The structure and function of the plasma membrane
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
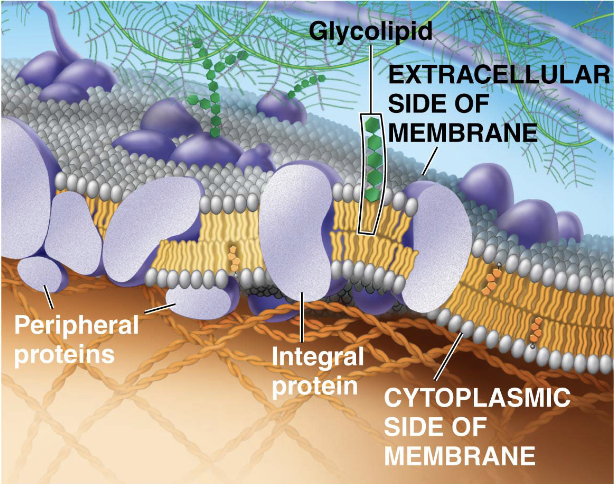
Plasma membrane
The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier controlling the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins
Physical barrier separating the inside/outside of cell
Much of our body is hydrophilic
Fats are hydrophobic
Fats in cell membrane provide a barrier to water
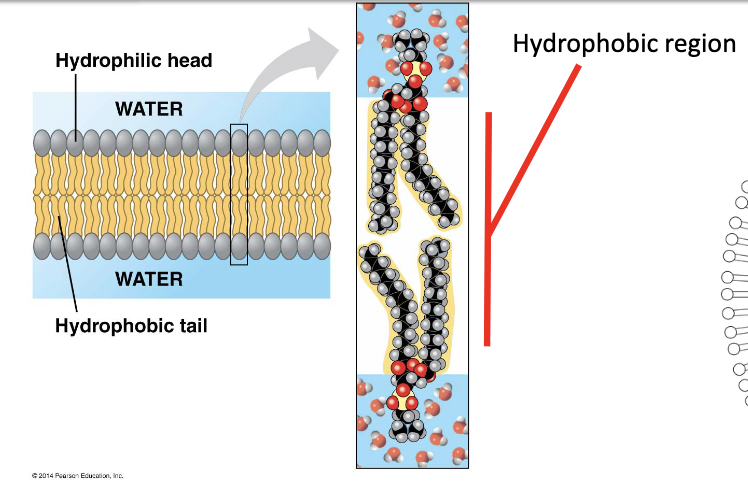
Phospholipid
hydrophilic polar heads (phosphate)
hydrophobic lipid tails (fatty acids)
arranged as a double layer around cytoplasm, tail to tail
Plasma Membraine Proteins
Membrane proteins mediate movement of hydrophilic substances
Are often amphipathic, meaning they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
Integral proteins
embedded partially or fully into the membrane
Peripheral membrane proteins
associated with the membrane, but not actually embedded in it
Allow cell-celll identification and facilitate intercellular communication
Plasma membrane proteins main functions
Transport
channels, transporters, may be general or selective, gated or not
Enzymatic activity
carry out chemical reaction, may or may not be a part of a team of enzymes
Signal transduction
external signalling molecule causing communication of information to the inside of the cell
Plasma membrane proteins other functions
Cell-Cell recognition
use of glycoproteins (carbohydrate + protein) as molecular signatures of the extracellular side of the cell
Intercellular joining
e.g. gap unctions or tight junctions
Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM)
e.g. fibronectin mediates contact between cell surface integrins and ECM can facillitate movement
Membranes are not static
the membrane is a mosaic of molecules bobbing in a fluid layer of phospholipids
cell specific and dynamic repertoire of membrane-bound proteins present as required