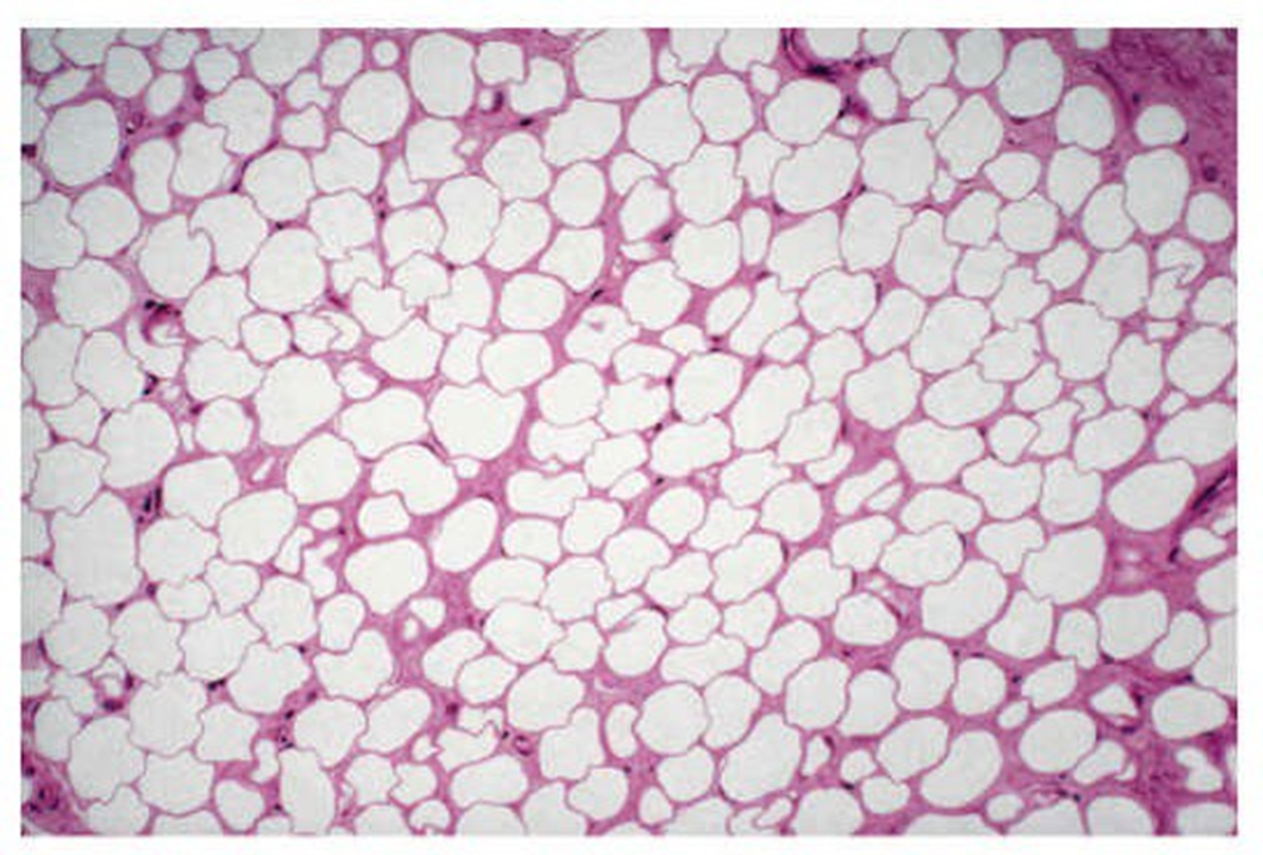
adipose tissue

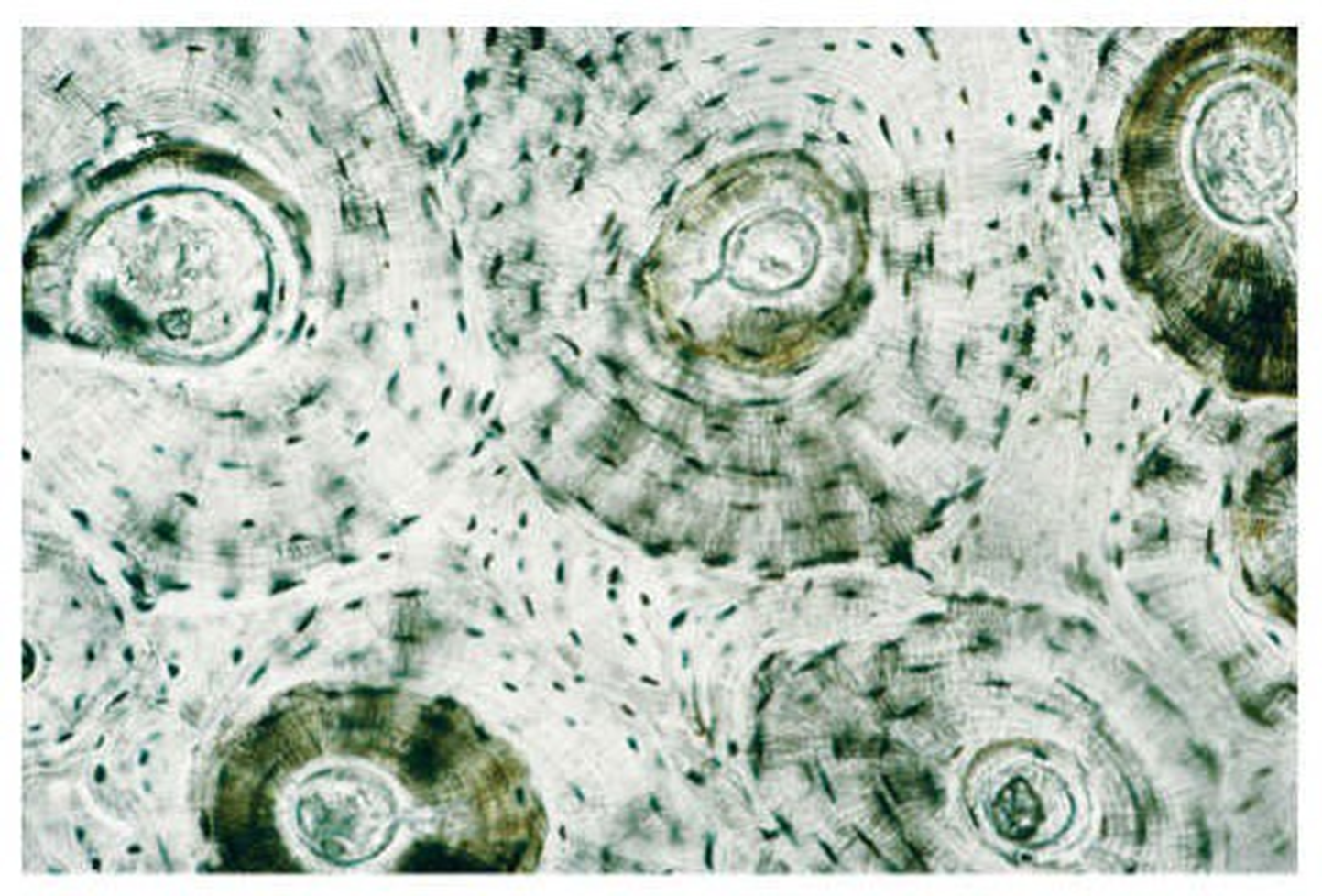
compact bone
arranged in circular-like structures --small darkly stained osteocytes that surround a central canal
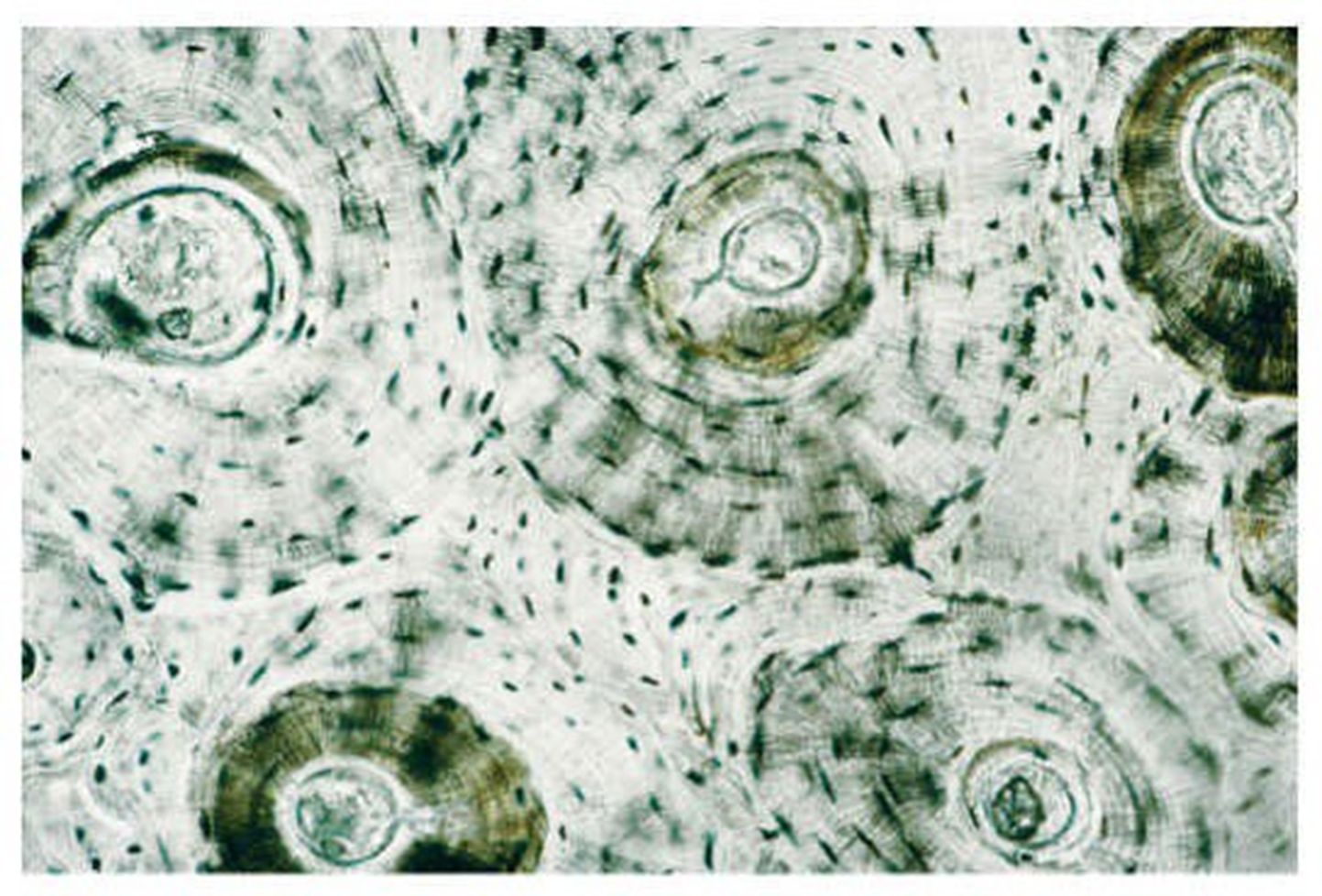
compact bone
skeletal muscle
-contains many striations and peripherally located nuclei -the cells are elongated and called muscle fibers - muscle tissue is connected to bones
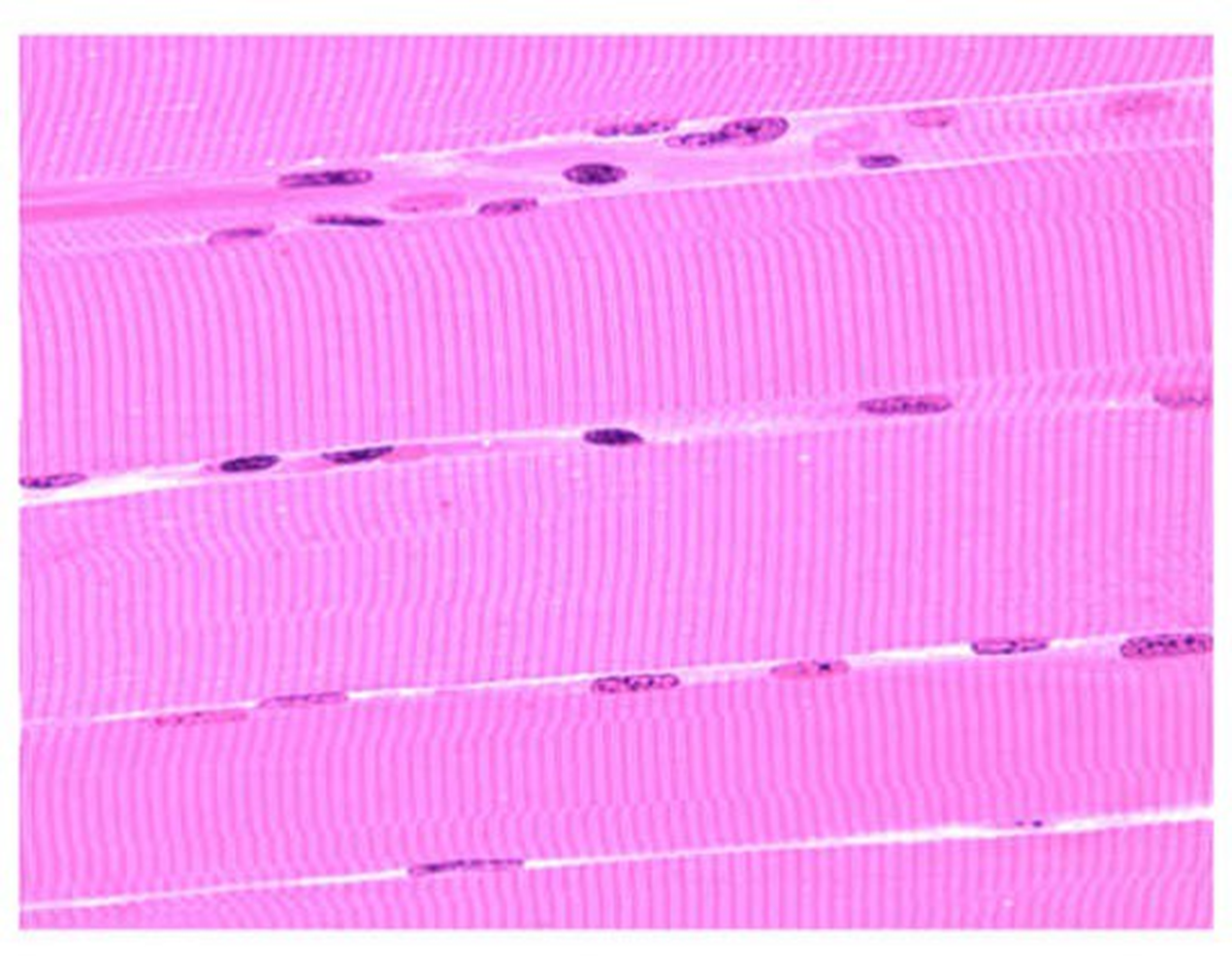
skeletal muscle
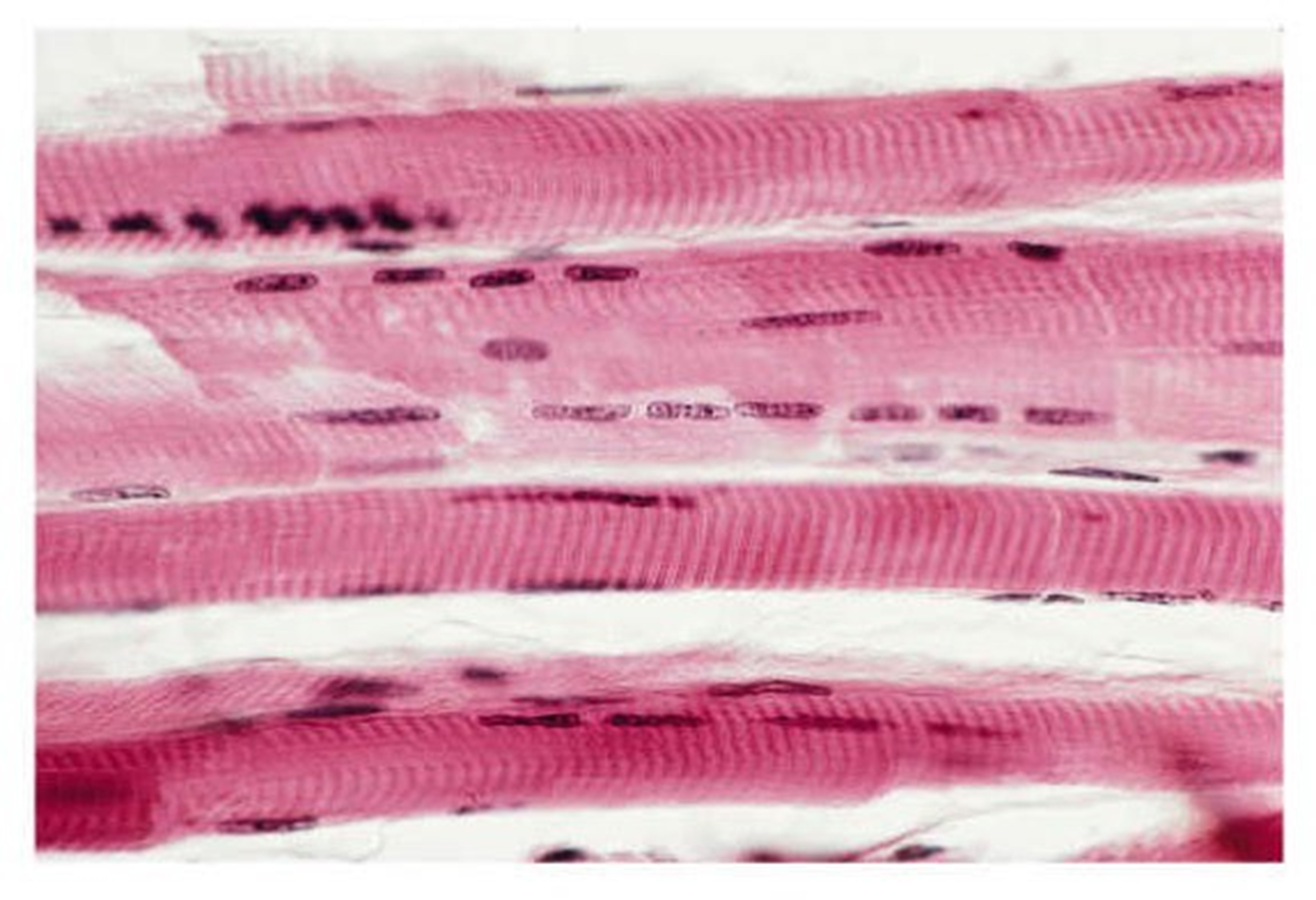

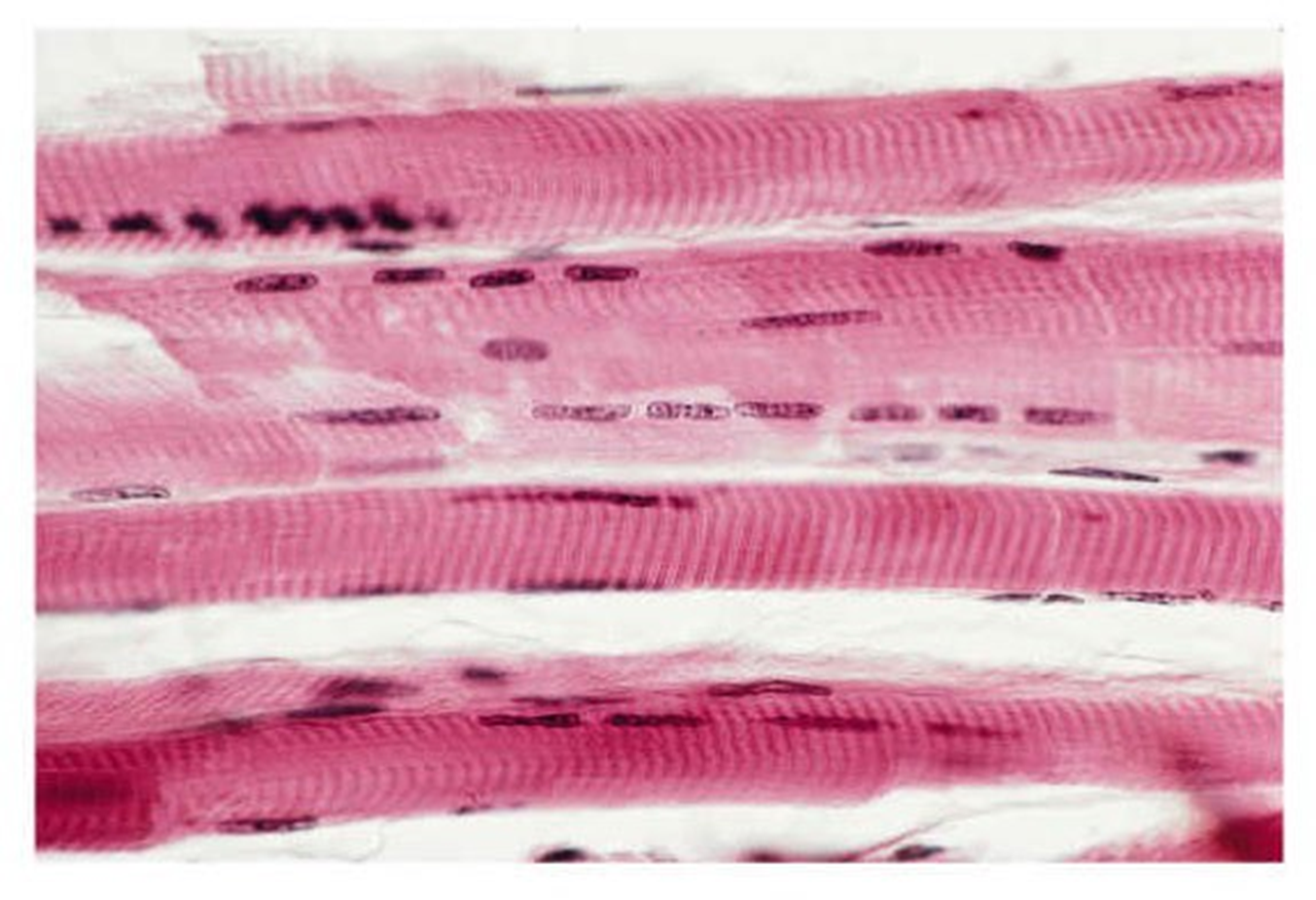
cardiac muscle
-contains striations -has 1-2 centrally located nuclei -muscle cells are connected by gap junctions known as intercalated discs which transmit electrical impulses -cells are attached at angles creating a branched appearance
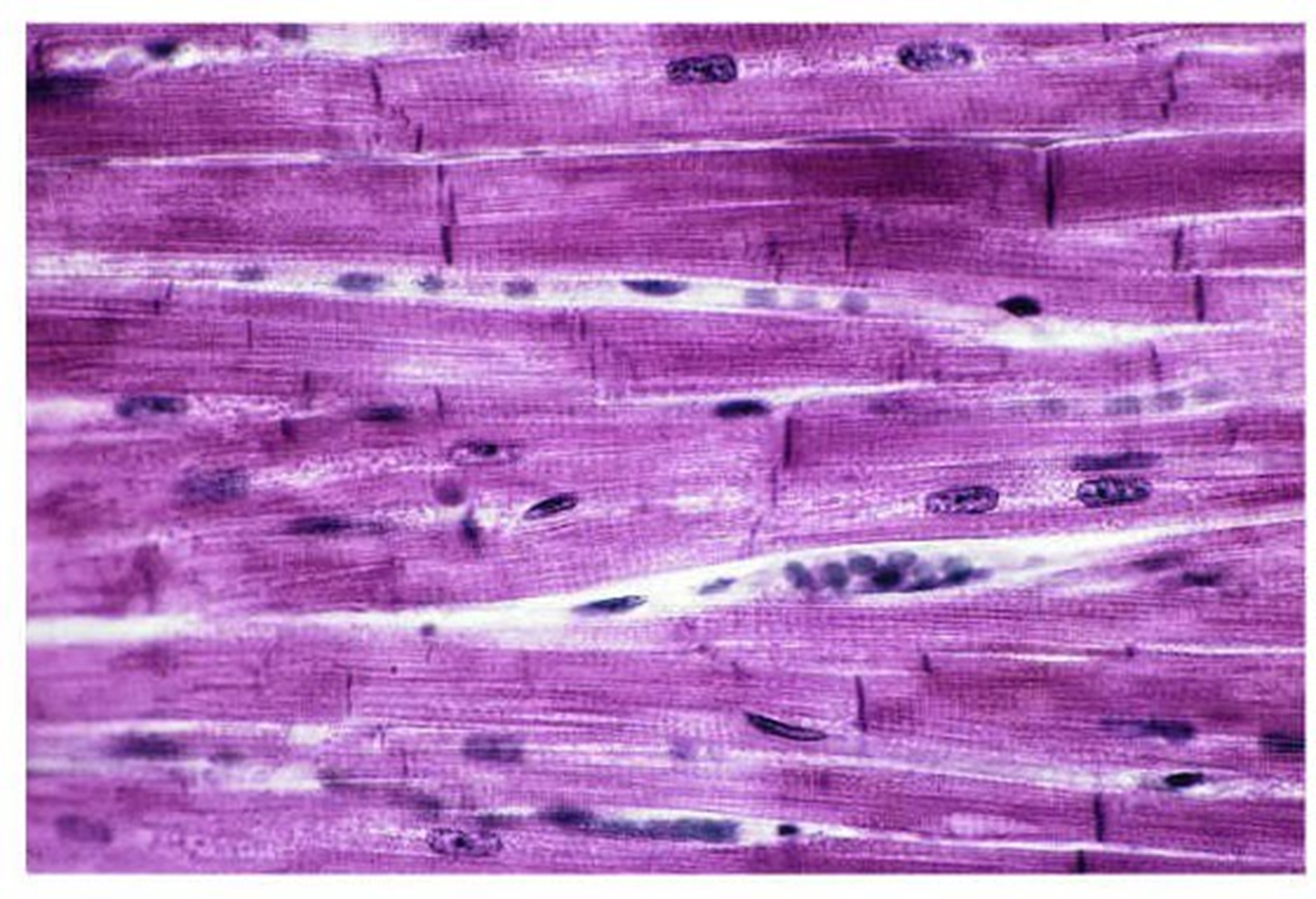
cardiac muscle


