Body Planes/Anatomical Terminology 1.3
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
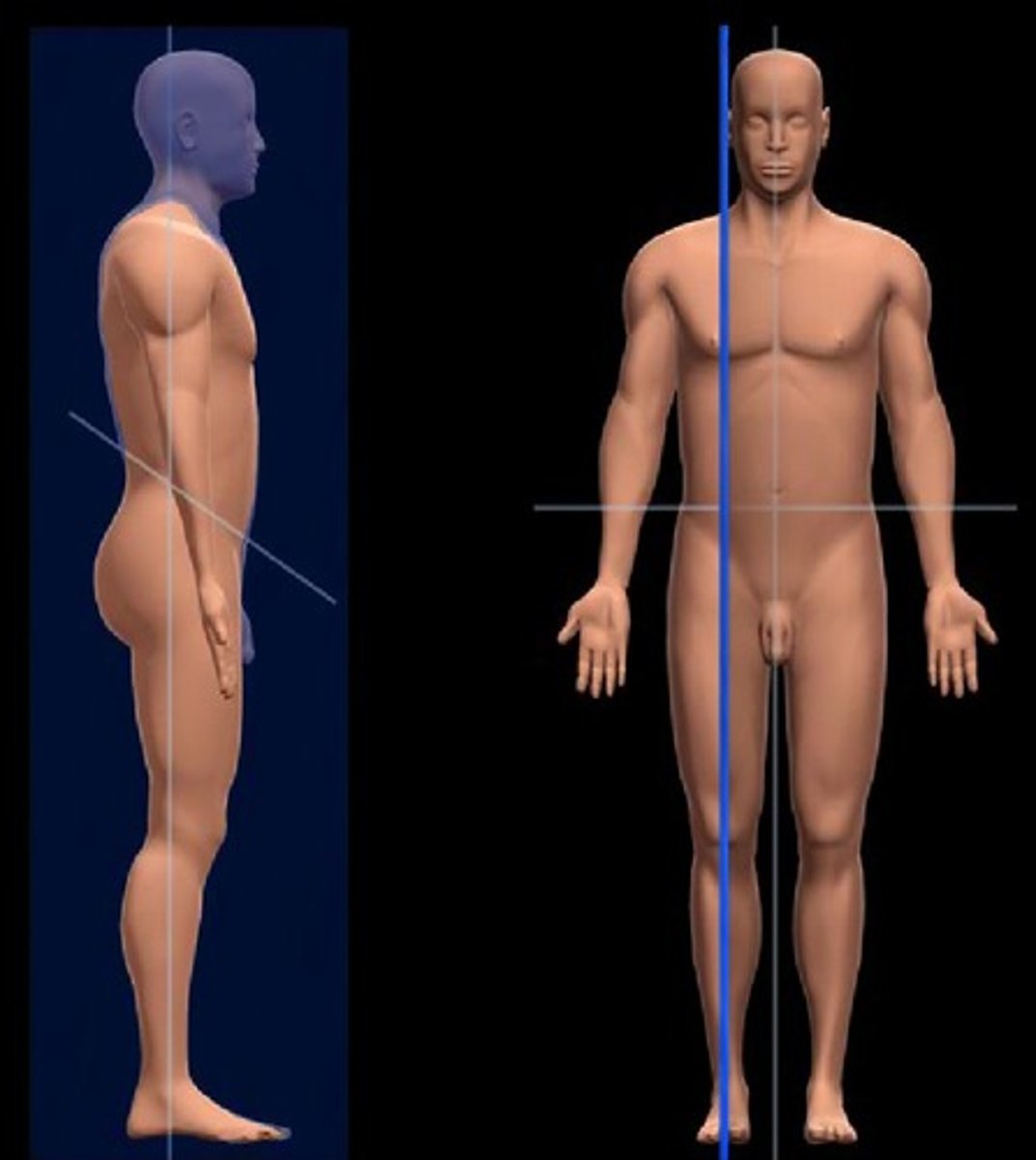
Anatomical Position
Standard reference position:
-standing erect with feet together
-face and eyes directed forward
-Skull/head - Frankfurt plane
-upper limbs at the side, palms forward
-the penis is erect
-lower limbs together, feet forward
Medial plane (midsagittal)
Longitutidal; divides body into right and left halves
Sagittal plane
-any plane parallel to median;-parallel to sagittal suture of skull
Coronal plane
-longitudinal; divides body into front and back-parallel to coronal suture-also called frontal
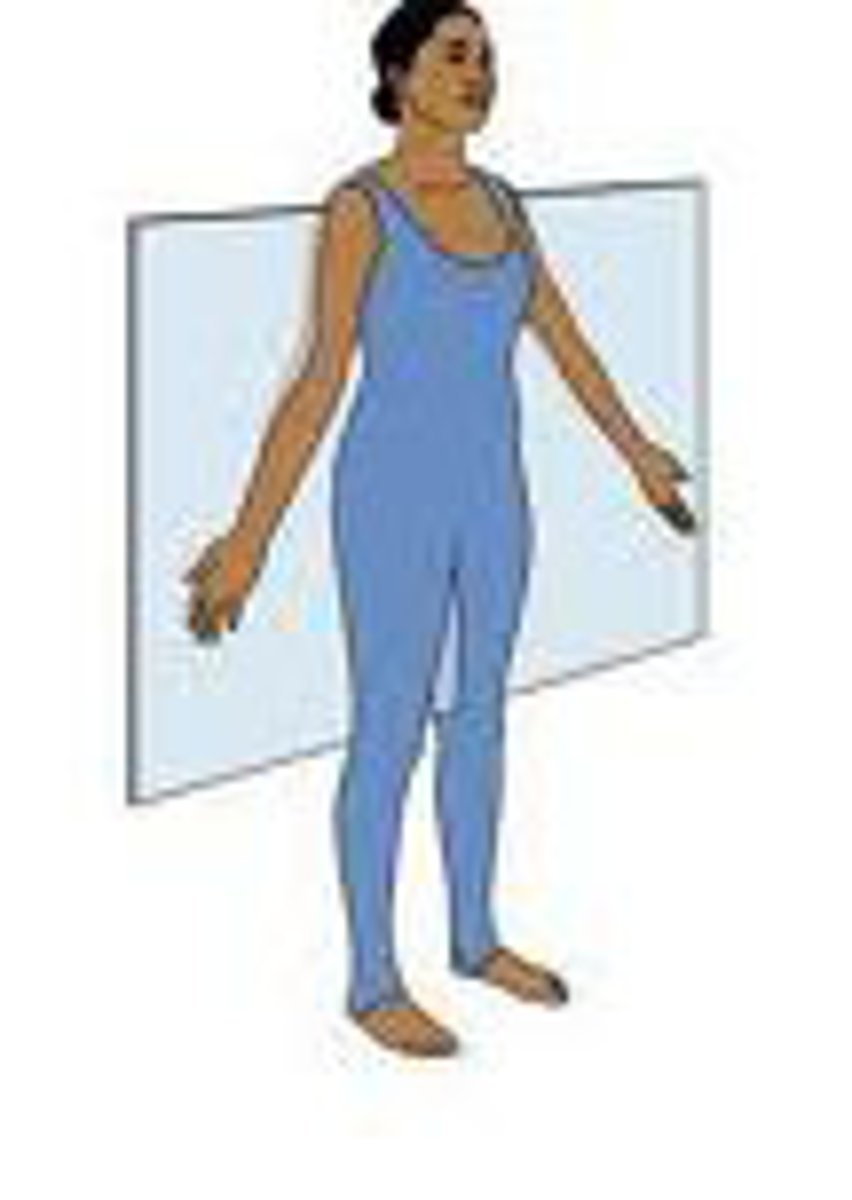

Frankfurt Plane
A horizontal plane that includes the orbitals and external acoustic meatus in anatomical position.
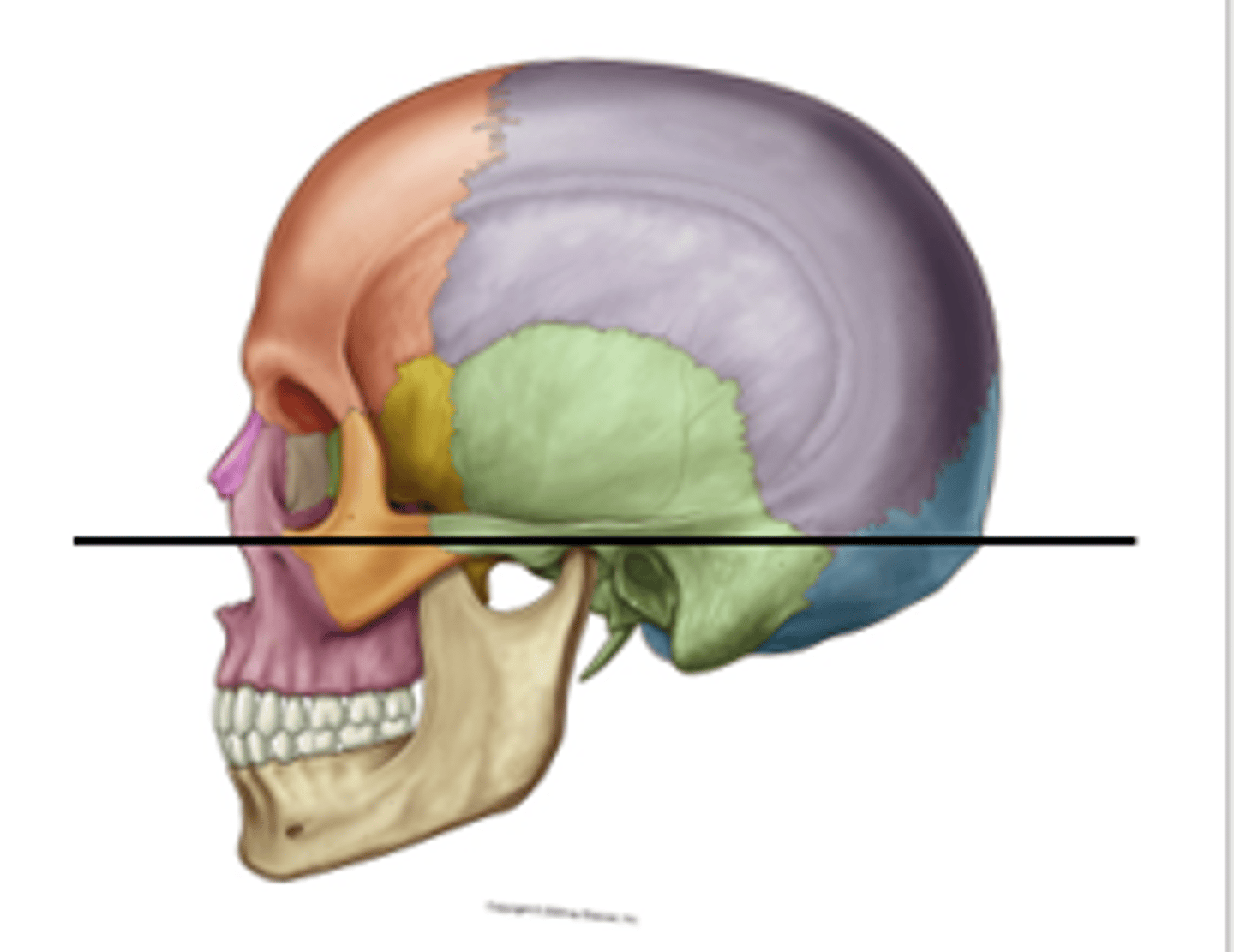
A horizontal plane that includes the orbitals and external acoustic meatus in anatomical position.
Frankfurt Plane
Transverse Plane
-divides body into top and bottom
-parallel to horizon (horizontal)
-also called transverse or transaxial
Penis
Anatomically considered erect in anatomical position.
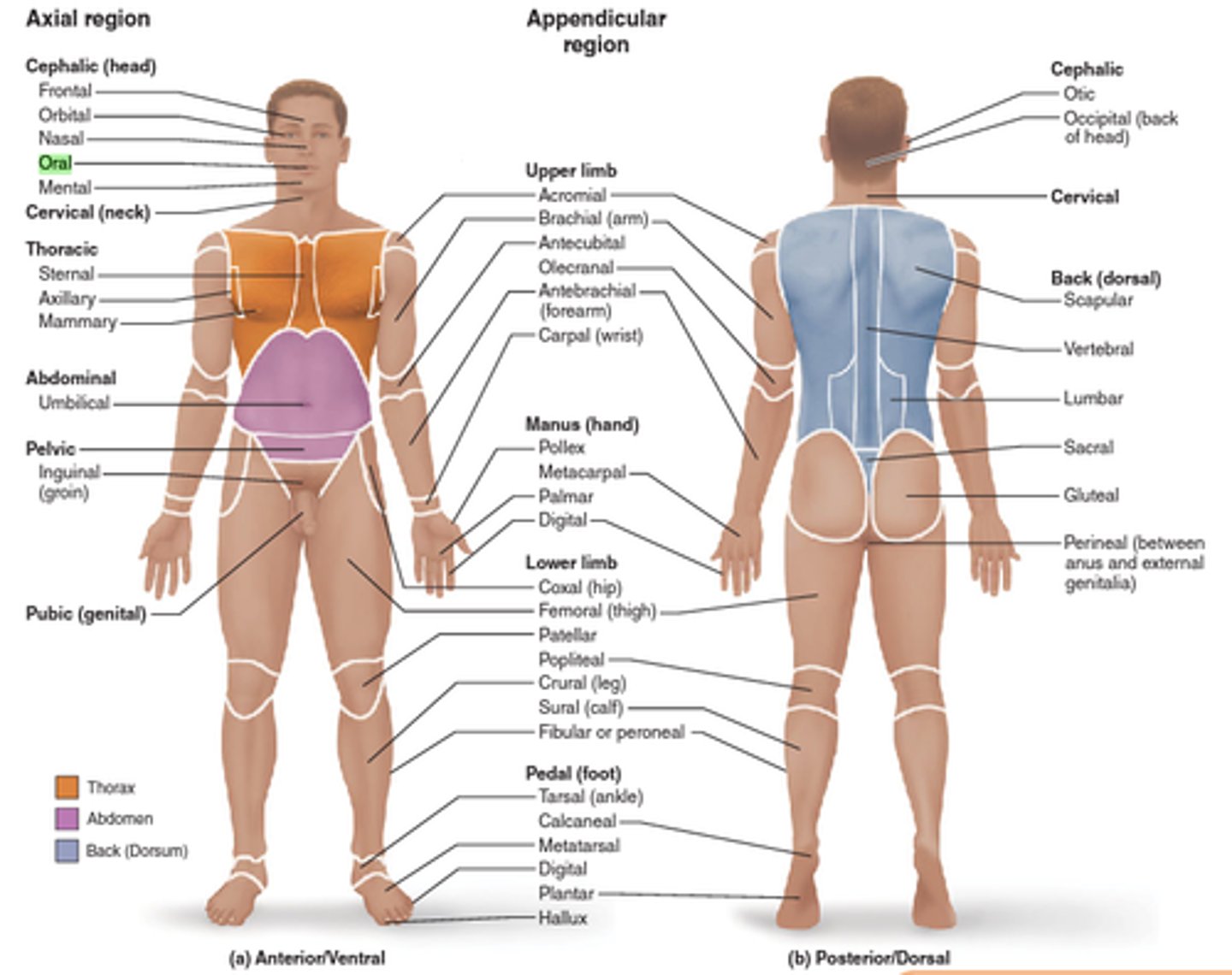
Directional and Regional Terms
Terms used to describe the location of body parts and regions.
Anterior
Refers to the front of the body.
Axial Region
The region of the body that includes the head, neck, and trunk.
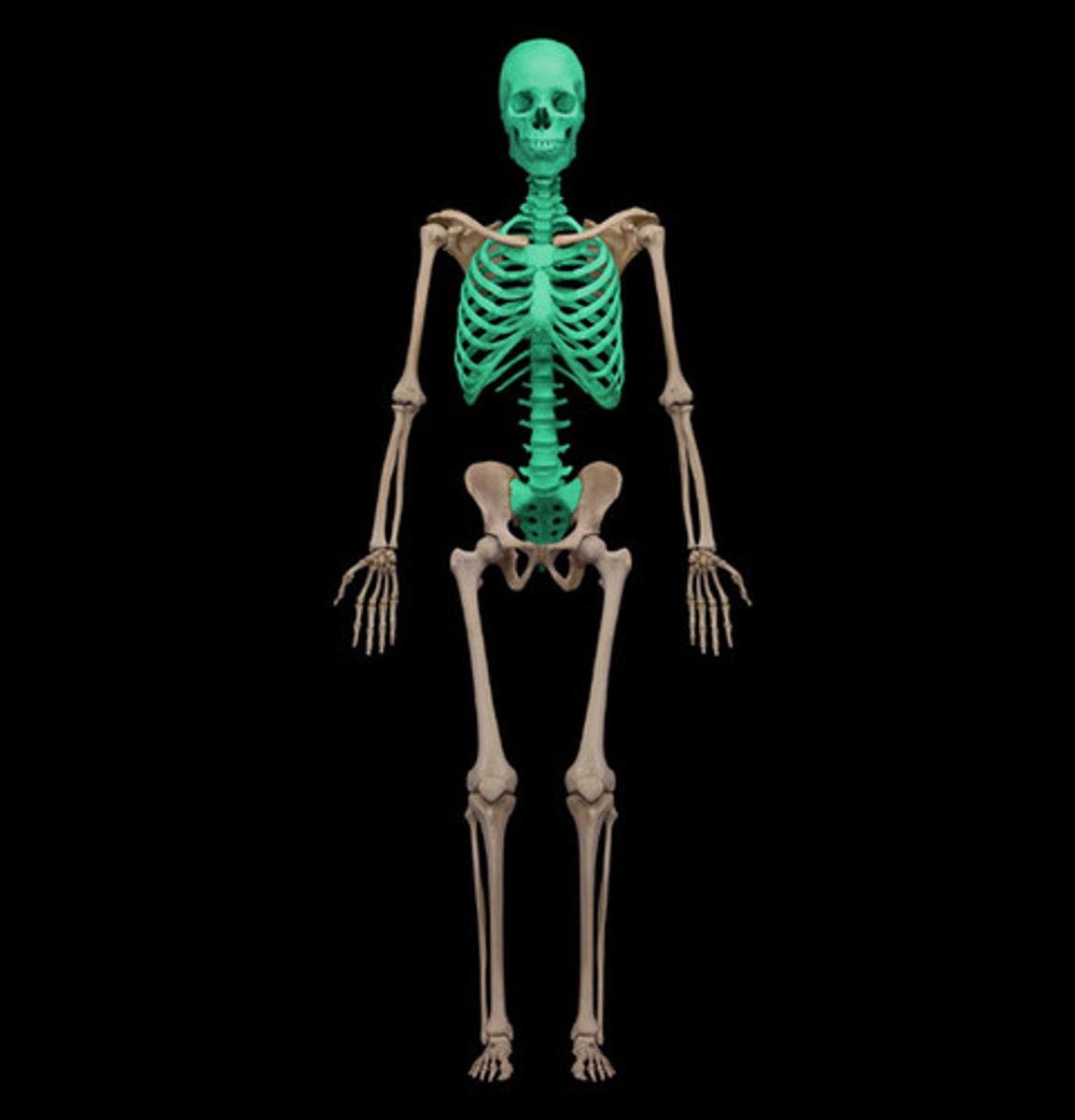
Appendicular Region
The region of the body that includes the upper and lower limbs.
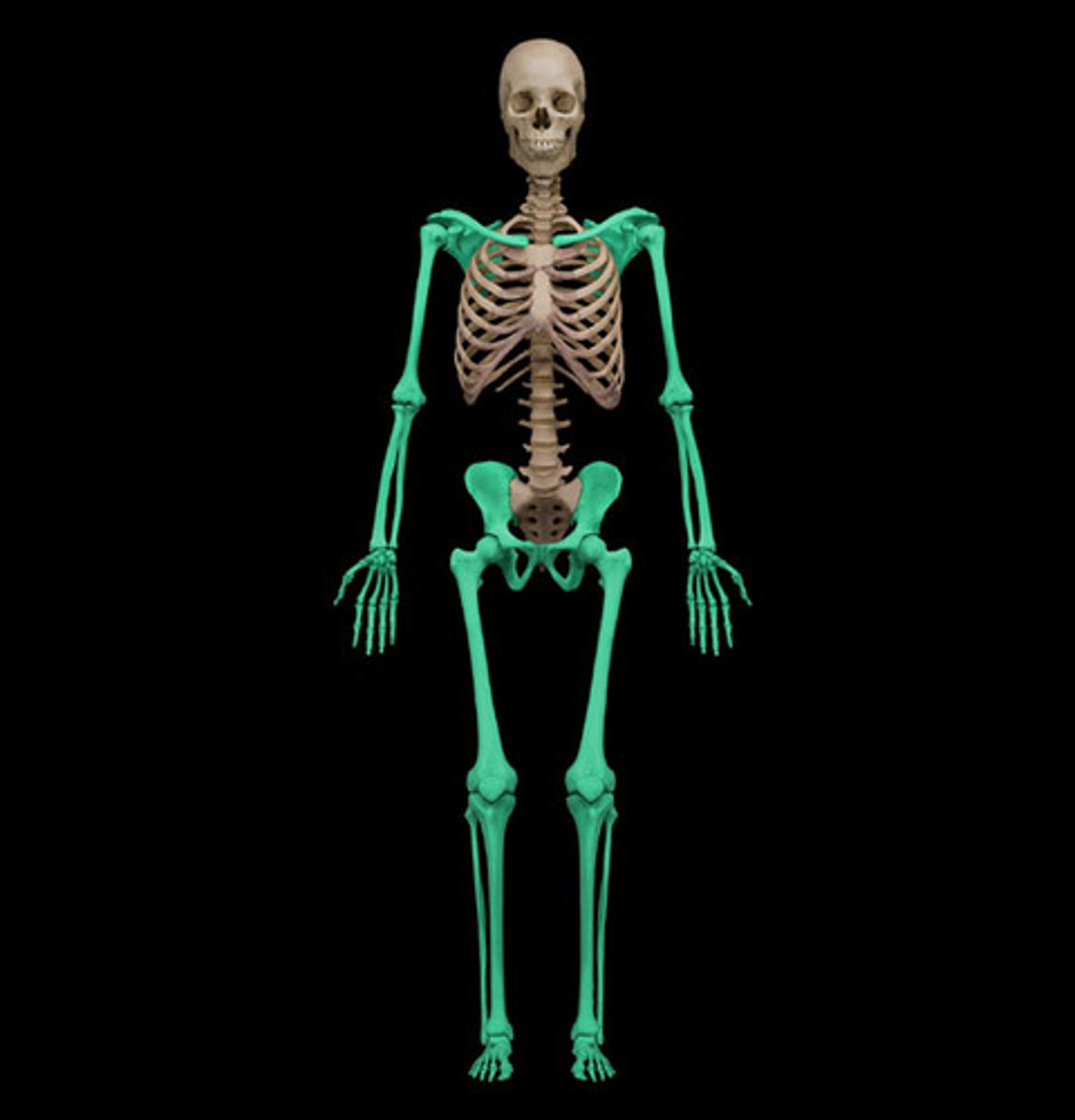
Upper Limb
Includes the arm, forearm, wrist, and hand.
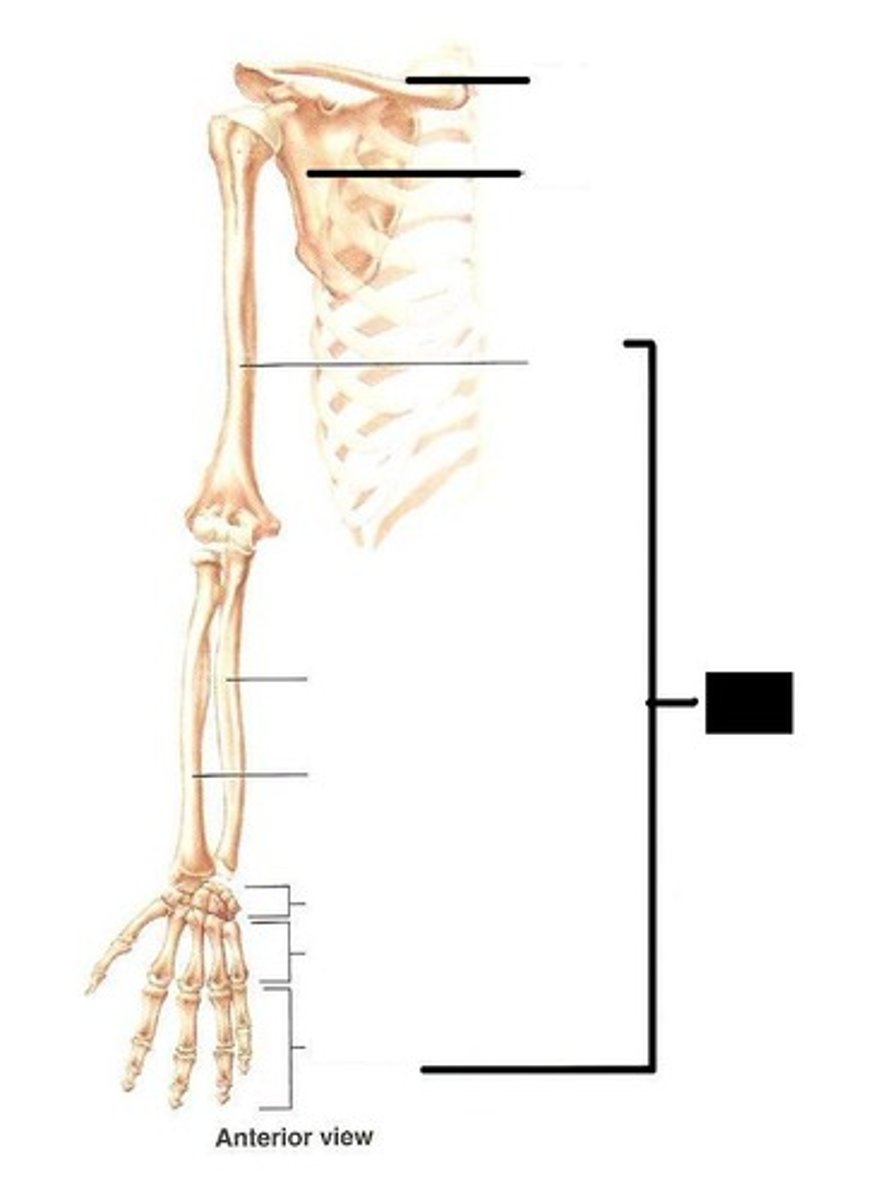
Acromial
Relating to the shoulder.
Brachial
Relating to the arm.
Antecubital
Relating to the front of the elbow.
Antebrachial
Forearm
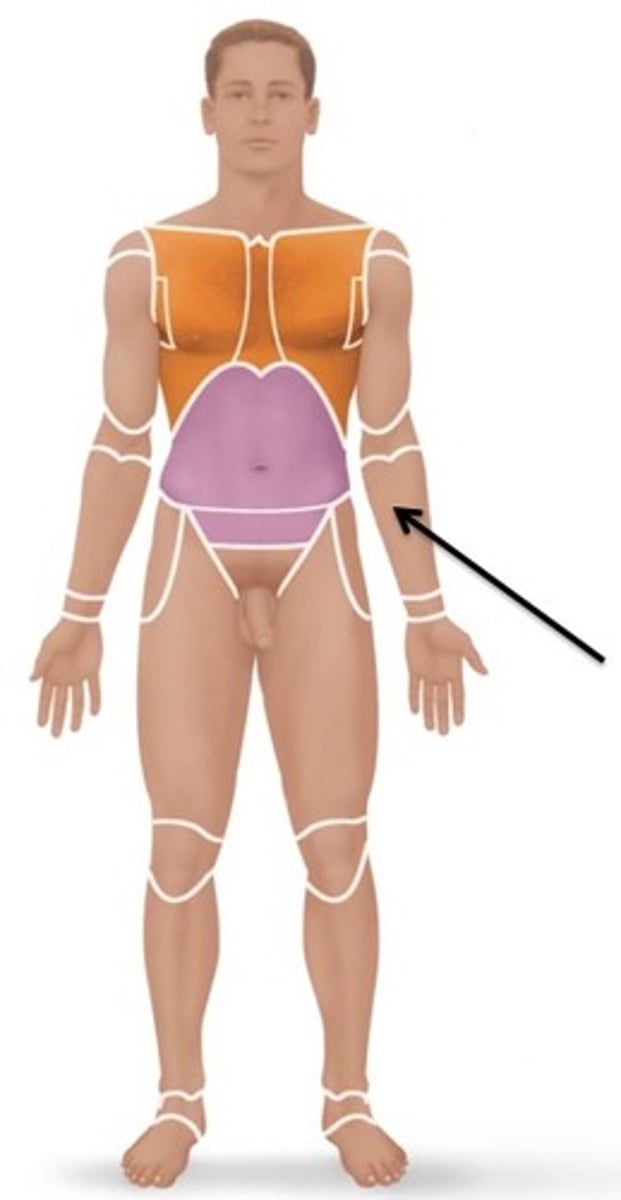
Cephalic
Relating to the head.
Frontal
Relating to the forehead.
Orbital
Relating to the eye socket.
