Psychology Ch 5: Sensation and Perception
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Define psychophysics
The scientific study between physical stimuli & the psychological experiences they produce in an organism
What does the term sensation mean?
Occurs when sensory receptors detect sensory stimuli
What are the sensory systems?
Vision - Balance (vestibular sense)
Hearing (audition) - Body position (proprioception)
Smell (olfaction) - Movement (kinesthesia)
Taste (gustation) - Pain (nociception)
Touch (somatosensation) - Temperature (thermoception)
The minimum amount of stimulus energy that a must be present for stimulus to be detected 50% of the time.
Absolute Threshold
The minimum difference in stimuli required to detect a change or a difference between stimuli.
Difference Threshold/ Just noticeable difference (JND)
Define perception
Way that sensory information is interpreted, organized, and consciously experienced
Not perceiving stimuli that remain relatively constant over prolonged periods of time.
Sensory adaptation
Failure to notice something that is completely visible because of a lack of attention
Inattentional blindness
Haley is waiting on an important phone call for a job offer, she thinks she heard her phone ringing but it actually didn’t. What factor of perception did Haley experience
Motivation
Change in stimulus detection as a function of current mental state.
Signal detection theory
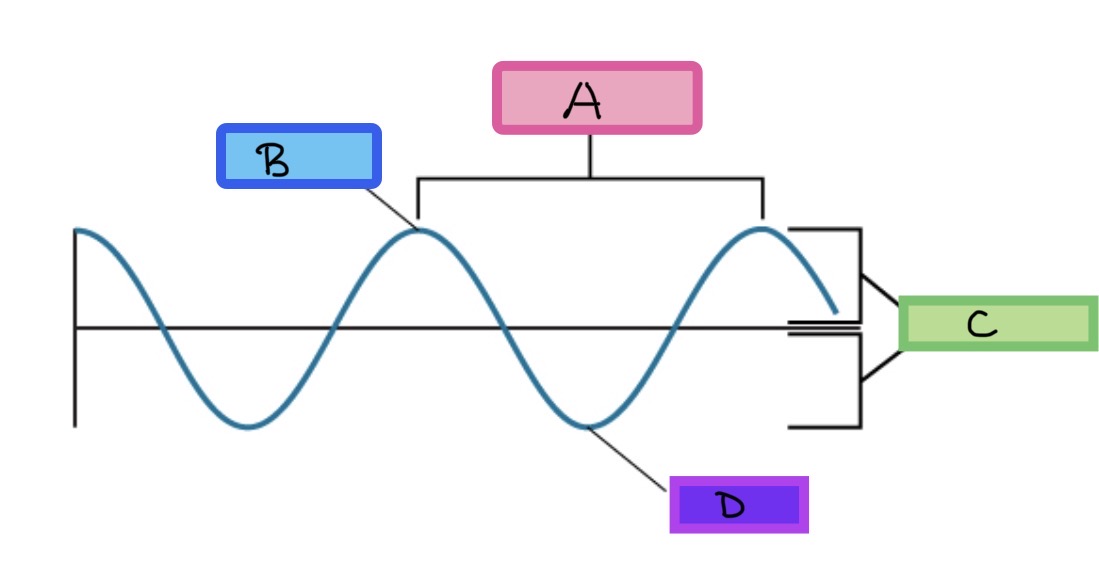
Label the figure
A: wavelength, B: Crest, C: Amplitude, D: Trough
Frequency
The number of waves that pass a given point in a given time period, expressed has hertz (Hz)
What is the range of wavelengths that humans can see
380-740nm
Define cones
Phototopic (daytime) vision, Bright light vision, color, good acuity, mostly center of eye (only in fovea, almost none in extreme periphery)
Define rods
scotopic (nighttime vision), low light vision, monochromatic, poor acuity, mostly in periphery of retina
Describe and list characteristics from the optic chiasm
The X-shaped structure just below the cerebral cortex, info sent from the right visual field is sent to the left hemisphere and information from the left visual field is sent to the right hemisphere, then information is sent to the occipital lobe for processing
Define the trichromatic theory of color vision
All colors can be produced by combing red, green, and blue, applies to the retina where color vision is controlled by 3 types of cones.
Define opponent process theory
Color is coded in opponent pairs black-white, yellow-blue, green-red,