smooth muscle
-lacks striations and contains spindle shaped cells -cells contain one centrally located nucleus -found along hollow organs including the digestive & respiratory tracts
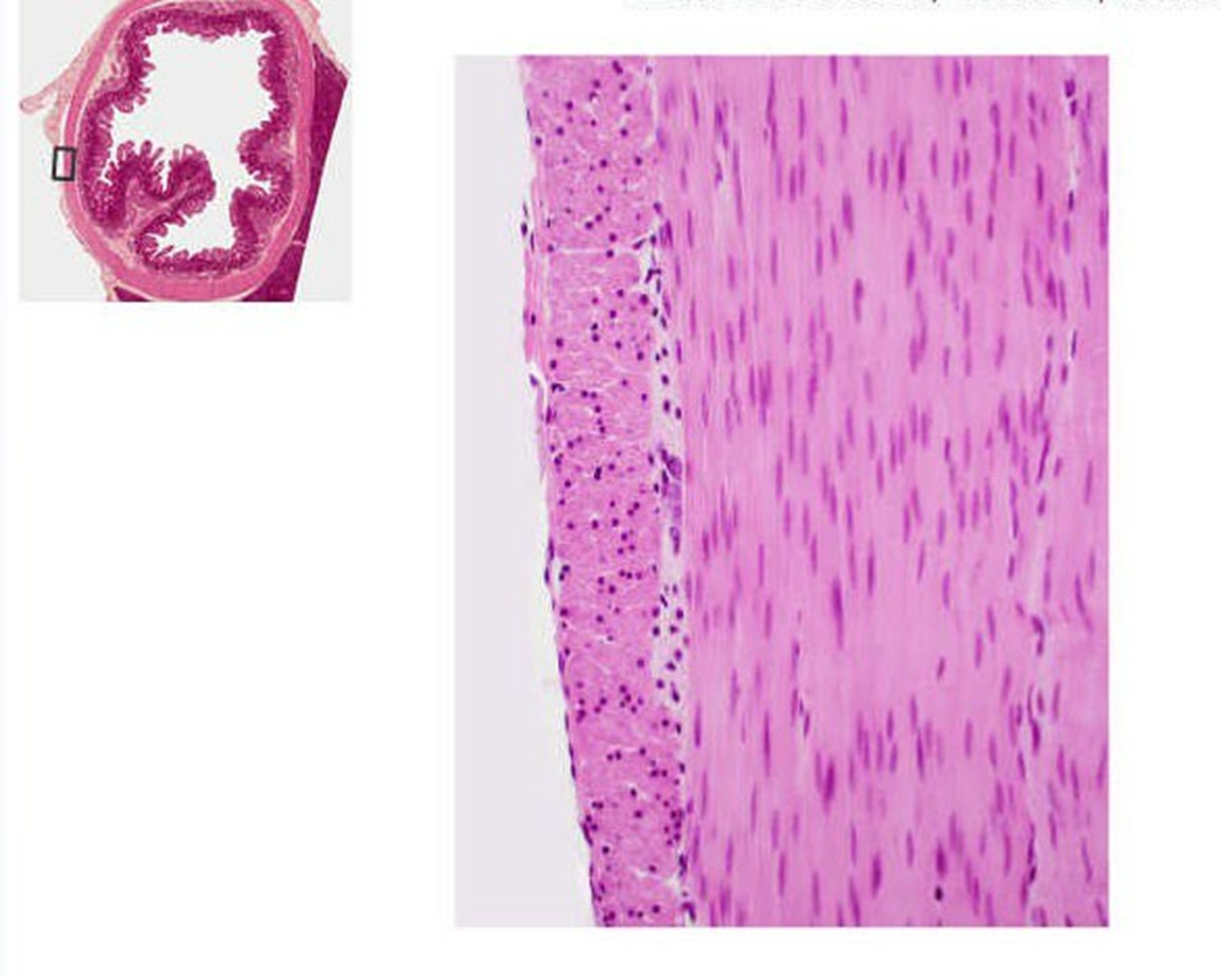
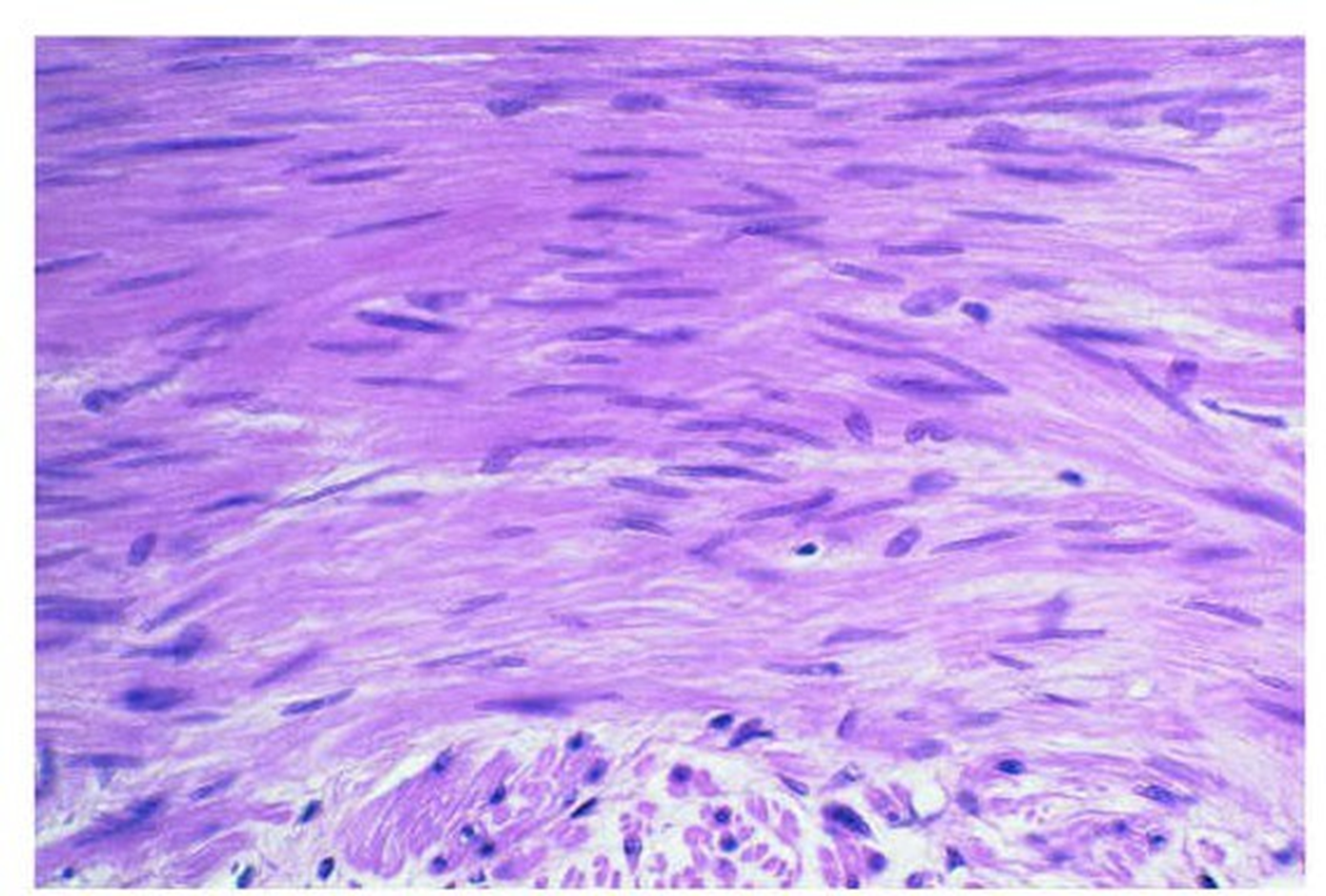
smooth muscle

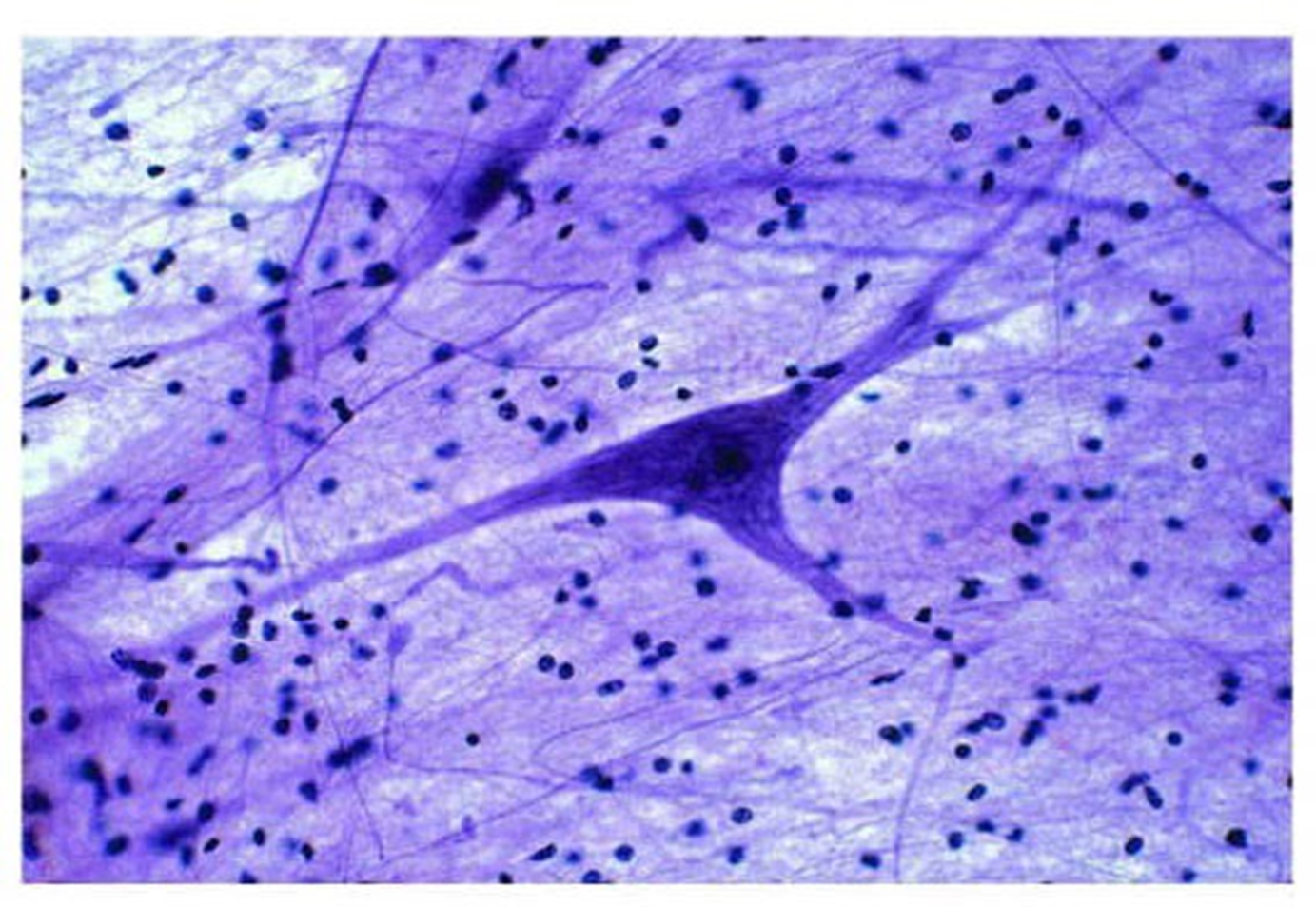
nervous tissue
-characterized by presence of neurons and neuroglia -neurons are the functional cells of ….
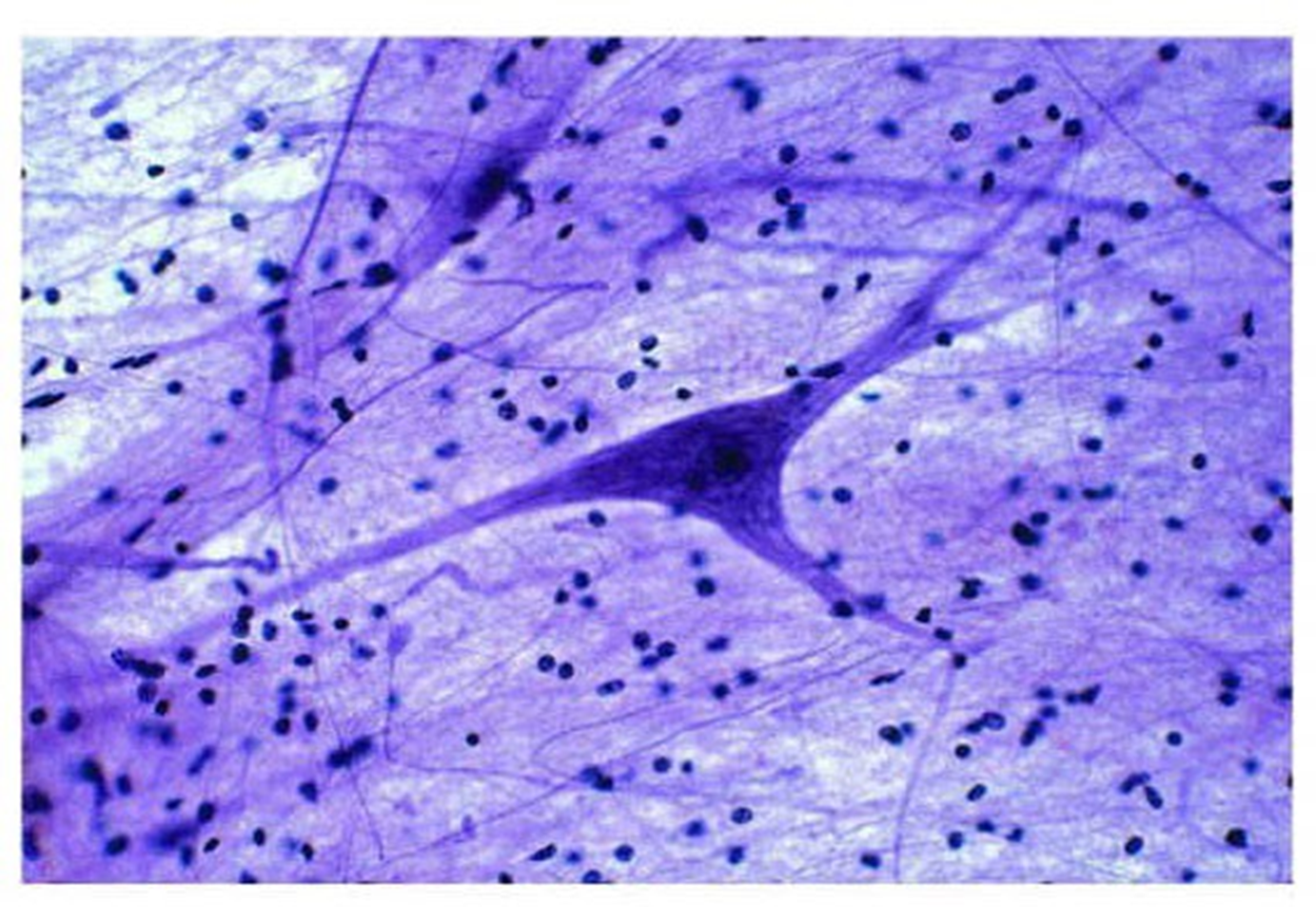
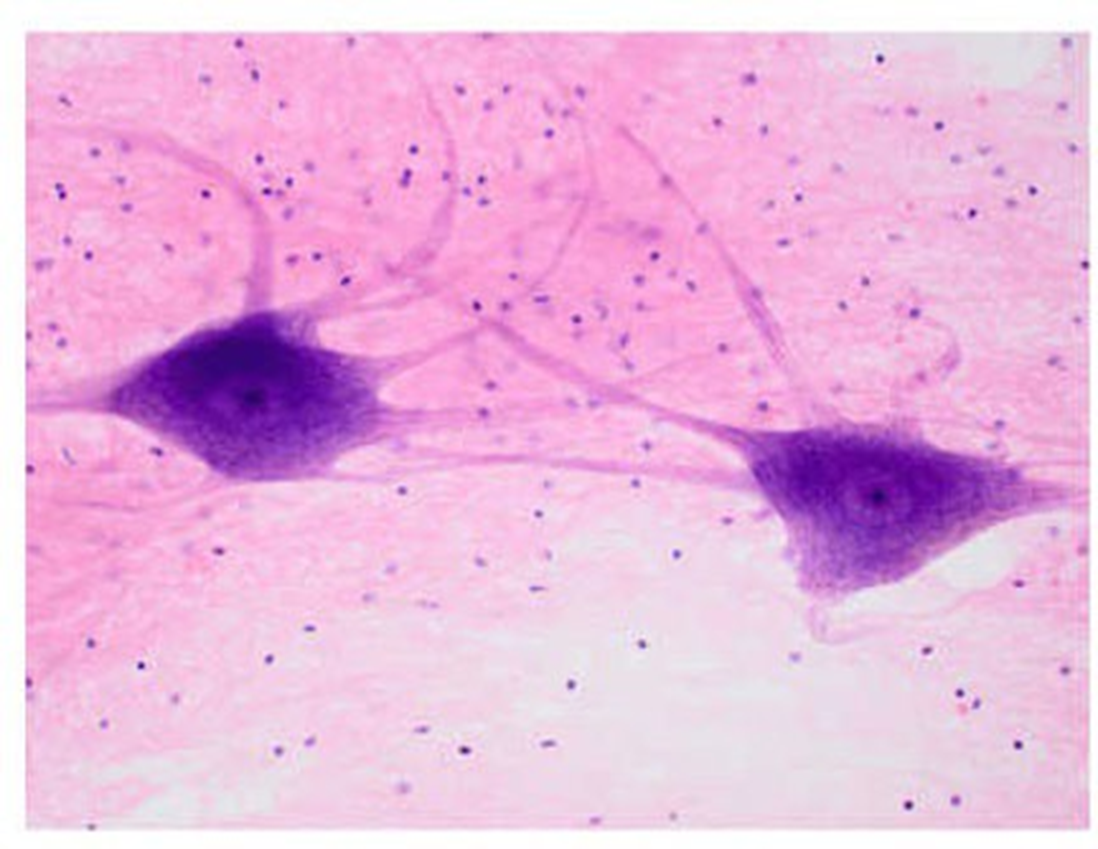
nervous tissue

long bone - diaphysis
shaft of the long bone
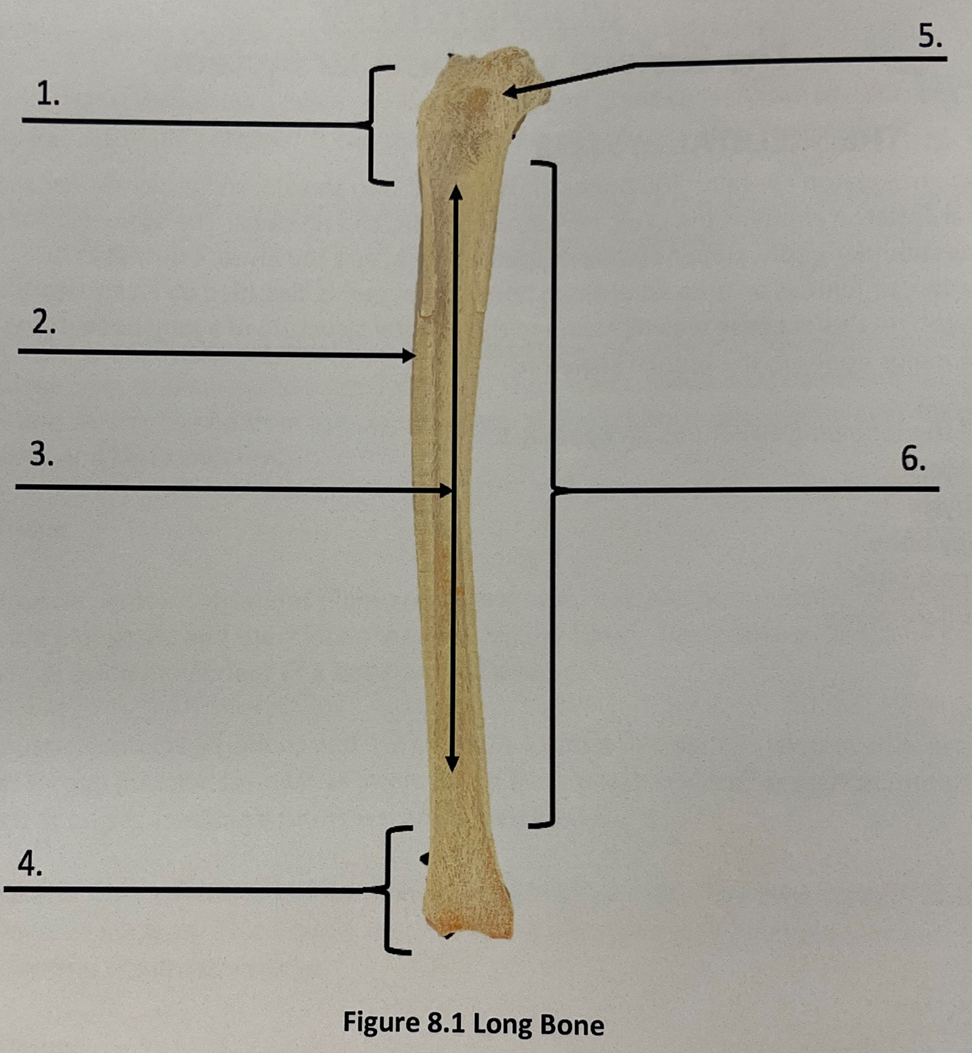
6
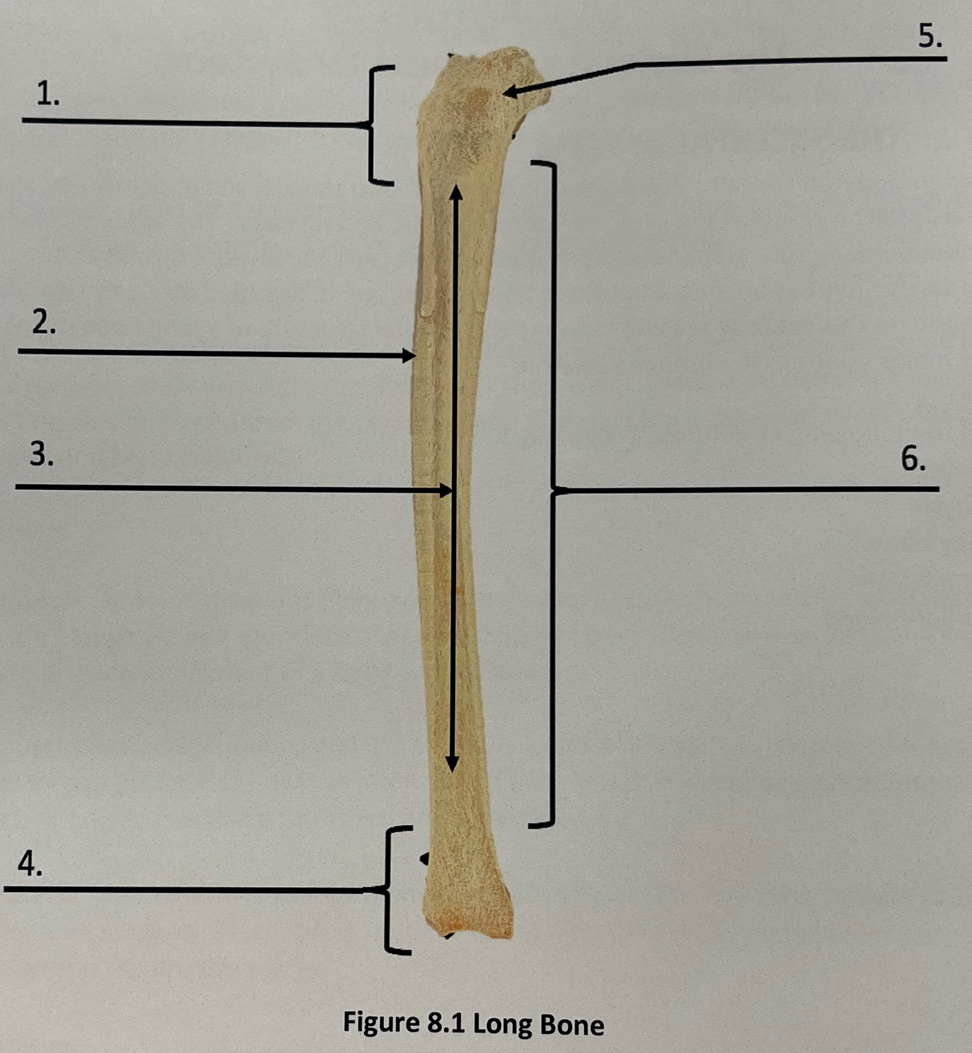
diaphysis
long bone - epiphysis proximal
rounded ends of a long bone
-closer to the body center


1.
Epiphysis (Proximal)
long bone- epiphysis distal
rounded ends of long bone
-farther away from center of body


Epiphysis (Distal)
long bone- spongy bone
Latticework of bone. Found in small flat bones, near the ends of long bones


Spongy bone
long bone- compact bone
dense outer layer with few internal spaces


Compact Bone
long bone- medullary cavity
inner most portion of the bone, where red and/or yellow bone marrow is located