Buccal
pertaining to the cheek
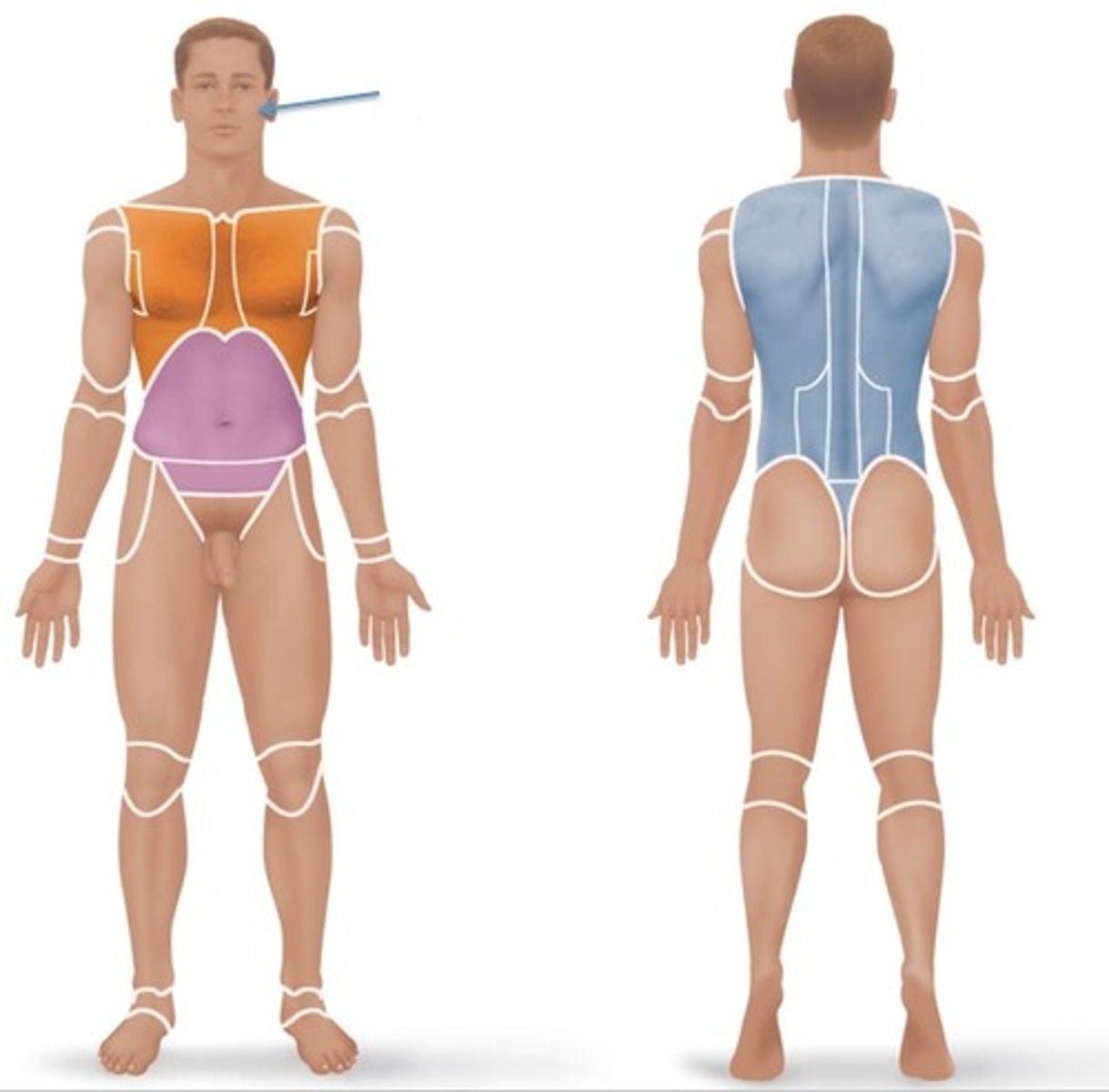
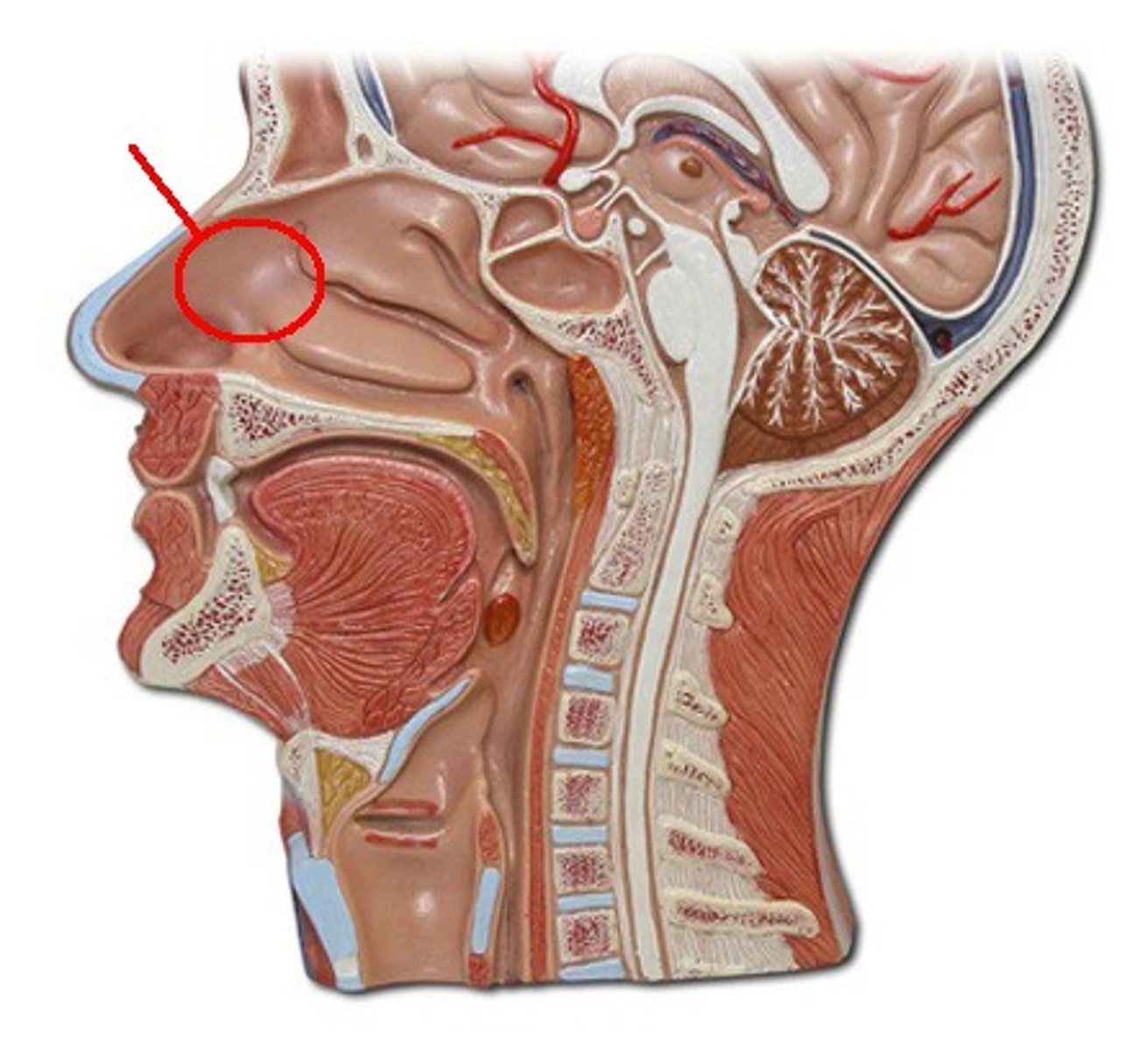
Nasal
Relating to the nose.
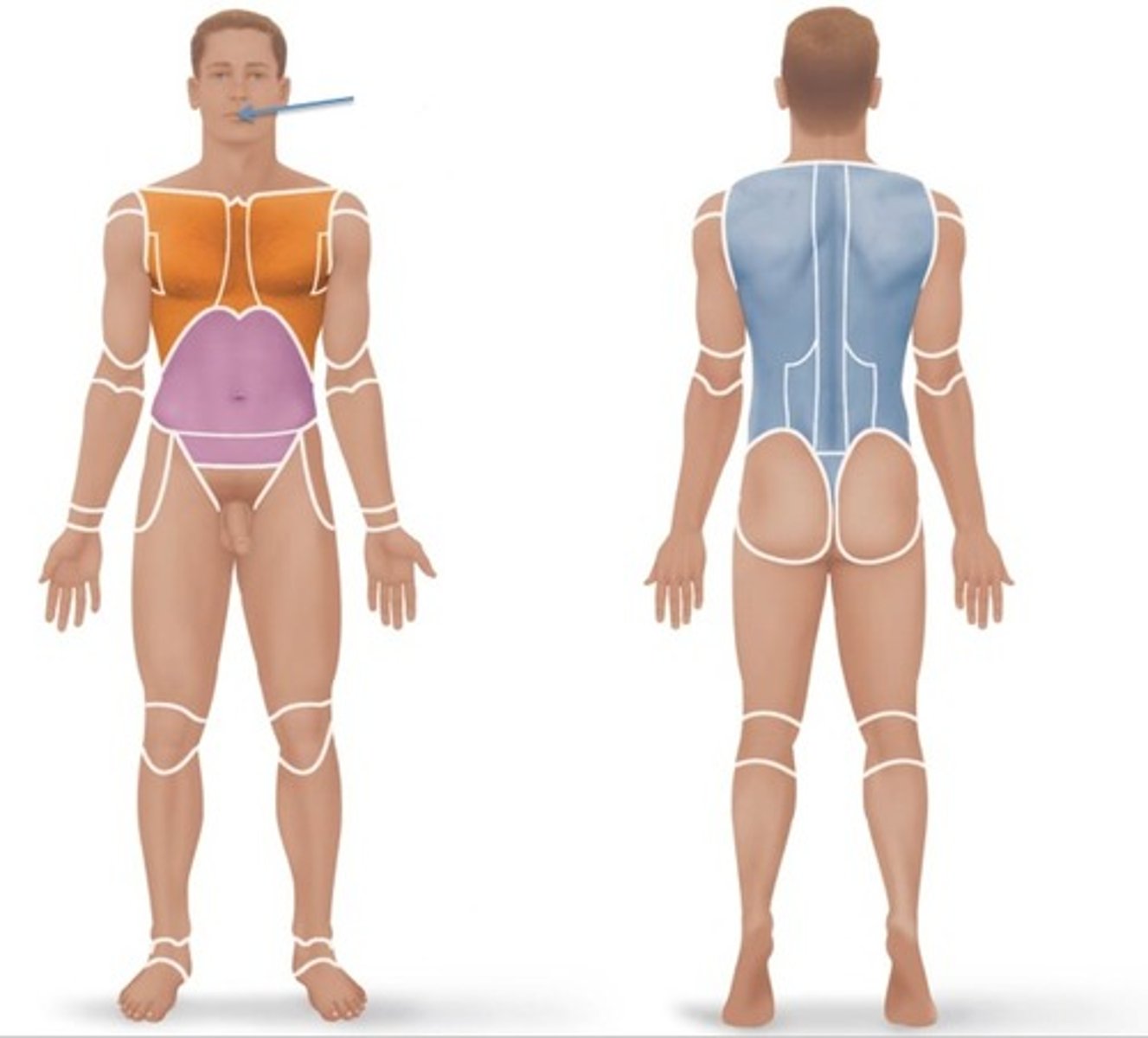
Oral
Relating to the mouth.
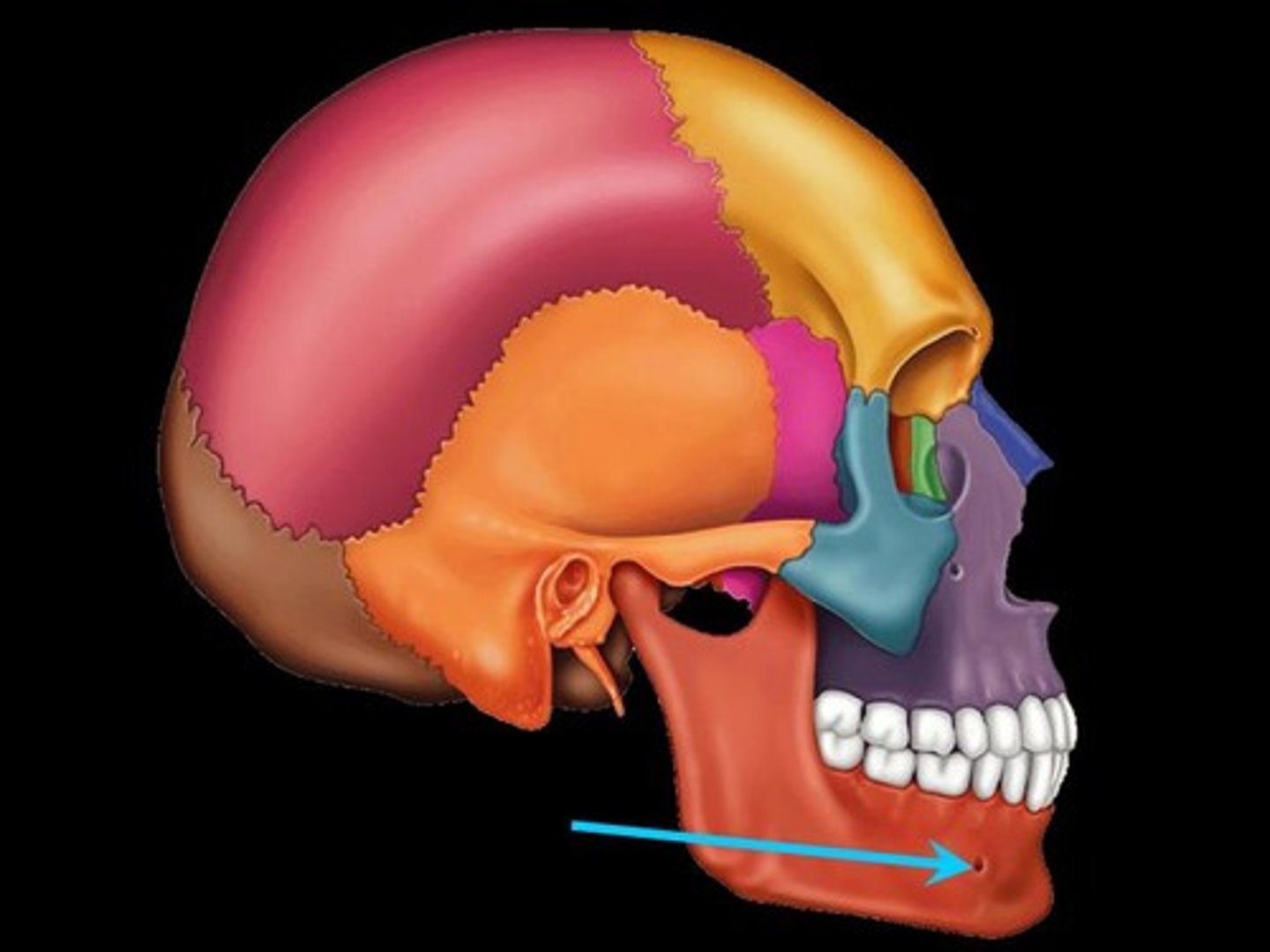
Mental
Relating to the chin.
Cervical
Relating to the neck.
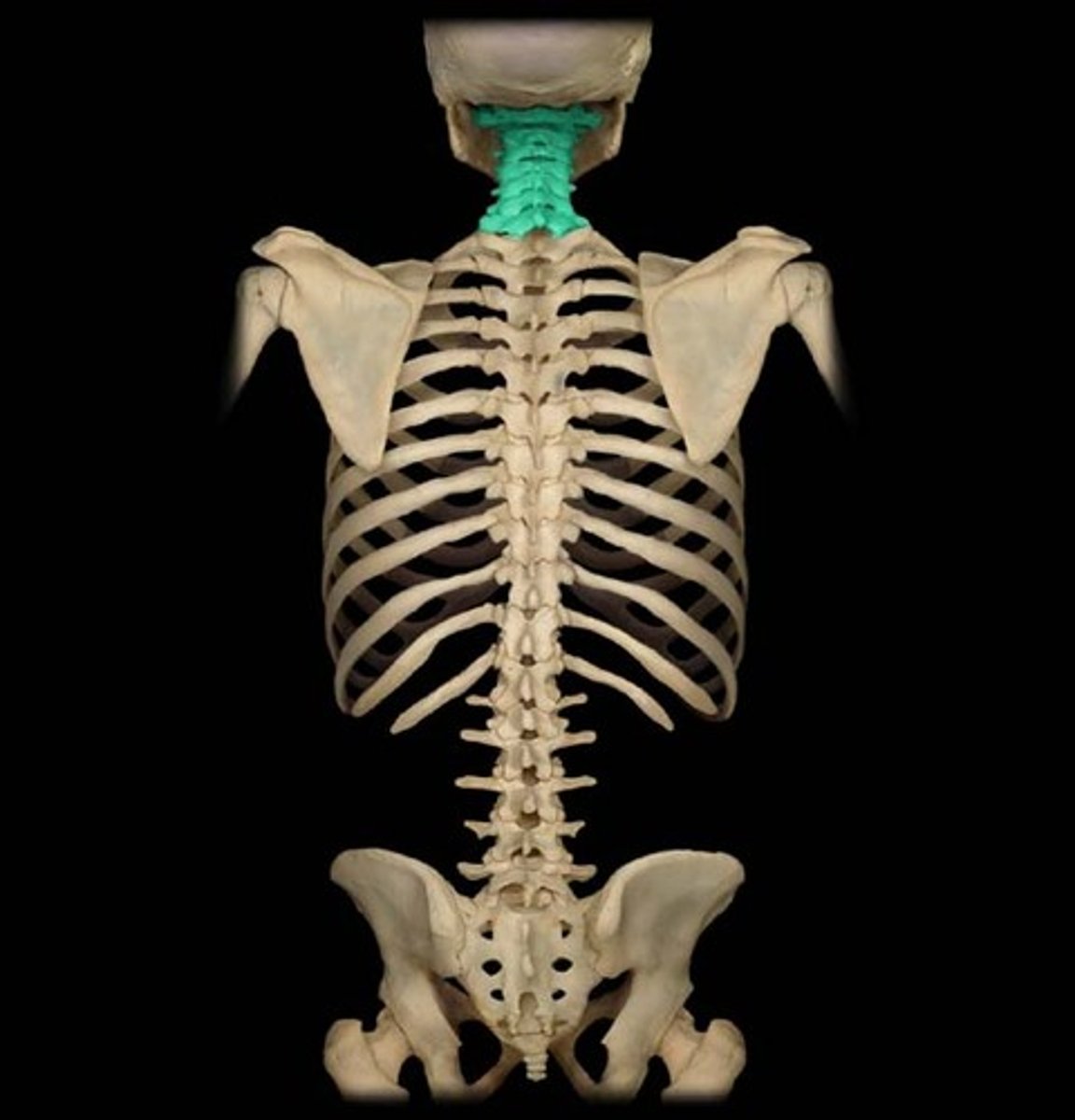
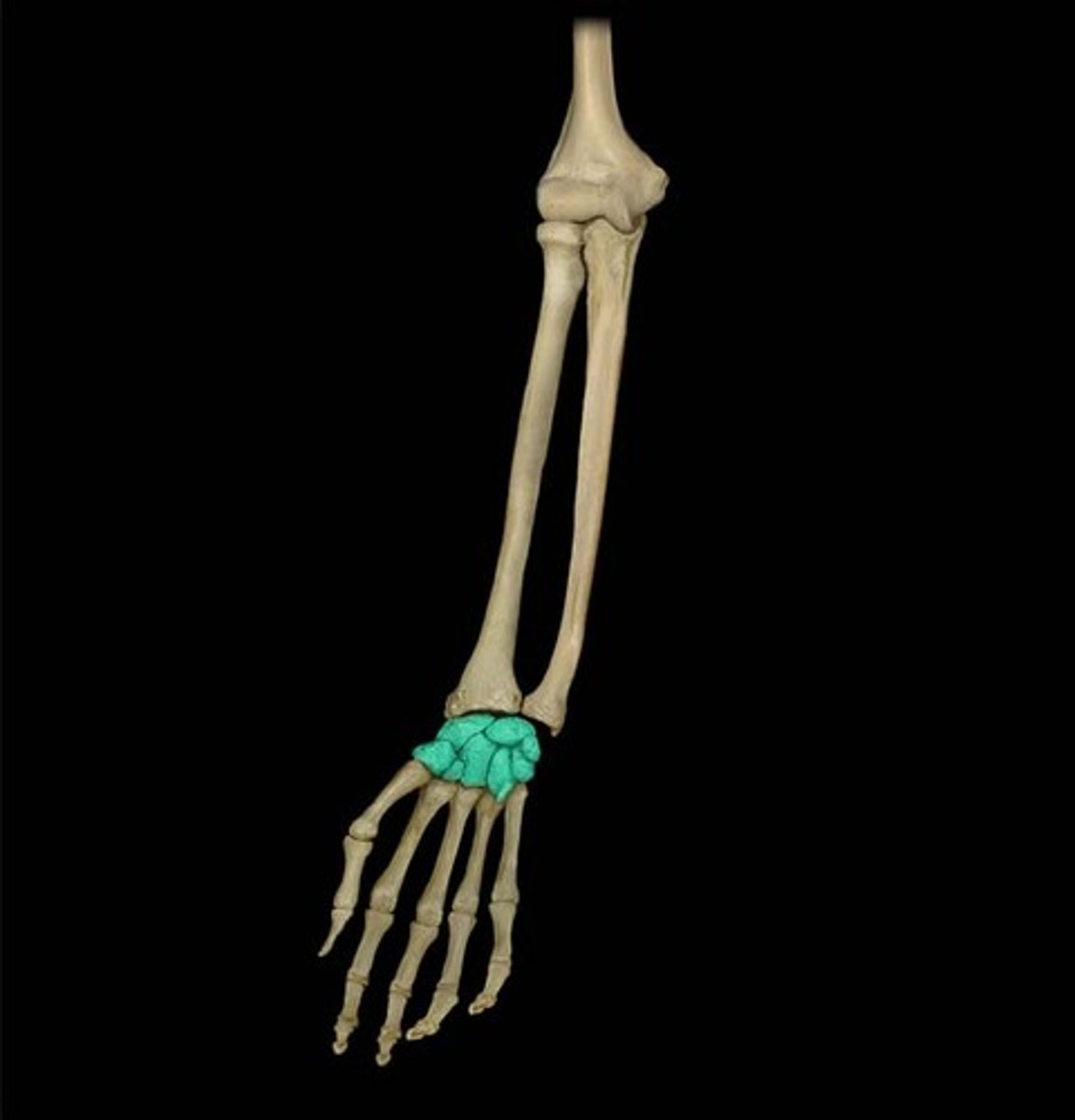
Carpal
Relating to the wrist.
Thoracic
Relating to the chest.
Axillary
Relating to the armpit.
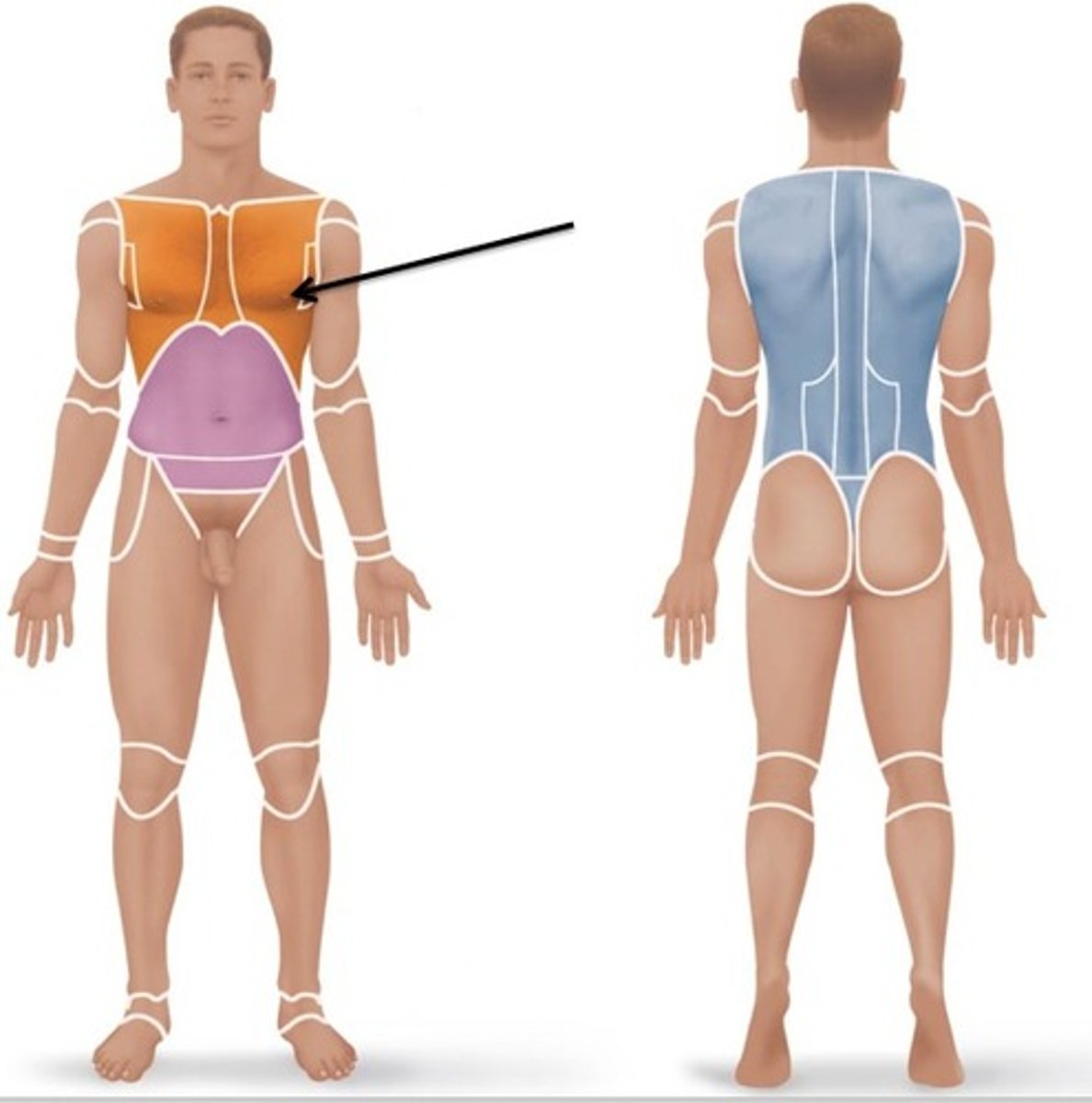
Sternal
Relating to the sternum.
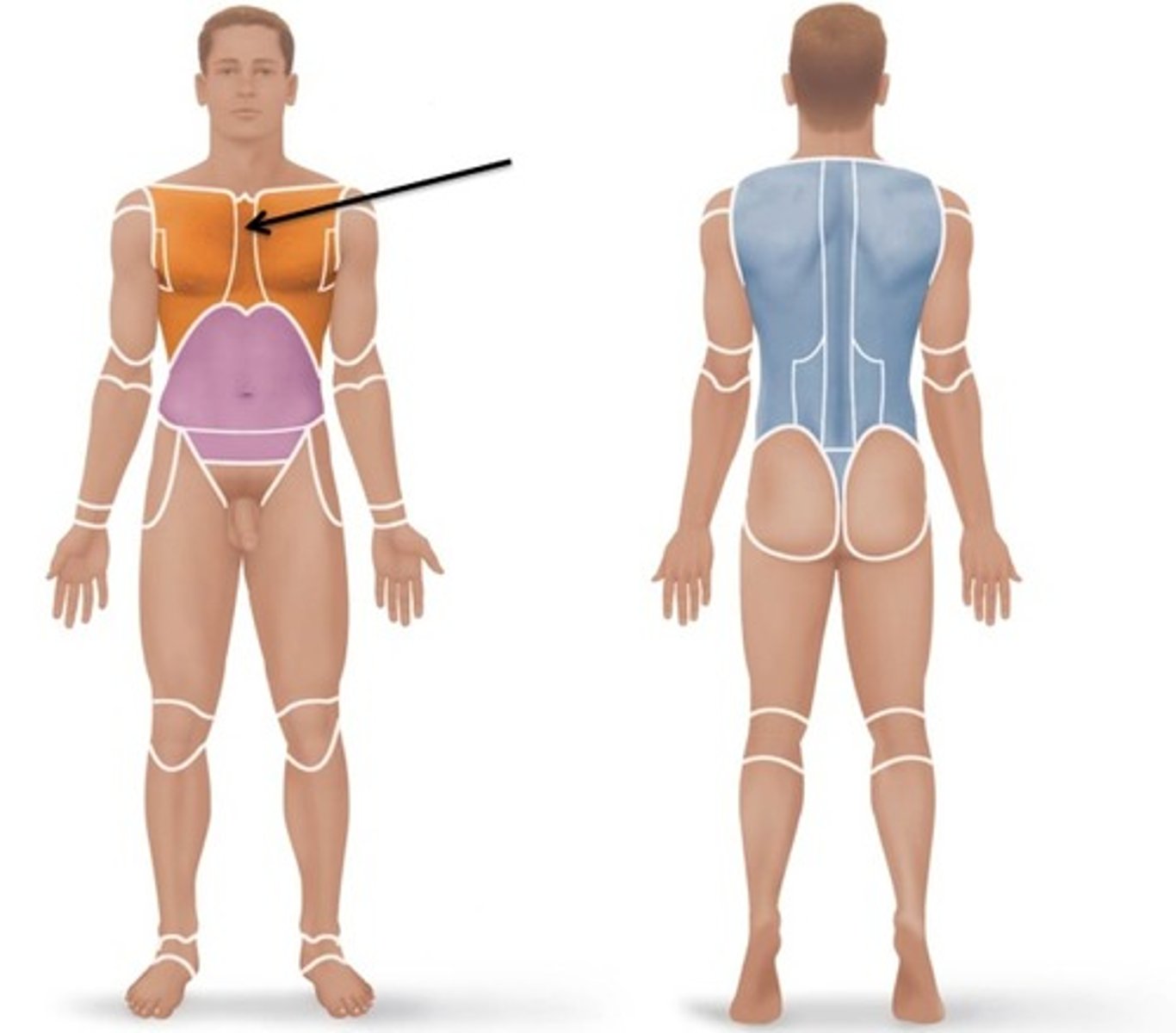
Mammary
Relating to the breast.
