Transposition of the Great Arteries
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is transposition?
presence of incorrect connections between the atria and ventricles and or the great arteries (PA or Aorta)
Variants:
D-TGA
CC-TGA/L-TGA
D TGA (Dectro Position)
Is a cyanotic heart defect
Characteristics of D-TGA
conotruncal septum grows straight down vs spiral
AO is anterior and right sided
PA is posterior and left sided
Atrioventricular concordance
Ventriculoarterial discordance
Systemic and pulmonary circulation runs in parallel
Cyanotic heart defect, required an ASD/PFO and/or PDA for survival
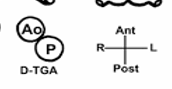
What is this diagram showing?
D-TGA:
AO is ANTERIOR and to the RIGHT of PA
PA is POSTERIOR and to the LEFT of AO
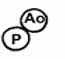
What is this diagram showing?
L TGA
AO is ANTERIOR and to the LEFT of PA
PA is POSTERIOR and to the RIGHT of AO

What is this diagram showing?
Normal orientation:
AO is POSTERIOR and to the RIGHT
PA is ANTERIOR and to the LEFT
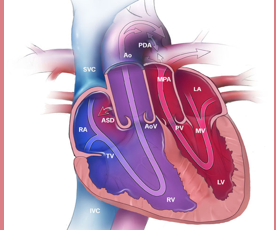
What is this an image of?
D-TGA
Clinical presentation of D-TGA
cyanosis
SOB
Weak pulse
Lack of Appetite
Poor weight gain (failure to thrive)
Diagnosed and treated shortly after birth
Associated with other defects:
VSD
Ao Arch Abnormalities
LVOTO
MV/TV abnormalities
PS
Coronary artery abnormalities
What is the APGAR score?
A = Appearance
P = Pulse
G = Grimace (reflexes)
A = Activity (muscle tone)
R = Respiration
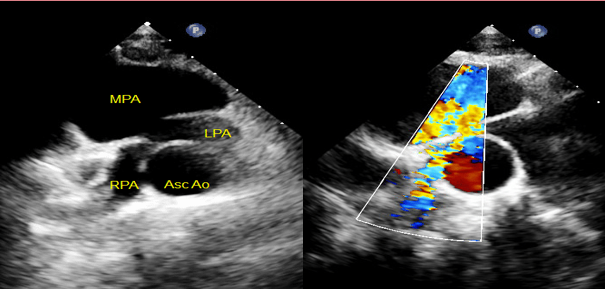
Pre-op Echo Findings of D-TGA
PLAX visualization of side-by-side/parallel course of AO & PA
AO will be anterior to PA
PSAX visualization of both semilunar valves in short axis with AO anterior
Establish patency of PDA, ASD/PFO or presence of VSD
Verify coronary anatomy (important for one of the repair options
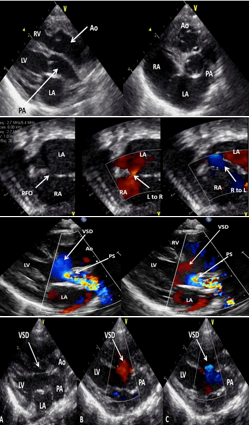
What are these images of?
D-TGA
Atrial Switch
surgical intervention for D-TGA
first successful repair option (Pre 1980)
replacement of a baffle (conduit) into the atria
Systemic venous return (deoxygenated) is baffled to the LV so it can exit to the lungs
Pulmonary return (oxygenated) is baffled to the RV so it can exit to systemic circulation
Variants:
Mustard: uses patient’s OWN tissue to create a baffle
Senning: uses a SYNTHETIC baffle
Common complications of Atrial Switch D-TGA
Baffle leaks
Obstructions
RV failure
Significant TR
Arterial Switch
currently the method of choice for D-TGA correction
Called the Jatene procedure
Dissection of AO & PA above their roots and detachment of coronaries
Great arteries are switched:
AO connects to the original PA root with implantation of the coronaries
PA connects to the original AO root - LeCompte Manuever: PA and branches may be moved to anterior position
More “normal” configuration is achieved
Complications of Arterial Switch D-TGA
Narrowing of the anastomosis sites
Narrowing PA branches (LeCompte)
Supravalvular PS
Rastelli Procedure D-TGA
Performed when there is D-TGA, a large VSD & significant PS
Patches the VSD to baffle blood flow from the LV across to the AO
Inserts a RV à PA valved conduit
Procedure also performed on other CHD:
Truncus Arteriosus
Pulmonary Atresia & VSD
Double Outlet RV with PS
Common complications of Rastelli D-TGA
conduit degeneration
stenosis/regurgitation of conduit valve
LVOTO
What does CC-TGA stand for?