Medullary Cavity
The human skeleton contains —— bones
206
Axial skeleton
Contains skull, vertebral column, sternum, & ribs
Provides protection & support for internal organs
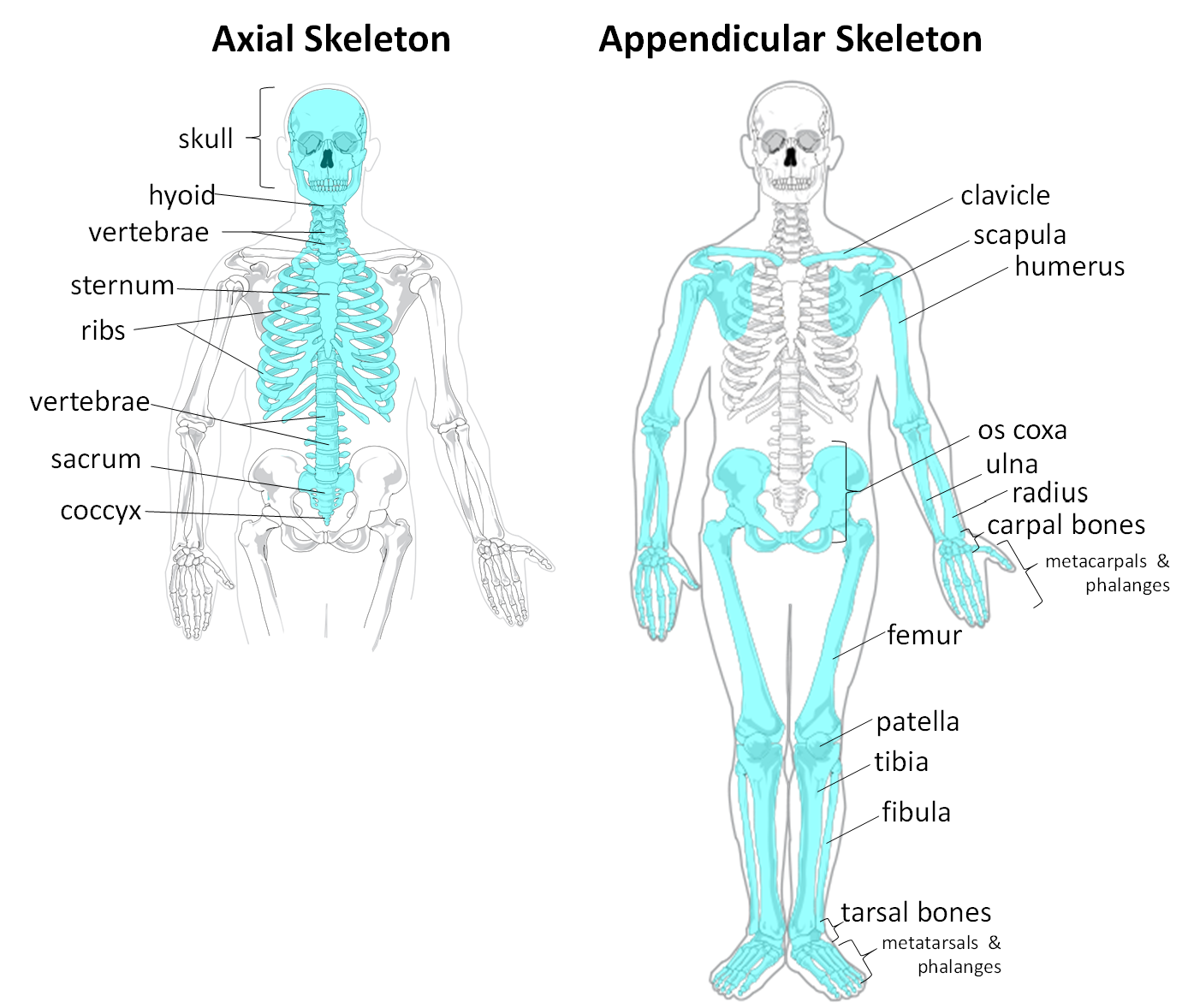
Appendicular skeleton
Contains pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, and limbs
Allows for movement
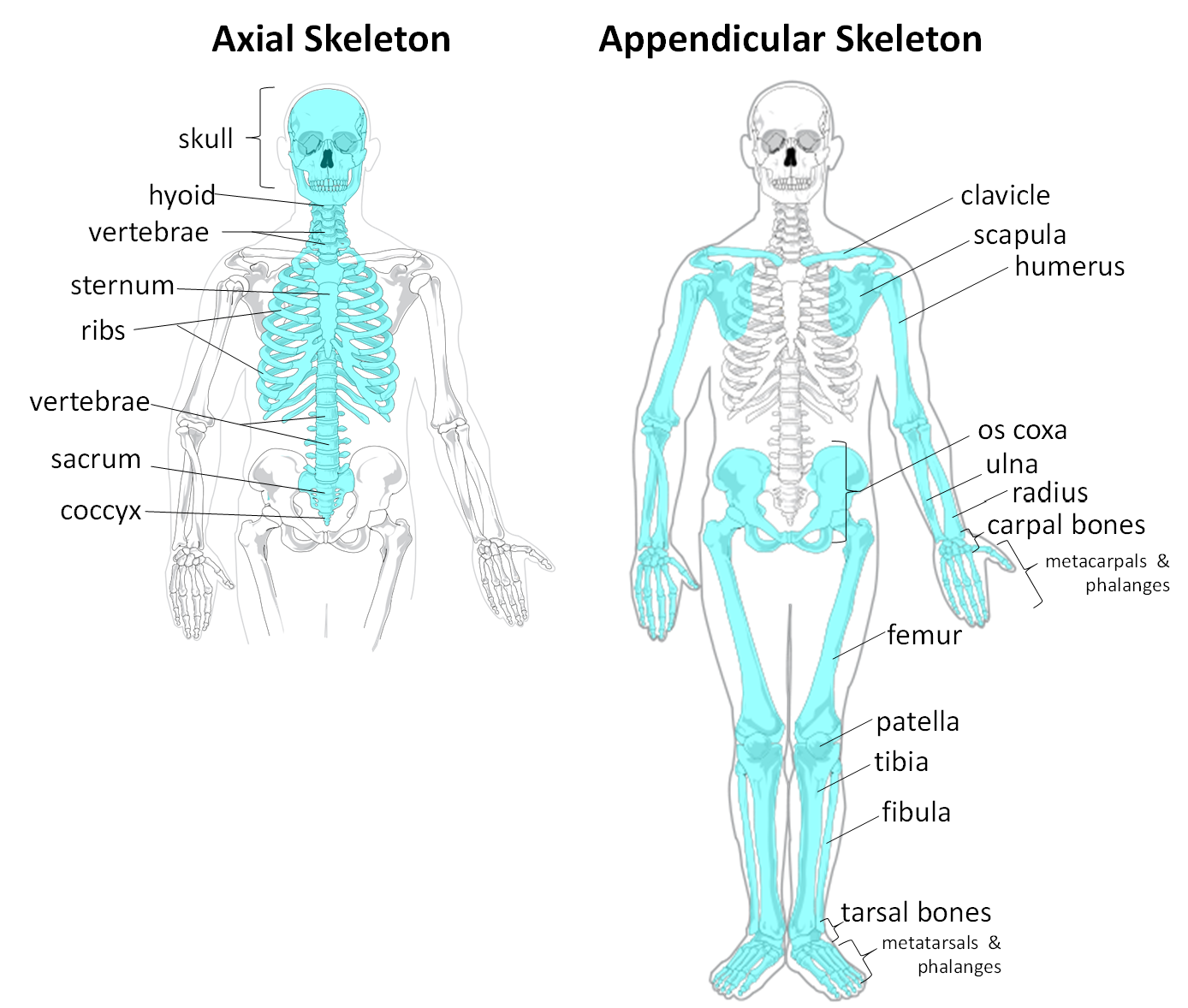
There are more bones in the —- skeleton
fetal
In fetuses, the hyaline model (——) has not ossified
cartilage
Fontanels
The bones of the cranium are connected by fibrous membranes called …. This allows for more flexibility during birth and growth
Nondisplaced fractures
a crack or break but the bones stays in its place
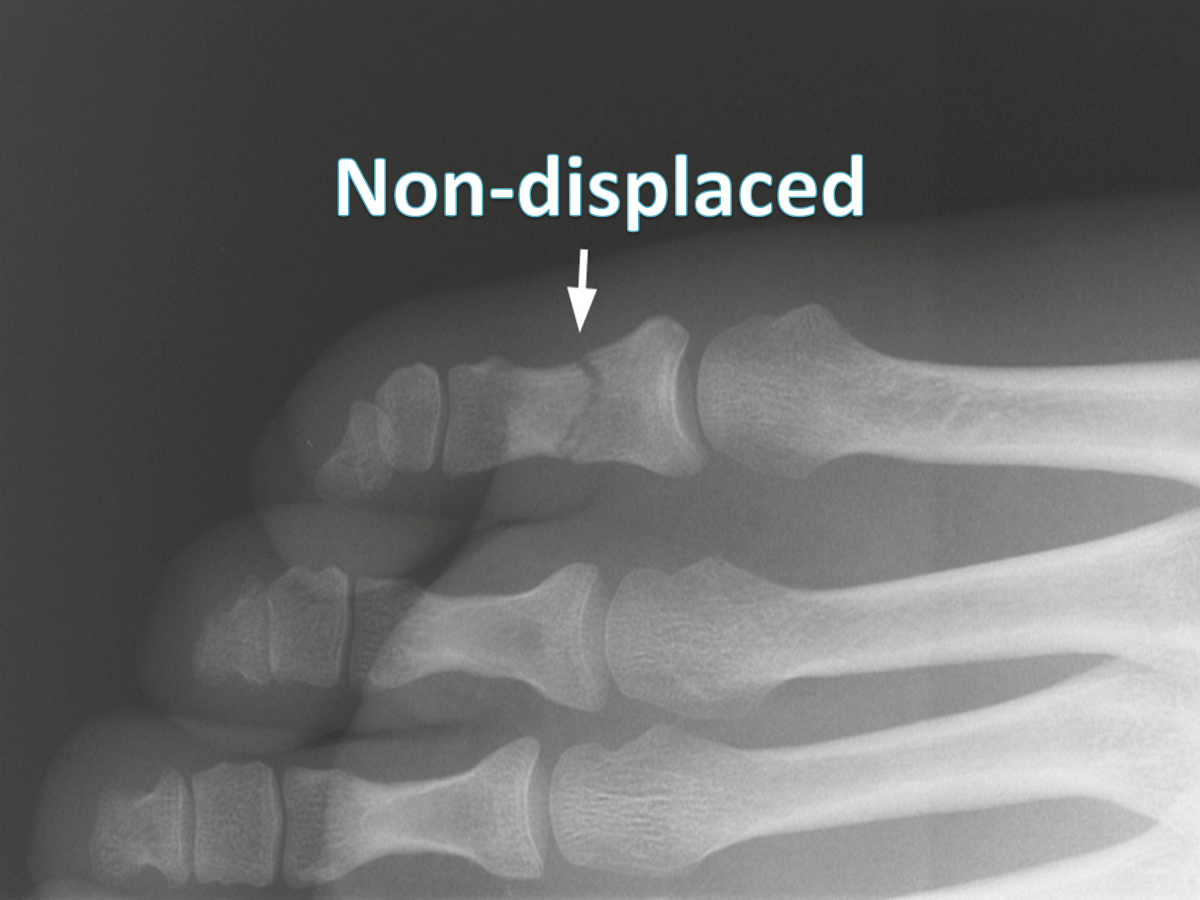
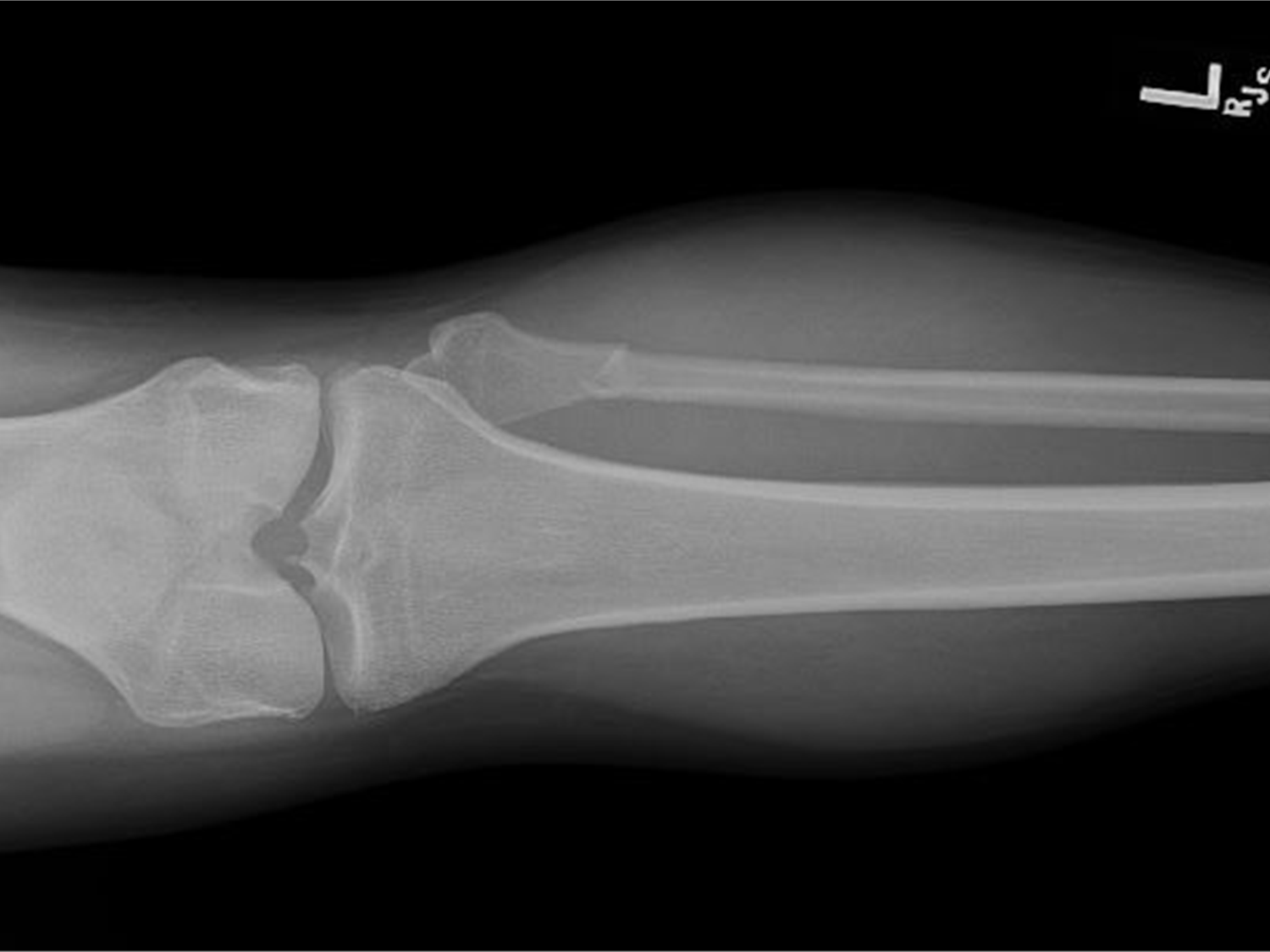
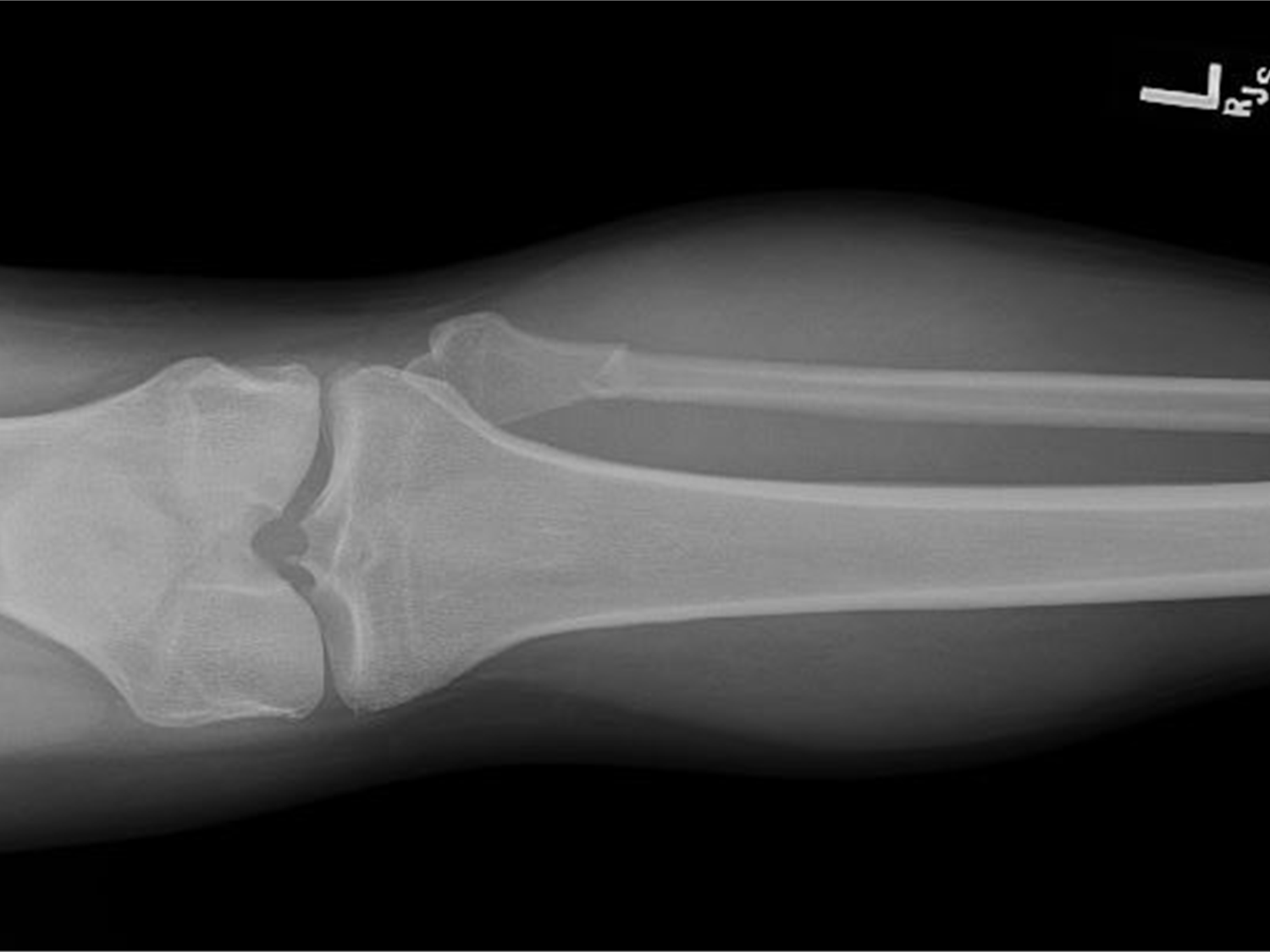
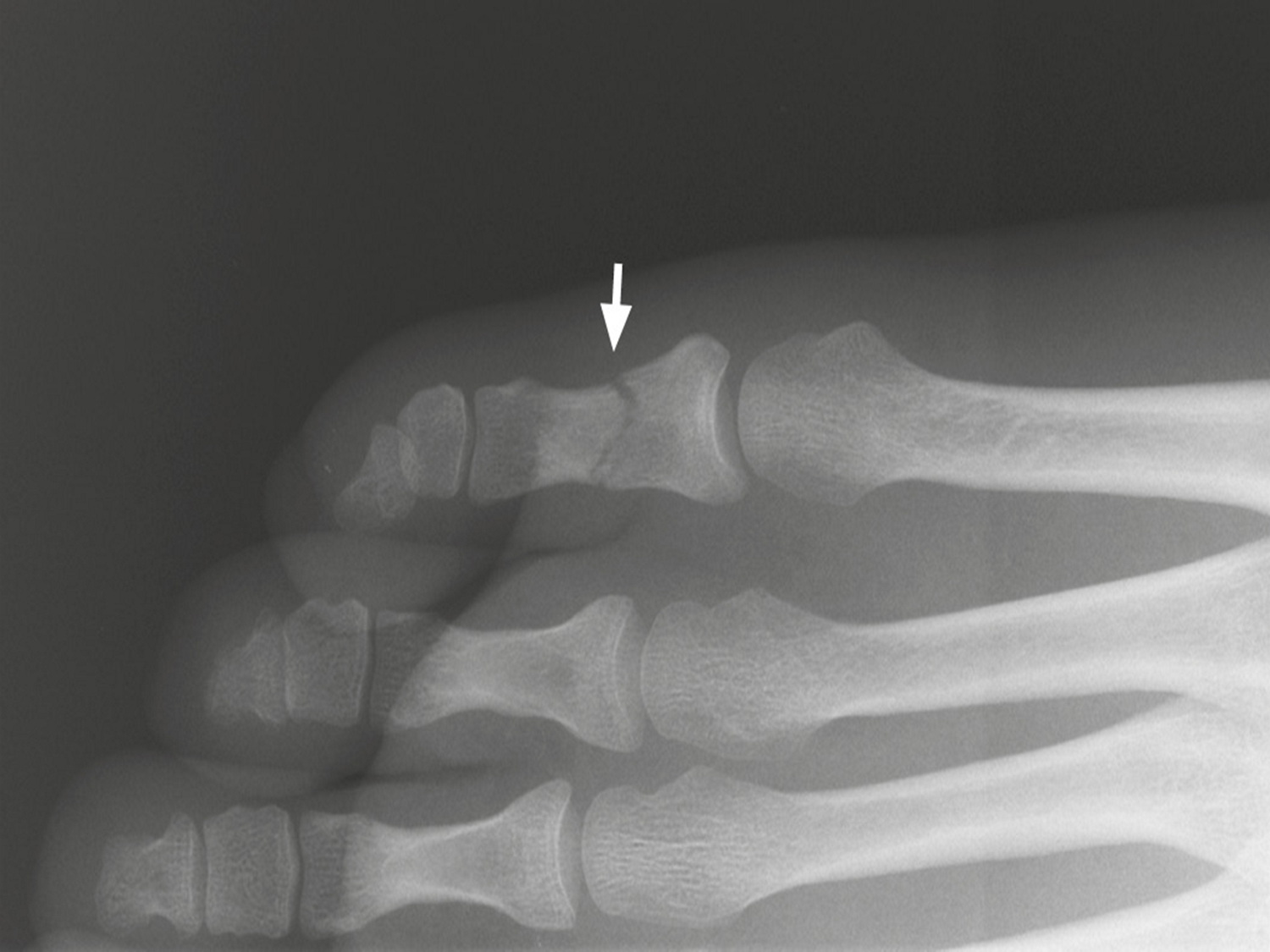
nondisplaced fracture
Displaced fracture
where a bone is broken and it does not align together correctly
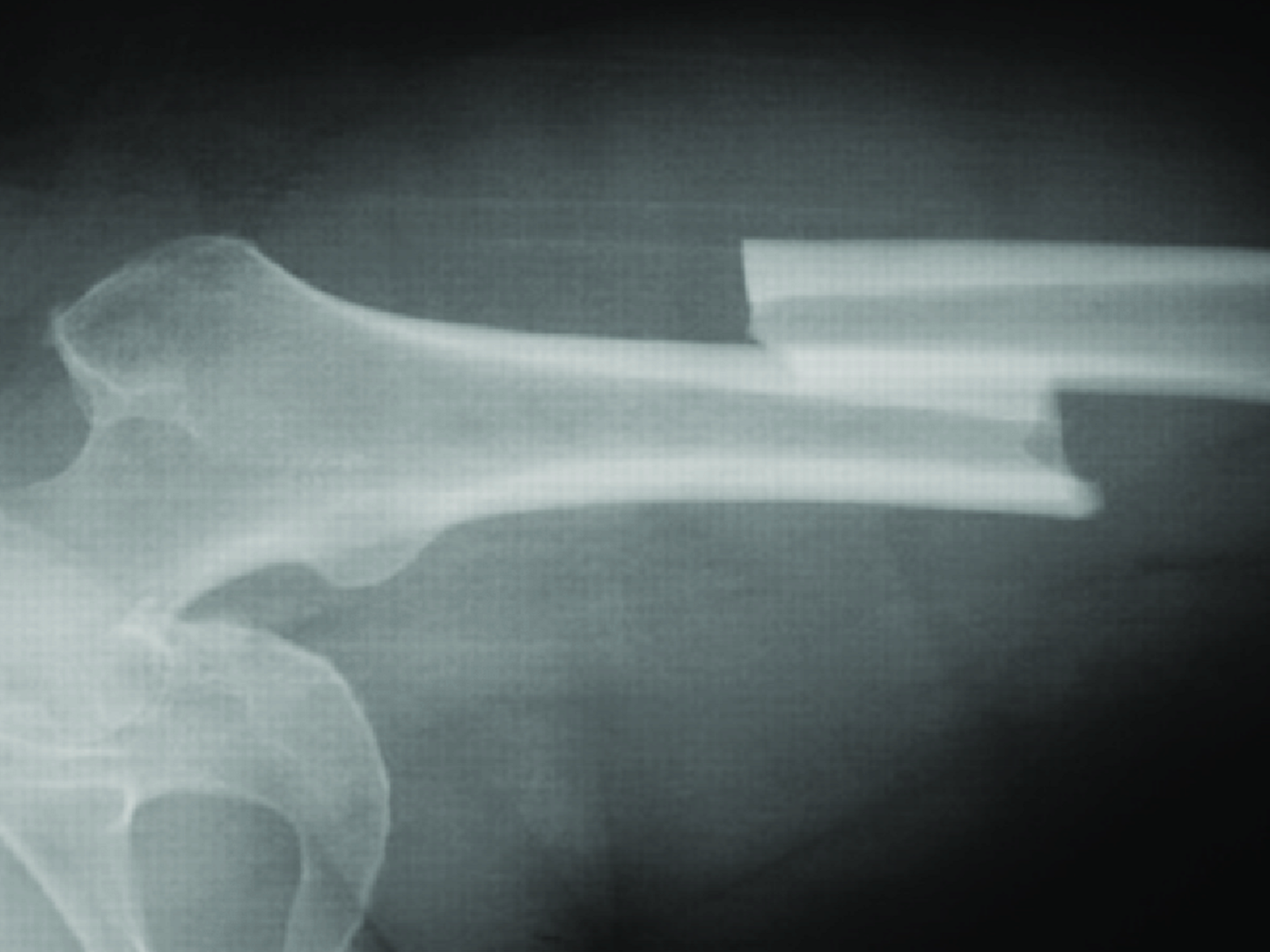
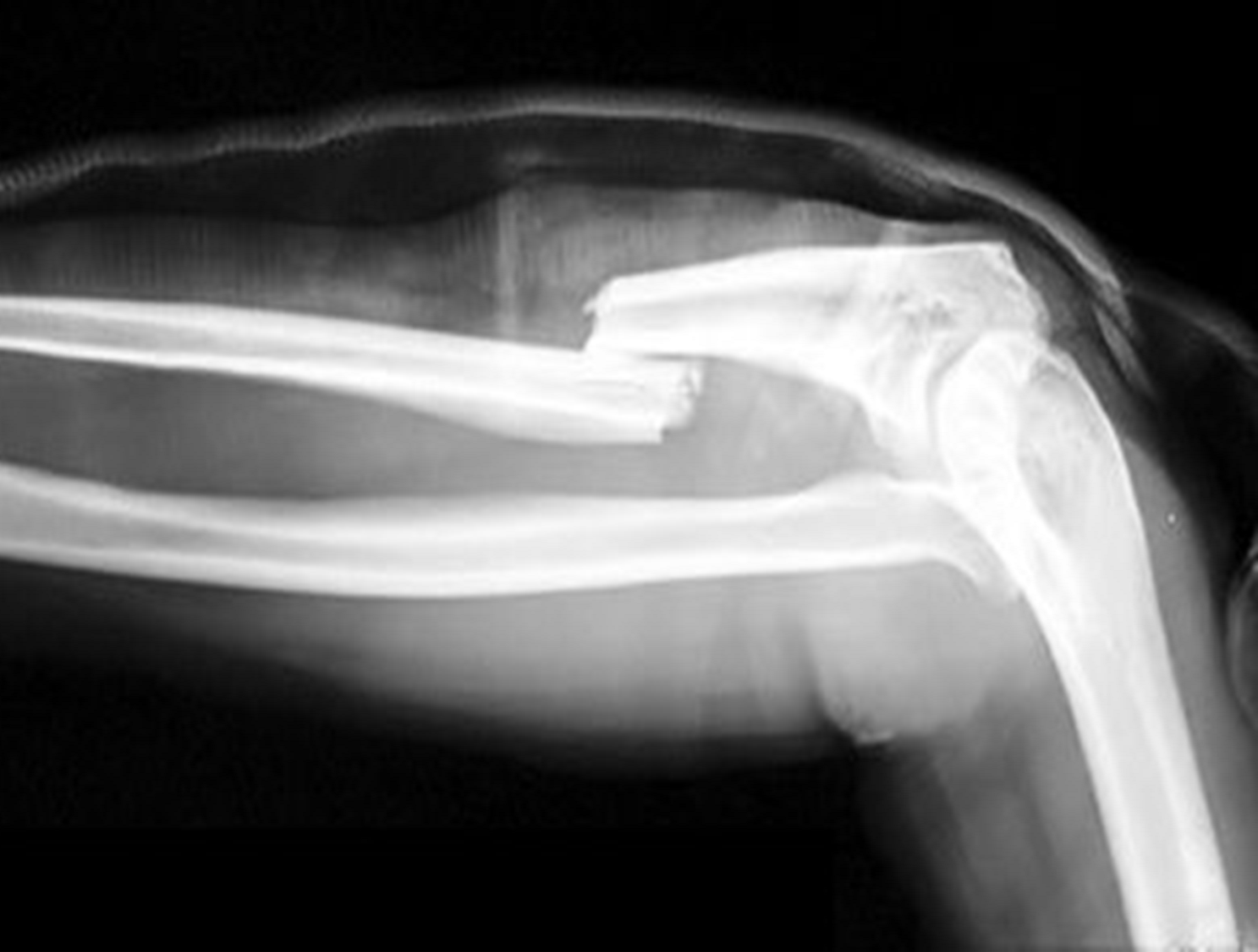
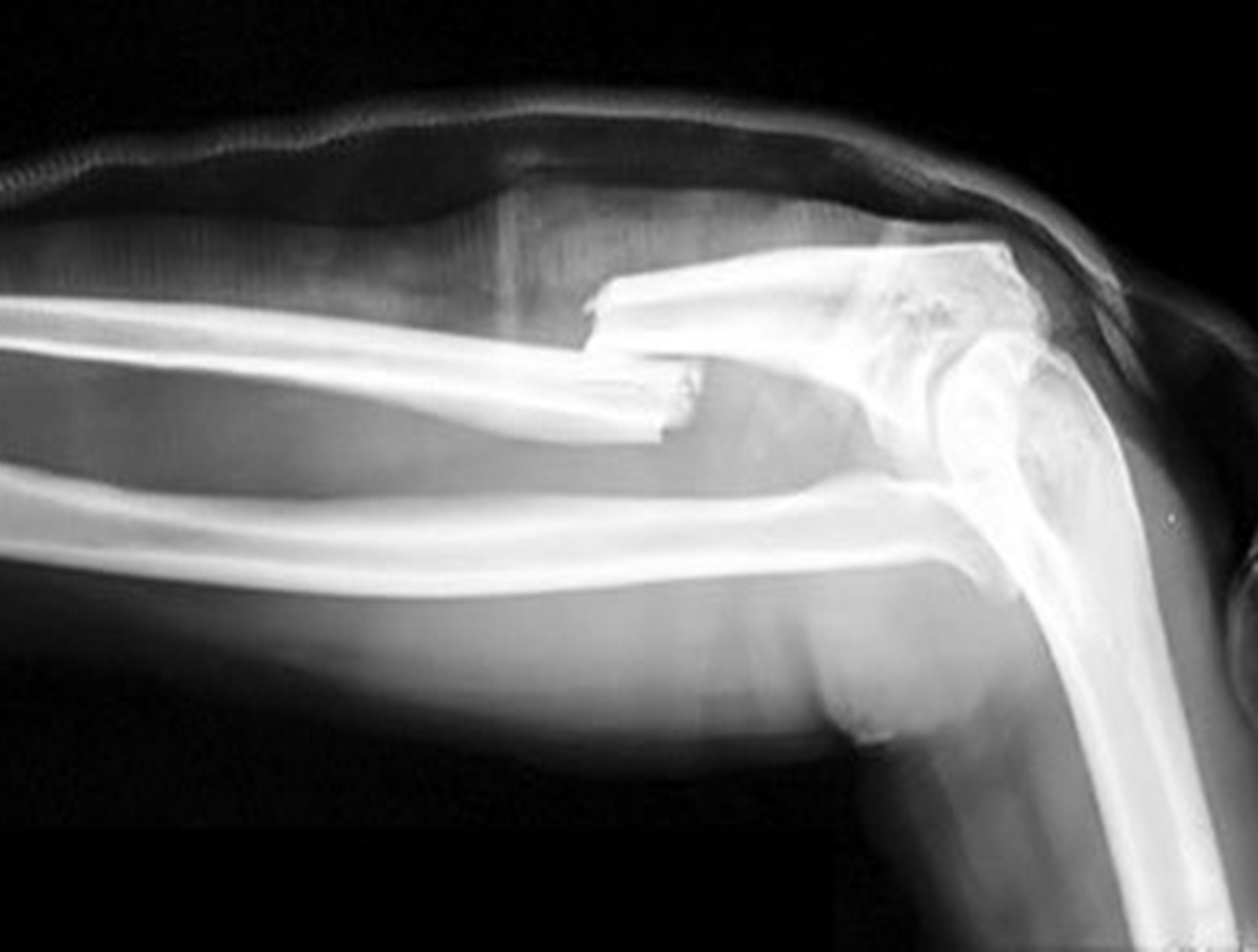