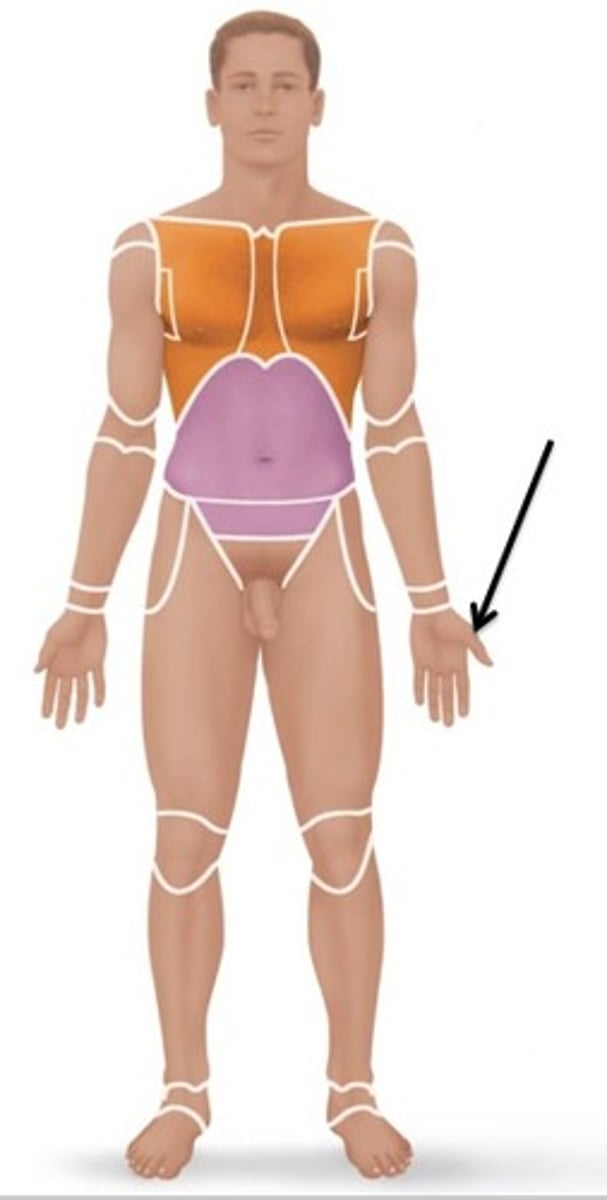
Manus
Relating to the hand.
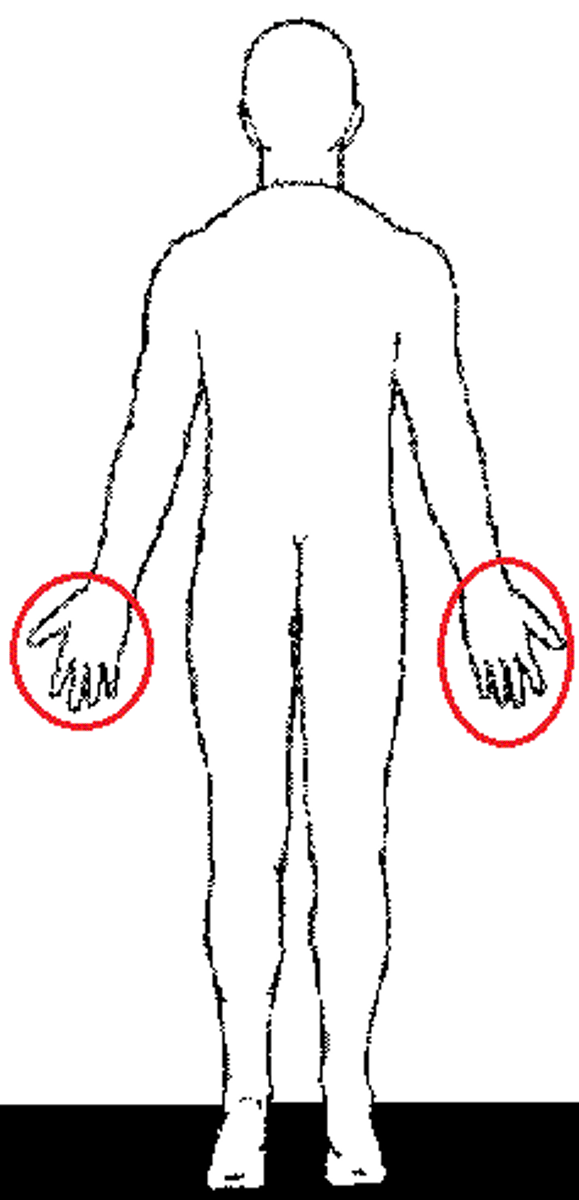
Pollex
Relating to the thumb.
Abdominal
Relating to the abdomen.
Umbilical
Relating to the navel.
Pelvic
Relating to the pelvis.
Inguinal
Relating to the groin.
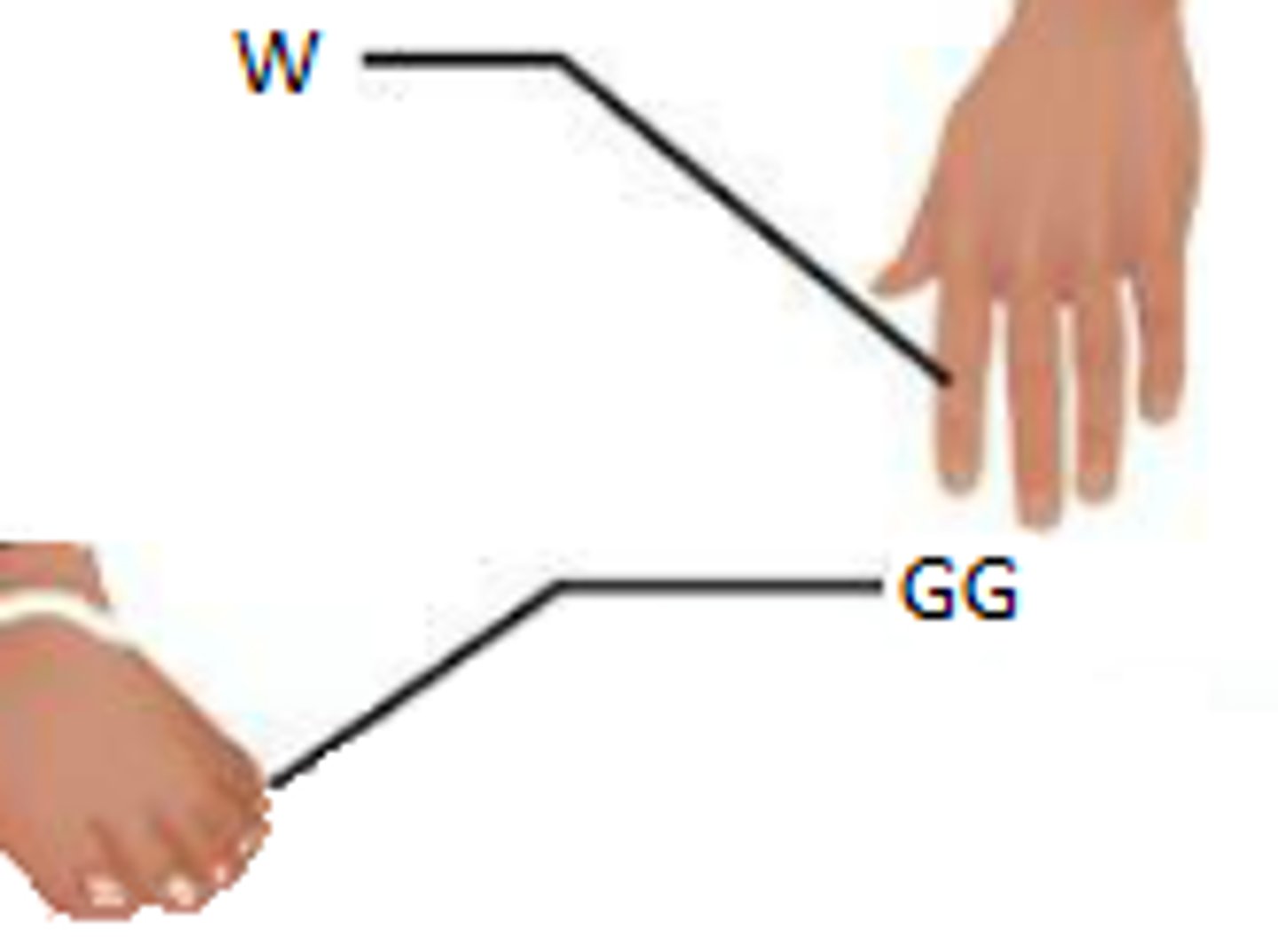
Palmar
Relating to the palm of the hand.
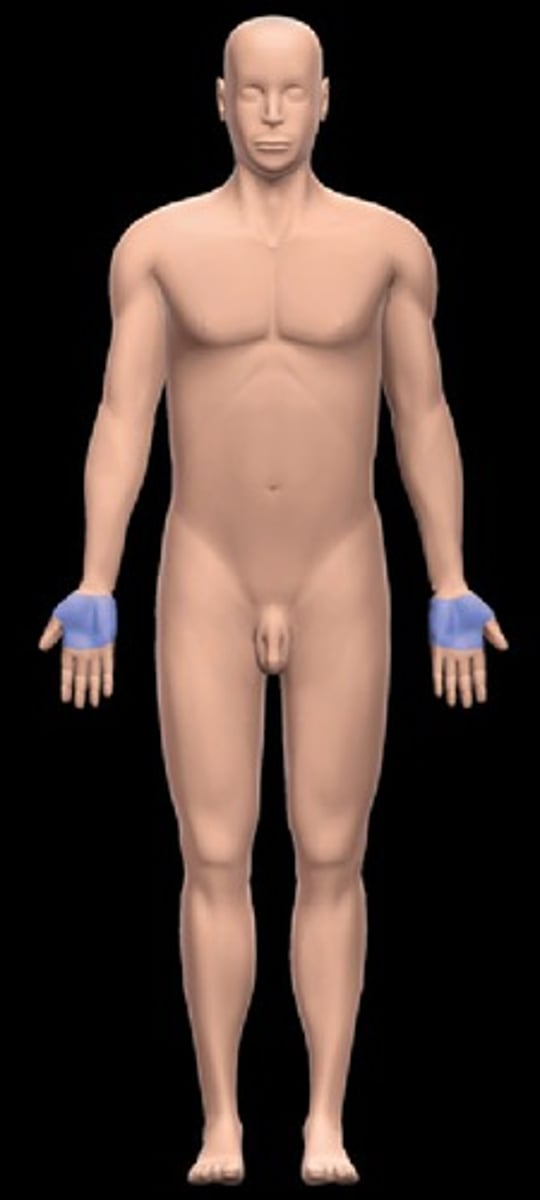
Digital
Relating to the fingers or toes.
Lower Limb
Includes the hip, thigh, leg, ankle, and foot.
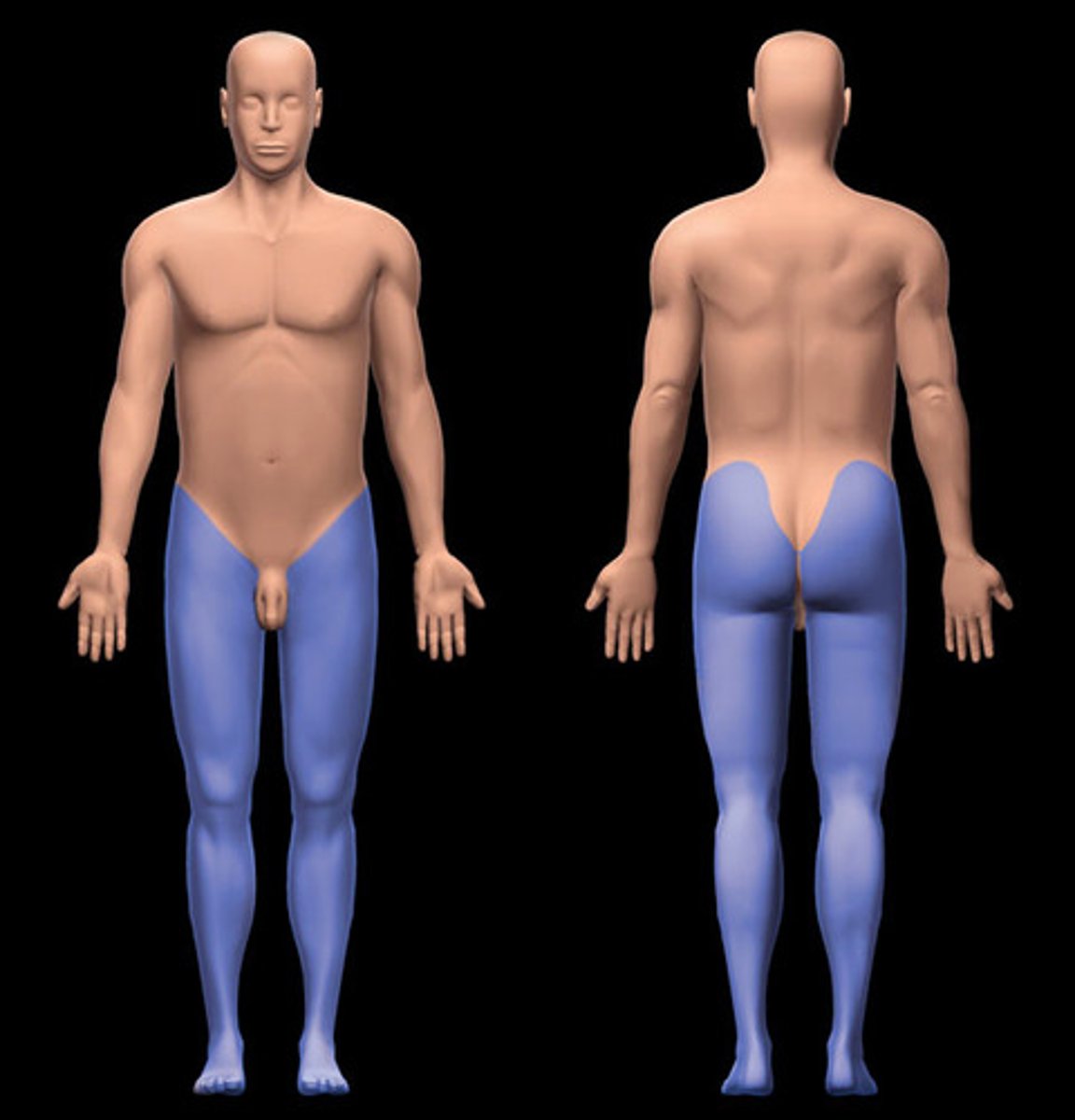
Coxal
Relating to the hip.
Femoral
Relating to the thigh.
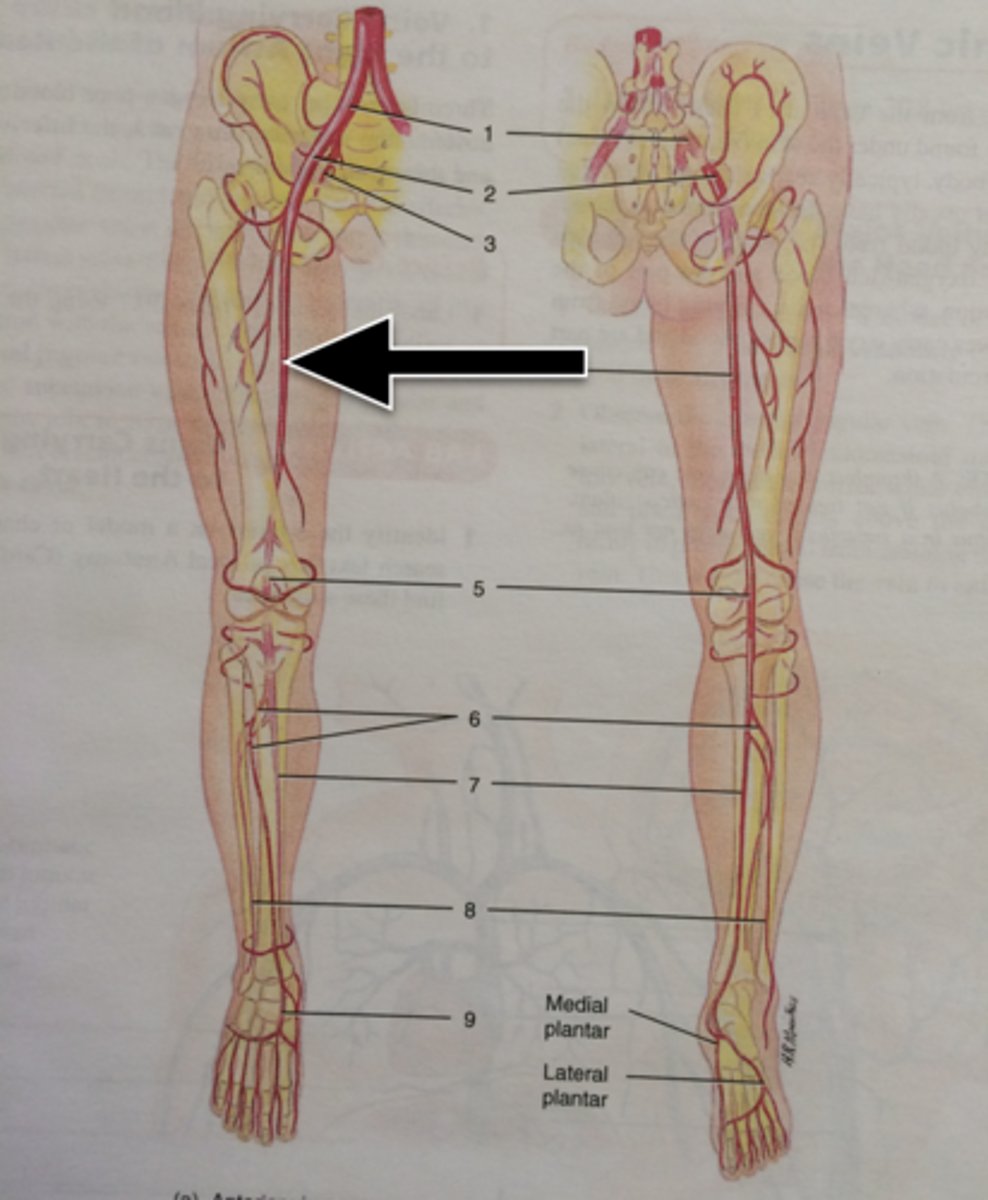
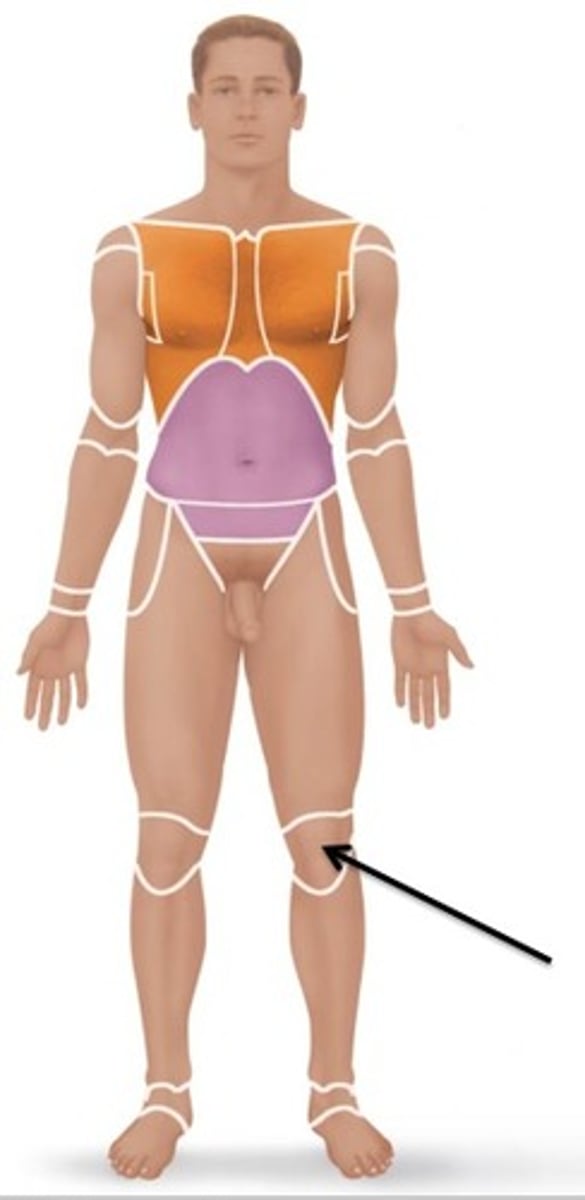
Patellar
Relating to the kneecap.
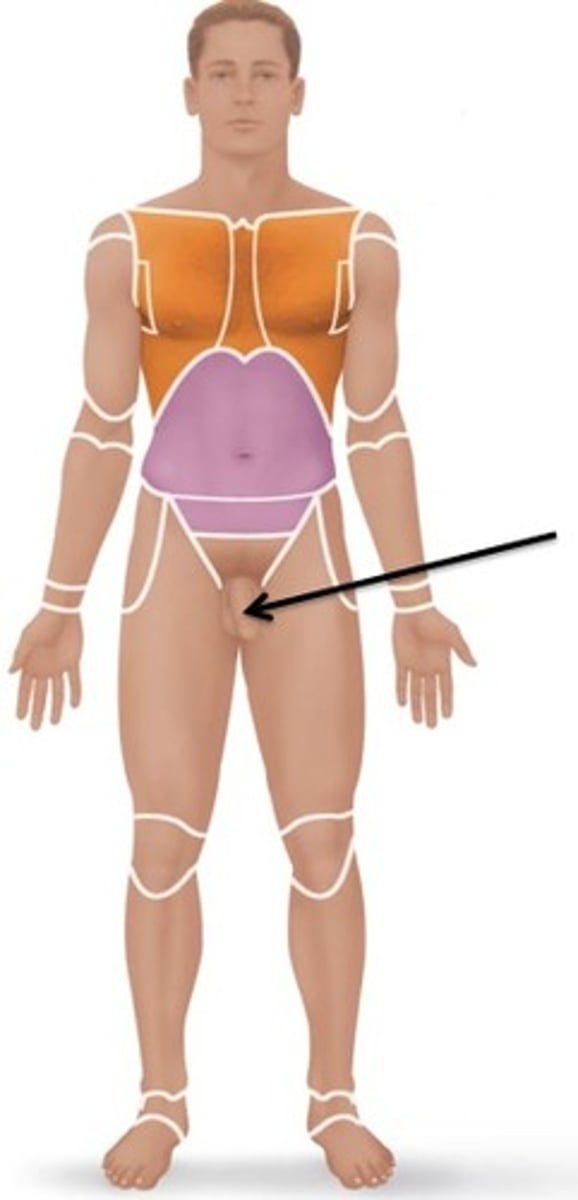
Pubic
Relating to the genital region.
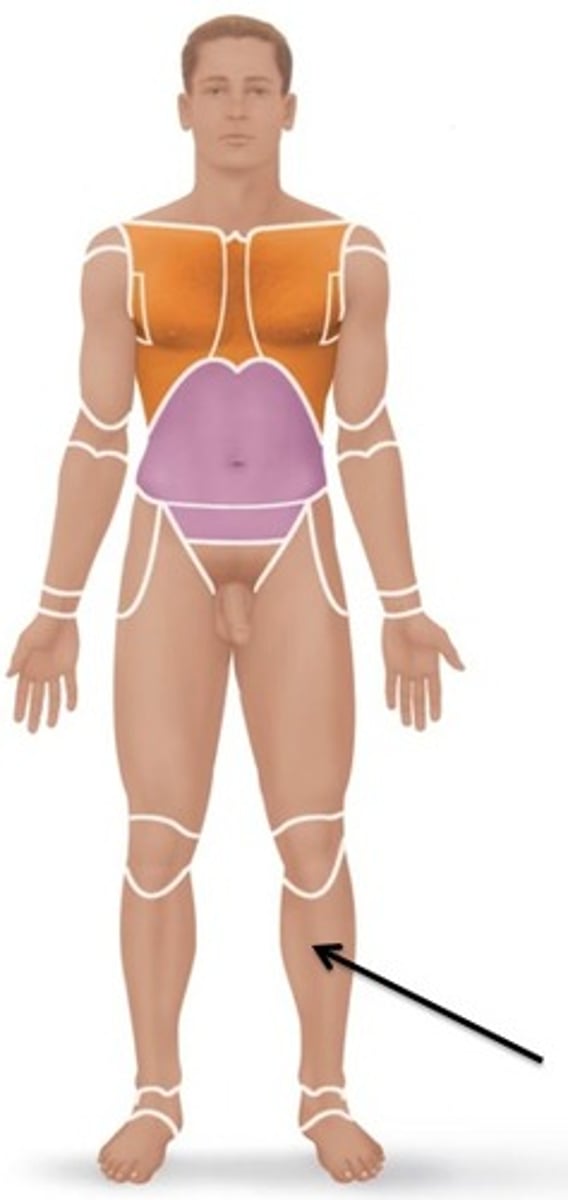
Crural
Relating to the leg.
Fibular or peroneal
Relating to the side of the leg.
Pedal
Relating to the foot.
Tarsal
Relating to the ankle.
Thorax
Relating to the chest.
Back
Relating to the posterior of the body.
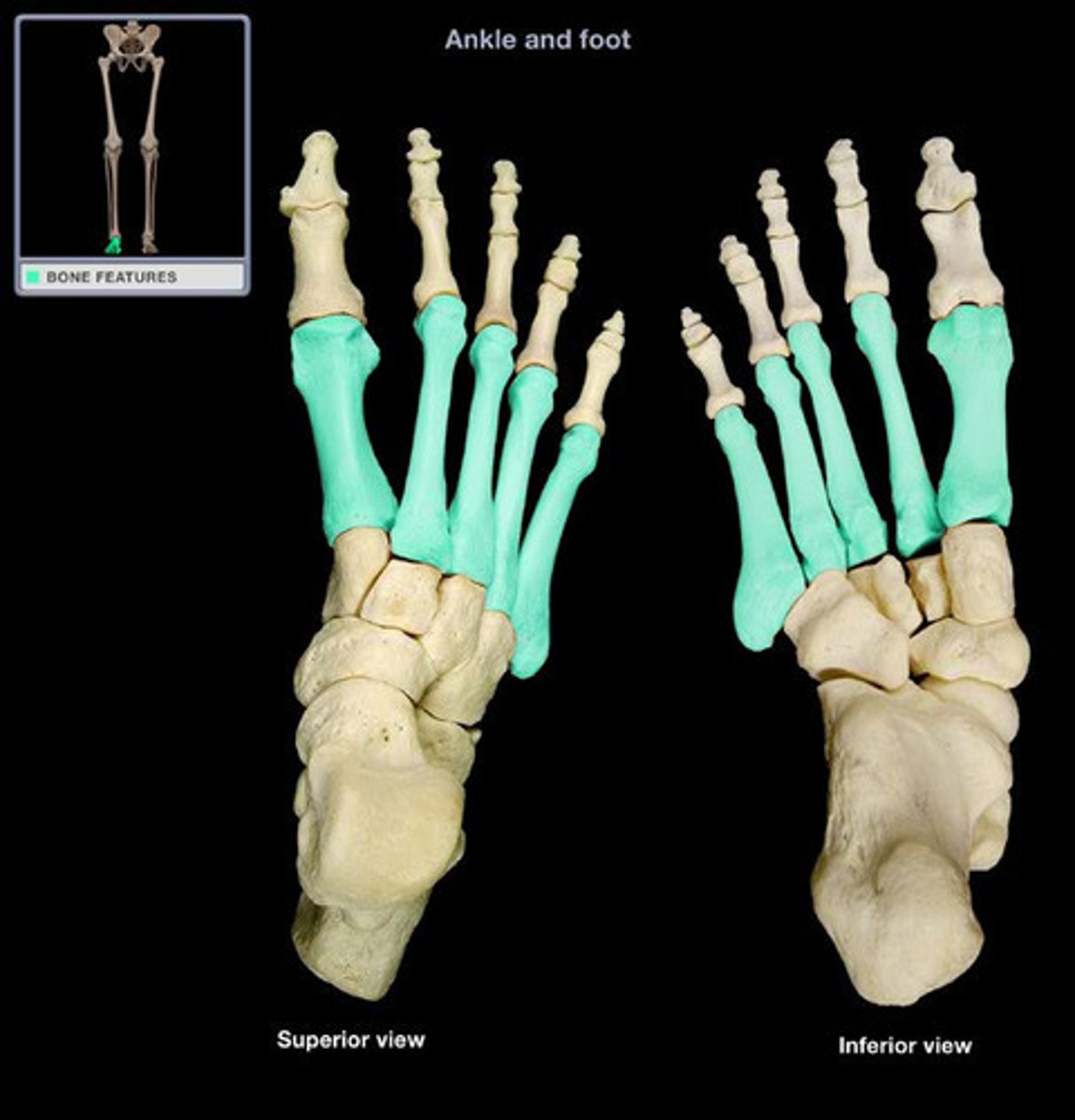
Metatarsal
Relating to the bones of the foot.
