6.5 - ATP-PC system
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Why does the body use anaerobic energy systems during very high intensity activity
Because there isn’t enough time to use oxygen for ATP production, so the body uses anaerobic systems to produce ATP quickly without oxygen
What is the main downside of using anaerobic energy systems for ATP production
They produce ATP quickly but have a limited capacity and can’t sustain ATP production for long durations
what does the anaerobic glycolysis system not depend on
oxygen being transported to working muscles
what fuel does the anaerobic glycolysis system use
glucose/glycogen
what rate of energy production does the anaerobic glycolysis system use
fast
what yield of ATP does the anaerobic glycolysis system use
small
What fuel does the ATP-PC system use
Phosphocreatine (PC)
What is the rate and yield of ATP in the ATP-PC system
Very fast rate, explosive/instantaneous - fast and simple chemical reactions
very small yield (0.7 ATP per PC molecule)
How long does the ATP-PC system supply energy for
Very short duration – up to 10 seconds of maximal effort continuous examples
ATP-PC system intensity of activity
very high/maximal (>95% max HR)
What types of activities rely heavily on the ATP-PC system
Short duration, high-intensity activities like sprints, kicks, throws, and jumps
What are the by-products of the ATP-PC system
inorganic phosphate (Pi)
ADP
Limitation - ATP-PC system
the amount of PC stored in muscles (after these are gone then major contribution stops until recovery can restore PC)
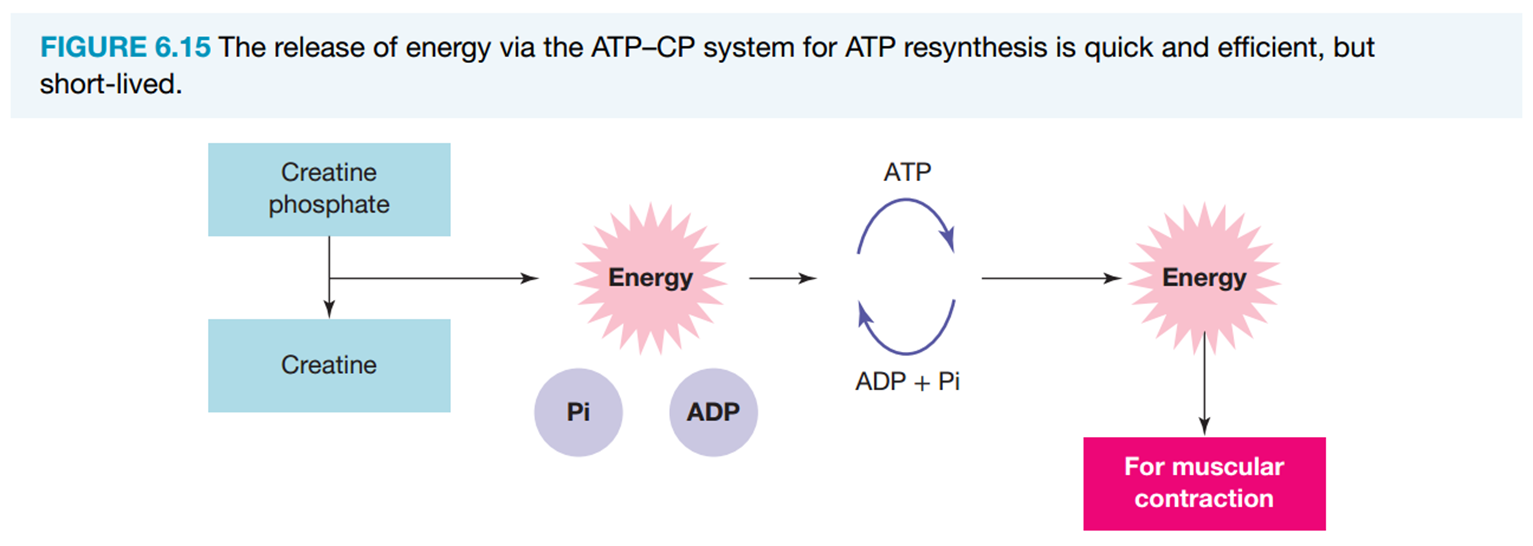
How is ATP resynthesised in the ATP-PC system
therefore…
When PC is broken down, the energy and phosphate group released resynthesise ATP from ADP and Pi
as rapidly as ATP is broken down for muscular contraction, it is continually resynthesised from ADP and Pi by the energy released by the breakdown of phosphocreatine
what is passive recovery
complete rest by standing, sitting or lying down to replenish CP at a faster rate immediately post exercise
Why is passive recovery important after using the ATP-PC system
It allows ATP and PC stores to be restored rapidly without using more PC
What happens if activity continues at a moderate or high intensity during recovery
It hinders PC restoration because PC is still being used
What condition must be met for passive recovery to be effective
The exercise must be at a very low intensity or complete rest so that PC is not required for energy
What does EPOC stand for and what does it involve
Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption – breathing rate remains elevated to supply extra oxygen for ATP resynthesis
What role does oxygen play during passive recovery
Oxygen helps resynthesise ATP, and this ATP is used to combine phosphate and creatine to restore PC in muscles
How does the body restore PC during passive recovery
Extra oxygen is used to produce ATP, which then fuels the recombination of phosphate and creatine back into PC
What happens during passive recovery in terms of ATP-PC restoration
70% restored within 30 seconds
98% restored within 3 minutes
100% restored within 10 minutes
What condition is assumed for the restoration times of ATP-PC
That total muscle depletion of PC has occurred
What happens if not all PC stores are used during activity
Less time is needed to resynthesise and restore the PC stores