displaced fracture
when a break occurs
-bleeding occurs until a clot is formed -fibroblasts invade the clot and secrete collagen fibers to form a callus linking -osteoblasts transform the cartilage formed by fibroblasts into bone
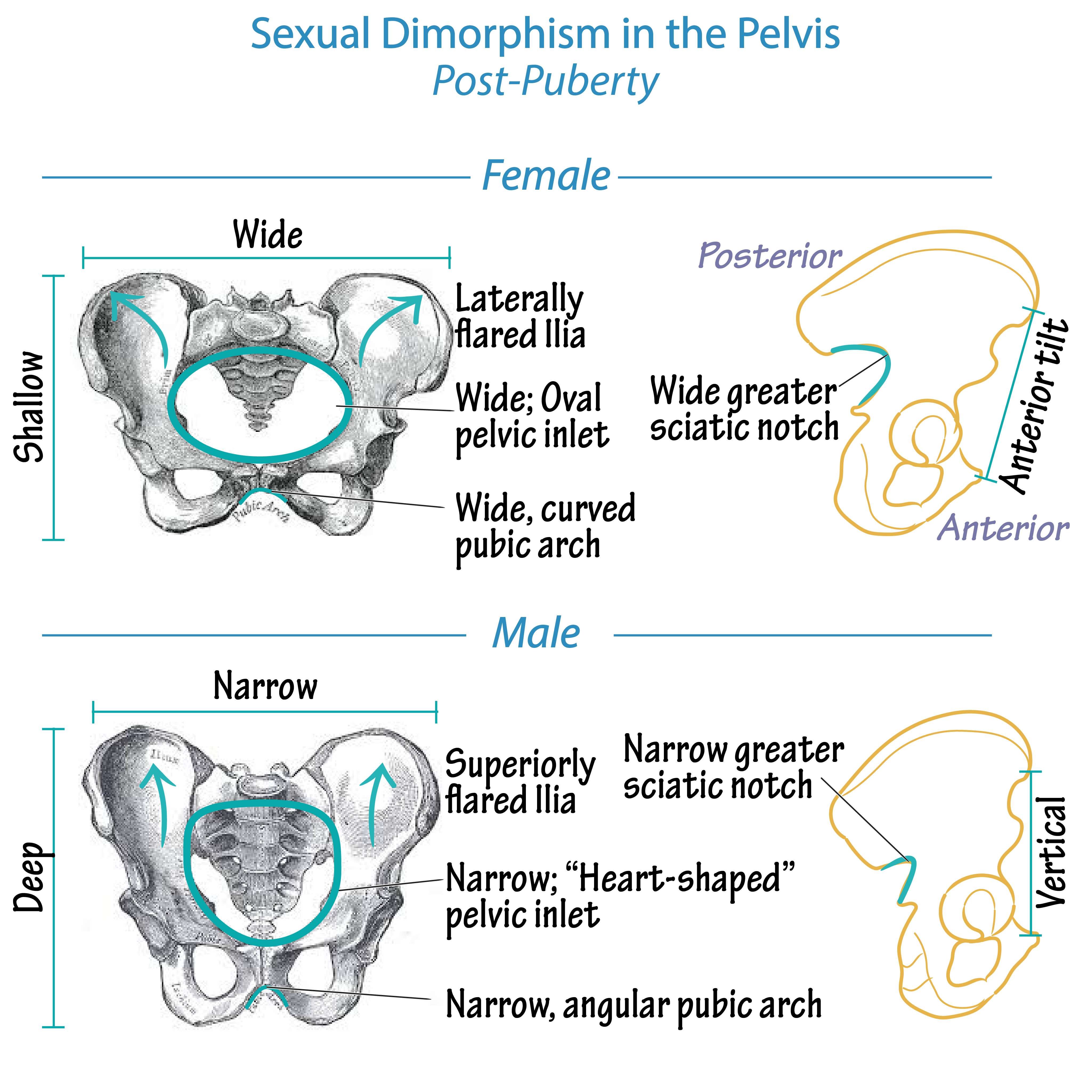
male pelvis post puberty
pelvic cavity is narrower and less roomy . coccyx is less movable. pelvis heavy and thick. pelvis inlet and outlet smaller
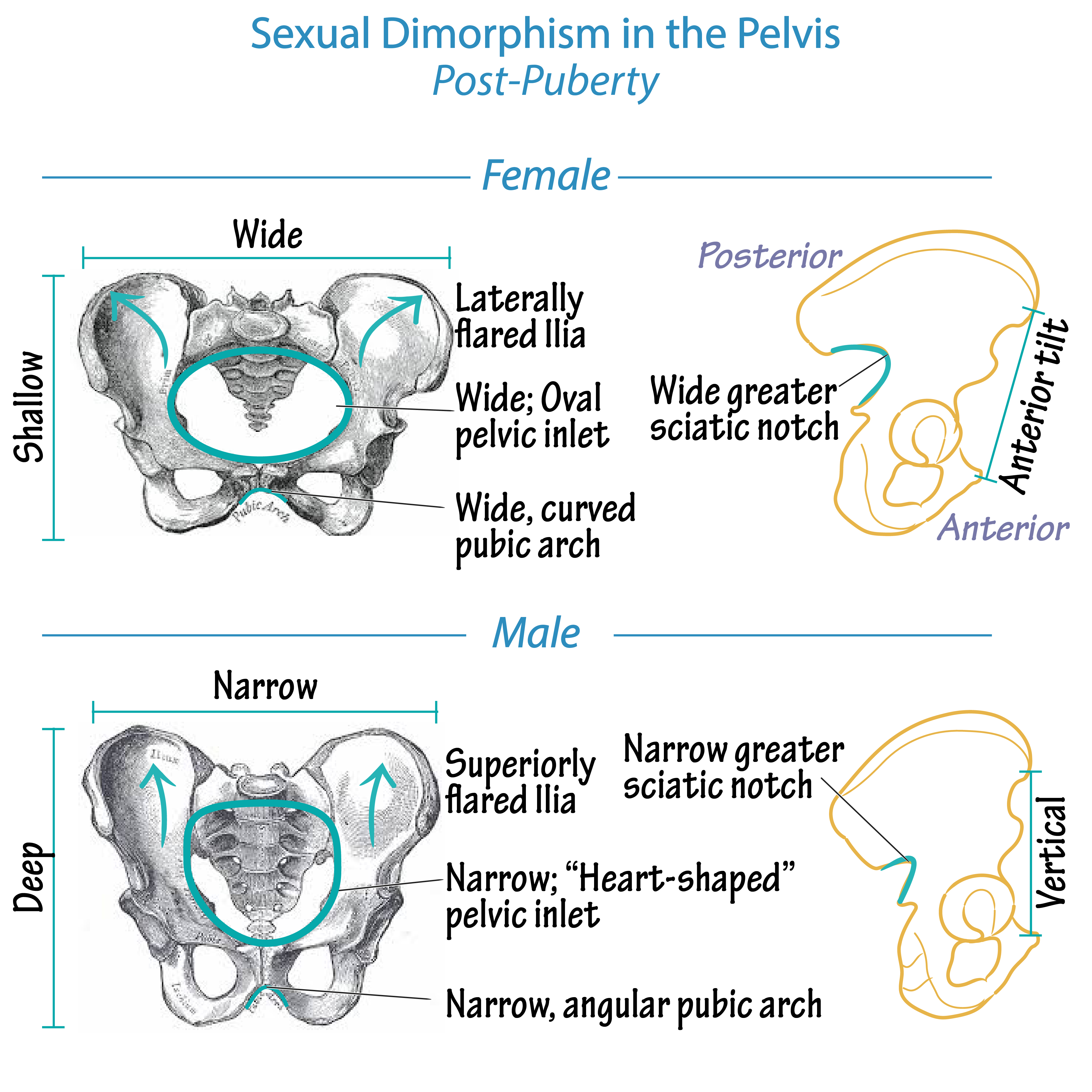
female pelvis post puberty
pelvic cavity is wider and deeper. coccyx more movable. pelvis light and thin. pelvic inlet and outlet larger
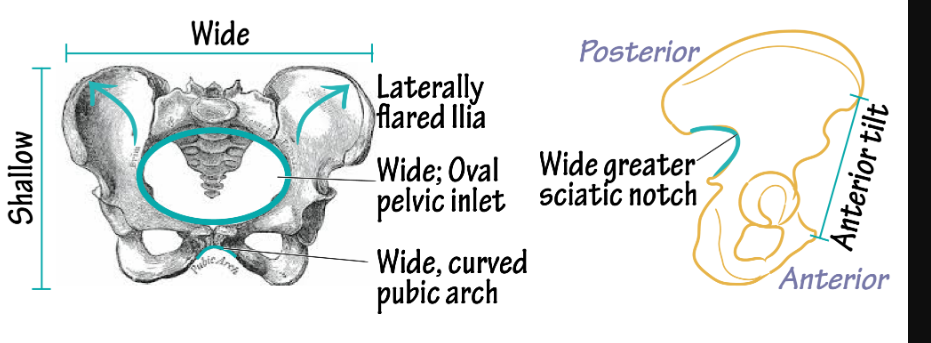
female pelvis
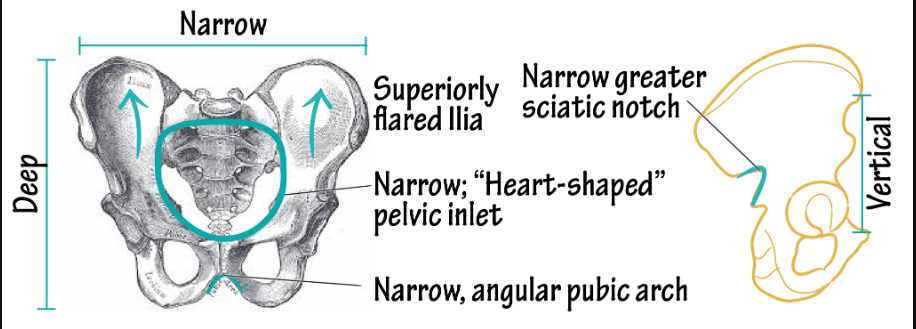
male pelvis
bipedal skeleton
-short, flat, bowl shaped pelvis -S-shaped vertebral column -femurs come in at angle -nondivergent toes
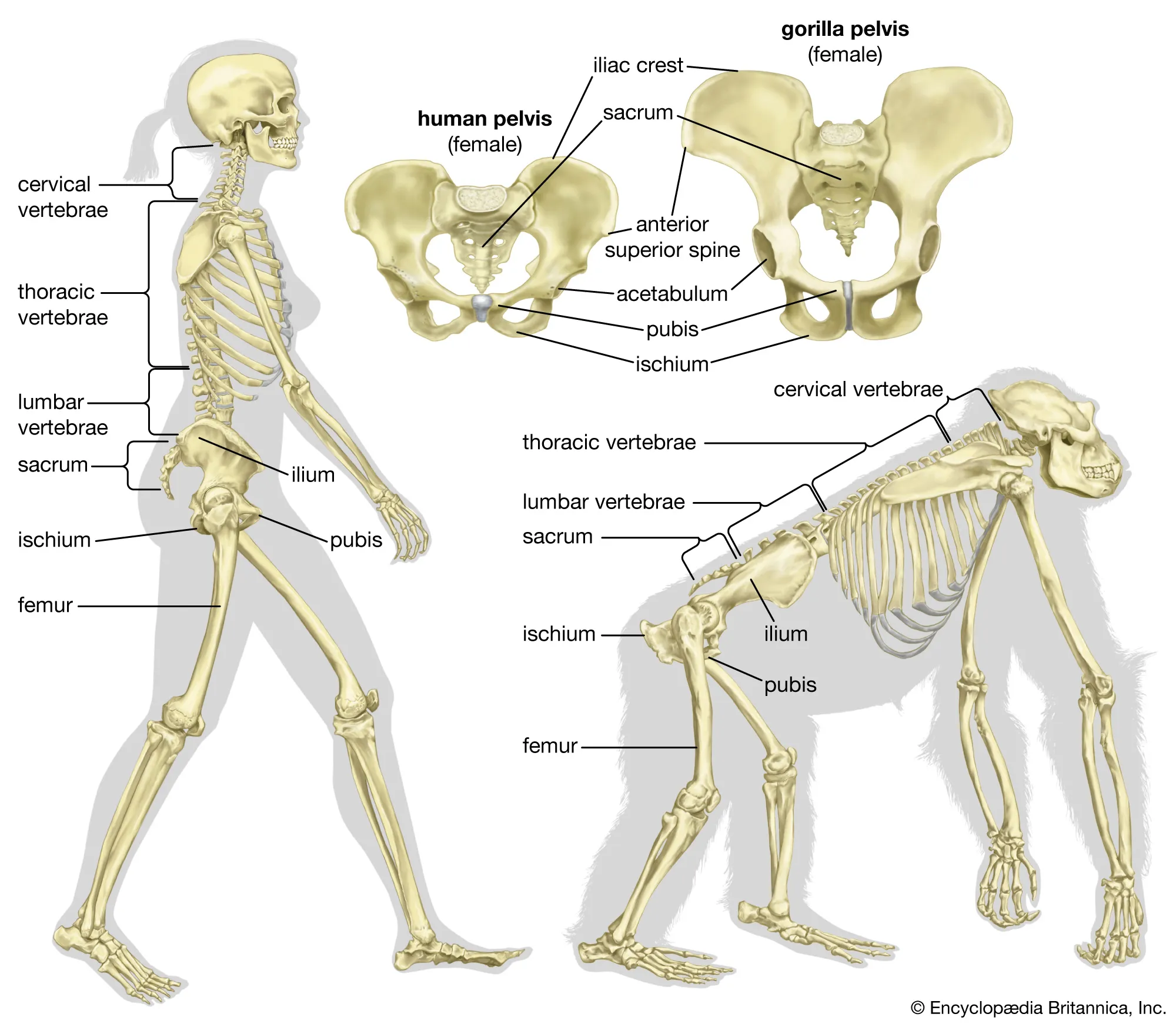
quadrupedal skeleton
-long, narrow pelvis -c-shaped vertebral column -femurs are straight down -divergent toes
blood flow is important for healing
-blood contains nutrients and oxygen. it also removes carbon dioxide & waste. -bones are continuously remodeling throughout life. due to this, bones have good blood supply. -ligaments are dense regular connective tissue and have limited amounts of blood supply
arthritis
inflammation of joints. -can cause narrow joint space -bone erosions -bone spurs
cartilage on the long bones prevent bones from rubbing against each other
Anterior Skull 1.
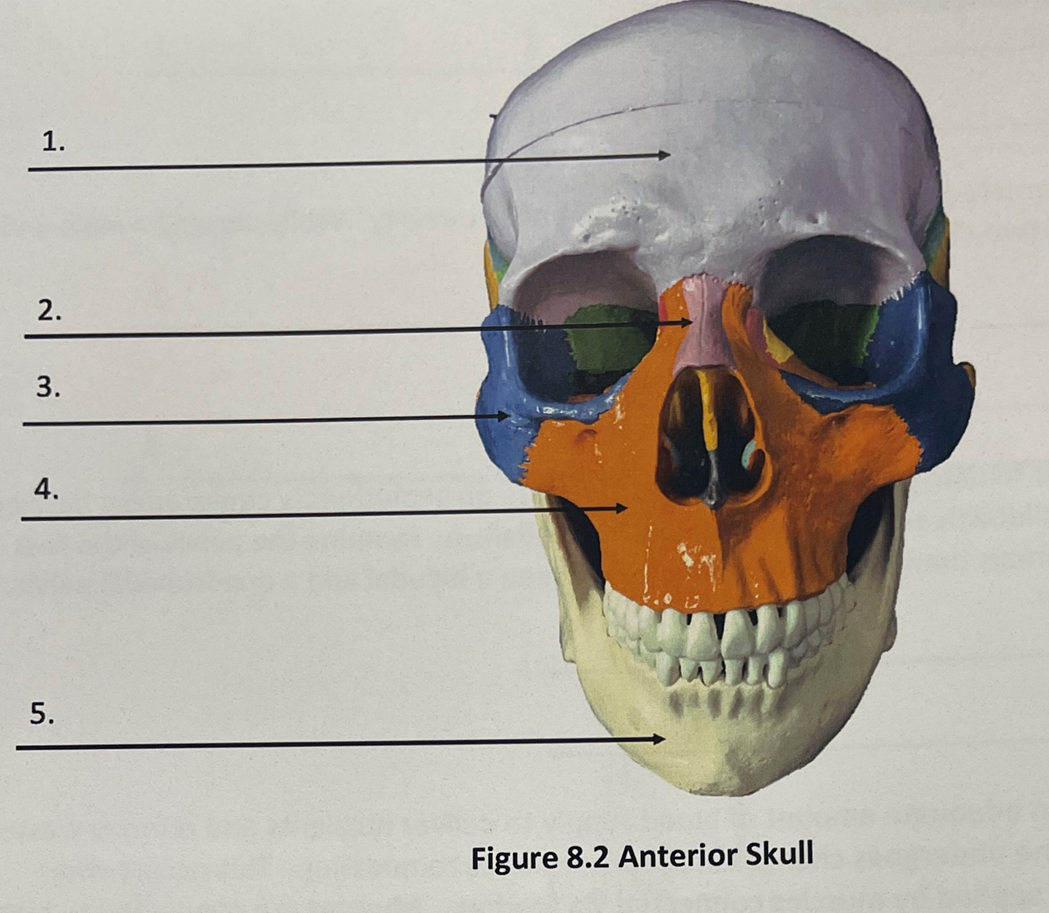
Frontal bone
Anterior skull 2.
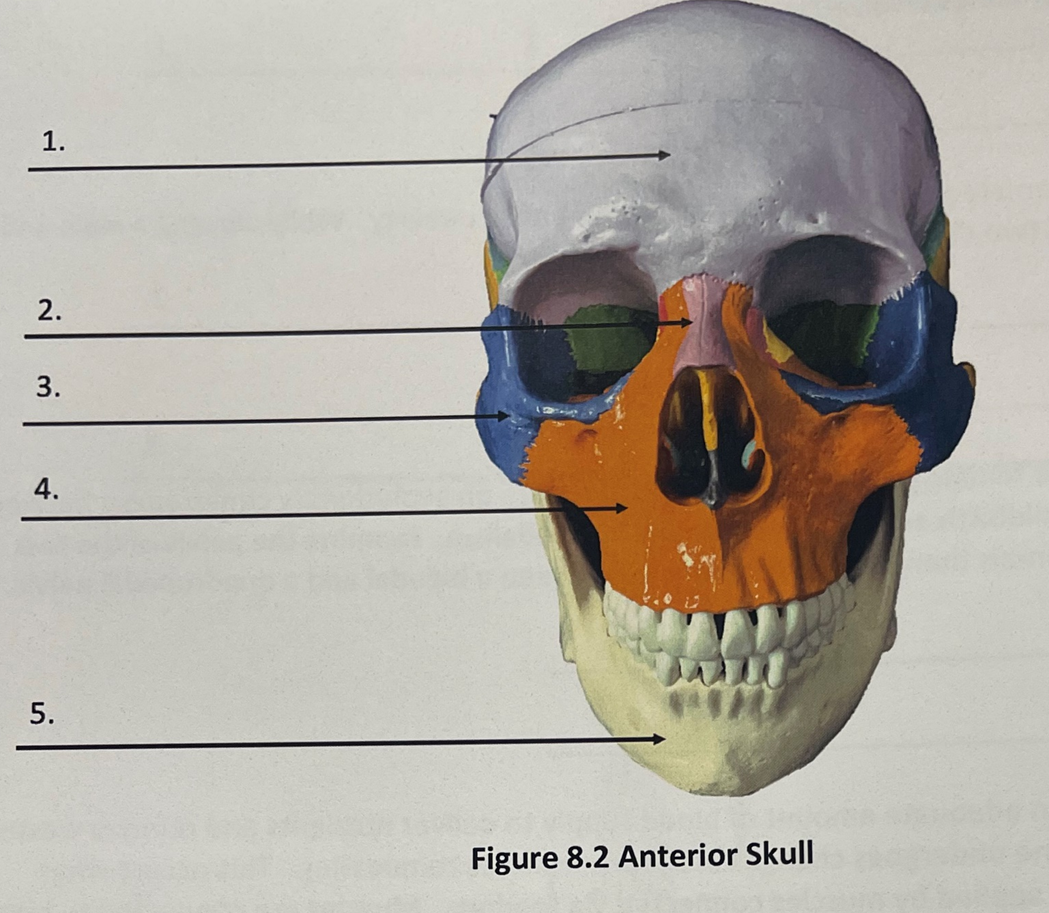
Nasal bone
Anterior skull 3.