Hallux
Relating to the big toe.
Posterior
Refers to the back of the body.
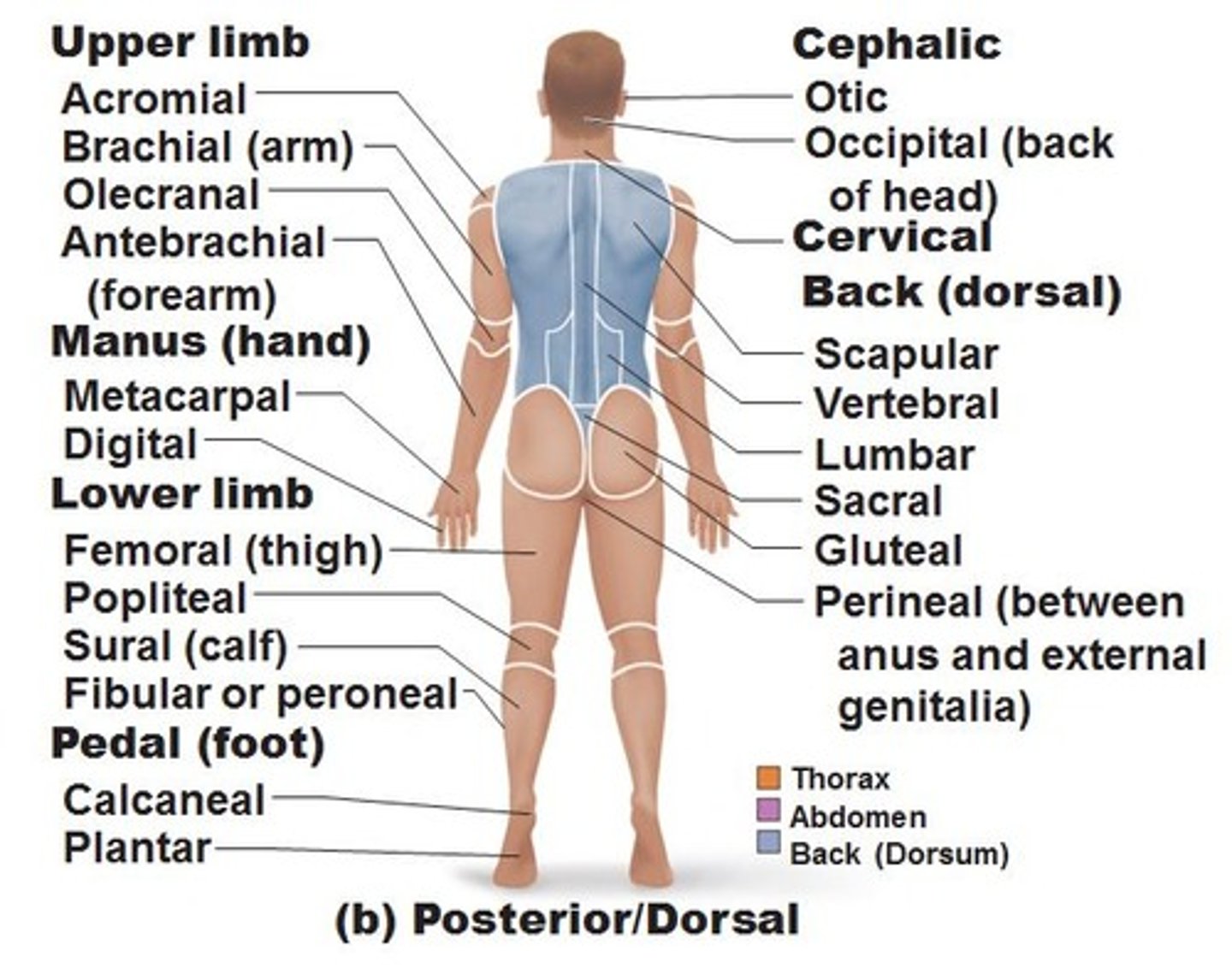
Otic
Relating to the ear.
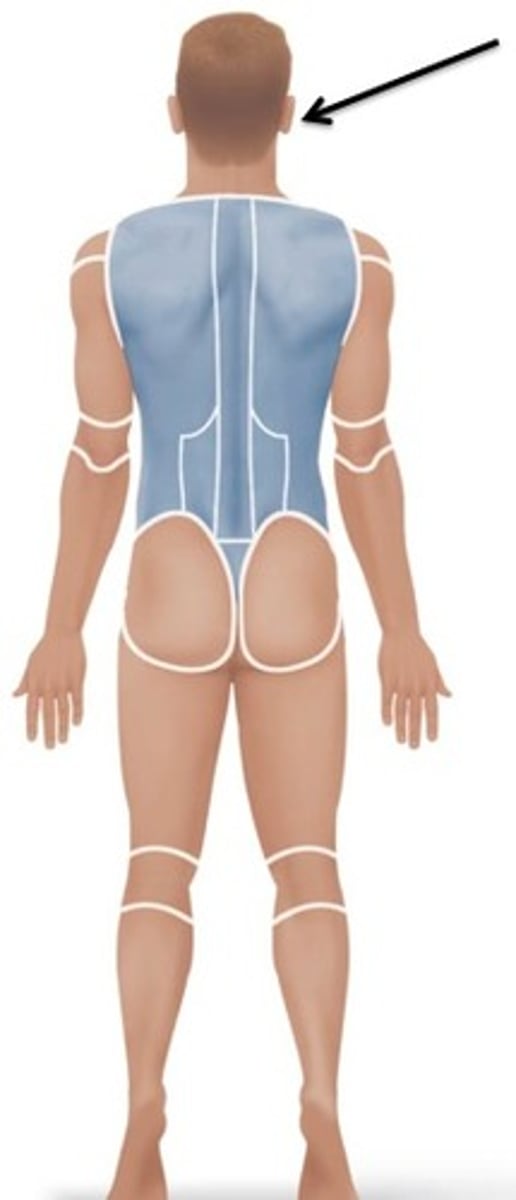
Occipital
Relating to the back of the head.
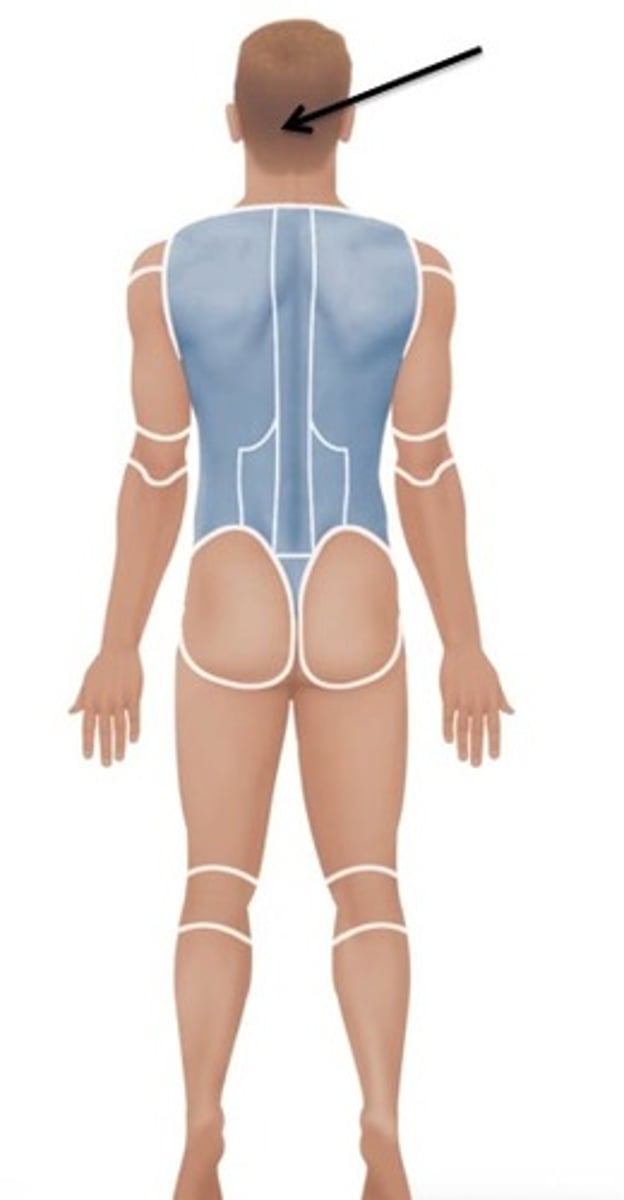
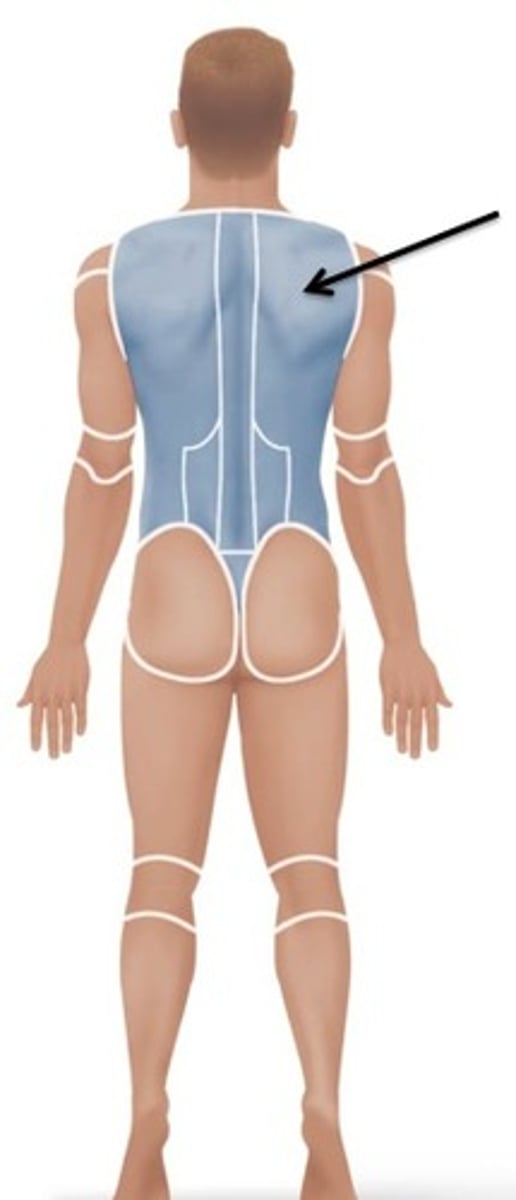
Scapular
Relating to the shoulder blade.
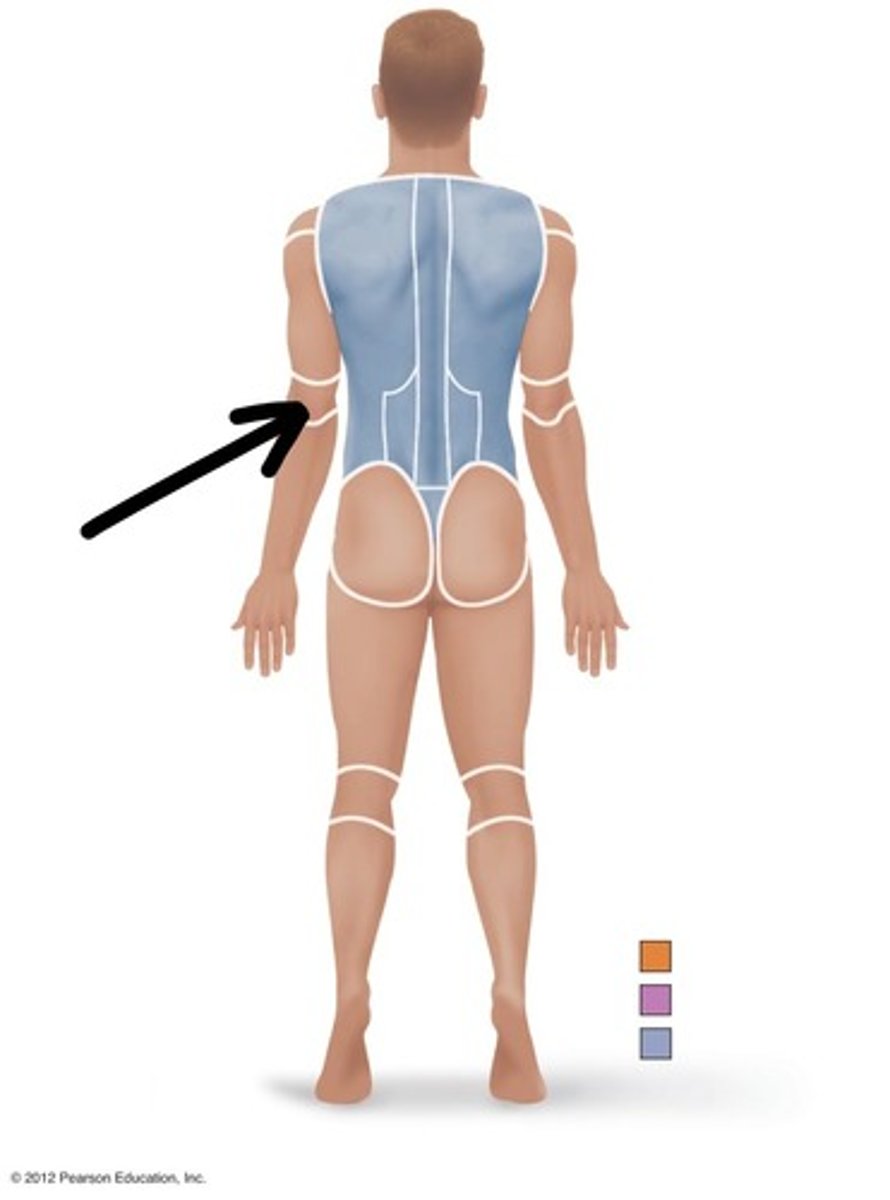
Olecranal
Relating to the back of the elbow.
Vertebral
Relating to the spine.
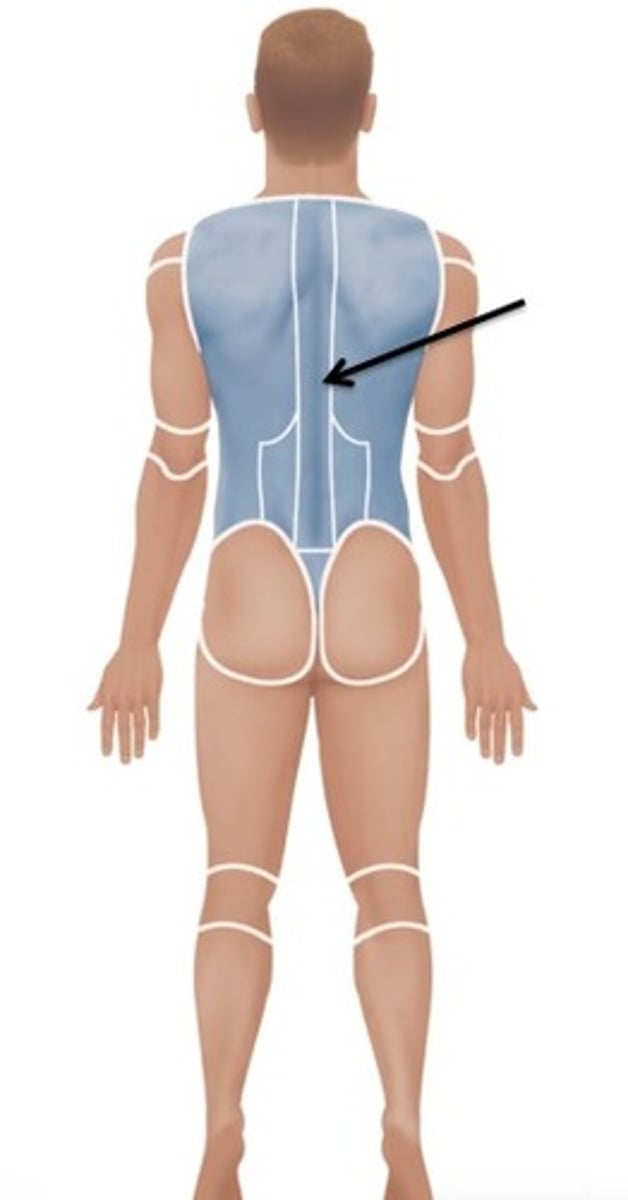
Lumbar
Relating to the lower back.
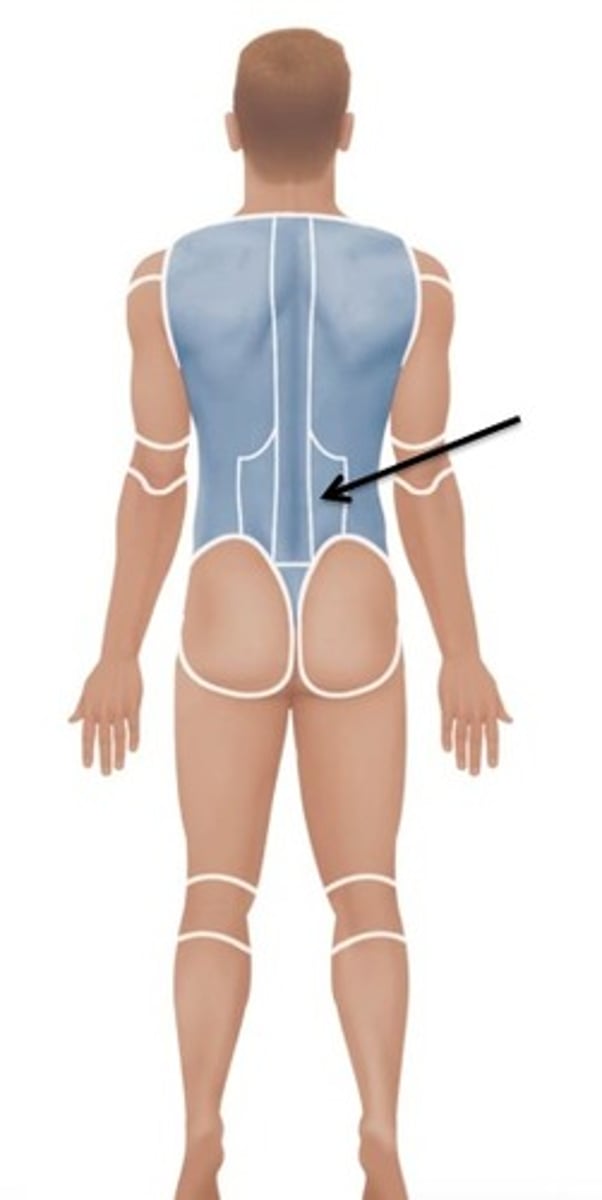
Sacral
Relating to the sacrum.
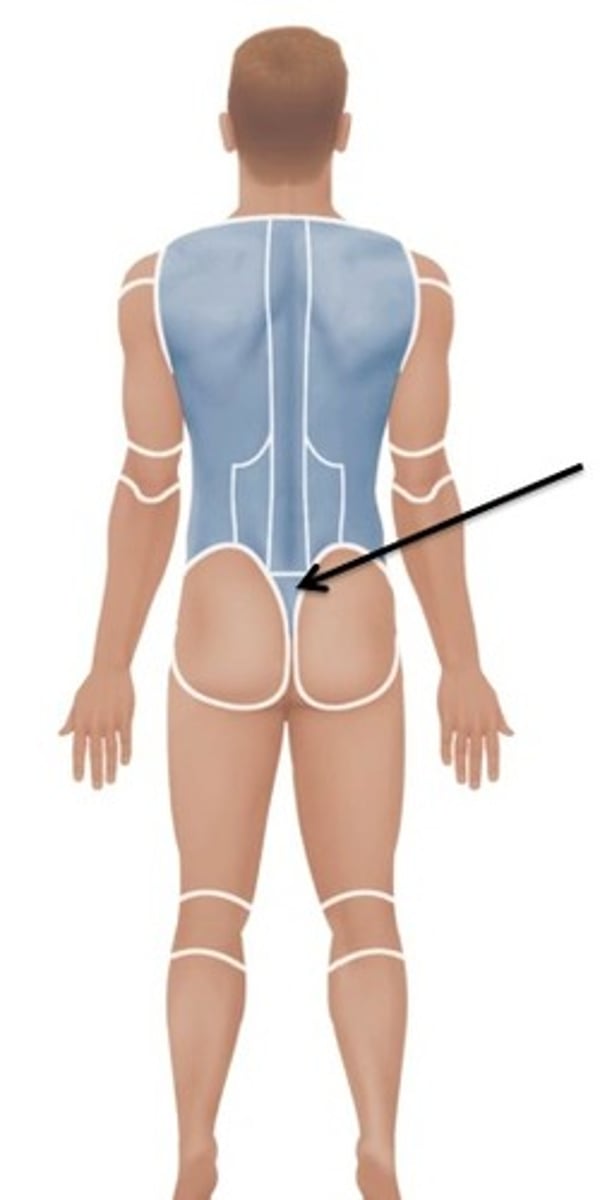
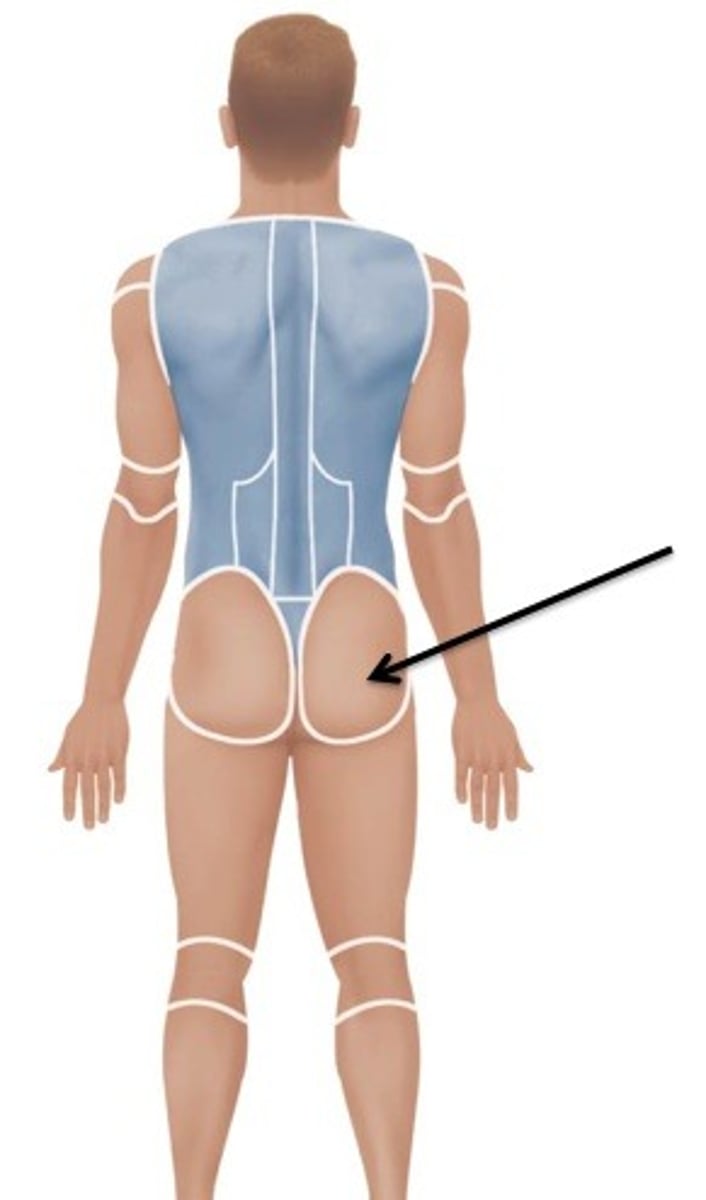
Gluteal
Relating to the buttocks.
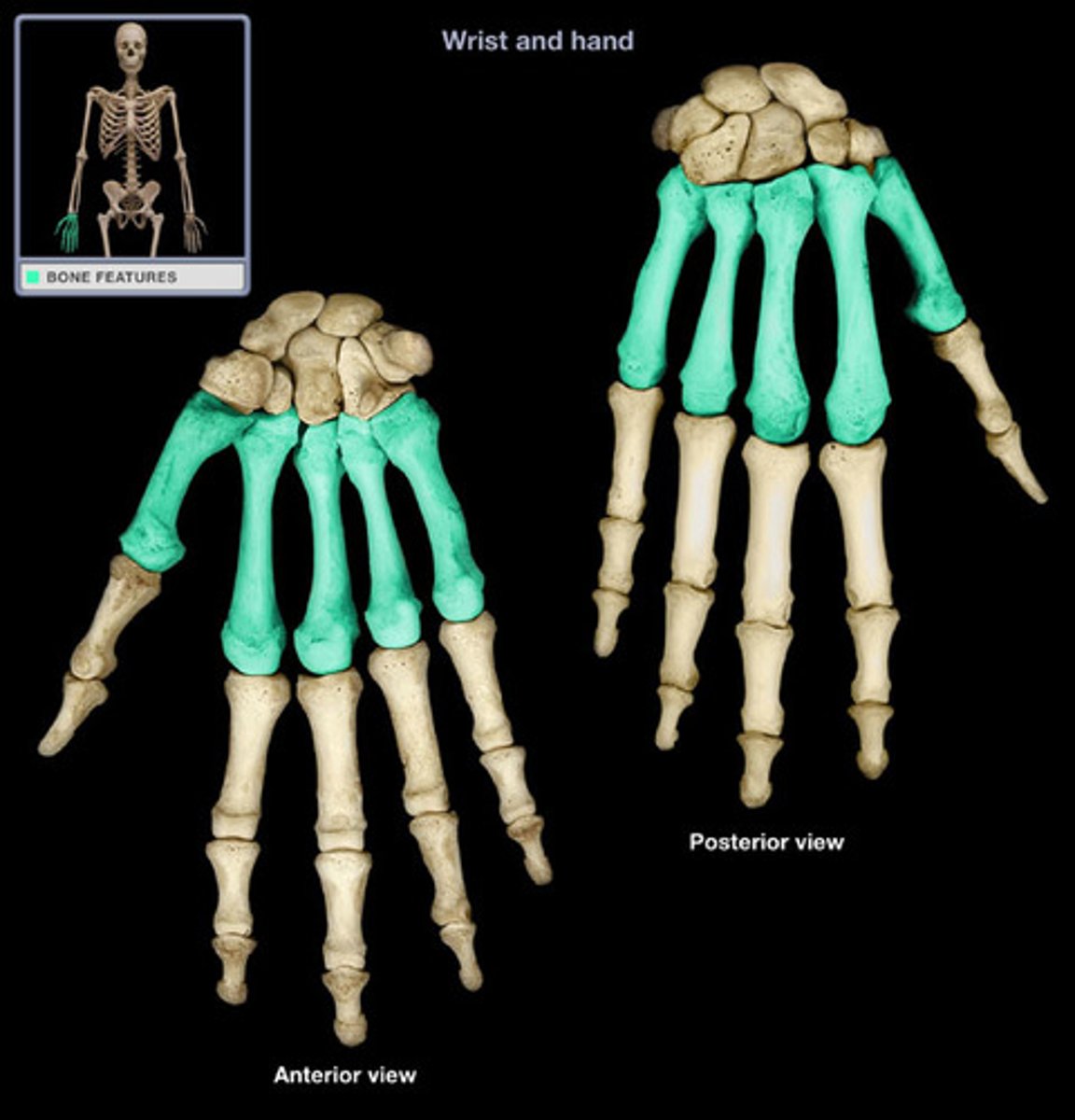
Metacarpal
Relating to the bones of the hand.
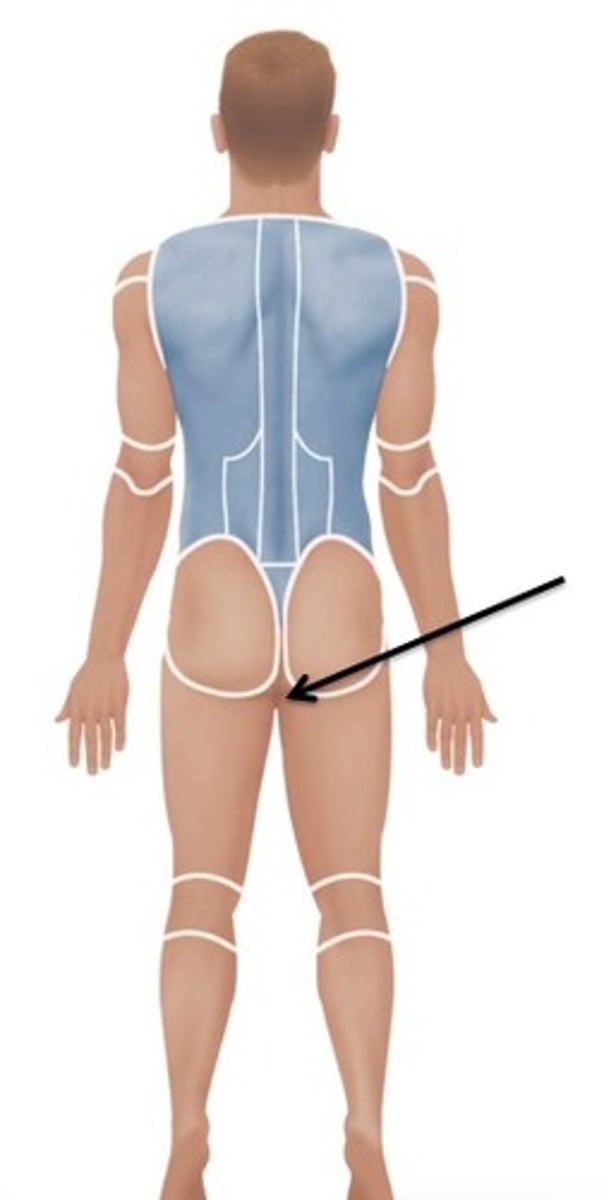
Perineal
Relating to the area between the anus and external genitalia.
