2.1 Carbohydrates
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Elements making carbohydrates
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Diagram of alpha glucose molecule
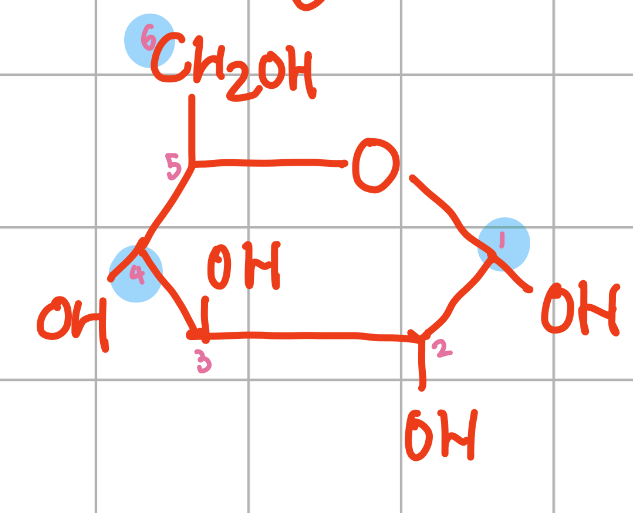
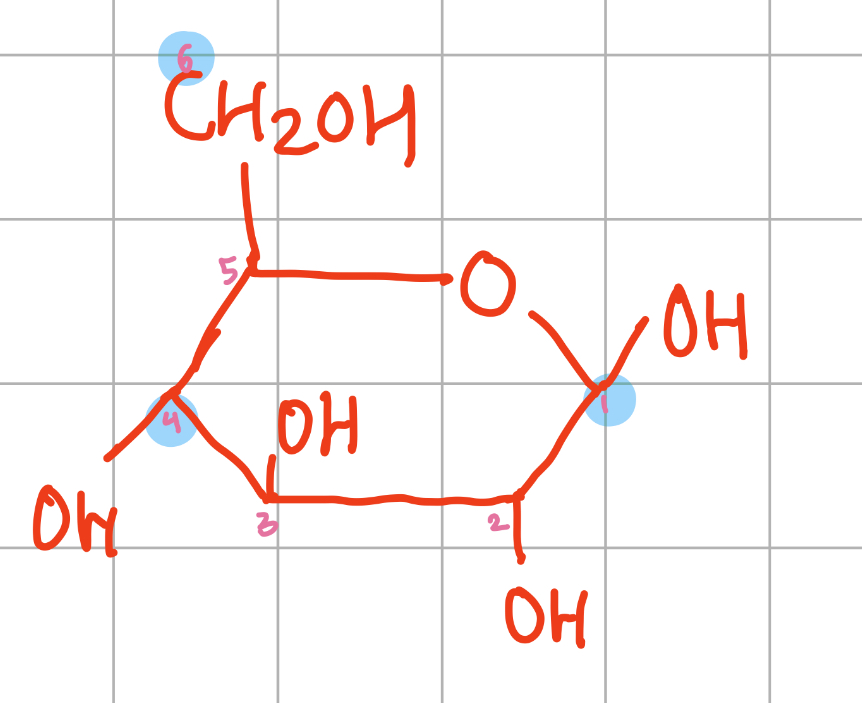
Diagram of beta glucose molecule
Monomer
One small molecule that repeats to join together to form polymers
Polymer
Large molecule made of many monomer repeating units
Macromolecule
Large, organic molecule, often polymers
Monosaccharide
One sugar (eg. Triose, Pentose)
Disaccharide
2 sugars joined together
Polysaccharide
Many sugars (monosaccharides) joined together
Role of covalent bonds in making polymers
Forms strong, primary connections that link monomers into long polymer chains
Reducing sugars examples
Glucose, fructose, galactose
Non reducing sugars example
Sucrose
How are glycosidic bonds formed?
Condensation reaction giving off water as a byproduct
Byproduct of condensation reaction
Water
Opposite of condensation reaction
Hydrolysis reaction
Hydrolysis reaction definition
Breaking chemical bond using a water molecule
Alpha glucose + alpha glucose
Maltose
Non reducing sugar test and hydrolysis
Benedict’s reagent detects reducing sugars only
If no color change: boil sample with dilute acid to hydrolyse the sucrose
Cool and neutralize with alkali
Then repeat Benedict’s test
Amylose
Type of starch
An a-glucose polymer with a-1,4 bonds only
Unbranched chain coils into a helix → compact, good for storage
Insoluble → little osmotic effect
Structures of amylopectin
has a-1,4 glycosydic bond backbones with a-1,6 branch points
Branched structure gives many ends for enzyme action
Allows for faster hydrolysis than amylose
Structures of glycogen
Similar to amylopectin but even more highly branched (MANY a-1,6 glycosydic bonds)
Very compact and insoluble
Many ends → extremely rapid glucose release
Animal storage polysaccharide
Structures of cellulose
B glucose polymer with B-1,4 glycosidic bonds only
Alternate monomers inverted
Straight chains linked by many hydrogen bonds → microfibrils
Bundles of microfibrils form fibers with high tensile strength
Molecular structure of cellulose
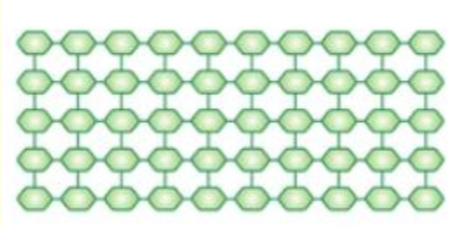
How is cellulose adapted to be responsible for cell wall?
cellulose microfibrils cross-linked in a matrix → allowing for rigidity and support
Resists stretching and prevents cell bursting under turgor pressure
Freely permeable to water and solutes, allowing growth via microfibril orientation
Glucose + fructose
Sucrose
Glucose + galactose
Lactose
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
1,4 glycosidic bonds create long straight chains (unbranched)
1,6 glycosidic bonds create branches