zygomatic bone
anterior skull 4.

maxilla
anterior skull 5

mandible
lateral skull 1
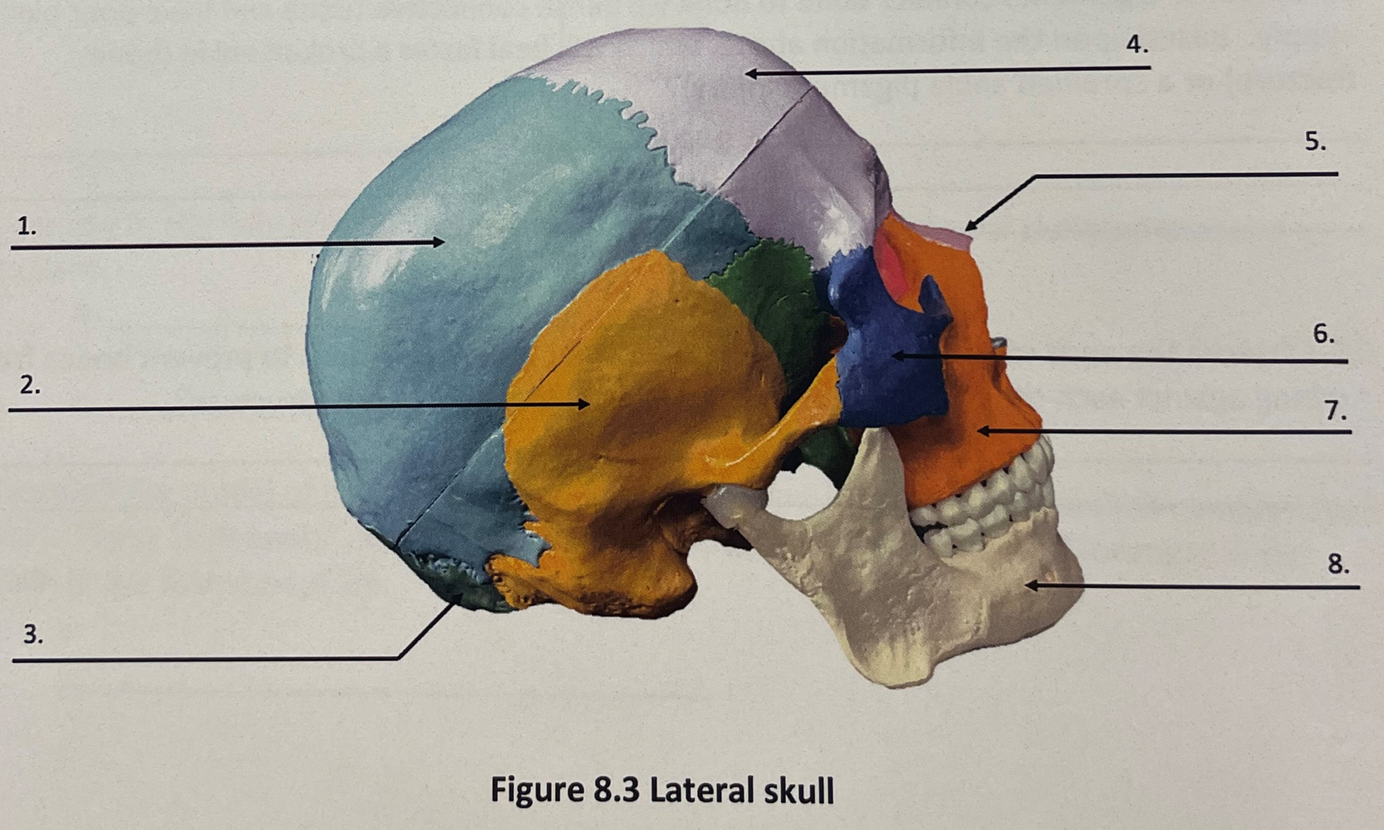
parietal bone
lateral skull 2
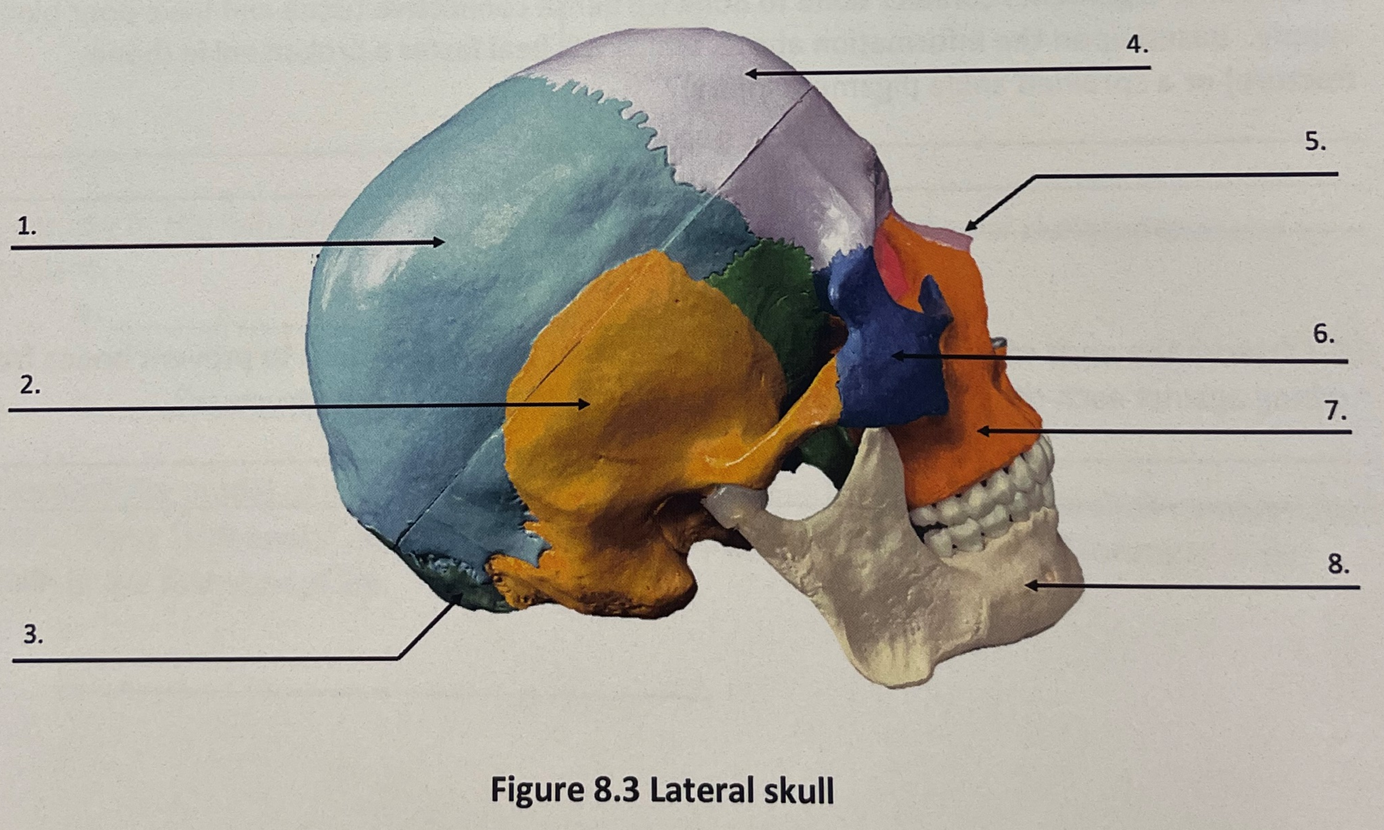
temporal bone
lateral skull 3
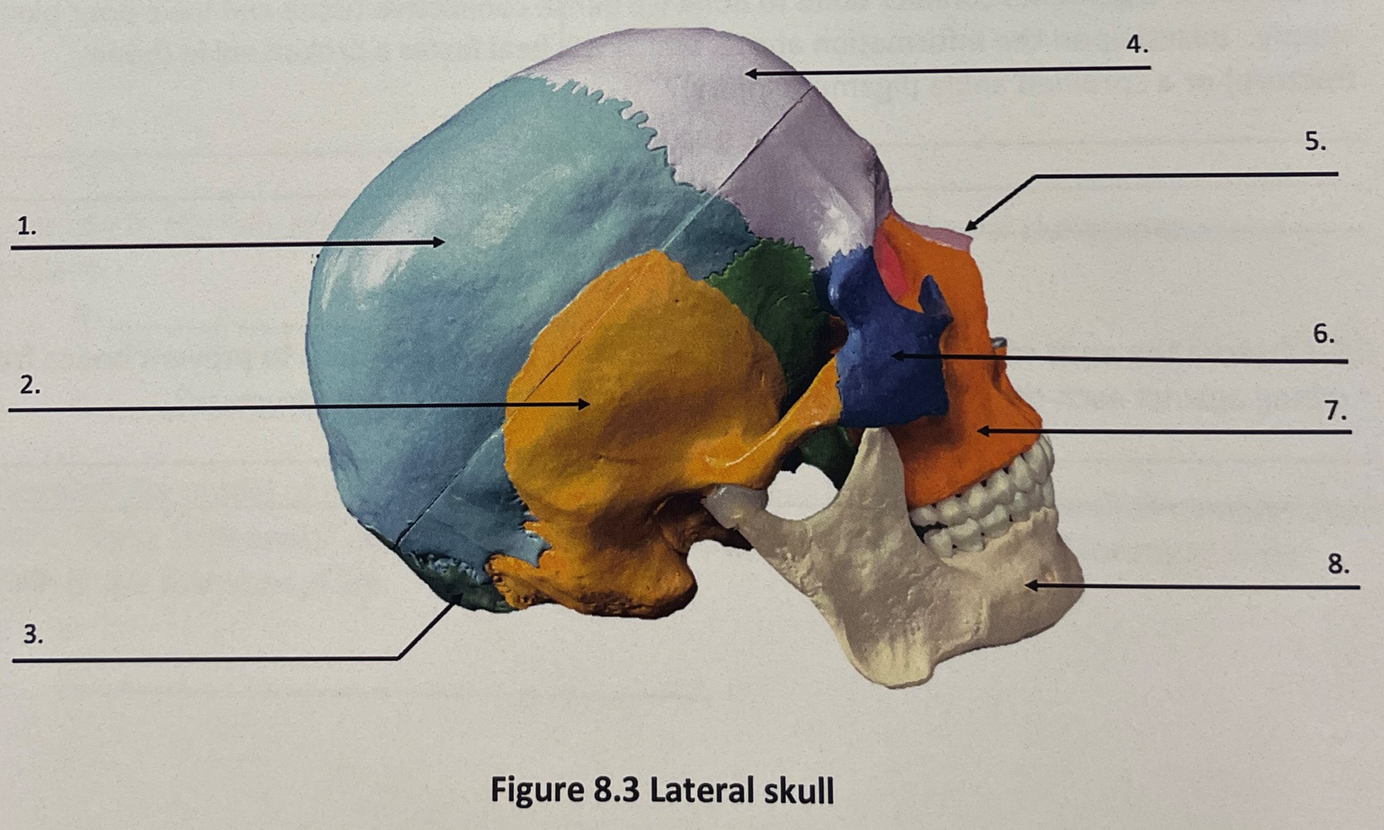
occipital bone
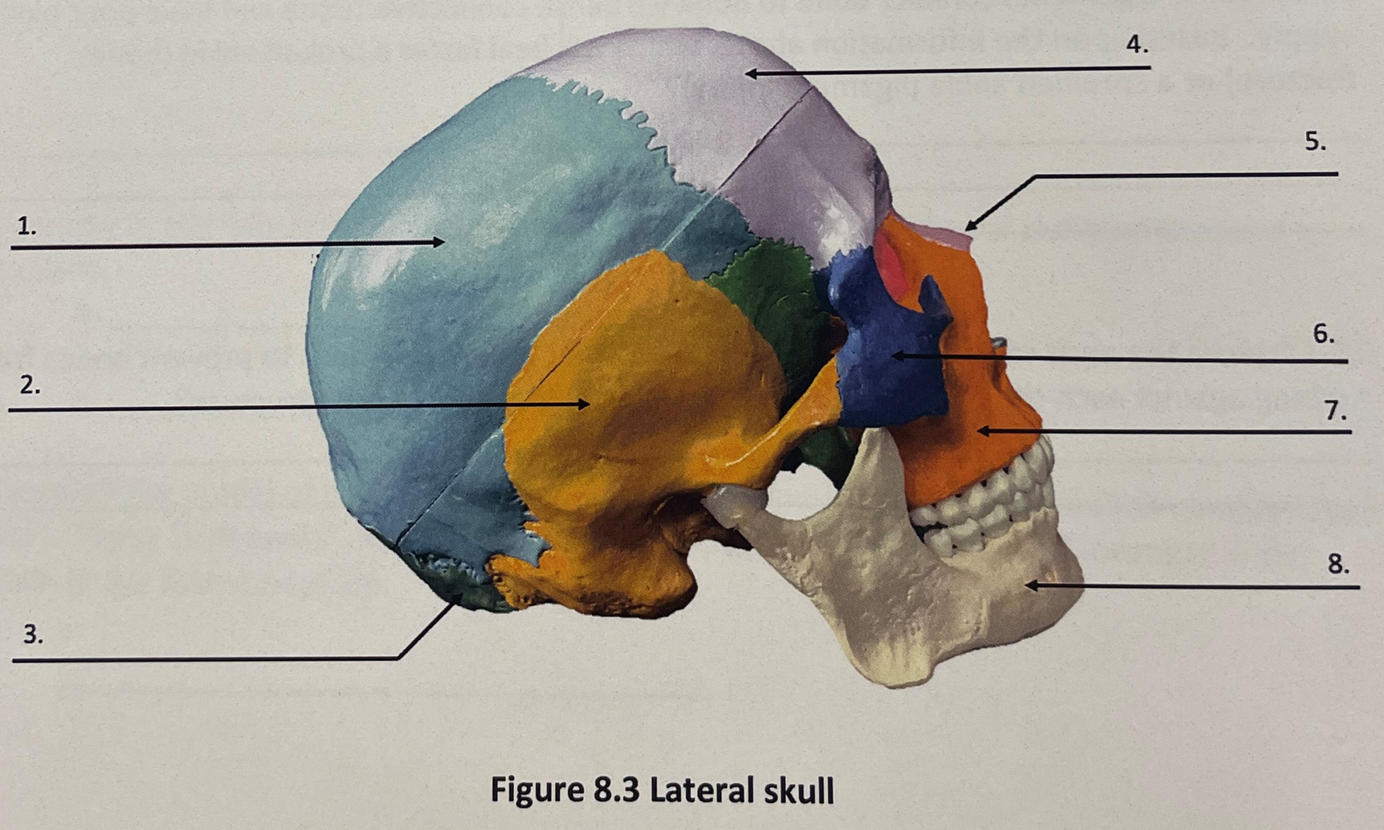
lateral skull 4
frontal bone
lateral skull 5