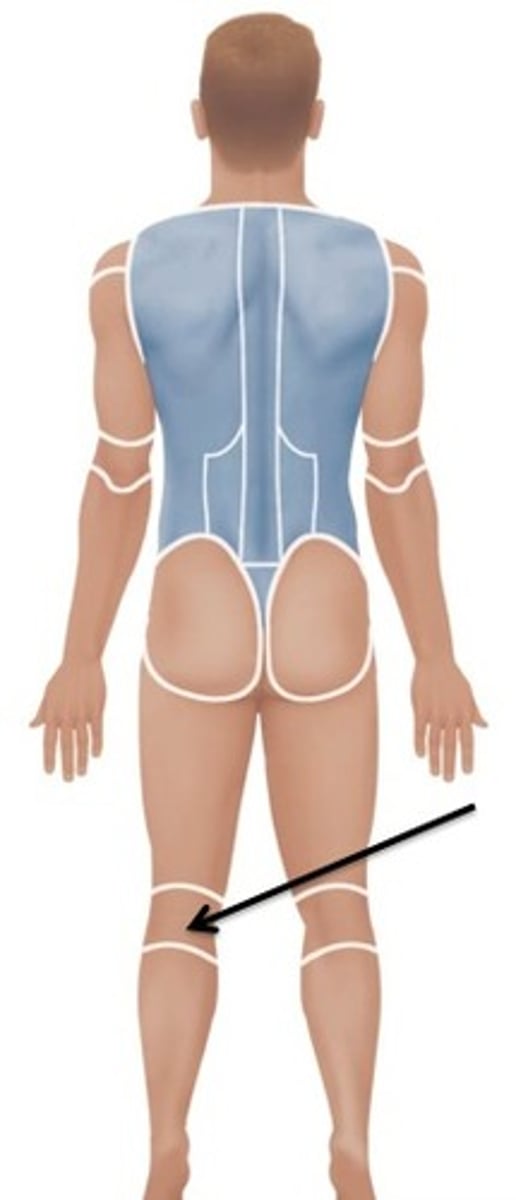
Popliteal
Relating to the back of the knee.
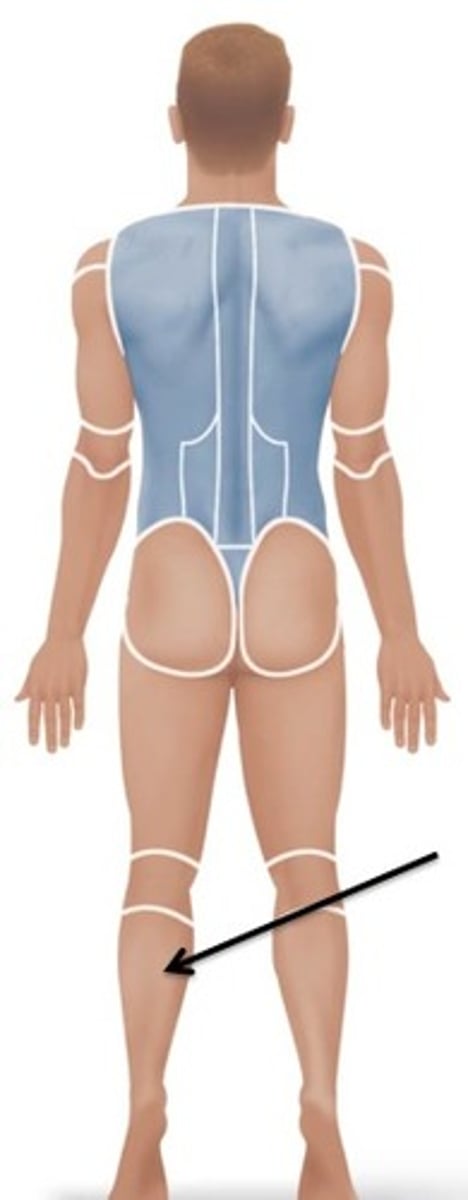
Sural
Relating to the calf of the leg.
Calcaneal
Relating to the heel.
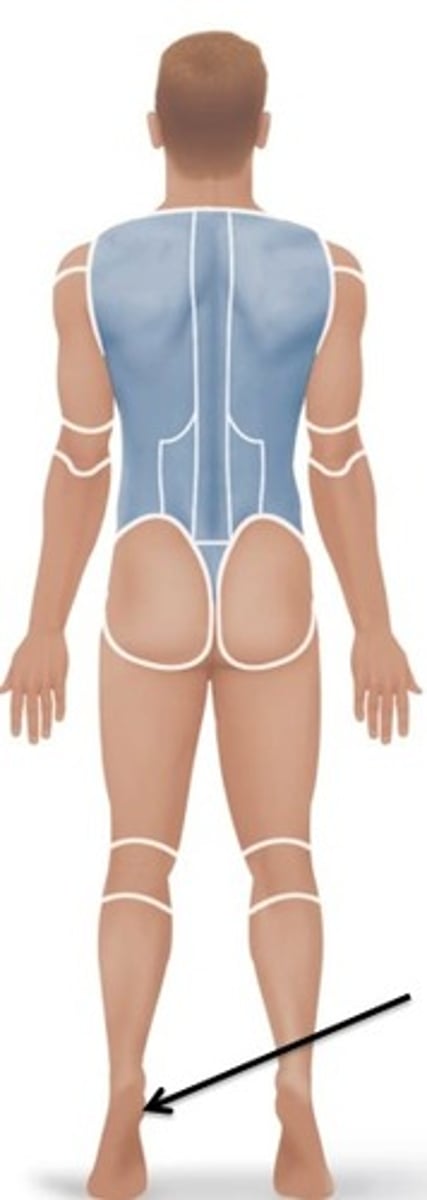
Plantar
Relating to the sole of the foot.

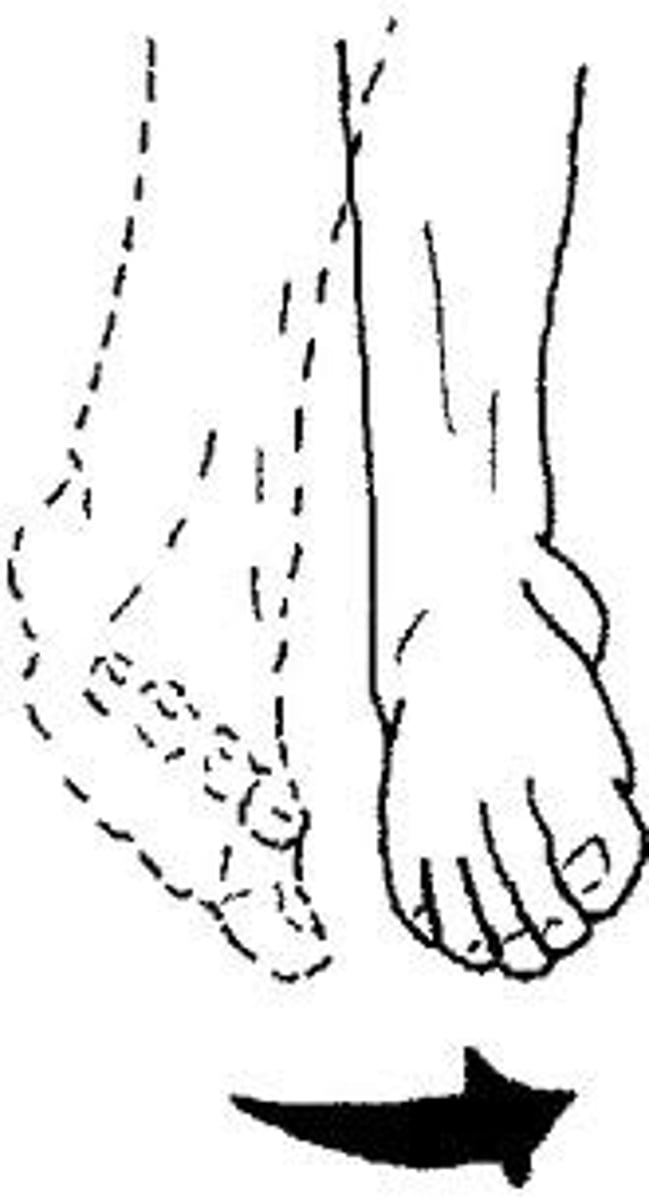
Inversion
Medial rotation of the sole of the foot.
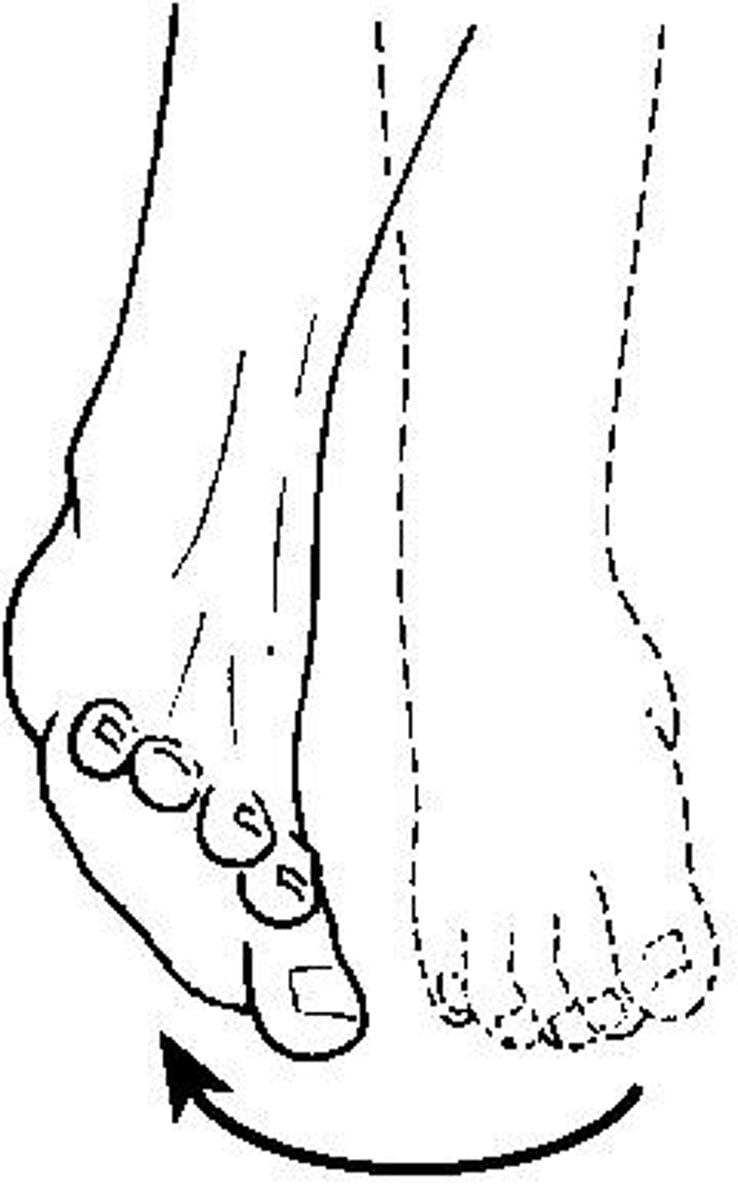
Eversion
Lateral rotation of the sole of the foot.
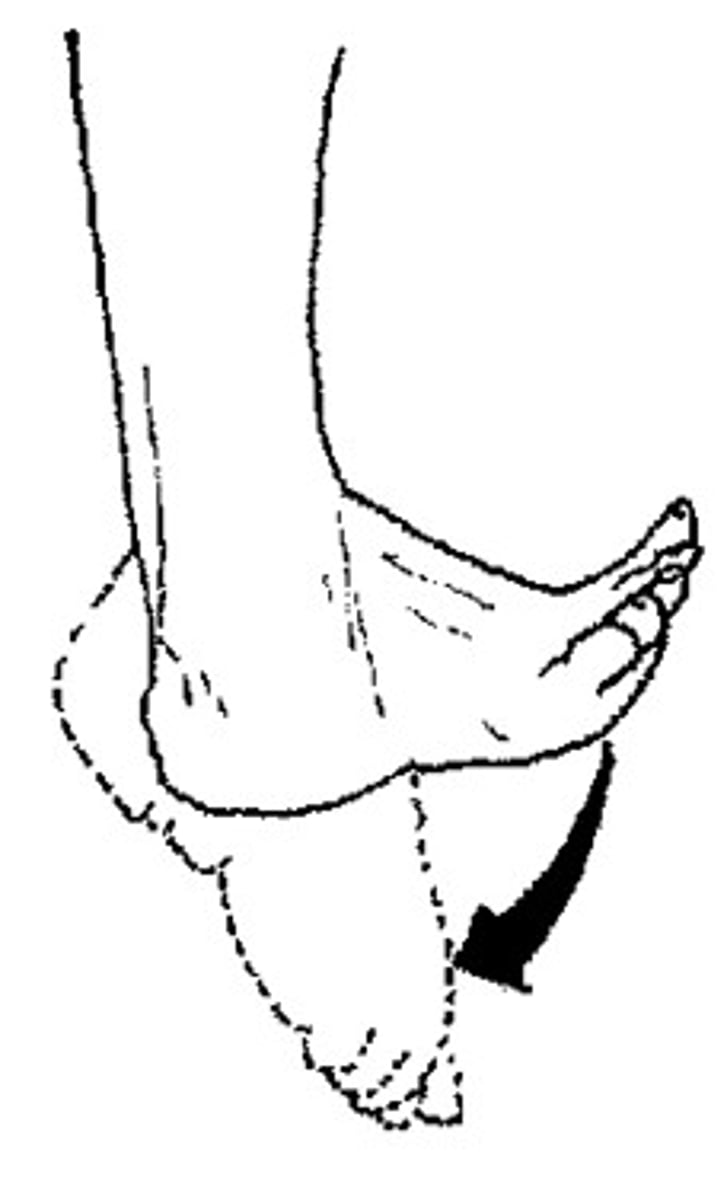
Plantar Flexion
Depression of the foot.
Dorsiflexion
Elevation of the foot.
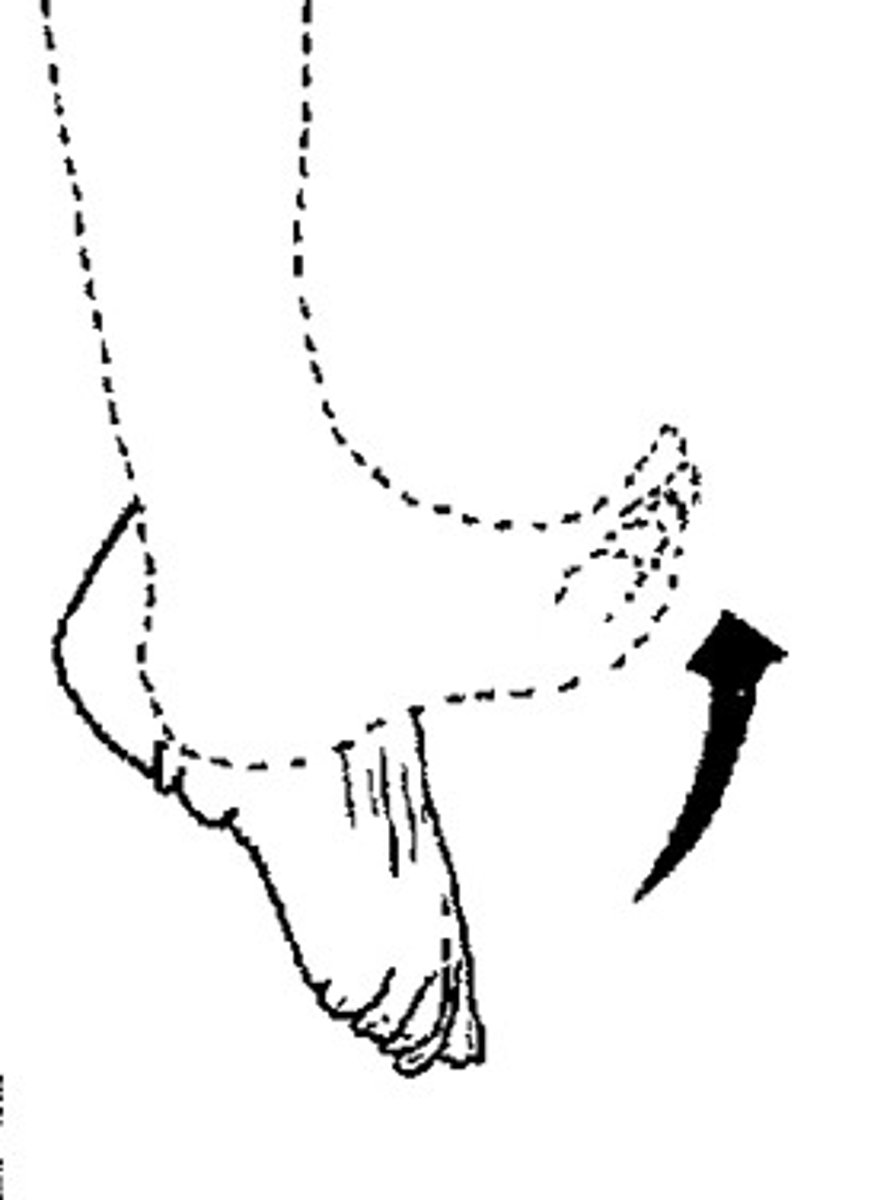
Dorsal
Back
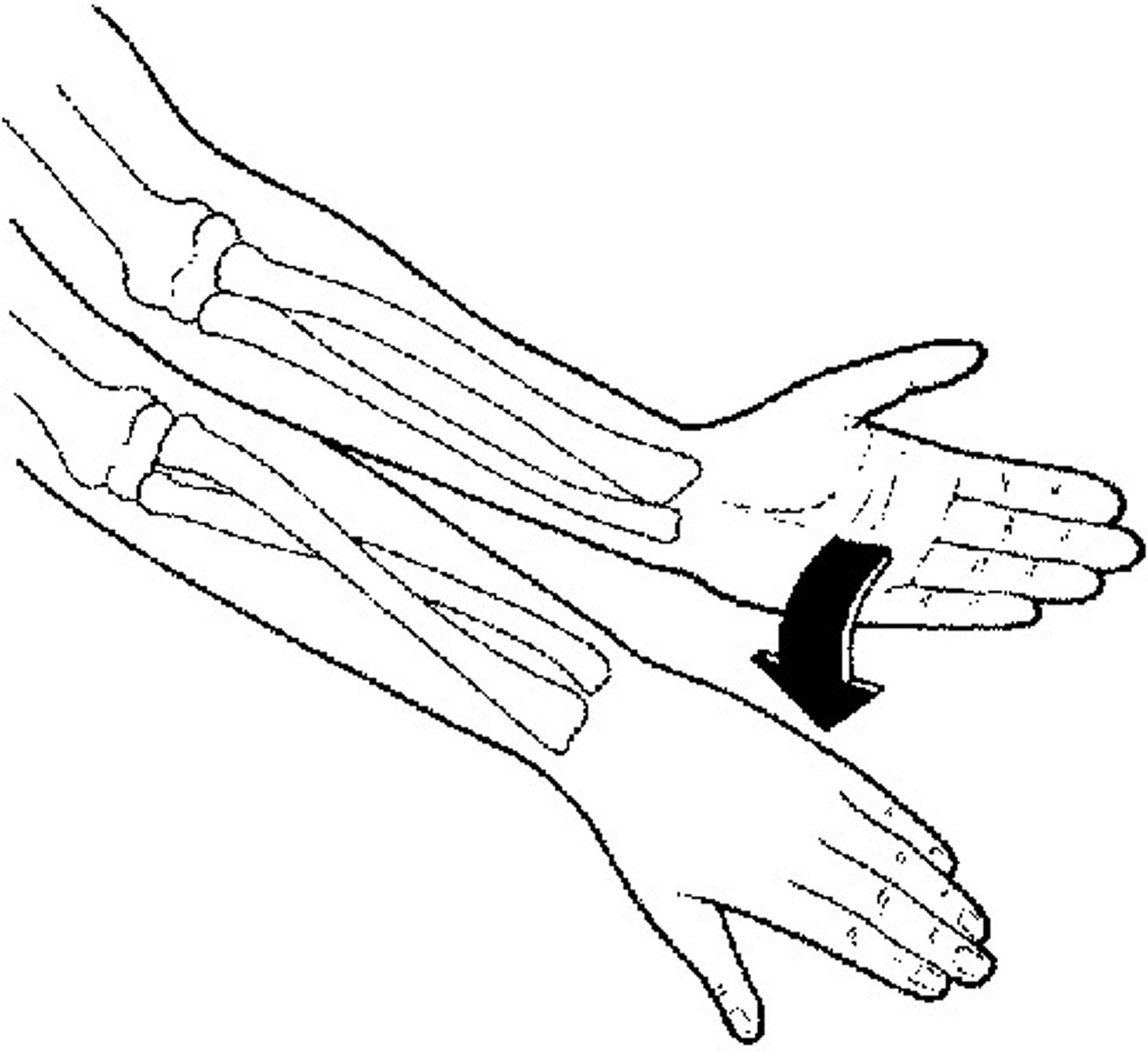
Pronation
Medial rotation of the forearm with the palm facing posteriorly; radius rotates over ulna
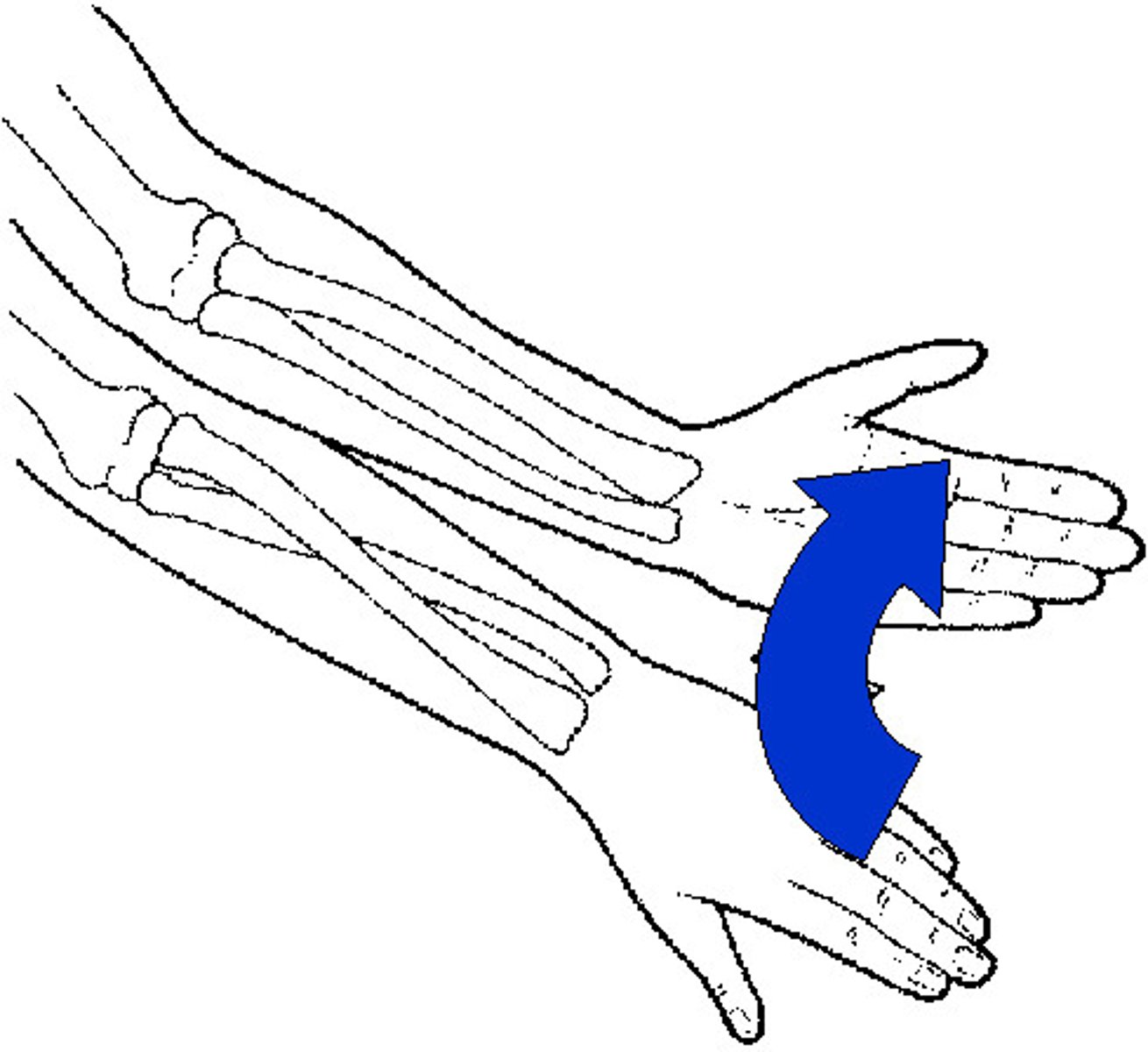
Supination
Lateral rotation of the forearm with the palm facing anteriorly; radius and ulna are parallel
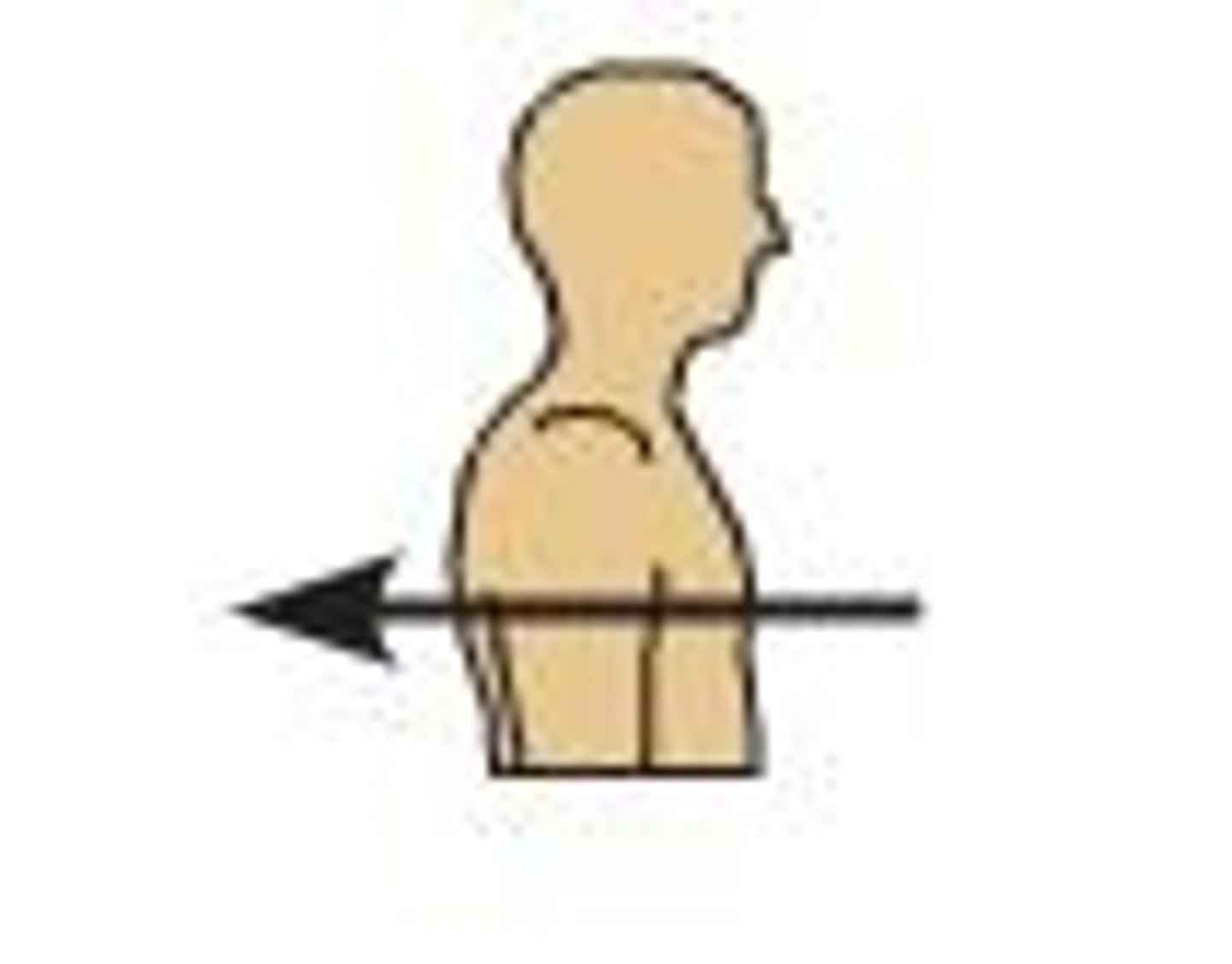
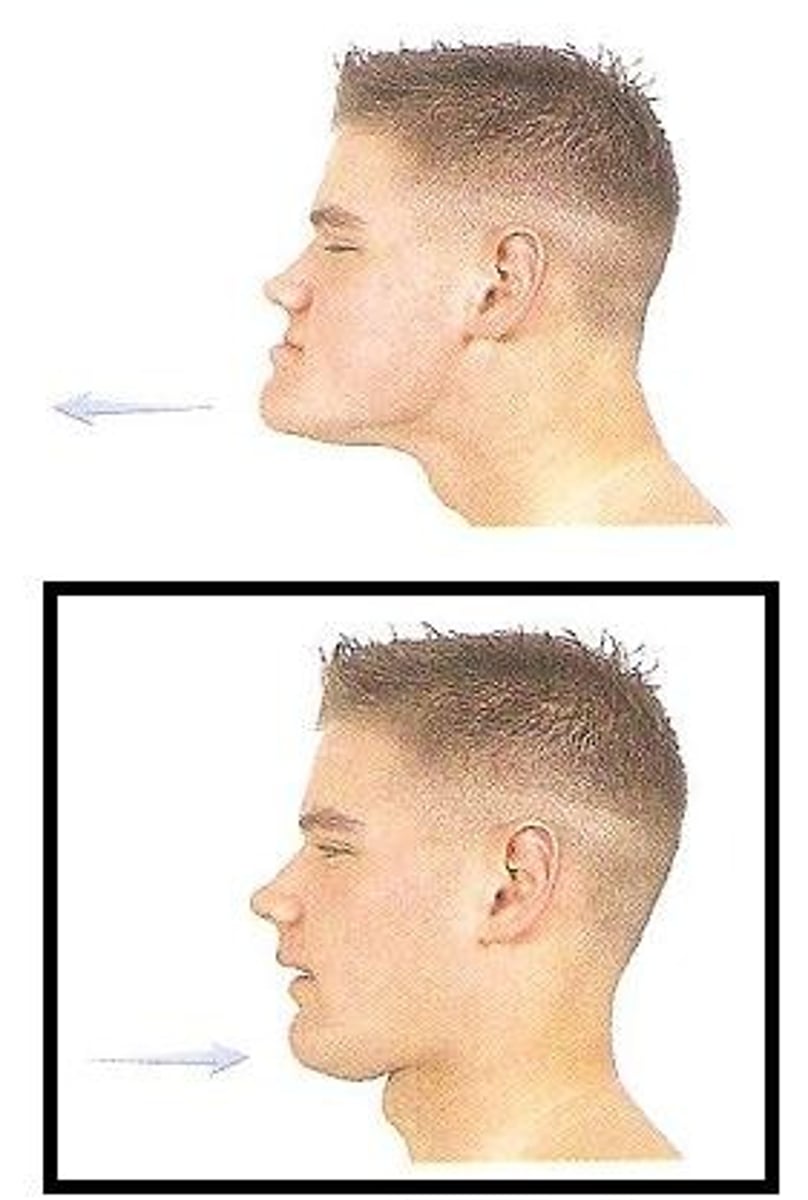
Protraction
Anterior movement of the mandible.