Congenitally Corrected TGA
What is CC-TGA AKA?
L-TGA Levocardia TGA
Characteristics of CC-TGA (levo TGA)
outer curve of the bulboventricular loop points to the LEFT side which causes ventricular inversion
Atrioventricular discordance, ventriculoarterial discordance
Systemic and pulmonary circulation runs in parallel vs crossed over
Anatomy is incorrect but circulation is technically “correct” and so named congenitally corrected
In isolation, it is not a cyanotic syndrome: Quite rare and often has “friends” in 90% of cases
Clinical Presentation of CC-TGA
possible to be mostly asymptomatic until adolescence/adulthood
Fatigue
Chest pain
SOV
Diagnosed in childhood in patients with additional CHD
Associated with other defects like VSD (more common perimembranous), PS, TV abnormalities (Ebstein-like), arrythmias, dextrocardia or mesocardiac, coarctation of the aorta
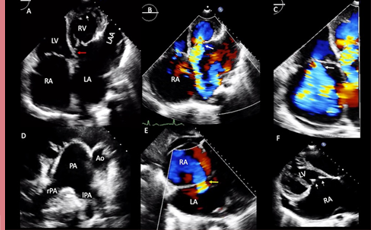
What are these images of?
CC-TGA
Pre op findings of CC-TGA
Septal insertion of left sided AV valve is more apically displaced than right sided valve in AP4
Notation of coarse trabeculation and moderator band in left sided ventricle (RV)
On axis PLAX not possible due to transposed and parallel great arteries
Usually has “friends” so look out for VSD, Pulmonary outflow tract obstruction, Ebstein’s anomaly, and conduction defects
RV dilation and systolic failure
Potential for large amount of TR
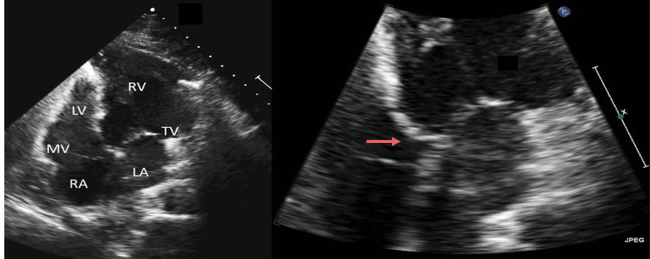
What are these images of?
CC-TGA
LV and RV swapped
TV and MV swapped
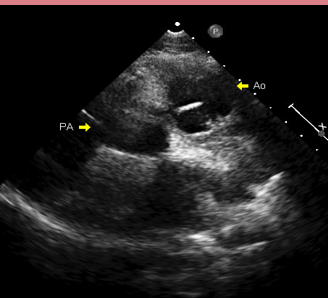
What is this an image of?
CC-TGA:
AO is ANTERIOR and to the LEFT of PA

What is this an image of?
CC TGA Fetal ECHO
Double Switch
Surgical intervention for CC TGA
Atrial switch AND Arterial switch
Systemic venous blood > RV/PA
Pulmonary venous blood > LV/AO
Coronaries reimplanted into “neo” AO
More “normal” configuration is achieved
In cases of CC-TGA + VSD + significant PS, Rastelli & Atrial Switch procedure may be performed
Common complications:
Baffle leaks
Obstructions
RV failure
Significant TR
Narrowing of anastomosis sites
Narrowing of PA branches (LeCompte)
Supravalvular PS