nasal bone
lateral skull 6

zygomatic bone
lateral skull 7

maxilla
lateral skull 8

mandible
skull
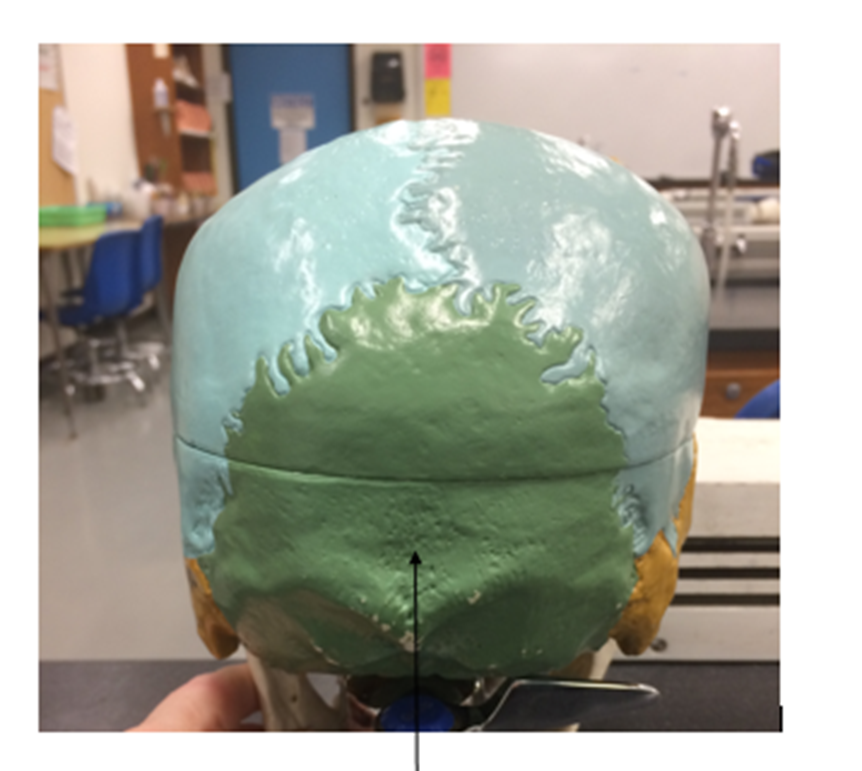

occipital bone
1 vertebral column
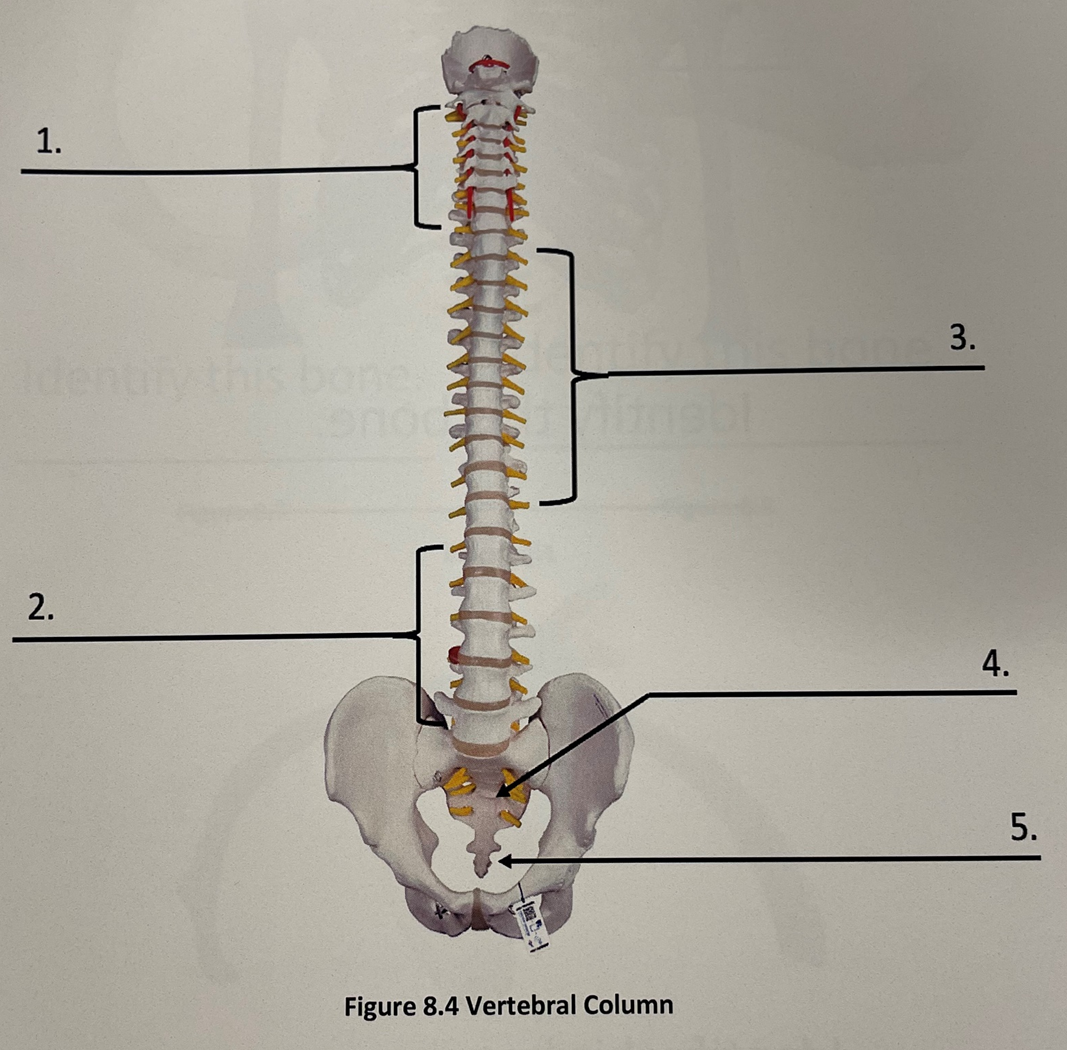
cervical vertebrae
vertebral column 2
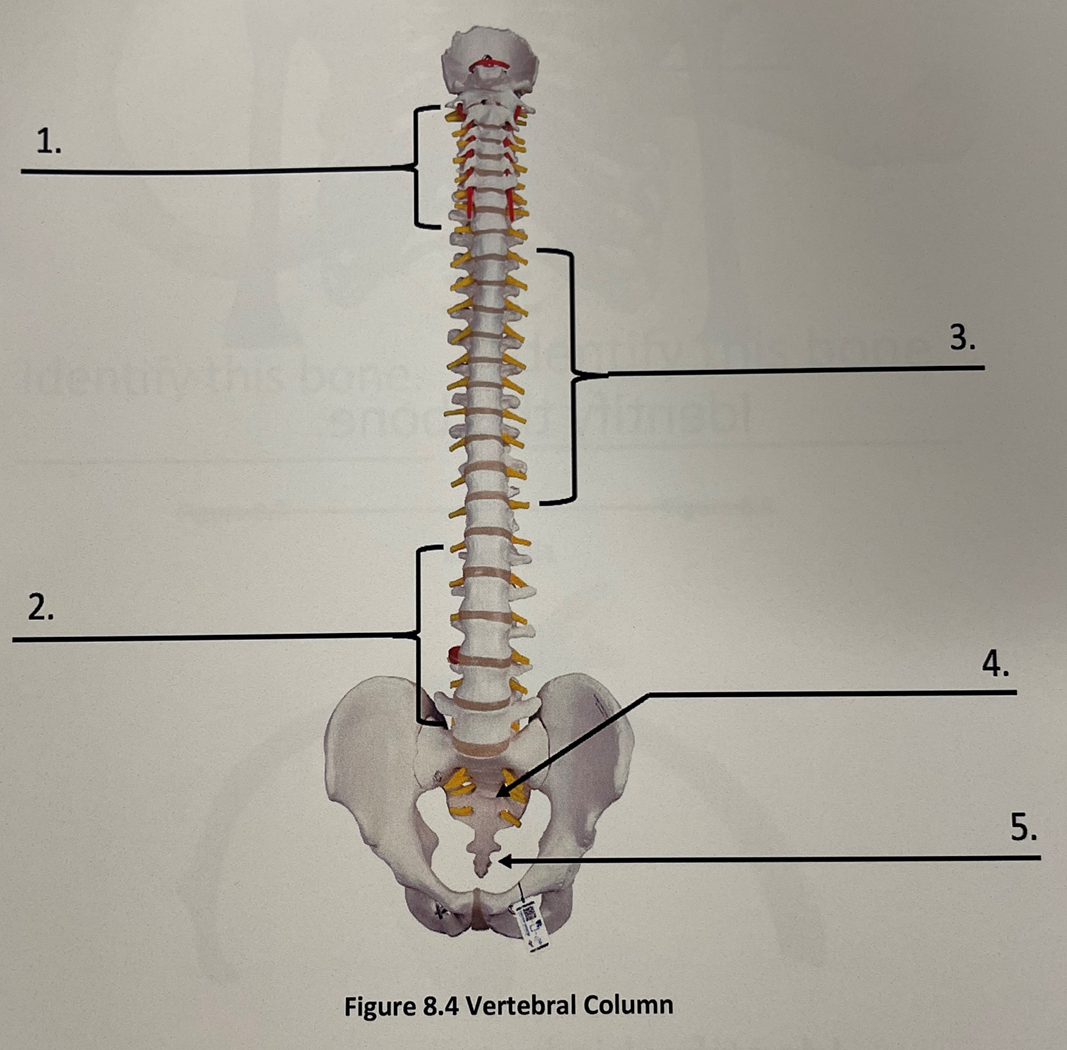
lumbar vertebrae
vertebral column 3
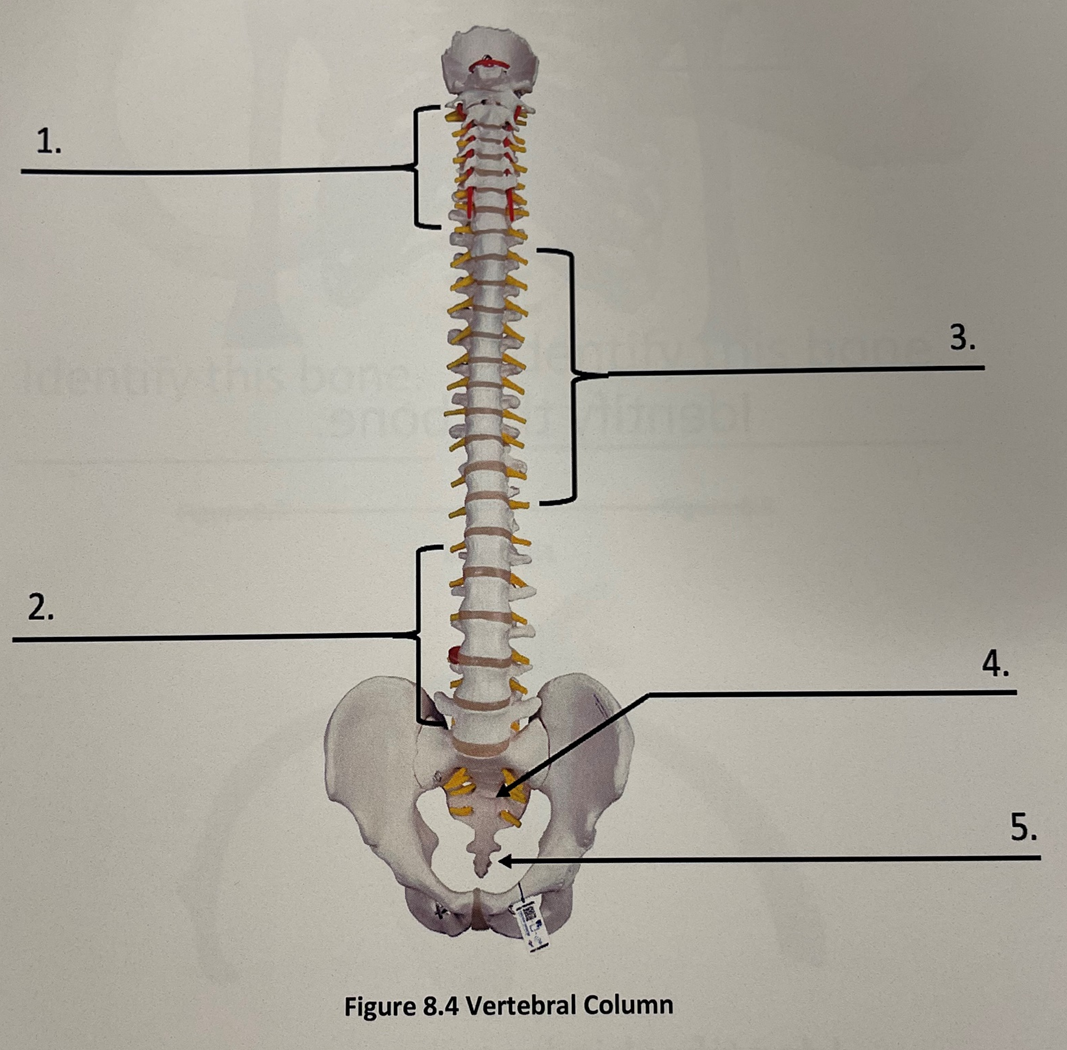
thoracic vertebrae
vertebral column 4
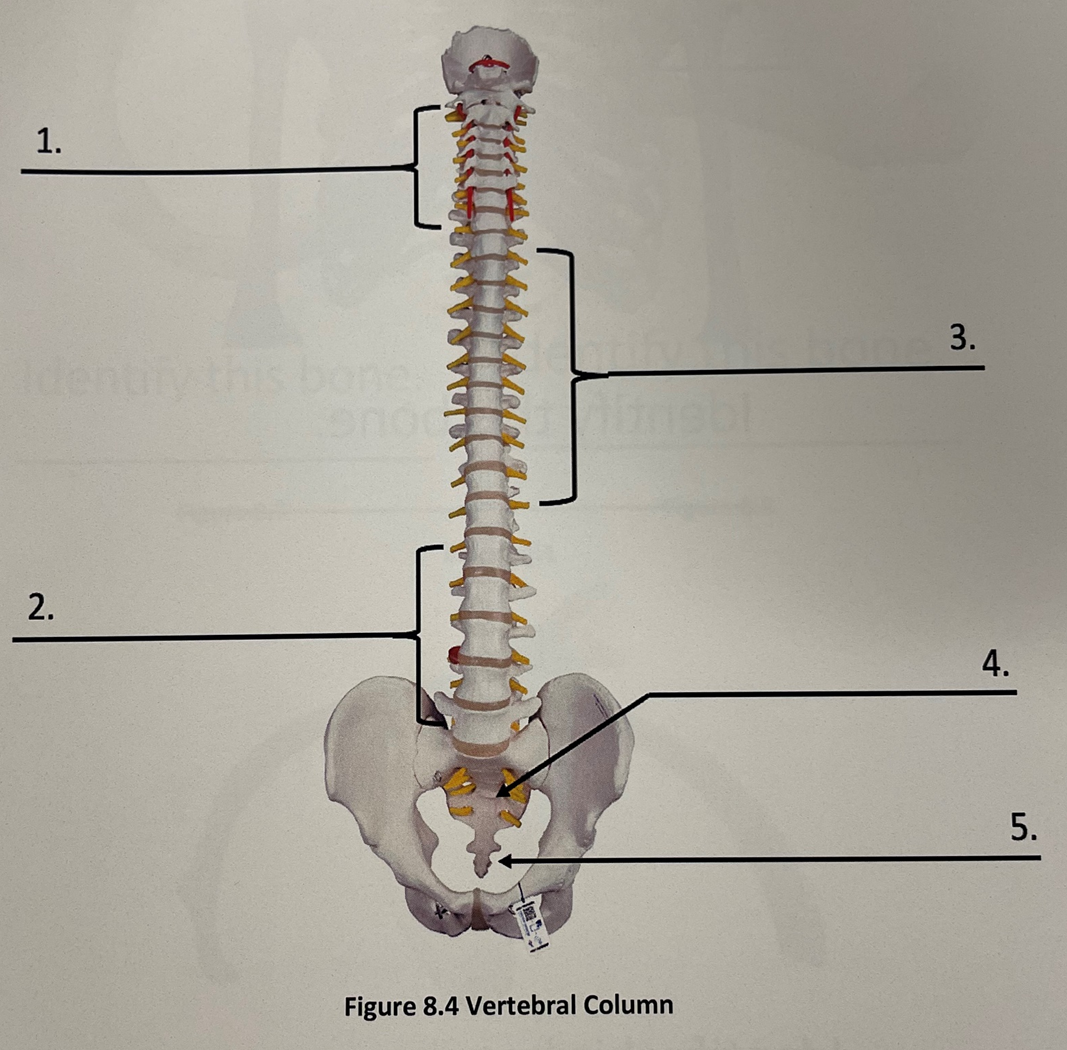
sacrum
vertebral column 5
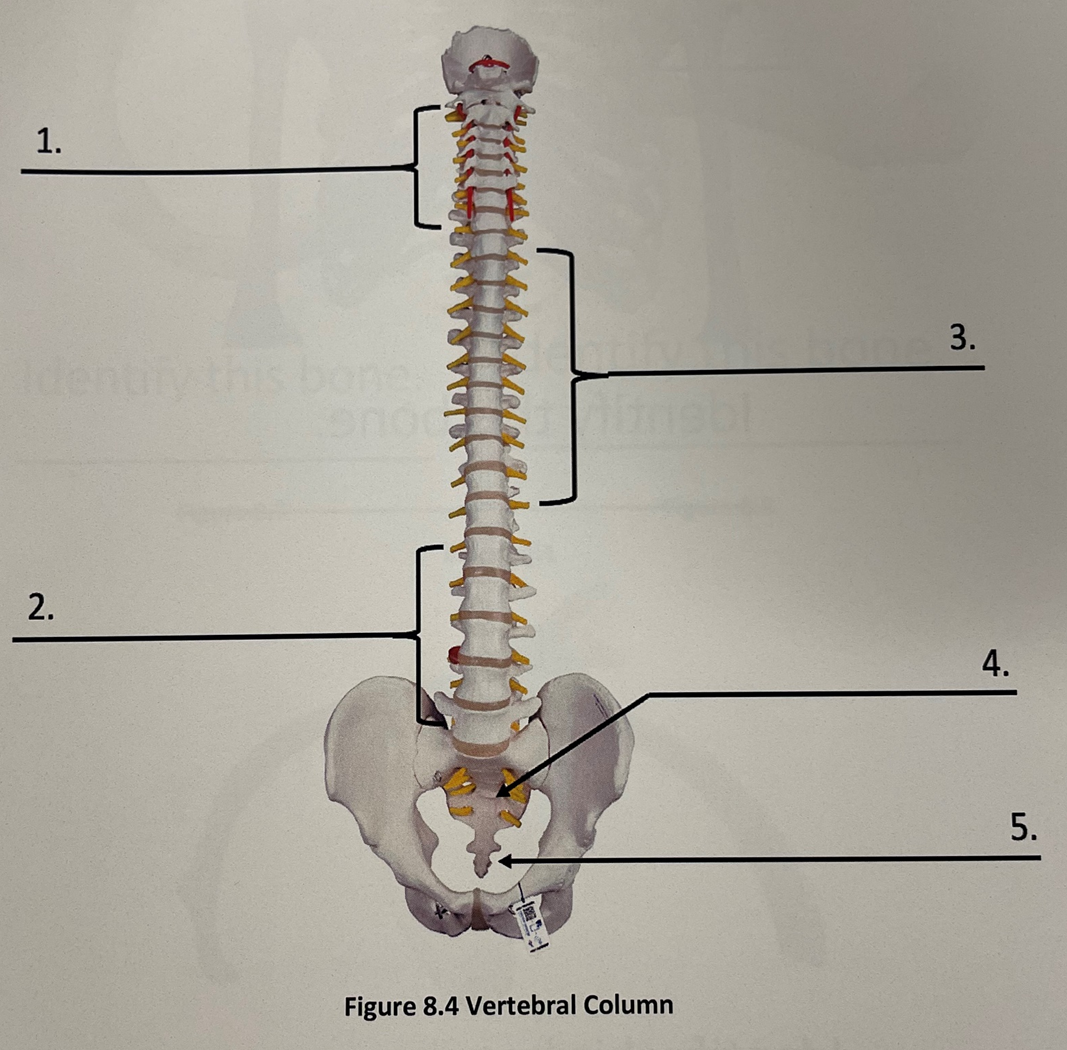
coccyx
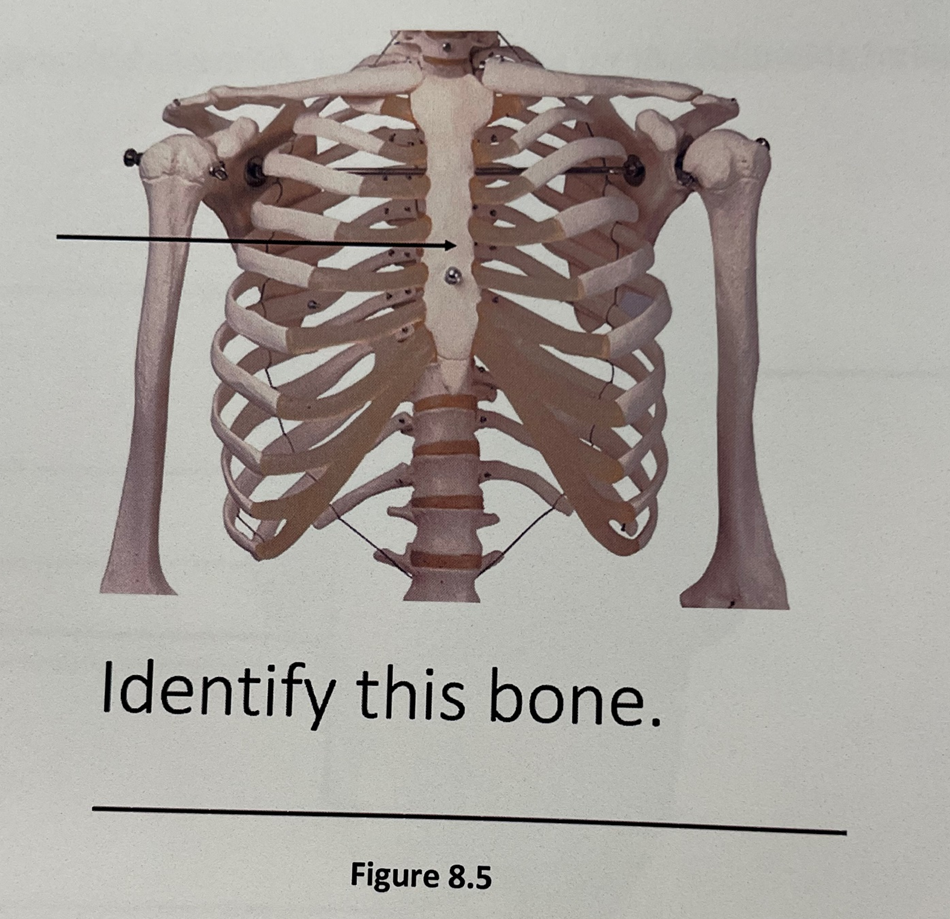
sternum
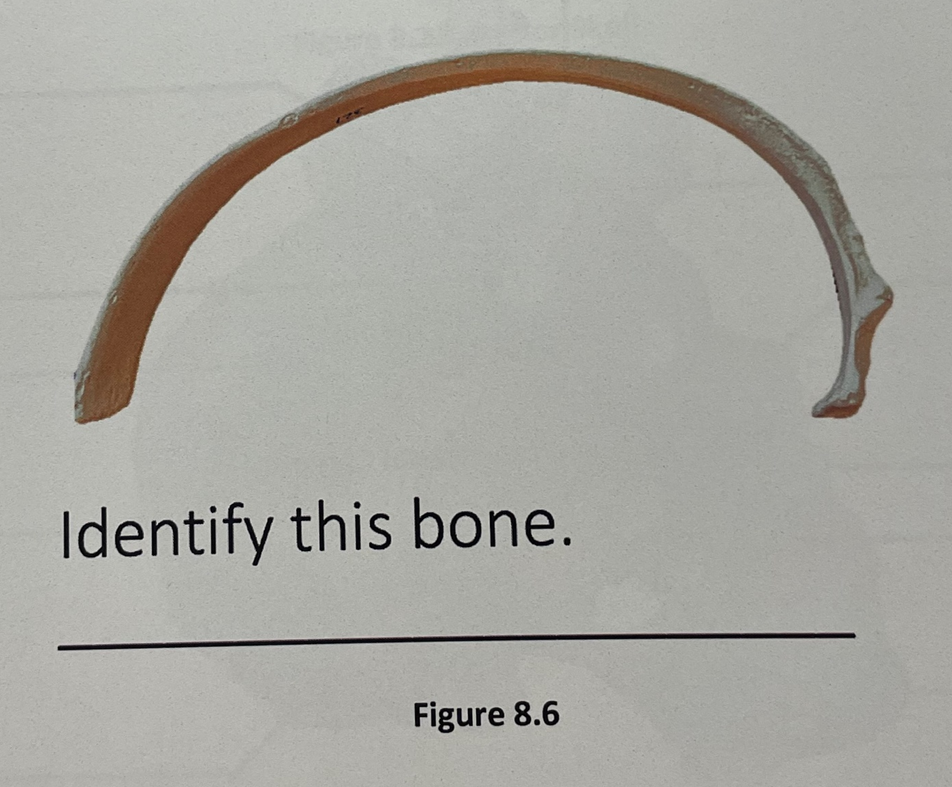
rib
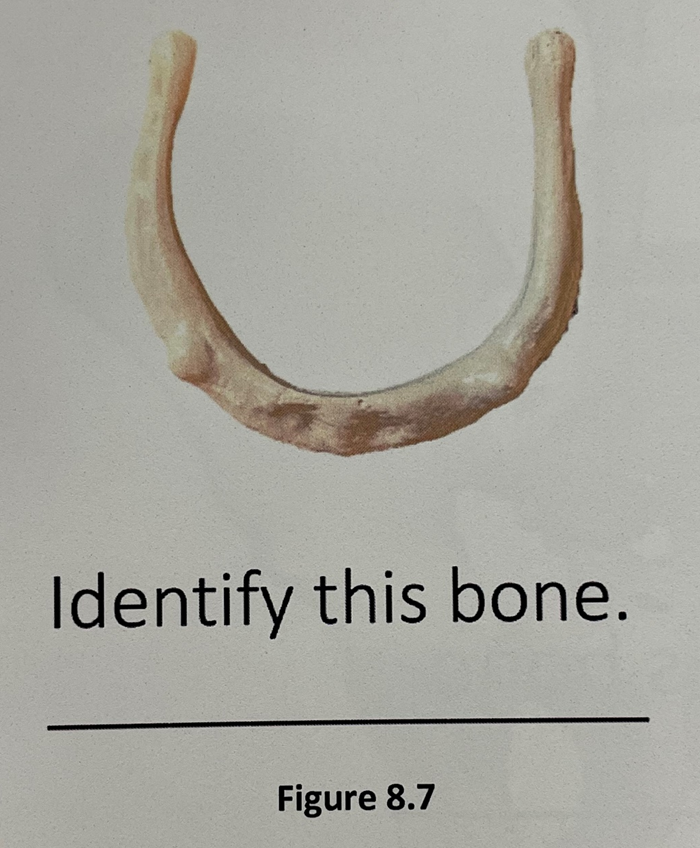
hyoid
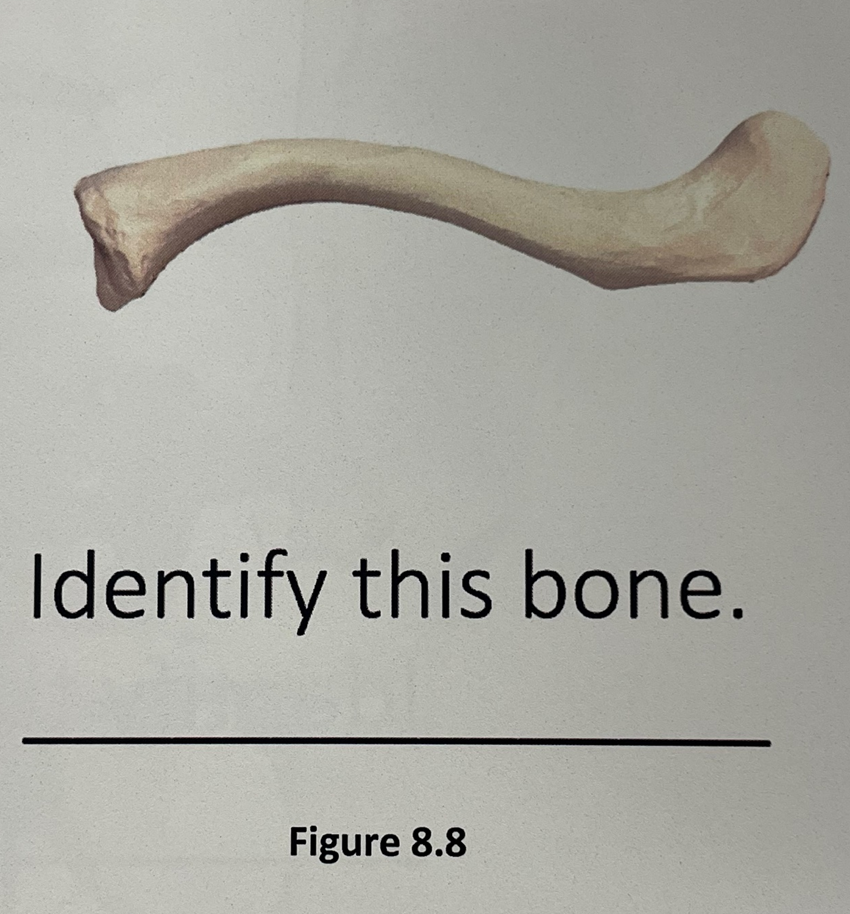
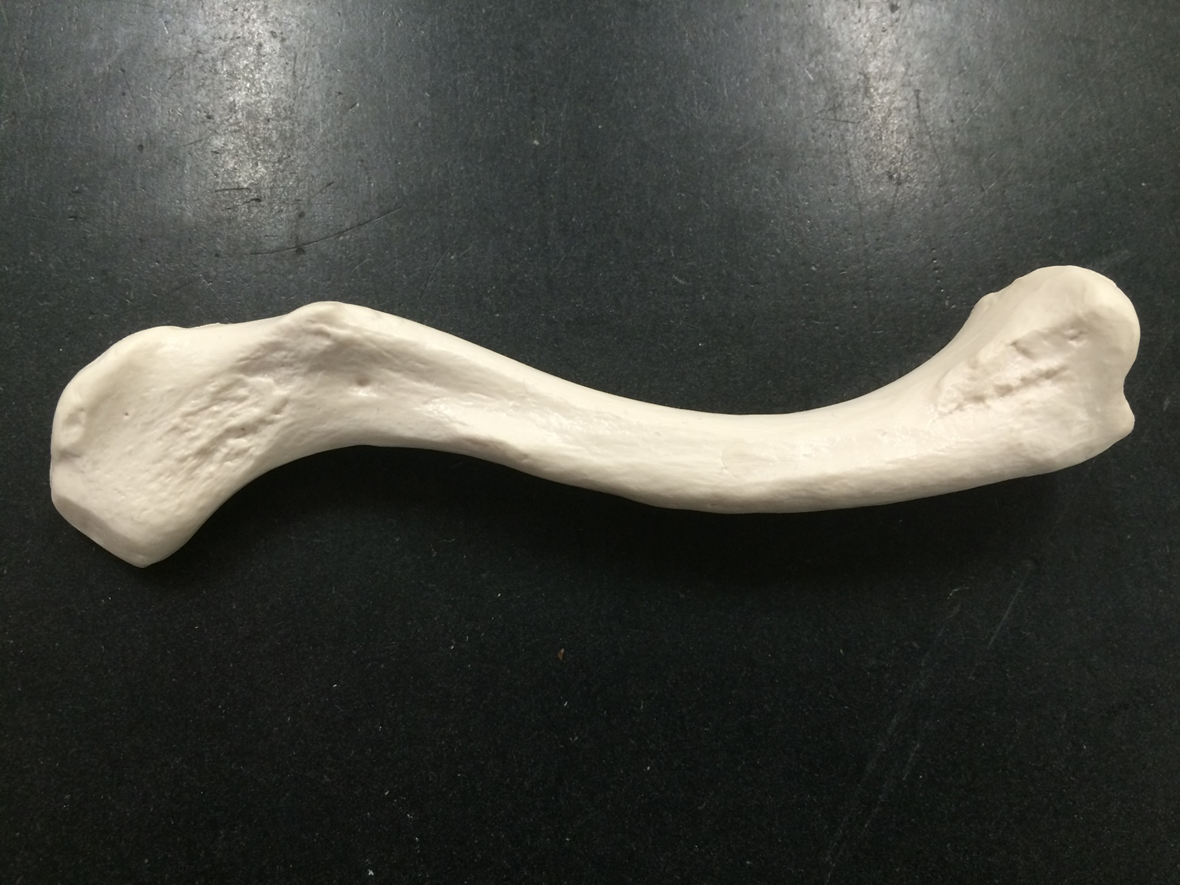
clavicle
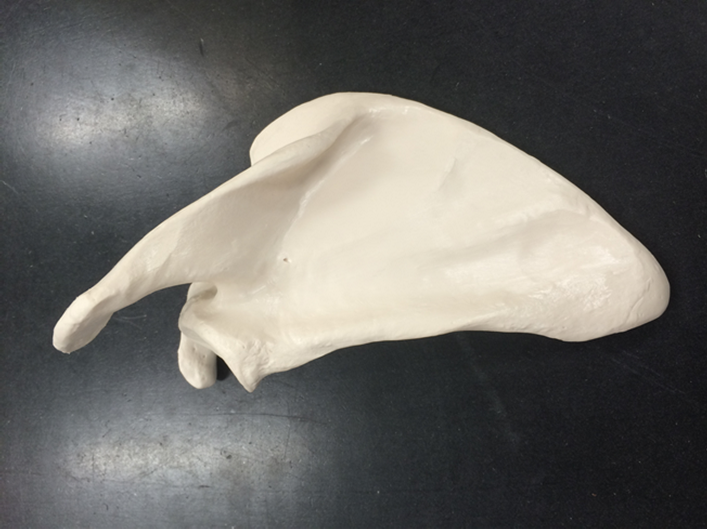
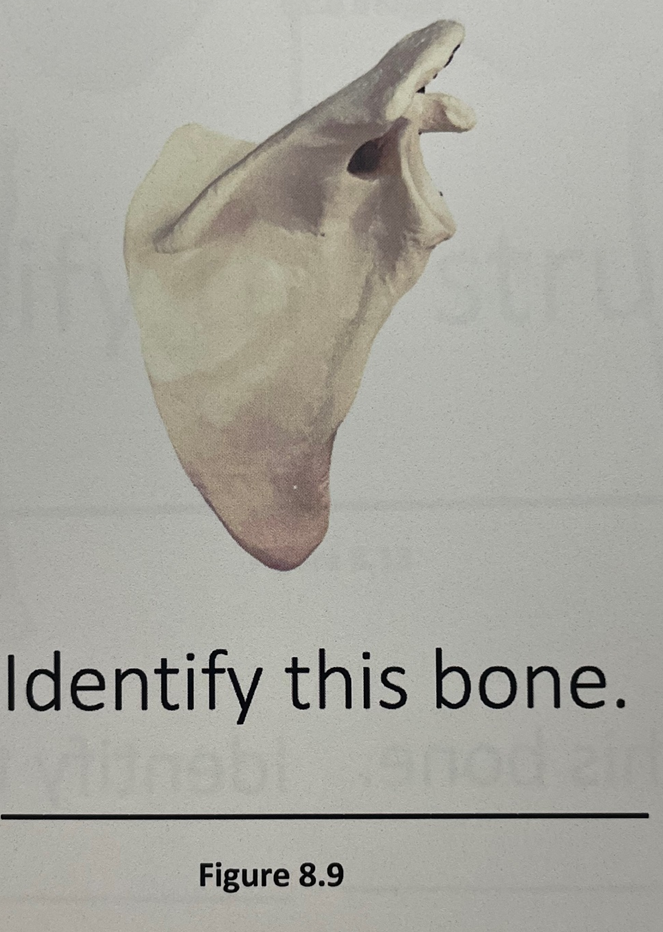