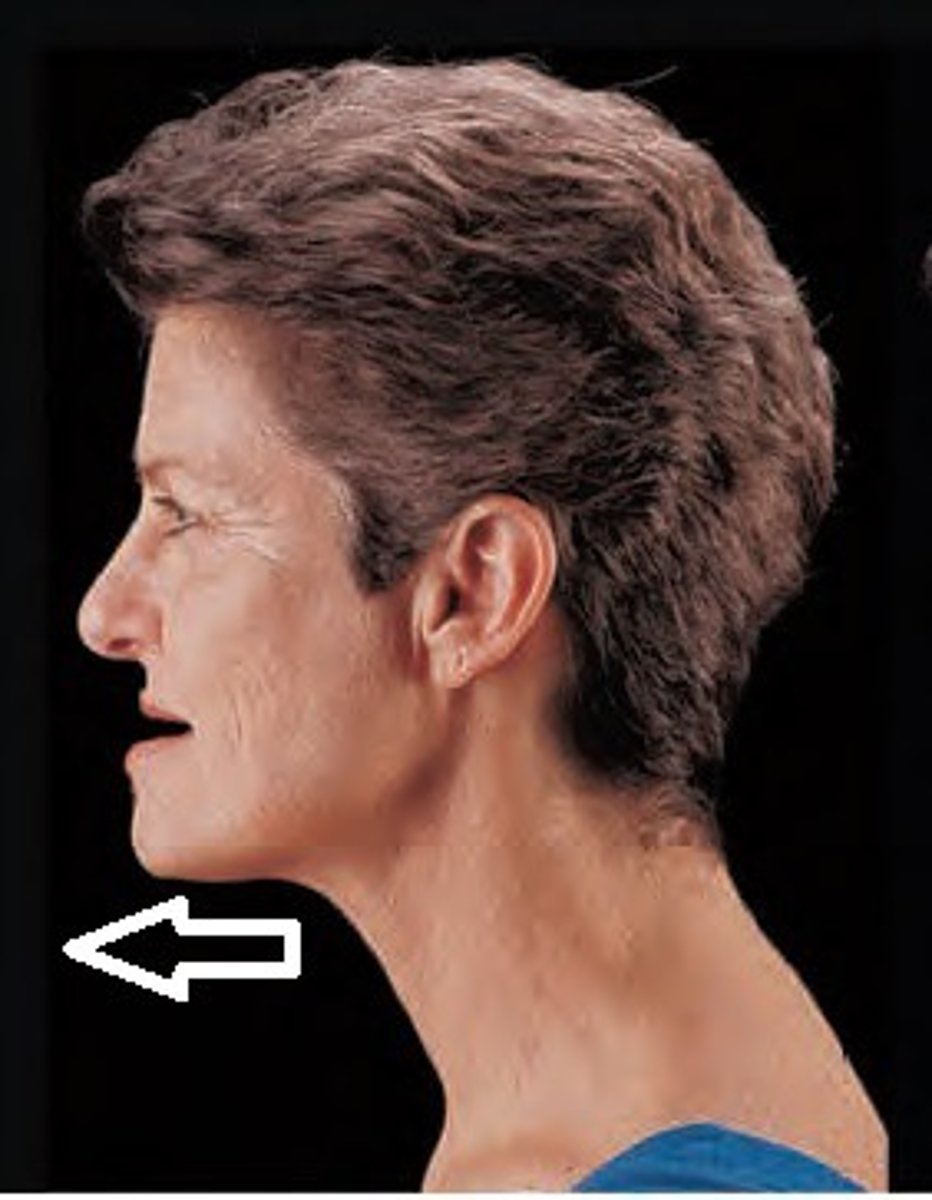
Retraction
Posterior movement of the mandible.
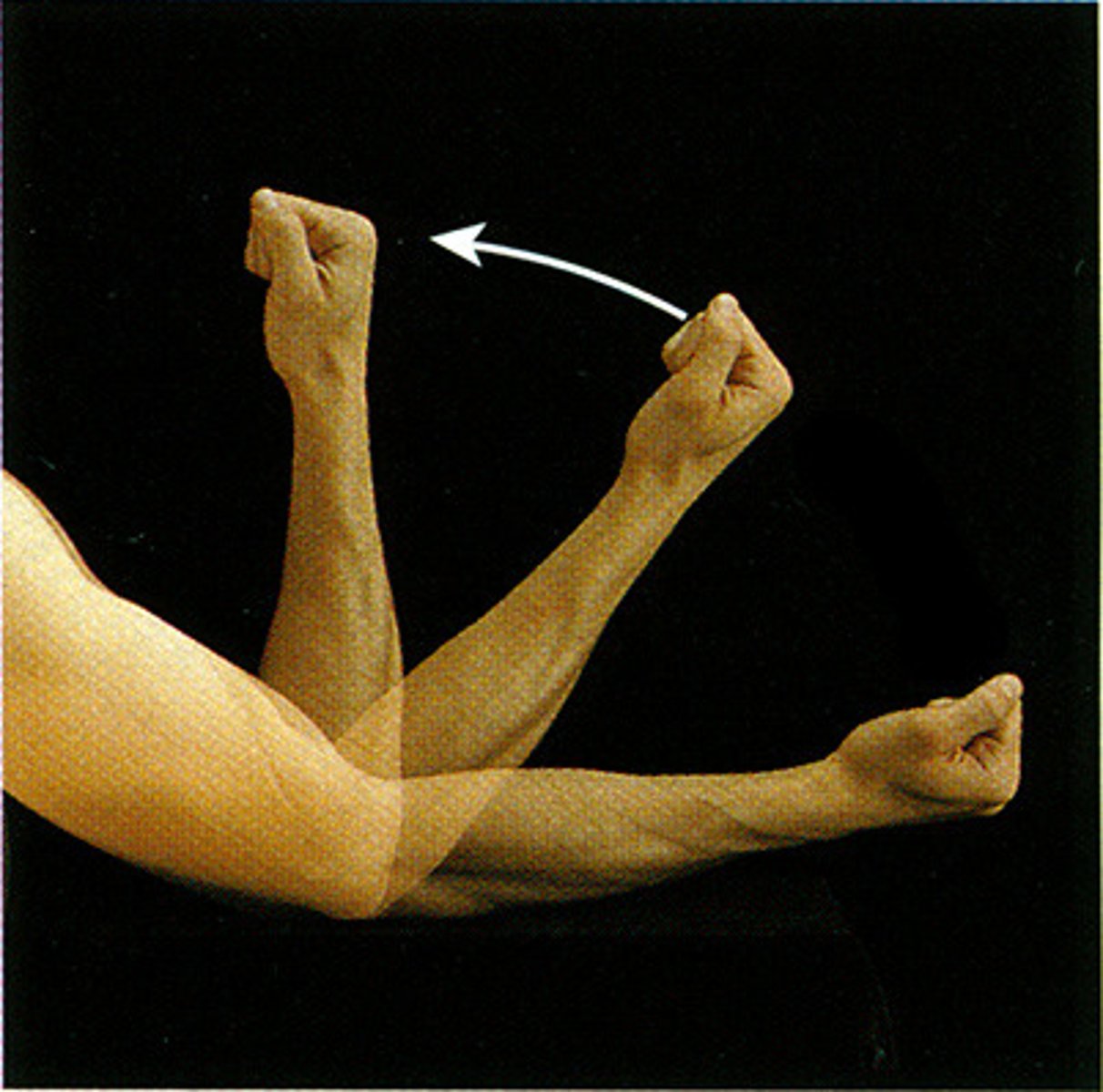
Flexion
The bending action that decreases the angle between two bones.
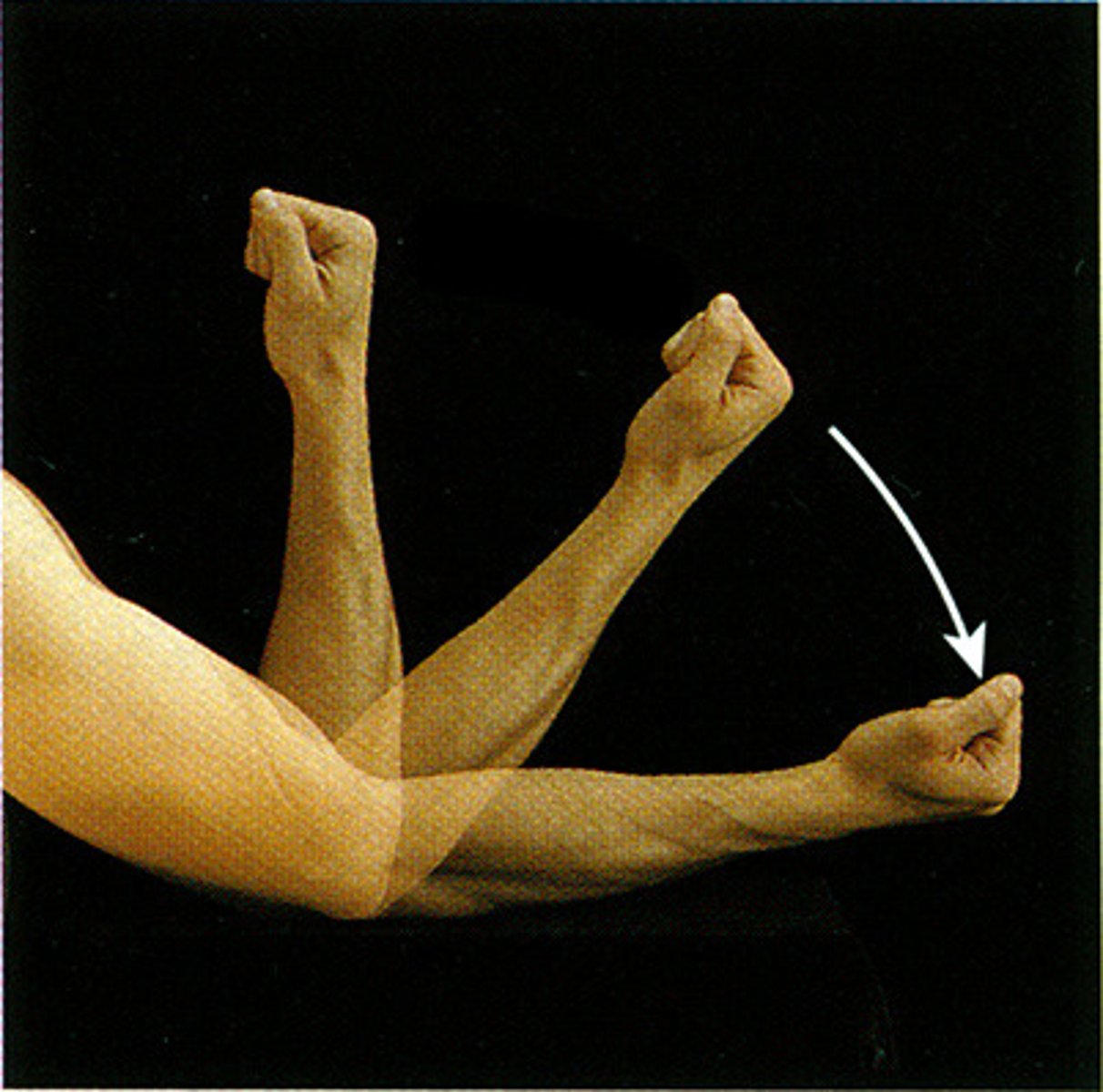
Extension
The straightening action that increases the angle between two bones.
Hyperextension
Bending a joint beyond its straight position.
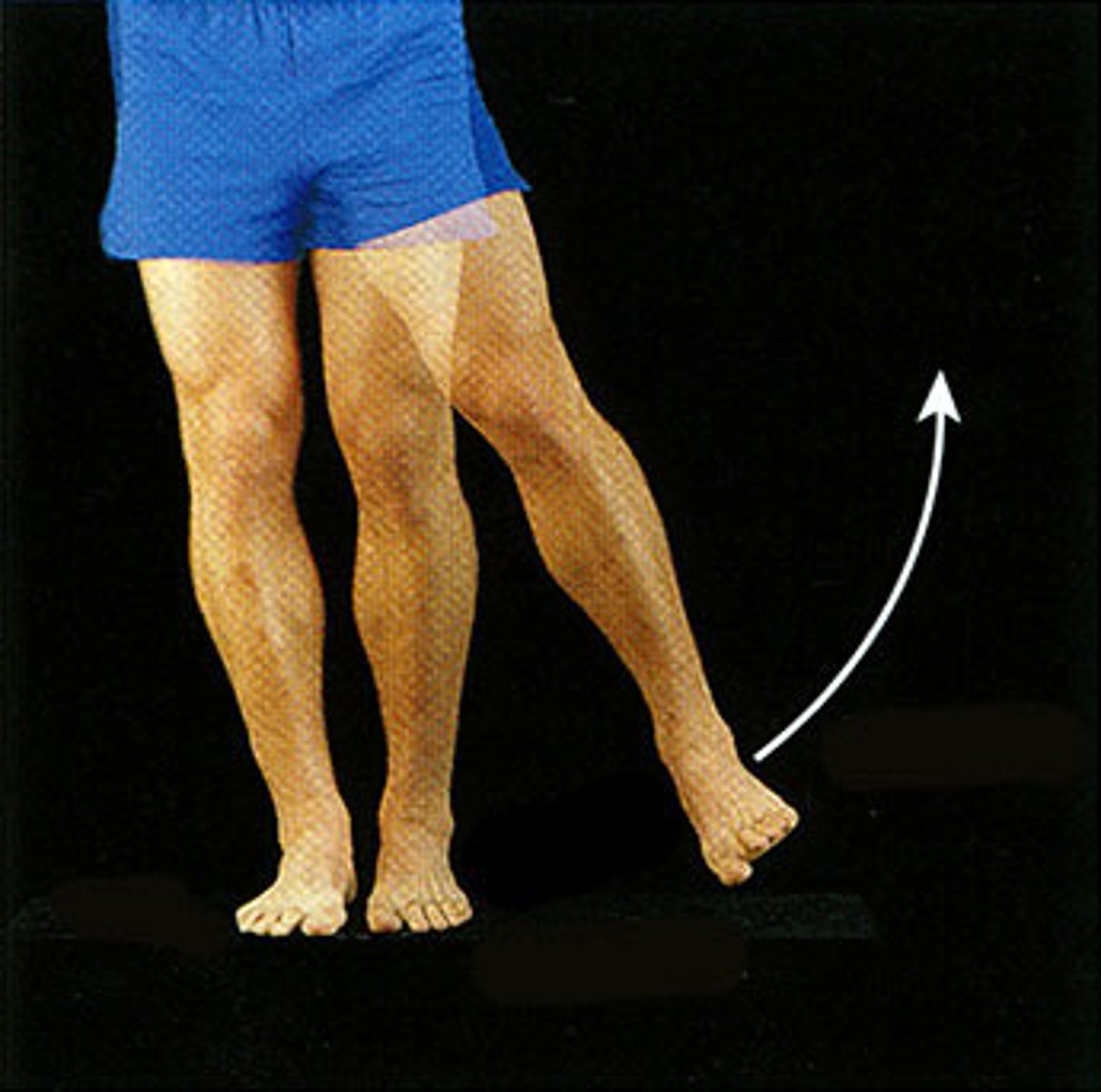
Abduction
The movement of a limb away from the body midline.
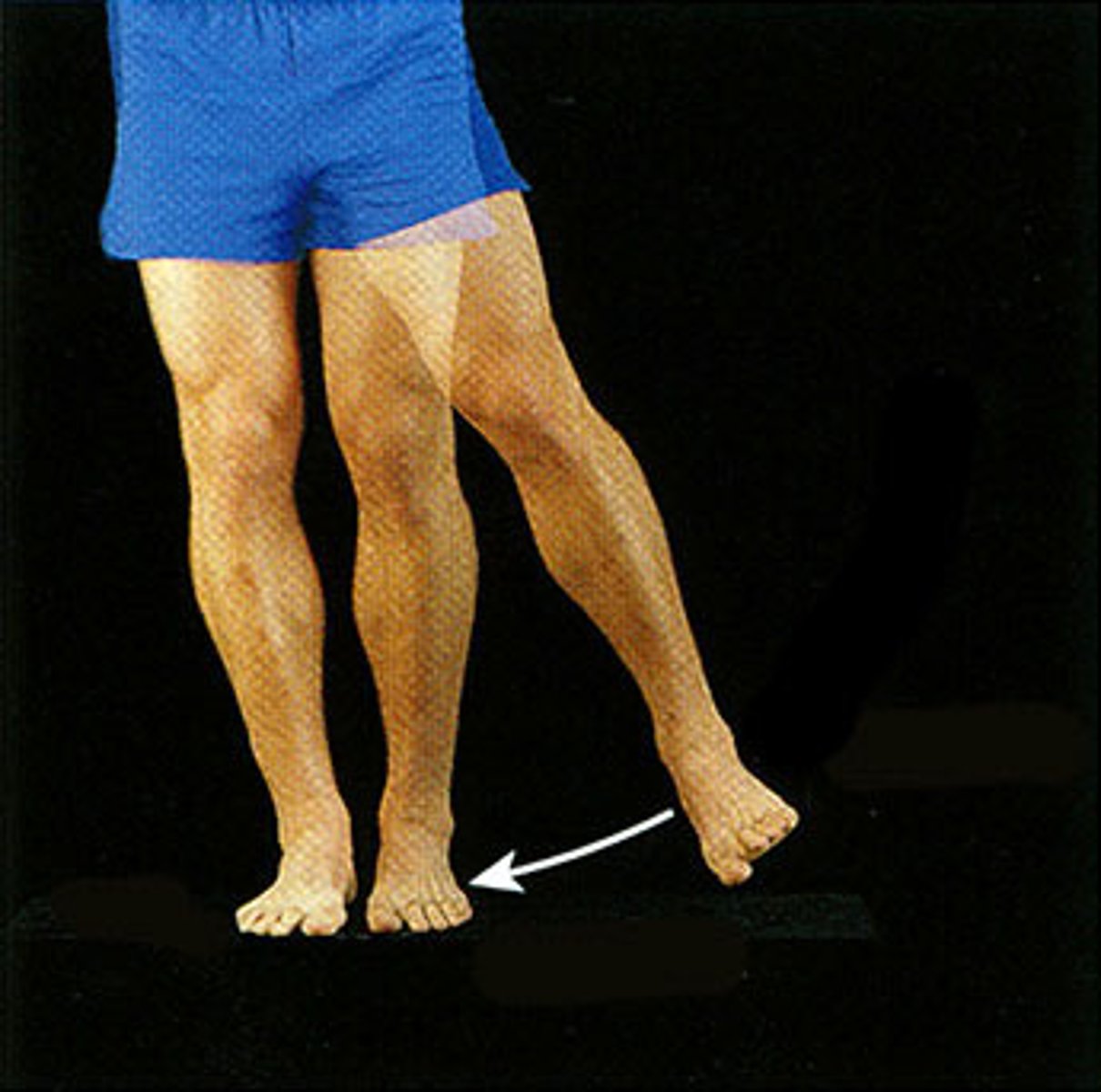
Adduction
The movement of a limb toward the body midline.
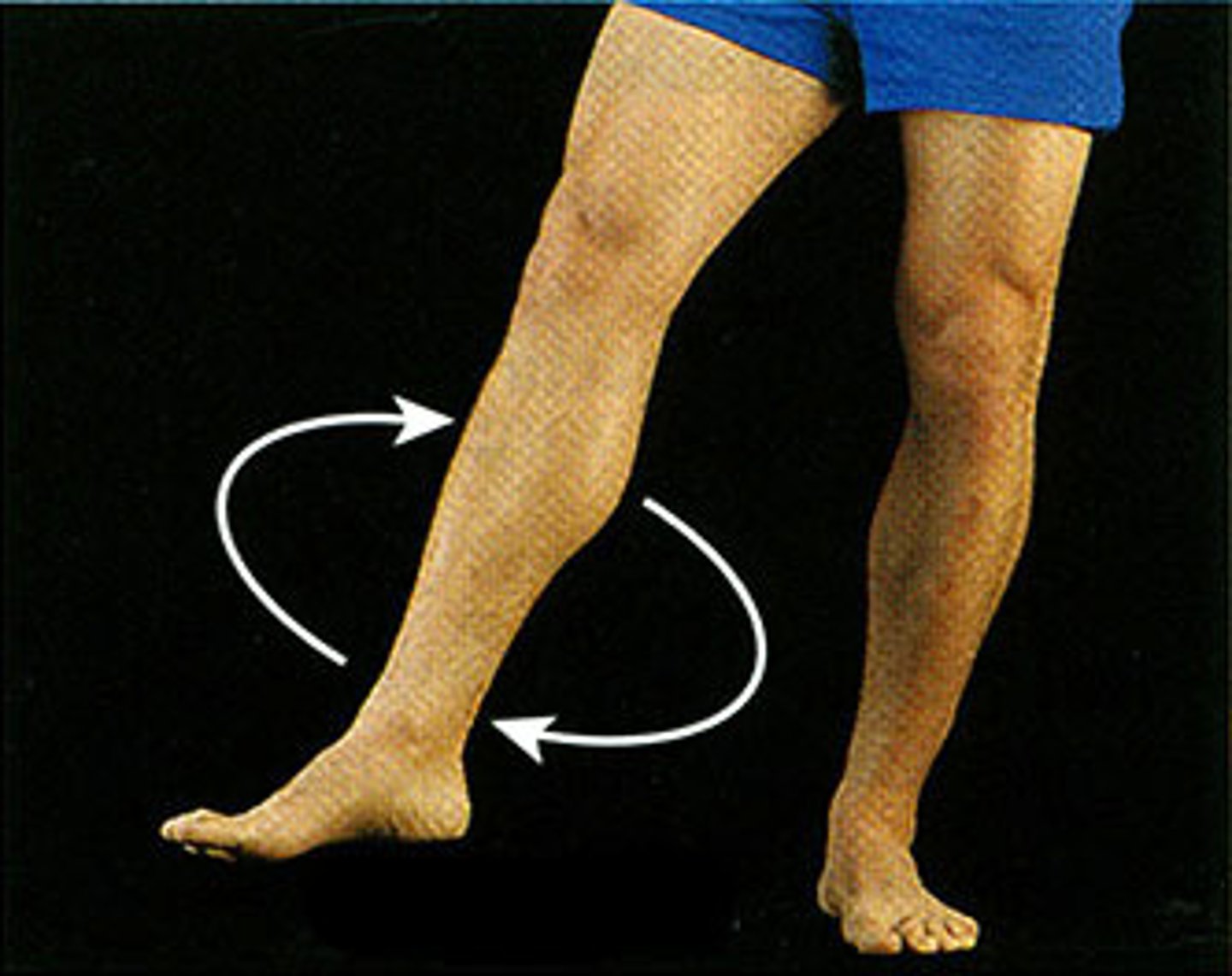
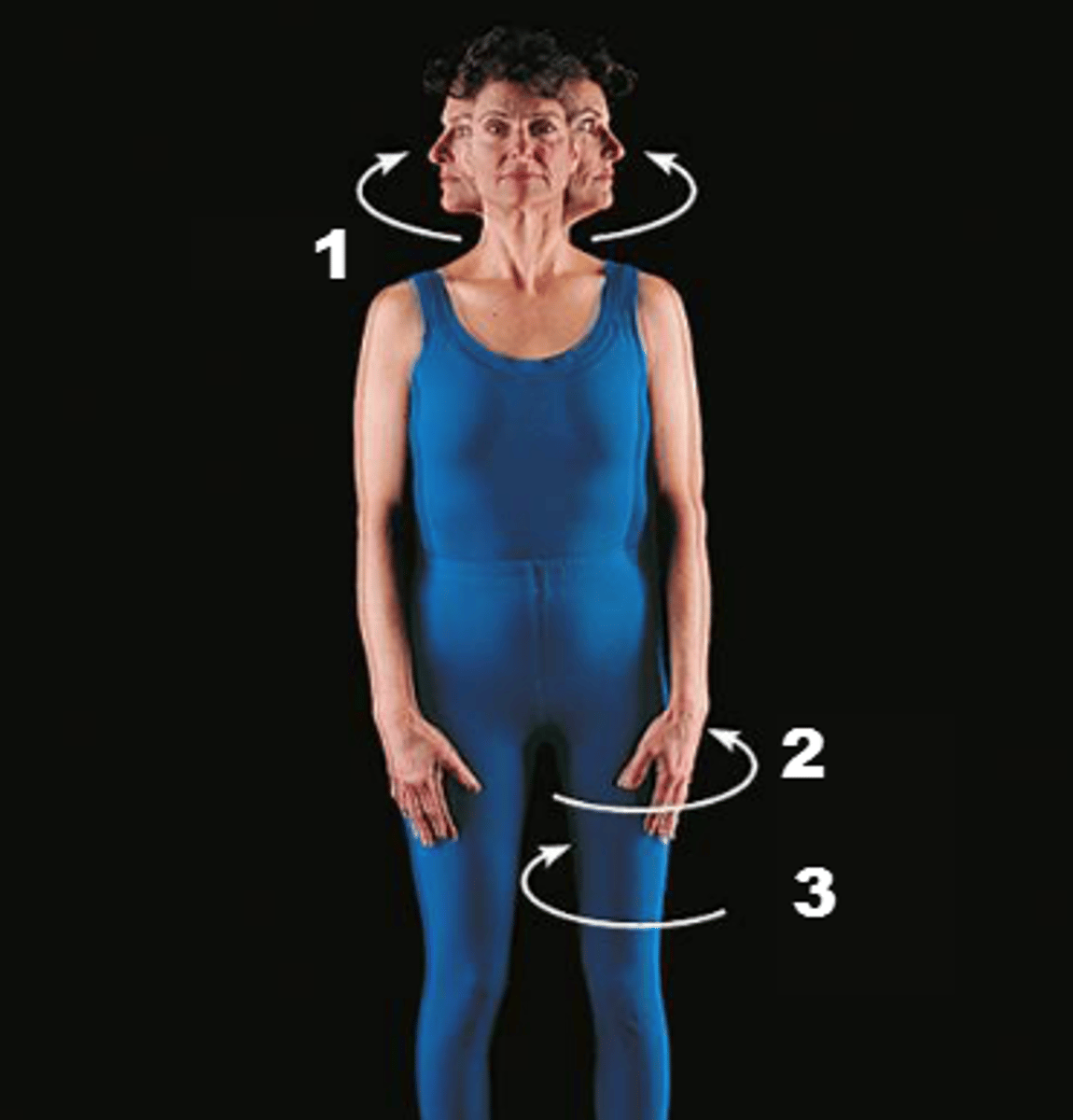
Circumduction
Moving a limb or finger in a cone shape in space.
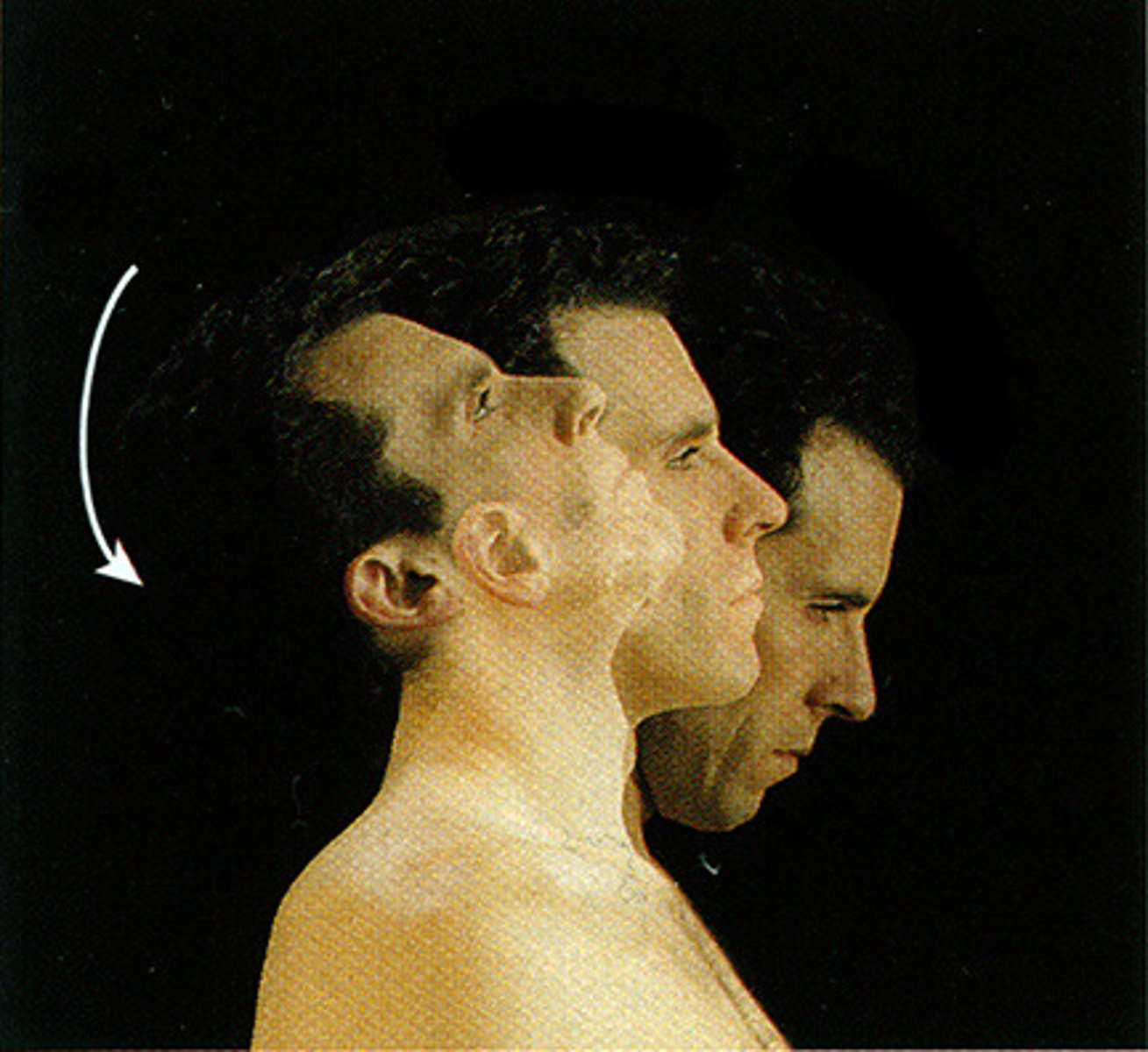
Rotation
The movement around an axis.
coronal (frontal) plane
vertical, divides the body into anterior and posterior sections
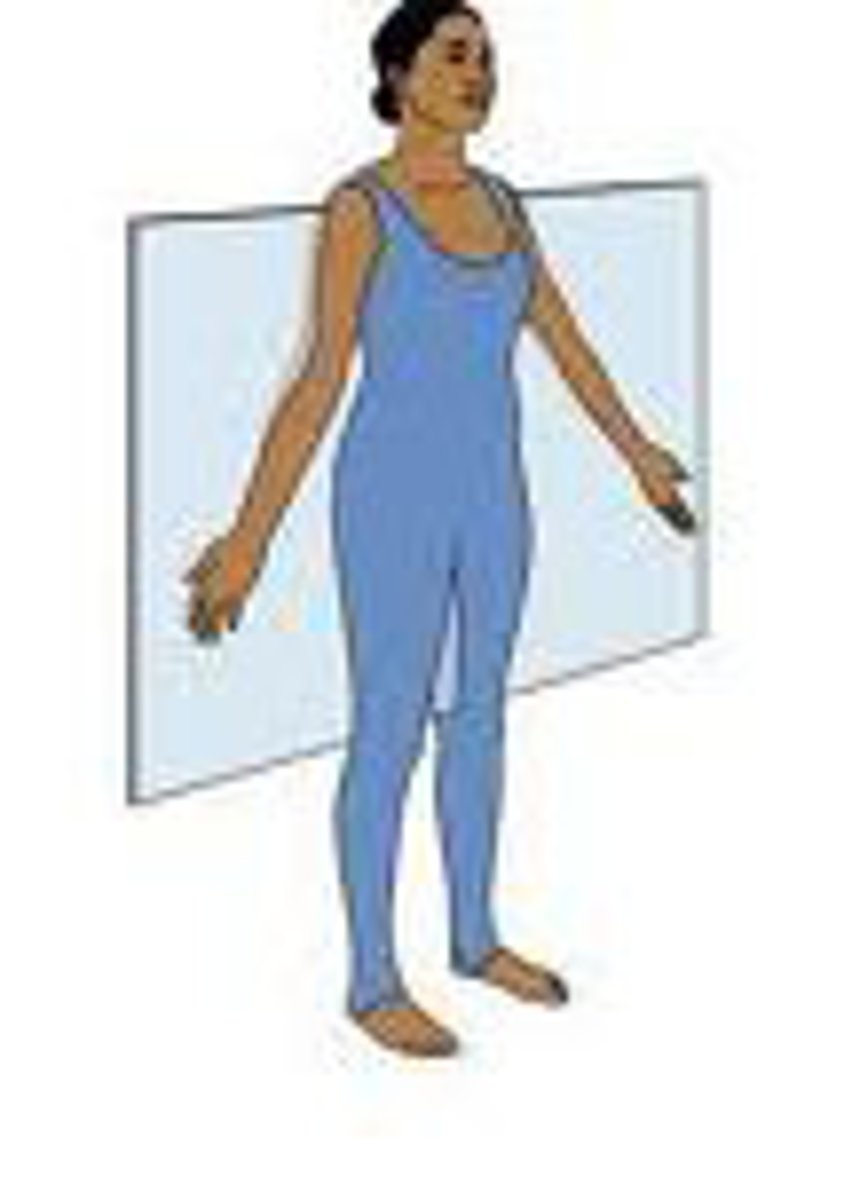

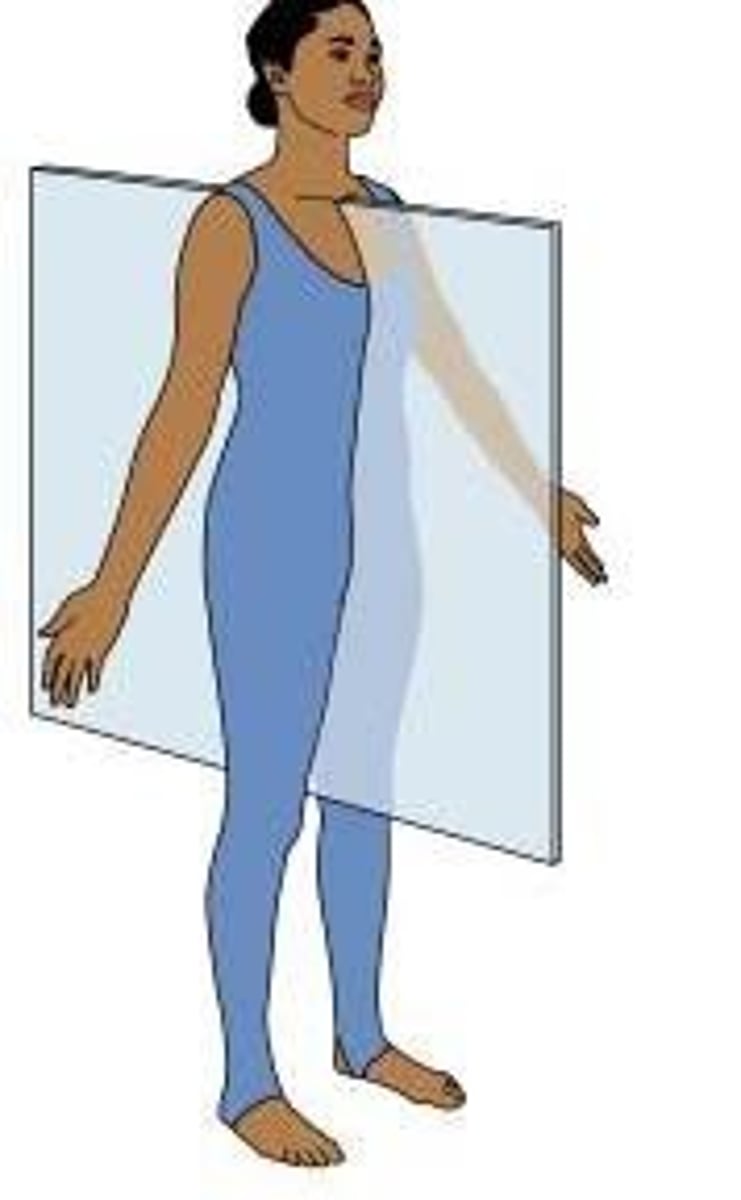
sagittal plane
vertical, divides the body into a right and left section
midsagittal (median) plane
vertical, divides the body into equal in size right and left sections
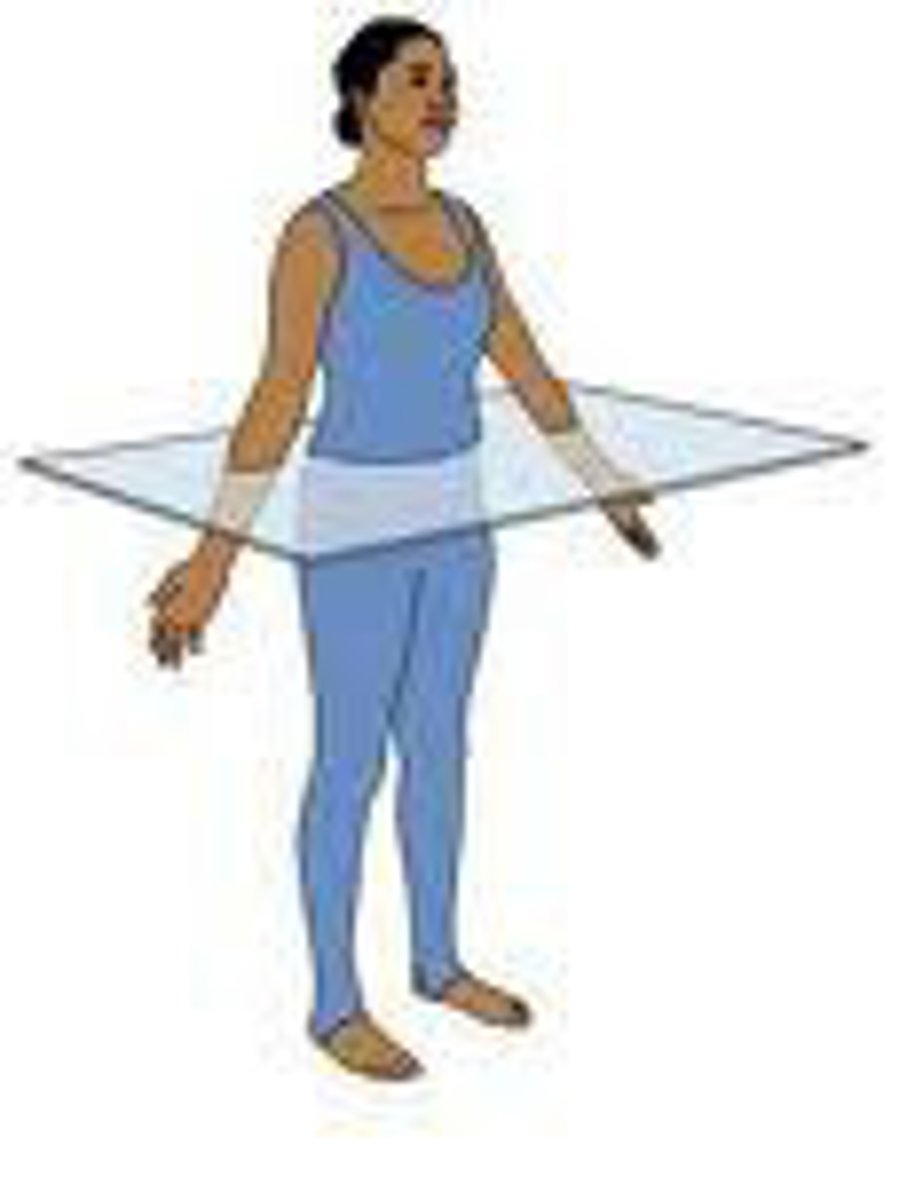
transverse plane
horizontal, divides the body into superior and inferior sections.
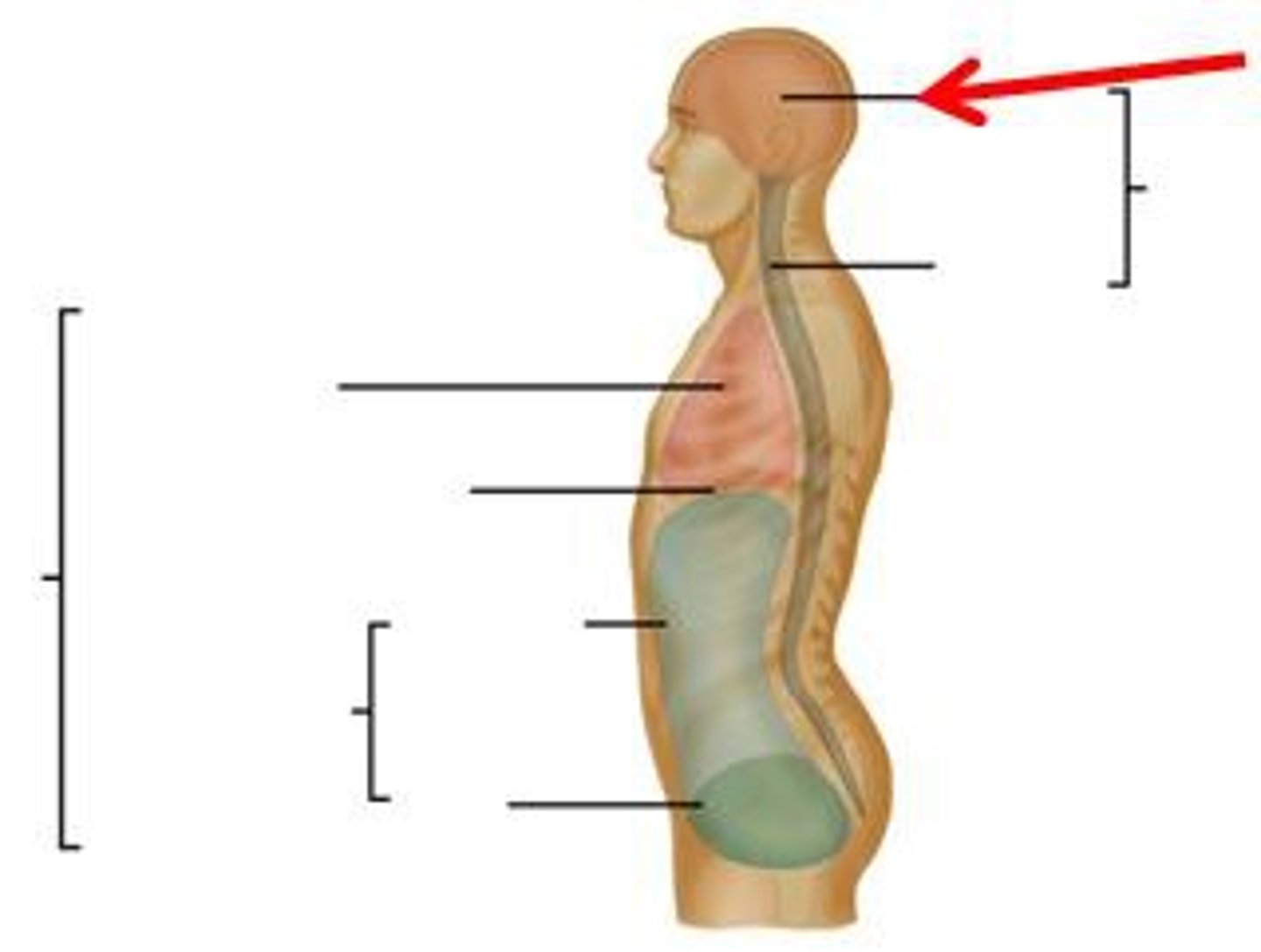
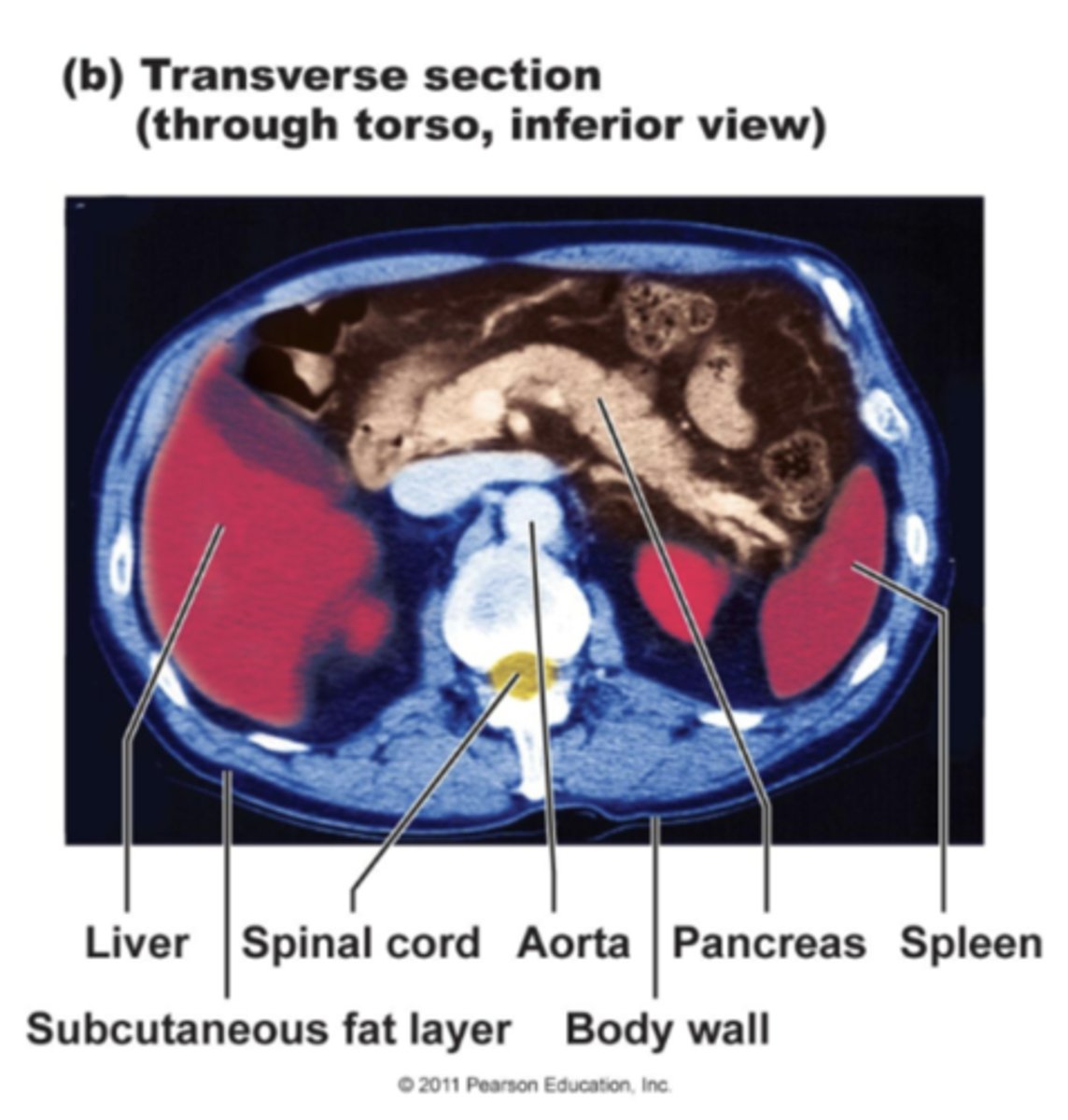
Coronal Section
Also called a 'Frontal' section, this body plane is capable of revealing a wide area. This image is taken of the thorax, and is cut parallel to both shoulder blades(scapulae).
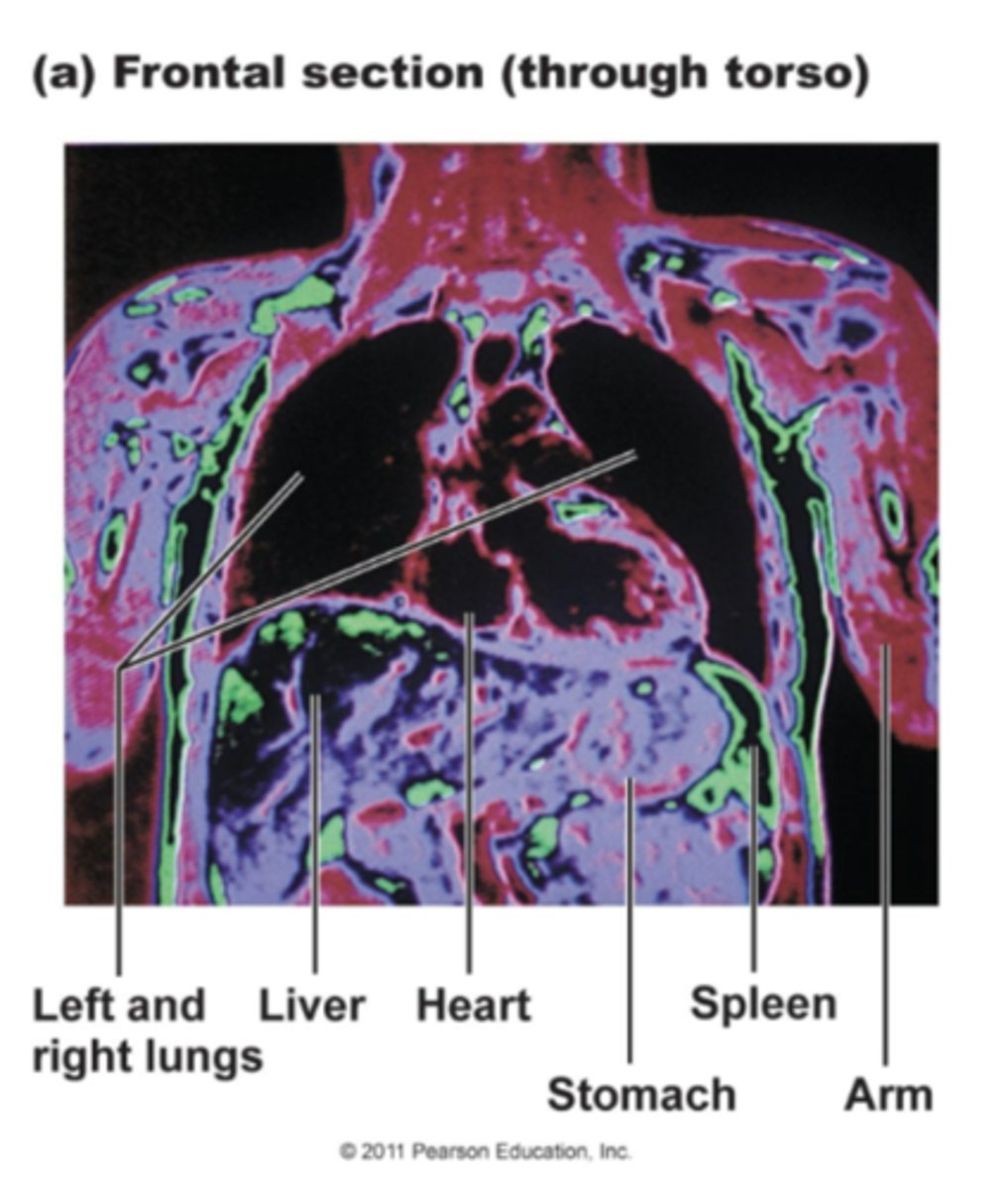
Sagittal Section
A sagittal, median or midsagittal plane is cut down the long length of the body. The body is split into right and left halves. If the plane is exactly in the center, then it is considered to be midsagittal.
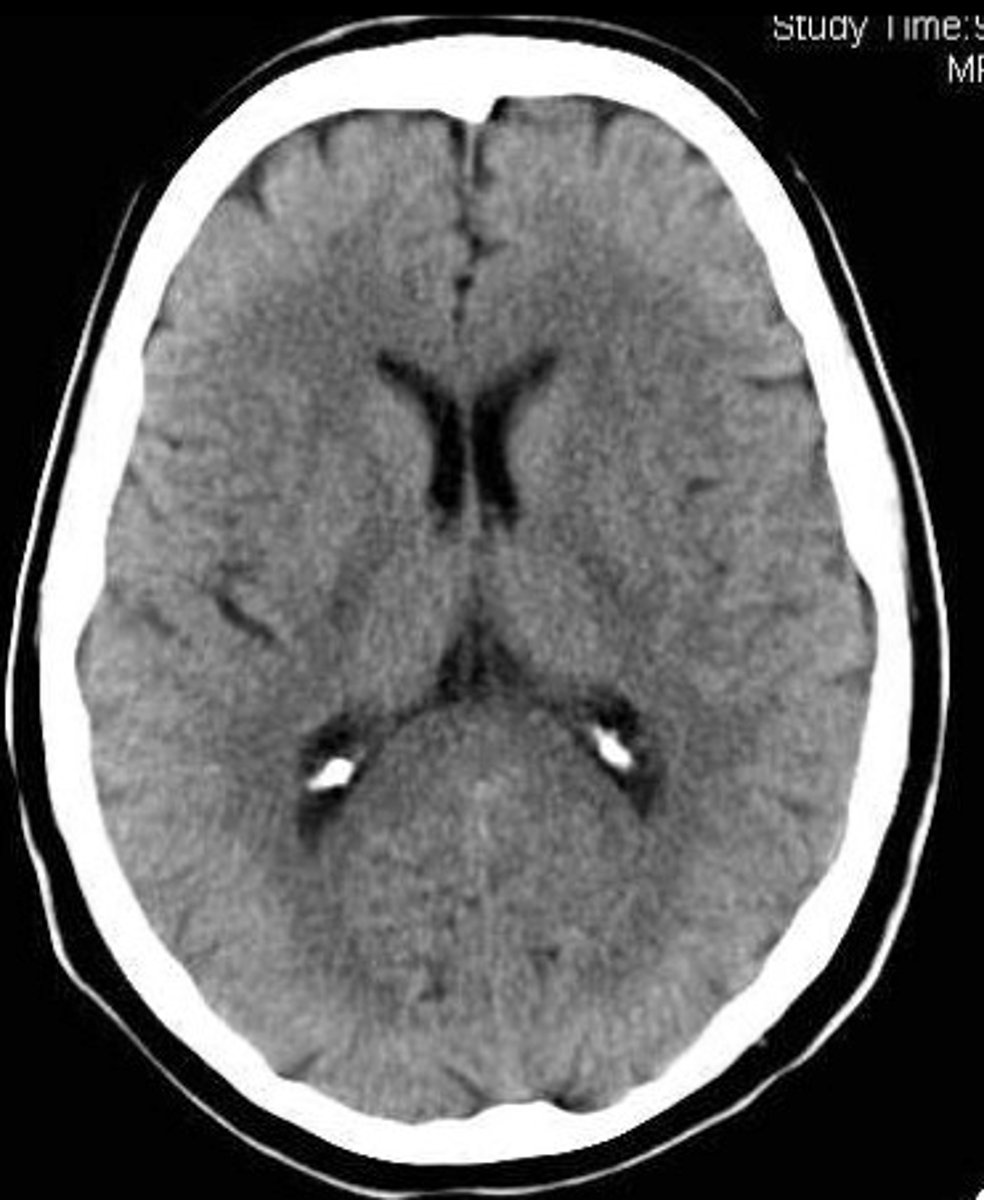
transverse section
The transverse plane is taken across the body.Often times used for brain or abdominal imaging.Can be taken at any level of the abdomen or multiple levels to yield a series.