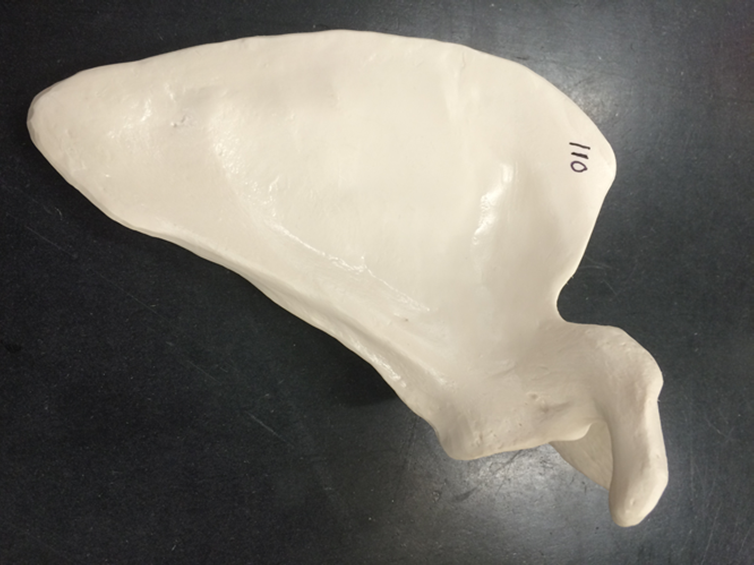
scapula
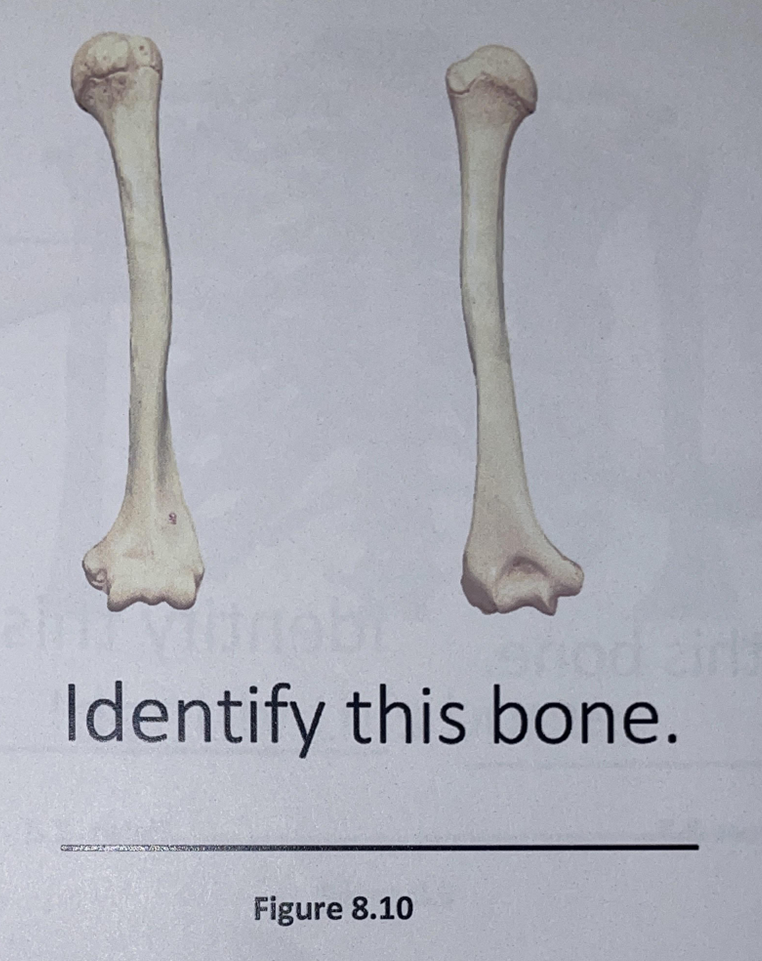
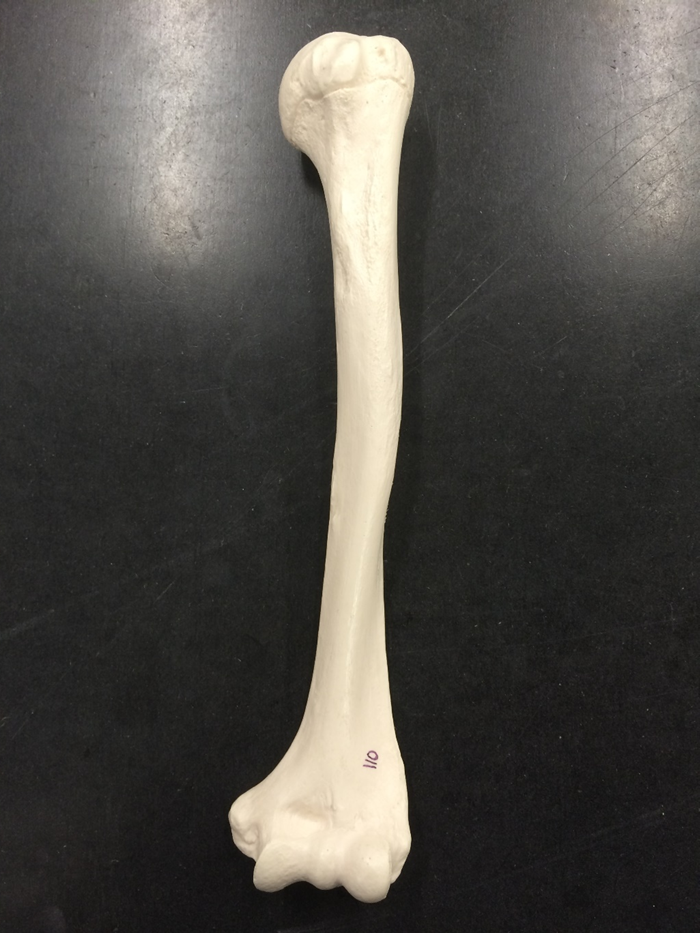
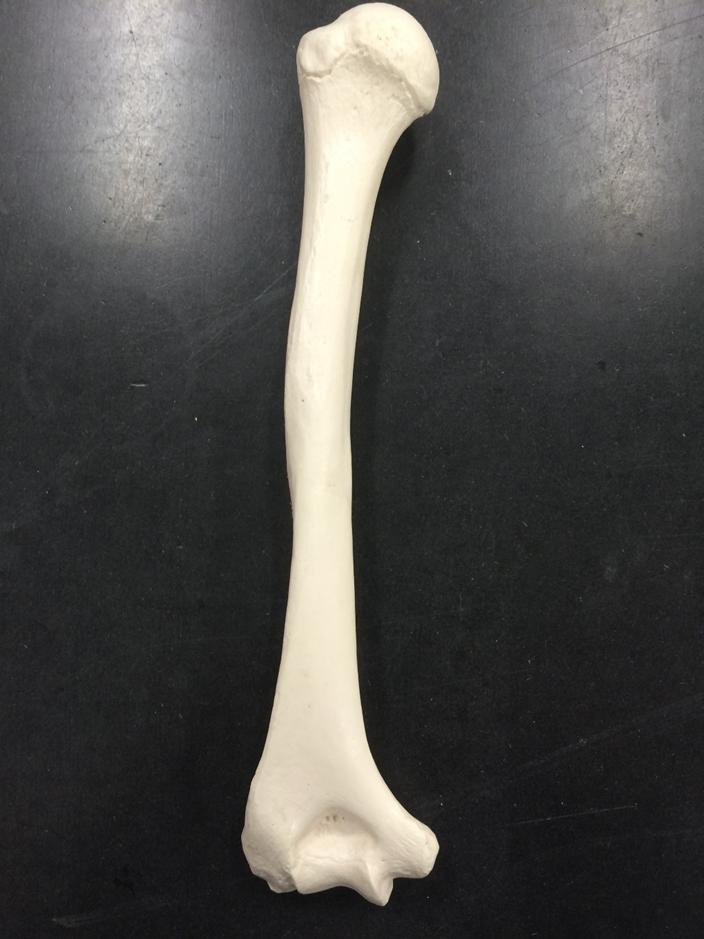
humerus
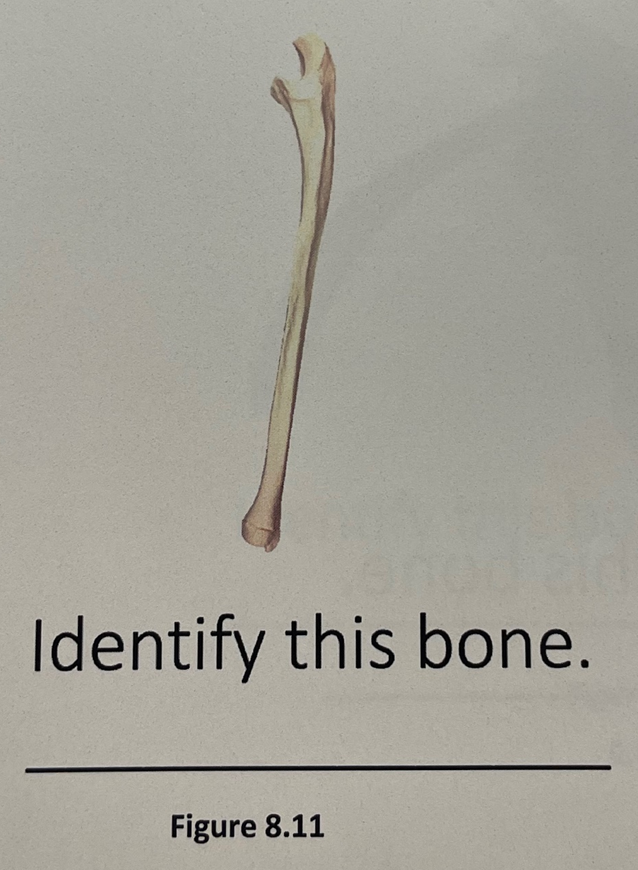
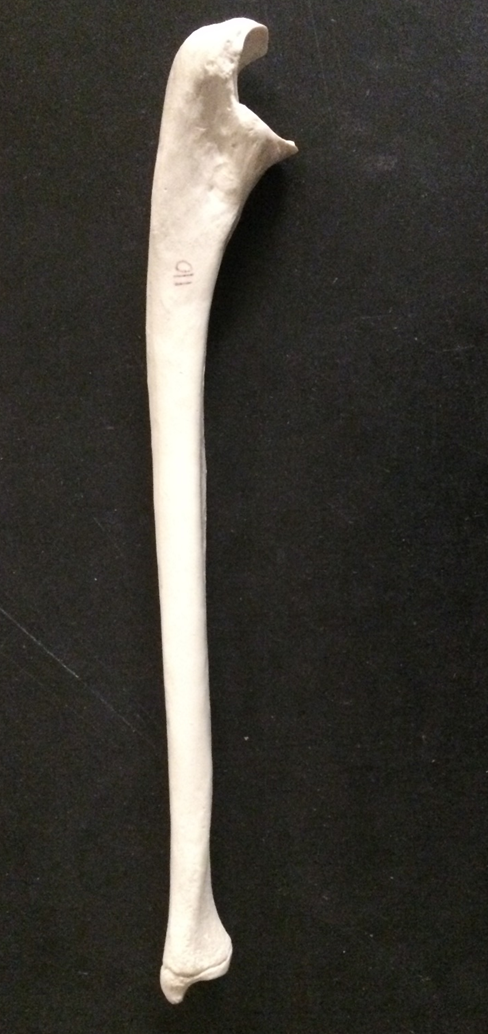

ulna
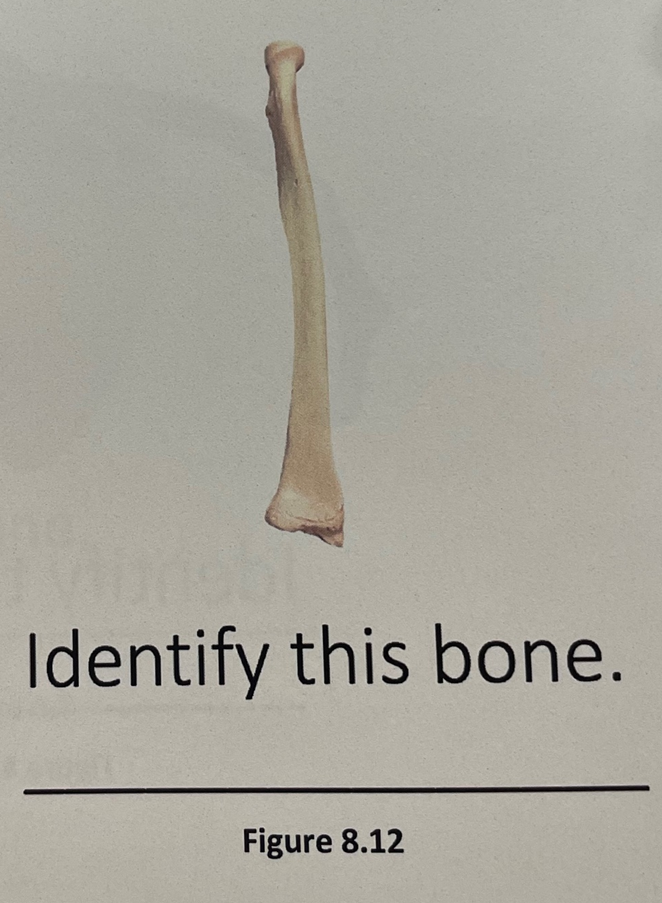


radius
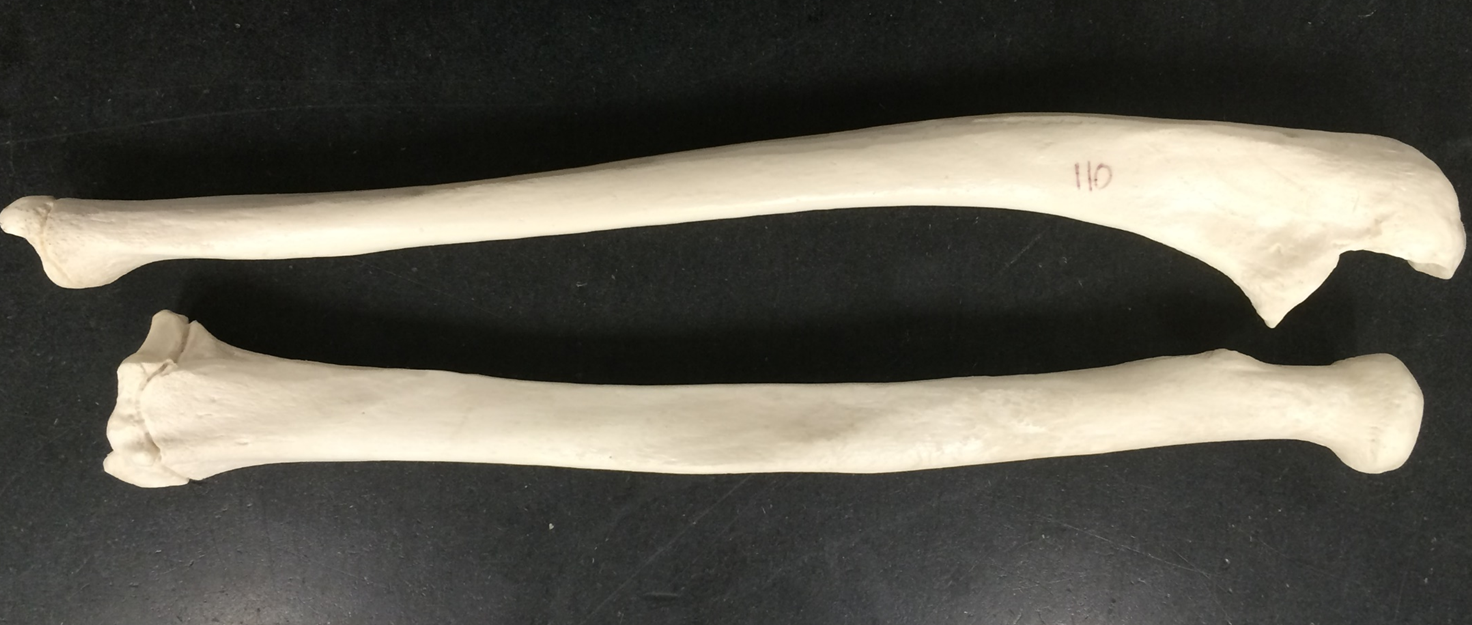
radius (top) ulna (bottom)
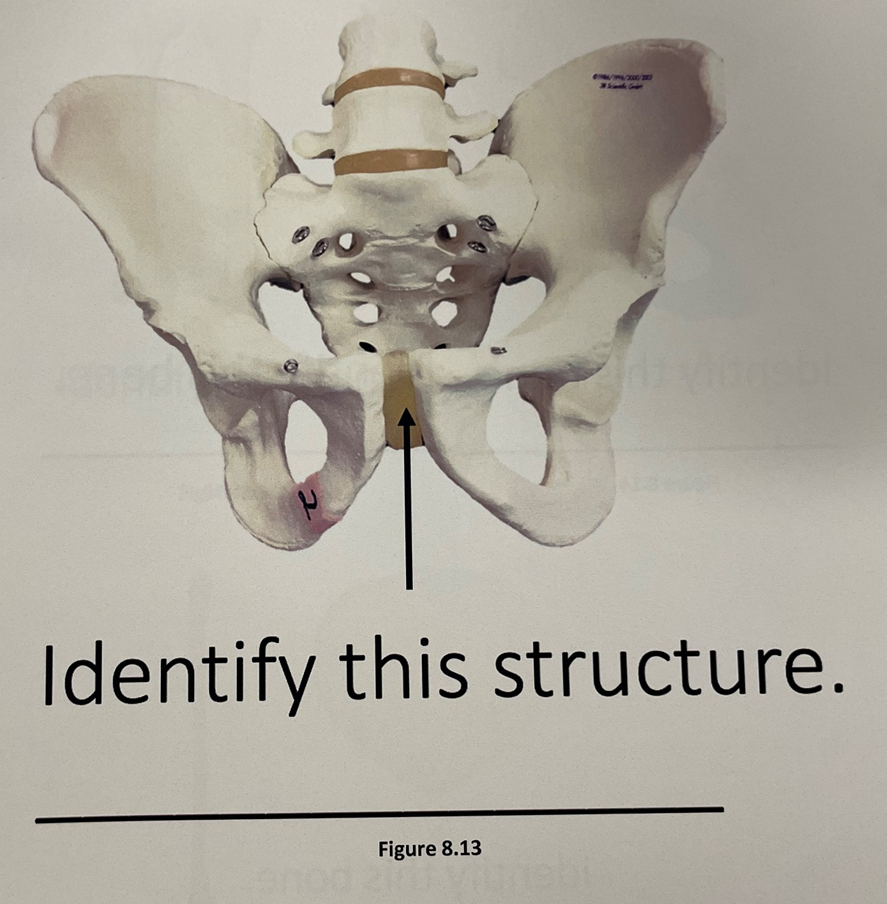
pubic symphysis
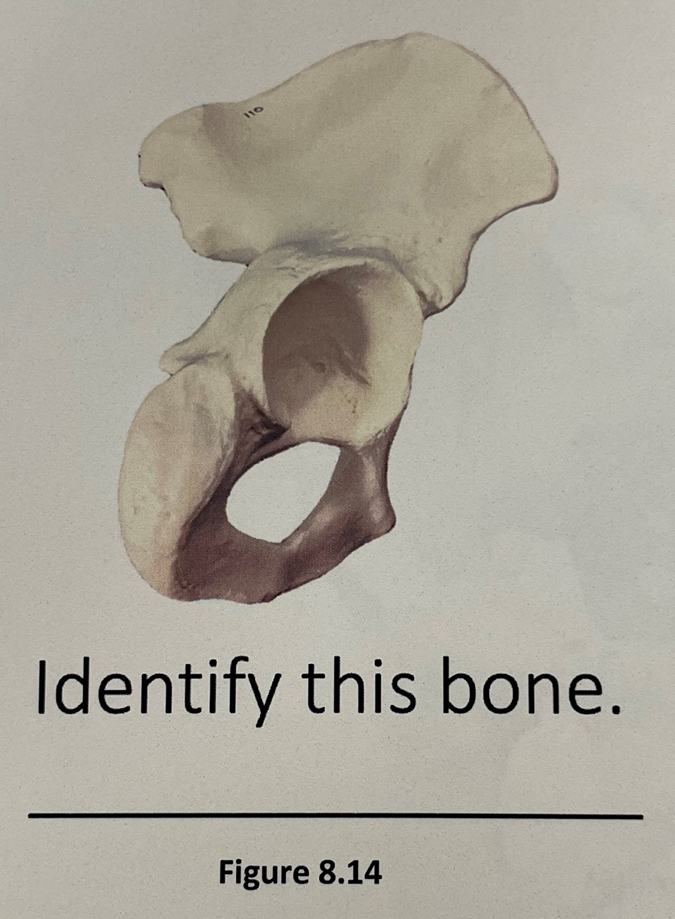
pelvic bones
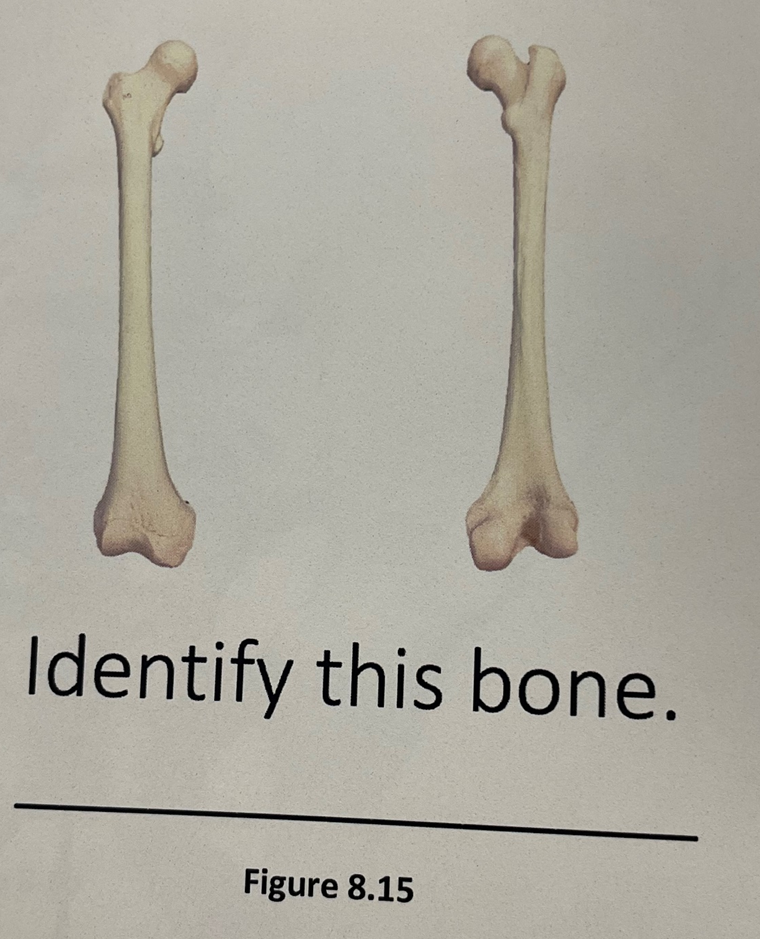