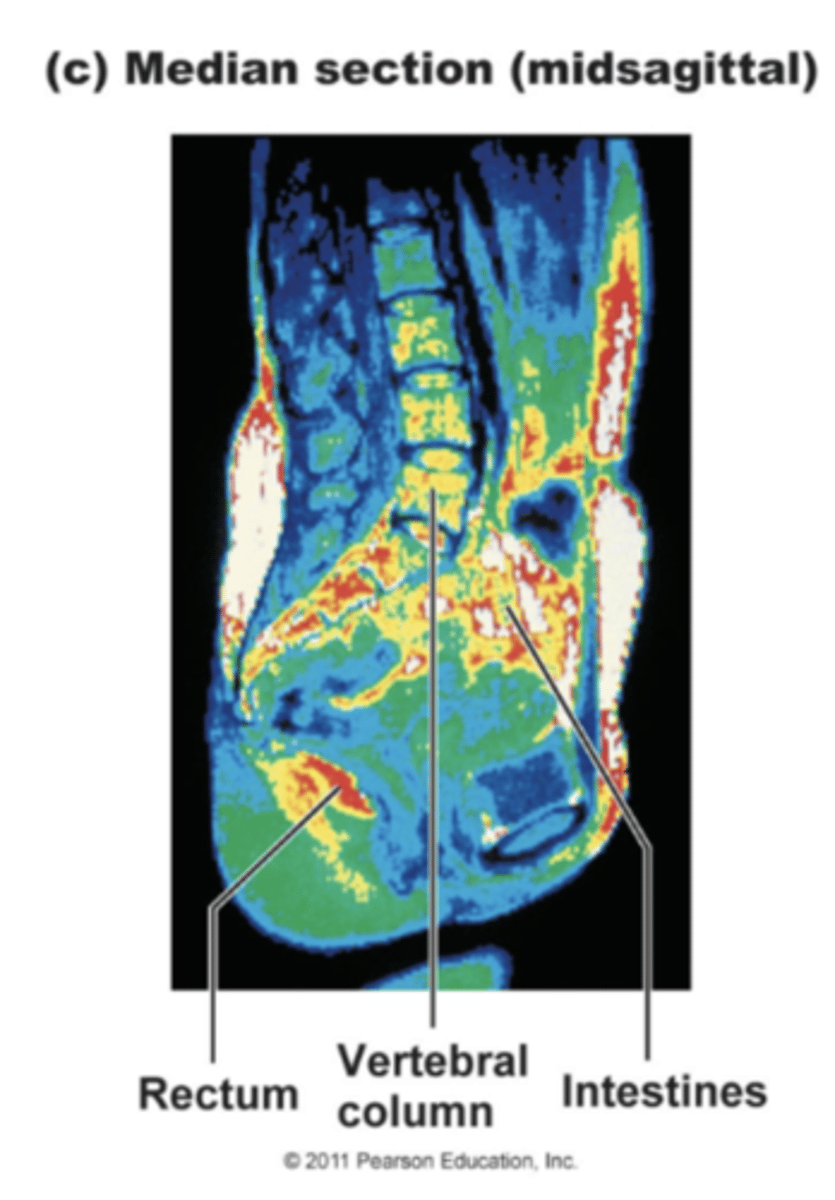
transverse; feet
Remember, a CT or MRI in the _______ plane is orientated as if the viewer is looking at it from the ______ up!!!!
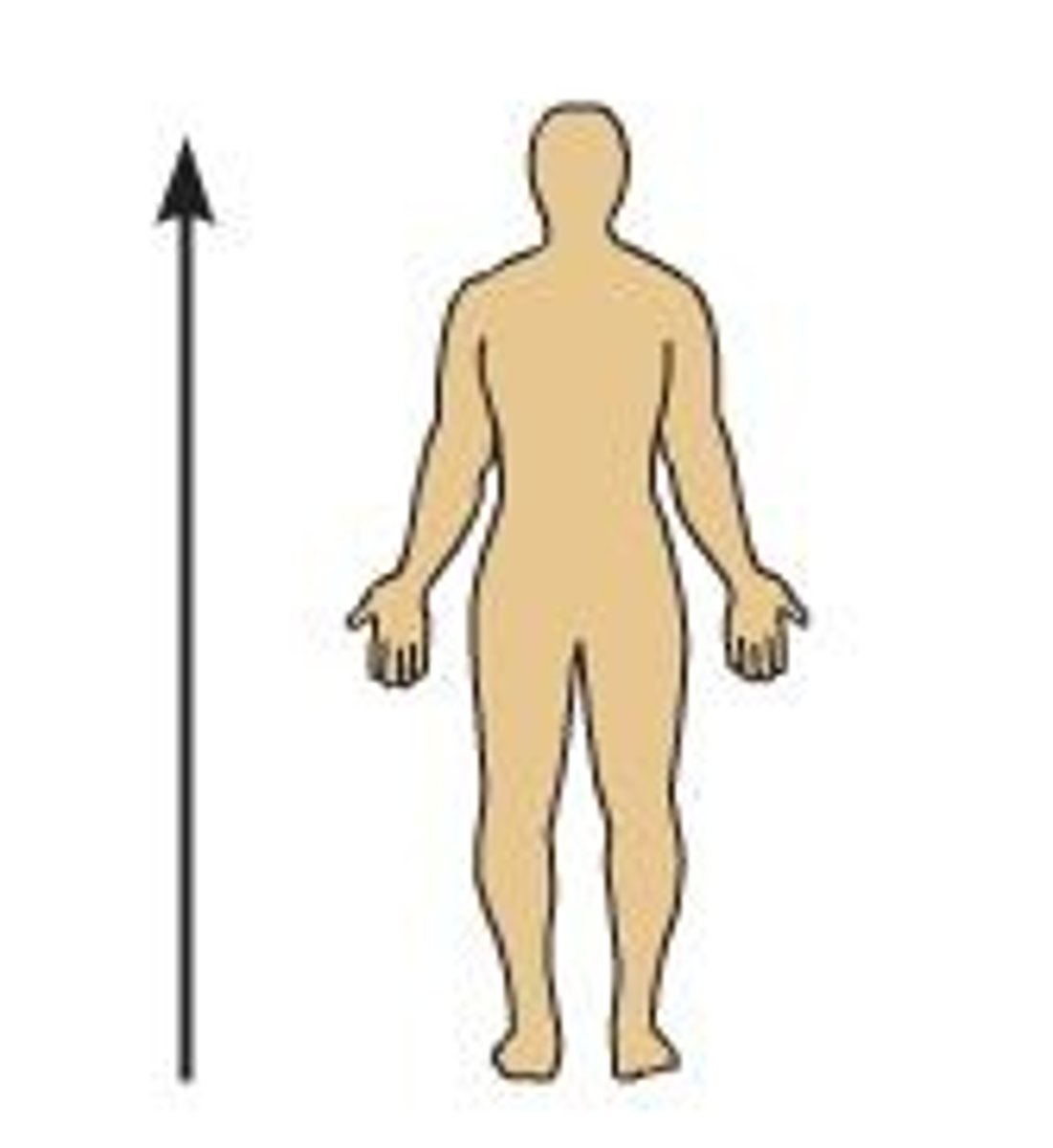
Superior (cranial)
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure of the body; above
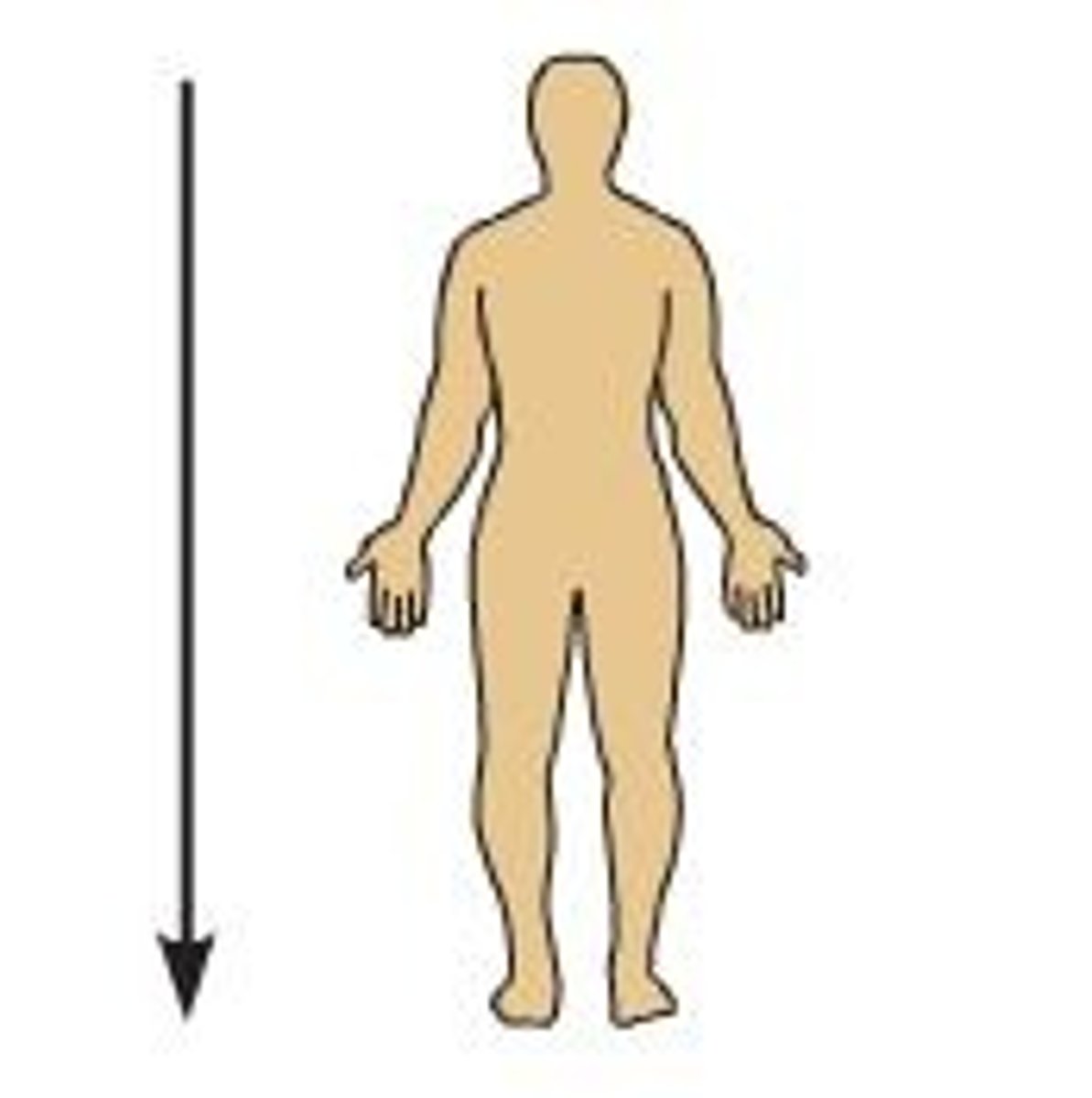
Inferior (Caudal)
Away from the head or toward the lower part of a structure of the body; below
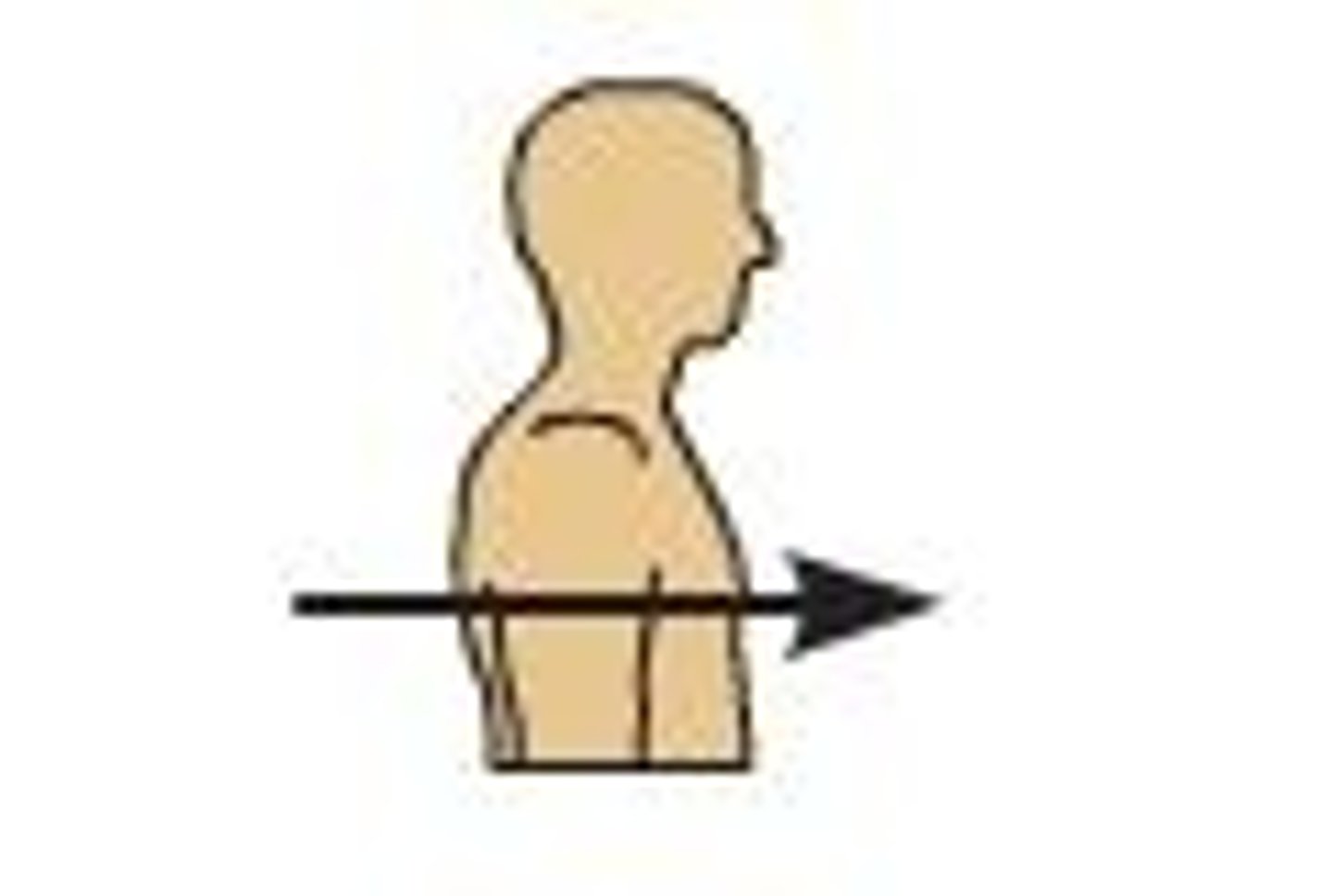
Anterior (ventral)*
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of
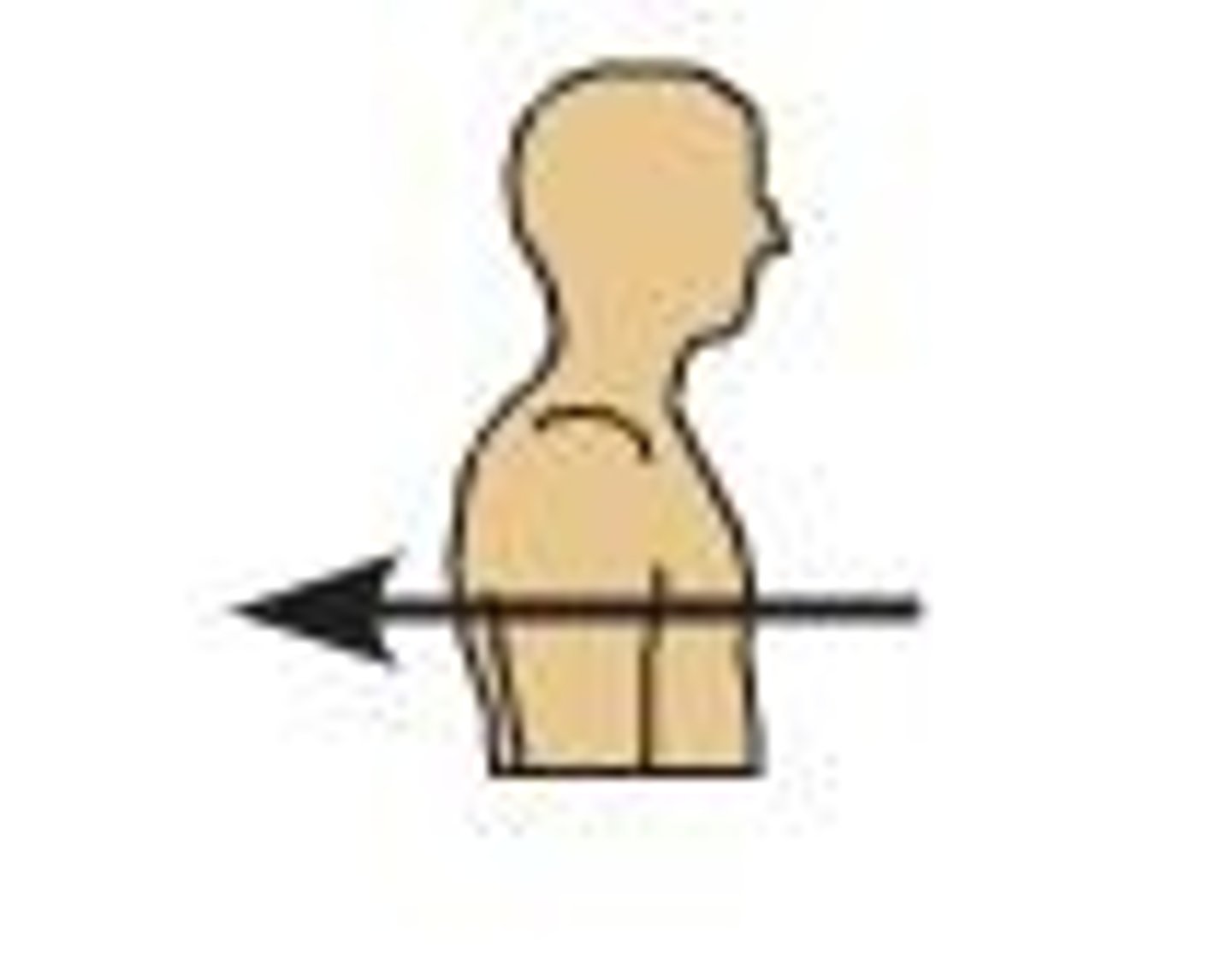
Posterior (dorsal)*
Toward or at the back of the body; behind
Medial
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of
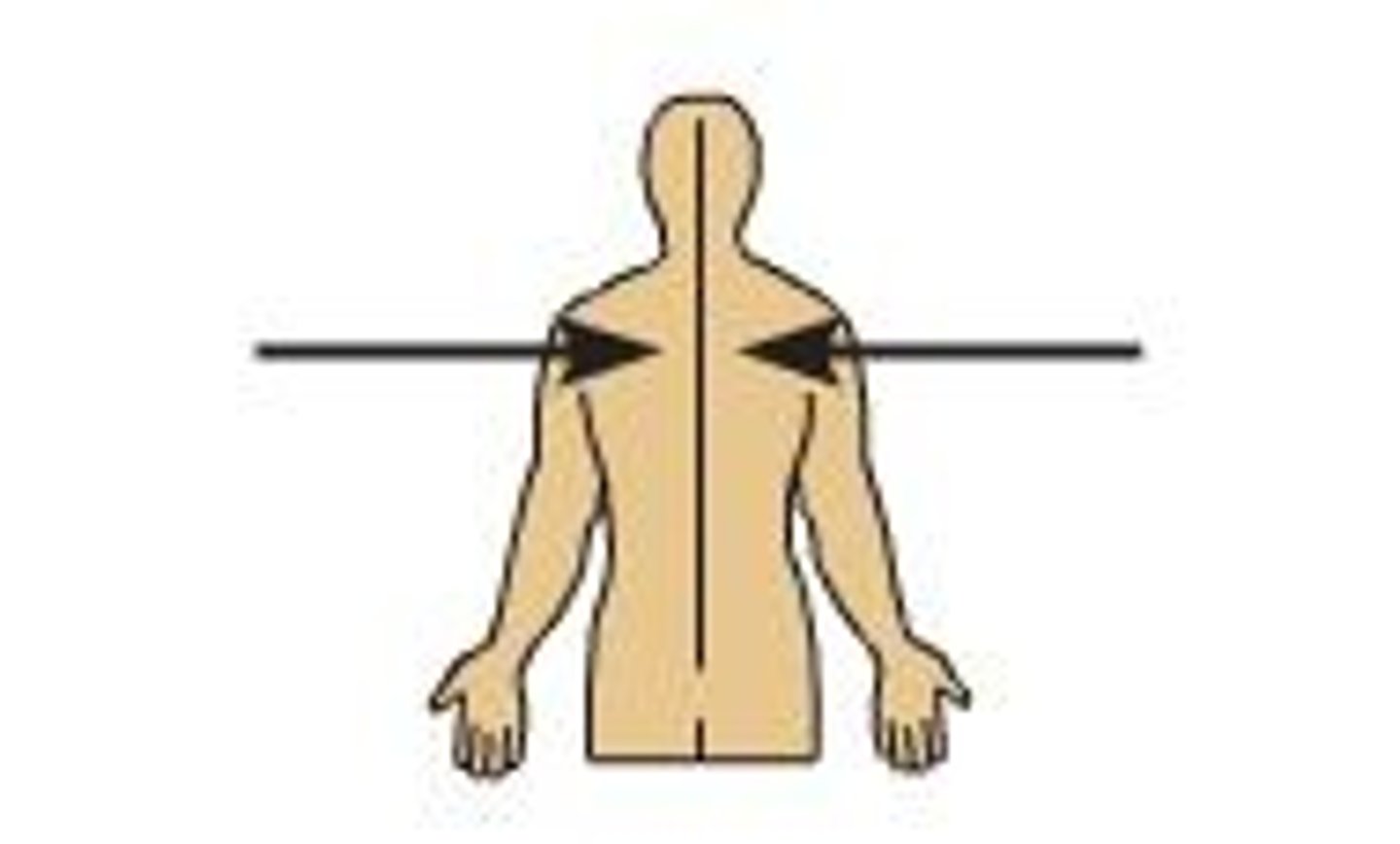
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
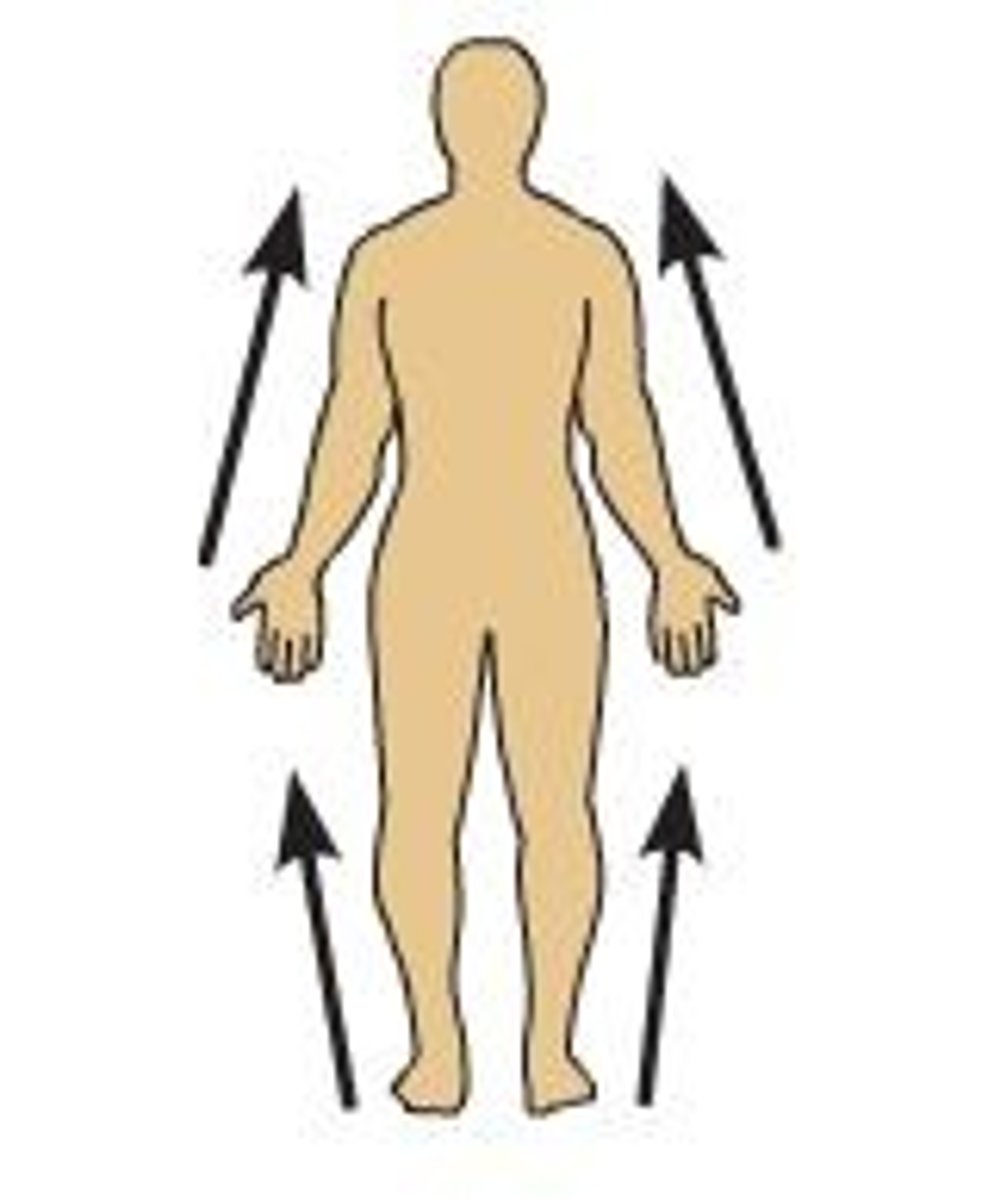
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
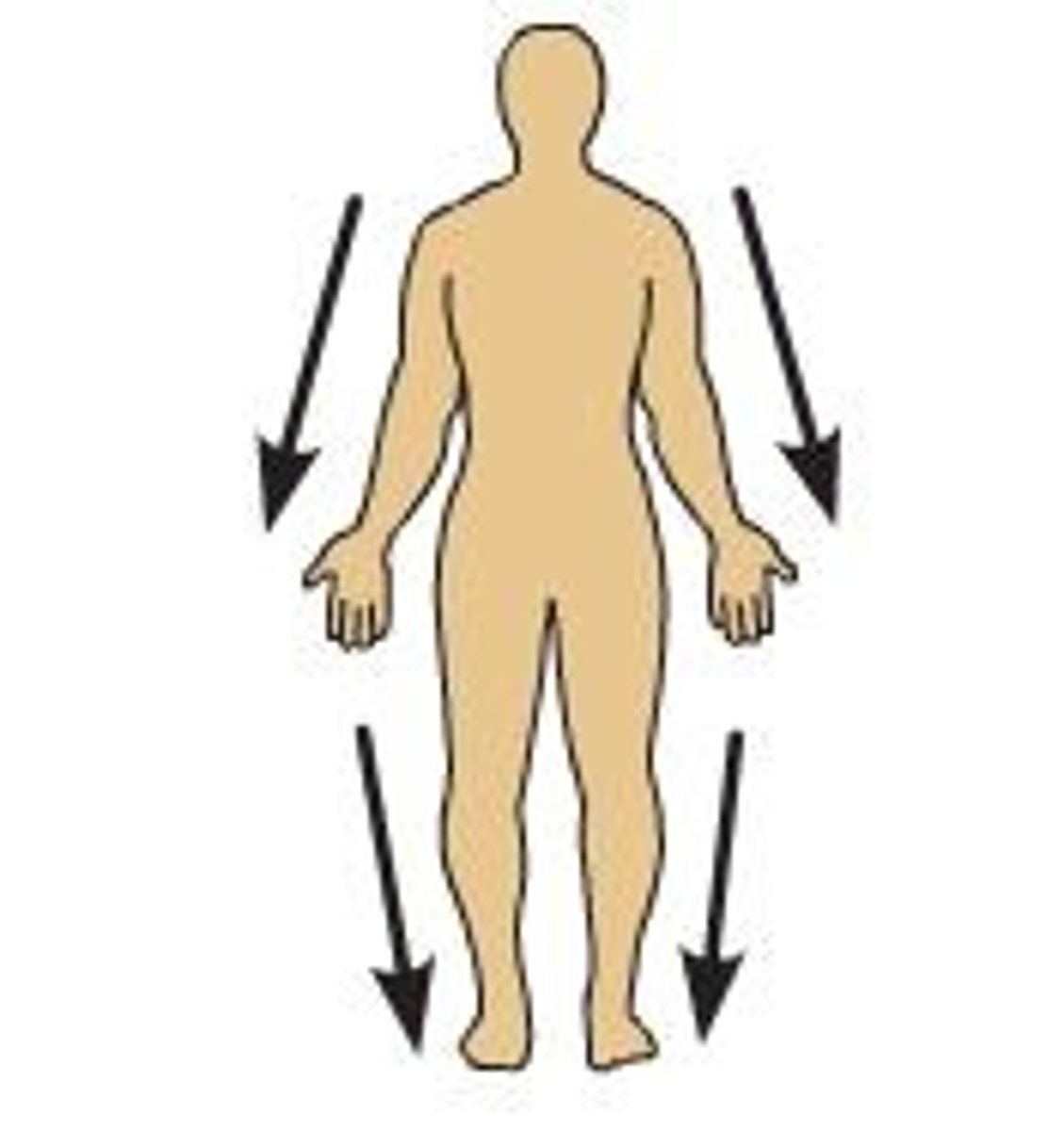
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Superficial (external)
Toward or at the body surface
Deep (internal)
Away from the body surface more internal