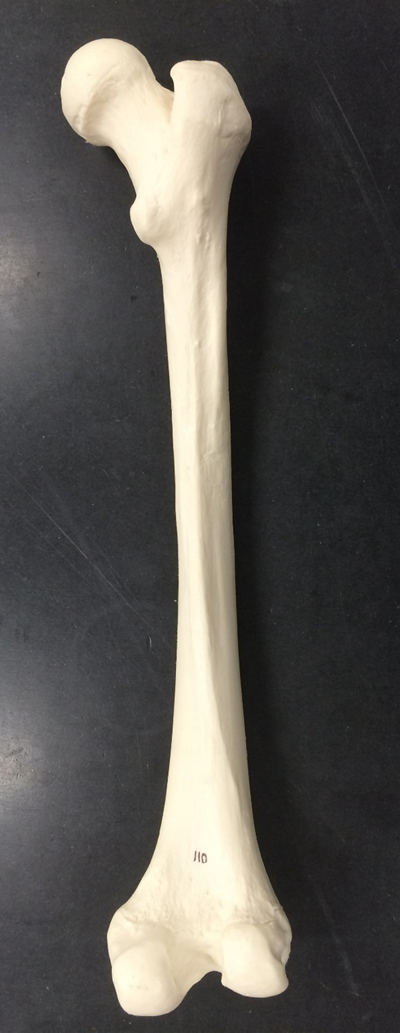
femur
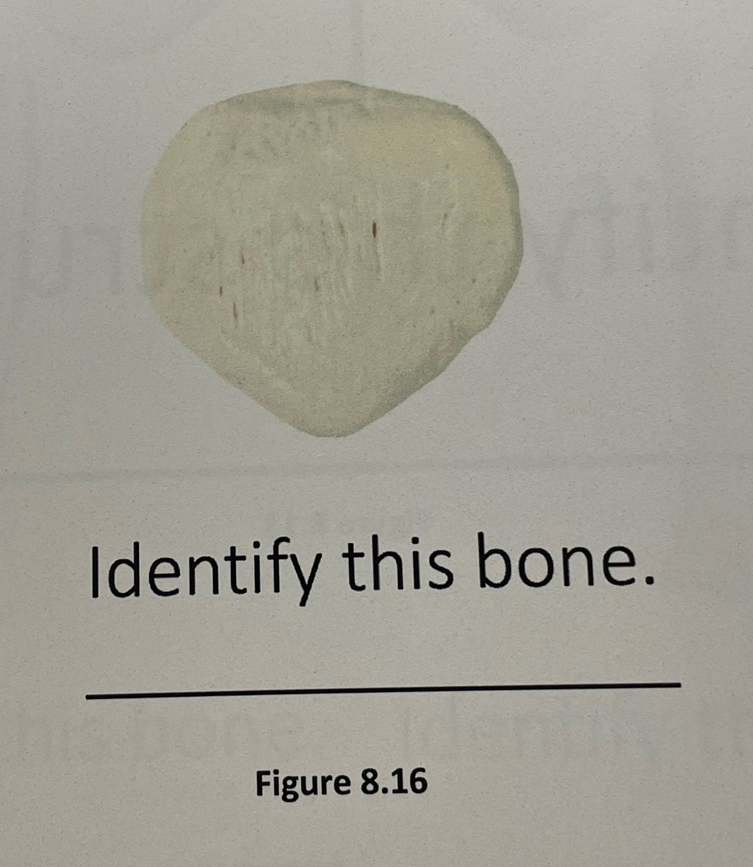
patella
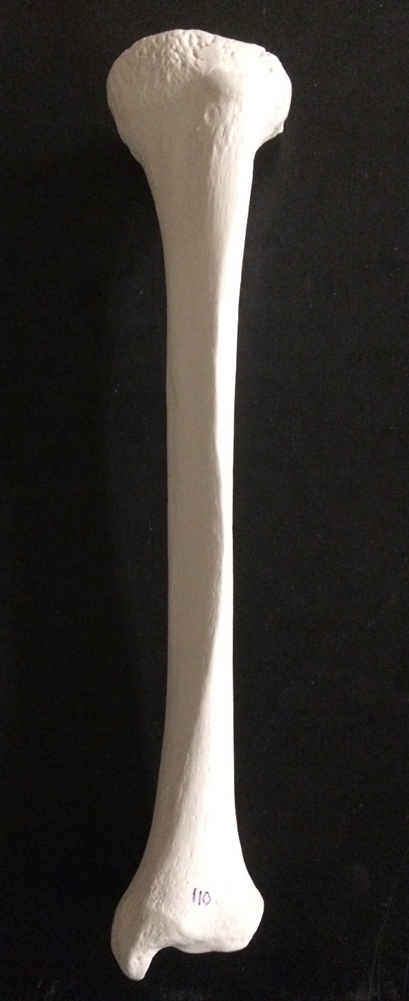
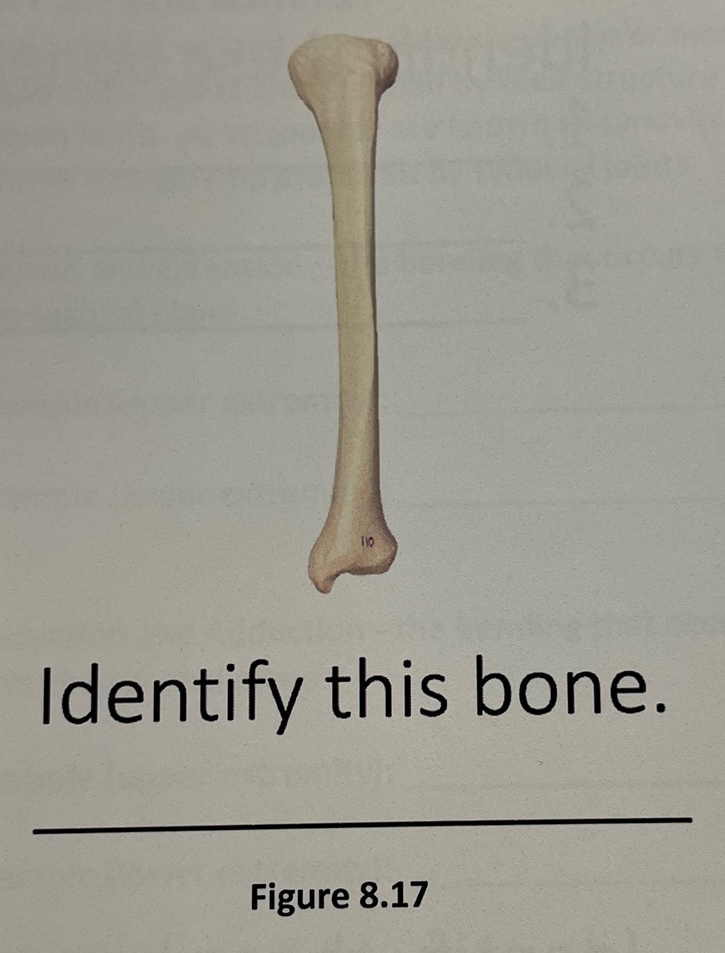
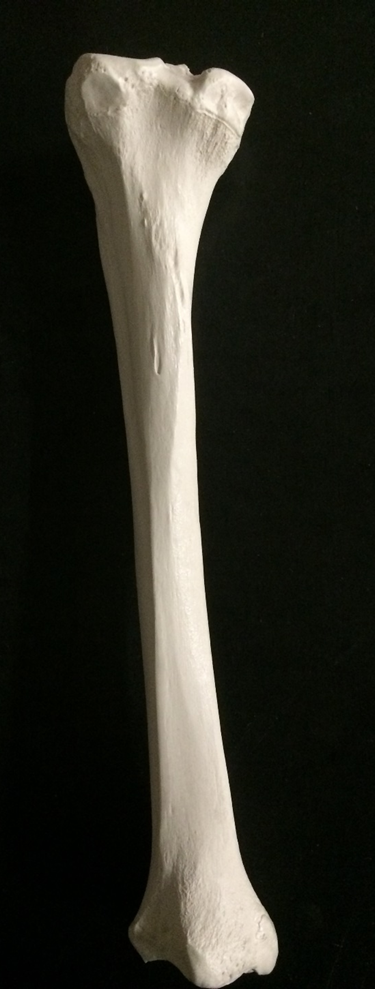

tibia


fibula
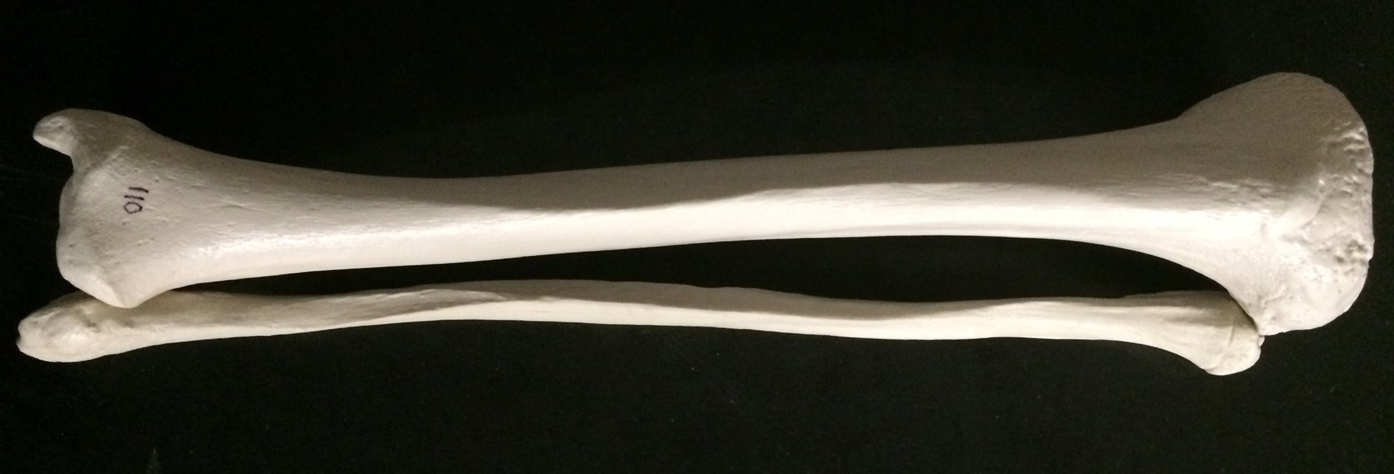

tibia (top) & fibula (bottom)
1
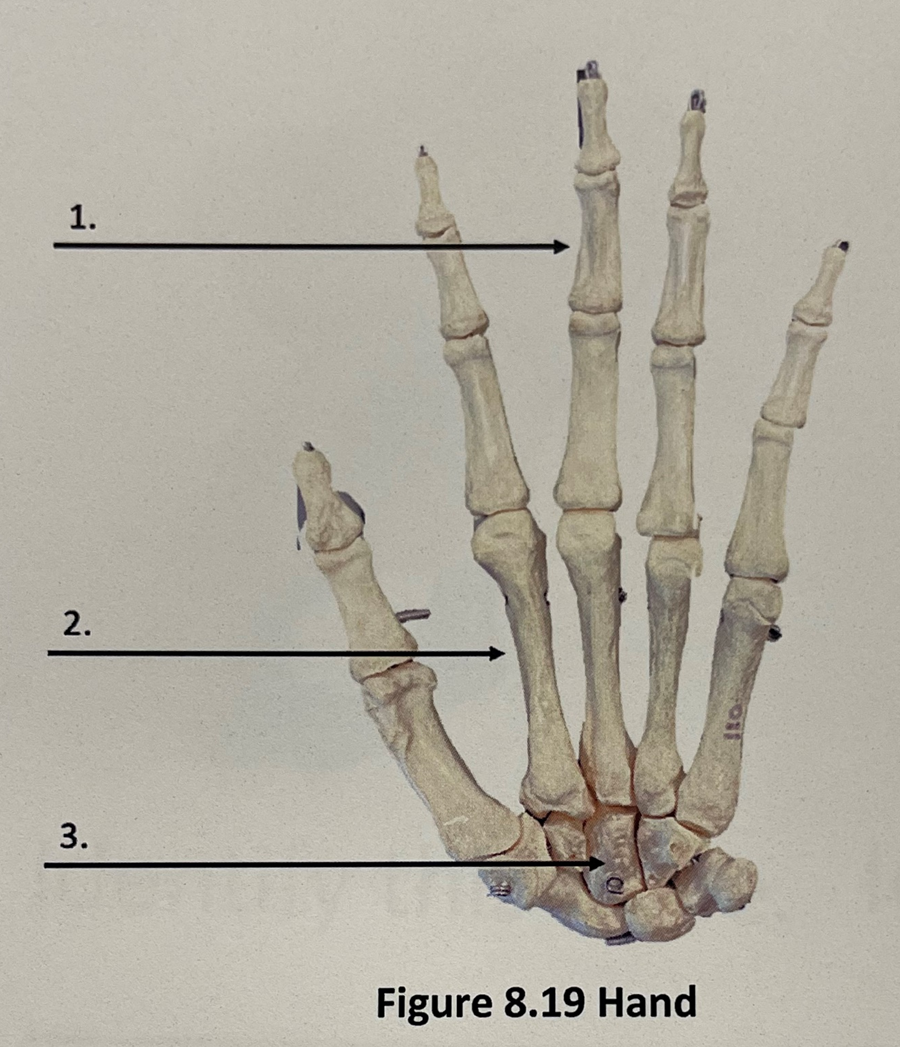
phalanges
2
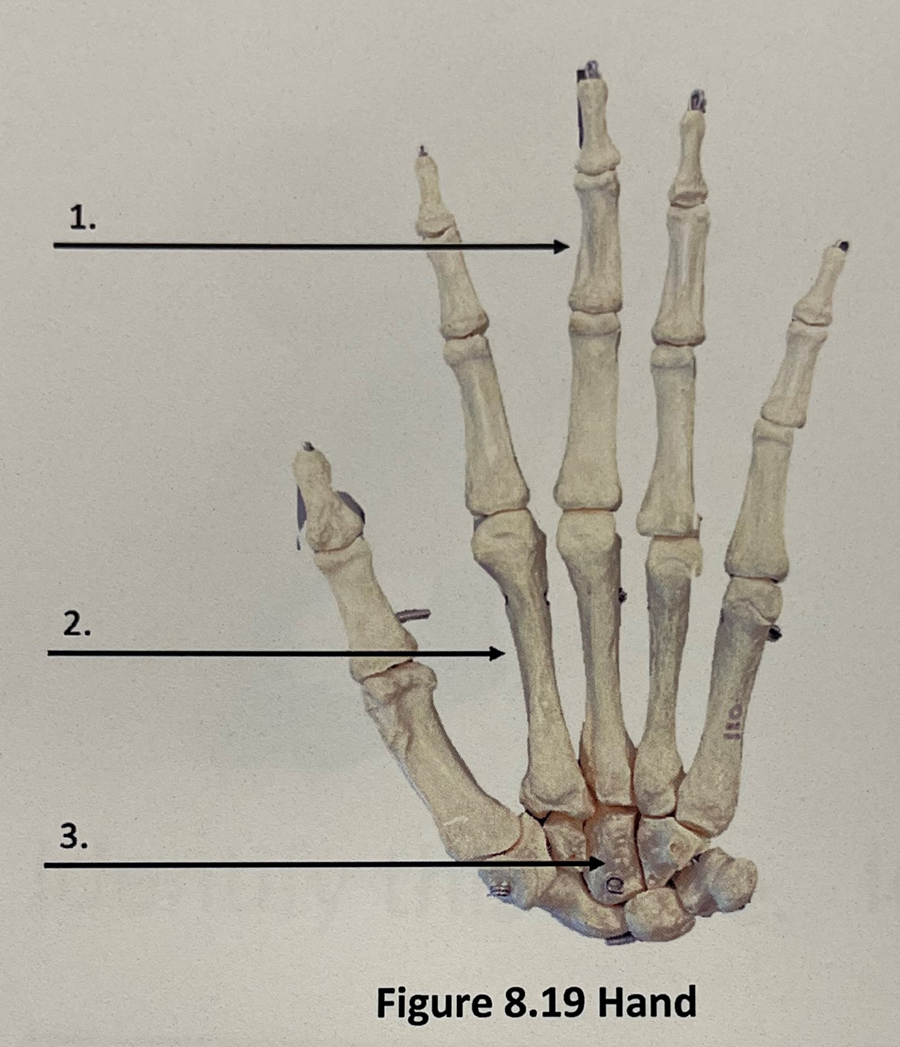
metacarpals
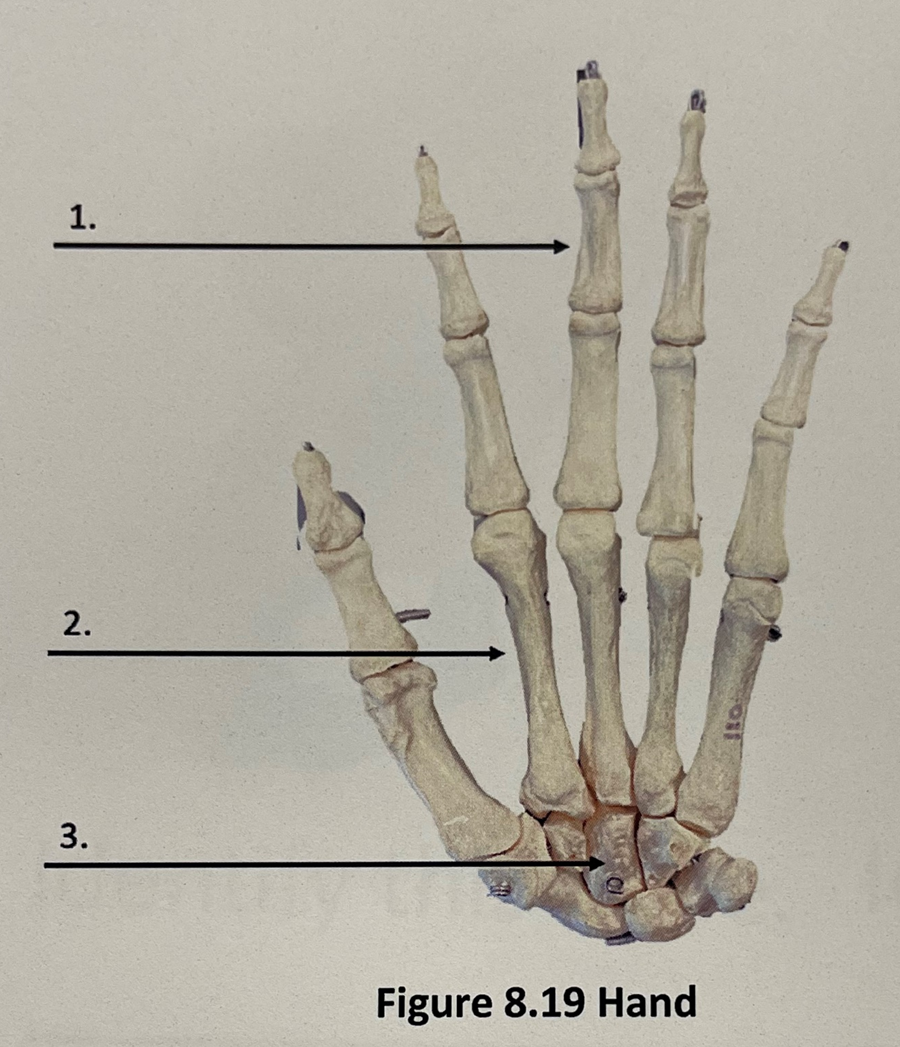
3
carpals
foot 1
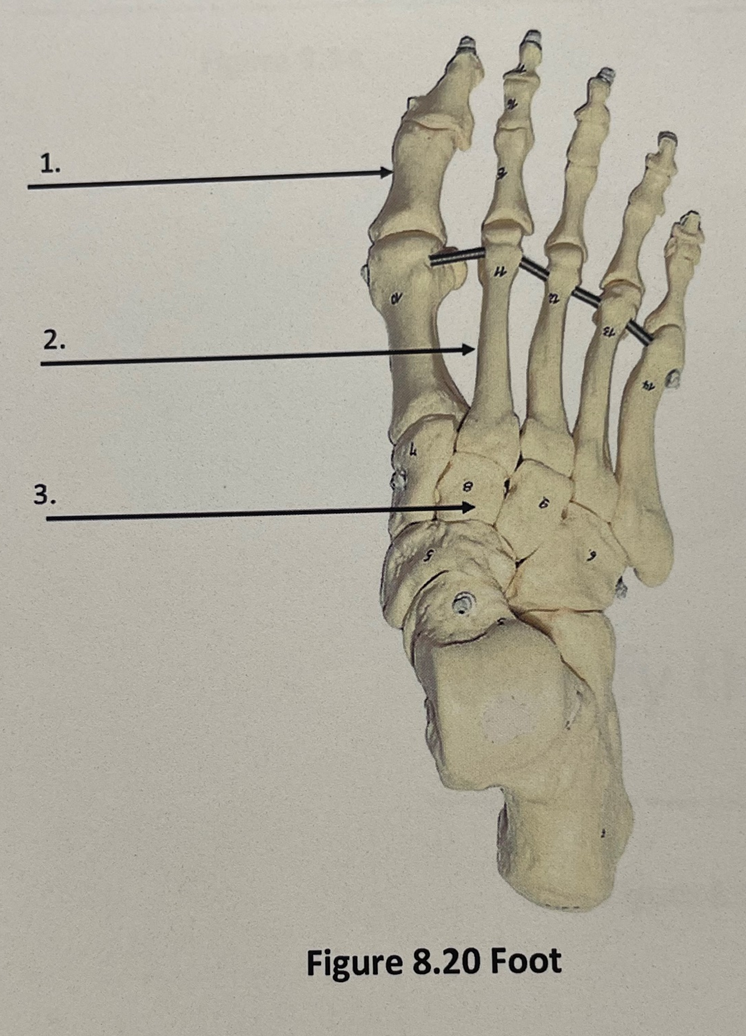
phalanges
2
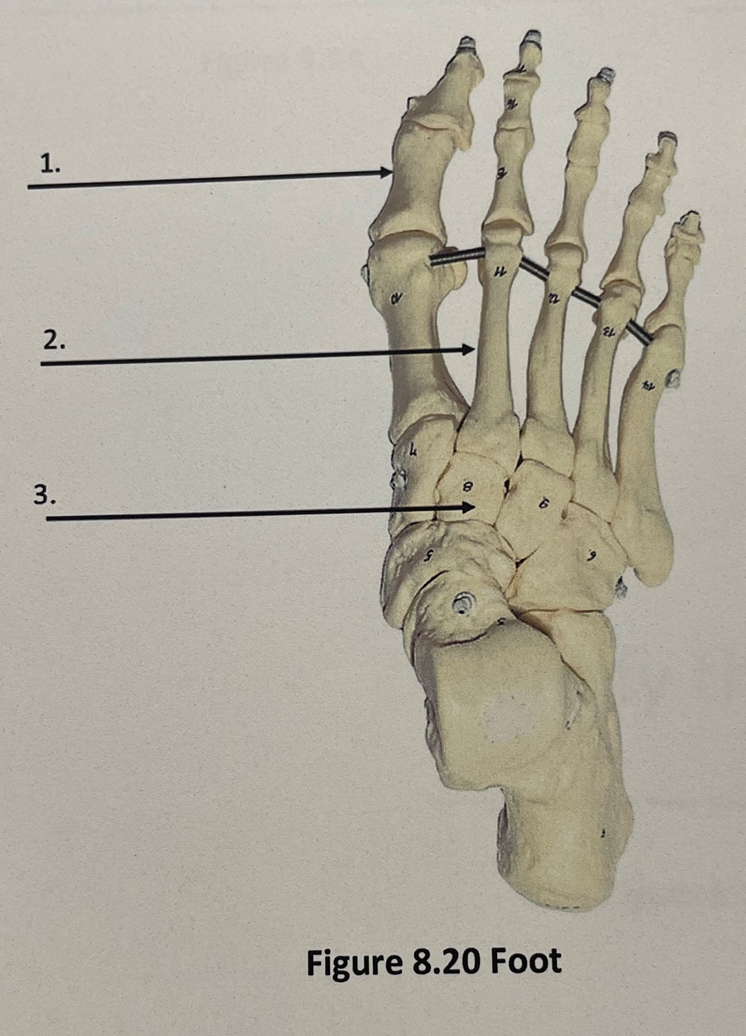
metatarsals
3
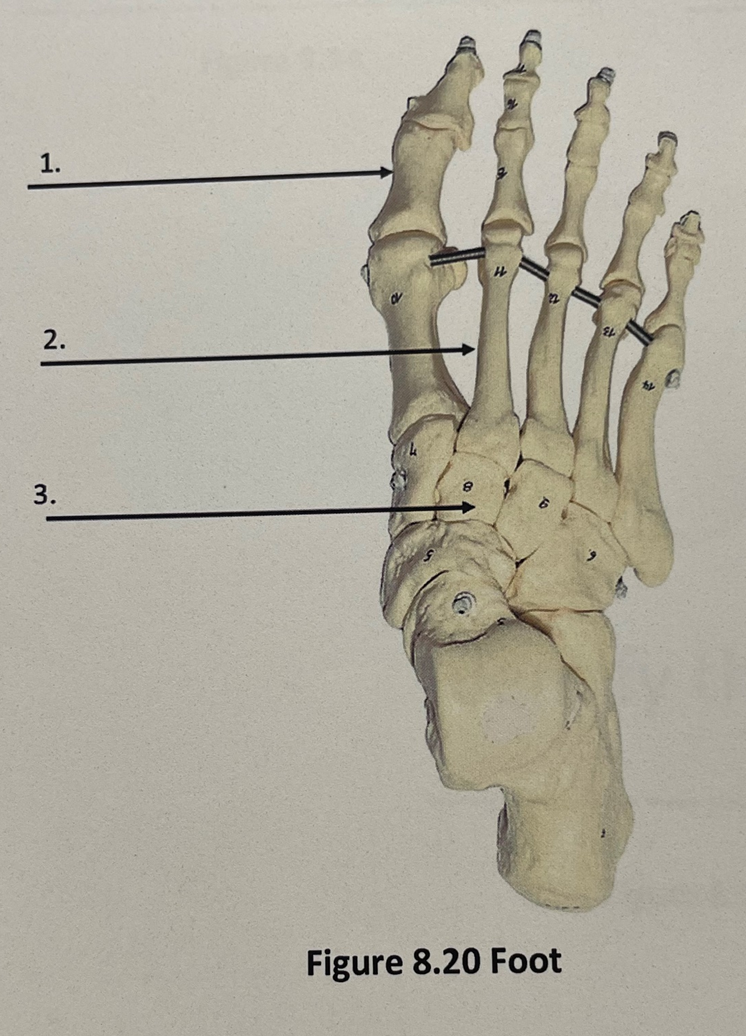
tarsals
flexion
-bending of a joint that brings bones closer together ex: bending knee
extension
straightening of the joint which makes the bone furthers apart -ex straightening of the knee
abduction
moving a limb away from the midline of the body -ex moving ur hand outward
adduction
moving a limb toward midline of the body -moving your hand inward
rotation
-bone turns around along its long axis -ex: windmill arms
supination
-bone is turned backwards -ex back of hand to palm